Abstract
To date, in vitro somatic embryogenesis is the only option for the mass vegetative propagation of cocoa. The somatic embryogenesis of Indonesian cocoa clones SUL1 and SUL2 was investigated, focusing on primary and cyclic secondary embryogenesis. The study showed that staminode explants were more effective than petal explants in generating primary somatic embryos (SEs), especially when cultured in liquid medium containing 2 mg/L 2,4-D and 0.25 mg/L kinetin, with the staminodes of SUL2 producing a significant number of globular SEs. In contrast, SUL1 showed limited SE production. The study also demonstrated that fragmenting cotyledons and hypocotyls of the SEs of SUL2 and culturing them on an induction medium supplemented with 2,4,5-T and proline resulted in a high yield of secondary SEs. This cyclic embryogenesis process, in which the SEs remained attached to the maternal tissue, facilitated continuous SE production and development. The addition of proline was found to improve the quality of SEs, leading to higher production of well-organized, milky SEs with a better-defined meristematic structure. These results suggest a promising protocol to produce SEs from cocoa, with implications for plant transformation and gene editing applications.
1. Introduction
Cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.) is one of the most important tree crops in the world, mainly for its valuable seeds, commonly known as cocoa beans. These beans provide the basic ingredients for the multi-billion-dollar chocolate industry and many other products. Cacao is cultivated exclusively in the tropical regions of the world. In Indonesia, cocoa beans rank as the fourth most important agricultural export product after palm oil, rubber, and coconut. Indonesia was the second-largest producer in the world and the leading producer in Asia from 1999–2002 [1]. Despite the great potential to expand cocoa production, Indonesia now ranks seventh after Ivory Coast, Ghana, Ecuador, Cameroon, Nigeria, and Brazil [2]. The most commonly cited reasons for this decline are aging trees (mostly planted in the 1980s and 1990s) and pest and disease pressure [3,4].
More than 70% of Indonesian cocoa is produced in Sulawesi, mainly by smallholders with less than 5 hectares of land [5]. They rely mainly on seed multiplication, resulting in heterogenous plantations because cocoa plants are mainly cross-pollinated. The introduction of different clones/cultivars in Sulawesi has resulted in uncontrolled crossbreeding with local or pre-existing clones in the field. Limited availability of quality planting material forces farmers to use these mixed clones [6], often resulting in unmarketable beans. Clonal propagation of elite clones by somatic embryogenesis offers the advantage of a highly uniform plant population produced in a short period.
The elite Sulawesi1 (SUL1) and Sulawesi2 (SUL2) clones were introduced to Sulawesi from Malaysia in the 1980s. They became popular among local cocoa farmers because of their high adaptability, vigor, and productivity, leading to rapid expansion of cultivation throughout Sulawesi. In 2009, the Indonesian government distributed these clones to cocoa farmers as part of a tree rejuvenation and replanting program. Over the decades, clones of SUL1 and SUL2 have continued to dominate cocoa plantations in Sulawesi. They are valued for their high yields and resistance to major diseases, particularly vascular streak dieback (VSD) [7,8]. They demonstrated adaptability to withstand the specific local conditions of Sulawesi, such as severe seasonal drought, flooding, intense winds, and acidic soils [7,8].
In vitro somatic embryogenesis remains the promising method for the mass vegetative propagation of cocoa [9,10,11,12,13]. Initially, the somatic embryogenesis of cocoa was studied using immature zygotic tissue as explants, but the resulting embryos failed to develop into plantlets [14,15]. It was later discovered that the floral parts of cocoa, particularly staminodes and petals, were the most efficient explants for the induction of somatic embryos (SEs), leading to successful plant regeneration [10,16,17,18,19,20]. A more recent study showed that cocoa trees produced by this method were comparable to those from seeds or cuttings, especially in terms of plant growth, yield, and disease resistance [21].
A major challenge in the somatic embryogenesis of cocoa is the strong genotypic effects on SE production [22]. Although it has been applied to a large number of varieties, certain desirable genotypes show a low initiation frequency or even recalcitrance [10,16,17,18,23,24,25,26,27]. Efforts to optimize SE production include investigating factors such as plant growth regulators (PGRs), explant types, culture medium composition, and in vitro culture conditions [28]. Liquid media, particularly in Erlenmeyer flasks and bioreactors, have been found to enhance SE yield.
Once primary somatic embryos (SEs) are obtained, new SEs can be initiated from the previously developed SEs themselves, a process called secondary somatic embryogenesis (SSE) [29]. A high SSE of cocoa was obtained by using cotyledons of primary SEs derived from staminodes. Compared with primary somatic embryogenesis, the SSE produced was more uniform in a shorter time [24]. This method can serve as a clonal propagation of elite genotypes and has been applied in selected cocoa clones from Colombia [30], Brazil [12], and Ecuador [10,13,25].
