Abstract
The rising cost of mineral fertilizers and the decreasing availability of manure in vegetable farming highlight the need for alternative fertilization strategies. To examine the possibility of applying byproducts from the food processing industry, sugar beet molasses, and compost from brewery sewage sludge in celery production, the field experiment was conducted over two years, using a randomized complete block design with three replications. The examined variants were T0—control (without fertilizer); T1—mineral fertilizer; T2—cattle manure; T3—sheep manure; T4—poultry manure; T5—supercompost; and T6—molasses. In the first year, there was no significant difference between T1 and T5 in thickened root yield, while these two variants achieved significantly higher yield compared with other variants. In both years, the highest leaf yield was achieved with T1, while no significant difference was found between T5, T6, and conventional organic fertilizers of animal origin. The highest amount of N was absorbed by roots in T1 (42.0 kg/ha and 51.2 kg/ha, respectively), while the lowest amount was absorbed in T0 (25.5 kg/ha and 26.7 kg/ha, respectively). A significantly higher amount of P2O5 was absorbed by roots in all organic fertilizer variants compared to T0 and T1. In both years, of all the nutrients, K2O was the most absorbed nutrient by the celery root, while CaO was absorbed in greater quantities than N. Based on two years of research, it can be concluded that compost from brewery sludge and sugar beet molasses can be used as an alternative source of nutrients for plants.
1. Introduction
Celery (Apium graveolens L.) belongs to the Apiaceae family and is an annual or biennial species native to the Mediterranean region and the Middle East [1]. It is an important vegetable in the human diet, commonly used as a spice and culinary flavoring [2]. Celery is rich in phenols, flavonoids, fibers, total fats, total sugar, protein, and starch [3]. The most abundant macro- and microelements in celery include P, K, Mg, Ca, Fe, Zn, and B [4]. Additionally, it is a good source of cellulose, vitamins, and carotene and a good source of volatile oils [1].
In celery production, both organic and mineral fertilizers are commonly used [5]. However, due to the decline in livestock farming, the availability of traditional organic fertilizers has decreased [6]. This has created a demand for alternative organic fertilizers to replace conventional sources. One potential solution is the utilization of byproducts from the food processing industry.
Among these, sugar beet processing byproducts, such as molasses, are produced in large quantities and can contribute to environmental pollution if not properly managed [7,8]. Molasses is a syrupy residue left after sugar crystallization from sugar beet. Due to its high mineral content and sugar residues that can stimulate the activity of microorganisms, molasses is particularly suitable for use as a fertilizer [3]. On the other hand, high levels of fermentable sugars can temporarily bind or immobilize plant-available nitrogen in organic form, leading to leaf yellowing due to a short-term nitrogen deficiency [9].
Molasses is used as a fertilizer, particularly in clay and sandy soils with poor structure [10]. Studies have shown its positive effect on various crops, including potato [11], sugar beet [7,8], spinach [10], and beetroot [12]. However, data on its application in celery remain scarce.
Due to its physical characteristics, molasses can be applied to soil with drip irrigation, as well as foliar application [3,7,8,10,12]. The application rate depends on the method of use and the crop, ranking from 0 to 4 t/ha in beetroot, 0 to 0.1 t/ha in sugarbeet, and 10 t/ha in potato [7,11,12].
Industrial sludge composition varies depending on raw materials and production processes [13]. Breweries produce significant sludge waste and are some of the biggest industrial users of water, and their water processing generates waste sludge, which is rich in organic matter and essential nutrients for plant growth [13,14]. This sludge can be a valuable soil amendment, replacing mineral fertilizers and addressing the sludge disposal issue sustainably [14,15]. The slow-release nitrates minimize leaching risks, benefiting crops, particularly in areas where there is a higher risk of leaching into deeper layers. The effects of applications are most noticeable on alkaline, sandy, and nutrient-poor soils [16]. Sewage sludge can also enhance soil fertility, increasing nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium levels while slightly decreasing soil pH [17]. Although concerns about heavy metals and pathogens exist, studies indicate that high sludge application rates do not significantly increase heavy metal concentrations in vegetables [15].
The rising costs of mineral fertilizers and the decreasing availability of manure in vegetable farming highlight the need for alternative fertilization strategies [6]. The aim of this study was to determine the effects of molasses and compost from brewery sludge on celery yield, as well as the uptake of N, P2O5, K2O, and CaO, and to compare their effects with conventional organic fertilizers of animal origin.
2. Materials and Methods
The experiment was conducted over two years, using a randomized complete block design with three replications, in Novi Sad, Vojvodina Province, Republic of Serbia. The fertilization treatments are given in Table 1.

Table 1.
The fertilization treatments in experiment.
The variations in the amounts of organic fertilizers (Table 1) applied between the first and second years are due to differences in their nitrogen (N) content. Prior to application, agrochemical analyses of all organic fertilizers and soil samples were conducted (Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4). Based on these analyses, application rates were adjusted to ensure a uniform nitrogen input of 170 kg N/ha across all treatments (excluding the control). This nitrogen rate was selected as it represents the maximum allowable nitrogen application in organic production. Additionally, according to the Nitrates Directive [18], the maximum amount of nitrogen that can be applied in nitrate-sensitive zones is 170 kg N/ha/year. Given that different organic fertilizers have varying nitrogen contents, their application rates were adjusted accordingly to achieve this target value.

Table 2.
Agrochemical analysis of organic manures.

Table 3.
