Development of Simple Sequence REPEAT Markers for Genetic Diversity Analysis Based on the cDNA Sequences of Chinese Yam (Dioscorea spp.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and DNA Extraction
2.2. RNA Extraction and cDNA Library Preparation
2.3. De Novo Transcriptome Assembly
2.4. Development and Primer Design of SSR Markers
2.5. PCR Amplification and Polymorphism Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
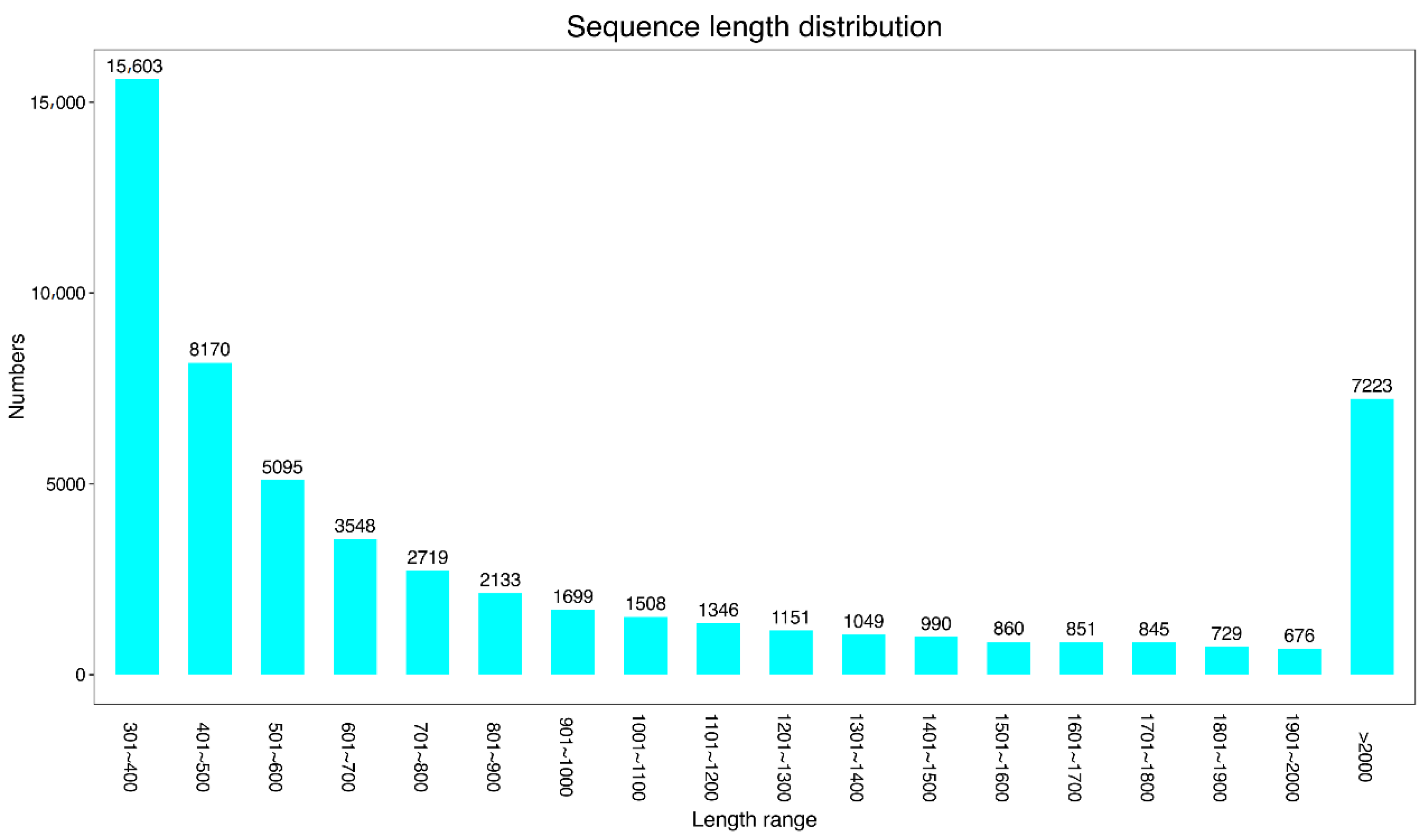
3.1. De Novo Transcriptome Assembly
3.2. UniGene Function
3.3. Microsatellite Feature Analysis
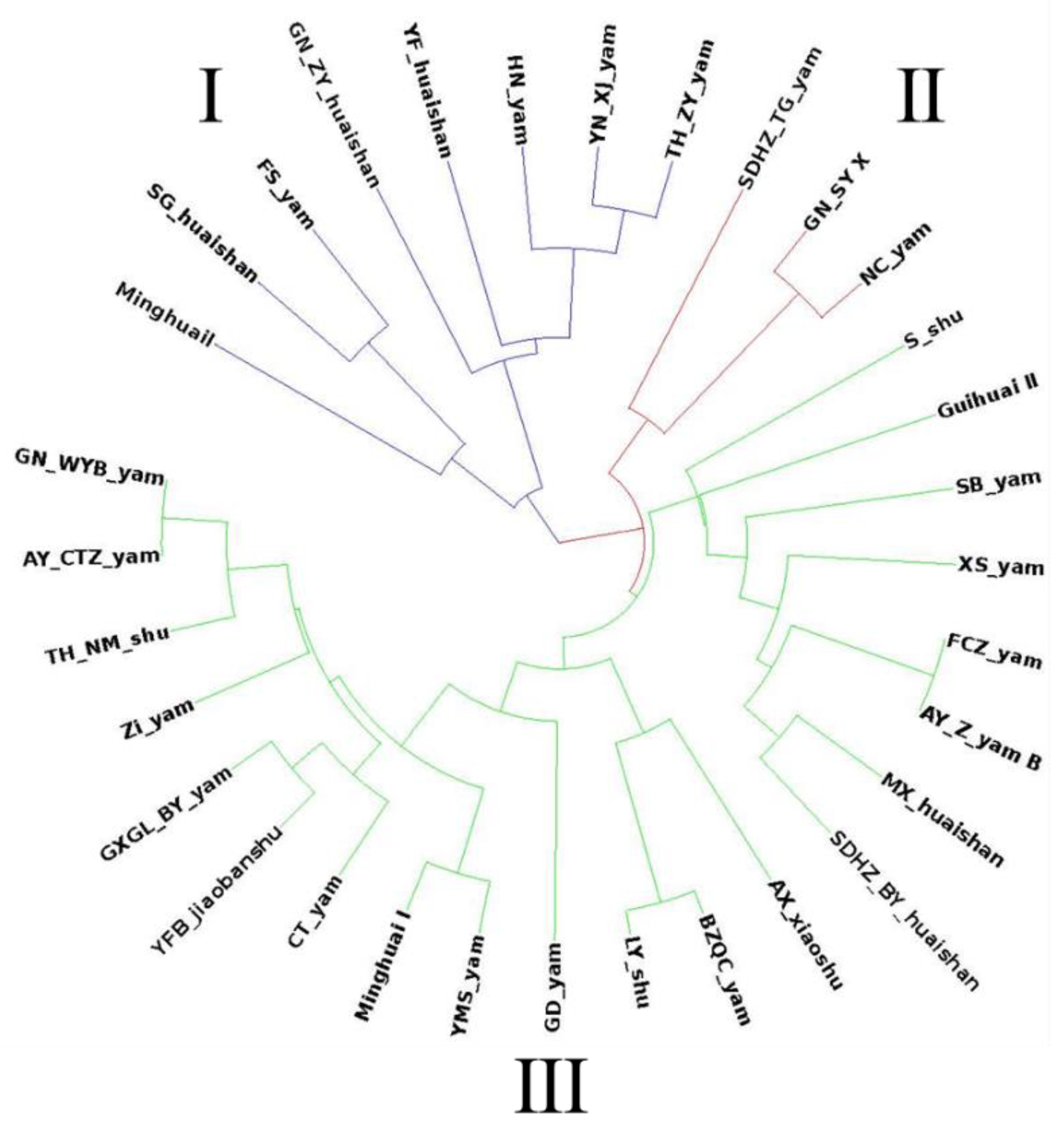
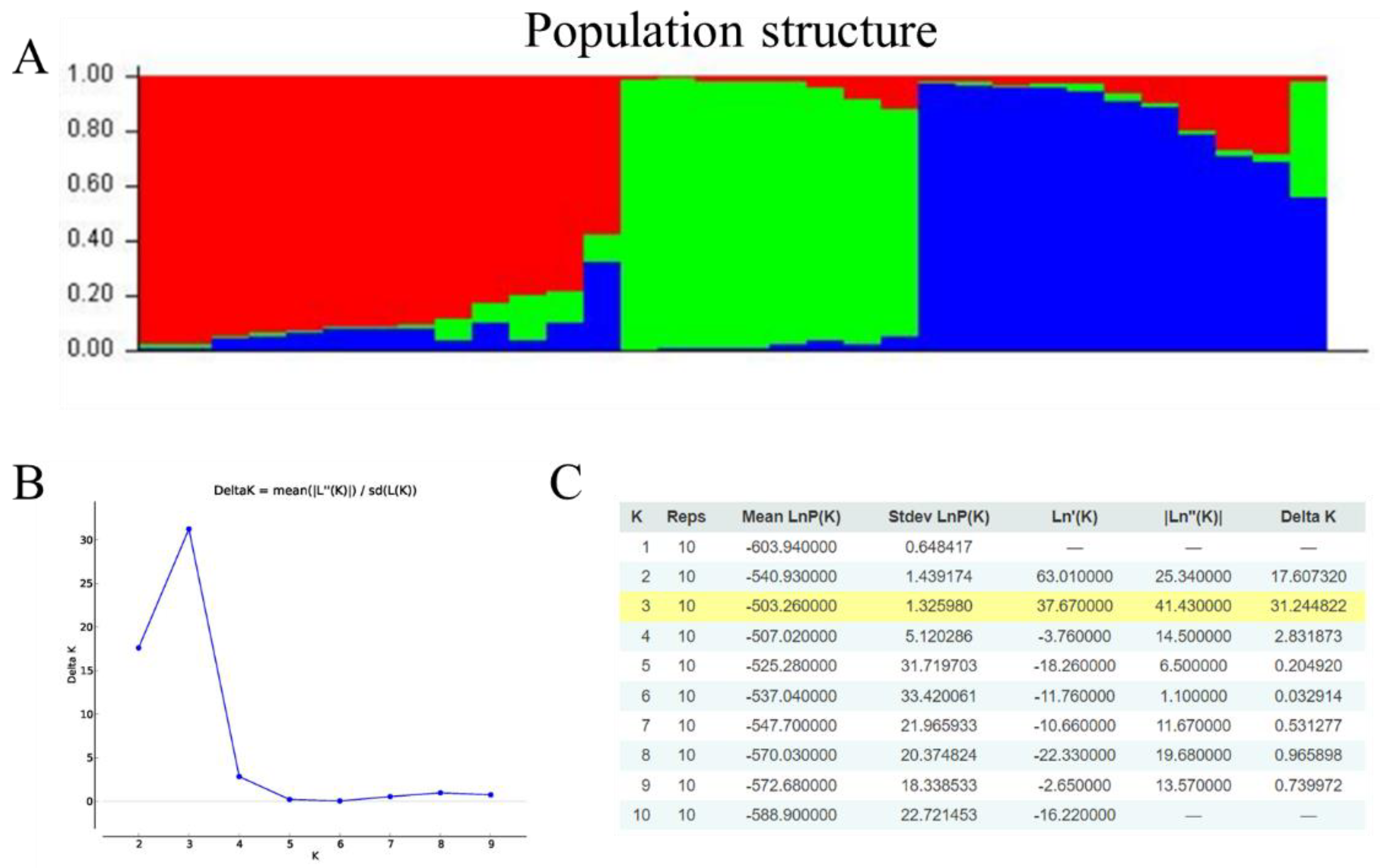
3.4. Genetic Diversity of Chinese Yam Germplasm
4. Discussion
4.1. Transcriptome Sequencing, Assembly, and Functional Annotation
4.2. SSR Markers
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azeteh, I.N.; Hanna, R.; Njukeng, A.P.; Oresanya, A.O.; Sakwe, P.N.; Kumar, P.L. Distribution and Diversity of Viruses Infecting Yams (Dioscorea spp.) in Cameroon. VirusDisease 2019, 30, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.F.; Podolyan, A.; Kidanemariam, D.B.; Pilotti, C.; Houliston, G.; Sukal, A.C. A Review of Viruses Infecting Yam (Dioscorea spp.). Viruses 2022, 14, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adenji, M.O.; Shoyinka, S.A.; Ikotun, T.; Asiedu, R.; Hughes, J.d.A.; Odu, B.O. Yield Loss in Guinea Yam (Dioscorea rotundata Poir.) Due to Infection by Yam Mosaic(Ymv) Genus Potyvirus. Ife J. Sci. 2012, 14, 237–244. [Google Scholar]
- Amusa, N.; Adegbite, A.A.; Muhammed, S.; Baiyewu, R.A. Yam Diseases and Its Management in Nigeria. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 2, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamiru, M.; Natsume, S.; Takagi, H.; White, B.; Yaegashi, H.; Shimizu, M.; Yoshida, K.; Uemura, A.; Oikawa, K.; Abe, A.; et al. Genome Sequencing of the Staple Food Crop White Guinea Yam Enables the Development of a Molecular Marker for Sex Determination. BMC Biol. 2017, 15, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.L.; Liu, P. A Study on the Floristic Geographical Elements of the Chinese Dioscorea. J. Zhejiang Norm. Univ. 1994, 17, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, F.G.; Hua, S.M.; Tu, Q.C.; He, P.Z.; Li, Q.X.; Zao, Y.Y. Genetic Relationship of Dioscorea polystachya Turcz. Resources Based on ISSR Markers. Fujian J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 28, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lin, D.; Huang, G.D.; Zhong, X.F. Study on Extraction of the Total Saponins of Chinese Yam. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2007, 7, 854–857. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.Y.; Liu, W.; Chou, G.X.; Wang, Y.L. Research Progress on Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Activities of Dioscorea opposita Thunb. Acta Chin. Med. Pharm. 