Abstract
(1) Background: Since microplastics in aquatic environments are difficult to prevent and can cause adverse physiological and biochemical reactions to various organisms, we aimed to analyze the effectiveness of using aquatic plants with well-developed roots and excellent water purification capabilities to remove microplastics in an eco-friendly manner. Additionally, we examined the differences in removal efficiency based on the sizes of the microplastic particles and the types of aquatic plants used. (2) Methods: Two types of polyethylene (PE) microplastic particles (46 µm and 140 µm) and two types of aquatic plants (Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps) were used in this study. These plants were cultivated in tap water containing microplastics for a duration of four months in an aquatic setup without soil. Water samples from the cultivation area were analyzed using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) to determine the reduction in microplastics. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was employed to examine the adsorption of microplastics on the plants’ roots. Plant growth was assessed by measuring plant height, plant width, and the number of branches (number of leaves). (3) Results: The results revealed significant reductions in the numbers of microplastics in the water of the cultivation boxes containing Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps, irrespective of the microplastic particle size or plant type. These reductions were further confirmed by the adsorption of microplastics on the roots of both plant species. Moreover, the presence of microplastics had no significant negative effects on the plants’ growth. These findings suggest that Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps are suitable plants for removing microplastics in aquatic environments. (4) Conclusions: To effectively reduce aquatic microplastics using plants, it is essential to establish a sustainable vegetation cover using perennial plants with well-developed roots and rapid reproductive capabilities. Follow-up research should consider not only the type of plant but also various aspects related to their tolerance to different environmental conditions.
1. Introduction
Plastics are lightweight, durable, versatile, low-corrosive, and inexpensive materials, making them widely used in many applications, and the worldwide plastic manufacturing volume is increasing [1,2]. The annual production of plastics has increased 200-fold from 1950 to 381 Mt in 2015, resulting in a significant amount of landfilled and dumped plastics [3], and the accumulation of plastics is expected to continue to increase due to their slow degradation rate compared to the rate at which we consume them [4].
In general, plastics such as polyethylene (PE) or polystyrene (PS) do not completely decompose when exposed to the natural environment but can be broken into small pieces by a variety of factors, resulting in numerous microplastics [5,6]. Microplastics generally refer to plastic particles smaller than 5 mm [7], and the occurrence of microplastics in surface waters was first reported in the early 1970s by Carpenter and Smit (1972) [8]. The UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme) defined solid plastic particles of 5 mm or less that cannot be decomposed in water as microplastics [9]. The International Organization for Standardization’s environmental aspects (ISO/TC 61/SC14) [10] define any solid plastic particle that is insoluble in water with any dimension between 1 µm and 1000 µm as a microplastic. Plastics are widely used in everyday life, and their high levels of production, rapid consumption, and resistance to complete decomposition have led to their large-scale release into and long-term persistence in aquatic and terrestrial environments [4,11,12]. Microplastics can be divided into primary microplastics, which are contained in bath products, cosmetics, and face washes [13,14], and secondary microplastics, which are generated from the degradation of plastic bags, food packaging, and tire dust on roads [15].
Microplastics are inherently light [4]. They can be carried by the wind or transported from soil to rivers and the sea through rainfall or runoff [4,16], making prevention measures challenging [17]. Rivers, in particular, carry 70–80% of plastics, resulting in extensive sedimentation in aquatic environments such as rivers and oceans [18].
The densities of microplastics vary depending on the type of particle, influencing their dispersion in aquatic environments. Low-density microplastics are found on water surfaces and in neustonic environments, while high-density microplastics settle in deeper waters and benthic zones [19,20,21].
Microplastics are present in high concentrations [22] in aquatic environments. When persistent organic pollutants are adsorbed on the surface of microplastics and ingested, they have adverse effects on organisms [23,24,25]. Increasing societal interest in the effects of these microplastics on human health and ecosystems has raised concerns about their formation, chemical interactions, and potential impacts on the environment [25,26], and research on their investigation and analysis has been actively conducted [19].
Methods for removing microplastics in aquatic environments include physical methods involving filtration and sedimentation; chemical methods to decompose, convert, and coagulate them; and biological methods to decompose them using microorganisms or plants, molds, and algae [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35]. Among these, the physical method is economical and has a high removal rate, but it is difficult to reuse adsorbents, resulting in waste; in cases involving the coagulation [36,37] and decomposition methods, operating costs may increase owing to the continuous injection of chemicals [36,37,38]. Biological methods are deemed safe and environmentally sustainable due to their minimal sludge production and absence of secondary toxin generation. Previous research on biological methods has focused on the removal of microplastics by microorganisms or sea creatures [29,39,40,41], and it has considered only the environment or the interrelationship between the plants and microplastics [29,39,42,43,44]. Additionally, studies on microplastic removal by phytoremediation have primarily focused on their implementation within wastewater treatment facilities. However, the efficacy of such treatment in eliminating all microplastics remains variable, leading to occasional discharge back into the environment [45,46,47]. Consequently, there is a pressing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly methodologies [48] to tackle microplastics contamination from aquatic flora across diverse environments beyond controlled settings such as wastewater treatment plants.
Phytoremediation strategies encompass several methodologies, including rhizofiltration, which involves the absorption and adsorption of pollutants through roots [42,43,44,45,46,47], and phytoaccumulation, which aims at reducing pollutant levels. Moreover, contaminants may be immobilized through adsorption or accumulation in roots (phytostabilization) or degraded within a plant (rhizodegradation).
