Characterization of Phytochemical and Nutrient Compounds from the Leaves and Seeds of Moringa oleifera and Moringa peregrina
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Proximate and Mineral Composition
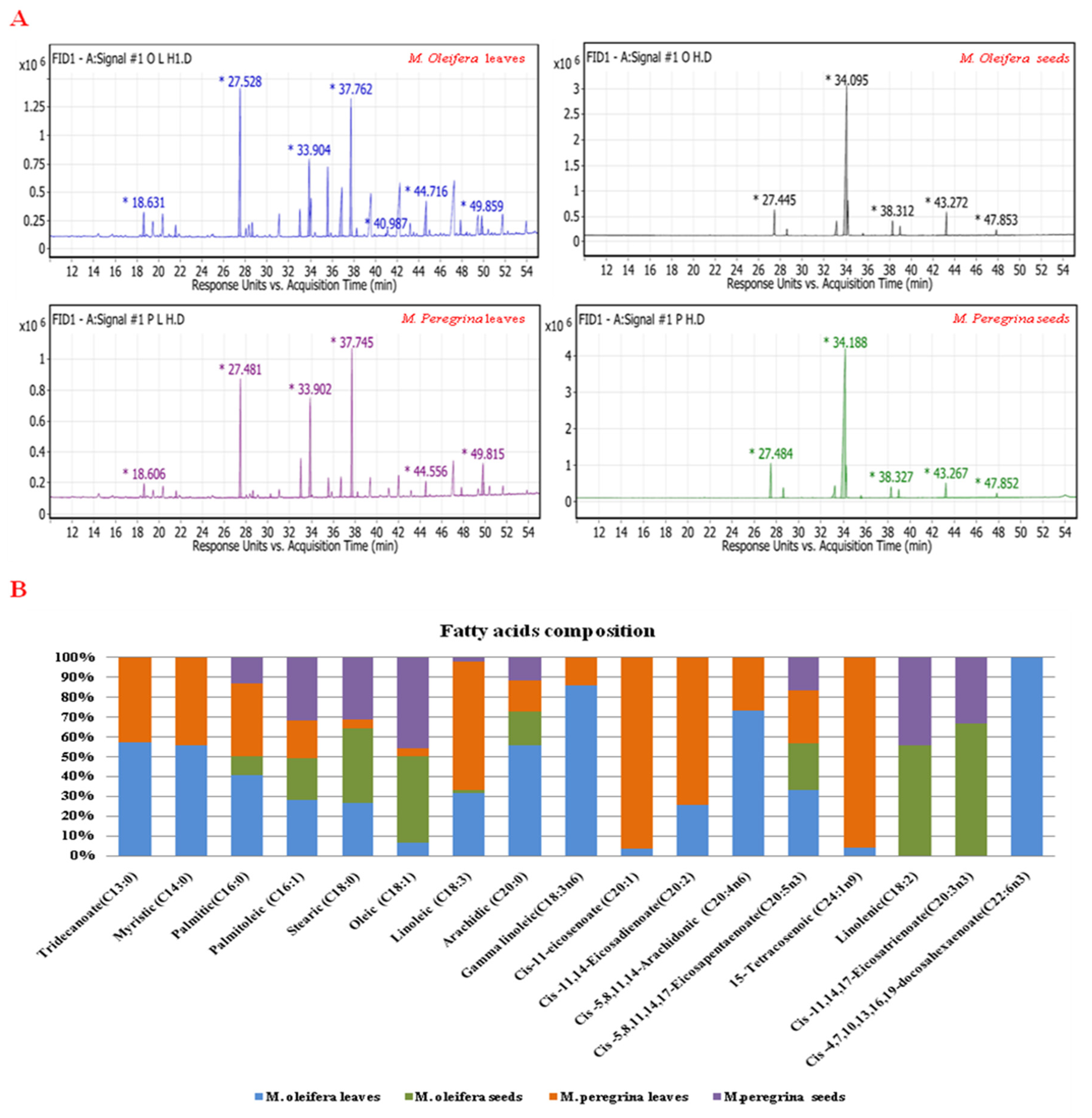
2.3. Gas Chromatographic Fatty Acid (FA) Analysis
2.4. Un-Saponified Compounds Profiling
2.5. Total Polyphenolic Contents Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Proximate and Mineral Composition Analysis
3.2. Fatty Acid (FA) Compositions
3.3. Un-Saponified Composition
3.4. Determination of Polyphenol Content
4. Discussion
4.1. Proximate and Mineral Composition Analysis
4.2. Fatty Acid (FA) Composition Profile
4.3. The Un-Saponified Matter
4.4. Polyphenols Compositions Profile
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fahey, J.W. Moringa oleifera: A review of the medical evidence for its nutritional, therapeutic, and prophylactic properties. Part 1. Trees Life J. 2005, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Mughal, M.H.; Ali, G.; Srivastava, P.; Iqbal, M. Improvement of drumstick (Moringa pterygosperma Gaertn.)—A unique source of food and medicine through tissue culture. Hamdard Med. 1999, 42, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, J.F. The horseradish tree, Moringa pterygosperma (Moringaceae)—A boon to arid lands? Econ Bot. 1991, 45, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakad, A.K.; Ikram, M.; Sharma, S.; Khan, S.; Pandey, V.V.; Singh, A. Biological, nutritional, and therapeutic significance of Moringa oleifera Lam. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 2870–2903. [Google Scholar]
- Salama, M.A.E.-B.; Owon, M.; Osman, M.; Ibrahim, A.; Matthäus, B. Effect of germination and roasting on oil profile of Moringa oleifera and Moringa peregrina seeds. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramabulana, T.; Mavunda, R.; Steenkamp, P.A.; Piater, L.; Dubery, I.; Madala, N. Perturbation of pharmacologically relevant polyphenolic compounds in Moringa oleifera against photo-oxidative damages imposed by gamma radiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 156, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingale, S.P.; Gandhi, F.P. Effect of aqueous extract of Moringa oleifera leaves on pharmacological models of epilepsy and anxiety in mice. Int. J. Epilepsy 2016, 3, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayas-Viera, M.D.M. Anticancer effect of Moringa oleifera leaf extract in human cancer cell lines. J. Health Disparities Res. Pract. 2016, 9, 102. [Google Scholar]
- Mun’im, A.; Puteri, M.U.; Sari, S.P. Anti-anemia effect of standardized extract of Moringa oleifera Lamk. Leaves on aniline induced rats. Pharmacogn. J. 2016, 8, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Asmari, A.K.; Albalawi, S.M.; Athar, M.T.; Khan, A.Q.; Al-Shahrani, H.; Islam, M. Moringa oleifera as an anti-cancer agent against breast and colorectal cancer cell lines. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterman, C.; Rojas-Silva, P.; Tumer, T.B.; Kuhn, P.; Richard, A.J.; Wicks, S.; Stephens, J.M.; Wang, Z.; Mynatt, R.; Cefalu, W.; et al. Isothiocyanate-rich Moringa oleifera extract reduces weight gain, insulin resistance, and hepatic gluconeogenesis in mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2015, 59, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, W.; Ejaz, S.; Anwar, K.; Ashraf, M. Exploration of the in vitro cytotoxic and antiviral activities of different medicinal plants against infectious bursal disease (IBD) virus. Open Life Sci. 2014, 9, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontual, E.V.; de Lima Santos, N.D.; de Moura, M.C.; Coelho, L.C.; do Amaral Ferraz Navarro, D.M.; Napoleão, T.H.; Paiva, P.M. Trypsin inhibitor from Moringa oleifera flowers interferes with survival and development of Aedes aegypti larvae and kills bacteria inhabitant of larvae midgut. Parasitol Res. 2014, 113, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkovich, L.; Earon, G.; Ron, I.; Rimmon, A.; Vexler, A.; Lev-Ari, S. Moringa oleifera aqueous leaf extract down-regulates nuclear factor-kappaB and increases cytotoxic effect of chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013, 13, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gismondi, A.; Canuti, L.; Impei, S.; Di Marco, G.; Kenzo, M.; Colizzi, V.; Canini, A. Antioxidant extracts of African medicinal plants induce cell cycle arrest and differentiation in B16F10 melanoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waiyaput, W.; Payungporn, S.; Issara-Amphorn, J.; Panjaworayan, N.T. Inhibitory effects of crude extracts from some edible Thai plants against replication of hepatitis B virus and human liver cancer cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2012, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Arya, V. A review on potential diuretics of Indian medicinal plants. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2011, 3, 613–620. [Google Scholar]
- Hamza, A.A. Ameliorative effects of Moringa oleifera Lam seed extract on liver fibrosis in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.N.; Singh, B.R.; Singh, R.L.; Prakash, D.; Dhakarey, R.; Upadhyay, G.; Singh, H.B. Oxidative DNA damage protective activity, antioxidant and anti-quorum sensing potentials of Moringa oleifera. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutar, N.G.; Bonde, C.; Patil, V.; Narkhede, S.; Patil, A.; Kakade, R. Analgesic activity of seeds of Moringa oleifera Lam. Int. J. Green Pharm. 2008, 2, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, B.; Mehta, A. Antiasthmatic activity of Moringa oleifera Lam: A clinical study. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2008, 40, 28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Armand-Stussi, I.; Basocak, V.; Pauly, G.; McCaulley, J. Moringa oleifera: An interesting source of active ingredients for skin and hair care. SÖFW-J. 2003, 129, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, A.V.; Devi, P.U.; Kamath, R. In vivo radioprotective effect of Moringa oleifera leaves. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 39, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fuglie, L.J. The Miracle Tree, Moringa oleifera: Natural Nutrition for the Tropics; Church World Service: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bennour, N.; Mighri, H.; Eljani, H.; Zammouri, T.; Akrout, A. Effect of solvent evaporation method on phenolic compounds and the antioxidant activity of Moringa oleifera cultivated in Southern Tunisia. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 129, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti, G.; Pagnossa, J.P.; Blasi, F.; Cossignani, L.; Piccoli, R.H.; Zengin, G.; Montesano, D.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Lucini, L. Phenolic profiling and in vitro bioactivity of Moringa oleifera leaves as affected by different extraction solvents. Int. Food Res. J. 2020, 127, 108712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocchetti, G.; Blasi, F.; Montesano, D.; Ghisoni, S.; Marcotullio, M.C.; Sabatini, S.; Cossignani, L.; Lucini, L. Impact of conventional/non-conventional extraction methods on the untargeted phenolic profile of Moringa oleifera leaves. Food Res. Int. 2019, 115, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldoni, T.; Merlin, N.; Karling, M.; Carpes, S.T.; Alencar, S.M.; Morales, R.; Silva, E.; Pilau, E.J. Bioguided extraction of phenolic compounds and UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS characterization of extracts of Moringa oleifera leaves collected in Brazil. Food Res. Int. 2019, 125, 108647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakaran, M.; Kim, S.-H.; Sasireka, A.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Chung, I.-M. Polyphenol composition and antimicrobial activity of various solvent extracts from different plant parts of Moringa oleifera. Food Biosci. 2018, 26, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuellar-Nuñez, M.; Luzardo-Ocampo, I.; Campos-Vega, R.; Gallegos-Corona, M.; De Mejía, E.G.; Loarca-Piña, G. Physicochemical and nutraceutical properties of moringa (Moringa oleifera) leaves and their effects in an in vivo AOM/DSS-induced colorectal carcinogenesis model. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouman, W.; Anwar, F.; Gull, T.; Newton, A.; Rosa, E.; Domínguez-Perles, R. Profiling of polyphenolics, nutrients and antioxidant potential of germplasm’s leaves from seven cultivars of Moringa oleifera Lam. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 83, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Pérez, C.; Quirantes-Piné, R.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A.; Segura-Carretero, A. Optimization of extraction method to obtain a phenolic compounds-rich extract from Moringa oleifera Lam leaves. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 66, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, P.; Kumar, S.; Riar, C.S.; Jindal, N.; Baniwal, P.; Guiné, R.; Correia, P.; Mehra, R.; Kumar, H. Recent advances in Drumstick (Moringa oleifera) leaves bioactive compounds: Composition, health benefits, bioaccessibility, and dietary applications. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddhuraju, P.; Becker, K. Antioxidant properties of various solvent extracts of total phenolic constituents from three different agroclimatic origins of drumstick tree (Moringa oleifera Lam.) leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2144–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyo, B.; Masika, P.J.; Hugo, A.; Muchenje, V. Nutritional characterization of Moringa (Moringa oleifera Lam.) leaves. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 12925–12933. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, I.M.; Barua, S.; Nazimuddin, M.; Begum, Z.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Hasegawa, H. Physicochemical properties of Moringa oleifera lam. Seed oil of the indigenous-cultivar of Bangladesh. J. Food Lipids 2009, 16, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakour, Z.T.A.; Radwa, H.; Elshamy, A.I.; El Gendy, A.E.N.G.; Wessjohann, L.A.; Farag, M.A. Dissection of Moringa oleifera leaf metabolome in context of its different extracts, origin and in relationship to its biological effects as analysed using molecular networking and chemometrics. Food Chem. 2022, 399, 133948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassey, K.; Mabowe, M.; Mothibe, M.; Witika, B.A. Chemical Characterization and Nutritional Markers of South African Moringa oleifera Seed Oils. Molecules 2022, 27, 5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, A.M.E.; Omar, F.A.; Emam, M.M.A.A.; Farag, M.A. UPLC-MS/MS and GC-MS based metabolites profiling of Moringa oleifera seed with its anti-Helicobacter pylori and anti-inflammatory activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, H.; Sadrameli, S.M.; Eslami, F.; Asoodeh, A. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of Moringa peregrina oil with response surface methodology and comparison with Soxhlet method. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 131, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, A.; Karuvantevida, N.; Rastrelli, L.; Kurup, S.S.; Cheruth, A.J. Traditional Uses, Pharmacological Efficacy, and Phytochemistry of Moringa peregrina (Forssk.) Fiori.—A Review. Front. Pharmacol 2018, 9, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardabiab, F.; Azizia, M.H.; Gavlighia, H.A.; Rashidinejad, A. Potential benefits of Moringa peregrina defatted seed: Effect of processing on nutritional and anti-nutritional properties, antioxidant capacity, in vitro digestibility of protein and starch, and inhibition of α-glucosidase and α-amylase enzymes. Food Chem. adv. 2022, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Abo El-Fadl, S.; Osman, A.; Al-Zohairy, A.M.; Dahab, A.A.; Abo El Kheir, Z.A. 2020. Assessment of total phenolic, flavonoid content, antioxidant potential and HPLC profile of three Moringa species leaf extracts. Sci. J. Flowers Ornam. Plants 2020, 7, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Durst, R.; Wrolstad, R. AOAC official method 2005.02: Determination of total monomeric anthocyanin pigment content of fruit juices, beverages, natural colorants, and wines by the pH differential method Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOAC (Association of Official Analytical Chemists). Official Methods of Analysis. AOAC: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Zhigang, Y.; Thomas, R.; Gitta, H.; Uwe, B. Continuous flow analysis of dissolved total phosphorus in seawater by UV-K 2 S 2 O 8 online digestion method. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2004, 4, 637–645. [Google Scholar]