2020, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.Y.; Hou, Y.J.; Jia, S.Y.; Si, R.H.; Zheng, B.W.; Liu, G.Z. Research Progress on Chemical Constituents of Dioscoreae rhizoma and Pharmacological Effects of Saponins. Inf. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 38, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, N. Study on Nutrition Content and Quality Evaluation of Different Chinese Yam (Dioscorea Opposite Thunb.) Cultivars. Ph.D. Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, M.J.; Li, J.C.; Meng, Y.J.; Yang, T.X.; Ge, S.J. Research Progress on Germplasm Resources Identification and Breeding of Chinese Yam. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2021, 11, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Shi, X.Y.; Chen, Q.; Fang, S.M.; Yang, R.X.; Peng, B. Theoretical Study on Corona Virus Disease 2019 Treated by Qingfei Paidu Decoction. Liaoning J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, 5, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, X.; Jiang, H.; Du, H.H.; Meng, Y.P. Research Progress on Dioscorea opposita in China. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2016, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Huo, W.X.; Yang, M.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Y.H.; Zhao, Z.H.; Tai, L.H. Genetic Diversity Analysis and Primary Core Collection Construction in Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) by ISSR Marker. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2015, 5, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Wang, L.J.; Lei, J.; Chai, S.S.; Yang, X.S.; Zhang, W.Y. Genetic Diversity Analysis and Construction of DNA Fingerprint of Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) Germplasm by cpSSR Marker. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2021, 33, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Li, J.J.; Wang, F.D.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, J.N.; Gao, J.W. Characterization and Development of EST-SSRs by Deep Transcriptome Sequencing in Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). Int. J. Genom. 2015, 2015, 473028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenta, S.; Kohei, I.; Cholgwang, K.; Tomohiro, B.; Munenori, S.; Takashi, I.; Toshiya, M.; Megumi, K.; Noriko, N.; Sachiko, I.; et al. Development of Capsicum EST-SSR Markers for Species Identification and in Silico Mapping onto the Tomato Genome Sequence. Mol. Breed. 2013, 31, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.Q.; Wang, L.Y.; Zhang, C.C.; Wei, K.; Zhang, C.C.; Wu, L.Y.; Qi, G.N.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, Q.M.; et al. Floral Transcriptome Sequencing for SSR Marker Development and Linkage Map Construction in the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saski, C.A.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Scheffler, B.E.; Asiedu, R. Genomic Resources for Water Yam (Dioscorea alata L.): Analyses of EST-Sequences, De Novo Sequencing and GBS Libraries. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e134031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.L.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.D.; et al. Trinity: Reconstructing a Full-Length Transcriptome without a Genome from RNA-Seq Data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jaroszewski, L.; Godzik, A. Clustering of Highly Homologous Sequences to Reduce the Size of Large Protein Databases. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 282–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, J.; Finn, R.D.; Eddy, S.R.; Bateman, A.; Punta, M. Challenges in homology search: HMMER3 and convergent evolution of coiled-coil regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, T.; Michalek, W.; Varshney, R.; Graner, A. Exploiting EST Databases for The Development and Characterization of Gene-Derived SSR-Markers in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavas, M.; Yıldırım, K.; Seçgin, Z.; Gökdemir, G. Discovery of Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) Markers in Hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) by Transcriptome Sequencing and SSR-Based Characterization of Hazelnut Cultivars. Scand. J. For. Res. 2020, 35, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Shi, Y.L.; Wang, X.F.; Sun, Z.M.; Huang, K.Y.; Gong, C.; Luan, M.B.; Chen, J.H. Development of SSR Markers via De Novo Transcriptome Assembly in Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz. Genome 2019, 62, 817–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabreena; Nazir, M.; Mahajan, R.; Hashim, M.J.; Iqbale, J.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ganai, B.A.; Zargar, S.M. Deciphering Allelic Variability and Population Structure in Buckwheat: An Analogy between the Efficiency of ISSR and SSR markers. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 6050–6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Muse, S.V. PowerMarker: An Integrated Analysis Environment for Genetic Marker Analysis. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2128–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.A.; Yang, S.H.; Rehman, H.M.; Baloch, F.S.; Lee, J.D.; Park, J.H.; Chung, G. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Korean Wild Soybean (Glycine soja Sieb. and Zucc.) Inferred from Microsatellite Markers. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2017, 71, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, H.D. Fast and Sensitive Protein Alignment Using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.X.; Wang, F.Q.; Du, J.F.; Hua, S.M.; Lei, F.G.; Xu, X.M.; Liang, K.J.; Zhang, Z.Y. Numerical Analysis of Morphological Variation of Germplasm Resources of Dioscorea. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2013, 38, 318–324. [Google Scholar]
