Comprehensive Genetic Analysis of Edible-Podded Pea Genotypes: Variability, Heritability, and Multivariate Approach Across Two Agro-Climatic Zones in India
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Cultural Practices
2.2. Location and Climatic Conditions
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Combined ANOVA
3.2. Phenotypic and Genotypic Coefficient of Variation
3.3. Broad-Sense Heritability (h2) and Genetic Advance as Percentage of Mean (GAPM)
3.4. Correlation Analysis
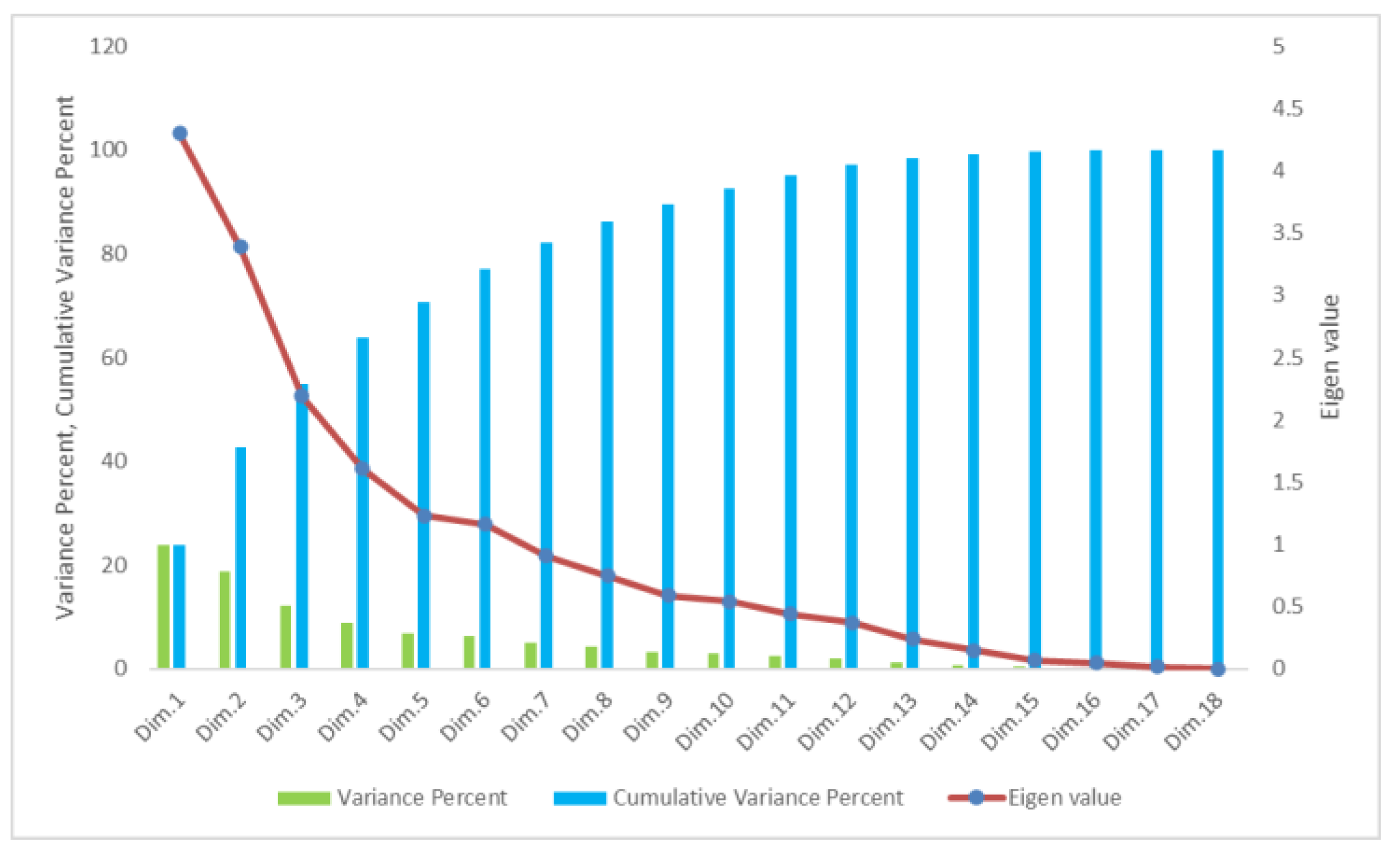
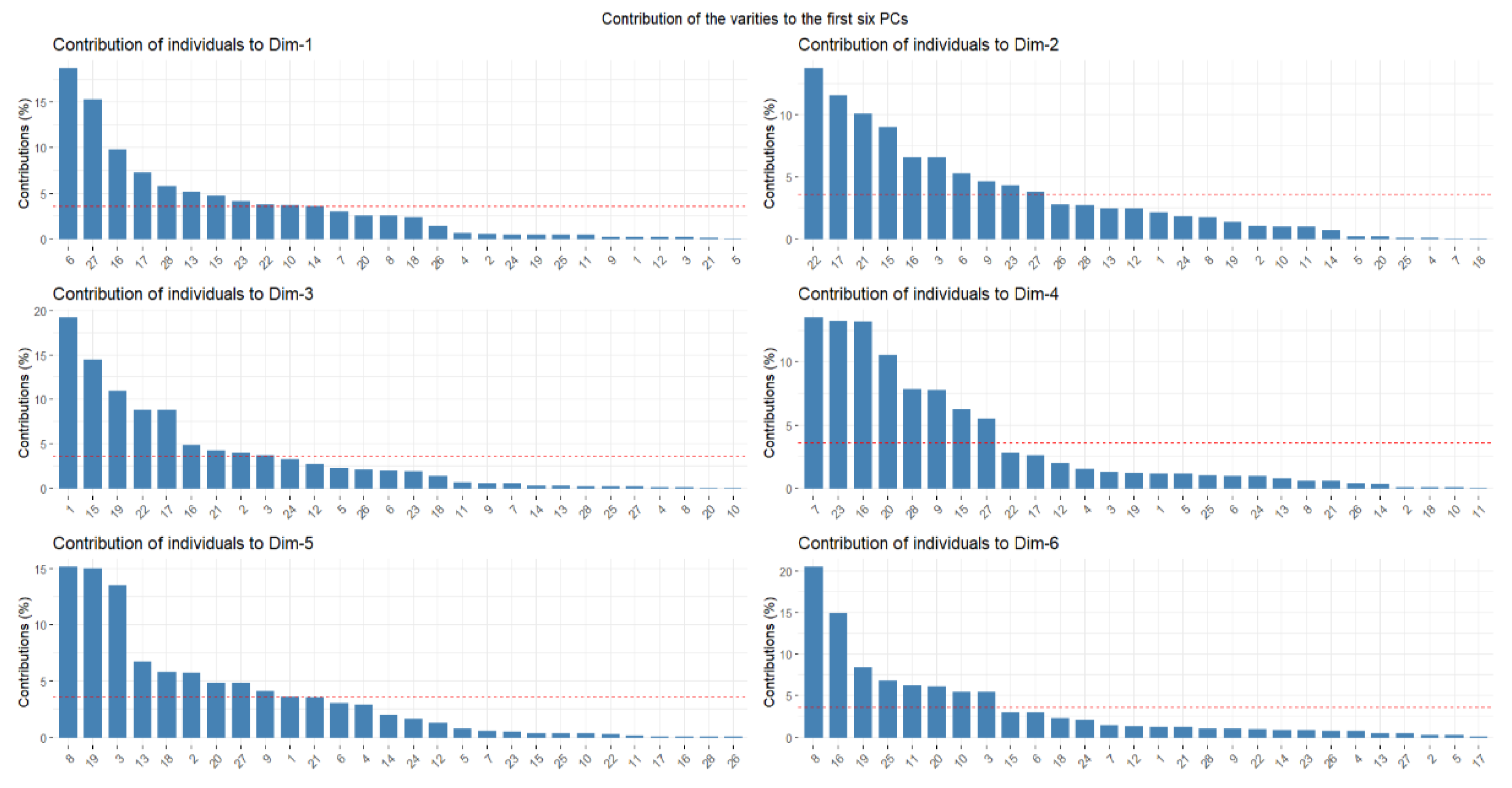
3.5. Principal Component Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sneedon, J.L. Identification of garden pea varieties. (I) Grouping, arrangement, and use of continuous characters. J. Nath. Inst. Agric. Bot. 1970, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- McGee, R.J.; Baggett, J.R. Inheritance of Stringless Pod in Pisum sativum L. J. Am. Soc. Hort. 1992, 117, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.R.; Baggett, J.R.; Lamborn, C. Origin, history, and genetic improvement of the snap pea (Pisum sativum L.). Plant Breed. Rev. 2001, 21, 93–138. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R.A.; Mahmud, F.; Reza, M.A.; Mahbub, M.; Shirazy, J.B.; Rahman, M. Genetic diversity, correlation and path analysis for yield and yield components of pea (Pisum sativum L.). World J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 13, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Koc, A.; Dumlu Gul, Z. Morphological characteristics and seed yield of east Anatolian local forage pea (Pisum sativum ssp. arvense L.) ecotypes. Turk. J. Field Crops 2012, 17, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Deshahalli Divakara, D.; Gore, P.G.; Tripathi, K.; Katral, A.; Roy Choudhury, D.; Abhishek, G.J.; Ragi, S.; Thippeswamy, D.; Muthusamy, V.; Sharma, D.K.; et al. Exploring genetic diversity of potential legume, Vigna angularis (Willd.) Ohwi and Ohashi through agro-morphological traits and SSR markers analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0312845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Gudi, S.; Amandeep; Upadhyay, P.; Shekhawat, P.K.; Nayak, G.; Goyal, L.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, P.; Kamboj, A.; et al. Unlocking the hidden variation from wild repository for accelerating genetic gain in legumes. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1035878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocianowski, J.; Księżak, J.; Nowosad, K. Genotype by environment interaction for seeds yield in pea (Pisum sativum L.) using additive main effects and multiplicative interaction model. Euphytica 2019, 215, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudra, S.G.; Hanan, E.; Sagar, V.R.; Bhardwaj, R.; Basu, S.; Sharma, V. Manufacturing of mayonnaise with pea pod powder as a functional ingredient. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 2402–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latha, G.K.; Kerure, P.; Kantharaj, Y.; Srinivasa, V.; Ramesh, A.N. Genetic Investigation in Garden Pea for Yield and Quality Characters. J. Exp. Agric. Int. 2024, 46, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Dhall, R.K.; Singh, H.; Kumar, P.; Bhatia, D.; Kumari, P.; Rana, N. Assessing Elemental Diversity in Edible-Podded Peas: A Comparative Study of Pisum sativum L. var. macrocarpon and var. saccharatum through Principal Component Analysis, Correlation, and Cluster Analysis. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyhart, J.L.; Lorenz, A.J.; Smith, K.P. Multi-trait improvement by predicting genetic correlations in breeding crosses. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2019, 9, 3153–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koij, F.S.; Saba, J. Using cluster analysis and principal component analysis to group lines and determine important traits in white bean. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 29, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.; Rosebrough, N.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.T.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marais, J.P.; De Wit, J.L.; Quicke, G.V. A critical examination of the Nelson-Somogyi method for the determination of reducing sugars. Anal. Biochem. 1966, 15, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, P.R.; Omeera, A.; Suradkar, P.P.; Dar, M.A. Effect of combination treatment of gamma irradiation and ascorbic acid on physicochemical and microbial quality of minimally processed eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2014, 103, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, C.S. Experimental Methods in Analytical Chemistry of Foods; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2000; Volume 3, 1, p. 116. [Google Scholar]
