Investigating the Effects of Optimized Mineral Fertilization on Plant Growth, Physiological Traits, Tuber Yield, and Biochemical Contents of Potato Crop
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
2.2. Fertilization Treatments
- -
- Optimum rates (T1; according to TCP) which were used as the control treatment, with an average of 117.5 kg/ha (N), 145 kg/ha (K2O), and 19 L (P2O5);
- -
- High rates (T2; +25% of the optimum rate);
- -
- Low rates (T3; −25% of the optimum rate).
2.3. Evaluation Criteria
2.3.1. Plant Growth Assessment
2.3.2. Evaluation of the Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters
2.3.3. Evaluation of Photosynthetic Active Radiation and Real Evapotranspiration
2.3.4. Yield and Yield Component Criteria
2.3.5. Sugar and Starch Content Evaluation
Total Soluble Sugar Determination
Starch Content Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Fertilization Regime and Variety on Plant Growth and Physiological Traits
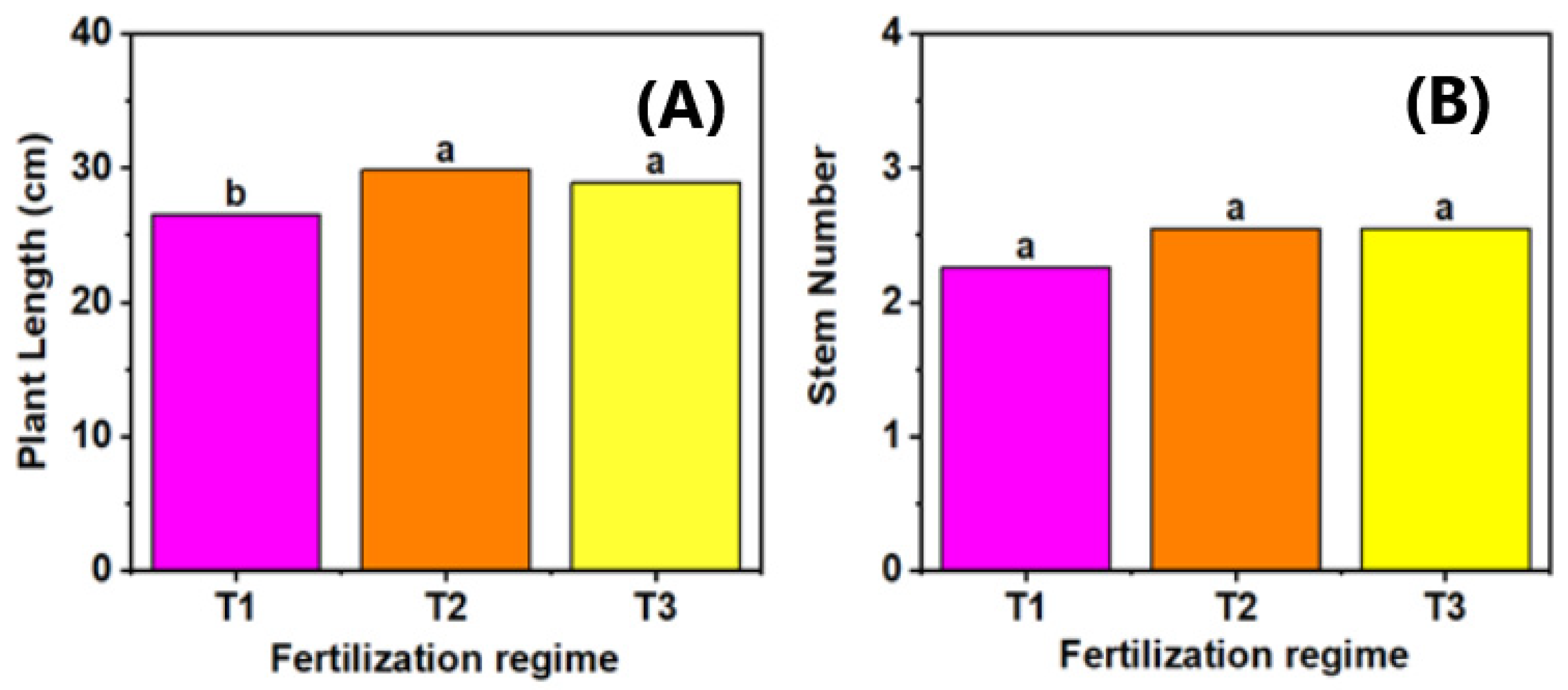
3.2. Effect of Fertilization Regime Across Varieties in Relation to Plant Growth
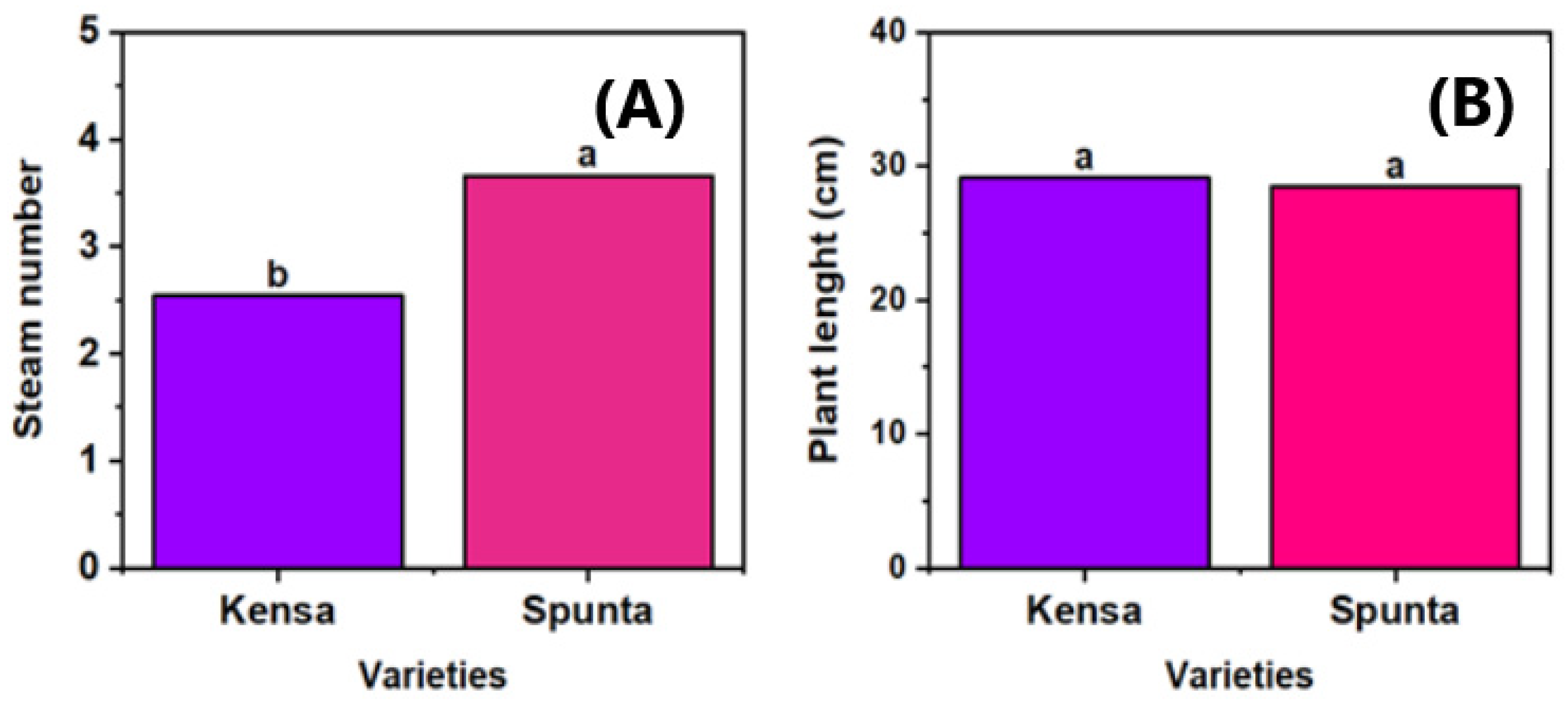
3.3. Effect of Varieties Across Fertilization Regimes in Relation to Plant Growth
3.4. Interaction Effects of Fertilization Regime × Variety on Plant Growth and Physiological Traits
Effects on Plant Growth and Physiological Traits
3.5. Effect of Fertilization Regime and Variety on Yield and Yield Components and Chemical Composition of Tubers and Leaves
3.5.1. Effect of Fertilization Regimes Across Varieties in Relation to Yield and Yield Components and Chemical Composition of Tubers and Leaves
3.5.2. Interaction Effects of Fertilization Regime × Variety on Yield and Yield Components and Chemical Composition of Tubers and Leaves
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wijesinha-Bettoni, R.; Mouillé, B. The Contribution of Potatoes to Global Food Security, Nutrition and Healthy Diets. Am. J. Potato Res. 2019, 96, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarre, D.A.; Brown, C.R.; Sathuvalli, V.R. Potato Vitamins, Minerals and Phytonutrients from a Plant Biology Perspective. Am. J. Potato Res. 2019, 96, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, S.L.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Alexopoulos, A.; Heleno, S.A.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Potato peels as sources of functional compounds for the food industry: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Production and Trade Statistics. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Bon, C.; Zid, S.B. Tunisia Production Systems and Constraints. 2020, pp. 1–5. Available online: https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5e459c86d426b45f5ca0d083/t/5ec32761bc8e465afe6d47e9/1589847912330/ARC_Tunisia_200519.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Horton, D. Potatoes: Production, Marketing, and Programs for Developing Countries, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Nesrine, D.; Boualem, B.; Lakhdar, D.M. Study of the Sustainability of Potato Farms in the Region of Oued Souf (Southern Algeria). Turk. J. Agric. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 11, 197–201. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Tang, J.; Wang, E.; Pan, Z.; Pan, X.; Hu, Q. Optimum planting date and cultivar maturity to optimize potato yield and yield stability in North China. Field Crops Res. 2021, 269, 108179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, J.; Fang, Q.; Dayananda, B.; Yu, Q.; Zhao, P.; Yin, H.; Pan, X. Identifying agronomic options for better potato production and conserving water resources in the agro-pastoral ecotone in North China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 272–273, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.C.; Jin, Y.I.; Nam, J.H.; Cheon, C.G.