Abstract
This study investigated the effects of substrates composed of various ratios of wood fiber and peat (0, 25, 50, 75, and 100% peat (v/v)) mixed with different amounts of lime (0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 g L−1) and start fertilizer (0, 2, and 4 g L−1 Multimix) on the growth and biomass accumulation of petunia (Petunia x hybrida Vilm ‘Finity F1 Purple’) and basil (Ocimum basilicum L. ‘Marian’) in an ebb-and-flow greenhouse system. Growth parameters included plant height, weight, canopy diameter, and chlorosis symptoms for petunia, along with substrate pH and EC measurements. Petunia showed optimal growth in substrates with higher peat content, while basil produced satisfactory biomass across a pH range of 5–7 regardless of substrate type. Optimal petunia cultivation in 100% wood fiber required a significant dose of start fertilizer without lime. Monitoring pH and EC using pour-through and press methods revealed a pH decrease in substrates with added start fertilizer, while substrates with higher wood fiber content were less acidic. Substrates with over 50% (v/v) wood fiber without lime showed a rapid pH increase over five weeks. The pour-through method generally underestimated EC values compared to the press method. These findings contribute to optimizing the wood fiber/peat blends for sustainable horticulture.
1. Introduction
Soilless culture is a method of growing plants without the use of soil as a rooting medium. This production system is broadly applied in modern horticulture due to its effectiveness [1]. Most plants grow and develop optimally in substrates with a slightly acidic to neutral pH, ranging from 5.4 to 6.4. Such conditions create environments where essential nutrients are easily available [1,2]. Substrates commonly used in horticulture, such as peat, are naturally acidic, with pH levels ranging from 3.5 to 5.5. Therefore, liming of substrates using dolomite limestone or calcium carbonate has become a standard practice in horticulture. The primary purpose of liming is to increase and adjust the pH of the substrate to an optimal range for better plant nutrient availability and to ensure conditions suitable for the requirements of specific crops. Lime provides calcium and neutralizes the acidity by reacting with hydrogen ions in the substrate. The liming requirement depends on the initial pH of the substrate, the desired target pH, and the buffering capacity of the substrate material [3].
The commonly used substrate peat derives from peatlands, which are important carbon reservoirs, and the policy regulations consider limiting the use of this material both for professional and hobby horticulture [4]. In response, more sustainable alternatives are being explored, with conifer wood fiber emerging as a promising option due to its useful properties and ease of reforestation [5]. Defibrated wood fiber from conifer species, such as Norway spruce (Picea abies), has been successfully incorporated as a growing media ingredient and has also been tested as a fully functional stand-alone substrate for hydroponic strawberry cultivation [6,7,8,9]. Situations where wood fiber is used as a stand-alone growing medium are almost exclusively related to hydroponic production techniques, where water containing dissolved nutrients is directly provided to the root zone. In other production systems, it is necessary that wood fiber is admixed with other organic materials such as peat, coir, or composts.
Previous studies indicate that no lime addition is needed for 100% pine wood fibers due to their optimal pH range of 5.5 to 6.4 [10,11]. More recently, the effect of the liming rate on pH development in peat-based substrates amended with up to 50% by volume of pine wood chips has been investigated [2]. The authors concluded that pine wood chips can be an alternative to perlite and can be used without changing the liming practices in the production of chrysanthemum and marigold.
Substrates combining peat and wood fiber continue to gain popularity [4,12], and despite previous studies, there remains a gap in the understanding of their long-term performance, subsequent pH drift, and general applicability in various plant cultures. The popularity has led to an increase in observed issues related to these factors during crop production (NORGRO AS; pers. comm.), and this unpredictability poses a concern for professional plant production.
