Environmental and Fecal Indicator Organisms on Fruit Contact Surfaces and Fruit from Blueberry Mechanical Harvesters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mechanical Harvester Survey
2.2. Swabbing from Harvester Surfaces
2.3. Fruit Sample Collection
2.4. Microbial Enumeration
2.5. Identification of Mechanical Harvester Microorganisms
3. Results
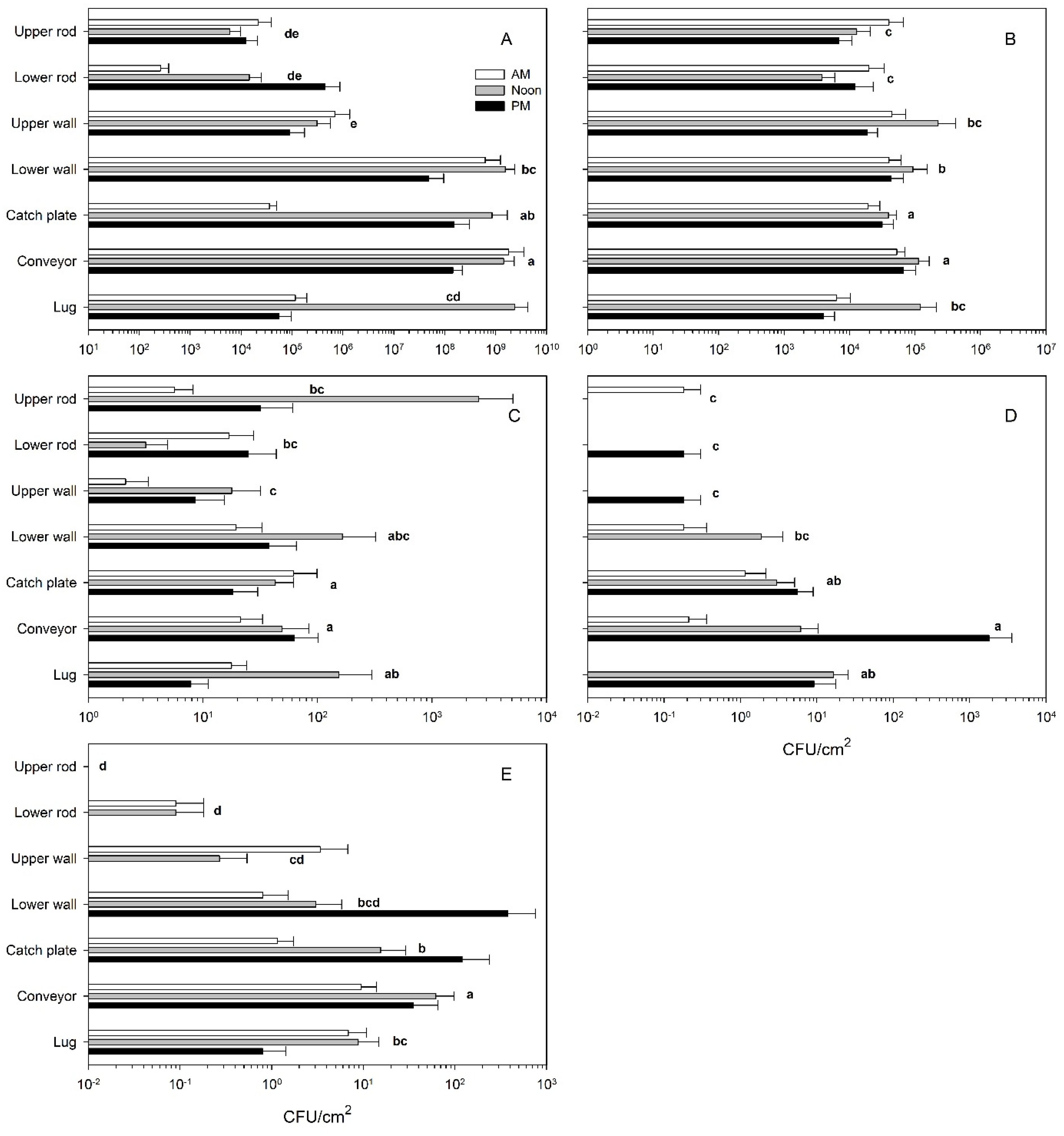
3.1. Microbial Loads on Harvester Surfaces
3.2. Microbial Loads on Top-Loader Harvester Surfaces
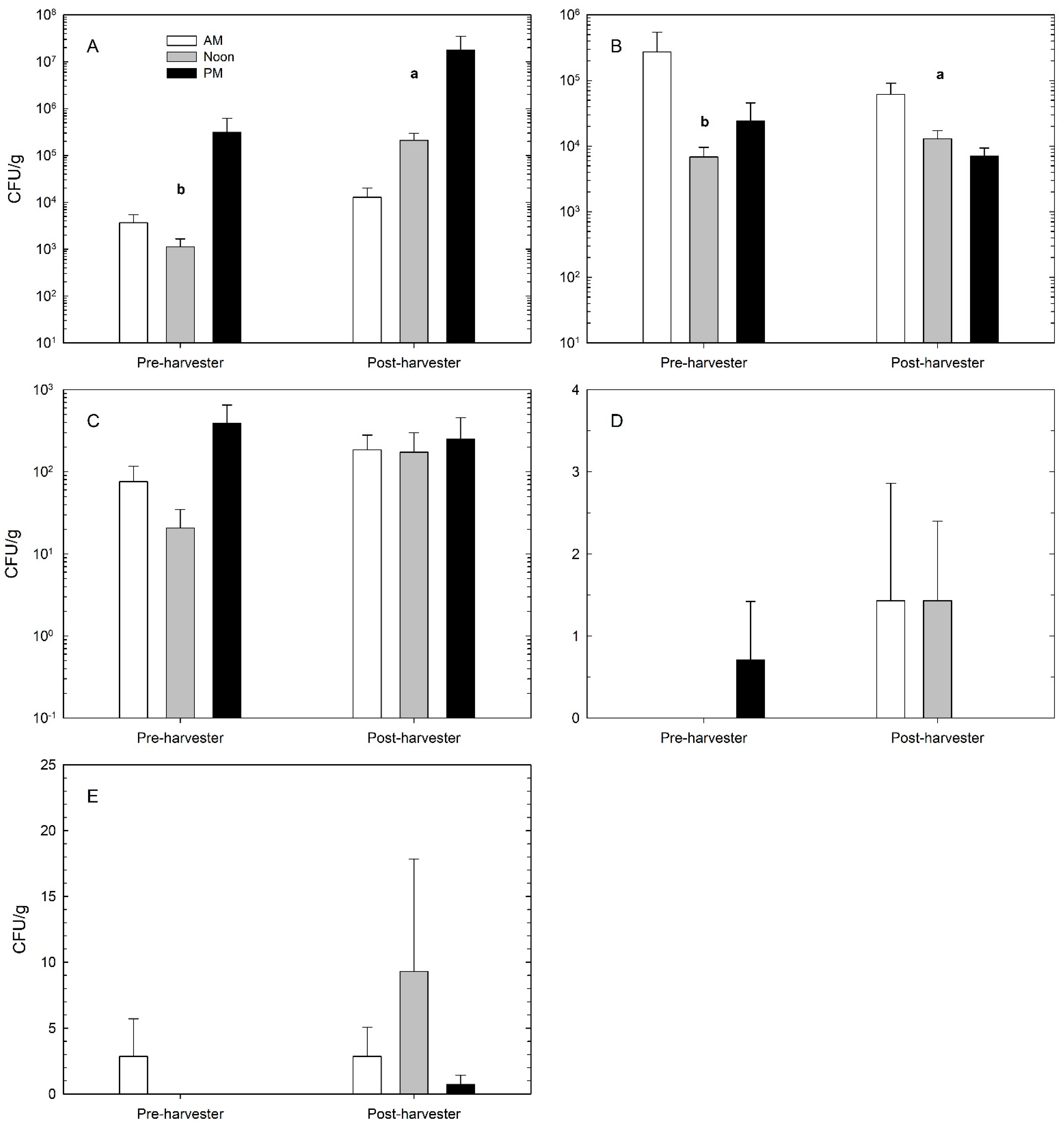
3.3. Microbial Loads on Fruit
3.4. Identification of Mechanical Harvester Microorganisms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grover, A.K.; Chopra, S.; Mosher, G.A. Food safety modernization act: A quality management approach to identify and prioritize factors affecting adoption of preventive controls among small food facilities. Food Control 2016, 66, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.R. Will the food safety modernization act help prevent outbreaks of foodborne illness? N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazula, H.; Quansah, J.; Allen, R.; Scherm, H.; Li, C.; Takeda, F.; Chen, J. Microbial loads on selected fresh blueberry packing lines. Food Control 2019, 100, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackett, R.E. Incidence, contributing factors, and control of bacterial pathogens in produce. Postharvest Biol. Tech. 1999, 15, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.-F.; Howard, R.J.; Strelkov, S.E.; Gossen, B.D.; Peng, G. Management of clubroot (Plasmodiophora brassicae) on canola (Brassica napus) in western Canada. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 36, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poumian, A.M. Disinfection of trucks and trailers. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz. 1995, 14, 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- Cárdenas, C.; Molina, K.; Heredia, N.; García, S. Evaluation of microbial contamination of tomatoes and peppers at retail markets in Monterrey, Mexico. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Microbiological Specifications for Foods. Sampling to assess control of the environment. In Microorganisms in Foods 7: Microbiological Testing in Food Safety Management; Buchanan, R., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 263–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savichtcheva, O.; Okabe, S. Alternative indicators of fecal pollution: Relations with pathogens and conventional indicators, current methodologies for direct pathogen monitoring and future application perspectives. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2463–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, M. An Evaluation of Blackberry Harvest Sanitation and the Ability of Foodborne Pathogens to Survive in Blackberry Products. Master’s Thesis, Department of Food Science and Technology, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mehra, L.K.; MacLean, D.D.; Savelle, A.T.; Scherm, H. Postharvest disease development on southern highbush blueberry fruit in relation to berry flesh type and harvest method. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quansah, J.K.; Gazula, H.; Holland, R.; Scherm, H.; Li, C.; Takeda, F.; Chen, J. Microbial quality of blueberries for the fresh market. Food Control 2019, 100, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, R.M. Fruit Microbial Hygiene Associated with Mechanical Harvesting and Injuries, and Stem Blight in Relation to Mechanical Hedging and Crown Bark Inclusions in Blueberry. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Plant Pathology, University of Georgia, Athens, GA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, J.A.; Reich, C.I.; Sharma, S.; Weisbaum, J.S.; Wilson, B.A.; Olsen, G.J. Critical evaluation of two primers commonly used for amplification of bacterial 16S rRNA genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Op De Beeck, M.; Lievens, B.; Busschaert, P.; Declerck, S.; Vangronsveld, J.; Colpaert, J.V. Comparison and validation of some ITS primer pairs useful for fungal metabarcoding studies. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Blom, J.; Klenk, H.-P.; Borriss, R. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Bacillus velezensis, and Bacillus siamensis form an “operational group B. amyloliquefaciens” within the B. subtilis species complex. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, R.J.; Ludwig, H.D.; Scherm, H. Epidemiology of Exobasidium leaf and fruit spot of rabbiteye blueberry: Pathogen overwintering, primary infection and disease progression on leaves and fruit. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, L.M.; Jaykus, L.-A.; Moll, D.; Martinez, M.C.; Ancisco, J.; Mora, B.; Moe, C.L. A field study of the microbiological quality of fresh produce. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, L.R.; Gonzalez, A.R. Food safety and produce operations: What is the future? HortScience 2001, 36, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prazak, A.M.; Murano, E.A.; Mercado, I.; Acuff, G.R. Prevalence of Listeria monocytogenes during production and postharvest processing of cabbage. J. Food Prot. 2002, 65, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, D.Y.C.; Goetsch, S.J. Introduction of Food Microbiology. Department of Animal Sciences and Industry; Kansas State University: Manhattan, KS, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen-the, C.; Carlin, F. Fresh and processed vegetables. In The Microbiological Safety and Quality of Food; Lund, B.M., Baird-Parker, A.C., Gould, G.W., Eds.; Aspen Publishers: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000; pp. 620–684. [Google Scholar]
- Kovaleva, V.A.; Shalovylo, Y.I.; Gorovik, Y.N.; Lagonenko, A.L.; Evtushenkov, A.N.; Gout, R.T. Bacillus pumilus—A new phytopathogen of Scots pine. J. For. Sci. 2015, 61, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Taguiam, J.D.; Evallo, E.; Balendres, M.A. Epicoccum species: Ubiquitous plant pathogens and effective biological control agents. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2021, 159, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottone, E.J. Bacillus cereus, a volatile human pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 382–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentur, H.N.; Dalzell, A.M.; Riordan, F.A.I. Central venous catheter infection with Bacillus pumilus in an immunocompetent child: A case report. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2007, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Deligios, M.; Fraumene, C.; Abbondio, M.; Mannazzu, I.; Tanca, A.; Addis, M.F.; Uzzau, S. Draft genome sequence of Rhodotorula mucilaginosa, an emergent opportunistic pathogen. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e00201-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordossis, T.; Avlami, A.; Velegraki, A.; Stefanou, I.; Georgakopoulos, G.; Papalambrou, C.; Legakis, N.J. First report of Cryptococcus laurentii meningitis and a fatal case of Cryptococcus albidus cryptococcaemia in AIDS patients. Med. Mycol. 1998, 36, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Suraiya, S.; Azira, N. PP-067 Intramuscular Epicoccum nigrum infection in an immunocompromised patient: A case report. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 14, S45–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
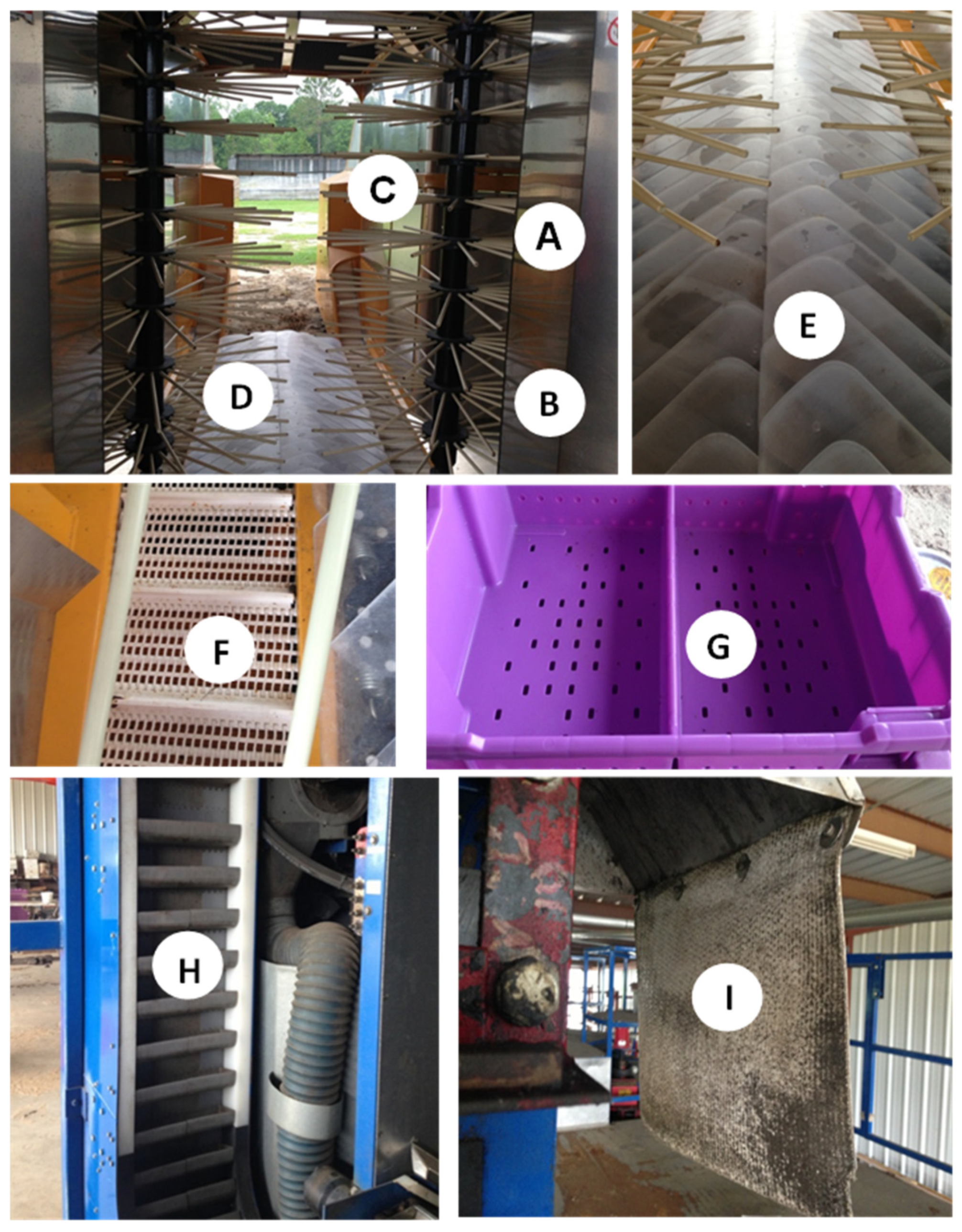

| Surface | Material |
|---|---|
| Shaking rod | Polyethylene |
| Tunnel sidewall | Aluminum or stainless steel |
| Catcher plates | Extruded polycarbonate |
| Conveyor belt | Acetal plastic or stainless steel |
| Filling flap | Rubberized canvas |
| Berry lug | High-density polyethylene |
| Organism Group | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | Total Aerobes | Yeasts and Molds | Coliforms | Fecal Coliforms | Enterococci |
| 2015 | |||||
| Surface (S) | <0.0001 | 0.0005 | 0.1989 | 0.4749 | 0.0023 |
| Time (t) | 0.3498 | 0.0012 | 0.1308 | 0.0348 | 0.5514 |
| S × t | 0.8214 | 0.0085 | 0.7533 | 0.6646 | 0.4467 |
| 2016 | |||||
| Surface (S) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0006 | 0.0030 | <0.0001 |
| Time (t) | 0.0214 | 0.6740 | 0.2312 | 0.0093 | 0.2308 |
| S × t | 0.7211 | 0.1297 | 0.6336 | 0.0775 | 0.5571 |
| Combined years | |||||
| Surface (S) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0046 | 0.0005 | <0.0001 |
| Time (t) | 0.3853 | 0.1128 | 0.7409 | 0.0080 | 0.3289 |
| S × t | 0.7432 | 0.3083 | 0.9977 | 0.0110 | 0.4800 |