Aquatic plants can alleviate pollutants by slowing down wetland runoff to prevent microplastics from settling in sediments [49]. Their effectiveness in wastewater treatment is attributed to their substantial biomass and resilience to both organic and inorganic contaminants [50], alongside their potential to enhance the water purification capacities of aquatic microorganisms [51]. This collective action makes them efficient agents in the removal of pollutants from aquatic environments [52]. By using native perennial plants suited to an environment, planting conditions can be maintained continuously and stably, allowing for plant restoration over large areas.
This study analyzed whether the numbers of microplastics in aquatic environments can be reduced through phytostabilization using Iris pseudacoru and Lythrum ancep, which are water-purifying perennial aquatic plants that grow naturally in Korea. We also analyzed microplastic particles to study their differences according to the size and type of plant. Furthermore, we investigated the impact of microplastic pollution on plant growth to continuously maintain planting conditions without secondary treatment methods.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microplastics
The microplastic used in this study was spherical white polyethylene (PE) powder, which is used in industrial and research applications, and it was purchased from ThyssenKrupp. White PE is widely used in paints and coatings, cosmetics, and personal care applications and has high electrical conductivity and oil resistance, which has ensured its use in a variety of fields, such as transparent agricultural films, disposable products, toys, and plant containers. It is a mass-produced plastic found not only in soil but also in aquatic environments.
There were two types of PE particle sizes in this study: 46 µm and 140 µm. As plastic waste accumulates in the environment and decomposes into smaller particles over time [53,54], we aimed to determine effective methods for removing particles of two specific sizes.
2.2. Plant Materials and Planting
Two aquatic plants were selected to investigate their adaptability and growth in microplastic pollution sources and their ability to remove microplastics (Table 1). Iris pseudacoru is a wild aquatic plant known for its effectiveness in removing organic matter and heavy metals from water, making it a valuable component in artificial wetlands. Its short and abundant roots are beneficial for collecting microplastics in aquatic environments. Lythrum anceps is known to establish an extensive underground root system through colonization by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, enhancing its ability to absorb nutrients and pollutants from various media [55,56,57].

Table 1.
The two kinds of hydrophyte used in this experiment.
Iris pseudacoru and Lythrum ancep (Figure 1) are water-purifying ornamental plants commonly used near watersides or in garden ponds. Since they do not participate in the ecological food chain, they can help reduce the risk of pollutants entering the food chain. These plants exhibit a wide temperature range for growth. They are highly adaptable to various environmental stress conditions, making them particularly resilient and beneficial for diverse environments.

Figure 1.
The two kinds of hydrophyte used in this experiment: Iris pseudacorus (left) and Lythrum anceps (right).
This study was conducted over four months in a greenhouse-type growing room of a plant factory called Sahmyook Eco-Farm Center at Sahmyook University, located at Hwarang University in Nowon-gu, Seoul. The experimental environment was a combined solar and convection plant factory with natural light, and three 24 W LED plant lamps (Designer Sunbell) were used as supplemental light in case of light shortage. To simulate the circadian cycle, the lights were turned on for 10 h per day (8 a.m. to 6 p.m.). The average air temperature and humidity were 25.8 °C and 97.7%, respectively, and the average water temperature was 26.3 °C (Table 2). The pH of the water in the cultivation zone was maintained as neutral (pH = 7.0). The water temperature in the cultivation zone where Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps were planted is shown in Table 1, and it had an average value of 26.3 °C. The temperature and humidity meters were part of a greenhouse complex ventilation system, the ‘MAGMA-1000’ (MAGMA-1000’), installed in the growing room, and the water temperature measurement system was a Caple temperature recorder (CP22-WA15).

Table 2.
Greenhouse-type cultivation room environment on the second floor of the Sahmyook Eco-Farm Center plant factory.
In April 2023, 60 unblooming Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps in 2-inch plastic pots were purchased from a cultivation farm. The first acclimatization process was conducted in a greenhouse cultivation room for 14 days to reduce growth disorders due to environmental changes. After the first purification process, the soil attached to the roots was lightly shaken off and then completely removed by rinsing with tap water, and the plants were then immersed in tap water for 14 days to perform the second purification in a hydroponic form.
The containers for the experiments were made of stainless steel to minimize the impact of plastic, and the dimensions were 1.2 m × 0.2 m × 0.3 m for width, length, and height, respectively. To float the plants in the containers, lids were made with sizes of 0.15 m × 1.25 m. Five holes with diameters of 0.6 m were drilled at 0.15 m intervals, taking into account the plant spacing (Figure 2). To confirm the effectiveness of removing floating microplastics using plant roots, each plant was floated in a cultivation box and fixed with a sponge inserted into the cover hole of the cultivation box (Figure 3). The planting beds were 1.5 m × 0.9 m × 3.0 m (W × D × H, respectively), and they were set up in two rows, with Iris pseudacorus on the right and Lythrum anceps on the left (Figure 4).
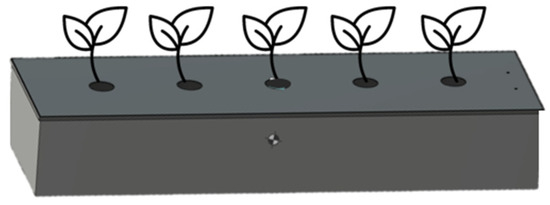
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the experimental plantings.
