Tree Peony as an Efficient Organic Selenium Bioreactor: Selenium Uptake, Accumulation, Speciation, and Nutritional Enhancement via Foliar Sodium Selenite Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Site
2.2. Plant Materials and Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Processing
2.4. Determination of Total Se Concentrations
2.5. Determination of Organic Se Concentrations
2.6. Se Speciation Analysis
2.7. Determination of Nutritional Quality of Tree Peony Seeds
2.8. Fatty Acid Profiling of Tree Peony Seed Oil
2.9. Statistical Analysis and Graph Drawing
3. Results
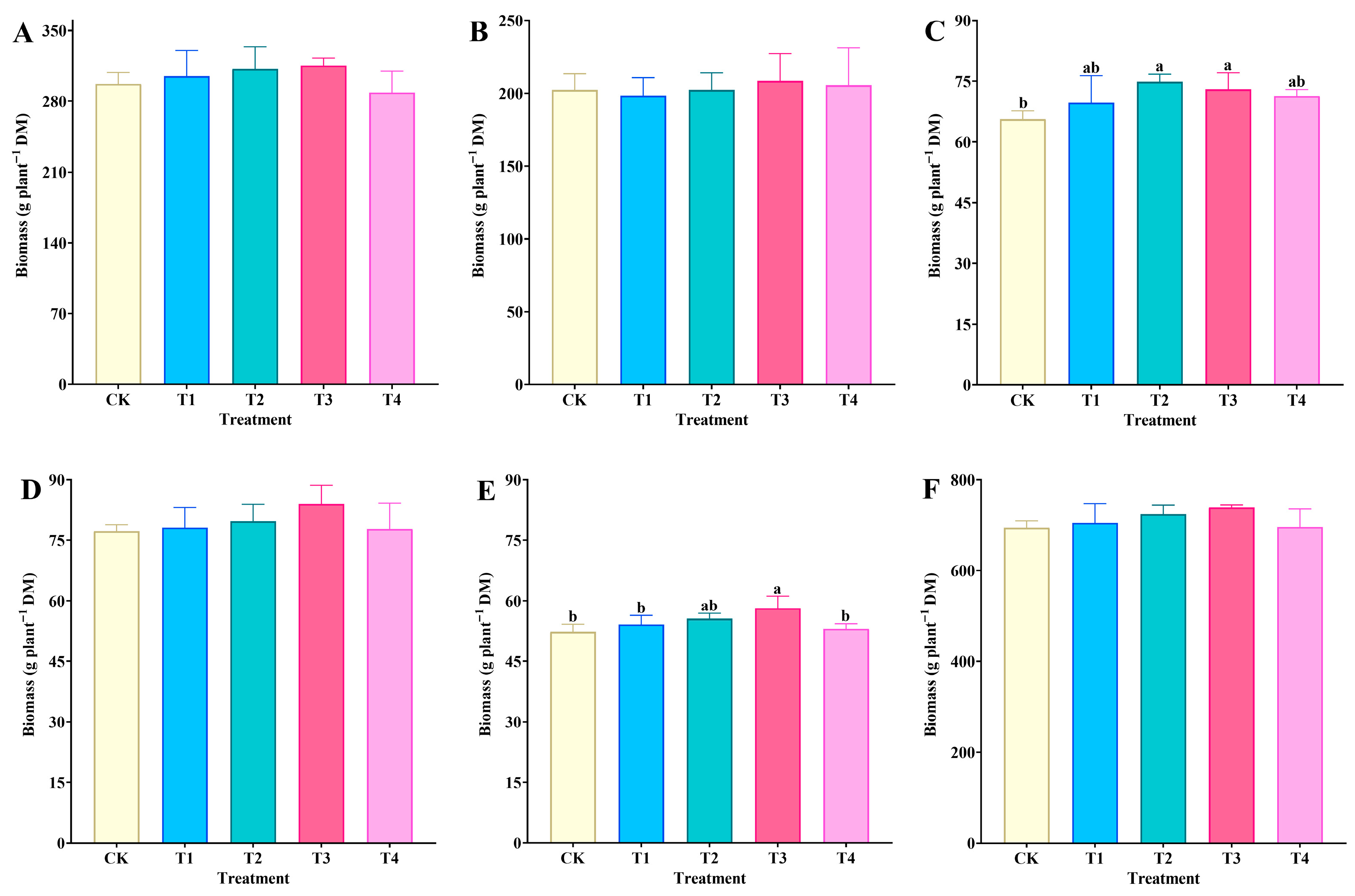
3.1. Effect of Spraying Na2SeO3 on Biomass of Tree Peony Organs
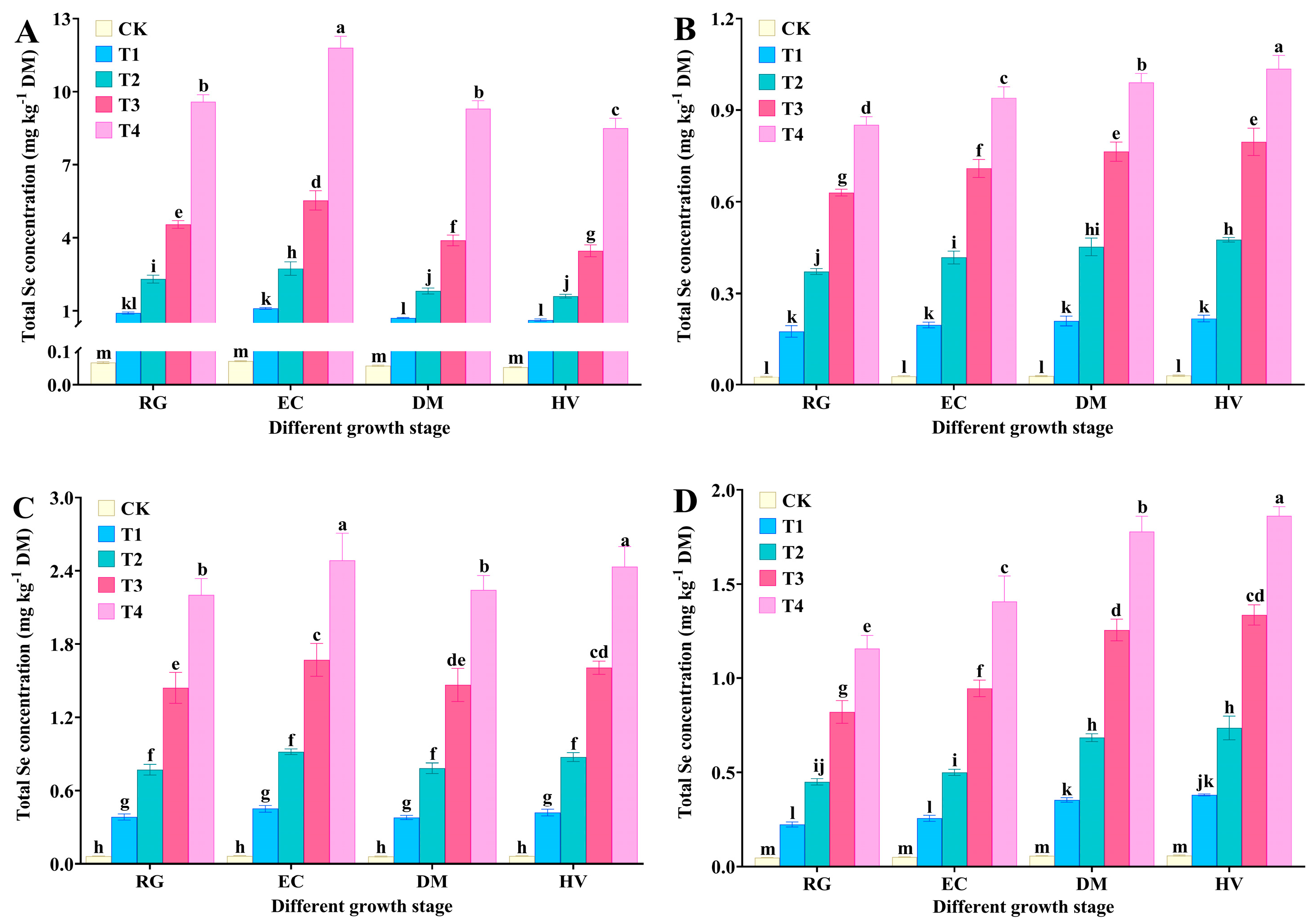
3.2. Effect of Spraying Na2SeO3 on Total Se Concentrations in Tree Peony Organs
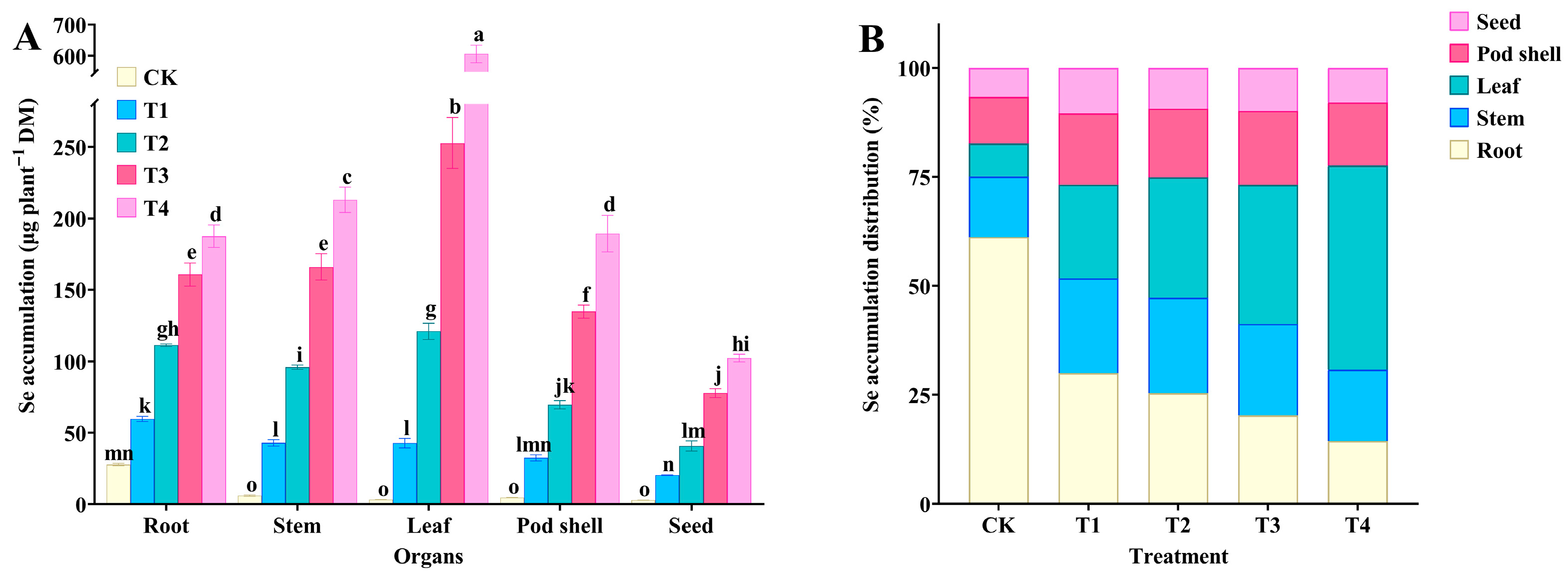
3.3. Effect of Spraying Na2SeO3 on Se Accumulation and Distribution in Tree Peony Organs
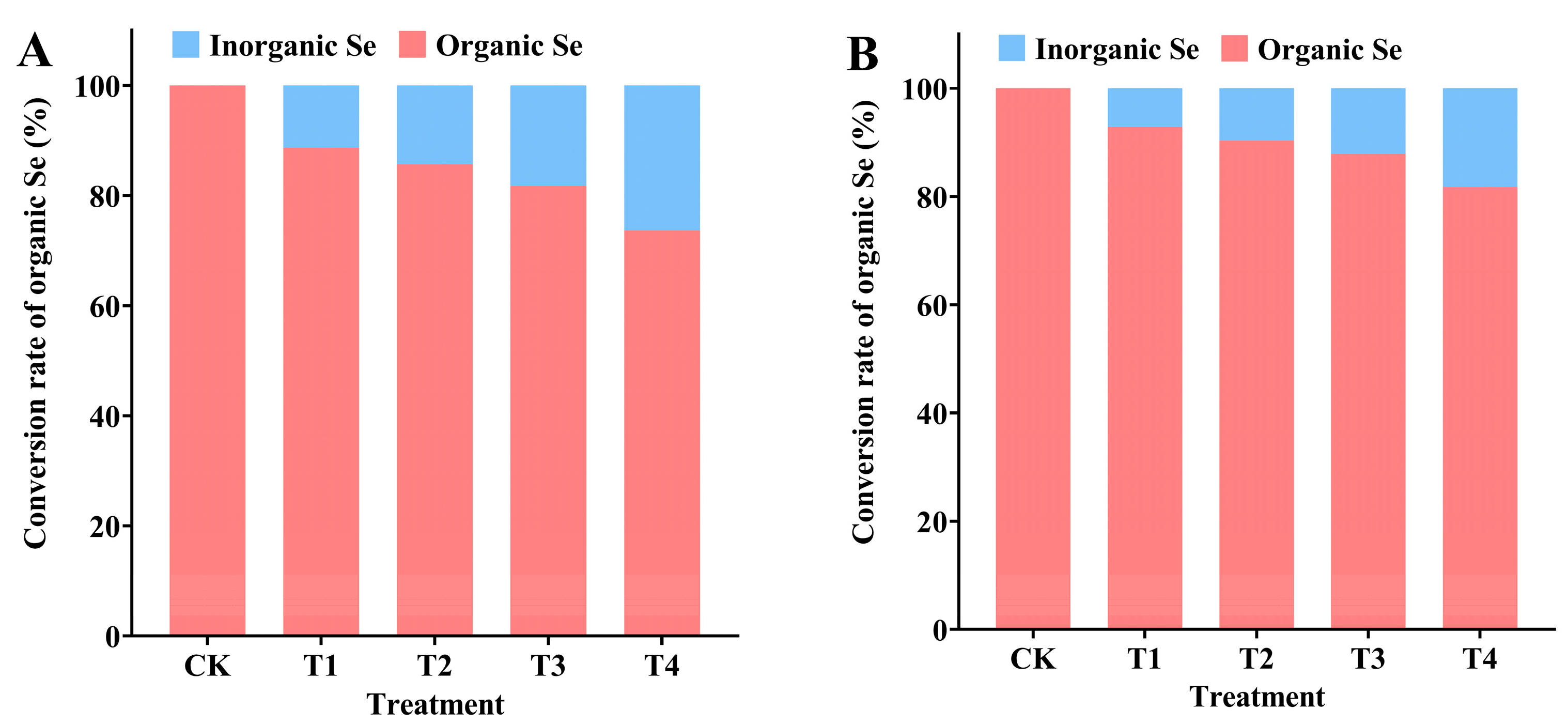
3.4. Effect of Spraying Na2SeO3 on Conversion of Organic Se in Tree Peony Leaves and Seeds
3.5. Effect of Spraying Na2SeO3 on Se Speciation in Tree Peony Leaves and Seeds
3.6. Effects of Spraying Na2SeO3 on the Nutritional Quality of Tree Peony Seeds
3.7. Effect of Spraying Na2SeO3 on the Fatty Acid Composition of Tree Peony Seed Oil
3.8. Comprehensive Evaluation of the Biological Effects of Spraying Na2SeO3 as an Agronomic Measure
4. Discussion
4.1. Foliar Application of Na2SeO3 Enhances Biomass Accumulation in Tree Peony
4.2. Foliar Application of Na2SeO3 Enhances Nutritional and Functional Quality of Tree Peony Seeds
4.3. Tree Peony as a Promising Se-Enriched Crop for Biofortification
4.4. Tree Peony Is an Efficient Bioreactor for Organic Se
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burk, R.F.; Hill, K.E. Regulation of Selenium Metabolism and Transport. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2015, 35, 109–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barchielli, G.; Capperucci, A.; Tanini, D. The Role of Selenium in Pathologies: An Updated Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Lauria, G.; Catalano, A.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Carocci, A. Biological Activity of Selenium and Its Impact on Human Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayman, M.P. Selenium and Human Health. Lancet 2012, 379, 1256–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Morais, E.G.; Silva, M.A.; Quispe, A.P.V.; Machado, G.G.L.; Prado, D.T.; Benevenute, P.A.N.; de Sousa Lima, J.; de Sousa, G.F.; de Barros Vilas Boas, E.V.; Guilherme, L.R.G. Foliar Sprays of Multi-Nutrient Fertilizer Containing Selenium Produce Functional Tomato Fruits with Higher Shelf Life. Plants 2024, 13, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Li, M.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, Z.; Wen, X.; Cong, W.; Ni, Y.; Zhang, F. Flow of Selenium in the “Soil-Crop-Food-Human” Chain. Food Sci. 2023, 44, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavon, M.; Nardi, S.; Dalla Vecchia, F.; Ertani, A. Selenium Biofortification in the 21st Century: Status and Challenges for Healthy Human Nutrition. Plant Soil 2020, 453, 245–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Qi, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Niu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Peng, T. Enhancement of Nutrient, Trace Element, and Organic Selenium Contents of Ratooning Rice Grains and Straw through Foliar Application of Selenite. Foods 2024, 13, 3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhou, F.; Cheng, N.; Chen, P.; Ma, Y.; Zhai, H.; Qi, M.; Liu, N.; Liu, Y.; Meng, L.; et al. Soil and Foliar Selenium Application: Impact on Accumulation, Speciation, and Bioaccessibility of Selenium in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 988627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Wang, L.; Gong, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, S.; Li, L. The Impact of Exogenous Sodium Selenite Treatment on the Nutritional Value and Active Constituents of Pueraria Lobata. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccinelli, M.; Malorgio, F.; Pintimalli, L.; Rosellini, I.; Pezzarossa, B. Biofortification of Lettuce and Basil Seedlings to Produce Selenium Enriched Leafy Vegetables. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, W. Brassica Rapa Selenium Transporter NPF2.20 (BrNPF2.20) Accounts for Se-Enrichment in Chinese Cabbage. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 289, 117466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zeng, L.; Luo, X.; Mehboob, M.Z.; Ao, T.; Lang, M. Identification and Functional Characterization of a Novel Selenocysteine Methyltransferase from Brassica juncea L. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 6401–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Long, W.; Liang, T.; Zhu, M.; Zhu, A.; Luo, X.; Fu, L.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, R.; Wu, X. Effect of Foliar Spraying of Organic and Inorganic Selenium Fertilizers during Different Growth Stages on Selenium Accumulation and Speciation in Rice. Plant Soil 2023, 486, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galinha, C.; Sánchez-Martínez, M.; Pacheco, A.M.G.; Freitas, M.D.C.; Coutinho, J.; Maçãs, B.; Almeida, A.S.; Pérez-Corona, M.T.; Madrid, Y.; Wolterbeek, H.T. Characterization of Selenium-Enriched Wheat by Agronomic Biofortification. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 4236–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros, G.H.; Van Rotterdam, A.M.D.; Bussink, D.W.; Bindraban, P.S. Selenium Fertilization Strategies for Bio-Fortification of Food: An Agro-Ecosystem Approach. Plant Soil 2016, 404, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Peng, Q.; Wang, D.; Cui, Z.; Huang, J.; Fu, D.; Liang, D. Effects of Selenite and Selenate Application on Distribution and Transformation of Selenium Fractions in Soil and Its Bioavailability for Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 8315–8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.U.; Tang, Z.; Zeng, R.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, T.; Ei, H.H.; Ye, X.; Jia, X.; Zhu, J. Accumulation, Mobilization, and Transformation of Selenium in Rice Grain Provided with Foliar Sodium Selenite. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 2892–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ali, F.; Wang, M.; Dinh, Q.T.; Zhou, F.; Bañuelos, G.S.; Liang, D. Understanding Boosting Selenium Accumulation in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Following Foliar Selenium Application at Different Stages, Forms, and Doses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.A.; De Sousa, G.F.; Bañuelos, G.; Amaral, D.; Brown, P.H.; Guilherme, L.R.G. Selenium Speciation in Se-Enriched Soybean Grains from Biofortified Plants Grown under Different Methods of Selenium Application. Foods 2023, 12, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, R.; Ai, C.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, X. Effect of Selenite on Organic Selenium Speciation and Selenium Bioaccessibility in Rice Grains of Two Se-Enriched Rice Cultivars. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, E.; Birringer, M.; Jiang, W.; Nakahodo, T.; Thompson, H.J.; Toscano, P.J.; Uzar, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z. Allium Chemistry: Synthesis, Natural Occurrence, Biological Activity, and Chemistry of Se-Alk(En)Ylselenocysteines and Their γ-Glutamyl Derivatives and Oxidation Products. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2001, 49, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Mu, M.; Wang, L.; Huang, R. Effect of Foliar Application of Selenite On Organic Se and Antioxidant Activity in Kiwifruit. Appl. Fruit Sci. 2024, 66, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Miao, P.; Xu, Z.; Yi, X.; Yin, X.; Li, D.; Pan, C. Exploring the Mechanism of Nano-Selenium Treatment on the Nutritional Quality and Resistance in Plum Plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 284, 116957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wei, X.; Zhou, Y. Effects of Foliar Selenium Application on Se Accumulation, Elements Uptake, Nutrition Quality, Sensory Quality and Antioxidant Response in Summer-Autumn Tea. Food Res. Int. 2024, 175, 113618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Xu, C.; Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Wu, P.; Cheng, T.; Hong, D. Out of the Pan-Himalaya: Evolutionary History of the Paeoniaceae Revealed by Phylogenomics. J. Syst. Evol. 2021, 59, 1170–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, S.; He, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wei, D.; Wang, Z.; Guo, L.; Shaaban, M.; Hou, X. Characterization of Agronomic and Seed Oil Features for Different Cultivars of Tree Peony. Plants 2023, 12, 3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Jiao, F.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, H.; Han, M.; Wu, Y.; Shi, B. Development Prospects and Strategies of Oil Tree Peony Industry in China. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2014, 29, 124–128. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Z.; Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Gu, S.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Y. Integrated Metabolomics Approach Reveals the Dynamic Variations of Metabolites and Bioactivities in Paeonia ostii ‘Feng Dan’ Leaves during Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, N.-N.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Peng, L.-P.; Liu, Z.-A.; Shu, Q.-Y. A Comprehensive Study of Three Species of Paeonia Stem and Leaf Phytochemicals, and Their Antioxidant Activities. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 273, 113985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, K.; Bai, Y.; Yang, P.; Li, C.; Song, X. Evaluation on the Fresh Eating Quality of Tree Peony Flowers. Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Song, T.; Hou, X.; Lu, Z.; Gao, J.; Yi, J.; Yang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, M.; Xia, Q.; et al. A Novel Pathway Based on the Comprehensive Utilization of Oil Peony Pods into High Yield Polysaccharides and Strong Adsorption Carbon. Plants 2022, 189, 115843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Z.; Yang, W.; Duan, Y.; Wang, W.; Niu, L.; Sun, D.; Zhang, Y. Bioactive Components and Antibacterial Activities of Hydrolate Extracts by Optimization Conditions from Paeonia ostii T. Hong & JX Zhang. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 188, 115737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Yi, J.; Deng, R. Characterization of Paeonia ostii Seed and Oil Sourced from Different Cultivation Areas in China. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 133, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Regenstein, J.M.; Wang, F. Roasted Tree Peony (Paeonia ostii) Seed Oil: Benzoic Acid Levels and Physicochemical Characteristics. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Nie, M.; Cheng, D.; Chen, J.; Lv, J.; Niu, Y. Effects of Foliar Application of Nano-Se on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Se Accumulation in Paeonia ostii. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2024, 71, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrypnik, L.; Feduraev, P.; Golubkina, N.; Maslennikov, P.; Antipina, M.; Katserov, D.; Nebreeva, S.; Murariu, O.C.; Tallarita, A.V.; Caruso, G. Selenium Improves the Nutritional and Antioxidant Properties of Oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) Grown in Hydroponics. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Liu, G.; Wu, Q. Speciation of Organic and Inorganic Selenium in Selenium-Enriched Rice by Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry after Cloud Point Extraction. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Wei, L.; Li, N.; Liu, B.; Si, J.; Guo, J.; Wei, H. Determination of 5 Kinds of Selenium Species in Rice by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Hydride Generation-Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2017, 8, 2185–2190. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Q.; Yang, Z.; Shui, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Khan, S.; Wang, J.; Gao, Z. Methods of Selenium Application Differentially Modulate Plant Growth, Selenium Accumulation and Speciation, Protein, Anthocyanins and Concentrations of Mineral Elements in Purple-Grained Wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, R.; Li, J.; Niu, L. Comparison of Different Extraction Methods for Seed Oil from the ‘Fengdan’ Peony Cultivar. Food Sci. 2017, 38, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ahammed, G.J.; Zhang, X.-N.; Zhang, L.; Yan, P.; Zhang, L.-P.; Fu, J.-Y.; Han, W.-Y. Melatonin-Mediated Regulation of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis and Antioxidant Defense Confer Tolerance to Arsenic Stress in Camellia sinensis L. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebell, L.F. Variation in Total Soluble Sugars of Conifer Tissues with Method of Analysis. Phytochemistry 1969, 8, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, E.A.; Gillespie, K.M. Estimation of Total Phenolic Content and Other Oxidation Substrates in Plant Tissues Using Folin–Ciocalteu Reagent. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 875–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.-S.; Yuan, R.-Y.; Chen, L.-G.; Wang, L.-S.; Hao, X.-H.; Wang, L.-J.; Zheng, X.-C.; Du, H. Systematic Qualitative and Quantitative Assessment of Fatty Acids in the Seeds of 60 Tree Peony (Paeonia Section Moutan DC.) Cultivars by GC–MS. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yin, D.; Zhang, T.; Hou, X.; Qiao, Q.; Song, P. Major Fatty Acid Compositions and Antioxidant Activity of Cultivated Paeonia ostii under Different Nitrogen Fertilizer Application. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e2000617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, P.; Gao, J.; Wang, X.; Yan, M.; Xue, N.; Qu, C.; Deng, R. Paeonia Veitchii Seeds as a Promising High Potential By-Product: Proximate Composition, Phytochemical Components, Bioactivity Evaluation and Potential Applications. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 125, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Xu, C.; Lu, B.; Zhu, X.; Luo, X.; He, B.; Elidio, C.; Liu, Z.; Ding, Y.; Yang, J.; et al. Comprehensive Evaluation of Rice Qualities under Different Nitrogen Levels in South China. Foods 2023, 12, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.H.; Zhao, F.-J.; Dobermann, A. What Is a Plant Nutrient? Changing Definitions to Advance Science and Innovation in Plant Nutrition. Plant Soil 2022, 476, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Liang, P.-X.; Xing, Y.; Yao, Z.-F.; Chen, J.-P.; Pan, L.-P.; Deng, Y.-Q.; Liu, Y.-X.; Huang, D.-L. Optimizing Selenium Application for Enhanced Quality and Nutritional Value of Spring Tea (Camellia sinensis). Horticulturae 2025, 11, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.C.; Faquin, V.; Andrade, F.R.; Carneiro, J.P.; Júnior, E.C.S.; Souza, K.R.D.; Pereira, J.; Guilherme, L.R.G. Physiological and Physicochemical Responses of Potato to Selenium Biofortification in Tropical Soil. Potato Res. 2019, 62, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zeng, Z.H.; Bu, Y.; Ren, C.Z.; Li, J.Z.; Han, J.J.; Tao, C.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.X.; Lu, G.X.; et al. Effects of Selenium Fertilizer on Grain Yield, Se Uptake and Distribution in Common Buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench). Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 61, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Wang, P.; Gao, W.; Wu, S.; Huang, B. Effects of Foliar Spraying with Different Concentrations of Selenium Fertilizer on the Development, Nutrient Absorption, and Quality of Citrus Fruits. HortScience 2021, 56, 1363–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Gou, Y.; Yu, T.; Cong, X.; Gui, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liao, Y.; Ye, J.; Cheng, S.; et al. Effects of Selenate on Se, Flavonoid, and Glucosinolate in Broccoli Florets by Combined Transcriptome and Metabolome Analyses. Food Res. Int. 2021, 146, 110463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Chen, Q.; Liao, X.; Yang, X.; Chao, W.; Cong, X.; Zhang, W.; Liao, Y.; Ye, J.; Qian, H.; et al. Exploring Effects of Exogenous Selenium on the Growth and Nutritional Quality of Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.). Horticulturae 2023, 9, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.X.; Chang, Q.S.; He, Y.L.; Zhao, X.L.; Liu, W.; Guo, Q.; Chen, K.; Hou, X.G. Selenite Foliar Application Increased the Accumulation of Medicinal Components in Paeonia ostii by Promoting Antioxidant Capacity, Reducing Oxidative Stress, and Improving Photosynthetic Capacity. Photosynthetica 2024, 62, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Liang, Y.; Gao, D.; An, X.; Kong, F. Spraying Foliar Selenium Fertilizer on Quality of Table Grape (Vitis vinifera L.) from Different Source Varieties. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 218, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.M.; Rimoldi Tavanti, R.F.; Gratão, P.L.; Alcock, T.D.; Reis, A.R.D. Selenate and Selenite Affect Photosynthetic Pigments and ROS Scavenging through Distinct Mechanisms in Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp) Plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 201, 110777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieliszek, M.; Bano, I.; Zare, H. A Comprehensive Review on Selenium and Its Effects on Human Health and Distribution in Middle Eastern Countries. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, M.L.O.; Oliveira, L.C.A.D.; Silva, V.M.; Montanha, G.S.; Reis, A.R.D. Selenium Increases Photosynthetic Capacity, Daidzein Biosynthesis, Nodulation and Yield of Peanuts Plants (Arachis hypogaea L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 190, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lei, N.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tong, L.; Wang, F.; Fan, B.; Maesen, P.; Blecker, C. Influence of Selenium Biofortification of Soybeans on Speciation and Transformation during Seed Germination and Sprouts Quality. Foods 2022, 11, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Ran, X.; Zeng, R.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Mao, C.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Yang, G. Effects of Sodium Selenite Spray on Apple Production, Quality, and Sucrose Metabolism-Related Enzyme Activity. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Sharma, S.; Singh, D. Influence of Selenium on Carbohydrate Accumulation in Developing Wheat Grains. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2018, 49, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, T.; Zhang, D. Effect of Exogenous Selenium Application on Selenium Content and Fruit Quality as Well as Its Physiological Mechanism in Walnut. J. Fruit Sci. 2022, 39, 1443–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.-A.A.; Darwesh, O.M.; Mekki, B.B.; El-Hallouty, S.M. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity, Biochemical Profile and Yield Components of Groundnut Plants Treated with Nano-Selenium. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 24, e00377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, K.; Wen, Q.; Ming, K.; Xiong, H.; Ning, F. Peanut Selenium Distribution, Concentration, Speciation, and Effects on Proteins after Exogenous Selenium Biofortification. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Functional Roles of Fatty Acids and Their Effects on Human Health. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2015, 39 (Suppl. S1), 18S–32S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, I.; Marzorati, M.; Van Den Abbeele, P.; Hora, K.; Holwerda, H.T.; Yazici, M.A.; Savasli, E.; Neri, J.; Du Laing, G. Fate and Bioaccessibility of Iodine in Food Prepared from Agronomically Biofortified Wheat and Rice and Impact of Cofertilization with Zinc and Selenium. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prom-u-thai, C.; Rashid, A.; Ram, H.; Zou, C.; Guilherme, L.R.G.; Corguinha, A.P.B.; Guo, S.; Kaur, C.; Naeem, A.; Yamuangmorn, S.; et al. Simultaneous Biofortification of Rice With Zinc, Iodine, Iron and Selenium through Foliar Treatment of a Micronutrient Cocktail in Five Countries. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 589835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.; Du, Y.; Rashid, A.; Ram, H.; Savasli, E.; Pieterse, P.J.; Ortiz-Monasterio, I.; Yazici, A.; Kaur, C.; Mahmood, K.; et al. Simultaneous Biofortification of Wheat with Zinc, Iodine, Selenium, and Iron through Foliar Treatment of a Micronutrient Cocktail in Six Countries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 8096–8106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Mao, H.; Zhao, H.; Huang, D. Increasing Se Concentration in Maize Grain with Soil- or Foliar-Applied Selenite on the Loess Plateau in China. Field Crops Res. 2013, 150, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, N.; Yuan, X.-Y.; Dong, S.-Q.; Wen, Y.-Y.; Gao, Z.-P.; Guo, M.-J.; Guo, P.-Y. Increasing Selenium and Yellow Pigment Concentrations in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica L.) Grain with Foliar Application of Selenite. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 170, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Hao, J.; Fan, S.; Dong, R.; Zeng, H.; Liu, C.; Han, Y. Effects of Selenate and Selenite on Selenium Accumulation and Speciation in Lettuce. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 192, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Suo, Y.; Si, X.; Li, L.; Qiu, L.; Cheng, P.; YU, H. Effects of selenium applicationon selenium distribution, yield and quality of different genotypes of peanut. J. Peanut Sci. 2020, 49, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xie, S.; Du, X.; Wang, Z.; Du, N. Effects of Selenium Concentration and Spraying Frequency by Foliar Application on Yield and Selenium Contentof Spring Maize. Acta Agric. Bor-Occid. Sin 2023, 32, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, C.; Ding, N.; Wu, G.; Ji, A.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y. Effects of Different Selenium Spraying Scheme on the Fruit Quality, Total Selenium and Organic Selenium Contents in ‘Red Fuji’ Apple Trees. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2013, 19, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kentelky, E.; Szekely-Varga, Z. Impact of Foliar Fertilization on Growth, Flowering, and Corms Production of Five Gladiolus Varieties. Plants 2021, 10, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, M.B.; Lipinski, V.M.; Fillipini, M.F.; Chacon Madrid, K.; Zezzi Arruda, M.A.; Wuilloud, R.G. Distribution, Accumulation and Speciation of Selenium at the Different Growth Stages of Four Garlic Clones. Food Addit. Contam. 2021, 38, 1506–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y. Selenium Accumulation Characteristics and Biofortification Potentiality in Turnip (Brassica rapa var. rapa) Supplied with Selenite or Selenate. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 8, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.-F.; Zhao, Z.-Q.; Han, Z.-Y.; Huang, L.-Q.; Lv, C.-H.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Liu, X.-W. Selenium Uptake and Fruit Quality of Pear (Pyrus communis L.) Treated with Foliar Se Application. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2019, 182, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, H.; Xiong, H. Distribution and Effects of Natural Selenium in Soybean Proteins and Its Protective Role in Soybean β-Conglycinin (7S Globulins) under AAPH-Induced Oxidative Stress. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tian, X.; Shi, Y.-X. Effects of Se application on Se accumulation and transformation and content of gross Protein and mineral elements in wheat grain. Acta Agronomica Sin. 2016, 42, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, H. Selenium Accumulation, Speciation, and Its Effect on Nutritive Value of Flammulina velutipes (Golden Needle Mushroom). Food Chem. 2021, 350, 128667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ali, F.; Qi, M.; Peng, Q.; Wang, M.; Bañuelos, G.S.; Miao, S.; Li, Z.; Dinh, Q.T.; Liang, D. Insights into Uptake, Accumulation, and Subcellular Distribution of Selenium among Eight Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Cultivars Supplied with Selenite and Selenate. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yin, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; He, J.; Zhang, R.; Rao, S.; Cong, X.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, M. Selenium Speciation and Volatile Flavor Compound Profiles in the Edible Flowers, Stems, and Leaves of Selenium-Hyperaccumulating Vegetable Cardamine Violifolia. Food Chem. 2023, 427, 136710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Li, L.; Hui, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Wu, W.; Wei, X.; Guo, Y. Selenium Biofortification and Its Effect on Multi-Element Change in Auricularia Auricular. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, L.; Liu, X. Effects of Foliar Application of Selenate and Selenite at Different Growth Stages on Selenium Accumulation and Speciation in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Food Chem. 2019, 286, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Yang, W.; Wang, M.; Miao, Y.; Cui, Z.; Li, Z.; Liang, D. Effects of Selenium Application on Se Content and Speciation in Lentinula Edodes. Food Chem. 2018, 265, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chu, C. Selenium Uptake, Transport, Metabolism, Reutilization, and Biofortification in Rice. Rice 2022, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L. Preparation of Paeoniflorin from the Stems and Leaves of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. ‘Zhongjiang’ through Green Efficient Microwave-Assisted Extraction and Subcritical Water Extraction. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 163, 113332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Deng, R.; Yan, M.; Zhang, S.; Yi, J.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y. Extraction, Isolation and Bioactivity of Oligostilbenes from Oil Peony Seed Shells. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 101004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Deng, R.; Wang, Y.; Qu, M.; Liu, P.; Gao, J. Extraction, Separation, and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides from Peony Seed Shell. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 222 Pt 3, 119843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatment | Inorganic Se Concentration (mg kg−1 DM) | Organic Se Concentration (mg kg−1 DM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf | Seed | Seed Meal | Leaf | Seed | Seed Meal | |
| CK | ND | ND | ND | 0.053 ± 0.001 e | 0.058 ± 0.003 e | 0.081 ± 0.003 e |
| T1 | 0.070 ± 0.007 d | 0.027 ± 0.003 d | 0.038 ± 0.003 d | 0.545 ± 0.041 d | 0.353 ± 0.002 d | 0.495 ± 0.002 d |
| T2 | 0.232 ± 0.017 c | 0.071 ± 0.008 c | 0.102 ± 0.011 c | 1.385 ± 0.059 c | 0.664 ± 0.058 c | 0.949 ± 0.072 c |
| T3 | 0.631 ± 0.046 b | 0.162 ± 0.004 b | 0.229 ± 0.003 b | 2.829 ± 0.207 b | 1.173 ± 0.052 b | 1.655 ± 0.063 b |
| T4 | 2.242 ± 0.173 a | 0.341 ± 0.022 a | 0.476 ± 0.022 a | 6.262 ± 0.252 a | 1.522 ± 0.038 a | 2.128 ± 0.041 a |
| Organs | Treatment | Se Speciation Concentration (mg kg−1 DM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Se4+ | Se6+ | SeMet | SeCys2 | MeSeCys | ||
| Leaf | CK | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| T1 | ND | 0.063 ± 0.004 d (10.94%) | 0.108 ± 0.006 d (18.75%) | 0.199 ± 0.013 d (34.55%) | 0.206 ± 0.027 d (35.76%) | |
| T2 | ND | 0.223 ± 0.010 c (14.86%) | 0.273 ± 0.016 c (18.19%) | 0.526 ± 0.030 c (35.04%) | 0.479 ± 0.044 c (31.91%) | |
| T3 | ND | 0.613 ± 0.036 b (19.40%) | 0.532 ± 0.030 b (16.84%) | 1.165 ± 0.077 b (36.88%) | 0.849 ± 0.068 b (26.88%) | |
| T4 | ND | 2.159 ± 0.201 a (27.85%) | 1.388 ± 0.097 a (17.90%) | 2.978 ± 0.124 a (38.41%) | 1.228 ± 0.095 a (15.84%) | |
| Seed | CK | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| T1 | ND | 0.021 ± 0.001 d (5.82%) | 0.106 ± 0.002 d (29.36%) | 0.234 ± 0.002 d (64.82%) | ND | |