- Maqueda, C.; Morillo, E. Determination of calcium by atomic-absorption spectrometry in samples dissolved by acid mixtures. Fresenius J. Anal Chem. 1990, 338, 253–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Goupy, P.; Hugues, M.; Boivin, P.; Amiot, M.J. Antioxidant composition and activity of barley (Hordeum vulgare) and malt extracts and of isolated phenolic compounds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 1625–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuckle, J.L. IBM SPSS Amos 19 User’s Guide; Amos Development Corporation: Crawfordville, FL, USA, 2010; Volume 635. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, D.B. Multiple range and multiple F tests. Biometrics 1955, 11, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, H.; Ghazal, G.A. Physicochemical properties of Moringa oleifera seeds and their edible oil cultivated at different regions in Egypt. Food Nutr. Sci. 2016, 7, 472. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmud, G.F.; El Ghadban, E.A.E.; Shahat, M.S. Chemical and Nutrient Evaluation of Moringa Oleifera Seed and Oil Cultivated in Egypt. Bull. Nat. Nutr. Inst. A. R. Egypt 2017, 49, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Aja, P.; Ibiam, U.; Uraku, A.; Orji, O.; Offor, C.; Nwali, B. Comparative proximate and mineral composition of Moringa oleifera leaf and seed. Glob. Adv. Res. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 2, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Ranhotra, G.; Gelroth, J.; Glaser, B.; Stallknecht, G. Nutritional profile of three spelt wheat cultivars grown at five different locations. Cereal Chem. 1996, 73, 533–535. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, U.; Singh, B. Tropical grain legumes as important human foods. Econ. Bot. 1992, 46, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, D.; Raymer, P.; Savage, S. Variation of protein and fat concentration among commercial corn hybrids grown in the southeastern USA. J. Prod. Agric. 1989, 2, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Chen, X. Current status and potential of Moringa oleifera leaf as an alternative protein source for animal feeds. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Dabbas, M.M. Antioxidant activity of different extracts from the aerial part of Moringa peregrina (Forssk.) Fiori, from Jordan. Pak. J. Pharm Sci. 2017, 30, 2151–2157. [Google Scholar]
- Somali, M.; Bajneid, M.; Al-Fhaimani, S. Chemical composition and characteristics of Moringa peregrina seeds and seeds oil. J Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1984, 61, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debebe, M.; Eyobel, M. Determination of proximate and mineral compositions of Moringa oleifera and Moringa stenopetala leaves cultivated in Arbaminch Zuria and Konso, Ethiopia. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 16, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olusanya, R.N.; Kolanisi, U.; Van Onselen, A.; Ngobese, N.Z.; Siwela, M. Nutritional composition and consumer acceptability of Moringa oleifera leaf powder (MOLP)-supplemented mahewu. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 129, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Baky, H.H.; El-Baroty, G.S. Characterization of Egyptian Moringa peregrine seed oil and its bioactivities. Int. J. Manage. Sci. Bus Res. 2013, 2, 98–108. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, F.; Zafar, S.N.; Rashid, U. Characterization of Moringa oleifera seed oil from drought and irrigated regions of Punjab, Pakistan. Grasas Y Aceites 2006, 57, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbe, A.; Affiku, J.P. Proximate study, mineral and anti-nutrient composition of Moringa oleifera leaves harvested from Lafia, Nigeria: Potential benefits in poultry nutrition and health. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2011, 1, 296–308. [Google Scholar]
