Abstract
In a previously published study, to optimize the vibrating and comb-brushing harvesting, the main factors and their parameter values were obtained based on the FEM and RSM. However, the study was based on the extensive cultivation mode which need to be improve. To realize the mechanization of the harvesting of Lycium barbarum L., as well as to face the standardized hedge cultivation mode, a vibrating and comb-brushing harvester machine was designed, which was primarily composed of an execution system, a motion system, and a control system. The mathematical model between the harvest effect index and the operation parameters was established based on response surface methodology (RSM). The effects of various parameters on the harvest index were analyzed, and the best parameter combination was determined: a vibration frequency of 38.73 Hz, a brush speed of 14.21 mm/s, and an insertion depth of 26.07 mm. The field experiment showed that the harvesting rate of ripe fruit was 83.65%, the harvesting rate of unripe fruit was 7.22%, the damage rate of the ripe fruit was 11.49%, and the comprehensive picking index was 87.85. The findings provided a reference for the development of L. barbarum harvesting mechanization in a standardized hedge cultivation mode.
1. Introduction
Lycium barbarum L. (L. barbarum) is an infinite inflorescence deciduous shrub plant belonging to Lycium barbarum in the eggplant family [1,2,3,4]. Its ripe fruit are rich in polysaccharides, carotene, and other important physiological active ingredients [5,6,7,8]. It has the functions of protecting the liver, kidney, eyesight, and nerves as well as fighting off cancer [9,10]. At present, the manual harvesting method of L. barbarum has the problems of low efficiency and a high cost [11,12]. With the increase in planting area and a reduction in the labor force, the development of mechanized harvesting technology is necessary [11,13,14,15,16].
L. barbarum is a species that is distributed worldwide. However, only China has cultivated and exploited it to a large scale, and, as such, its harvest research is mainly concentrated in China [15,17,18,19,20,21,22]. The current harvest research of L. barbarum mainly focuses on designing different mechanical structures and obtaining the best harvest parameters [20,23,24]. However, there are still several problems such as diverse and inconsistent evaluation indexes, which make it difficult to quantitatively evaluate the comprehensive harvest effect [1,10,24]. Among the various harvesting methods of L. barbarum, the vibrating harvester has a high efficiency but inflicts great damage. By contrast, the comb-brushing harvester has a low efficiency but inflicts little damage [25]. Previous studies have attempted to combine methods to efficiently harvest L. barbarum by taking together the advantages of the high efficiency of a vibrating harvester and the low damage rates of comb-brushing. Many researchers have attempted to design vibrating and comb-brushing harvesters with different mechanical structures and have demonstrated that a combined harvesting method can improve the overall harvesting performance [1,12,25]. However, that research was based on a traditional extensive cultivation mode. Under the old mode, the shrubs are short and a large number of branches are contact with the land, which leads to the loss of the fruit. In addition, the branches can be staggered and the fruit leaves can overlap, which restricts the development of mechanization. Therefore, all major production areas carry out a standardized hedge cultivation mode to provide an agronomic basis for mechanized harvesting. The new mode can raise the height of the shrubs, reduce the distribution density of the branches, and improve the yield and quality of the fruit [26]. At present, the standardized rate of L. barbarum planting in Ningxia has reached 71%. Agronomic integration research based on the new mode is necessary for the realization of the mechanization of L. barbarum harvesting. Previous research has shown that frequency, amplitude, and comb-brushing speed affect the harvesting effect and it is necessary to optimize the influencing factors and determine the values to provide a theoretical basis and a foundational dataset for the research and development of a vibrating and comb-brushing harvester in the future [1,12,25].