- Kamunya, S.M.; Wachira, F.N.; Pathak, R.S.; Korir, R.; Sharma, V.; Kumar, R.; Bhardwaj, P.; Chalo, R.; Ahuja, P.S.; Sharma, R.K. Genomic Mapping and Testing for Quantitative Trait Loci in Tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze). Tree Genet. Genomes 2010, 6, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.Y.; Lee, T.C.; Tsai, H.T.; Tsai, Y.Z.; Lin, S.F. Construction of an Integrated Genetic Map Based on Maternal and Paternal Lineages of Tea (Camellia sinensis). Euphytica 2013, 191, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, D.; Li, J.X.; Yu, B.; Qiao, X.Y.; Huang, H.L.; He, Y.M. De Novo Characterization of Leaf Transcriptome Using 454 Sequencing and Development of EST-SSR Markers in Tea (Camellia sinensis). Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 31, 524–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darkwa, D.; Agre, A.P.; Olasanmi, B.; Iseki, K.; Matsumoto, R.; Powell, A.; Bauchet, G.; Koeyer, D.D.; Muranaka, S.; Adebola, P.; et al. Comparative Assessment of Genetic Diversity Matrices and Clustering Methods in White Guinea Yam (Dioscorea rotundata) Based on Morphological and Molecular Markers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Sun, J.Y.; Shan, N.; Chen, X.; Wang, P.; Zhu, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhou, Q.H.; Huang, Y.J. Uncovering the Genetic Diversity of Yams (Dioscorea spp.) in China by Combining Phenotypic Trait and Molecular Marker Analyses. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 9970–9986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agre, P.A.; Dassou, A.G.; Loko, L.E.Y.; Idossou, R.; Dadonougbo, E.; Gbaguidi, A.; Mondo, J.M.; Muyideen, Y.; Adebola, P.O.; Asiedu, R. Diversity of White Guinea Yam (Dioscorea rotundata Poir.) Cultivars from Benin as Revealed by Agro-Morphological Traits and SNP Markers. Plant Genet. Resour. 2021, 19, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.C.; Jiang, D.; Zhao, Z.Y. Development of Chloroplast Genomic Resources in Chinese Yam. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 6293847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Li, J.; Luo, Z.X.; Yuan, S.B.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhang, T.; Zhong, W.H.; Yuan, Q.J.; Huang, L.Q. Characterization and Development of EST-Derived SSR Markers in Cultivated Sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas). BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloutier, S.; Niu, Z.; Datla, R.; Duguid, S. Development and Analysis of EST-SSRs for Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 119, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Chen, X.; Hong, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhou, G.Y.; Li, X.S.; Guo, B.Z. Utility of EST-Derived SSR in Cultivated Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) and Arachis Wild Species. BMC Plant Biol. 2009, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.L.; Qi, X.Q.; Wang, L.H.; Zhang, Y.X.; Hua, W.; Li, D.H.; Lv, H.X.; Zhang, X.R. Characterization of the Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) Global Transcriptome Using Illumina Paired-End Sequencing and Development of EST-SSR Markers. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; He, Q.; Liu, X.X.; Xu, W.L.; Li, L.B.; Gao, J.W.; Wang, F.D. Transcriptome Analysis of the Roots at Early and Late Seedling Stages Using Illumina Paired-End Sequencing and Development of EST-SSR Markers in Radish. Plant Cell Rep. 2012, 31, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, R.K.; Hendre, P.S.; Varshney, R.K.; Bhat, P.R.; Krishnakumar, V.; Singh, L. Identification, Characterization and Utilization of Est-Derived Genic Microsatellite Markers for Genome Analyses of Coffee and Related Species. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 114, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.J.; Yang, C.; Tian, B.; Yang, J.B.; Liu, A.Z. Exploiting EST Databases for the Development and Characterization of EST-SSR Markers in Castor Bean (Ricinus communis L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpatla, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Mining and Survey of Simple Sequence Repeats in Expressed Sequence Tags of Dicotyledonous Species. Genome 2005, 48, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Fang, B.P.; Chen, J.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Luo, Z.X.; Huang, L.F.; Chen, X.L.; Li, Y.J. De Novo Assembly and Characterization of Root Transcriptome Using Illumina Paired-End Sequencing and Development of cSSR Markers in Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas). BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróblewska, A. Genetic Diversity and Spatial Genetic Structure of Chamaedaphne Calyculata (Ericaceae) at the Western Periphery in Relation to Its Main Continuous Range in Eurasia. Folia Geobot. 2013, 49, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.X.; Huang, S.; Liang, K.J.; Ma, H.B.; Lei, F.G.; Hua, S.M.; Xu, X.M. Genetic Diversity of Germplasm Resources on Dioscorea by SRAP Markers. Chin. Wild Plant Resour. 2011, 30, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.M.; Tu, Q.C.; Lei, F.G. Genetic Diversity of Dioscorea polystachya Turcz. Revealed by RAPD Markers. J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2009, 10, 195–200. [Google Scholar]


| No | Name | Abbreviated Name | The Geographical Place of Origin (China) | Lat/Long | Species | Characterizations | Tuber Shape |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hainan Yam | HN_yam | Hainan Province | 108°37′–111°03′ E/18°10′–20°10‘ N | Dioscorea alata | Purple skin and white flesh | Flat block shape |
| 2 | Guannanziyu Yam | GN_ZY_huaishan | Lianyungang City, Jiangsu Province | 118°24′–119°48′ E/34°0′–35°7′ N | Dioscorea | Purple skin and purple flesh | Long column shape |
| 3 | Yongfenghuaishan | YF_huaishan | Ji’an City, Jiangxi Province | 114°58′ E/27 °07′ N | Dioscorea | Yellow skin and white flesh | Long column shape |
| 4 | Taiheziyu Yam | TH_ZY_yam | Ji’an City, Jiangxi Province | 114°58′ E/27 °07′ N | Dioscorea | Purple skin and purple flesh | Long column shape |