- Nel, A.A. Determination of Sunflower Seed Quality for Processing. Ph.D Thesis, Dept. of Plant Production and Soil Sciences. University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa, 2001; pp. 40–56. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, H.E.; Abohassan, A.A. Morphological and analytical characterization of Moringa peregrina populations in western Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Theor. Appl. Sci. 2012, 4, 174–184. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, A.R.; Silva, M.M.; Ribeiro, B.D. Health issues and technological aspects of plant-based alternative milk. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131, 108972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, R.K.; Sivanesan, I.; Keum, Y.-S. Phytochemicals of Moringa oleifera: A review of their nutritional, therapeutic and industrial significance. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoddami, A.; Wilkes, M.A.; Roberts, T.H. Techniques for analysis of plant phenolic compounds. Molecules 2013, 18, 2328–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaknin, Y.; Mishal, A. The potential of the tropical “miracle tree” Moringa oleifera and its desert relative Moringa peregrina as edible seed-oil and protein crops under Mediterranean conditions. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 225, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukandoul, S.; Casal, S.; Zaidi, F. The potential of some moringa species for seed oil production. Agriculture 2018, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, F.; Gilani, S. Fatty acids in Moringa oleifera oil. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2007, 29, 343–345. [Google Scholar]
- Nibret, E.; Wink, M. Trypanocidal and antileukaemic effects of the essential oils of Hagenia abyssinica, Leonotis ocymifolia, Moringa stenopetala, and their main individual constituents. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, U.; Anwar, F.; Moser, B.R.; Knothe, G. Moringa oleifera oil: A possible source of biodiesel. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 8175–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiman, R.; Ashley, D.A.; Brown, J.H. Comparison of two seed oils used in cosmetics, moringa and marula. Ind. Crops Prod. 2008, 28, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizi, S.; Sumbul, S.; Versiani, M.A.; Saleem, R.; Sana, A.; Siddiqui, H. GC/GCMS analysis of the petroleum ether and dichloromethane extracts of M oringa oleifera roots. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbatran, S.A.; Abdel-Salam, O.M.; Abdelshfeek, K.A.; Nazif, N.M.; Ismail, S.I.; Hammouda, F.M. Phytochemical and pharmacological investigations on Moringa peregrina (Forssk) Fiori. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2005, 11, 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Belitz, H.-D.; Grosch, W.; Schieberle, P. Food Chemistry; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Belo, Y.N.; Al-Hamimi, S.; Chimuka, L.; Turner, C. Ultrahigh-pressure supercritical fluid extraction and chromatography of Moringa oleifera and Moringa peregrina seed lipids. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 3685–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hak, H.N.G.; Moustafa, A.R.A.; Mansour, S.R. Toxic effect of Moringa peregrina seeds on histological and biochemical analyses of adult male Albino rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Awady, M.; Hassan, M.; El-Sayed, S.; Gaber, A. Comparison of the antioxidant activities, phenolic and flavonoids contents of the leaves-crud extracts of Moringa peregrine and Moringa oleifera. Int. J. Biosci. 2016, 8, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Dhara, R.; Bhattacharyya, D.K.; Ghosh, M. Analysis of sterol and other components present in unsaponifiable matters of mahua, sal and mango kernel oil. J. Oleo Sci. 2010, 59, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalas, S.; Tsaknis, J. Extraction and identification of natural Antioxidant from the seeds of the Moringa oleifera tree variety of Malaw. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2002, 79, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiyo, F.C.; Moodley, R.; Singh, M. Cytotoxicity, Antioxidant and Apoptosis Studies of Quercetin-3-O Glucoside and 4-(β-D-Glucopyranosyl-1→4-α-L-Rhamnopyranosyloxy)-Benzyl Isothiocyanate from Moringa oleifera. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedraza-Hernández, J.; Elghandour, M.M.; Khusro, A.; Salem, M.Z.; Camacho-Diaz, L.M.; Barbabosa-Pliego, A.; Salem, A. Assessment on bioactive role of Moringa oleifera leaves as anthelmintic agent and improved growth performance in goats. Trop Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahay, S.; Yadav, U.; Srinivasamurthy, S. Potential of Moringa oleifera as a functional food ingredient: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 2, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Özcan, M.M. Moringa spp.: Composition and bioactive properties. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 129, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quideau, S.; Deffieux, D.; Douat-Casassus, C.; Pouységu, L. Plant polyphenols: Chemical properties, biological activities, and synthesis. Nat. Prod. 2011, 50, 586–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manach, C.; Scalbert, A.; Morand, C.; Rémésy, C.; Jiménez, L. Polyphenols: Food sources and bioavailability. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 727–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonaka, G. Isolation and structure elucidation of tannins. Pure Appl. Chem. 1989, 61, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, L.; Doriya, K.; Kumar, D.S. Moringa oleifera: A review on nutritive importance and its medicinal application. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2016, 5, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djemoui, D.; Saidi, M.; Rahmani, Z.; Djemoui, A. Influence of phenolic compounds on antioxidant capacity of leaves extracts of Moringa oleifera from tamanrasset region. Int. J. Fundam. Appl. 2019, 11, 280–293. [Google Scholar]
- Rajput, H.; Prasad, S.; Srivastav, P.; Singh, N.; Suraj, L.; Chandra, R. Chemical and phytochemical properties of fresh and dried Moringa oliferiea (PKM-1) leaf powder. Chem. Sci. Rev. Lett. 2017, 6, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar]
- Juhaimi, F.A.; Ghafoor, K.; Ahmed, I.M.; Babiker, E.E.; Özcan, M.M. Comparative Study of Mineral and Oxidative Status of Sonchus oleraceus, Moringa oleifera and Moringa peregrina Leaves. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 1745–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.-O.; Park, C.-I.; Jin, S.-J.; Park, M.-R.; Choi, I.-Y.; Park, C.-H.; Adnan, M. Comparison in Content of Total Polyphenol, Flavonoid, and Antioxidant Capacity from Different Organs and Extruded Condition of Moringa oleifera Lam. Processes 2022, 10, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Nabey, A.A.; Abou-Tor, E.-S.M.; Magda, S.S. Chemical and Technological Studies of Moringa oliefera Lam. Leaves and Its Phenolic Extracts. Alex. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento, J.A.; Araujo, K.L.G.V.; Epaminonolas, P.S.; Soledade, L.E.B.; Gueiroz, N.; Souza, A.G. Ethanolic extracts of Moringa oleifera Lam. Evaluation of its potential as an antioxidant additive for fish oil. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 114, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vongsak, B.; Sithisarn, P.; Mangmool, S.; Thongpra- ditchote, S.; Wongkrajang, Y.; Gritsanapan, W. Maximizing total phenolics, total flavonoids contents and antioxidant activity of Moringa oleifera leaf extract by the appro- priate extraction methods. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 44, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, M.; Oyedemi, S.; Masika, P.J.; Muchenje, V. Polyphenolic content and antioxidant properties of Moringa oleifera leaf extracts and enzymatic activity of liver from goats supplemented with Moringa oleifera leaves/sunflower seed cake. Meat Sci. 2012, 91, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, S.; Bhanger, M.I. Effect of season and production location on antioxidant activity of Moringa oleifera leaves grown in Pakistan. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehshahri, S.; Wink, M.; Afsharypuor, S.; Asghari, G.; Mohagheghzadeh, A. Antioxidant activity of methanolic leaf extract of Moringa peregrina (Forssk.) Fiori. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 7, 111. [Google Scholar]
