Biological Control of the Raspberry Eriophyoid Mite Phyllocoptes gracilis Using Entomopathogenic Fungi
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
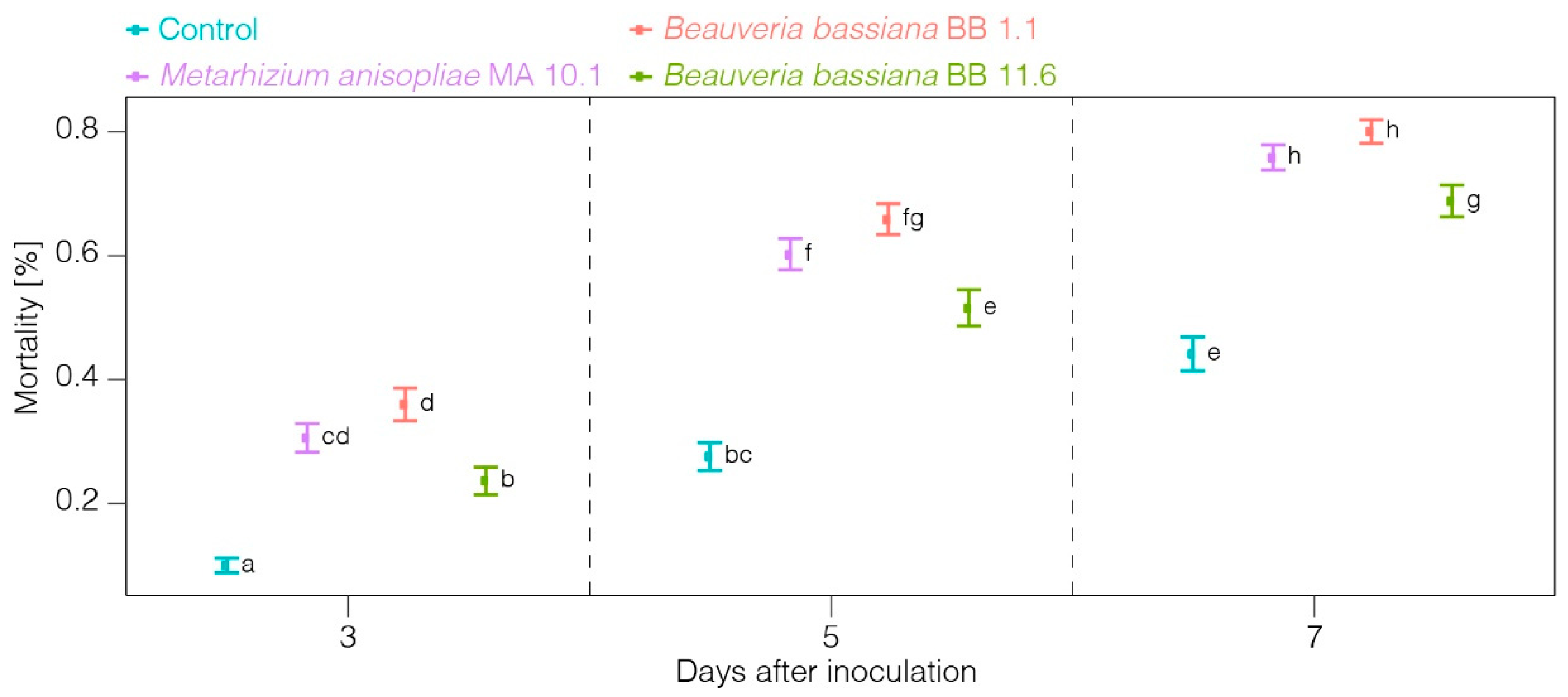
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baroffio, C. Culture des Framboises—Maladies et ravageurs. In Guide des Petits Fruits; Ançay, A., Baroffio, C., Michel, V., Häseli, A., Kopp, M., Eds.; Editions Fruit Union Suisse: Zug, Switzerland, 2017; p. 73. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, S.C.; Taylor, C.E. Some aspects of the biology of the raspberry leaf and bud mite (Phyllocoptes (Eriophyes) Gracilis Nal.) Eriophyidae in Scotland. J. Hortic. Sci. 1976, 51, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.C.; Woodford, J.A.T.; Birch, A.N.E. Arthropod pests of Rubus in Europe: Pest status, current and future control strategies. J. Hortic. Sci. 1997, 72, 831–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wekesa, V.W.; Hountondji, F.C.C.; Dara, S.K. Mite Pathogens and Their Use in Biological Control. Prospects for Biological Control of Plant Feeding Mites and Other Harmful Organisms; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 309–328. [Google Scholar]
- Lacey, L.A.; Frutos, R.; Kaya, H.K.; Vail, P. Insect pathogens as biological control agents: Do they have a future? Biol. Control 2001, 21, 230–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.A.; Pell, J.K. Entomopathogenic fungi as biological control agents. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 61, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro-Ilan, D.I.; Fuxa, J.R.; Lacey, L.A.; Onstad, D.W.; Kaya, H.K. Definitions of pathogenicity and virulence in invertebrate pathology. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2005, 88, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, G. The “Galleria bait method” for detection of entomopathogenic fungi in soil. J. Appl. Entomol. 1986, 102, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.S.; Lim, U.T. Laboratory bioassay of Beauveria bassiana against Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae) on leaf discs and potted bean plants. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2015, 65, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefort, F.; Fleury, D.; Fleury, I.; Coutant, C.; Kuske, S.; Kehrli, P.; Maignet, P. Pathogenicity of entomopathogenic fungi to the green peach aphid Myzus persicae Sulzer (Aphididae) and the European tarnished bug Lygus rugulipennis Poppius (Miridae). Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2014, 24, 379–386. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Kumar, P.; Malik, A. Effect of temperature and humidity on pathogenicity of native Beauveria bassiana isolate against Musca domestica L. J. Parasit. Dis. 2015, 39, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luz, C.; Fargues, J. Temperature and moisture requirements for conidial germination of an isolate of Beauveria bassiana, pathogenic to Rhodnius prolixus. Mycopathologia 1997, 138, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthurs, S.; Thomas, M.B. Effects of temperature and relative humidity on sporulation of Metarhizium anisopliae var. acridum in mycosed cadavers of Schistocerca gregaria. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2001, 78, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, D.K.; Burditt, D.K.; Crittenden, C.R. Laboratory methods for rearing rust mites (Phyllocoptruta oleivora and Aculus pelekassi) on Citrus. J. Econ. Entomol. 1964, 57, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalon, B.; Dean, H.A. Hirsutella thompsonii a fungal parasite of the citrus rust mite Phyllocoptruta oleivora in the Rio Grande Valley of Texas. Entomophaga 1974, 19, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikunthan, G.; Manjunatha, M. Fusarium species: Acaropathogenic fungi as potential control agents against coconut mite, Aceria guerreronis. In Trends in Acarology; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 2010; pp. 445–447. [Google Scholar]