Chemical composition of molasses.

Table 4.
Soil properties (soil depth: 0–30 cm).
Supercompost is a sludge that is produced as a byproduct in a wastewater treatment plant at a “Carslberg” brewery in Čelarevo, Republic of Serbia. It is formed through the fermentation of organic material of plant origin, has a gray-brown color, granule size smaller than 25 mm, and a mildly alkaline reaction. The heavy metal content is below the maximum allowed concentration, making it suitable for agricultural use.
Molasses is a thick, dark syrup remaining after the crystallization of sugar from sugar beet juice. At the “Sunoko” sugar beet factory in Pećinci, Republic of Serbia, molasses is produced during sugar extraction. This byproduct is rich in minerals, enhancing its value as a soil amendment. The chemical composition of molasses used in this experiment remained consistent across both years, and it is given in Table 3.
Before applying the fertilizers, agrochemical analyses of all organic fertilizers and soils were performed. The agrochemical analysis of the soil at the two experimental years showed that the soil was slightly alkaline, according to Thun’s classification (Table 4). Based on the Scheffer–Schachtschabel classification, it was identified as low-humus soil. In terms of calcium carbonate content, the soils were categorized as carbonate soils [19]. Regarding nutrient levels, phosphorus and potassium content in the first year were within medium to optimal ranges, whereas in the second year, phosphorus levels were very high, and readily available potassium content was high [20]. These soil characteristics provide important context for assessing the effects of different fertilization treatments.
Applied amounts of nutrients in two trial years are given in Table 5.

Table 5.
Applied amounts of nutrients (kg/ha).
The variety used in the experiment was Diamant, from the Beyo Zaden seed company, with a medium-length growing season. It forms a round and smooth, thickened, white-fleshed root. The leaf rosette is upright, and the leaves are tall. It is intended for fresh consumption, but it can also be stored and used for industrial processing.
The celery was produced in an open field, while the seedlings were grown in a protected environment in a tunnel-type structure without additional heating. Sowing was carried out in mid-April in containers with 209 holes. The experimental plot size was 14 m2, within which this study was conducted on accounting plots of 7 m2. Number of plants per experimental plot was 80, while 40 plants were in the accounting plot. All present plants were examined on the accounting plots.
The total amount of organic fertilizer, as well as 0.8 t/ha of mineral fertilizer with a formulation of 9:12:25, was applied one week before transplanting by spreading the fertilizer across the entire surface of the soil and incorporating it using a seedbed preparation machine. The remaining amount of fertilizer, 0.288 t/ha of ammonium nitrate (AN), was applied in two feedings during the growing season. Typhons with sprinklers were used for irrigation.
Seedlings were transplanted at the 5-leaf stage, with a row spacing of 70 cm and 25 cm between plants in the row. Harvesting was carried out 160 days after transplanting when the thickened roots were fully developed.
All plants were used for analyses. Immediately after harvest, the mass of the plants, the mass of the leaves, and the mass of the thickened roots were weighed in the field, and yields of thickened roots and leaves were calculated. Thereafter, samples of the thickened roots and leaves were analyzed for the amount of N, P2O5, K2O, and CaO accumulated in the leaves and the amount of N, P2O5, K2O, and CaO accumulated in the roots. The quantity of N, P2O5, K2O, and CaO removed by leaves and thickened roots was calculated based on the leaves and roots yields; dry matter content; and contents of N, P, K, and Ca in dry matter.
The dry matter content of the leaves and roots was determined by drying the samples in a drying oven (POL EKO SLW 240 ECO INOX) to a constant weight at 105 °C. The total N content in the plant material was determined by the Kjeldahl method, the total P content by the ammonium vanadate–molybdate method, and the K and Ca content by flame photometry.
The pH value of the soil was measured in a suspension of soil and H2O (1:2.5) using a Metrel MA 3657 pH meter in accordance with ISO 10390 standard [21]. The calcium carbonate (CaCO3) content in the soil was determined volumetrically with a Scheibler calcimeter. The total nitrogen (N) and carbon (C) contents in the soil were analyzed using a CHNS analyzer (Elementar Vario EL, GmbH, Hanau, Germany). Plant-available P and K in the soil were extracted using an AL solution (0.1 M ammonium lactate and 0.4 M acetic acid, pH 3.75) at a soil-to-solution ratio of 1:20 (w/v) [20]. The dry matter content in organic fertilizers was determined gravimetrically (at 70 °C for 24 h). The total N content in the organic fertilizers was measured with a CHNS analyzer (Elementar Vario EL). Potassium concentration in the organic fertilizers was determined after wet digestion with a mixture of HNO3:HCIO4 (4:1, v/v), using an atomic absorption spectrometer (“Shimadzu 6300”) with a flame technique, while phosphorus concentration in the solutions was measured colorimetrically using a “Jenway 6105” spectrophotometer (Jenway Ltd., Dunmow, UK).
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) method was used to determine sucrose, glucose, fructose, raffinose, and inositol according to the ICUMSA protocol GS4-22 (2002) [22]. The dry matter content of molasses was determined with a refractometer according to the ICUMSA Method GS4-13 [23], while the pH value was determined by a pH meter.
2.1. Climatic Conditions
Agroecological conditions have a significant impact on yield and quality of crops, so it is important to consider meteorological data when analyzing research results.
The total amount of precipitation during the growing season from transplanting to harvest is given in Figure 1.