- Asghari, G.; Palizban, A.; Bakhshaei, B. Quantitative analysis of the nutritional components in leaves and seeds of the Persian Moringa peregrina (Forssk.) Fiori. Pharmacogn. Res. 2015, 7, 242. [Google Scholar]



| No. | Component | M. oleifera | M. peregrina | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves | Seeds | Leaves | Seeds | ||
| 1 | Total Protein | 33.6 a ± 2.08 | 24 c ± 1 | 35.3 a ± 3.5 | 29 b ± 1 |
| 2 | Total Carbohydrates | 38.6 a ± 1.2 | 33.6 b ± 1.15 | 34.3 b ± 0.57 | 24 c ± 1 |
| 3 | Total oil | 22 d ± 1 | 36 b ± 1 | 25.1 c ± 1.25 | 42 a ± 1 |
| 4 | Total ASH | 5.3 ± 0.6 | 6.3 ± 0.57 | 5.6 ± 1.2 | 4.9 ± 0.45 |
| 5 | Total Nitrogen (TN) | 5.4 a ± 0.55 | 3.8 b ± 0.26 | 5.6 a ± 0.77 | 4.6 b ± 0.65 |
| 6 | Total Phosphorus (TP) | 0.34 b ± 0.007 | 0.52 a ± 0.08 | 0.27 b ± 0.04 | 0.32 b ± 0.07 |
| 7 | Total Potassium (TK) | 2.53 a ± 0.20 | 0.87 c ± 0.072 | 1.9 b ± 0.1 | 0.58 d ± 0.015 |
| 8 | Total Calcium (TCa) | 1.97 c ± 0.28 | 3.6 a ± 0.2 | 0.94 d ± 0.075 | 2.8 b ± 0.26 |
| No. | Fatty Acids | Formula | M. oleifera | M. peregrina | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves | Seeds | Leaves | Seeds | |||
| 1 | Tridecanoate (C13:0) | C13H26O2 | 3.91 a ± 0.30 | 0 | 2.91 b ± 0.10 | 0 |
| 2 | Myristic (C14:0) | C14H28O2 | 1.68 a ± 0.20 | 0 | 1.37 b ± 0.20 | 0 |
| 3 | Palmitic (C16:0) | C16H32O2 | 24.68 a ± 0.50 | 5.81 d ± 0.20 | 22.21 b ± 0.23 | 7.82 c ± 0.14 |
| 4 | Palmitoleic (C16:1) | C16H30O2 | 1.86 a ± 0.21 | 1.35 b ± 0.05 | 1.24 b ± 0.15 | 2.12 a ± 0.04 |
| 5 | Stearic (C18:0) | C18H36O2 | 3.50 c ± 0.50 | 5.0 a ± 0.1 | 0.63 d ± 0.15 | 4.07 b ± 0.02 |
| 6 | Oleic acid (C18:1) | C18H34O2 | 10.89 c ± 0.40 | 74.15 b ± 0.15 | 6.66 d ± 0.35 | 77.47 a ± 0.14 |
| 7 | Linoleic (C18:3) | C18H32O2 | 9.38 b ± 0.10 | 0.44 d ± 0.01 | 18.95 a ± 0.06 | 0.59 c ± 0.03 |
| 8 | Arachidic (C20:0) | C20H40O2 | 11.26 a ± 0.25 | 3.58 b ± 0.20 | 3.15 b ± 0.15 | 2.33 c ± 0.05 |
| 9 | Gamma linoleic (C18:3n6) | C18H30O2 | 20.24 a ± 0.27 | 0 | 3.33 b ± 0.15 | 0 |
| 10 | Cis-11-eicosenoate (C20:1) | C20H38O2 | 1.05 b ± 0.04 | 0 | 28.05 a ± 0.15 | 0 |
| 11 | Cis-11,14-Eicosadienoate (C20:2) | C21H38O2 | 0.27 b ± 0.025 | 0 | 0.78 a ± 0.03 | 0 |
| 12 | Cis-5,8,11,14-Arachidonic Acid (C20:4n6) | C20H32O2 | 6.69 a ± 0.20 | 0 | 2.48 b ± 0.20 | 0 |
| 13 | Cis-5,8,11,14,17 Eicosapentaenoate (C20:5n3) | C21H32O2 | 1.6 a ± 0.20 | 1.14 b ± 0.05 | 1.25 b ± 0.05 | 0.83 c ± 0.06 |
| 14 | 15-Tetracosenoic (C24:1n9) | C25H48O2 | 0.31 b ± 0.025 | 0 | 7 a ± 0.1 | 0 |
| 15 | Linolenic acid(C18:2) | C18H30O2 | 0 | 2.06 a ± 0.15 | 0 | 1.65 b ± 0.02 |
| 16 | Cis-11,14,17-Eicosatrienoate (C20:3n3) | C21H36O2 | 0 | 6.47 a ± 0.30 | 0 | 3.22 b ± 0.085 |
| 17 | Cis-4,7,10,13,16,19 docosahexaenoate (C22:6n3) | C24H36O2 | 2.73 a ± 0.20 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total saturated fatty acids | 45.02 ± 0.11 | 10.80 ± 0.02 | 37.11 a ± 0.11 | 11.98 d ± 0.02 | ||
| Total unsaturated fatty acids | 54.93 ± 0.95 | 89.19 ± 0.30 | 62.9 d ± 0.95 | 88.02 a ± 0.30 | ||
| No. | Component | Formula | M. oleifera | M. peregrina | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves | Seeds | Leaves | Seeds | |||
| 1 | Heptacosane | C27H56 | 24.84 a ± 0.15 | 8.42 c ± 0.065 | 10.8 b ± 0.10 | 2.86 d ± 0.035 |
| 2 | 2-Oleoylglycerol | C21H40O4 | 0.33 c ± 0.057 | 0.69 b ± 0.015 | 0.86 a ± 0.01 | 0 |
| 3 | Octacosane | C28H58 | 9.4 a ± 0.11 | 8.14 c ± 0.015 | 8.78 b ± 0.12 | 2.95 d ± 0.049 |
| 4 | Nonacosane | C29H60 | 38.68 a ± 0.23 | 8.24 c ± 0.055 | 30.11 b ± 0.12 | 2.92 d ± 0.055 |
| 5 | Hexadecyl ester | C27H38F15NO3 | 0.42 a ± 0.057 | 0 | 0.29 b ± 0.001 | 0 |
| 6 | Hexatriacontane | C36H74 | 4.68 b ± 0.19 | 5.42 a ± 0.070 | 3.94 c ± 0.60 | 2.10 d ± 0.10 |
| 7 | Hentriacontane | C31H64 | 4.27 a ± 0.025 | 0.53 d ± 0.020 | 4.09 b ± 0.107 | 1.68 c ± 0.010 |