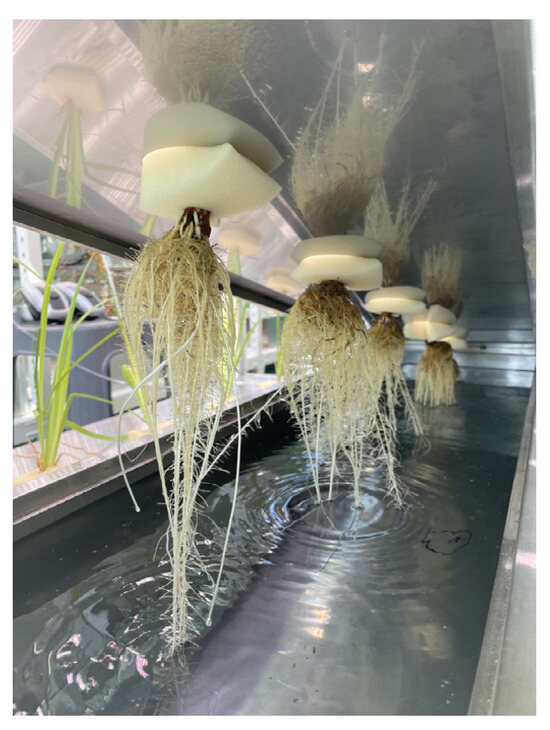

Figure 3.
Plant roots fixed using sponges.
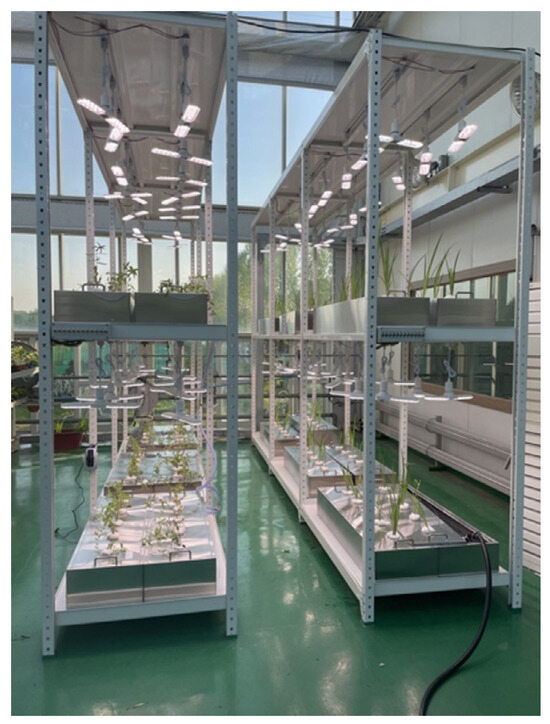

Figure 4.
Experimental cultivation stands (second floor greenhouse-type cultivation room in the Sahmyook Eco Farm Center plant factory).
2.3. Exposure Experimental Set-Up
The grow boxes were filled with 70 L of tap water and treated with two types of PE powder (46 µm and 140 µm) at a concentration of 1 mg/L. The bubble generator (Resun Air-4000) was set to allow the water to flow through the planting bed, considering that the microplastics would not float or sink but be adsorbed by the plant roots and the effect of the flow rate in the natural environment. For each plant type, a control consisting of one box with five plants was maintained with regular tap water. The treatment group was set up with 5 boxes (25 ea plants) treated with microplastic particles at a size of 46 µm and 5 boxes (25 ea plants) treated with microplastic particles at a size of 140 µm on Iris pseudacorus. Lythrum anceps was set in the same way as Iris pseudacorus.
2.4. Analyzing the Adsorption of Microplastics by Plants and the Concentration of Microplastics in Aquatic Environments
To analyze the microplastic removal content in the aquatic environment (in a cultivation box) planted with Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps, pre- and post-treatment water quality was analyzed using FT-IR with a microscope (NicoletTM iN10MX FT-IR microscope, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). In this work, only samples from the liquid solution were considered. The plants themselves were not subjected to any additional analysis (i.e., tissue examination).
Samples collected from the cultivation stand were subjected to treatments with varieties of PE powders measuring 46 µm and 140 µm, at concentrations of 1 mg/L. Three samples were obtained from the same box. Each sample was placed in 500 mL beakers and filtered under reduced pressure through a metal mesh filter (20 µm, 25 mm diameter). The filter was divided into four compartments across the front of the filter using an Omnic Picta Program (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) to obtain the IR spectra from all areas by ultra-fast mapping. The IR spectra obtained from each compartment were library-matched with the plastic IR spectra and considered as plastics when the matching rate was more than 70%, and quantitative data were collected by counting (Figure 5).
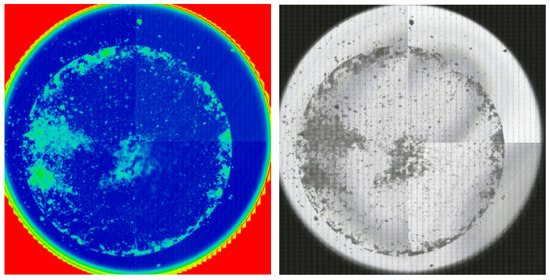
Figure 5.
Microplastics analysis using FT-IR (Lythrum, 140 µm).
To identify the adsorbed microplastic particles from the plant roots, some roots from Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps were removed and analyzed using a JEOL scanning electron microscope (JSM-6510). Microplastic adsorption analysis of the roots was performed once post-mortem (at 90 days). Root samples were examined for each plant as follows: 3 roots from the plants in the control group, 3 roots from the plants treated with microplastic particles sized 46 µm, and 3 roots from the plants treated with microplastic particles sized 140 µm.