This study therefore aimed to evaluate substrates based on peat and defibrated Norway spruce wood fiber, with varying lime and start fertilizer levels, for basil and petunia production. The choice of species was based on their requirements for pH and different stress tolerance [1]. It also assessed pH drift and evaluated pH and EC measurement methods across all growing media. The hypotheses tested were (i) wood fiber and peat blends provide comparable growing conditions to peat substrates; and (ii) wood fiber incorporation alters pH and EC differently compared to standard peat-based substrates.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment 1: Effects of Liming on Wood Fiber/Peat Blends
Plants of petunia (Petunia x hybrida Vilm ‘Finity F1 Purple’) and basil (Ocimum basilicum L. ‘Marian’) (NORGRO AS, Hamar Norway) were grown in D.9 × H.10 cm (300 cm3) pots in a greenhouse. The pots were placed on a table with an ebb-and-flow system for fertigation. Temperature was set at 21/18 °C day/night with a relative humidity of 75%. The plants received a daily average of 9 MJ/m2 of radiation with a maximum photon flux density of 700 μmol/m2 s (18 h of daylight). The petunia seeds were sown on 25 November 2022 and the seedlings were transferred to the pots on 14 December 2022. Basil seeds were sown on 8 December 2022. The experiment was initiated on 14 December and terminated on 26 January 2023 when the best-performing plants reached the commercial stage. The system was adjusted to fertigate the plants once a day for 8 min with a water level of 5 cm. The nutrient solution with EC 2 mS/cm was prepared by mixing 50:50 YaraTera Kristalon Scarlet and YaraTera Calcinit (Yara, Oslo, Norway).
The experimental design included five randomly distributed pots of each species (one plant of petunia and two plants of basil in each pot, respectively) grown in substrate combinations that included blends composed of wood fiber and peat. Peat was loosened/fluffed and moistened (by hand) to a moisture content of 50% (by weight). The peat moss was then blended separately (by hand) with 25%, 50%, and 75% (v/v) of a disc-refined Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) H. Karst.) wood fiber (Fibergrow®, Gjøvik, Norway), resulting in blends containing 100% wood fiber (WF100), 75% (WF75), 50% (WF50), 25% (WF25), and 0% (WF0) (v/v). Each blend was also amended with five levels of dolomite lime, namely 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 g L−1 of the substrate. The liming application doses were gradually (by 2 g) upgraded and downgraded from the commercial standard, which is approximately 4 g of lime per liter of substrate. For petunia, the plant height, plant fresh weight, and broadest canopy diameter were recorded, as well as measurements of substrate pH. Measurements were conducted during the last day of the experiment, before the termination of the plants. Each pot was extracted one hour after irrigation using the pour-through method using 100 mL of water and leachate was tested immediately after collection as described by a previous study [13]. In addition, chlorosis symptoms were assessed using a 0–4 scale (0—no chlorosis). For basil, recordings of plant height, plant weight, and substrate pH (pour-through method using 100 mL of water) were conducted after the plant culture was terminated.
2.2. Experiment 2: Effect of Liming and Start Fertilizer on Wood Fiber/Peat Blends
Plants of petunia (Petunia x hybrida Vilm ‘Finity F1 Purple’) were grown in pots and placed on an ebb-and-flow table system. The same design and agronomic parameters as for Experiment 1 were used. Different blends of substrates composed of wood fiber and peat were tested, and adding start fertilizer (0, 1, and 2 g L−1 of Multimix (Haifa, Matam-Haifa, Israel)) and lime (0, 2, and 4 g L−1 of dolomite lime) was also included. The petunia seeds were sown on 9 March 2023 and the seedlings were transferred to the substrates on 22 March 2023. The experiment was terminated on 27 April 2023. pH and EC of the substrates were measured weekly for the 5-week duration of the experiment. On the day of the analysis, each pot was extracted one hour after irrigation using the pour-through method with 100 mL of water and leachate was tested immediately after collection [13], and analyzed for pH and EC using a hand-held sensor (Hanna Instruments, Villafranca Padovana, Italy). In addition to the pour-through method, pH and EC were also recorded using a press method, where the substrate was compressed to release drained water for measurement. At the end of the experiment, plant weight was recorded, and substrates were analyzed for pH and EC using the press method as described in a previous study [14].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The analyses and visualizations were conducted using a Microsoft® Excel® for Microsoft 365 and MiniTab® Statistical Software program package (Release 17.2.1 Minitab Inc., State College, PA, USA). The confidence intervals (CIs) might be superior to statistical tests and p-values [15]; therefore, in order to simplify the figures and improve readability of the study outcome, the approach based on CI was used for the descriptive statistical analysis. It can be noted that when 95% confidence intervals do not overlap, the difference between them results in p < 0.05 using the same assumptions for computing the intervals. In addition, General Linear Model was performed to obtain significance levels of the applied factors and their interactions. The results of the statistical tests are presented in Supplementary Tables S1 and S2.