| 8 | Acetic acid | C31H48O3 | 0.70 b ± 0.10 | 0.55 c ± 0.35 | 0.92 a ± 0.015 | 0 |
| 9 | Campesterol | C28H48O | 1.01 d ± 0.011 | 6.76 b ± 0.028 | 2.81 c ± 0.020 | 21.83 a ± 0.026 |
| 10 | Stigmasterol | C29H48O | 1.01 d ± 0.007 | 16.38 a ± 0.026 | 15.59 b ± 0.075 | 14.06 c ± 0.025 |
| 11 | Stigmasterol-7-en-ol, (3β,5α) | C29H48O | 0 | 3.02 b ± 0.025 | 13.81 a ± 0.060 | 1.56 c ± 0.045 |
| 12 | Sitosterol | C29H50O | 5.78 c ± 0.11 | 29.24 b ± 0.11 | 5.86 c ± 0.10 | 34.13 a ± 0.075 |
| 13 | Fucosterol | C29H50O | 0.346 d ± 0.05 | 7.95 b ± 0.036 | 0.533 c ± 0.015 | 15.85 a ± 0.12 |
| 14 | 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 | C27H44O3 | 0.440 b ± 0.010 | 0.58 a ± 0.020 | 0.443 b ± 0.015 | 0 |
| 15 | Tetracosanol-1-ol | C24H50O | 0.44 b ± 0.015 | 0 | 3.35 a ± 0.070 | 0 |
| 16 | Gamma-Sitosterol | C29H50O | 3.64 a ± 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 17 | Beta-Sitosterol | C29H50O | 4.77 a ± 0.10 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 18 | l-Alanine, n-pentadecafluorooctanoyl-, hexadecyl ester | C27H38F15NO3 | 0 | 0.47 a ± 0.020 | 0 | 0 |
| 19 | 7-Methyl-Z-tetradecane-1-ol acetate | C17H32O2 | 0 | 0 | 0.85 a ± 0.0100 | 0 |
| No. | Component | Formula | M. oleifera | M. peregrina | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves | Seeds | Leaves | Seeds | |||
| 1 | Gallic acid | C7H6O5 | 0.11 d ± 0.015 | 5.6 b ± 0.30 | 0.70 c ± 0.010 | 7.30 a ± 0.10 |
| 2 | Chlorogenic acid | C16H18O9 | 0.14 d ± 0.01 | 6.5 a ± 0.15 | 0.32 c ± 0.010 | 5.88 b ± 0.010 |
| 3 | Catechin | C15H14O6 | 3.67 c ± 0.090 | 4.48 a ± 0.05 | 0 | 3.90 b ± 0.10 |
| 4 | Methyl gallate | C8H8O5 | 3.4 a ± 0. 46 | 0 | 1.45 b ± 0.010 | 0.50 c ± 0.10 |
| 5 | Caffeic acid | C9H8O4 | 2.27 c ± 0.005 | 0 | 4.67 a ± 0.010 | 3.86 b ± 0.03 |
| 6 | Syringic acid | C9H10O5 | 2.59 a ± -0.09 | 0.58 d ± 0.015 | 1.9 b ± 0.1 | 1.76 c ± 0.01 |
| 7 | Rutin | C27H36O19 | 2.31 c ± 0.03 | 6 a ± 0.1 | 1.54 d ± 0.01 | 2.8 b ± 0.1 |
| 8 | Ellagic acid | C14H6O8 | 1.67 a ± 0.19 | 0 | 1.58 a ± 0.01 | 0 |
| 9 | Coumaric acid | C9H8O3 | 0 | 2.3 a ± 0.1 | 0.41 c ± 0.01 | 0.8 b ± 0.14 |
| 10 | Vanillin | C8H8O3 | 0.11 b ± 0.005 | 0.75 a ± 0.01 | 0.08 c ± 0.01 | 0.013 d ± 0.005 |
| 11 | Ferulic acid | C10H10O4 | 0.38 b ± 0.01 | 0.10 c ± 0.011 | 0.59 a ± 0.01 | 0.6 a ± 0.014 |
| 12 | Naringenin | C15H12O5 | 0. 59 c ± 0.014 | 1.28 a ± 0.01 | 0.65 b ± 0.01 | 0.026 d ± 0.001 |
| 13 | Daidzein | C15H10O4 | 0. 5 b ± 0.014 | 2.64 a ± 0.01 | 0 | 0.24 c ± 0.07 |
| 14 | Quercetin | C15H10O7 | 0. 52 b ± 0.014 | 1.92 a ± 0.01 | 0 | 0.36 c ± 0.02 |
| 15 | Cinnamic acid | C9H8O2 | 3 c ± 0.1 | 6.02 a ± 0.01 | 0 | 4.03 b ± 0.02 |
| 16 | Apigenin | C15H10O5 | 0.016 b ± 0.011 | 0 | 0 | 0.43 a ± 0.0028 |
| 17 | Kaempferol | C15H10O6 | 0. 42 a ± 0.014 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 18 | Hesperetin | C16H14O6 | 0. 69 a ± 0.014 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdalla, H.A.M.; Ali, M.; Amar, M.H.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q.-F. Characterization of Phytochemical and Nutrient Compounds from the Leaves and Seeds of Moringa oleifera and Moringa peregrina. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8111081
Abdalla HAM, Ali M, Amar MH, Chen L, Wang Q-F. Characterization of Phytochemical and Nutrient Compounds from the Leaves and Seeds of Moringa oleifera and Moringa peregrina. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(11):1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8111081
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdalla, Heba A. M., Mohammed Ali, Mohamed Hamdy Amar, Lingyun Chen, and Qing-Feng Wang. 2022. "Characterization of Phytochemical and Nutrient Compounds from the Leaves and Seeds of Moringa oleifera and Moringa peregrina" Horticulturae 8, no. 11: 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8111081
APA StyleAbdalla, H. A. M., Ali, M., Amar, M. H., Chen, L., & Wang, Q.-F. (2022). Characterization of Phytochemical and Nutrient Compounds from the Leaves and Seeds of Moringa oleifera and Moringa peregrina. Horticulturae, 8(11), 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8111081