2.5. Grow Survey
Pre- and post-planting growth surveys were conducted from May through to August to examine the water quality adaptation of the aquatic plants. Heights were measured from the bases to the tips of the longest leaves, and widths were measured at points 15 cm above the bases in the planted states. The number of leaves was counted for Iris pseudacorus, and the number of branches was counted for Lythrum anceps.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS 26.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA) program. Normality and homogeneity of variance were tested using Shapiro–Wilk and Levene tests, respectively. As a result, parametric statistical methods were used. Paired-sample t-tests were performed to determine significant differences between the pre- and post-microplastic removal states of each plant species, as well as differences between the microplastic particle sizes. One-way ANOVA was performed to test the significant effect of the microplastic concentration removal level according to microplastic particle size, and Duncan’s test was applied. A descriptive statistical analysis was conducted to determine the changes in plant growth following microplastic removal.
3. Results
3.1. The Plants Removed Microplastics from the Aquatic Environment
We measured the removal rate of microplastics in the water by the plants and found that each plant species had a positive effect on microplastic removal. The number of microplastics in the cultivation box with Iris pseudacorus decreased by 72.1% from 253 ea to 70 ea, and the number of microplastics in the cultivation box with Lythrum anceps decreased by 70.2% from 204 ea to 61 ea. The correlation between microplastic removal rate and plant type showed a significant difference between Iris pseudacorus (t = 11.068, p < 0.001) and Lythrum anceps (t = 13.113, p < 0.001) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Pre- and post-test comparison of microplastics removal averages.
When measuring removal by microplastic particle size, the number of microplastics in a cultivation box with a microplastics particle size of 46 µm decreased from 223 ea to 78 ea (a 64.9% reduction), and the number of microplastics in a cultivation box with a microplastics particle size of 140 µm decreased from 234 ea to 53 ea (a 77.3% reduction). In the pre- and post-comparison of the average microplastic removal capacity, significant differences were observed between plant species and microplastic particle sizes: Iris pseudacorus, t = 11.068, p < 0.001; Lythrum anceps, t = 13.113, p < 0.001; 46 µm, t = 10.773, p < 0.001; and 140 µm, t = 12.344, p < 0.001 (Table 3).
The pre- and post-test measurements of the effectiveness of Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps in removing microplastics from the water showed that both Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps had positive impacts on reducing microplastics in the water.
The microplastic removal rate for the plots planted with Iris pseudacorus decreased by 79.7%, from 241 ea to 92 ea, for the 46 µm microplastic particle size, and it decreased by 81.5%, from 265 ea to 49 ea, for the 140 µm microplastic particle size (Figure 6). The microplastic removal rate for the Lythrum anceps planted plots decreased by 68.7%, from 204 ea to 64 ea, for the microplastic particle size of 46 µm, and it decreased by 68.7%, from 183 ea to 57 ea, for the microplastic particle size of 140 µm (Figure 6).
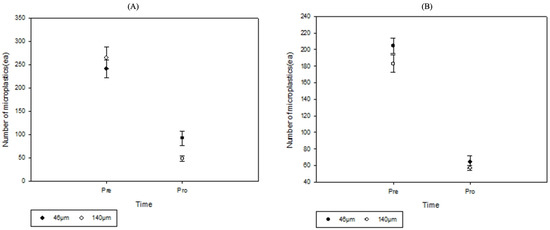
Figure 6.
Analysis of the microplastic concentrations in the aquatic environments: (A) Iris pseudacorus and (B) Lythrum anceps.
There was a correlation between the degree of microplastic removal and both the plant species and the size of the microplastic particle, with a significant differences between Iris pseudacorus (F = 39.014, p < 0.001) and Lythrum anceps (F = 33.801, p < 0.001), depending on the microplastic particle size (Table 4).

Table 4.
Microplastic removal effect depending on microplastic particle size.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to identify adsorbed particles on the roots of Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps (Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9). This confirmed that the microplastic particles were removed by adsorption on the plant roots.
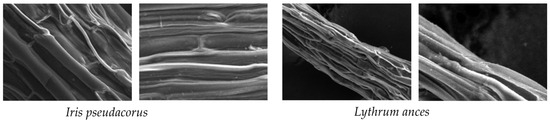
Figure 7.
SEM images of the control (L: ×55 and R: ×650).
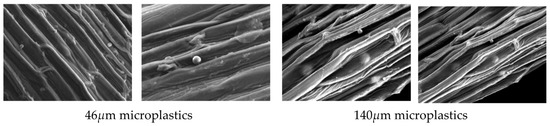
Figure 8.
SEM images of Iris pseudacorus (L: ×55 and R: ×650).
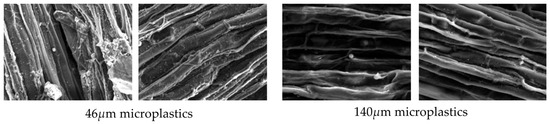
Figure 9.
SEM images of Lythrum anceps (L: ×55 and R: ×650).
3.2. Plant Growth as a Function of Microplastic Concentration
When Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps were grown in microplasticized tap water for 4 months from May to August, both the heights, widths, and numbers of leaves for Iris pseudacorus increased slightly over time (Figure 10). At a microplastic particle size of 140 µm, the initial width of a Lythrum anceps sample decreased from 8.3 cm to 5.1 cm. In addition, both the height and leaf number of a Lythrum anceps sample increased over time (Figure 11). The growth of Iris pseudacorus surpassed that of Lythrum anceps; however, neither species exhibited a rapid growth rate in the final analysis. This trend was also observed in the control group, suggesting that the growing environment, rather than the presence of microplastics, was the determining factor. The correlation between plant growth changes (height, width, branch number, and leaf number) and microplastic concentration was not statistically significant.