3. Results
3.1. Experiment 1: Effects of Liming on Wood Fiber/Peat Blends
In general, a clear trend for the production of higher and heavier plants was observed in substrates with a higher percentage of peat (Figure 1A,B). The tallest petunia plants were observed in substrates containing 75% and 100% peat. Slightly shorter plants were observed in the 50% peat substrate. However, a less pronounced trend was observed for plant diameter (Figure 1C). Despite the high variability between plants within each treatment, significant statistical differences were observed for plant height, weight, and diameter (Supplementary Table S1).
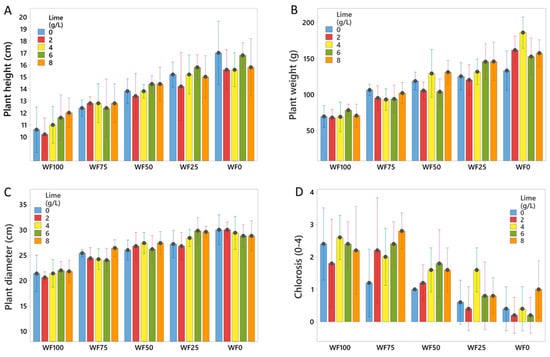
Figure 1.
Height (A), fresh weight (B), diameter (C), and chlorosis (D) observed in petunia plants grown in pots with substrate mixes of peat and wood fiber (WF) and different amounts of added lime (0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 g L−1) for six weeks. WF100, WF75, WF25, and WF0 are 100, 75, 50, 25, and 0% wood fiber in the mix, respectively. The numbers are mean values of 5 replicates, with one pot each. Black dots represent means, and bars represent 95% CI of the mean. Means are different (p < 0.05) when CIs are not overlapping.
The liming rate had only a marginal effect on plant performance, which was mainly affected by the amount of wood fiber in the blend (Figure 1). In addition, an increased percentage of wood fiber in the substrate mix increased the risk of petunia chlorosis (Figure 1D). The most severe chlorosis symptoms were observed in WF100 and WF75, while the lowest was in WF0. The effect of liming on chlorosis occurrence was not clear across the tested substrates (Figure 1D). However, a reduced level of discoloration was observed in substrates WF75, WF50, and WF25, but only where little or no lime was applied (Figure 1D).
The recorded data for basil plant height and weight are presented in Figure 2. Plant height was relatively uniform across substrates; however, it was highly dependent on the liming (Figure 2A). In general, lack of liming led to the growth retardation of the basil plants, especially in substrates that contained more peat (WF50, WF25, and WF0). In some substrates, even if the plants were relatively tall (WF100 and WF75), the biomass production was lower compared to WF50, WF25, and WF0 (Figure 2B).
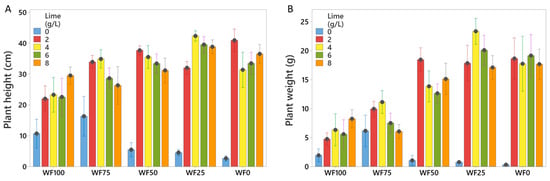
Figure 2.
Height (A) and fresh weight (B) of basil plants grown in pots with substrate mixes of peat and wood fiber (WF) and different amounts of added lime (0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 g L−1) for six weeks. WF100, WF75, WF25, and WF0 are 100, 75, 50, 25, and 0% wood fiber in the mix, respectively. The numbers are mean values of 5 replicates, with one pot each. Black dots represent means, and bars represent 95% CI of the mean. Means are different (p < 0.05) when CIs are not overlapping.