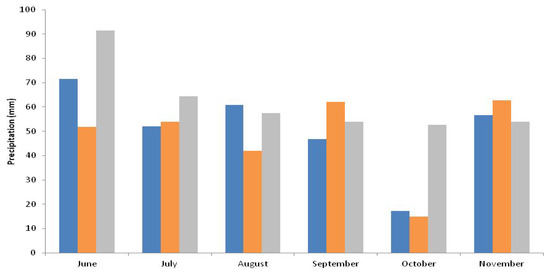
Figure 1.
Precipitation during the experiment (from June to November in two years). The blue bars represent precipitation in first year, the orange bars represent precipitation in second year, while grey bars indicate the long-term (1991–2020) average precipitation.
The average monthly temperatures during the growing season from transplanting to harvest are given in Figure 2.
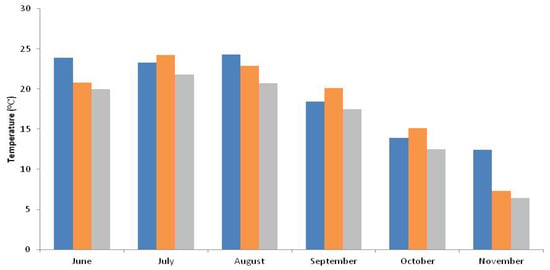
Figure 2.
Average monthly temperatures during the experiment (from June to November in two years). The blue bars represent temperatures in first year, the orange bars represent temperatures in second year, while grey bars indicate the long-term (1991–2020) average monthly temperatures.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
The research results were analyzed using the analysis of variance (ANOVA) method for a one-factor experiment, using the statistical software “Statistica 14”, and the significance of differences between the means of the treatments was tested using Fisher’s least significant difference test (LSD test) at the level of significance of α = 0.05. Lowercase letters mark significance in the difference among fertilizing variants. Variants that are significantly different do not have common letters.
3. Results
All tested organic fertilizer variants and T0 resulted in significantly lower plant mass compared to T1 (Figure 3). The application of T5 significantly increased plant mass compared to animal-based organic fertilizers. In T6, a significantly higher plant mass was achieved compared to T3 and T4, while no significant difference was observed compared to T2.
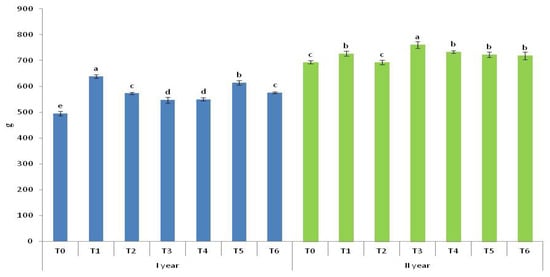
Figure 3.
Mass of plant (g). T0—control; T1—mineral fertilizer; T2—cattle manure; T3—sheep manure; T4—poultry manure; T5—supercompost; T6—molasses. Lowercase letters mark significance in the difference among fertilizing variants. Variants that are significantly different do not have common letters. Values are the means ± SD (n = 3).
In the second year, there was no significant difference in plant mass between T1, T4, T5, and T6.
Compared to T1, in T0 and T3, leaf mass per plant was 15.7% and 12.8% lower, respectively (Figure 4). There was no significant difference between T5 and T6, although a slightly higher leaf mass was observed in T5.
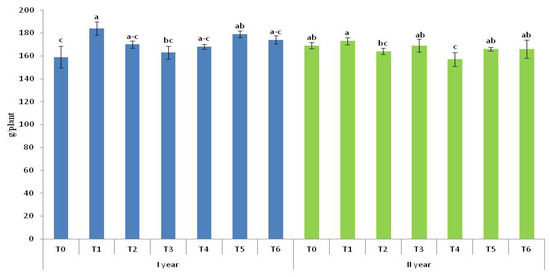
Figure 4.
Mass of leaves (g/plant). T0—control; T1—mineral fertilizer; T2—cattle manure; T3—sheep manure; T4—poultry manure; T5—supercompost; T6—molasses. Lowercase letters mark significance in the difference among fertilizing variants. Variants that are significantly different do not have common letters. Values are the means ± SD (n = 3).
In the second year, compared to T1, significantly lower leaf mass per plant was observed in T2 and T4, while no significant difference was found compared to the remaining variants. In T5 and T6, the leaf mass per plant was the same. Compared to T5 and T6, 5.7% lower plant mass was observed in T4.
Root mass varied significantly between variants in both years (Figure 5). Notably, T1 and T5 showed comparable results, while T0 consistently had the lowest root mass. The effect of T6 on the mass of the celery thickened root was similar to the effect of T2, but significantly higher compared to T3 and T4.
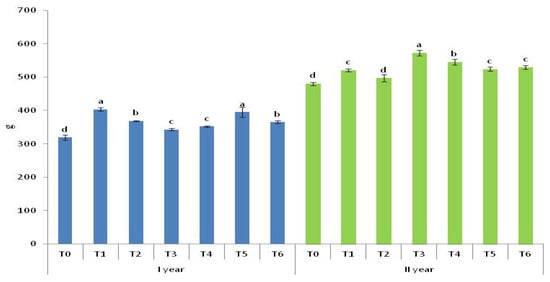
Figure 5.
Mass of thickened root (g). T0—control; T1—mineral fertilizer; T2—cattle manure; T3—sheep manure; T4—poultry manure; T5—supercompost; T6—molasses. Lowercase letters mark significance in the difference among fertilizing variants. Variants that are significantly different do not have common letters. Values are the means ± SD (n = 3).