| 5 | Yunnanxiangjiao Yam | YN_XJ_yam | Yunnan Province | 97°31′–106°11′ E/21°8′–29°15′ N | Dioscorea persimilis | Yellow skin and white flesh | Long column shape |
| 6 | Minghuai No. 2 | Minghuai II | Fujian Province | 115°40′–120°30′ E/23°30′–28°20′ N | Dioscorea alata | Purple skin and white flesh | Flat block shape |
| 7 | Foshou Yam | FS_yam | Huanggang City, Hubei Province | 116°04′–115°31′ E/30°31′–31°09′ N | Dioscorea alata | Yellow skin and white flesh | Flat block shape |
| 8 | Shangehuaishan | SG_huaishan | Quanzhou City, Fujian Province | 118°67′ E/24°88′ N | Dioscorea | Yellow skin and white flesh | Long column shape |
| 9 | Shandonghezetiegun Yam | SDHZ_TG_yam | Heze City, Shangdong Province | 114°48′–116°24′ E/34°39′ –35°52′ N | Dioscorea persimilis | Yellow skin and white flesh | Long column shape |
| 10 | Changting Yam | CT_yam | Longyan City, Fujian Province | 115°51′–117°45′ E/24°23′–26°02′ N | Dioscorea | Yellow skin and white flesh | Long column shape |
| 11 | Shuangbao Yam | SB_yam | Qidong City, Jiangsu Province | 121°25′–121°54′ E/31°41′–32°16′ N | Dioscorea persimilis | Yellow skin and white flesh | Long column shape |
| 12 | Guangxi GuilingBaiye Yam | GXGL_BY_yam | Guilin City, Guangxi Province | 110°10′ E/25°18′ N | Dioscorea | Yellow skin and white flesh | Flat block shape |
| 13 | Nancheng Yam | NC_yam | Nancheng City, Jiangxi Province | 116°64′ E/27°55′ N | Dioscorea persimilis | Yellow skin and white flesh | Long column shape |
| 14 | Minghuai No. 1 | Minghuai Ⅰ | Fujian Province | 115°40′–120°30′ E/23°30′–28°20′ N | Dioscorea | Purple skin and white flesh | Flat block shape |
| 15 | Liuyueshu | LY_shu | Unknown | Unknown | Dioscorea alata | Yellow skin and white flesh | Cylinder shape |
| 16 | Guannanweiyibai Yam | GN_WYB_yam | Lianyungang City, Jiangsu Province | 118°24′–119°48′ E/34°0′–35°7′ N | Dioscorea alata | Yellow skin and white flesh | Long column shape |
| 17 | Anyuanzi Yam Chengtuo | AY_CTZ_yam | Ganzhou City, Jiangxi Province | 113°54′–116°38′ E/24°29′–27°09′ N | Dioscorea alata | Purple skin and white flesh | Cylinder shape |
| 18 | Zi Yam | Zi_yam | Unknown | Unknown | Dioscorea persimilis | Purple skin and purple flesh | Flat block shape |
| 19 | Guangdong Yam | GD_yam | Guangdong Province | 109°39′–117°19′ E/20°13′–25°31′ N | Dioscorea alata | Purple skin and white flesh | Flat block shape |
| 20 | Xishi Yam | XS_yam | Heze City, Shangdong Province | 114°48′–116°24′ E/34°39′–35°52′ N | Dioscorea alata | Yellow skin and white flesh | Long column shape |
| 21 | Anshaxiaoshu | AX_xiaoshu | Yongan City, Fujian Province | 117°37′ E/25°98′ N | Dioscorea alata | Yellow skin and white flesh | Cylinder shape |
| 22 | Yongfengbaijaiobanshu | YFB_jiaobanshu | Ji’an City, Jiangxi Province | 114°58′ E/27°07′ N | Dioscorea | Yellow skin and white flesh | Flat block shape |