After the termination of the experiment, pH of each substrate was measured using the pour-through method (Figure 3). Trends in pH values across the substrates were similar for both petunia and basil plants; however, pH in substrates with petunia was generally slightly lower compared to substrates with basil. The effect of the amount of lime on substrate pH was related to the percentage of wood fiber in the growing medium. The more wood fiber the substrate contained, the less rapid the pH change. A specific drift in pH was observed, indicating that wood fiber, though slightly acidic initially, tended to increase the pH of the substrate when blended with peat (Figure 3).
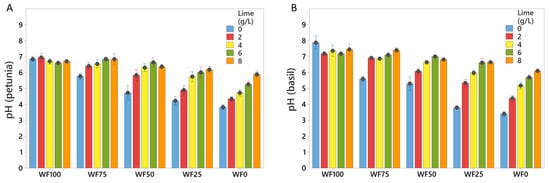
Figure 3.
pH in pots with substrate mixes and added lime with petunia (A) and basil (B) after 6 weeks. The substrates are mixes of peat and wood fiber (WF), and different amounts of added lime (0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 g L−1). WF100, WF75, WF25, and WF0 mean 100, 75, 50, 25, and 0% of wood fiber in the mix, respectively. The numbers are mean values of 5 replicates, with one pot each. Black dots represent means, and bars represent 95% CI of the mean. Means are different (p < 0.05) when CIs are not overlapping.
Furthermore, the two model plants showed different preferences for the growing media type and pH (Figure 4). Petunia showed optimal growth in WF0 with a pH of approximately 5.0, indicating that high pH values or a high percentage of wood fiber was unsuitable for this species (Figure 4A). Conversely, basil was more adaptable, producing satisfactory biomass across a pH range of 5–7 and being less affected by the substrate type compared to petunia (Figure 4B).
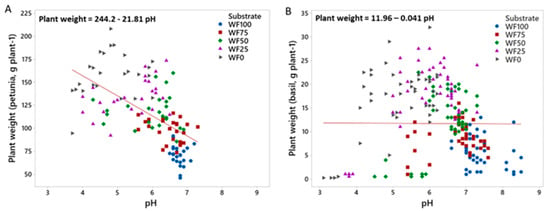
Figure 4.
(A) The relationship between the substrate pH and biomass production of petunia and (B) basil plants when grown in pots with substrate mixes of peat and wood fiber (WF). WF100, WF75, WF25, and WF0 are 100, 75, 50, 25, and 0% wood fiber in the mix, respectively. The numbers are mean values of 5 replicates, with one pot each. Regression coefficients: petunia R2 = 32.44%, basil R2 = 0.00%. Pearson correlation coefficient for petunia: r = −0.589, for basil: r = −0.006.
3.2. Experiment 2: Effect of Liming and Start Fertilizer on Wood Fiber/Peat Blends
In Experiment 2, where only petunia plants were studied, the liming rate and mineral start fertilizer were tested using the same blends as in Experiment 1. The best-performing petunia plants were obtained in WF25 and WF0, and the highest dose of start fertilizer generally improved plant growth and biomass accumulation (Figure 5). The effect of start fertilizer was most pronounced in WF50 for all liming doses, as well as in WF100 where no lime was applied (Figure 5).
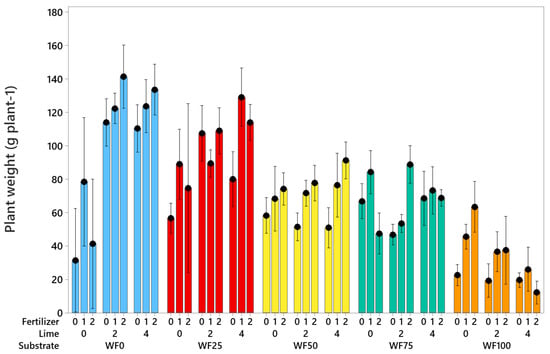
Figure 5.