In the second year, there was no significant difference between T1, T5, and T6. The effect of T5 and T6 on the celery root mass was significantly greater than that of T2.
The application of T1 resulted in the highest celery leaf yield, while that of T0 was 15.4% lower (Figure 6). Higher leaf yields were achieved with T5 and T6 compared to the variants with animal-based organic fertilizers, although no significant differences were found between the variants.
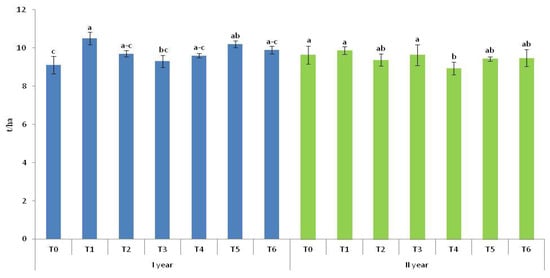
Figure 6.
Leaf yield (t/ha). T0—control; T1—mineral fertilizer; T2—cattle manure; T3—sheep manure; T4—poultry manure; T5—supercompost; T6—molasses. Lowercase letters mark significance in the difference among fertilizing variants. Variants that are significantly different do not have common letters. Values are the means ± SD (n = 3).
In the second year, T5 and T6 showed comparable results, which were higher than those of T2 and T4. The highest leaf yield was achieved with T1, with no significant difference observed compared to the remaining variants, except for T4, where the lowest leaf yield was recorded.
Root yield varied significantly between variants in both years (Figure 7). Notably, T1 and T5 showed comparable results, while T0 consistently yielded the lowest. There was no significant difference between T6, T3, and T4. Unlike the first year, the application of T3 resulted in the highest yield in the second year. There was no significant difference between T6 and T4. A higher root yield was achieved in T6 compared to T0 and T2 at 10.2% and 6.3%, respectively.
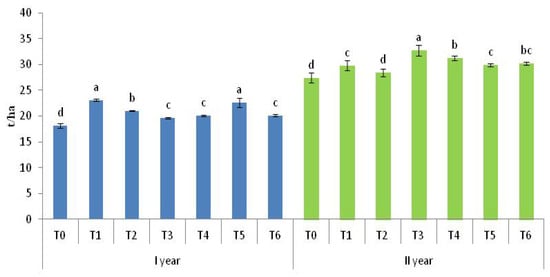
Figure 7.
Root yield (t/ha). T0—control; T1—mineral fertilizer; T2—cattle manure; T3—sheep manure; T4—poultry manure; T5—supercompost; T6—molasses. Lowercase letters mark significance in the difference among fertilizing variants. Variants that are significantly different do not have common letters. Values are the means ± SD (n = 3).
In the celery root, the highest accumulation was of K2O, followed by P2O5, CaO, and N (Table 6). In the first year, T5 accumulated more N by roots compared to T2, T3, and T4, with increases of 17.7%, 23.8%, and 30.5%, respectively. When comparing T6 to T3 and T4, there was no difference in the amount of N accumulated by the celery root. In the second year, no significant difference was recorded between T3, T4, and T5, while significantly less N was recorded in T6 compared to the others.

Table 6.
Amount of N, P2O5, K2O, and CaO accumulated in roots (kg/ha).
Compared to T5, all other variants recorded significantly less P2O5. There was no significant difference between T2, T3, T4, and T6. All organic fertilizer variants accumulated significantly more P2O5 compared to T1. Compared to T4, significantly less P2O5 was accumulated in all other variants. In T5 and T6, more P2O5 was accumulated compared to T1, with increases of 17.1% and 26.8%, respectively.
The amount of K2O accumulated in roots varied significantly between variants in both years. Notably, T2 and T6 showed comparable results in the first year, and T4 and T6 showed comparable results in the second year. In both years, the lowest amount of K2O was recorded in T0. In the second year, in T6, more K2O was accumulated in roots compared to T1, T2, and T3, with increases of 33.6%, 10.1%, and 7.3%, respectively. The application of T5 and T1 resulted in a similar amount of K2O accumulation.
The highest amount of CaO was accumulated in T1 in the first year and in T0 in the second year. Compared to these two variants, significantly less CaO was accumulated in all variants. There was no significant difference between T5 and T6 in the first year, while in the second year, a noticeable difference between these two variants was recorded. The least amount was recorded in T4 in the first year and in T5 in the second year.
In the celery leaves, the highest accumulation was of CaO, followed by N, K2O, and P2O5 (Table 7). The amount of N varied significantly between variants in both years. T5 and T6 did not differ significantly in the amount of N accumulated in celery leaves in the second year, while in the first year, T6 accumulated less N.

Table 7.
Amount of N, P2O5, K2O, and CaO accumulated in leaves (kg/ha).
The highest amount of P2O5 was found to accumulate in celery leaves in T1 in both years. Notably, T1, T2, T4, T5, and T6 showed comparable results in the first year. When comparing T5 and T6, more P2O5 was accumulated in T5 in the first year, while in the second year, it was the opposite.
In both years, the highest K2O accumulation was observed in T1, whereas the lowest amount was recorded in T5 (Table 7). Compared to T1, significantly less K2O was recorded in all other variants. The application T6 resulted in significantly higher K2O accumulation in both years compared to T5. Compared to T0, significantly less K2O was accumulated in T3, T5, and T6 in the first year and in T3, T4, T5, and T6 in the second year.