Cyclic somatic embryogenesis is the iterated production of SEs on fragments of SEs from the previous cycle, directly or indirectly after a limited callus phase [31]. This repeatability can be maintained over an extended period by perpetuating successive cycles of embryogenesis (secondary, tertiary, and so on) without depending on the original explant. Cyclic somatic embryogenesis is an attractive method for massive clonal propagation because the multiplication rate is generally higher than that of other tissue culture regeneration systems. This method has been described in other crops such as walnut [32], oil palm [33], and rubber [34].
In this study, we describe the responsiveness of SUL1 and SUL2 clones to produce primary SEs and the ability of SUL2 primary SEs to generate cyclic somatic embryogenesis. To our knowledge, these are the first reports of cyclic somatic embryogenesis in elite Indonesian SUL1 and SUL2.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
The experiments were conducted on the elite genotypes of Indonesian cocoa, PBC123 or ‘Sulawesi 01’ (SUL1), and BR25, known as ‘Sulawesi 02’ (SUL2). Immature flower buds (about 5–6 mm long) of SUL1 and SUL2 were collected in the morning (6 a.m.) from trees growing in a field plantation of the Agriculture Faculty of Tadulako University in Palolo Valley, Central Sulawesi Province, Indonesia. The collected flower buds were transported the same day to Ghent University, Belgium, for dissection and culture initiation. Upon arrival, the flower buds were disinfected by following the protocol of Guiltinan and Maximova [23] with some modifications. They were gently washed with 70% ethanol for 1 min, followed by three rinses with running tap water. The buds were then immersed in 10% (v/v) commercial bleach (8%) sodium hypochlorite with 1 drop of Tween20® for 10 min under agitation. The buds were then rinsed three times with sterile distilled water. Flowers that opened during the sterilization process were discarded to avoid contamination. In a horizontal laminar flow hood, the solution was poured over and the flowers were thoroughly washed three times with autoclaved distilled water to remove any residual sodium hypochlorite. The flower buds were then cut at the distal end to isolate staminodes and petals.
2.2. Primary Somatic Embryogenesis
The first experiment examined the in vitro response of SUL1 and SUL2 by comparing the ability of petal and staminode floral parts to produce primary SEs.
Immature flower buds were aseptically dissected to isolate petals and staminodes according to Guiltinan and Maximova [23]. Ten of each explant were individually placed horizontally in 90 mm Petri dishes containing 25 mL of callus induction medium (IND1) as described by Fontanel et al. [25] enriched with Guiltinan and Maximova’s amino acids (43.55 mg/L arginine, 18.76 mg/L glycine, 32.80 mg/L leucine, 45.65 mg/L lysine, and 51.05 mg/L tryptophan) [23]. The IND1 medium contained Driver and Kuniyuki Walnut (DKW) basic salts and vitamins [35] supplemented with 1, 2, or 3 mg/L 2,4-D, picloram, or IAA; 0.25 mg/L kinetin (KIN) and amino acids; 30 g/L glucose; and solidified with 3 g/L gelrite (Table S1). Media were adjusted to pH 5.8 before adding gelrite and autoclaved at 121 °C for 20 min. After six weeks, explants with calluses were transferred to the same medium without the growth regulator (INDexp) [25]. Each of the two semi-solid media in Petri dishes, Erlenmeyer flasks, and SETIS bioreactors [36] contained five explants. Each Erlenmeyer flask contained 100 mL and was sealed with aluminum foil. They were placed on a rotary shaker (100 rpm) at 26 ± 2 °C in the dark and subcultured every 14 days for four months. The volume of media in the temporary immersion system (SETIS™, Vervir, Lochrist, Belgium) was 250 mL and the immersion time was 1 min, 4 times per day. The system was wrapped in aluminum foil to keep the culture dark. The resulting SEs were maintained on gelled medium until they reached the cotyledonary stage. The obtained primary SEs at the cotyledonary stage were then used as explants to induce secondary SEs.