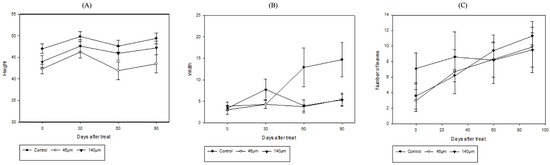
Figure 10.
Iris pseudacorus growth changes in an aquatic environment polluted with microplastics: (A) heights, (B) widths, and (C) numbers of leaves.
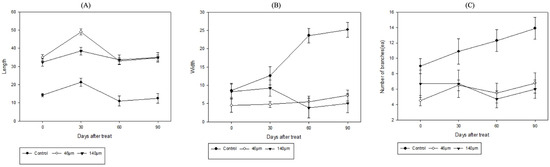
Figure 11.
Lythrum anceps growth changes in an aquatic environment polluted with microplastics: (A) lengths, (B) widths, and (C) numbers of branches.
4. Discussion
This study investigated the removal of microplastics according to the type of microplastic particle size and plant type and determined the effect of microplastics on plant growth. Currently, microplastics are classified as contaminants of emerging concern, and most microplastics generated in our daily lives flow into various aquatic environments, such as sewage treatment plants and rivers, through sewage. Microplastics in sewage treatment plants are treated using sedimentation or filtration, microbial treatments, and reverse osmosis; however, these are generally not effective or highly efficient [58,59,60]. In addition, research is needed on economical and efficient methods that can be applied not only to sewage treatment plants but also to various aquatic environments such as rivers, soils, and coastal waters, which can also have a positive impact on the landscape. Accordingly, we investigated the removal of microplastics from an aquatic environment using plants capable of adsorbing microplastics through their roots. We also examined variables such as sizes of the microplastic particles and growth rates of the plants to determine whether these plants could be sustainably maintained in polluted environments.
After a total of four months of experimentation, it was confirmed that the numbers of microplastics in the water in the cultivation boxes planted with Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps were reduced. The microplastics in the aquatic environments were significantly reduced regardless of the type of plant or the size of microplastic particle. These results were consistent with previous studies reporting the effect of planting plants on reducing microplastics in aquatic environments [61,62].
The validity of the results regarding the removal of microplastics from water through plants can be confirmed by the adsorption of microplastics by the roots of Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps. Plants absorb nutrients through their roots and adsorb suspended solids [63,64], which can promote the purification process of pollutants in an aquatic environment. This is consistent with the results of previous studies [65,66,67,68] showing that plants can accelerate the purification process of pollutants in an aquatic environment.
Upon measuring the reductions in microplastics based on particle size, it was confirmed that larger microplastic particles had a significantly greater reduction effect on both Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps. Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps are widely used as phytoremediation plants. They each have a dense root biomass. Although root mass was not investigated in this study, above-ground growth increased during the experiment, and the root condition appeared good upon visual inspection. Yellow irises were observed to have a higher frequency of fine roots than those of Lythrum anceps. The growth conditions for Iris pseudacoru were better than those of Lythrum anceps in terms of above-ground growth. Therefore, it could be inferred that larger particles of floating microplastics were more readily adsorbed by the roots of Iris pseudacoru, with high growth activities.
As a result of measuring plant growth changes to determine the growth status of plants in aquatic environments polluted with microplastics, it was confirmed that the heights, widths, and numbers of branches (leaf numbers for Iris pseudacorus) of Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps all increased. The sizes of the microplastic particles did not negatively impact plant growth, which was consistent with previous studies [47,54,69,70]. As a result, it appeared that microplastics in the aquatic environments did not have significant negative impacts on the growth of the roots of Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps. Therefore, the aboveground growth was also smooth. Neither Iris pseudacorus nor Lythrum anceps bloomed during the experiment. However, it was noteworthy that the control plants also failed to bloom, suggesting that the absence of flowering was likely due to unsuitable environmental conditions rather than the influence of microplastic stress. This inference aligned with findings from previous research [71]. The average temperature of the experimental environment was 25.8 °C and the humidity was 97.7%. These were within the plants’ optimal growth ranges. Nonetheless, the water temperature in the cultivation zone rose to an average of 29.6 °C during the flowering season in June and July, possibly attributable to inadequate ventilation.
The efficiency of microplastic reduction is influenced by both the particle sizes of microplastics and the stress tolerance of plants. To achieve effective reductions in aquatic microplastics through plant stabilization, it is essential to select plants with well-developed roots, rapid reproduction rates, and relatively long lifespans. Establishing sustainable vegetation cover to maintain continuous ecosystem function and restoring large-scale contaminated land are crucial [72]. This underscores the importance of considering various factors related to plant tolerance, not just the plant species, when implementing phytostabilization.
This study had several limitations. Firstly, investigating root mass is imperative. Phytostabilization relies on the principle of blocking movement or accumulating contaminants around the roots, which is accompanied by chemical and microbiological processes [73]. Therefore, variations in movement blockage depend on root biomass, while plant growth and absorption efficiency are influenced by temperature and pH. Additional research is warranted to investigate the potential correlations between temperature, PH, and microplastics, as these factors may influence plant growth and absorption efficiency.