| 23 | Guannansuyu No. 10 | GN_SY Ⅹ | Lianyungang City, Jiangsu Province | 118°24′–119°48′ E/34°0′–35°7′ N | Dioscorea alata | Yellow skin and white flesh | Long column shape |
| 24 | Anyuanzi Yam No.b | AY_Z_yam B | Ganzhou City, Jiangxi Province | 113°54′–116°38′ E/24°29′–27°09′ N | Dioscorea alata | Purple skin and purple flesh | Cylinder shape |
| 25 | Shanshu | S_shu | Unknown | Unknown | Dioscorea alata | Yellow skin and white flesh | Cylinder shape |
| 26 | Shandonghezebaiyuhuaishan | SDHZ_BY_huaishan | Heze City, Shangdong Province | 114°48′–116°24′ E/34°39′–35°52′ N | Dioscorea alata | Yellow skin and white flesh | Long column shape |
| 27 | BKQC_yam | Bikeqichang Yam | Neimenggu Province | 126°04′–97°12′ E/37°24′–53°23′ N | Dioscorea | Yellow skin and white flesh | Long column shape |
| 28 | Yangmingshan Yam | YMS_yam | Taiwan Province | 119°18′–124°34′ E/20°45–25°56′ N | Dioscorea persimilis | Yellow skin and white flesh | Long column shape |
| 29 | Fengchengzi Yam | FCZ_yam | Fengcheng City, Jiangxi Province | 115°78′ E/28°20′ N | Dioscorea alata | Purple skin and purple flesh | Flat block shape |
| 30 | Taihenuomishu | TH_NM_shu | Ji’an City, Jiangxi Province | 114°58′ E/27°07′ N | Dioscorea alata | Yellow skin and white flesh | Flat block shape |
| 31 | Guihuai No. 2 | Guihuai Ⅱ | Guangxi Province | 110°10′ E/25°18′ N | Dioscorea persimilis | Yellow skin and white flesh | Long column shape |
| 32 | Mingxihuaishan | MX_huaishan | Sanming City, Fujian Province | 26°13′ E/117°36′ N | Dioscorea | Yellow skin and white flesh | Long column shape |
| Description | Statistics |
|---|---|
| Unigene | 56,195 |
| ≥500 bp | 32,503 |
| ≥1000 bp | 17,249 |
| N50 | 1583 |
| Total length | 56,209,464 |
| Max length | 16,900 |
| Min length | 301 |
| Average length | 1000.26 |
| Marker | Repeat Motif | Primer Pair (5′-3′) | Major.Allele.Frq | Genotype No | Allele No | Availability | Gene Diversity | Heterozygosity | PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s1–5 | (T)39 | TTGCGTGTTGCCCTTCTTTG | 0.8214 | 2 | 2 | 0.875 | 0.2934 | 0 | 0.2503 |
| GGCCGAGAGTTTGGAGGAAA | |||||||||
| s2–9 | (AC)25 | AAAGAAGCAGCAGCAACAGC | 0.8846 | 2 | 2 | 0.8125 | 0.2041 | 0.2308 | 0.1833 |
| AGAGGCTGAAGACACCGTTG | |||||||||
| s2–12 | (AC)25 | GGTGGTCCAGTAACAGTCGG | 0.5 | 2 | 2 | 0.625 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.375 |
| TTGCCCACAAAGTCACCAGT | |||||||||
| s2–14 | (GA)24 | GGTTTCCTTGGGATGCCAGA | 0.5455 | 3 | 2 | 0.6875 | 0.4959 | 0.0909 | 0.3729 |
| CACCCGGAGATCAGACACAC | |||||||||
| s2–19 | (TA)23 | CACTCCATCATCGTCTCCGG | 0.9355 | 2 | 2 | 0.9688 | 0.1207 | 0.129 | 0.1134 |
| ATCGAACCAGCCCAACGAAT | |||||||||
| s2–26 | (CT)22 | CCCGTAAGAACACCGACCAA | 0.7391 | 4 | 3 | 0.7188 | 0.4045 | 0.1739 | 0.3507 |
| TGGGGGTGAGGGAGAACTAG | |||||||||
| s2–29 | (AT)22 | CGGACTCCATCGCTTCTCTC | 0.8095 | 2 | 2 | 0.6563 | 0.3084 | 0.381 | 0.2608 |
| CAGCAACAACGCCATCCAAA | |||||||||
| s3–10 | (AAG)14 | GACGAAGCTGCCATTGAAGC | 0.931 | 2 | 2 | 0.9063 | 0.1284 | 0 | 0.1202 |