The amount of CaO varied significantly between variants in both years. In T5, more CaO was accumulated compared to T1, T2, T3, and T4, with increases of 39.1%, 44.9%, 55.4%, and 8.3%, respectively. When comparing T5 and T6, more CaO in leaves was accumulated in T5 in both years, but the significant difference was only observed in the first year. In T6, more CaO was accumulated in leaves compared to T1, T2, and T3, with increases of 27.2%, 27.5%, and 18.4%, respectively.
4. Discussion
The effect of T5 on plant mass and thickened root mass was, in terms of significance, equal to that of T1 in both years, except in the first year regarding plant mass. Additionally, the leaf yield and thickened root yield did not differ significantly between T1 and T5 in both years. Compost from brewery sludge is rich in macro- and micronutrients. The high concentration of nitrate and phosphate and the availability of “slow-release” nutrients upon the degradation of organic material can be adequate for plant growth, eliminating the need for additional mineral fertilizers [14,15]. Compost from waste sludge is a valuable soil amendment that increases the organic matter content in the soil and improves soil physical properties, pH, and cation exchange capacity, with no significant increase in soil heavy metals [13,14,24]. The positive effect of applying compost from waste sludge has been noted in tomato production [14], cucumber [15,16], haricot bean [13], lettuce [25], sweet potato [24], and common bean [26].
In the first year, all tested organic fertilizer variants and the control resulted in lower plant mass, leaf mass, and thickened root mass compared to T1. These results are consistent with those of Navarro et al. [27], who state that the superior effect of mineral fertilizer may be due to the greater availability of N, which would result in faster and greater growth. Mineral fertilizers have a quicker nutritional effect and improve plant growth and development [28]. No difference was observed between the applied organic fertilizers, whereas in this study, a similar trend was observed only in the case of leaf mass [27]. For plant mass and thickened root mass, a significant difference between organic fertilizers was not observed, except between T3 and T4, while T2, T5, and T6 resulted in significantly higher values. The observed differences among organic fertilizers are due to the varying rates of mineralization, which depend on the type of fertilizer, the degree of decomposition of organic matter, temperature, and microbial activity, all of which influence their value as a nutrient source for plants, which is also different [29,30].
In the second year, the plant mass, thickened root mass, and root yield were highest in T3, significantly greater than in T1. The intensive use of mineral fertilizers in previous years likely contributed to an accumulation of phosphorus content to very high levels and an increase in readily available potassium (Table 4). Such conditions may have led to a decline in soil microbiota diversity, activity, and functionality, which negatively impacted crop yield. In contrast, manure effectively enhanced soil fertility and supported the growth of beneficial soil microbiota [31]. Substituting chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers can help reduce environmental pollution and serve as a key strategy to achieve the goal of zero growth in chemical fertilizer usage [32].
The application of T6 resulted in a significantly lower yield of thickened roots compared to T1 in the first year, while in the second year, no statistically significant difference was observed between these two variants. This is consistent with Al-Dhumri et al. [33], who reported no significant difference in sugar beet root yield between the molasses and mineral fertilizer variants, noting that molasses can be applied as a soil amendment and can fully replace mineral fertilizers. Abofard et al. [8] reported the opposite, with significantly higher sugar beet root yield achieved in the molasses variant. Molasses is an organic soil amendment that improves the physical and chemical properties of the soil, thereby enhancing yield and yield-related traits [8,33]. In this study, the effect of T6 on root yield was significantly higher than that of T3 and T4 in the first year and greater than that of T2 in the second year. The presence of polysaccharides in molasses may improve plant growth and soil microorganisms that release regulators promoting plant growth and yield [34]. In both years, T6 significantly increased the thickened root mass and root yield compared to T0. These findings are in line with previous research, where the use of molasses resulted in significantly higher yields of sugar beet, spinach, and potatoes compared to the control [7,10,11]. Although the results suggest some variability between years, the study was not evaluating the interaction between seasonal conditions and fertilizer efficacy, which can be observed as a potential limitation.
In a two-year study, 22.1% more N was accumulated in the celery root than in the leaf. This contrasts with the findings of Godlewska et al. [35], who observed greater N accumulation in the celery leaf. In both years, T1 resulted in significantly more N being absorbed by the root compared to other variants. This aligns with numerous studies reporting the positive effect of mineral fertilizers and the increase of N availability and plant uptake [27,28]. In T5, significantly more N was accumulated in both years compared to other organic fertilizer variants. However, Ahmed et al. [13] reported a contrasting result, with significantly greater N accumulation in the grain and straw of haricot bean in the sewage sludge treatment compared to mineral fertilizer. Many authors have discussed the chemical composition of compost from waste sludge and its effects on plants and soil properties [13,14,15,24]. The amount of N accumulated in the leaves in T1 was significantly higher compared to the T6 variant in the first year and T5 and T6 in the second year, while there was no significant difference compared to other organic fertilizer variants. This is partially consistent with Navaro et al. [27]. These inconsistent findings suggest that N accumulation in plant tissues is influenced by soil N availability, which in turn depends on the nature and maturity of the organic materials [27]. The form of N absorbed by the plant also affects N accumulation in the leaves. The highest accumulation occurs when 100% nitrate form is absorbed, and as the availability of ammoniacal form increases, accumulation significantly decreases [36]. In T2, T4, and T5, large amounts of P2O5 were applied, with different amounts of N accumulated in the leaves. Bishop et al. [37] and Li et al. [38] reported on the impact of phosphorus availability on N accumulation in celery plant tissues, stating that with increased phosphorus availability, N accumulation in the leaves decreases.