Fresh weight of petunia plants after 7 weeks of growth and as affected by the substrate type, liming, and fertilizer rate. WF0, WF25, WF75, and WF100 are 0, 25, 50, 75, and 100% wood fiber in the mix, respectively. Fertilizer: 0, 1, and 2 = 0, 1, and 2 g Multimix L−1, respectively, and lime: 0, 2, and 4 = 0, 2, and 4 g L−1, respectively. The numbers are mean values of 5 replicates, with one pot each. Black dots represent means, and bars represent 95% CI of the mean. Means are different (p < 0.05) when CIs are not overlapping.
It can be observed that for petunia production in 100% wood fiber, a significant dose of start fertilizer is necessary (Figure 6A), but no lime is required (Figure 6B).


Figure 6.
(A) Effect of start fertilizer (1 M and 2 M = 1 and 2 g Multimix g L−1, respectively), and (B) liming rate (lime at 0, 2, and 4 = 0, 2, and 4 g L−1, respectively), on petunia grown in pots with 100% wood fiber (WF100). Photos taken after 7 weeks of growth, at termination of Experiment 2.
Development of substrate pH during the plant growth period was also evaluated using the pour-through method. Since the trends in pH were affected by the incorporation of start fertilizer, the data presented in Figure 7 focus on the most extreme situations where no or 2 g start fertilizer per liter was applied to the substrates. The use of start fertilizer can slightly decrease the pH of substrates based on peat and wood fiber combinations (Figure 7A vs. Figure 7B). This effect is especially pronounced in WF100 where no lime was applied (Figure 7A,B). In substrates where no lime was added and which had a high percentage of wood fiber (more than 50% (v/v)), pH rapidly increased during the 5-week growing period (blue lines, Figure 7).
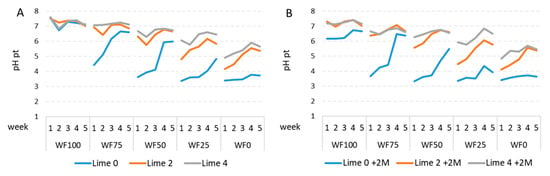
Figure 7.
(A) Weekly changes in pH (pt—pour-through method) in wood fiber (WF)/peat mix substrates (WF100, WF75, WF25, and WF0 are 100, 75, 50, 25, and 0% wood fiber in the mix, respectively) with different amounts of lime added (lime at 0, 2, and 4 = 0, 2, and 4 g L−1, respectively) and (B) with 2 g of start fertilizer (+2 M) added in the production of petunia plants in a greenhouse. The numbers are mean values of 5 replicates, with one pot each.
In substrates with the lowest percentage of wood fiber, the two pH/EC measurement methods showed weak consistency in substrates where no lime was added (Figure 8A,B). The incorporation of a higher peat percentage significantly increased the consistency of the methods for all substrates (Figure 8C–E). While the overall linear relationship between the two methods was high (r2 = 0.95), it was observed that with more wood fiber incorporated into the blend, the variance was higher (Figure 8F).
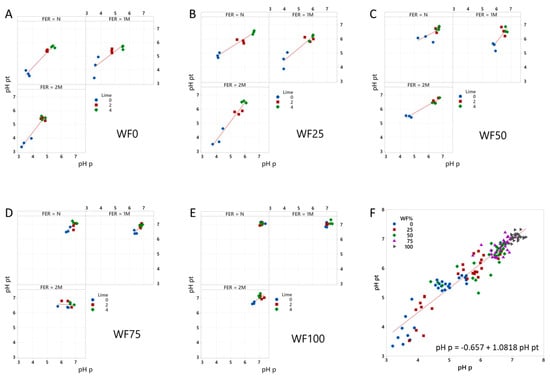
Figure 8.
The relationship between the press (p) and pour-through (pt) methods for pH measurement. (A) The peat substrate with no wood fiber added (WF0), (B) substrate with 25% wood fiber (WF25), (C) substrate with 50% wood fiber (WF50), (D) substrate with 75% wood fiber (WF75), (E) wood fiber substrate with no peat added (WF100). (F) The overall linear relationship between the methods (regression coefficient: R2 = 89.79%. Pearson correlation coefficient: r = 0.949). Effects of start fertilizer (FER = N: no fertilizer, FER = 1 M: 1 g Multimix g L−1, FER = 2 M: 2 g Multimix g L−1), and lime (lime at 0, 2, and 4 = 0, 2, and 4 g L−1, respectively).