A few months ago, our research team published a paper named “Parameter Optimization of Vibrating and Comb-Brushing Harvesting of Lycium barbarum L. Based on FEM and RSM” [25]. To optimize vibrating and comb-brushing harvesting, the main parameter was obtained based on the finite element method (FEM) and response surface methodology (RSM). However, the study was based on the extensive cultivation mode, which was natural growth and simple pruning. As the harvesting device vibrated vertically and combed horizontally, it was not suitable for the standardized hedge cultivation mode with drooping branches. Thus, the purpose of this study was to design a new harvesting structure and optimize the vibrating and comb-brushing harvesting method on the basis of the hedge cultivation mode. Through analyzing its main system, the value range of the related working parameters was obtained. On this basis, we explored the relationship between the parameters of the vibration frequency, the brush speed, and the insertion depth on the harvest indexes of the harvesting rate of ripe fruit, the harvesting rate of unripe fruit, the damage rate of ripe fruit, and the comprehensive picking index. Field experiments were conducted to obtain and verify the best working parameters of the harvest method, and to provide a reference for the development of L. barbarum harvesting mechanization.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Standardized Hedge Cultivation Mode
In this study, we investigated the cultivation mode of L. barbarum in Ningxia Zhengqihong Industry Development Co., Ltd., Guyuan City, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (36°17′32.9″ N, 106°6′41.5″ E). The main variety planted was Keqi No. 2, which exhibits good growth conditions, more fruit, no diseases or insect pests, and no obvious defects. For the convenience of harvesting, the shrubs were artificially pruned into a standardized hedge cultivation mode (Figure 1) when the shrubs were 2–3 years old. The data of the cultivation mode are shown in Table 1.

Figure 1.
The standardized hedge cultivation mode: (a) schematic diagram; (b) real picture.

Table 1.
The data of the standardized hedge cultivation mode.
2.2. Overall Structure and Operating Principle
2.2.1. Overall Structure
The structure of the vibrating and comb-brushing harvester is shown in Figure 2. The structure consisted of an executive system, a motion system, and a control system. The execution system included a vibrating comb-brush bar, a vibration source, and a shock absorber connector. The motion system consisted of two cross ball screw sliding tables where the sliding tables used 42BYG stepper motors as a power source to drive the executive system movement within two degrees of freedom. The control system included a battery, a CNC SHIELD V3 engraving machine expansion board, an A4988 driver board, and an Arduino UNO R3 MCU (manufactured by Shenzhen Two Trees Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China).
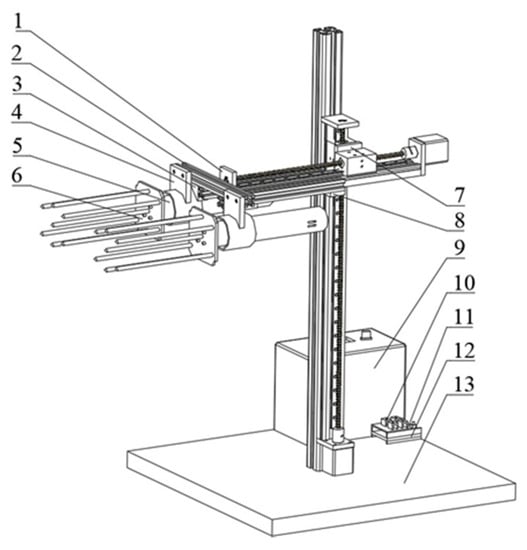
Figure 2.
Structure of vibrating and comb-brushing harvester: (1) ball screw slide table, (2) aluminum profile, (3) aluminum profile connector, (4) shock absorber connector, (5) vibration source, (6) vibrating comb-brush bar, (7) slide table connector, (8) bottom plate, (9) battery, (10) A4988 driver board, (11) CNC SHIELD, (12) Arduino UNO R3, and (13) mounting bracket.
2.2.2. Operating Principle
When the harvester worked, the control system managed the insertion depth and brush speed of the execution system through the motion system. The executive system moved horizontally to insert the vibrating comb-brush bar into the branches. The executive system then drove the branches and fruit to vibrate, and then moved vertically downward at a certain speed to achieve the combined vibrating and comb-brushing effect.
2.3. Design of Key Systems
2.3.1. Execution System
The structure of the execution system is shown in Figure 3. The vibration was transmitted to the branches and fruit through the flexible vibrating comb-brush bar. With the downward movement of the execution system, the fruit could be harvested under the action of vibration and comb-brushing.
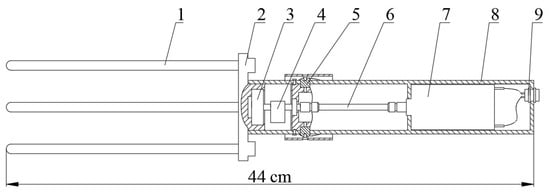
Figure 3.
Structure of the execution system: (1) vibrating comb-brush bar, (2) mounting plate, (3) bearing, (4) eccentric block, (5) damping block, (6) transmission shaft, (7) motor, (8) shell, and (9) power connector.