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Yu, H.S. Early drought effect on canopy development and tuber growth of potato cultivars with different maturities. Field Crops Res. 2018, 215, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubaker, H.; Saadaoui, W.; Dasgan, H.Y.; Tarchoun, N.; Gruda, N.S. Enhancing Seed Potato Production from In Vitro Plantlets and Microtubers through Biofertilizer Application: Investigating Effects on Plant Growth, Tuber Yield, Size, and Quality. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, A.; Petropoulos, S. Tissue culture of potato for seed production. In The Potato Crop: Managemenet, Production and Food Security; Villa, P.M., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 61–89. ISBN 9781631172557. [Google Scholar]
- Refaie, M.M.; Merghany, M.M.; Khalil, M.M.; Kabil, F.F. Microtuber and Minituber Manipulation for Potato Pre-Basic Seed Production Under Egyptian Conditions. Plant Arch. 2020, 20, 2159–2164. [Google Scholar]
- Naumann, M.; Koch, M.; Thiel, H.; Gransee, A.; Pawelzik, E. The Importance of Nutrient Management for Potato Production Part II: Plant Nutrition and Tuber Quality. Potato Res. 2020, 63, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulung, L.E.A.; Amin, M.; Manoppo, C.N. Response of growth and production of potato plants to application of NPK fertilizer. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 306, 01018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, S.A.; Fernandes, Â.; Polyzos, N.; Antoniadis, V.; Barros, L.; C.F.R. Ferreira, I. The Impact of fertilization regime on the crop performance and chemical composition of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) cultivated in central Greece. Agronomy 2020, 10, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.E.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Selim, D.A.F.H.; Elbagory, M.; Othman, M.M.; Omara, A.E.D.; Mohamed, M.H. Plant growth, yield and quality of potato crop in relation to potassium fertilization. Agronomy 2021, 11, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mitra, B.; Luthra, S.K.; Saha, A.; Hassan, M.M.; Hossain, A. Study on morphological, physiological characteristics and yields of twenty-one potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) cultivars grown in eastern sub-himalayan plains of India. Agronomy 2021, 11, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewide, I.; Singh, S.; Kassa, H. Biomass production and nutritional quality of potato tuber as affected by blended fertilizer (NPSB), cattle manure, vermicompost and mineral NP in southwestern Ethiopia. Plant Sci. Today 2021, 8, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soratto, R.P.; Fernandes, A.M. Phosphorus effects on biomass accumulation and nutrient uptake and removal in two potato cultivars. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, S.; Guo, X.; Li, Q.; Hui, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H. An Evaluation of Potato Fertilization and the Potential of Farmers to Reduce the Amount of Fertilizer Used Based on Yield and Nutrient Requirements. Agronomy 2024, 14, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.L.B.R.; Zotarelli, L.; Dukes, M.D.; van Santen, E.; Asseng, S. Nitrogen fertilizer rate and timing of application for potato under different irrigation methods. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 283, 108312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Naumann, M.; Pawelzik, E.; Gransee, A.; Thiel, H. The Importance of Nutrient Management for Potato Production Part I: Plant Nutrition and Yield. Potato Res. 2020, 63, 97–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmanov, Y.T.; Chernenok, V.G.; Kuzdanova, R.S. Potato in response to nitrogen nutrition regime and nitrogen fertilization. Field Crops Res. 2019, 231, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milroy, S.P.; Wang, P.; Sadras, V.O. Defining upper limits of nitrogen uptake and nitrogen use efficiency of potato in response to crop N supply. Field Crops Res. 2019, 239, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bélanger, G.; Walsh, J.R.; Richards, J.E.; Milburn, P.H.; Ziadi, N. Nitrogen fertilization and irrigation affects tuber characteristics of two potato cultivars. Am. J. Potato Res. 2002, 79, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Lakshmi, G.A.; Krishna, G.K.; Patni, B.; Prakash, S.; Bhattacharyya, M.; Singh, S.K.; Verma, K.K. Climate Change and Its Impact on Crops: A Comprehensive Investigation for Sustainable Agriculture. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blecharczyk, A.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Sawinska, Z.; Rybacki, P.; Radzikowska-Kujawska, D. Impact of Crop Sequence and Fertilization on Potato Yield in a Long-Term Study. Plants 2023, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocent, U.; Balekye, A.; Prossy, N.; Mwesige, R.; George, K.; Benon, M. Effects of fertilizer application on yield and yield related parameters of low yielding potato varieties in Uganda. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2021, 17, 1540–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frąckowiak, K.; Potarzycki, J.; Grzebisz, W.; Szczepaniak, W. Potato nutritional status at the onset of tuberization—A yield prediction tool. Plant Soil Environ. 2020, 66, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zierer, W.; Rüscher, D.; Sonnewald, U.; Sonnewald, S. Tuber and Tuberous Root Development. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2021, 72, 551–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cambouris, A.N.; Luce, M.S.; Zebarth, B.J.; Ziadi, N.; Grant, C.A.; Perron, I. Potato response to nitrogen sources and rates in an irrigated sandy soil. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Qiu, S.; Ding, W.; Xu, X.; He, P. Synergizing potato productivity and environmental performance with Nutrient Expert recommendation approach in northern China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 382, 135258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, C.J.; Kelling, K.A.; Stark, J.C.; Porter, G.A. Optimizing Phosphorus Fertilizer Management in Potato Production. Am. J. Potato Res. 2014, 91, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, C.J.; Bierman, P.M. Potato yield and tuber set as affected by phosphorus fertilization. Am. J. Potato Res. 2008, 85, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Song, B.; Zhao, Z. Effects of potassium fertilization on potato starch physicochemical properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabian, S.; Farhangi-Abriz, S.; Qin, R.; Noulas, C.; Sathuvalli, V.; Charlton, B.; Loka, D.A. Potassium: A vital macronutrient in potato production—A review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Singh, B.P.; Kumar, P. An overview of the factors affecting sugar content of potatoes. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2004, 145, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J. The effect of climate change on global potato production. Am. J. Potato Res. 2003, 80, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rykaczewska, K. The Effect of High Temperature Occurring in Subsequent Stages of Plant Development on Potato Yield and Tuber Physiological Defects. Am. J. Potato Res. 2015, 92, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila-Valdés, A.; Quinet, M.; Lutts, S.; Martínez, J.P.; Lizana, X.C. Tuber yield and quality responses of potato to moderate temperature increase during Tuber bulking under two water availability scenarios. Field Crops Res. 2020, 251, 107786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, R.; Singh, D.; Kumar, J. Photoperiod effect on yield attributing traits of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Res. Environ. Life Sci. 2016, 9, 771–774. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, L.; Meng, M.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.; Liang, H. Effect of Photoperiod on Dry Matter Accumulation and Partitioning in Potato. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravia, D.; Farfán-Vignolo, E.R.; Gutiérrez, R.; De Mendiburu, F.; Schafleitner, R.; Bonierbale, M.; Khan, M.A. Yield and Physiological Response of Potatoes Indicate Different Strategies to Cope with Drought Stress and Nitrogen Fertilization. Am. J. Potato Res. 2016, 93, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margus, K.; Eremeev, V.; Loit, E.; Runno-Paurson, E.; Mäeorg, E.; Luik, A.; Talgre, L. Impact of Farming System on Potato Yield and Tuber Quality in Northern Baltic Sea Climate Conditions. Agriculture 2022, 12, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, L.P.; de Oliveira, R.C.; Lana, R.M.Q.; Luz, J.M.Q.; Guimarães, J.P.A.; Alves, E. de O. Accumulation of macronutrients and productivity of potato with foliar application of biofertilizer. Int. J. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2021, 48, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemens-Hulscher, M.; Lammerts van Bueren, E.T.; Struik, P.C. Identifying nitrogen-efficient potato cultivars for organic farming. Euphytica 2014, 199, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.C.; da Silva, J.R.R.; Lana, R.M.Q.; de Azevedo Pereira, A.I.; Castoldi, R.; de Camargo, R.; Luz, J.M.Q. Fertilizer application levels in potato crops and the diagnosis and recommendation integrated system (DRIS). Agronomy 2021, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajaldeen, Z.A.; Allela, W.B.M.A. Effect of potassium and biological fertilization on vegetative growth characteristics of two potatoes cultivars (Solanum tuberosum L.). Int. J. Health Sci. 2022, 6, 8027–8035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, R.; Paswan, S. Influence of higher levels of NPK fertilizers on growth, yield, and profitability of three potato varieties in Surma, Bajhang, Nepal. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parganiha, S.; Kumar Sharma, P.; Yadav, V.; Kumar Samadhiya, V.; Parganiha, S.; Author, C. Effect of NPK on growth, yield and quality of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) under Chhattisgarh plain. Pharma Innov. J. 2022, 11, 2214–2217. [Google Scholar]
- Rietra, R.P.J.J.; Heinen, M.; Dimkpa, C.O.; Bindraban, P.S. Effects of Nutrient Antagonism and Synergism on Yield and Fertilizer Use Efficiency. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2017, 48, 1895–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munthali, C.; Kinoshita, R.; Onishi, K.; Rakotondrafara, A.; Mikami, K.; Koike, M.; Tani, M.; Palta, J.; Aiuchi, D. A Model Nutrition Control System in Potato Tissue Culture and Its Influence on Plant Elemental Composition. Plants 2022, 11, 2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muleta, H.D.; Aga, M.C. Role of Nitrogen on Potato Production: A Review. J. Plant Sci. 2019, 7, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Aragon, B.; Montoya-Martínez, A.C.; Parra-Cota, F.I.; de los Santos-Villalobos, S. Genomic Insight into a Potential Biological Control Agent for Fusarium-Related Diseases in Potatoes: Bacillus cabrialesii Subsp. cabrialesii Strain PE1. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, C.; Deng, Y. Effect of potassium on nitrate removal from groundwater in agricultural waste-based heterotrophic denitrification system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, D.R.; Koch, K.E.; Shieh, W.J. Effect of environmental factors on whole plant assimilate partitioning and associated gene expression. J. Exp. Bot. 1996, 47, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadaoui, W.; Tarchoun, N.; Msetra, I.; Pavli, O.; Falleh, H.; Ayed, C.; Amami, R.; Ksouri, R.; Petropoulos, S.A. Effects of drought stress induced by D-Mannitol on the germination and early seedling growth traits, physiological parameters and phytochemicals content of Tunisian squash (Cucurbita maxima Duch.) landraces. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1215394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chincinska, I.A.; Liesche, J.; Krügel, U.; Michalska, J.; Geigenberger, P.; Grimm, B.; Kühn, C. Sucrose transporter StSUT4 from potato affects flowering, tuberization, and shade avoidance response. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, J.; Bjorkman, O. Photosynthetic Response and Adaptation to Temperature in Higher Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 1980, 31, 491–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwitz, G.; Bardsley, A.H.; Keliher, P.N. Determination of phenol in the presence of sulfite (sulfur dioxide) by the 4-aminoantipyrine spectro-photometric method. Anal. Chim. Acta 1981, 128, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; van der Putten, P.E.L.; Datema, M.; Mossink, L.; Lommen, W.J.M.; Struik, P.C.; van Ittersum, M.K. Physiological Age of Potato Seed Tubers of Contrasting Cultivars Hardly Affects Crop Performance in a Temperate Climate; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2024; ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Workineh, G.; Loha, G.; Hidoto, L. Response of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) to nitrogen fertilizer application at Angecha, Southern Ethiopia. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 2017, 7, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Setu, H.; Mitiku, T. Response of potato to nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers at Assosa, western Ethiopia. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, S.; Pandino, G.; Mauromicale, G. Optimizing nitrogen fertilization to improve qualitative performances and physiological and yield responses of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Agronomy 2020, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, P.M.; Sarmiento, L.; Rada, F.J.; Machado, D.; Rodrigues, A.C. Leaf area index of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) crop under three nitrogen fertilization treatments. Agron. Colomb. 2017, 35, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelalem, A.; Tekalign, T.; Nigussie, D. Response of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) to different rates of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization on vertisols at Debre Berhan, in the central highlands of Ethiopia. Afr. J. Plant Sci. 2009, 3, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel Naby, H.M.; El-Gamily, E.L.; Gab Allah, A.A.A. Response of Potato Plants to Sources and Rates of Potassium Fertilizer. J. Plant Prod. 2018, 9, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, W.; Li, P.; Shi, P.; Xu, G.; Cheng, S.; Cheng, Y.; Fan, Z.; Wang, X. Effects