The pour-through method generally provided lower and less spread EC values compared to the press method (Figure 9). This trend was not dependent on the application of start fertilizer (Figure 9A). The pour-through method used in this study provided results approximately 0.5 mS/cm lower than those obtained using the press method (Figure 9B). When only data from 100% peat were considered, fewer inconsistencies were noted (Figure 9A).
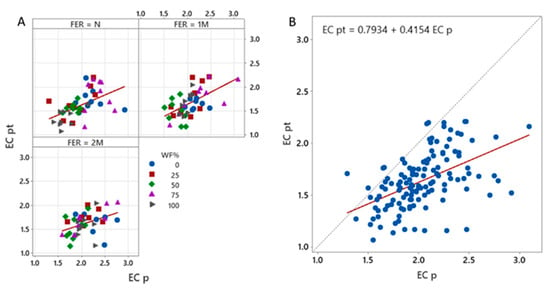
Figure 9.
The relationship between the press (p) and pour-through (pt) methods for EC measurement in substrate mixes of peat and wood fiber (WF% at 0, 25, 50, 75, and 100 = 100, 75, 50, 25, and 0% wood fiber in the mix, respectively). (A) Effects of start fertilizer (FER = N: no fertilizer, FER = 1 M: 1 g Multimix g L−1, FER = 2 M: 2 g Multimix g L−1); (B) the overall linear trend between the two methods (regression coefficient: R2 = 24.87%. Pearson correlation coefficient: r = 0.505).
4. Discussion
The results from Experiment 1 showed that higher percentages of peat in substrates generally led to the production of taller and heavier petunia plants. This suggests that peat provides better growing conditions for petunia compared to wood fiber. The increased risk of chlorosis with higher wood fiber content further indicates that petunia plants are sensitive to the pH and chemical properties of wood fiber substrates [1]. This sensitivity is consistent with previous findings, which noted that iron deficiency is a common disorder in petunia production, exacerbated by suboptimal pH levels, especially when pH exceeds 6.4 [16].
The effect of liming on chlorosis occurrence was not clear, although substrates with higher wood fiber content and no or low lime added showed reduced discoloration. This could imply that the interaction between lime and wood fiber affects the availability of essential nutrients or pH balance differently, which is similar to the previous reports [10].
For basil, the plant height was uniform across substrates but highly dependent on liming. Lack of liming led to growth retardation, particularly in substrates with higher peat content. This indicates that basil requires a balanced pH for optimal growth, and the buffering capacity of wood fiber may help maintain more stable pH levels [1].
In Experiment 2, the petunia plants performed best in substrates with 25% and 0% wood fiber, and the highest dose of start fertilizer improved growth and biomass accumulation. This aligns with previous findings that high nutrient availability is critical for optimal growth in wood fiber substrates [11,17]. The results suggest that for successful petunia production in 100% wood fiber, substantial initial fertilization is essential, but lime is not required. This observation is consistent with previous work, which reported that liming of a 100% pine tree substrate did not improve African marigold performance, emphasizing the importance of initial nutrient incorporation [18].
A noteworthy observation was that the substrate pH rapidly increased during the 5-week growing period in materials composed mostly of wood fiber (more than 50% (v/v)) and without high lime admixtures. A similar trend of increased pH in blends of coir and Hydrafiber® wood fiber compared to peat/bark mixes was also observed [19], indicating that the pH has a tendency to change in these types of substrates. On the other hand, it is also known that petunia tends to increase substrate pH during production [20], and therefore, the choice of model plant species could have intensified the observed effect. However, the significant rise in substrate pH was noted shortly after initial irrigation. It can be hypothesized that this change in pH could be due to the leaching of simple organic acids formed when the lignocellulosic material is decomposed during wood heating [21], which is inherent to the wood fiber production process. However, further studies are needed to confirm this hypothesis. Furthermore, the buffer capacity of wood fiber is known to be low. A previous study has pointed to major pH responses in wood fiber at even low additions of acid or NaOH and demonstrated a pH buffer test for growing media constituents, making it possible to predict the need for lime in substrate mixtures [22].