The execution system provided vibration through the centrifugal force generated by the rotating eccentric block. The exciting force F, vibration amplitude S, and excitation acceleration a could be described by the following:
where F is the exciting force of the vibrating comb-brush bar (N), m is the mass of the eccentric block (kg), r is the distance between the centroid of the eccentric block and the center of rotation (m), ω is the angular frequency of the motor rotation (rad/s), S is the vibration amplitude of the vibrating substance (mm), G is the mass of the vibrating substance (kg), and a is the excitation acceleration of the vibrating substance (N/kg).
2.3.2. Motion System
The motion system consisted of two ball screw slides mounted vertically. The screw slides were driven by a stepper motor. The speed of the stepper motor could be adjusted by the pulse of the MCU. The movement length L and rotational speed Vr could be obtained as follows:
where L is the movement length of the screw slides (mm), h is the lead of the screw (mm), R is the rotational angle of the motor (°), Vr is the rotational speed of the stepper motor (r/s), p is the step angle after subdivision (°), and f is the pulse frequency (Hz).
As the lead of the screw was 8 mm, the speed of the sliding table Vl was obtained as follows:
where Vl is the speed of the screw slide table (mm/s).
2.3.3. Control System
The circuit diagram of the control system is shown in Figure 4. The rated speed of the vibration motor in the execution system was 3200 rpm and the speed was controlled by a PWM DC governor (manufactured by Shenzhen Quanqiuyi Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China). The screw slide platform was driven by a 42BYG stepper motor (manufactured by Shenzhen Global Yi Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China) and powered by a DC-24120 large-capacity lithium polymer battery (manufactured by Shenzhen Dipuwei Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China). The motor was controlled by an Arduino MCU, a CNC SHIELD V3, and an A4988 (manufactured by Shenzhen Two Trees Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China). The development environment was Arduino IDE. The Arduino MCU adopted an acceleration and deceleration calculation method. The moving length or speed of the sliding table could be controlled by changing the rotational angle or pulse frequency of the stepping motor.
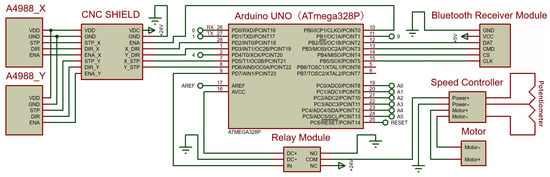
Figure 4.
Circuit diagram of the harvester control system.
2.4. Performance Experiment
The main goal of the vibrating and comb-brushing harvest method is to achieve ripe fruit harvesting, reduce ripe fruit damage, and reduce unripe fruit harvesting as well as flower and leaf shedding. Therefore, based on the research of [1,10,11,12,23,24,25], the harvesting rate of ripe fruit (I1), the harvesting rate of unripe fruit (I2), and the damage rate of ripe fruit (I3) were selected as the evaluation indexes for the experiments and calculated according to the following:
where n1 is the amount of ripe fruit harvested, n2 is the amount of ripe fruit unharvested, n3 is the amount of unripe fruit harvested, n4 is the amount of unripe fruit unharvested, and n5 is the amount of damaged ripe fruit harvested.
To comprehensively evaluate the harvesting effect, weight distribution was carried out on the measurement results to obtain a single comprehensive picking index (I), which could be described by the following:
where I2s is the score of unripe fruit harvested and I3s is the score of damaged ripe fruit harvested.
Through a principal analysis and literature review, it could be determined that the main factors affecting the performance of the harvester were vibration frequency, brush speed, and insertion depth of the comb-brush bar into the branch. The value range of each factor was determined by a preliminary test: the vibration frequency (X1) was 20~40 Hz, the brush speed (X2) was 10~40 mm/s, and the insertion depth (X3) was 10~50 mm. The insertion depth and brush speed were adjusted by the motion system and the vibration frequency was measured by a VICTOR 6236P rotation speed/line speed meter (manufactured by Shenyang Zizun Science and Technology Co., Ltd., Shenyang, China).
A three-factor and three-level quadratic orthogonal rotation combination test was used in the experiment conducted for the present study. The factor codes are shown in Table 2 and the test schemes and results are presented in Table 3. A total of 17 groups of tests were carried out; a group of 5 tests was carried out and the average value of the 5 test results was taken as the test result of the group [27,28,29]. Design-Expert 12 software was used to design the experimental scheme and analyze the results.

Table 2.
The codes of factors.