of irrigation and fertilization on different potato varieties growth, yield and resources use efficiency in the Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 261, 107351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzebisz, W.; Szczepaniak, W.; Bocianowski, J. Potassium fertilization as a driver of sustainable management of nitrogen in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Field Crops Res. 2020, 254, 107824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.S.; Brown, H.E.; Moot, D.J. Assessing potato canopy growth and development at the individual leaf level to improve the understanding of the plant source–sink relations. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2021, 49, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozumder, M.; Banerjee, H.; Ray, K.; Paul, T. Evaluation of potato (Solanum tuberosum) cultivars for productivity, nitrogen requirement and eco-friendly indices under different nitrogen levels. Indian J. Agron. 2001, 59, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, M.F.; Fowler, J.H.; Allen, E.J. Responses of potato (Solanum tuberosum) to potassium fertilizers. J. Agric. Sci. 2001, 136, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaji, H.M.; Jajoo, A.; Oukarroum, A.; Brestic, M.; Zivcak, M.; Samborska, I.A.; Cetner, M.D.; Łukasik, I.; Goltsev, V.; Ladle, R.J. Chlorophyll a fluorescence as a tool to monitor physiological status of plants under abiotic stress conditions. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016, 38, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murchie, E.H.; Lawson, T. Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis: A guide to good practice and understanding some new applications. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 3983–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.P.; Humphries, S. Photoinhibition of photosynthesis in nature. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1994, 45, 633–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keutgen, A.J.; Keutgen, N.; Wszelaczyńska, E.; Pobereżny, J.; Milczarek, D.; Tatarowska, B.; Flis, B. Evaluation of Photosynthetic and Yield Traits in Ten Potato Clones and Cultivars Under Farming Conditions in Poland. Potato Res. 2020, 63, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabò, I.; Spetea, C. Impact of the ion transportome of chloroplasts on the optimization of photosynthesis. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 3115–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hadidi, E.; El-Dissoky, R.; AbdElhafez, A. Foliar Calcium and Magnesium Application Effect on Potato Crop Grown in Clay Loam Soils. J. Soil Sci. Agric. Eng. 2017, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, A.L.G.; Soratto, R.P.; Fernandes, A.M.; Assunção, N.S.; Fernandes, F.M.; Yagi, R. Potassium fertilization for fresh market potato production in tropical soils. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 3351–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessema, G.L.; Mohammed, A.W.; Abebe, D.T. Genetic variability studies for tuber yield and yield attributes in Ethiopian released potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) varieties. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seid, E.; Tessema, L. Evaluation of tuber quality, yield and yield related traits of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) genotypes at Holetta, Central Ethiopia. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2024, 5, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambui, C.A.; Svennerstam, H.; Gruffman, L.; Nordin, A.; Ganeteg, U.; Näsholm, T. Patterns of plant biomass partitioning depend on Nitrogen source. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, S.L.; Stark, J.C.; Salaiz, T. Response of four potato cultivars to rate and timing of nitrogen fertilizer. Am. J. Potato Res. 2005, 82, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, J.E.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, S.L.; Wang, H.J. Nitrate accumulation and leaching in surface and ground water based on simulated rainfall experiments. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatments and Fertilzer Application Rates | Percentage of NPK Applied in Relation to Plant Life Cycle Stages | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetative Growth and Sprouting | Tuberization | Tuber Bulking | ||
| T1: Optimum rates | N (3.68 g/plant) | 60% | 20% | 20% |
| P2O5 (0.57 mL/plant) | 40% | 30% | 30% | |
| K2O (4.52 g/plant) | 20% | 30% | 50% | |
| T2: High rates (+25% of T1) | N (4.60 g/plant) | 60% | 20% | 20% |
| P2O5 (0.71 mL/plant) | 40% | 30% | 30% | |
| K2O (5.65 g/plant) | 20% | 30% | 50% | |
| T3: Low rates (−25% of T1) | N (2.76 g/plant) | 60% | 20% | 20% |
| P2O5 (0.43 mL/plant) | 40% | 30% | 30% | |
| K2O (3.39 g/plant) | 20% | 30% | 50% | |
| S.O.V. | DF | SN | SD | PL | TLN | Phot.L | Fo | Fm | Fv/Fm | RET | PAR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variety (V) | 1 | 7.13 * | 33.74 * | 13.63 ns | 406.12 * | 3838.82 ** | 38,388.69 ** | 10,522.88 * | 0.06 ** | 4272.35 * | 1561.12 ** |
| Fertilization regime (F) | 2 | 1.58 ns | 5.56 * | 50.39 * | 1168.64 ** | 1152.00 ** | 11,520.37 ** | 21,268.79 ** | 0.02 ** | 3025.90 ** | 3577.02 ** |
| V × F | 2 | 1.80 ns | 10.30 * | 25.58 ns | 17.37 * | 1176.91 * | 11,769.13 ** | 22,056.07 * | 0.01 * | 5494.41 * | 5209.57 * |
| Error | 152 | 1.66 | 2.20 | 1.78 | 32.02 | 36.62 | 1022.56 | 1589.90 | 0.002 | 2056.30 | 2043.80 |
| CV (%) | - | 22.19 | 20.57 | 33.29 | 24.10 | 39.23 | 17.64 | 19.45 | 5.83 | 19.48 | 15.20 |
| Variety | Treatment | TLN | Phot.L. | SD | Fo | Fm | Fv/Fm Ratio | RET (mmH2O/day) | PAR (μmol/m2/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘Spunta’ | T1: Optimal rates (control) | 22.04 * ± 4.45 b | 12.62 ± 4.12 c | 7.06 ± 1.44 b | 553.26 ± 43.1 b | 1753.40 ± 488.18 b | 0.68 ± 0.04 c | 170.60 ± 19.75 a | 396.29 ± 14.95 b |
| T2: High rates (+25% T1) | 37.74 ± 11.27 a | 15.44 ± 6.51 b | 8.51 ± 2.26 a | 598.89 ± 74.97 ab | 1718.59 ± 367.85 b | 0.74 ± 0.03 b | 87.03 ± 16.33 b | 457.26 ± 20.84 a | |
| T3: Low rates (−25% T1) | 35.42 ± 8.29 a | 15.66 ± 5.54 b | 7.45 ± 1.35 ab | 420.22 ± 63.10 c | 2356.26 ± 204.65 a | 0.70 ± 0.03 c | 66.54 ± 20.80 bc | 469.70 ± 29.11 a | |
| ‘Kensa’ | T1: Optimal rates (control) | 35.14 ± 9.34 a | 16.37 ± 6.14 b | 5.93 ± 1.08 b | 624.52 ± 51.16 a | 1530.48 ± 89.89 c | 0.75 ± 0.04 b | 64.67 ± 19.82 bc | 197.76 ± 14.95 d |
| T2: High rates (+25% T1) | 39.96 ± 9.58 a | 21.62 ± 5.01 a | 7.66 ± 1.09 a | 621.22 ± 66.70 a | 1601.15 ± 87.02 c | 0.79 ± 0.05 a | 86.31 ± 26.32 b | 260.48 ± 19.68 c | |
| T3: Low rates (−25% T1) | 23.59 ± 5.14 b | 12.81 ± 3.15 c | 5.68 ± 1.42 c | 618.70 ± 58.11 a | 1732.33 ± 90.65 b | 0.73 ± 0.03 bc | 75.74 ± 23.71 b | 276.01 ± 15.80 c |
| Tuber Size | Carbohydrate Contents | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S.O.V. | DF | Yield/Plant | Tubers/ Plant | Tubers Diameter | C1 > 50 mm | 40 mm < C2 < 50 mm | C3 < 40 mm | Gluc.T | Fruct.T | Sucr.T | Starch T | Gluc.L | Fruct.L | Sucr.L | Starch L |
| Variety (V) | 1 | 1095.20 ** | 66.76 ** | 0.18 ns | 15.43 ** | 9.38 ** | 2.00 * | 0.81 ns | 0.02 ns | 0.84 * | 2.75 * | 3.55 ** | 1.07 ** | 0.64 * | 12.79 ** |
| Fertilization regime (F) | 2 | 2188.38 ** | 20.32 ** | 44.96 ** | 9.37 ** | 3.57 * | 1.85 ** | 0.43 ns | 0.29 * | 0.58 * | 46.96 * | 0.03 ns | 0.67 ** | 0.39 * | 3.49 * |