- Omoto, C.; Dennehy, T.J.; McCoy, C.W.; Crane, S.E.; Long, J.W. Detection and characterization of the interpopulation variation of citrus rust mite (Acari: Eriophyidae) resistance to dicofol in Florida citrus. J. Econ. Entomol. 1994, 87, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajanzad, S.; Mallik, B.; Chandrashekar, S.C. Bioefficacy of six isolates of Hirsutella thompsonii Fisher against citrus rust mite, Phyllocoptruta oleivora Ashmead (Acari: Eriophyidae) and two spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidea). Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2006, 9, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Goodrich, B.; Gabry, J.; Ali, I.; Brilleman, S. Rstanarm: Bayesian Applied Regression Modeling via Stan. R Package Version 2.21.1. 2020. Available online: https://mc-stan.org/rstanarm (accessed on 13 March 2021).
- Length, R.V. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, aka Least-Squares Means. R Package Version 1.5.4. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=emmeans (accessed on 13 March 2021).
- Chandler, D. Chapter 5—Basic and applied research on entomopathogenic fungi. In Microbial Control of Insect and Mite Pests; Lacey, L.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 69–89. [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist, E.E.; Bruin, J.; Sabelis, M.W. Eriophyoid Mites: Their Biology, Natural Enemies and Control; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Chandler, D.; Davidson, G.; Pell, J.K.; Ball, B.V.; Shaw, K.; Sunderland, K.D. Fungal biocontrol of Acari. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2000, 10, 357–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, S.B.; Tamai, M.A.; Rossi, L.S.; Castiglioni, E. Beauveria bassiana pathogenicity to the citrus rust mite Phyllocoptruta oleivora. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2005, 37, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalmath, B.; Mallik, B.; Onkarappa, S.; Girish, R.; Srinivasa, N. Isolation, genetic diversity and identification of a virulent pathogen of eriophyid mite, Aceria guerreronis (Acari: Eriophyidae) by DNA marker in Karnataka, India. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 16790–16799. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minguely, C.; Norgrove, L.; Burren, A.; Christ, B. Biological Control of the Raspberry Eriophyoid Mite Phyllocoptes gracilis Using Entomopathogenic Fungi. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7030054
Minguely C, Norgrove L, Burren A, Christ B. Biological Control of the Raspberry Eriophyoid Mite Phyllocoptes gracilis Using Entomopathogenic Fungi. Horticulturae. 2021; 7(3):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7030054
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinguely, Camille, Lindsey Norgrove, Alexander Burren, and Bastien Christ. 2021. "Biological Control of the Raspberry Eriophyoid Mite Phyllocoptes gracilis Using Entomopathogenic Fungi" Horticulturae 7, no. 3: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7030054
APA StyleMinguely, C., Norgrove, L., Burren, A., & Christ, B. (2021). Biological Control of the Raspberry Eriophyoid Mite Phyllocoptes gracilis Using Entomopathogenic Fungi. Horticulturae, 7(3), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7030054