Table 3.
The experiment schemes and results.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Regression Analysis
After an analysis from the implementation of Design-Expert 12 software, a regression mathematical model was obtained that took the harvesting rate of the ripe fruit as the response function and the coding value of each factor as the independent variable.
A variance analysis (ANOVA) was performed on the harvesting rate of the ripe fruit, as shown in Table 4. The results showed that the regression model was p = 0.0003 (<0.05), indicating that the model had a statistical significance. The factors X1, X3, X1X2, and X32 were significant (p < 0.05) whereas the other factors were not. The lack of fit was p = 0.5526 (>0.05), indicating that none of the factors were irrelevant.

Table 4.
ANOVA of the harvesting rate of ripe fruit.
As above, the regression mathematical model of the harvesting rate of the unripe fruit using the codes of the factor as the independent variable was as follows:
The ANOVA was performed on the harvesting rate of the unripe fruit, as shown in Table 5. The results showed that the regression model was p = 0.0115 (<0.05), indicating that the model had a statistical significance. The factors X1, X2, X3, and X1X2 were significant (p < 0.05) whereas the other factors were not. The lack of fit was p = 0.1848 (>0.05), indicating that none of the factors were irrelevant.

Table 5.
ANOVA of the harvesting rate of unripe fruit.
As above, the regression mathematical model of the damage rate of the ripe fruit using the codes of the factor as the independent variable was as follows:
The ANOVA was performed on the damage rate of the ripe fruit, as shown in Table 6. The results showed that the regression model was p = 0.0147 (<0.05), indicating that the model had a statistical significance. The factors X1, X2, and X3 were significant (p < 0.05) whereas the other factors were not. The lack of fit was p = 0.1799 (>0.05), indicating that none of the factors were irrelevant.

Table 6.
ANOVA of the damage rate of ripe fruit.
As above, the regression mathematical model of the comprehensive picking index using the codes of the factor as the independent variable was as follows:
The ANOVA was performed on the comprehensive picking index, as shown in Table 7. The results showed that the regression model was p = 0.0155 (<0.05), indicating that the model had a statistical significance. The factors X1, X2, and X3 were significant (p < 0.05) whereas the other factors were not. The lack of fit was p = 0.3131 (>0.05), indicating that none of the factors were irrelevant.

Table 7.
ANOVA of the comprehensive picking index.
3.2. Response Surface Analysis
The response surface methodology was used to analyze the influence of various factors on the harvesting rate of the ripe fruit and the response surface of the regression equation is presented in Figure 5. It could be seen from Equation (13) and Table 3 that, among all factors, the vibration frequency had the greatest influence, followed by the insertion depth and brush speed. The interaction between the vibration frequency and the brush speed was significant. As shown in Figure 5a, with an increase in the vibration frequency, the impact times and impact force on the fruit increased and the harvesting rate of the ripe fruit gradually increased. However, the vibration frequency could not continue to increase. It was found in the actual test that when the vibration frequency exceeded 50 Hz, the amplitude noticeably decreased and tended to disappear with an increase in the frequency. Due to inertia, the vibrating comb-brush bar was unable to keep up with the rapidly changing excitation force so the system no longer vibrated. As shown in Figure 5b, with a decrease in the insertion depth, the harvesting rate of the ripe fruit gradually increased. This was because the vibrating comb-brush bar could be regarded as a simple supported beam. Therefore, the further away from the fixed end of the force, the greater the amplitude. As shown in Figure 5c, with a decrease in the brush speed, the harvesting rate of the ripe fruit rapidly increased at first but then slowly decreased.
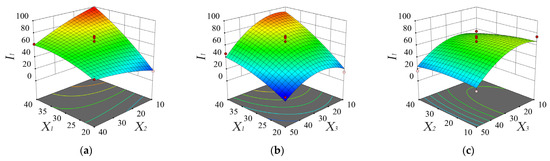
Figure 5.
Response surface and contour plots of the harvesting rate of ripe fruit affected by the vibration frequency X1 and brush speed X2 (a), the vibration frequency X1 and insertion depth X3 (b), and the brush speed X2 and insertion depth X3 (c).