Phosphorus is a highly mobile element in plants. On average, for both years, celery roots absorbed 75.0 kg P2O5/ha, while the leaves accumulated 15.9 kg P2O5/ha. This is consistent with the results of Godlewska et al. [35], who found significantly greater phosphorus accumulation in the root compared to the leaf. In both years, T6 resulted in significantly higher P2O5 absorption by the roots compared to T0 and T1. Although no P2O5 was added to the soil with the molasses application, the presence of polysaccharides in molasses may have improved plant growth and influenced microbial activity in the process of mineralizing organic phosphorus compounds into forms accessible to plants [34].
The accumulation of P2O5 in the celery leaves was similar in both years of this study, differing by only 1.7%. In both years, the highest accumulation occurred in T1, even though higher amounts of P2O5 were applied in T2, T4, and T5. This may be explained by the higher solubility and faster nutrient availability associated with mineral fertilizers [27]. In the study by Bishop et al. [37], an increase in phosphorus led to a higher accumulation of P2O5 in celery leaves, while Li et al. [38] observed the same but also noted a negative impact on leaf accumulation, likely due to imbalances in nutrient uptake.
On average, over both years, 76.9 kg K2O/ha was accumulated in the root and 25.0 kg K2O/ha in the leaf. This is consistent with the findings of Godlewska et al. [35] and Golubkina et al. [39], who observed significantly greater potassium accumulation in the root than in the leaf. In the second year of the study, celery roots absorbed more K2O than in the first year. In addition to the higher yield, the greater K2O uptake was also influenced by the soil conditions at the experiment site, which had a higher content of easily available K2O (Table 4). In both years, a large amount of K2O was absorbed by the roots in T6, where the highest amount of potassium was also applied (Table 5), and the smallest amount was absorbed in T0. As the amount of applied K2O increases, its availability to plants also increases. Consequently, the amount of absorbed K2O increases, as does the potassium content in the dry matter [37,40,41,42]. Low K2O uptake was observed in T1 as well as in the control. In both years, in all organic fertilizer variants, except for T5 in the second year, a significantly larger amount of K2O was absorbed compared to T1. Several studies have reported that potassium availability increases with enhanced biological activity in soils, which is achieved by applying organic fertilizers [43,44].
The accumulation of K2O in the leaves in both years was similar (25.1 and 24.9 kg K2O/ha). In both years, the highest accumulation was in T1, with significantly less in all organic fertilizer variants. This finding contradicts the results of Navaro et al. [27]. The lowest accumulation was in T5, where the least K2O was applied (Table 5). This is consistent with Bishop et al. [37], where an increase in the K2O dose led to higher potassium content in celery plant tissue. Similarly, Cserni et al. [42] observed significantly higher potassium content in the celery leaves in the organic fertilizer variant compared to the control and different doses of mineral fertilizers. Nutrient interactions in the substrate play an important role in plant nutrient uptake. High concentrations of available elements in the growing media do not always lead to increased nutrient uptake by the plant due to an imbalance of elements [38,45].
On average, over both years, 15.3% more CaO was accumulated in the leaves than in the roots. This is in agreement with Godlewska et al. [35], whose study found significantly more Ca accumulated in the leaves. In both years, the highest accumulation of CaO was in the root of T0 and T1, while significantly less was taken up in the organic fertilizer variants. Similarly, in both years, the highest accumulation of CaO in the leaves was in T5, which contains a small amount of potassium. In the animal-based organic fertilizer variants and T1, significantly less CaO was accumulated in the leaves. Since different amounts of K2O were added to these fertilizers, affecting their availability to plants, the reason for the lower accumulation could be the antagonism between Ca and K [33,41]. As K2O availability increases, Ca concentration in celery leaves increases up to a certain threshold, after which it begins to decrease [37,40]. Li et al. [41] emphasize that as the availability of K2O increases, the concentration of Ca in the leaves immediately decreases, while the concentration in the root does not change significantly.