| Organism Group | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface and Sampling Time | Total Aerobes | Yeasts and Molds | Coliforms | Fecal Coliforms | Enterococci |
| Vertical conveyor | |||||
| AM | 4.87 ± 0.4 | 5.02 ± 0.3 | 1.27 ± 0.3 | 0.12 ± 0.1 | 0.20 ± 0.1 |
| Noon | 7.63 ± 1.1 | 4.85 ± 0.2 | 0.90 ± 0.2 | 0.44 ± 0.2 | 0.77 ± 0.1 |
| PM | 5.12 ± 1.0 | 4.58 ± 0.2 | 0.53 ± 0.2 | 0.55 ± 0.3 | 0.52 ± 0.1 |
| Filling flap | |||||
| AM | 3.81 ± 0.8 | 4.33 ± 0.4 | 0.62 ± 0.1 | n.d. 1 | n.d. |
| Noon | 5.15 ± 0.8 | 4.97 ± 0.2 | 0.96 ± 0.2 | 0.09 ± 0.1 | 0.09 ± 0.1 |
| PM | 4.96 ± 1.5 | 3.88 ± 1.0 | 1.00 ± 0.3 | n.d. | 0.32 ± 0.3 |
| ANOVA p-values | |||||
| Surface (S) | 0.2319 | 0.1846 | 0.8518 | 0.0727 | 0.1190 |
| Time (t) | 0.2693 | 0.2189 | 0.7292 | 0.4506 | 0.2577 |
| S × t | 0.4352 | 0.3753 | 0.0930 | 0.5314 | 0.4718 |
| Organism Group | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | Total Aerobes | Yeasts and Molds | Coliforms | Fecal Coliforms | Enterococci |
| 2015 | |||||
| Location (L) | 0.1667 | 0.2894 | 0.9710 | 0.3559 | 0.4645 |
| Time (t) | 0.8896 | 0.3784 | 0.9319 | 0.3827 | 0.7671 |
| L × t | 0.9352 | 0.8609 | 0.7368 | 0.3827 | 0.4983 |
| 2016 | |||||
| Location (L) | 0.0849 | 0.1016 | 0.1038 | 1.0000 | 0.3559 |
| Time (t) | 0.9867 | 0.9650 | 0.6154 | 0.6127 | 0.3827 |
| Combined years | |||||
| Location (L) | 0.0235 | 0.0446 | 0.1619 | 0.4000 | 0.2229 |
| Time (t) | 0.9041 | 0.5027 | 0.7685 | 0.7841 | 0.4358 |
| L × t | 0.3119 | 0.9206 | 0.8910 | 0.1172 | 0.5990 |
| Genbank Accession | Tentative ID 1 | Percent Identity | Query Coverage | Other Matches (>98% Identity) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | ||||
| MT605426.1 | Bacillus sp. | 100% | 100% | B. altitudinis, subtilis, aerophilus, stratophericus, aerius, pumilus * |
| KX588618.1 | Stenotrophomonas rhizophila | 100% | 100% | S. maltophilia * |
| MN945445.1 | Bacillus subtilis | 100% | 99% | B. siamensis, amyloliquefaciens, velezensis |
| KC172020.1 | Bacillus aerophilus | 99.90% | 90% | B. aerius, altitudinis, pumilus *,**, sporothermodurans |