The response surface methodology was used to analyze the influence of various factors on the harvesting rate of the unripe fruit and the response surface of the regression equation is presented in Figure 6. It could be seen from Equation (14) and Table 4 that, among all factors, the vibration frequency had the greatest influence, followed by the insertion depth and brush speed. The interaction between the vibration frequency and the brush speed was significant. As shown in Figure 6a, with an increase in the vibration frequency, the harvesting rate of the unripe fruit gradually increased. As shown in Figure 6b, with a decrease in the insertion depth, the harvesting rate of the unripe fruit gradually increased. As shown in Figure 6c, with a decrease in the brush speed, the harvesting rate of the unripe fruit gradually increased. This was because the unripe fruit were mostly concentrated at the end of branches; an increase in the vibration frequency and comb-brushing time could lead to the fracture of the end branches.
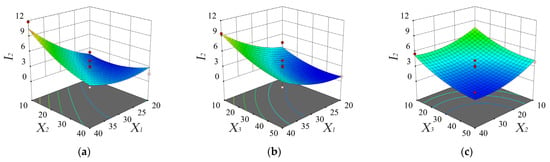
Figure 6.
Response surface and contour plots of the harvesting rate of unripe fruit affected by the vibration frequency X1 and brush speed X2 (a), the vibration frequency X1 and insertion depth X3 (b), and the brush speed X2 and insertion depth X3 (c).
The response surface methodology was used to analyze the influence of various factors on the damage rate of the ripe fruit and the response surface of the regression equation is presented in Figure 7. It could be seen from Equation (15) and Table 5 that, among all factors, the vibration frequency had the greatest influence, followed by the insertion depth and the brush speed. The interaction effect of each factor was not significant. As shown in Figure 7a, with an increase in the vibration frequency, the damage rate of the ripe fruit gradually increased. As shown in Figure 7b, with a decrease in the insertion depth, the damage rate of the ripe fruit gradually increased. As shown in Figure 7c, with a decrease in the brush speed, the damage rate of the ripe fruit gradually increased. This was because the number of hits to the ripe fruit increased.
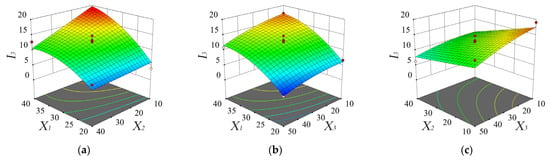
Figure 7.
Response surface and contour plots of the damage rate of ripe fruit affected by the vibration frequency X1 and brush speed X2 (a), the vibration frequency X1 and insertion depth X3 (b), and the brush speed X2 and insertion depth X3 (c).
The response surface methodology was used to analyze the influence of various factors on the comprehensive picking index and the response surface of the regression equation is shown in Figure 8. It could be seen from Equation (16) and Table 6 that, among all factors, the vibration frequency had the greatest influence, followed by the insertion depth and the brush speed. The interaction effect of each factor was not significant. As shown in Figure 8a, with an increase in the vibration frequency, the comprehensive picking index gradually increased. As shown in Figure 8b, with a decrease in the insertion depth, the comprehensive picking index rapidly increased at first but then slowly decreased. As shown in Figure 8c, the brush speed had little effect on the comprehensive picking index; with a decrease of the brush speed, the comprehensive picking index slowly increased.
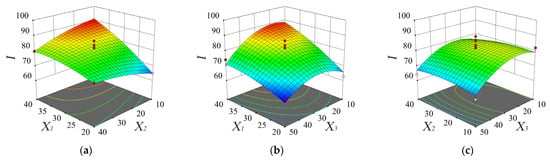
Figure 8.
Response surface and contour plots of the comprehensive picking index affected by the vibration frequency X1 and brush speed X2 (a), the vibration frequency X1 and insertion depth X3 (b), and the brush speed X2 and insertion depth X3 (c).
3.3. Field Experiment Verification
Based on the comprehensive picking index, the optimal parameter combination of each factor was obtained: a vibration frequency of 38.73 Hz, a brush speed of 14.21 mm/s, and an insertion depth of 26.07 mm. The field experiment (Figure 9) was repeated 10 times to reduce the impact of random errors. The result showed that the harvesting rate of the ripe fruit was 83.65%, the harvesting rate of the unripe fruit was 7.22%, the damage rate of the ripe fruit was 11.49%, and the comprehensive picking index was 87.85.