5. Conclusions
The findings of this study clearly demonstrate that compost from brewery sludge and sugar beet molasses provides similar celery root yields to mineral fertilizer, indicating their potential as partial substitutes on moderately alkaline soils. When comparing food industry byproducts with conventional animal-based organic fertilizers, their effect on celery nutrient uptake was different, depending on the nutrients, soil conditions, and nutrient content of organic fertilizers. Based on two years of research, it can be concluded that compost from brewery sludge and sugar beet molasses can be used as alternative sources of N, P2O5, and K2O for plants due to the high cost of mineral fertilizers and the decreasing availability of manure. In addition, their use will reduce the pressure on the environment and the potential pollution caused by the large quantities produced by food processing industries. Furthermore, future research should focus on long-term field trials with other vegetable species and research of residual effects of byproducts on the second crop, as well as the impact on soil characteristics and the possible accumulation of heavy metals in the soil, which could potentially limit the use of byproducts due to their frequent use as alternative fertilization sources.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.A. and R.Č.; methodology, B.A. and R.Č.; software, Đ.V.; validation, B.A., M.Ž., and I.M.; formal analysis, I.M., M.P.D., and D.K.; investigation, B.A., J.Č., Đ.V., and M.Ž.; resources, D.L., M.I., J.Č., and M.Ž.; data curation, B.A.; writing—original draft preparation, B.A.; writing—review and editing, D.K.; visualization, Đ.V. and D.K.; supervision, I.M. and M.P.D.; funding acquisition, B.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The support of the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia (contract No. 451-03-137/2025-03/200117).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the technical support of the “Sunoko” sugarbeet factory Pećinci (member of MK Group), Carlsberg Srbija, family farm Drljača from Futog, Radman and Mandić farms from Čelarevo, and Bjekić farm from Bački Jarak.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, M.Y.; Hou, X.L.; Wang, F.; Tan, G.F.; Xu, Z.S.; Xiong, A.S. Advances in the research of celery, an important Apiaceae vegetable crop. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 38, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsenov, D.; Župunski, M.; Pajević, S.; Nemeš, I.; Simin, N.; Alnuqaydan, A.M.; Watson, M.; Aloliqi, A.A.; Mimica-Dukić, N. Roots of Apium graveolens and Petroselinum crispum—Insight into Phenolic Status against Toxicity Level of Trace Elements. Plants 2021, 10, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milić, A.; Adamović, B.; Nastić, N.; Tepić Horecki, A.; Pezo, L.; Šumić, Z.; Pavlić, B.; Živanov, M.; Pavković, N.; Vojnović, Đ. Cluster and Principal Component Analyses of the Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Celery (Apium graveolens L.) Under Different Fertilization Schemes. Foods 2024, 13, 3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domagała-Świątkiewicz, I.; Gąstoł, M. Comparative study on mineral content of organic and conventional carrot, celery and red beet juices. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2012, 11, 173–183. [Google Scholar]
- Babalar, M.; Daneshvar, H.; Diaz-Pérez, J.C.; Nambeesan, S.; Tabrizi, L.; Delshad, M. Effects of organic and chemical nitrogen fertilization and postharvest treatments on the visual and nutritional quality of fresh-cut celery (Apium graveolens L.) during storage. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamović, B.; Cabilovski, R.; Vojnović, Đ.; Ilin, Ž. Effect of mulching on nutrient uptake and efficiency of fertilizers in mid-early cabbage production. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2023, 22, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şanli, A.; Kardoĝan, T.; Tosun, B. The Effects of Sugar Beet Molasses Applications on Root Yield and Sugar Content of Sugar Beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Tarla Bitk. Merk. Araştırma Enst. Derg. 2015, 24, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abofard, M.M.; Gaber, A.A.M.; Abdel-Mogib, M.; Mahmoud, N.; Bakr, M.N.; Elwafa, S.F.A. Effect of the application of molasses and vinasses on the yield and quality of sugar beet and soil fertility. Egypt. Sugar J. 2021, 17, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynne, A.T.; Meyer, J.H. An Economic assessment of using molasses and condensed molasses solids as a fertilizer in the South African sugar industry. In Proceedings of the 76th Annual Congress of the South Afrian Sugar Technologists Association, Mount Edgecombe, South Africa, 30 July–2 August 2002; Volume 76, pp. 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Pyakurel, A.; Dahal, B.R.; Rijal, S. Effect of Molasses and Organic Fertilizer in Soil fertility and Yield of Spinach in Khotang, Nepal. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortnik, A.; Bortnik, T.; Gavryliuk, V. Efficiency of molasses waste when growing potatoes (Solanum tuberosum) as a new promising organic fertilizer. Agroecol. J. 2023, 1, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeeka, P.W.M.; Seran, T.H. The effects of goat manure and sugarcane molasses on the growth and yield of beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.). J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 65, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Mohammed, M.; Merga, B. Effects of brewery waste sludge on haricot bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) productivity and soil fertility. Cogent Food Agric. 2019, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocks, C.; Barker, A.J.; Guy, S. The Composting of Brewery Sludge. J. Inst. Brew. 2002, 108, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgen, D.; Alpaslan, M.N.; Delen, N. Agricultural recycling of treatment-plant sludge: A case study for a vegetable–processing factory. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 84, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristina, G.; Camelin, E.; Pugliese, M.; Tommasi, T.; Fino, D. Evaluation of anaerobic digestates from sewage sludge as a potential solution for improvement of soil fertility. Waste Manag. 2019, 99, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alayu, E.; Leta, S. Brewery sludge quality, agronomic importance and its short-term residual effect on soil properties. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 2337–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council Directive of 12 December 1991 Concerning the Protection of Waters Against Pollution Caused by Nitrates from Agricultural Sources (91/676/EEC). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A01991L0676-20081211 (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Belić, M.; Nešić, L.; Ćirić, V. Pedology Practicum; Agriculture Faculty: Novi Sad, Serbia, 2014; p. 67. Available online: http://polj.uns.ac.rs/sites/default/files/udzbenici/PRAKTIKUM-IZ-PEDOLOGIJE.pdf (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Enger, H.; Riehm, H.; Domingo, W.R. Studies on the chemical soil analysis as a basis for assessing the nutrient status of soils. II Chemical extraction methods for phosphorus and potassium determination. Kungl. Lantbr. Högsk. Ann. 1960, 26, 199. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- ISO 10390; Soil, Treated Biowaste and Sludge—Determination of pH. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- ICUMSA Method GS4-22 (2002); The Determination of Sucrose and Betaine by HPLC in Beet Molasses—Official. International Commission for Uniform Methods of Sugar Analysis: Grünstadt, Germany, 2002.