Comparing the pour-through and press methods for EC measurement revealed that the press method generally provided higher EC values. This suggests that the pour-through method may underestimate nutrient availability in substrates with high wood fiber content. The consistency of the two methods improved with higher peat content, indicating that substrate composition significantly affects EC measurement accuracy. A higher consistent relationship between the press and pour-through methods in sphagnum moss was found, emphasizing the role of substrate composition in measurement consistency [20].
Overall, the findings highlight the potential of wood fiber/peat blends as sustainable horticultural substrates, with specific adjustments needed for liming and fertilization to optimize plant growth and substrate stability. Soilless culture substrates may be recycled for many crop cycles, and the ongoing degradation of organic matter can affect their physiochemical properties and nutrient availability over time. Future research should therefore explore the interactions between substrate composition, pH stability, nutrient availability, substrate recycling, and prolonged use to develop more effective and sustainable growing media.
5. Conclusions
The present study demonstrates the potential of wood fiber and peat blends as substrates for petunia and basil cultivation, highlighting the impact of substrate composition, pH, and the application of lime and start fertilizer on plant growth and biomass accumulation. Key findings are as follows:
- Petunia performance: Petunia plants thrived in substrates with higher peat content, while higher wood fiber content increased the risk of chlorosis. Optimal growth was observed with substantial initial fertilization in substrates with 25% or 0% wood fiber, with no lime added.
- Basil growth: Basil plants showed flexibility across a pH range of 5–7, regardless of substrate type. Lack of liming led to growth retardation, particularly in substrates with higher peat content.
- pH dynamics: A rapid increase in pH was observed in substrates with high wood fiber content (more than 50%) where no lime was applied, suggesting the leaching of acidic compounds during initial irrigation. This is likely due to the release of various acids from steam-exploded wood fiber.
- EC measurement methods: Comparing the pour-through and press methods for measuring electrical conductivity (EC), the press method generally provided higher EC values. This suggests that the pour-through method may underestimate nutrient availability in substrates with high wood fiber content, with consistency improving with higher peat content.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae10090895/s1, Table S1: p-Values obtained by General Linear Model (multi-factor ANOVA) for petunia and basil architecture parameters and substrate pH across analyzed substrate types, liming rate, and their interactions as obtained in Experiment 1; Table S2: p-Values obtained by General Linear Model (multi-factor ANOVA) for petunia weight as affected by analyzed substrate types, liming, and start fertilizer dose, and their interactions, as obtained in Experiment 2.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.L.W., K.K., A.S. and T.K.H.; methodology, T.L.W., K.K. and T.K.H.; formal analysis, T.L.W., K.K. and T.K.H.; investigation, T.L.W. and T.K.H.; data curation, T.L.W.; writing—original draft preparation, T.L.W.; writing—review and editing, K.K., A.S., S.M.A. and T.K.H.; visualization, T.L.W.; project administration, A.S.; funding acquisition, T.L.W., K.K., T.K.H. and A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Norwegian Agricultural Agreement Research Fund/Foundation for Research Levy on Agricultural Products, grant numbers 302129/344229, and Grofondet, grant numbers 190024/230058.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Nelson, P. Greenhouse Operation and Management, 7th ed.; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, W.G.; Jackson, B.E.; Fonteno, W.C.; Whipker, B.E. Liming Requirements of Greenhouse Peat-based Substrates Amended with Pine Wood Chips as a Perlite Alternative. HortTechnology 2020, 30, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, G.; Lerner, B.L. Physical and chemical characteristics and analysis of plant substrate. Ornam. Hortic. 2022, 28, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschler, O.; Osterburg, B.; Weimar, H.; Glasenapp, S.; Ohmes, M.