- Azene, Y.; Menzir, A.; Dejene, T. Genetic variability and association of traits in Ethiopian durum wheat (Triticum turgidium L. Var. Durum) landraces at Dabat research station, north Gondar. Cogent. Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1778604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Aysh, F.M.; Habib, N.J.; Nejla, S.; Murshed, R.; Basaam, A.T. Genetic Variability and Association of Quality Characters and Pod Yield in Garden Peas (Pisum sativum L.). Walailak J. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Červenski, J.F.; Danojević, D.; Savić, A. Chemical composition of selected winter green pea (Pisum sativum L.) genotypes. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2017, 82, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhall, R.K.; Kaur, R. Variation in biochemical attributes and rust reaction in response to crop geometry in mono- picking garden pea for mechanical harvesting. Veg. Sci. 2021, 48, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhall, R.K.; Kaur, R.; Sharma, P.; Singh, H.; Yadav, S.; Kumari, P. Standardized agronomic practices for mechanical harvesting of the single-harvest garden pea in India. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, E.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, G.D.; Manuja, S.; Rana, S.S. Effect of sowing dates on phenological traits, yield and its contributing attributes on snow pea genotypes. Legume Res. 2023, 46, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.K.; Kanwar, H.S.; Kumar, M.; Vikram, A.; Kumar, R. Potential productivity of edible podded pea cultivars in Mid-Hills of Himachal Pradesh. India Int. J. Econ. Plants 2015, 1, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Karaköy, T.; Toklu, F.; Karagöl, E.T.; Uncuer, D.; Çilesiz, Y.; Ali, A.; Nadeem, M.A.; Özkan, H. Genome-wide association studies revealed Dar Tseq loci associated with agronomic traits in Turkish faba bean germplasm. Genet. Resour. Crop Ev. 2023, 71, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, M.; Persaud, R.; Gobind, N.; Khan, A.; Subramanian, G.; Corredor, E. Genotype by environment interactions of grain yield performance and lodging incidence in advance breeding lines of rice across environments in Guyana. Int. J. Agric. Pol. Res. 2022, 10, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, O.B.; Ige, S.A.; Azeez, M.A.; Afolabi, M.S.; Abdulmaliq, S.Y.; Mahamood, J. Heritability and genetic advance for grain yield and its component characters in maize (Zea mays L.). Int. J. Plant Res. 2012, 2, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magomere, K.M.; Nchimbi-Msolla, S.; Tryphone, G.M. Genetic parameters estimate of iron and zinc nutrients in common bean genotypes. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2024, 20, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidou, F.; Ratnakumar, P.; Halilou, O.; Mponda, O.; Kapewa, T.; Monyo, E.; Faye, I.; Ntare, B.R.; Nigam, S.N.; Upadhyaya, H.D.; et al. Selection of intermittent drought tolerant lines across years and locations in the reference collection of groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Field Crops Res. 2012, 126, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevaiah, C.; Appunu, C.; Aitken, K.; Suresha, G.S.; Vignesh, P.; Mahadeva Swamy, H.K.; Valarmathi, R.; Hemaprabha, G.; Alagarasan, G.; Ram, B. Genomic selection in sugarcane: Current status and future prospects. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 708233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Sharma, A.; Lata, H. Genetic variability for pod yield and related traits in garden pea (Pisum sativum L.) Electron. J. Plant Breed. 2020, 11, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasker, K.; Shashibushan, D.; Krishna, K.M.; Bhave, M.H.V. Genetic variability, heritability and genetic advance of grain yield in pearl millet [Pennisetum glaucum (L.) R. Br.]. Int. J. Pure Appl. Biosci. 2017, 5, 1228–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.M.; Chaudhari, S.; Devi, N.; Shivanna, A.; Gowda, A.; Boddepalli, V.N.; Pradhan, H.; Schafleitner, R.; Jegadeesan, S.; Somta, P. Genetics, genomics, and breeding of black gram [Vigna mungo (L.) Hepper]. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1273363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, S.L.; Heslop-Harrison, P.; Amas, J.; Ortiz, R.; Edwards, D. Epistasis and pleiotropy-induced variation for plant breeding. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2024, 22, 2788–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panwar, S.; Thakur, S.; Mushtaq, M.; Kumar, A. Estimation of Correlation Coefficient and Path Analysis in Field Pea (Pisum sativum L.). Int. J. Environ. Clim. 2023, 13, 1871–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, P.; Katoch, V.; Chadha, S.; Kumari, V. Genetic variability for pod yield and component traits in sugar snaps (Pisum sativum var. saccharatum). Legume Res. 2023, 46, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamatha, R.M.; Sharma, R.K.; Bhardwaj, A.; Kumar, R. Variability and character association study for horticultural traits in vegetable pea (Pisum sativum var. hortense L.) under east-Indian climatic conditions. J. Ecol. Environ. 2022, 40, 2118–2124. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Kumar, M.; Dogra, R.K.; Bharat, N.K. Variability and character association studies in garden pea (Pisum sativum var. hortense L.) during winter season at mid hills of Himachal Pradesh. Legume Res. 2015, 38, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlarik, A.; Ćeran, M.; Živanov, D.; Grumeza, R.; Skøt, L.; Sizer-Coverdale, E.; Lloyd, D. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization and correlation analysis of pea (Pisum sativum L.) diversity panel. Plants 2022, 11, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallie, D.R. L-Ascorbic acid: A multifunctional molecule supporting plant growth and development. Scientifica 2013, 2013, 795964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, H.; Gao, S.; Xiong, B.; Yan, Q.; Wei, P.; Wang, Z.; Tong, Y.; Le, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; et al. A Research on Mathematical Model and Prediction Method for Raw Tobacco Material Quality Based on Cluster Classification. IOP Conf. Series Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 692, 032071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorter, H.; Nagel, O. The role of biomass allocation in the growth response of plants to elevated CO2. Ann. Bot. 2000, 86, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ouafi, L.; Alane, F.; Rahal-Bouziane, H.; Abdelguerfi, A. Agro-morphological diversity within field pea (Pisum sativum L.) genotypes. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 11, 4039–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.R.; Ahmed, N.; Singh, D.B.; Srivastva, K.K.; Singh, R.K.; Mir, A. Genetic variability determination in garden pea (Pisum sativum L. sub sp. hortense Asch. and Graebn.) by using the multivariate analysis. Legume Res. 2017, 40, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ali, Z.; Qureshi, A.S.; Ali, W.; Gulzar, H.; Nisar, M.; Ghafoor, A. Evaluation of genetic diversity present in pea (Pisum sativum L.) germplasm based on morphological traits, resistance to powdery mildew and molecular characteristics. Pak. J. Bot. 2007, 39, 2739–2747. [Google Scholar]
- Kuneva, V.; Sabeva, M. Evaluation of the genetic variability of winter pea varieties (pisum sativum L.) from the collection of ipgr-sadovo. Sci. Papers Ser. A. Agron. 2023, 66, 385–941. [Google Scholar]
- Ton, A.; Mart, D.; Karaköy, T.; Türkeri, M.; Torun, A.A.; Anlarsal, A.E. Characterization of some local pea (Pisum sativum L.) genotypes for agro-morphological traits and mineral concentrations. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2022, 46, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| S. No. | Genotypes | Edible-Podded Type | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Airtel | Snow pea | USA |
| 2. | Oregon Sugar Pod | Snow pea | USA |
| 3. | Arka Sampoorna | Snow pea | IIHR, Bangalore |