High temperatures can accelerate microplastic decomposition, potentially enhancing plant absorption and toxicity [74]. Furthermore, introducing plants into real environments for microplastic removal might subject them to temperature stress, leading to growth limitations, chlorophyll formation inefficiencies, and developmental disorders [75]. Moreover, it can induce alterations in root structure and inhibit growth [76,77]. Consequently, specific discussions on the effects of optimal temperatures and pH levels on absorption efficiency are warranted.
Secondly, the microplastics used in this study were larger than the pore size of plant root cell walls, which is 4 nm [78], and they were, therefore, unlikely to be absorbed into the root cell walls during the study period. Therefore, removal through absorption was not confirmed. However, there have been cases where microplastics have been broken down into nanoparticles and absorbed into cell walls [79], potentially affecting seed or plant growth [12]. Therefore, long-term follow-up research focusing on these aspects is essential. Nevertheless, as ornamental plants with negligible roles in an ecosystem’s food chain, the introduction of Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps into aquatic environments is expected to pose minimal risk while providing ornamental value and reducing microplastics.
5. Conclusions
While research on aquatic microplastic removal by plants is still in its infancy, the results of this study confirm that removing microplastics from water through aquatic plants is effective and does not significantly affect plant growth. These results suggest that Iris pseudacorus and Lythrum anceps, which are commonly planted near watersides, are suitable plants for the effective removal of aquatic microplastics. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate and use a variety of plants with the aim of reducing microplastics in the environment through phytoremediation. Additionally, future research should focus on understanding the mechanisms behind these effects. Follow-up evaluations should also be conducted through long-term studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.K. and S.C.; methodology, Y.K. and K.P.; software, S.C.; validation, K.P. and J.B.; formal analysis, J.B.; investigation, S.C. and J.B.; resources, Y.K. and K.P.; data curation, S.C.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.K.; writing—review and editing, S.C. and K.P.; visualization, S.C.; supervision, Y.K. and K.P.; project administration, Y.K.; funding acquisition, Y.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Sahmyook University Project (RI12023016) in 2023.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from author Sueran Choi upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Sahmyook University for enabling them to conduct this research and to SU-AgRI, the school enterprise of Sahmyook University, for providing the research facilities.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Laist, D.W. Impacts of Marine Debris: Entanglement of Marine Life in Marine Debris Including a Comprehensive List of Species with Entanglement and Ingestion Records. In Marine Debris: Sources, Impacts, and Solutions; Coe, J.M., Rogers, D.B., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 99–139. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, J.; Kraak, M.H.S.; Parsons, J.R. Plastics in the Marine Environment: The Dark Side of a Modern Gift. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Whitacre, D.M., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Paul Chen, J. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review on occurrence, environmental effects, and methods for microplastics detection. Water Res. 2018, 137, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saud, S.; Yang, A.; Jiang, Z.; Ning, D.; Fahad, S. New insights in to the environmental behavior and ecological toxicity of microplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 10, 100298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, H.A. Plastic in Cosmetics. Are We Polluting the Environment through Our Personal Care? United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP): Nairobi, Kenya, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- An, D.; Kim, J. Proposing policy for the prevention of marine pollution from microplastics. J. Environ. Policy Admin. 2018, 26, 77–102. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, E.J.; Smith, K.L. Plastics on the Sargasso Sea Surface. Science 1972, 175, 1240–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Plastic in Cosmetics [Fact Sheet]; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- ISO/TR 21960:2020; Plastics-Environmental Aspects-State of Knowledge and Methodologies. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Vernier, Switzerland, 2020.
- Rochman, C.M. Microplastics research—From sink to source. Science 2018, 360, 28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weithmann, N.; Möller, J.N.; Löder, M.G.J.; Piehl, S.; Laforsch, C.; Freitag, R. Organic fertilizer as a vehicle for the entry of microplastic into the environment. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaap8060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, M.R. Plastic ‘scrubbers’ in hand cleansers: A further (and minor) source for marine pollution identified. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1996, 32, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitko, V.; Hanlon, M. Another source of pollution by plastics: Skin cleaners with plastic scrubbers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1991, 22, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Bai, X.; Ye, Z. Removal and generation of microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.; Sinclair, C.; Boxall, A. Occurrence, Degradation, and Effect of Polymer-Based Materials in the Environment. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Whitacre, D.M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 227, pp. 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- Andrady, A.L. Persistence of Plastic Litter in the Oceans. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Bergmann, M., Gutow, L., Klages, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, A.A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eerkes-Medrano, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Aldridge, D.C. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review of the emerging threats, identification of knowledge gaps and prioritisation of research needs. Water Res. 2015, 75, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spacilova, M.; Dytrych, P.; Lexa, M.; Wimmerova, L.; Masin, P.; Kvacek, R.; Solcova, O. An Innovative Sorption Technology for Removing Microplastics from Wastewater. Water 2023, 15, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morét-Ferguson, S.; Law, K.L.; Proskurowski, G.; Murphy, E.K.; Peacock, E.E.; Reddy, C.M. The size, mass, and composition of plastic debris in the western North Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1873–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kye, H.; Kim, J.; Ju, S.; Lee, J.; Lim, C.; Yoon, Y. Microplastics in water systems: A review of their impacts on the environment and their potential hazards. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Wu, S.; Wei, G. Adverse effects of microplastics and nanoplastics on the reproductive system: A comprehensive review of fertility and potential harmful interactions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzellitti, S.; Canesi, L.; Auguste, M.; Wathsala, R.H.G.R.; Fabbri, E. Microplastic exposure and effects in aquatic organisms: A physiological perspective. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 68, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-K.; Zoh, K.-D. A review on occurrence and environmental risk assessment for microplastics in freshwater systems. Korean J. Public Health 2019, 56, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pico, Y.; Alfarhan, A.; Barcelo, D. Nano- and microplastic analysis: Focus on their occurrence in freshwater ecosystems and remediation technologies. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Wang, M.W.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.F.; Xia, J. Research on ecotoxicology of microplastics on freshwater aquatic organisms. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2019, 31, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, G.; Yu, H.; Xing, J. Dynamic membrane for micro-particle removal in wastewater treatment: Performance and influencing factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perren, W.; Wojtasik, A.; Cai, Q. Removal of Microbeads from Wastewater Using Electrocoagulation. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 3357–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Monnot, M.; Sun, Y.; Asia, L.; Wong-Wah-Chung, P.; Doumenq, P.; Moulin, P. Microplastics in different water samples (seawater, freshwater, and wastewater): Removal efficiency of membrane treatment processes. Water Res. 2023, 232, 119673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariza-Tarazona, M.C.; Villarreal-Chiu, J.F.; Barbieri, V.; Siligardi, C.; Cedillo-González, E.I. New strategy for microplastic degradation: Green photocatalysis using a protein-based porous N-TiO2 semiconductor. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 9618–9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Offiong, N.-A.O.; Bi, Y.; Zhou, R.; Ren, H. A systematic review of electrocoagulation technology applied for microplastics removal in aquatic environment. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 456, 141078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhatib, D.; Oyanedel-Craver, V.; Carissimi, E. Electrocoagulation applied for the removal of microplastics from wastewater treatment facilities. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 118877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbir, S.; Faheem, M.; Ali, N.; Kerr, P.G.; Wang, L.-F.; Kuppusamy, S.; Li, Y. Periphytic biofilm: An innovative approach for biodegradation of microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, S.; Gautam, A. A Procedure for Measuring Microplastics using Pressurized Fluid Extraction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5774–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai Lei, M.L.; Bao LianJun, B.L.; Shi Lei, S.L.; Wong, C.; Zeng, E. A review of methods for measuring microplastics in aquatic environments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 11319–11332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorghe, D.; Sari, M.A.; Chellam, S. Boron removal from hydraulic fracturing wastewater by aluminum and iron coagulation: Mechanisms and limitations. Water Res. 2017, 126, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundbæk, K.B.; Koch, I.D.W.; Villaro, C.G.; Rasmussen, N.S.; Holdt, S.L.; Hartmann, N.B. Sorption of fluorescent polystyrene microplastic particles to edible seaweed Fucus vesiculosus. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 2923–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyajian, G.E.; Carreira, L.H. Phytoremediation: A clean transition from laboratory to marketplace? Nat. Biotech. 1997, 15, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, O.; Labana, S.; Budhiraja, R.; Jain, R. Phytoremediation: An overview of metallic ion decontamination from soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 61, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwaminger, S.P.; Fehn, S.; Steegmüller, T.; Rauwolf, S.; Löwe, H.; Pflüger-Grau, K.; Berensmeier, S. Immobilization of PETase enzymes on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for the decomposition of microplastic PET. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 4395–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, W.Y.; Ying Tang, D.Y.; Khoo, K.S.; Kay Lup, A.N.; Chew, K.W. Nature’s fight against plastic pollution: Algae for plastic biodegradation and bioplastics production. Eviron. Sci. Ecotech. 2020, 4, 100065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masiá, P.; Sol, D.; Ardura, A.; Laca, A.; Borrell, Y.J.; Dopico, E.; Laca, A.; Machado-Schiaffino, G.; Díaz, M.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. Bioremediation as a promising strategy for microplastics removal in wastewater treatment plants. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayo, J.; Olmos, S.; Lopez-Castellanos, J. Microplastics in an urban wastewater treatment plant: The influence of physicochemical parameters and environmental factors. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.A.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.J.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Accumulation of microplastic on shorelines woldwide: Sources and sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourgkogiannis, N.; Kalavrouziotis, I.K.; Karapanagioti, H.K. Questionnaire based survey to managers of 101 wastewater treatment plants in Greece confirms their potential as plastic marine litter sources. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumya, S.; Gregory, W.H.; Xagoraraki, I.; Goel, R. Factors affecting bulk to total bacteria ratio in drinking water distribution systems. Water Res. 2018, 42, 3393–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalčíková, G.; Žgajnar Gotvajn, A.; Kladnik, A.; Jemec, A. Impact of polyethylene microbeads on the floating freshwater plant duckweed Lemna minor. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guittonny-Philippe, A.; Petit, M.-E.; Masotti, V.; Monnier, Y.; Malleret, L.; Coulomb, B.; Combroux, I.; Baumberger, T.; Viglione, J.; Laffont-Schwob, I. Selection of wild macrophytes for use in constructed wetlands for phytoremediation of contaminant mixtures. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 147, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateos-Cárdenas, A.; Scott, D.T.; Seitmaganbetova, G.; Frank, N.A.M.v.P.; John, O.H.; Marcel, A.K.J. Polyethylene microplastics adhere to Lemna minor (L.), yet have no effects on plant growth or feeding by Gammarus duebeni (Lillj.). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.; Bae, B.; Kim, Y. Feasibility Test for Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals-Contaminated Soils using Various Stabilizers. J. Korean Geo-Environ. Soc. 2012, 13, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, B.; Andreou, D.; Green, I.D.; Britton, J.R. Microplastics in freshwater fishes: Occurrence, impacts and future perspectives. Fish. Fish. 2021, 22, 467–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ma, J.; Ji, R.; Pan, K.; Miao, A.-J. Microplastics in aquatic environments: Occurrence, accumulation, and biological effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, E.S. Green Plastics: An Introduction to the New Science of Biodegradable Plastics; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Calheiros, C.S.C.; Pereira, S.I.A.; Franco, A.R.; Castro, P.M.L. Diverse Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi (AMF) Communities Colonize Plants Inhabiting a Constructed Wetland for Wastewater Treatment. Water 2019, 11, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, K.J.; Peterson, R.L. Relationships among Three Pathways for Resource Acquisition and their Contribution to Plant Performance in the Emergent Aquatic Plant Lythrum salicaria (L.). Plant Biol. 2007, 9, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía, A.C.; Velasco, A.C.; Sánchez, P.Z.; Cisneros, B.J. Photo-Oxidation Treatment of the Reject Stream of a Nanofiltration Membrane System. In Membranes: Materials, Simulations, and Applications; Maciel-Cerda, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; García-Pacheco, R.; Molina, S.; Rodríguez-Sáez, L.; Rabadán, J.; García-Calvo, E. Fouling prevention, preparing for re-use and membrane recycling. Towards circular economy in RO desalination. Desalination 2016, 393, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.H.D.; Hadibarata, T. Microplastics removal through water treatment plants: Its feasibility, efficiency, future prospects and enhancement by proper waste management. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjate, E.; Ramos, S.; Almeida, C.M.R. Potential interferences of microplastics in the phytoremediation of Cd and Cu by the salt marsh plant Phragmites australis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozman, U.; Blažič, A.; Kalčíková, G. Phytoremediation: A promising approach to remove microplastics from the aquatic environment. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 338, 122690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, C.; Wang, X.; Cheng, H.; Xing, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Ge, T.; Du, A.; Wang, Z. Water Spinach (Ipomoea aquatica F.) Effectively Absorbs and Accumulates Microplastics at the Micron Level—A Study of the Co-Exposure to Microplastics with Varying Particle Sizes. Agriculture 2024, 14, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Chai, X. Removal of water nutrients by different aquatic plant species: An alternative way to remediate polluted rural rivers. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 110, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, L.A.; Fontaneto, D.; Bocchi, S.; Gomarasca, S. Evaluation of water quality and ecological system conditions through macrophytes. Desalination 2009, 246, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrucio, M.; Esteves, F. Uptake rates of nitrogen and phosphorus in the water by Eichhornia crassipes and Salvinia auriculata. Rev. Bras. Biol. 2000, 60, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Cui, Y.; Dong, Y. Phytoremediation of Polluted Waters Potentials and Prospects of Wetland Plants. Acta Biotechnol. 2002, 22, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mant, C.; Costa, S.; Williams, J.; Tambourgi, E. Phytoremediation of chromium by model constructed wetland. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1767–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dovidat, L.C.; Brinkmann, B.W.; Vijver, M.G.; Bosker, T. Plastic particles adsorb to the roots of freshwater vascular plant Spirodela polyrhiza but do not impair growth. Limnol. Ocean. Lett. 2020, 5, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boots, B.; Russell, C.W.; Green, D.S. Effects of Microplastics in Soil Ecosystems: Above and Below Ground. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11496–11506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayab, G.; Zhou, J.; Jia, R.; Lv, Y.; Yang, Y.; Brown, R.W.; Zang, H.; Jones, D.L.; Zeng, Z. Climate warming masks the negative effect of microplastics on plant-soil health in a silt loam soil. Geoderma 2022, 425, 116083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.P.G.C.; Rangel, A.O.S.S.; Castro, P.M.L. Remediation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soils: Phytoremediation as a Potentially Promising Clean-Up Technology. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 622–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.S.; Park, J.H.; Robinson, B.; Naidu, R.; Huh, K.Y. Chapter four—Phytostabilization: A Green Approach to Contaminant Containment. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 112, pp. 145–204. [Google Scholar]
- Fonte, E.; Ferreira, P.; Guilhermino, L. Temperature rise and microplastics interact with the toxicity of the antibiotic cefalexin to juveniles of the common goby (Pomatoschistus microps): Post-exposure predatory behaviour, acetylcholinesterase activity and lipid peroxidation. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 180, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobell, D.B.; Hammer, G.L.; McLean, G.; Messina, C.; Roberts, M.J.; Schlenker, W. The critical role of extreme heat for maize production in the United States. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamaoui, M.; Jemo, M.; Datla, R.; Bekkaoui, F. Heat and drought stresses in crops and approaches for their mitigation. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yang, P.; Tang, H.; Wu, W.; Yin, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L. Response of maize phenology to climate warming in Northeast China between 1990 and 2012. Reg. Environ. Change 2014, 14, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpita, N.C. Limiting Diameters of Pores and the Surface Structure of Plant Cell Walls. Science 1982, 218, 813–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, I.; Adeel, M.; Ahmad, M.A.; Shakoor, N.; Jiangcuo, G.D.; Azeem, K.; Ishfaq, M.; Shakoor, A.; Ayaz, M.; Xu, M.; et al. Uptake and Accumulation of Nano/Microplastics in Plants: A Critical Review. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).