-F. Peat Replacement in Horticultural Growing Media: Availability of Bio-Based Alternative Materials. Thünen Working Paper, 1 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gruda, N.S. Increasing sustainability of growing media constituents and stand-alone substrates in soilless culture systems. Agronomy 2019, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woznicki, T.; Jackson, B.E.; Sønsteby, A.; Kusnierek, K. Wood Fiber from Norway Spruce—A Stand-Alone Growing Medium for Hydroponic Strawberry Production. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woznicki, T.; Kusnierek, K.; Roos, U.; Andersen, S.; Zimmer, K.; Sønsteby, A. Exploration of alternative growing media in strawberry production with focus on wood fiber from Norway spruce. In Proceedings of the III International Symposium on Growing Media, Composting and Substrate Analysis 1305, Milan, Italy, 24–28 June 2019; pp. 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Woznicki, T.; Kusnierek, K.; Vandecasteele, B.; Sønsteby, A. Reuse of coir, peat, and wood fiber in strawberry production. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1307240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurdal, S.M.; Woznicki, T.L.; Haraldsen, T.K.; Kusnierek, K.; Sønsteby, A.; Remberg, S.F. Wood Fiber-Based Growing Media for Strawberry Cultivation: Effects of Incorporation of Peat and Compost. Horticulturae 2022, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, B.E.; Wright, R.D.; Gruda, N. Container medium pH in a pine tree substrate amended with peatmoss and dolomitic limestone affects plant growth. HortScience 2009, 44, 1983–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruda, N.; Schnitzler, W. Wood fiber substrates as a peat alternative for vegetable productions. Holz Als Roh-Und Werkst. 2006, 64, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlile, W.; Cattivello, C.; Zaccheo, P. Organic growing media: Constituents and properties. Vadose Zone J. 2015, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.D. The pour-through nutrient extraction procedure. HortScience 1986, 21, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoggins, H.L.; Bailey, D.A.; Nelson, P.V. Development of the press extraction method for plug substrate analysis: Quantitative relationships between solution extraction techniques. HortScience 2001, 36, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenland, S.; Senn, S.J.; Rothman, K.J.; Carlin, J.B.; Poole, C.; Goodman, S.N.; Altman, D.G. Statistical tests, P values, confidence intervals, and power: A guide to misinterpretations. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 31, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, W.G.H.J.; Whipker, B. Fert, Dirt, and Squirt: Monitoring pH and EC of Greenhouse Crops. E-Gro Diagn. Ser. 2018, 12. Available online: http://www.fertdirtandsquirt.com/books.php (accessed on 20 May 2024).
- Fain, G.B.; Gilliam, C.H.; Sibley, J.L.; Boyer, C.R.; Witcher, A.L. Wholetree substrate and fertilizer rate in production of greenhouse-grown petunia (Petunia × hybrida Vilm.) and marigold (Tagetes patula L.). HortScience 2008, 43, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.D.; Browder, J.F. Chipped pine logs: A potential substrate for greenhouse and nursery crops. HortScience 2005, 40, 1513–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, R.W.; Helms, K.M.; Jackson, B.E.; Machesney, L.M.; Lee, J.A. Evaluation of Peat Blended with Pine Wood Components for Effects on Substrate Physical Properties, Nitrogen Immobilization, and Growth of Petunia (Petunia × hybrida Vilm.-Andr.). HortScience 2022, 57, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, R.W.; Fisher, P.R.; Argo, W.R. Quantifying the Acidic and Basic Effects of Fifteen Floriculture Species Grown in Peat-based Substrate. HortScience 2017, 52, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundqvist, B.; Karlsson, O.; Westermark, U. Determination of formic-acid and acetic acid concentrations formed during hydrothermal treatment of birch wood and its relation to colour, strength and hardness. Wood Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, H.; Geuijen, I. RHP pH buffer test on growing media constituents. In Proceedings of the I International Symposium on Growing Media, Compost Utilization and Substrate Analysis for Soilless Cultivation 1389, Quebec, QC, Canada, 11–15 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).