| MN865799.1 | Bacillus velezensis | 99.61% | 99% | B. subtilis, amyloliquefaciens, methylotrophicus |
| MT642947.1 | Bacillus cereus * | 99.55% | 97% | B. tropicus, thuringiensis, paranthracis |
| GQ250095.1 | Bacillus pumilus *,** | 99.46% | 91% | B. altitudinis, xiamenensis |
| MT122832.1 | Bacillus aquimaris | 99.16% | 98% | B. vietnamensis |
| MK968313.1 | Microbacterium paraoxydans | 97.66% | 99% | |
| Yeasts | ||||
| MG471022.1 | Sporobolomyces koalae | 100% | 94% | |
| KP346984.1 | Sporidiobolus pararoseus | 99.65% | 95% | |
| JQ425370.1 | Rhodotorula glutinis | 99.50% | 96% | Rhodotorula mucilaginosa * |
| KR262386.1 | Exobasidium maculosum ** | 99.46% | 92% | |
| KP346983.1 | Sporidiobolus pararoseus | 99.32% | 95% | |
| KT899784.1 | Cryptococcus laurentii * | 99.25% | 96% | Papiliotrema laurentii |
| KX067832.1 | Sporidiobolus pararoseus | 99.15% | 100% | |
| Filamentous fungi | ||||
| MN398977.1 | Penicillium citrinum | 100% | 99% | Penicillium brevicompactum |
| KX664336.1 | Epicoccum nigrum *,** | 100% | 97% | |
| EU489900.1 | Uncultured Ascomycota | 99.81% | 99% | Dothidomycete, Phoma herbarum, Leptosphaeria sacchari |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Holland, R.M.; Chen, J.; Gazula, H.; Scherm, H. Environmental and Fecal Indicator Organisms on Fruit Contact Surfaces and Fruit from Blueberry Mechanical Harvesters. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8010020
Holland RM, Chen J, Gazula H, Scherm H. Environmental and Fecal Indicator Organisms on Fruit Contact Surfaces and Fruit from Blueberry Mechanical Harvesters. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleHolland, Renee M., Jinru Chen, Himabindu Gazula, and Harald Scherm. 2022. "Environmental and Fecal Indicator Organisms on Fruit Contact Surfaces and Fruit from Blueberry Mechanical Harvesters" Horticulturae 8, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8010020
APA StyleHolland, R. M., Chen, J., Gazula, H., & Scherm, H. (2022). Environmental and Fecal Indicator Organisms on Fruit Contact Surfaces and Fruit from Blueberry Mechanical Harvesters. Horticulturae, 8(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8010020