| 4. | PED-2021-4 | Sugar Snap pea | PAU, Ludhiana |
| 5. | Tardio | Snow pea | PAU, Ludhiana |
| 6. | Sugar Bon | Snow pea | USA |
| 7. | PED-2018-5 | Sugar Snap pea | PAU, Ludhiana |
| 8. | PED-2021-6 | Snow pea | PAU, Ludhiana |
| 9. | PED-2021-2 | Snow pea | PAU, Ludhiana |
| 10. | PED-2018-7 | Sugar Snap pea | PAU, Ludhiana |
| 11. | Namdhari Afila | Snow pea | Namdhari Seeds |
| 12. | Mithi Phali | Snow pea | PAU, Ludhiana |
| 13. | Tarbedo Sugar | Snow pea | PAU, Ludhiana |
| 14. | PED-2021-7 | Snow pea | PAU, Ludhiana |
| 15. | Dwarf Grey Sugar | Snow pea | PAU, Ludhiana |
| 16. | PED-2018-1 | Sugar Snap pea | PAU, Ludhiana |
| 17. | Sugar Daddy | Snow pea | USA |
| 18. | PED-2021-1 | Snow pea | PAU, Ludhiana |
| 19. | Sugar Snappy | Sugar Snap pea | USA |
| 20. | PED-2021-5 | Sugar Snap pea | PAU, Ludhiana |
| 21. | PED-2021-3 | Snow pea | PAU, Ludhiana |
| 22. | PED-2018-6 | Sugar Snap pea | PAU, Ludhiana |
| 23. | Namdhari-NA | Snow pea | Namdhari Seeds |
| 24. | PED-2018-8 | Sugar Snap pea | PAU, Ludhiana |
| 25. | Him Palam Mithiphali 1 (HPM-1) | Snow pea | CSKHPKV, Palampur |
| 26. | Him Palam Mithiphali 2 (HPM-2) | Snow pea | CSKHPKV, Palampur |
| 27. | Honey Snap | Sugar Snap pea | USA |
| 28. | Royal Snow | Sugar Snap pea | USA |
| Trait | Source of Variation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSg (Df = 27) | MSe (Df = 1) | MSgxe (Df = 27) | MS Error | |
| NFA | 9.03 *** | 207.86 *** | 3.75 *** | 0.13 |
| DTF | 23.70 *** | 1592.24 *** | 21.05 *** | 4.47 |
| DTFF | 47.38 *** | 744.88 *** | 9.98 ** | 4.48 |
| DTPF | 22.22 *** | 1755.83 *** | 23.56 *** | 3.57 |
| PH | 5968.72 *** | 15,246.63 *** | 232.27 *** | 7.00 |
| NB | 4.957 *** | 9.00 *** | 0.02 *** | 0.007 |
| NS | 5.80 *** | 3.06 *** | 0.60 *** | 0.03 |
| PB | 44.34 *** | 117.17 *** | 7.80 *** | 0.20 |
| PL | 12.77 *** | 56.47 *** | 1.99 *** | 0.03 |
| NPPP | 48.71 *** | 151.24 *** | 9.52 *** | 0.26 |
| TPW | 1537.31 *** | 1348.11 *** | 4.25 ** | 2.13 |
| Y | 6960.83 *** | 18,818.00 *** | 367.98 *** | 9.65 |
| DM | 66.63 *** | 519.76 *** | 20.54 *** | 0.20 |
| TS | 9.57 *** | 2.13 *** | 1.56 *** | 0.011 |
| RS | 1.59 *** | 6.90 *** | 0.50 *** | 0.001 |
| SP | 2.65 *** | 3.38 *** | 0.76 *** | 0.005 |
| AA | 1068.10 *** | 393.11 *** | 176.65 *** | 1.45 |
| F | 2.06 *** | 5.77 *** | 0.21 *** | 0.001 |
| Trait | σ2g | σ2p | σ2e | GCV | PCV | ECV | h2 (%) | GA | GAPM (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NFA | 2.22 | 4.57 | 2.34 | 13.47 | 19.30 | 13.82 | 49 | 2.15 | 19.38 |
| DTF | 1.50 | 20.70 | 10.88 | 1.62 | 6.02 | 4.01 | 7 | 0.68 | 0.90 |