| T2 | ND | 0.073 ± 0.009 c (10.47%) | 0.186 ± 0.009 c (26.69%) | 0.438 ± 0.042 c (62.84%) | ND | |
| T3 | ND | 0.139 ± 0.009 b (11.25%) | 0.348 ± 0.015 b (28.16%) | 0.749 ± 0.030 b (60.60%) | ND | |
| T4 | ND | 0.248 ± 0.005 a (14.88%) | 0.436 ± 0.009 a (26.15%) | 0.947 ± 0.036 a (56.81%) | 0.036 ± 0.000 (2.16%) | |
| Treatment | 100 Seed Weight (g) | Kernel Percentage (%) | Crude Fat Content (%) | Soluble Protein Content (mg g−1 DM) | Soluble Sugar Content (mg g−1 DM) | Starch Content (mg g−1 DM) | Total Phenols Content (mg g−1 DM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 21.31 ± 0.79 | 68.77 ± 0.73 | 28.66 ± 0.37 b | 110.42 ± 7.36 b | 103.09 ± 3.12 c | 151.94 ± 4.30 bc | 7.11 ± 0.30 d |
| T1 | 21.69 ± 0.70 | 69.71 ± 1.01 | 28.74 ± 0.49 b | 125.43 ± 4.19 ab | 121.15 ± 3.25 b | 169.91 ± 6.11 a | 20.61 ± 1.22 c |
| T2 | 22.35 ± 0.91 | 68.88 ± 0.86 | 30.01 ± 0.74 a | 133.35 ± 5.06 a | 139.11 ± 5.22 a | 163.70 ± 6.13 ab | 22.69 ± 0.31 ab |
| T3 | 22.71 ± 0.31 | 69.54 ± 1.21 | 29.14 ± 0.39 ab | 135.37 ± 9.54 a | 143.40 ± 4.59 a | 156.65 ± 3.70 bc | 24.17 ± 1.40 a |
| T4 | 21.13 ± 0.38 | 68.59 ± 1.14 | 28.46 ± 0.43 b | 117.27 ± 4.52 b | 120.68 ± 2.26 b | 147.11 ± 6.37 c | 21.00 ± 0.33 bc |
| Treatment | C16:0 | C18:0 | C18:1 | C18:2 | C18:3 | UFA | PUFA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6.84 ± 0.09 a | 2.61 ± 0.03 | 25.58 ± 0.10 c | 25.42 ± 0.06 b | 38.48 ± 0.30 c | 89.47 ± 0.46 b | 63.90 ± 0.36 c |
| T1 | 6.61 ± 0.09 b | 2.31 ± 0.34 | 26.28 ± 0.10 b | 25.82 ± 0.10 a | 39.31 ± 0.15 b | 91.07 ± 0.50 a | 65.13 ± 0.21 a |
| T2 | 6.47 ± 0.06 bc | 2.50 ± 0.02 | 26.20 ± 0.04 b | 24.12 ± 0.11 e | 40.26 ± 0.19 a | 90.58 ± 0.09 a | 64.38 ± 0.08 b |
| T3 | 6.82 ± 0.03 a | 2.47 ± 0.03 | 25.90 ± 0.13 c | 24.57 ± 0.05 d | 39.91 ± 0.14 a | 90.39 ± 0.21 a | 64.49 ± 0.12 b |
| T4 | 6.37 ± 0.06 c | 2.57 ± 0.05 | 26.77 ± 0.02 a | 24.78 ± 0.07 c | 39.05 ± 0.17 b | 90.61 ± 0.11 a | 63.84 ± 0.11 c |
| Character | F1 | F2 | F3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seed biomass (g plant−1 DM) | 0.288 | −0.003 | −0.099 |
| Total Se (mg kg−1 DM) | −0.056 | 0.337 | −0.023 |
| Organic Se (mg kg−1 DM) | −0.037 | 0.330 | −0.027 |
| Soluble protein (mg g−1 DM) | 0.245 | −0.015 | 0.006 |
| Soluble sugar (mg g−1 DM) | 0.261 | 0.050 | −0.066 |
| Starch (mg g−1 DM) | −0.006 | −0.167 | 0.301 |
| Total phenols (mg g−1 DM) | 0.027 | 0.184 | 0.156 |
| Crude fat (%) | 0.408 | −0.187 | −0.218 |
| UFA (%) | −0.215 | 0.178 | 0.418 |
| PUFA (%) | −0.097 | −0.066 | 0.382 |
| Eigenvalue | 5.375 | 2.879 | 1.314 |
| Contribution ratio (%) | 53.745 | 28.786 | 13.143 |
| Cumulative contribution ratio (%) | 53.75 | 82.53 | 95.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, K.; Zhou, W.; Li, S.; Shi, S.; Shi, M.; Gao, S.; Shi, G. Tree Peony as an Efficient Organic Selenium Bioreactor: Selenium Uptake, Accumulation, Speciation, and Nutritional Enhancement via Foliar Sodium Selenite Application. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091112
Hu K, Zhou W, Li S, Shi S, Shi M, Gao S, Shi G. Tree Peony as an Efficient Organic Selenium Bioreactor: Selenium Uptake, Accumulation, Speciation, and Nutritional Enhancement via Foliar Sodium Selenite Application. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(9):1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091112
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Kun, Wenbin Zhou, Shiqi Li, Shuaiying Shi, Mengqiang Shi, Shuangcheng Gao, and Guoan Shi. 2025. "Tree Peony as an Efficient Organic Selenium Bioreactor: Selenium Uptake, Accumulation, Speciation, and Nutritional Enhancement via Foliar Sodium Selenite Application" Horticulturae 11, no. 9: 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091112
APA StyleHu, K., Zhou, W., Li, S., Shi, S., Shi, M., Gao, S., & Shi, G. (2025). Tree Peony as an Efficient Organic Selenium Bioreactor: Selenium Uptake, Accumulation, Speciation, and Nutritional Enhancement via Foliar Sodium Selenite Application. Horticulturae, 11(9), 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091112