2.3. Cyclic Somatic Embryogenesis
For the induction of secondary SEs, cotyledons and hypocotyls of primary SEs of the SUL2 clone were cut into approximately 4 mm fragments at the cotyledonary stage. They were cultured on semi-solid modified Callus Multiplication Medium (CM2) [25] in 90 mm Petri dishes. The CM2 medium consisted of MS macronutrients [37], DKW micronutrients and vitamins, 0.25 mg/L adenine, and 30 g/L glucose, solidified with 3 g/L gelrite. Modifications included the addition of 1 mg/L Guiltinan and Maximova’s amino acids [23] and 0, 1, or 2 mg/L 2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4,5-T) combined with 0, 1, or 2 mg/L proline. The best combination of 2,4,5-T and proline was further tested for the next cycle. Proline was filter-sterilized and added to the culture media after autoclaving. The media were adjusted to a pH of 5.8 before the addition of gelrite and autoclaved at 121 °C for 20 min. The cultures were kept in the dark at 26 ± 2 °C and subcultured for nine weeks at three-week intervals. After this period, the cultures were transferred to a modified expression medium (EM2) [25] in Erlenmeyer flasks. EM2 contained MS macronutrients, DKW micronutrients and vitamins, and 40 g/L sucrose. Modifications included the addition of 1 mg/L amino acids and the exclusion of 3 g/L gelrite. Flasks inoculated with ten explants each were sealed with aluminum foil, placed on an orbital shaker at 100 rpm in the dark at 26 ± 2 °C and subcultured every three weeks for up to 12 weeks. After this period, the embryogenic tissues with attached secondary SEs were transferred to a semi-solid EM2 medium and subcultured every three weeks on fresh semi-solid EM2 medium until they reached the cotyledonary stage. Simultaneously, new secondary SEs were produced by repetitive embryogenesis. The embryogenic tissue was maintained for up to 10 months to allow continuous asynchronous development of secondary SEs. The number of secondary SEs produced was recorded.
At the cotyledonary stage, the secondary SEs were divided into two batches. One batch was used as explants to induce the third cycle of somatic embryogenesis (cyclic embryogenesis), and the other batch was transferred to a maturation medium for further research. To induce tertiary and quaternary SEs, 1 mg/L 2,4,5-T was chosen in combination with 1 mg/L proline. White, translucent, and morphologically abnormal secondary SEs were used as explants to initiate a tertiary line. These were cultured and maintained in media with procedures identical to those used for secondary somatic embryogenesis. The culture conditions were similar to those described above.
2.4. Histological Examination
Milky and translucent SEs underwent Carnoy’s procedure [38] for histology. Fixation was performed in acetic acid and 94% ethanol (1:3 v/v) for 48 h. After dehydration in an ascending ethanol series (v/v) (70%, 80%, and 94%) for 15 min each, 94% ethanol and butanol and erythrosine (1:0.001), butanol alone for 15 min, 94% butanol and paraffin (1:1) at 37° for 24 h, and 94% butanol and paraffin (1:1) at 70° for 3 h, the samples were embedded in paraffin. Then, 3 µm sections were cut using a microtome (Microm HM 360, Walldorf, Germany). These sections were stained with safranin and fast green using a staining robot (Mirastainer II, Avantor, Radnor, Philadelphia, PA, USA) programmed according to the following scheme: xylol for 90 min, 96% ethanol for 10 min, 2% safranin for 100 min, 2% safranin for 20 min, ethanol and HCl for 5 min, 96% ethanol for 5 min, butanol for 5 min, 1% fast green for 3 min, butanol for 5 min, 96% ethanol for 3 min, and xylol for 60 min. After dewaxing and staining, sections were permanently mounted in Canada balsam, dried for at least 48 h and observed under an Olympus BX41 microscope equipped with a Jenoptik ProResC10 camera.
2.5. Experimental Design and Evaluations
2.5.1. Procedures for Primary Somatic Embryogenesis
Embryogenic and non-embryogenic calluses were distinguished based on texture and color. Callus that did not produce SEs were classified as non-embryogenic. The total number and percentage of calluses that produced direct/indirect primary SEs were evaluated after 8 weeks of culture. The effect of embryogenic tissue production on three culture systems (semi-solid medium in Petri dishes, liquid medium in Erlenmeyer flasks, and temporary immersion bioreactors) was recorded after 6 weeks. Statistical analysis was performed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 25.0. Mean differences were compared using the Tukey B test at p = 0.05.
2.5.2. Cyclic Somatic Embryogenesis
The number of secondary SEs produced per explant was recorded, as well as the quality of the SEs produced (normal or abnormal). The number of SEs produced from the maintenance of the embryogenic tissue (in the repetitive SE) was determined by counting the newly formed globular SEs after 4 weeks.