| V × F | 2 | 954.68 * | 4.84 * | 13.14 ns | 0.93 * | 1.46 * | 0.02 * | 0.62 ns | 0.17 ns | 0.15 * | 4.93 * | 3.79 * | 0.43 * | 2.10 * | 5.06 ** |
| Error | 152 | 234.80 | 1.86 | 5.27 | 0.90 | 1.02 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.84 | 0.26 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 1.70 |
| CV(%) | - | 13.67 | 24.85 | 10.07 | 27.86 | 26.39 | 17.89 | 29.70 | 24.70 | 14.84 | 25.66 | 35.45 | 45.67 | 33.46 | 35.98 |
| Carbohydrate Content (mg/g Fresh Weight) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Fertilization Regime | Tuber Diameter (mm) | Gluc.T | Fruct.T |
| T1: Optimal rates (control) | 22.03 b * | 1.42 a | 1.42 b |
| T2: High rates (+25% T1) | 22.55 b | 1.44 a | 1.64 a |
| T3: Low rates (−25% T1) | 23.80 a | 1.46 a | 1.46 b |
| Variety | |||
| Kensa | 22.83 a | 0.81 a | 0.40 a |
| Spunta | 22.76 a | 0.76 a | 0.37 a |
| Tuber Size | Carbohydrate Content (mg·g−1 FW) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variety | Treatment | Yield/Plant (g) | Tubers/Plant | C1 > 50 | 40 < C2 < 50 | C3 < 40 | Sucr.T | Starch T | Gluc.L | Fruct.L | Sucr.L | Starch L |
| Spunta | T1 | 615.40 ± 17.4 a | 6.44 ± 2.11 a | 3.66 ± 0.87 ab | 2.14 ± 0.27 a | 0.63 ± 0.09 a | 0.37 ± 0.08 c | 6.36 ± 0.33 c | 1.52 ± 0.06 b | 0.73 ± 0.04 c | 0.75 ± 0.04 a | 1.37 ± 0.04 c |
| T2 | 472.52 ± 18.64 c | 5.44 ± 1.08 b | 3.22 ± 0.69 b | 1.96 ± 0.65 ab | 0.49 ± 0.07 b | 0.48 ± 0.07 ab | 7.73 ± 0.41 b | 1.33 ± 0.05 c | 0.68 ± 0.03 c | 0.62 ± 0.04 b | 1.64 ± 0.06 b | |
| T3 | 566.05 ± 10.72 b | 6.15 ± 1.14 a | 4.30± 1.02 a | 2.00 ± 0.55 ab | 0.26 ± 0.07 c | 0.45 ± 0.05 b | 7.53 ± 0.97 b | 1.03 ± 0.03 d | 0.39 ± 0.02 d | 0.22 ± 0.02 c | 2.04 ± 0.08 a | |
| Kensa | T1 | 399.40 ± 15.21 d | 5.26 ± 0.30 c | 2.78 ± 0.06 c | 1.37 ± 0.14 b | 0.40 ±0.05 b | 0.13 ± 0.09 d | 7.16 ± 0.83 b | 0.57 ± 0.02 e | 0.69 ± 0.03 c | 0.61 ± 0.04 b | 0.91 ± 0.03 d |
| T2 | 436.74 ± 15.73 c | 5.70 ± 0.13 ab | 3.18 ± 0.17 b | 2.03 ± 0.15 ab | 0.31 ± 0.05 c | 0.52 ± 0.03 a | 8.41 ± 0.16 a | 1.55 ± 0.05 b | 0.94 ± 0.05 b | 0.56 ± 0.03 b | 1.62 ± 0.08 b | |
| T3 | 368.66 ± 11.61 e | 5.59 ± 0.69 b | 3.37 ± 0.65 ab | 1.26 ± 0.07 c | 0.26 ± 0.07 c | 0.45 ± 0.05 b | 7.56 ± 0.83 b | 1.89 ± 0.06 a | 1.06 ± 0.07 a | 0.79 ± 0.05 a | 0.81 ± 0.02 d | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chabani, H.; Tarchoun, N.; Amami, R.; Saadaoui, W.; Mezghani, N.; Alexopoulos, A.A.; Petropoulos, S.A. Investigating the Effects of Optimized Mineral Fertilization on Plant Growth, Physiological Traits, Tuber Yield, and Biochemical Contents of Potato Crop. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11010011
Chabani H, Tarchoun N, Amami R, Saadaoui W, Mezghani N, Alexopoulos AA, Petropoulos SA. Investigating the Effects of Optimized Mineral Fertilization on Plant Growth, Physiological Traits, Tuber Yield, and Biochemical Contents of Potato Crop. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleChabani, Hadjer, Neji Tarchoun, Roua Amami, Wassim Saadaoui, Najla Mezghani, Alexios A. Alexopoulos, and Spyridon A. Petropoulos. 2025. "Investigating the Effects of Optimized Mineral Fertilization on Plant Growth, Physiological Traits, Tuber Yield, and Biochemical Contents of Potato Crop" Horticulturae 11, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11010011
APA StyleChabani, H., Tarchoun, N., Amami, R., Saadaoui, W., Mezghani, N., Alexopoulos, A. A., & Petropoulos, S. A. (2025). Investigating the Effects of Optimized Mineral Fertilization on Plant Growth, Physiological Traits, Tuber Yield, and Biochemical Contents of Potato Crop. Horticulturae, 11(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11010011