| DTFF | 12.17 | 23.04 | 19.20 | 4.24 | 5.84 | 5.80 | 52 | 5.22 | 6.35 |
| DTPF | 0.68 | 20.85 | 20.17 | 1.04 | 5.76 | 5.69 | 3 | 0.31 | 0.39 |
| PH | 1935.72 | 2097.27 | 161.54 | 45.50 | 47.36 | 13.14 | 92 | 87.07 | 90.05 |
| NB | 1.62 | 1.70 | 0.07 | 38.46 | 39.34 | 8.31 | 95 | 2.57 | 77.43 |
| NS | 1.88 | 2.04 | 0.16 | 22.22 | 23.17 | 6.57 | 92 | 2.70 | 43.90 |
| PB | 13.93 | 16.47 | 2.53 | 23.82 | 25.89 | 10.16 | 85 | 7.07 | 45.13 |
| PL | 3.98 | 4.80 | 0.83 | 25.15 | 27.64 | 11.46 | 83 | 3.74 | 47.14 |
| NPPP | 15.18 | 18.35 | 3.18 | 20.43 | 22.47 | 9.35 | 83 | 7.29 | 38.28 |
| TPW | 508.34 | 520.63 | 12.82 | 41.89 | 42.39 | 6.51 | 98 | 45.89 | 85.27 |
| Y | 2248.30 | 2464.24 | 215.94 | 46.15 | 48.32 | 14.30 | 91 | 93.30 | 90.81 |
| DM | 19.56 | 27.5 | 7.94 | 28.22 | 33.46 | 17.98 | 71 | 7.68 | 49.03 |
| TS | 3.08 | 3.41 | 0.33 | 39.44 | 41.49 | 12.89 | 90 | 3.44 | 77.23 |
| RS | 0.47 | 0.63 | 0.14 | 52.07 | 59.57 | 28.95 | 76 | 1.24 | 93.74 |
| SP | 0.82 | 1.00 | 0.18 | 37.72 | 41.59 | 17.52 | 82 | 1.7 | 70.46 |
| AA | 343.16 | 381.77 | 38.6 | 38.82 | 40.94 | 13.02 | 90 | 36.18 | 75.81 |
| F | 0.66 | 0.74 | 0.08 | 61.33 | 65.14 | 21.97 | 89 | 1.57 | 118.93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yadav, S.; Dhall, R.K.; Singh, H.; Kumar, P.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, P.; Kumari, P.; Rana, N. Comprehensive Genetic Analysis of Edible-Podded Pea Genotypes: Variability, Heritability, and Multivariate Approach Across Two Agro-Climatic Zones in India. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11010022
Yadav S, Dhall RK, Singh H, Kumar P, Sharma P, Kumar P, Kumari P, Rana N. Comprehensive Genetic Analysis of Edible-Podded Pea Genotypes: Variability, Heritability, and Multivariate Approach Across Two Agro-Climatic Zones in India. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleYadav, Saurabh, Rajinder Kumar Dhall, Hira Singh, Parteek Kumar, Priti Sharma, Pradeep Kumar, Priyanka Kumari, and Neha Rana. 2025. "Comprehensive Genetic Analysis of Edible-Podded Pea Genotypes: Variability, Heritability, and Multivariate Approach Across Two Agro-Climatic Zones in India" Horticulturae 11, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11010022
APA StyleYadav, S., Dhall, R. K., Singh, H., Kumar, P., Sharma, P., Kumar, P., Kumari, P., & Rana, N. (2025). Comprehensive Genetic Analysis of Edible-Podded Pea Genotypes: Variability, Heritability, and Multivariate Approach Across Two Agro-Climatic Zones in India. Horticulturae, 11(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11010022