| CATGATCAAGAACGCTGGCG | |||||||||
| s3–12 | (TCT)14 | AGCTCACAACACACTGCAGA | 0.54 | 7 | 4 | 0.7813 | 0.6296 | 0.16 | 0.5801 |
| GGAGGAGGAGCTGCAAAGAG | |||||||||
| s3–19 | (TCA)13 | ACCATCTCCCTCACCTCCTC | 0.8125 | 2 | 2 | 0.75 | 0.3047 | 0.375 | 0.2583 |
| GTTGTCGATGGACCAGTGGT | |||||||||
| s4–1 | (TAAA)9 | CCTTCCCATCACGTCCTCTG | 0.963 | 2 | 2 | 0.8438 | 0.0713 | 0.0741 | 0.0688 |
| TGCAAATGGTCCTGCGGAAT | |||||||||
| s4–11 | (ATTT)7 | GCTGCAAGTTCGCATTATCCT | 0.8095 | 4 | 3 | 0.6563 | 0.3163 | 0.2857 | 0.2791 |
| AACTAACCACCCAGCGCAAT | |||||||||
| s4–12 | (CTTT)7 | AGCTCAGCTCTCGAACCCTA | 0.8269 | 4 | 3 | 0.8125 | 0.301 | 0.2692 | 0.2802 |
| CAAAACACCGAAACCCCGAC | |||||||||
| s4–13 | (TAGA)7 | ATCGGAGTACTCCCTGGCTT | 0.7222 | 2 | 2 | 0.8438 | 0.4012 | 0.5556 | 0.3207 |
| GCTACCACCGGAGCTATCAC | |||||||||
| s4–3 | (AGAT)9 | TTGGTGAGGAGGAGGAGGAG | 0.48 | 4 | 3 | 0.7813 | 0.5696 | 0.24 | 0.475 |
| TAACTGTTGTTGGGCCAGCA | |||||||||
| s5–1 | (CTTTC)8 | TGAACGCCCACCTCAAAACT | 0.7679 | 2 | 2 | 0.875 | 0.3565 | 0.4643 | 0.293 |
| ATCAGGAGGAGCTGGAGTGT | |||||||||
| s5–4 | (ATATC)7 | TCAAAGCCATGGAGACGACC | 0.5357 | 8 | 5 | 0.875 | 0.6193 | 0.1786 | 0.5634 |
| CGGTGTCAGTGAACGAGGAA | |||||||||
| s5–7 | (AGATT)6 | GGACACAAACACACTCATGCA | 0.5833 | 5 | 3 | 0.75 | 0.5417 | 0.1667 | 0.4598 |
| TGGCTCACACACTTACCCAA | |||||||||
| s6–5 | (AT)12(GT)11(GA)7 | TCGTTAGATTGCGGAGGAGC | 0.7742 | 2 | 2 | 0.9688 | 0.3496 | 0 | 0.2885 |
| GGGTAGCATAGCAAGGGCAA | |||||||||
| Mean | 0.6944 | 3.2917 | 2.5417 | 0.7643 | 0.3991 | 0.2051 | 0.3352 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, L.; Chen, Y.; Sun, J.; Ouyang, C.; Li, B.; Zeng, H.; Chen, X.; Luan, M. Development of Simple Sequence REPEAT Markers for Genetic Diversity Analysis Based on the cDNA Sequences of Chinese Yam (Dioscorea spp.). Horticulturae 2022, 8, 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8121163
Wang H, Wang Y, Xiong L, Chen Y, Sun J, Ouyang C, Li B, Zeng H, Chen X, Luan M. Development of Simple Sequence REPEAT Markers for Genetic Diversity Analysis Based on the cDNA Sequences of Chinese Yam (Dioscorea spp.). Horticulturae. 2022; 8(12):1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8121163
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hong, Yue Wang, Lingzhi Xiong, Yingde Chen, Jiali Sun, Changdong Ouyang, Baihua Li, Hanyi Zeng, Xiaorong Chen, and Mingbao Luan. 2022. "Development of Simple Sequence REPEAT Markers for Genetic Diversity Analysis Based on the cDNA Sequences of Chinese Yam (Dioscorea spp.)" Horticulturae 8, no. 12: 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8121163
APA StyleWang, H., Wang, Y., Xiong, L., Chen, Y., Sun, J., Ouyang, C., Li, B., Zeng, H., Chen, X., & Luan, M. (2022). Development of Simple Sequence REPEAT Markers for Genetic Diversity Analysis Based on the cDNA Sequences of Chinese Yam (Dioscorea spp.). Horticulturae, 8(12), 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8121163