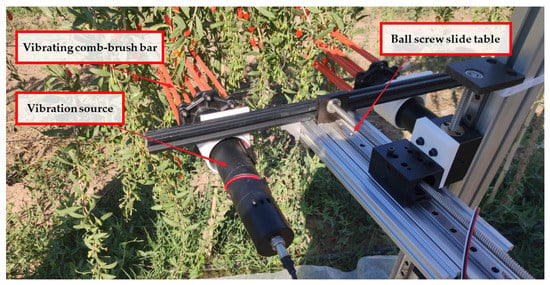
Figure 9.
Field experiment.
Compared with the relevant experiments [1,12,25], it was found that the harvesting method by vibrating and comb-brushing was effective. In all cases, the harvesting rate of the ripe fruit was more than 80% and both the harvesting rate of the unripe fruit and the damage rate of the ripe fruit were less than 15%. Therefore, the vibrating and comb-brushing harvesting method could be used for harvesting L. barbarum. We also found a few interesting phenomena in the field experiment. First, the higher the maturity of the ripe fruit, the easier it was to fall off. This could be because the connecting force of the stalk gradually decreased with the ripening of the fruit. Therefore, a reasonable selection of harvesting times may effectively improve the harvesting rate of ripe fruit. Second, because the ripe fruit and unripe fruit on the branches grew in turn, the harvesting could be stopped after harvesting in the ripe fruit area, thus reducing the harvesting rate of the unripe fruit. Finally, the vibrating and comb-brushing harvesting depended on the vibrating comb-brush bar to hit and brush the fruit to make it fall off, which led to a high damage rate of the ripe fruit. If the fruit could be harvested without touching, the rate of ripe fruit damage could be reduced.
4. Conclusions
In this study, faced with the standardized hedge cultivation mode of L. barbarum, a vibrating and comb-brushing harvester was designed. To optimize the vibrating and comb-brushing harvest method, its main factors and parameter value ranges were obtained by the analysis of each system and a preliminary test of the harvester. By using the quadratic orthogonal rotation combination test, the mathematical models of the harvesting rate of the ripe fruit, the harvesting rate of the unripe fruit, the damage rate of the ripe fruit, and the comprehensive picking index were established. Furthermore, an optimized parameter combination was determined based on RSM with a vibration frequency of 38.73 Hz, a brush speed of 14.21 mm/s, and an insertion depth of 26.07 mm. The field experiment showed that the harvesting rate of the ripe fruit was 83.65%, the harvesting rate of the unripe fruit was 7.22%, the damage rate of the ripe fruit was 11.49%, and the comprehensive picking index was 87.85. These results provide a design basis for future research on the vibrating and comb-brushing harvest method of L. barbarum. However, the harvesting effect still needs to be improved. In further studies, according to the growth characteristics and cultivation mode, the mechanism of vibrating and comb-brushing harvesting should be studied. The harvesting time, area, and location could be optimized to increase the harvesting rate of the ripe fruit, reduce the harvesting rate of the unripe fruit, and the damage rate of the ripe fruit to achieve a better harvesting effect.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.C., S.G., Y.C. (Yun Chen), T.S. and J.C.; funding acquisition, Y.C. (Yu Chen) and J.C.; investigation, Q.C., S.Z., J.Z. (Jianguo Zhou), J.Z. (Jian Zhao) and J.C.; methodology, S.Z. and G.H.; software, G.H., J.Z. (Jianguo Zhou) and J.Z. (Jian Zhao); supervision, G.H. and J.Z. (Jianguo Zhou); validation, Q.C. and S.Z.; writing—original draft, Q.C.; writing—review and editing, S.Z., G.H. and Y.C. (Yu Chen) All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Xu, L.; Chen, J.; Wu, G.; Yuan, Q.; Ma, S.; Yu, C.; Duan, Z.; Xing, J.; Liu, X. Design and operating parameter optimization of comb brush vibratory harvesting device for wolfberry. Trans. CSAE 2018, 34, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Sugirbay, A.; Liu, F.; Chen, Y.; Hu, G.; Zhang, E.; Chen, J. Parameter optimization of winnowing equipment for machine-harvested Lycium barbarum L. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2019, 17, e0203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ma, T.; Inagaki, T.; Chen, Q.; Gao, Z.; Sun, L.; Cai, H.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, S.; et al. Finite Element Method Simulations and Experiments of Detachments of Lycium barbarum L. Forests 2021, 12, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, J. Detecting Maturity in Fresh Lycium barbarum L. Fruit Using Color Information. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagase, H.; Farnsworth, N.R. A review of botanical characteristics, phytochemistry, clinical relevance in efficacy and safety of Lycium barbarum fruit (Goji). Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1702–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhang, F.; Yan, H.; Qian, D.-W.; Wang, H.-Q.; Jin, L.; Duan, J.-A. Comparison of Functional Components and Antioxidant Activity of Lycium barbarum L. Fruits from Different Regions in China. Molecules 2019, 24, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skenderidis, P.; Lampakis, D.; Giavasis, I.; Leontopoulos, S.; Petrotos, K.; Hadjichristodoulou, C.; Tsakalof, A. Chemical Properties, Fatty-Acid Composition, and Antioxidant Activity of Goji Berry (Lycium barbarum L. and Lycium chinense Mill.) Fruits. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Z.; Deng, Q.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y. Immune activities of polysaccharides isolated from Lycium barbarum L. What do we know so far? Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 229, 107921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, J.; Yan, J.; Liu, S.; Guo, Y.; Chen, D.; Luo, Q. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides ameliorates renal injury and inflammatory reaction in alloxan-induced diabetic nephropathy rabbits. Life Sci. 2016, 157, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Hu, G.; Chen, J. Design and Testing of a Pneumatic Oscillating Chinese Wolfberry Harvester. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiao, H.; Ding, W.; Mei, S. Machanism simulation analysis and prototype experiment of Lycium barbarum harvest by vibration mode. Trans. CSAE 2015, 31, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Bu, L.; Hu, G.; Zhang, E. Design and experiment on vibrating and comb brushing harvester for Lycium barbarum. Trans. CSAM 2019, 50, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, J.D. Vibration characteristics of boxthorn (Lycium chinense Mill) branches. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2001, 17, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, J.D. Vibratory harvesting machine for boxthorn (Lycium chinense Mill.) berries. Trans. ASAE 2003, 46, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinpeng, W.; Song, M.; Hongru, X.; Ying, Z.; Hongping, Z. Research on Mechanized Harvesting Methods of Lycium barbarum Fruit. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, C.; Yalei, W.; Jian, Z.; Jun, C. Recognition of the position of Chinese wolfberry branches under the artificial background. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Kan, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z. Mechanism analysis and experiment on vibration harvesting of wolfberry. Trans. CSAE 2017, 33, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Han, B.; Chen, J. Research on laws of wolfberry dropping based on high-speed camera. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2018, 40, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Research on Key Technology of Wolfberry Vibration Harvest. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Experimental research on parameter optimization of portable vibrating and harvesting device of Chinese wolfberry. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2019, 41, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Sugirbay, A.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, F.; Bu, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J. FEM explicit dynamics simulation and NIR hyperspectral reflectance imaging for determination of impact bruises of Lycium barbarum L. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 155, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Q.; Chen, J. Simulation for Fitting the Bending Shape of Fruit Branches of Lycium barbarum Based on the Finite Element Method. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Tan, Y.; Li, W. Optimal design and experiment on variable pacing combing brush picking device for Lycium barbarum. Trans. CSAM 2018, 49, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, W. Design and experiment of vibrating wolfberry harvester. Trans. CSAM 2018, 49, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ma, T.; Inagaki, T.; Chen, Y.; Hu, G.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Gao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wang, M.; et al. Parameter Optimization of Vibrating and Comb-Brushing Harvesting of Lycium barbarum L. Based on FEM and RSM. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fan, G.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z. Effects of Hedgerow Cultivation on Leaf and Fruit Phenotypic and Yield of Lycium bar-barum L. North. Hortic. 2021, 1, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, M.; Mozafari-Vanani, L.; Dehghani-Soufi, M.; Jahanbakhshi, A. Effect of alumina nanoparticles as additive with diesel–biodiesel blends on performance and emission characteristic of a six-cylinder diesel engine using response surface methodology (RSM). Energy Convers. Manag. X 2021, 11, 100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Mao, Y.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, W.; Ye, W.; Duan, Y.; Xie, Q. Analysis and Optimization of Grinding Performance of Vertical Roller Mill Based on Experimental Method. Minerals 2022, 12, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karganroudi, S.S.; Moradi, M.; Attar, M.A.; Rasouli, S.A.; Ghoreishi, M.; Lawrence, J.; Ibrahim, H. Experimental and Numerical Analysis on TIG Arc Welding of Stainless Steel Using RSM Approach. Metals 2021, 11, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).