- ICUMSA Method GS4-13 (2009); The Determination of Refractometric Dry Substance (RDS) of Molasses—Accepted and Very Pure Syrups (Liquid Sugars), Thick Juice and Run-Off Syrups—Official. International Commission for Uniform Methods of Sugar Analysis: Grünstadt, Germany, 2009.
- Ragonezi, C.; Nunes, N.; Oliveira, M.C.O.; de Freitas, J.G.R.; Ganança, J.F.T.; de Carvalho, M.Â.A.P. Sewage Sludge Fertilization—A Case Study of Sweet Potato Yield and Heavy Metal Accumulation. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletto, C.; Santagata, S.; Zanin, G.; Sambo, P. Effect of the anaerobic digestion residues use on lettuce yield and quality. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 180, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.B.; Camargos, L.S.; Teixeira Filho, M.C.M.; Souza, L.A.; Coscione, A.R.; Lavres, J.; Abreu-Junior, C.H.; He, Z.; Zhao, F.; Jani, A.D.; et al. Residual effects of composted sewage sludge on nitrogen cycling and plant metabolism in a no-till common bean-palisade grass-soybean rotation. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1281670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, A.S.; Romero, J.A.S.; Sanjuan, M.C.S.; Bernardeau, M.A.B.; Iniesta, M.J.D. Medium-Term Influence of Organic Fertilization on the Quality and Yield of a Celery Crop. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou El-Magd, M.M.; El-Bassiony, A.M.; Fawzy, Z.F. Effect of organic manure with or without chemical fertilizer on growth, yield and quality of some varieties of broccoli plants. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2006, 2, 791–798. [Google Scholar]
- Citak, S.; Sonmez, S. Influence of Organic and Conventional Growing Conditions on the Nutrient Contents of White Head Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) during Two Successive Seasons. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1788–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, S.; Oyanagi, W. Decomposition characteristics of indigenous organic fertilisers and introduced quick compost and their short-term nitrogen availability in the semi-arid Ethiopian Rift Valley. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonanomi, G.; De Filippis, F.; Zotti, M.; Idbella, M.; Cesarano, G.; Al-Rowaily, S.; Abd-El Gawad, A. Repeated applications of organic amendments promote beneficial microbiota, improve soil fertility and increase crop yield. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 156, 103714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.; Chander, K.; Mundra, M.C.; Kapoor, K.K. Influence of inorganic fertilizers and organic amendments on soil organic matter and soil microbial properties under tropical conditions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1999, 29, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dhumri, S.A.; Al Mosallam, M.S.; Zhang, W.; Alharabi, S.; Abou-Elwafa, S.F. Application of Molasses as an Eco-Innovative Approach Substitutes Mineral Nitrogen Fertilization and Enhances Sugar Beet Productivity. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 14, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, T.; Kaneko, A.; Ohba, H.; Ohyama, T. Effect of application of molasses to paddy soil on the concentration of cadmium and arsenic in rice grain. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2012, 58, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godlewska, K.; Pacyga, P.; Michalak, I.; Biesiada, A.; Szumny, A.; Pachura, N.; Piszcz, U. Field-Scale Evaluation of Botanical Extracts Effect on the Yield, Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Celeriac (Apium graveolens L. Var. rapaceum). Molecules 2020, 25, 4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.; Liu, G.; Liu, M.; Liu, W.; He, H.; Abdelhamid, M.T. Do NH4:NO3 ratio and harvest time affect celery (Apium graveolens) productivity and product quality? Folia Hortic. 2019, 31, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, R.F.; Chlpman, E.W.; MacEachern, C.R. Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium on yields and nutrient levels in celery and head lettuce grown on sphagnum peat. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1973, 4, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Ao, Y. Effect of phosphorus on celery growth and nutrient uptake under different calcium and magnesium levels in substrate culture. Hortic. Sci. 2010, 37, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubkina, N.A.; Kharchenko, V.A.; Moldovan, A.I.; Koshevarov, A.A.; Zamana, S.; Nadezhkin, S.; Soldatenko, A.; Sekara, A.; Tallarita, A.; Caruso, G. Yield, Growth, Quality, Biochemical Characteristics and Elemental Composition of Plant Parts of Celery Leafy, Stalk and Root Types Grown in the Northern Hemisphere. Plants 2020, 9, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inthichack, P.; Nishimura, Y.; Fukumoto, Y. Effect of Potassium Sources and Rates on Plant Growth, Mineral Absorption, and the Incidence of Tip Burn in Cabbage, Celery, and Lettuce. Hort. Environ. Biotechnol. 2012, 53, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qin, J.; Mattson, N.S.; Ao, Y. Effect of potassium application on celery growth and cation uptake under different calcium and magnesium levels in substrate culture. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 158, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cserni, I.; Hüvely, A.; Petö, J. The impact of potassium fertilization on development and magnesium content of celery. Gradus 2020, 7, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, S.A.; Zickermann, J.; Kornahrens, M. Poultry manure effect on growth and yield of maize. West Afr. J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwo, A.A.; Adetunji, M.T.; Azeez, J.O.; Elemo, K.O. Kinetics of potassium release and fixation in some soils of Ogun State, Southwestern, Nigeria as influenced by organic manure. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2018, 7, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, E.; Pardes, C.; Pérez-Murcia, M.D.; Bustamante, M.A.; Moral, R. Spent mushroom substrates as component of growing media for germination and growth of horticultural plants. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4227–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