3. Results
3.1. Primary Somatic Embryogenesis
3.1.1. Effect of Type and Concentration of Auxins
Petals (Figure 1a) and staminodes (Figure 1b) of SUL2 responded to callus induction within 1 to 2 weeks after culture. The callus showed heterogeneity, characterized by a compact and in some cases soft texture with slow growth and white color, as well as friable and fast-growing structures with yellow, brown, or dark brown and mixed textures. Subsequent subcultures on a PGR-free medium resulted in the formation of primary SEs, revealing that only friable brown or white-brown calluses possessed embryogenic potential, whereas compact or soft calluses did not produce SEs. The percentage of callus induction ranged from 43 to 93%. Of all auxin types (2,4-D, picloram, and IAA) and concentrations (1, 2, and 3 mg/L) tested, only 1 and 2 mg/L 2,4-D resulted in the development of direct SEs and embryogenic tissue. SUL2 showed a greater embryogenic response, featuring both direct and indirect primary SEs. In the presence of 2 mg/L 2,4-D, 13.3% of petals exhibited the direct formation of primary SEs (Table 1 and Table S2). These SEs appeared as translucent globular structures around the cut end (Figure 1c) after 3–4 weeks of culture. Unfortunately, these SEs did not further develop to the heart stage after transfer to the INDexp medium without PGR. Instead, they gradually turned dark brown and underwent overgrowth of callus. In contrast, SUL1 showed only indirect SE formation on 6.7% of staminode explants initially grown on a medium containing 2 mg/L 2,4-D. However, almost all SEs aborted after several subcultures on semi-solid medium. No embryogenic response was observed from the petals of this clone. Staminodes of SUL2 did not show direct somatic embryogenesis, but they first produced embryogenic tissues. When cultured in PGR-free medium, 23.3% individual or groups of globular SEs were produced from staminodes initially cultured in IND callus induction medium containing 2 mg/L 2,4-D. During regular subculture, some SEs were covered with white to dark brown callus tissue and failed to proliferate. More than 2 mg/L 2,4-D did not produce embryogenic tissue in either clone. Instead, it induced roots. The exclusion of growth regulators prevented callus initiation or direct SE in both explants.
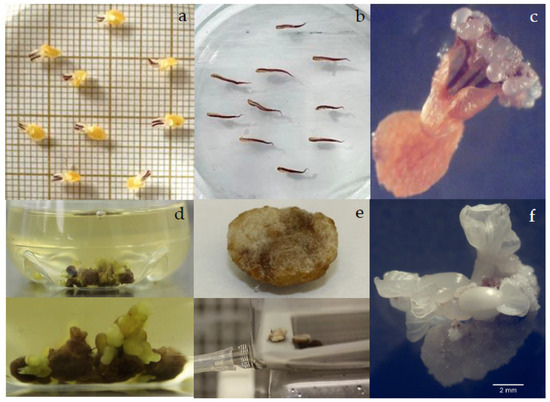
Figure 1.
Primary somatic embryogenesis in SUL2. Isolated (a) petal and (b) staminodes in callus induction medium five days after culture. (c) Direct formation of globular primary SEs in petal explant cultured in IND medium supplemented with 2 mg/L 2,4-D and 0.25 mg/L kinetin. (d) Clumps of callus turned soft brown after two weeks in shaken Erlenmeyer flask with clusters of SEs at different developmental stages; (e) compact white callus in temporary immersion bioreactor; (f) indirect primary SEs on staminodes cultured in semi-solid medium.

Table 1.
Induction of primary somatic embryos on petal and staminode explants of SUL2 on modified IND media with different concentrations of 2,4-D on the percentage of callus-producing embryos, number of callus-producing embryos, and total number of embryos. The embryogenic response was determined after 8 weeks of culture on INDexp media.
3.1.2. Effect of the Culture System
Given the low production of primary SEs in semi-solid medium, further research was conducted to scale up embryogenic tissue production using three culture systems: semi-solid medium in Petri dishes, liquid medium in Erlenmeyer flasks, and temporary immersion bioreactors. In this study, two-month-old staminodes and petal-derived calluses grown in IND medium containing 1 and 2 mg/L 2,4-D were used. Staminodes-derived calluses initially cultured on IND medium containing 2 mg/L 2,4-D showed the best response (Table 2). These explants induced somatic embryos after two weeks in PGR-free liquid medium in Erlenmeyer flasks. Four weeks later, many embryos were present, mainly in clusters, most at the torpedo stage (Figure 1d), and milky or translucent. In contrast, all explants cultured in temporary immersion gave rise to compact, non-embryogenic calluses (Figure 1e).

Table 2.
The number and percentage of embryogenic tissue produced by SUL2 clone on semi-solid and liquid medium.
3.2. Cyclic Somatic Embryogenesis
Because of the limited availability of primary SEs from SUL1, only primary SEs at the cotyledonary stage of SUL2 (Figure 2a) were tested for cyclic embryogenesis. Cyclic somatic embryogenesis was observed for three consecutive cycles. Cotyledons and hypocotyls of primary SEs (Figure 2a) were fragmented and randomly cultured in the induction medium (CM2) supplemented with 1 or 2 mg/L 2,4,5-T, alone or in combination with 1 or 2 mg/L proline and control (without 2,4,5-T and proline). The highest secondary SEs were obtained from both cotyledons and the hypocotyl in medium containing 1 mg/L 2,4,5-T and 1 mg/L proline (Table 3). These secondary SEs were white, translucent, or abnormal. Both direct and indirect secondary SEs were observed in cotyledon (Figure 2b) and hypocotyl (Figure 2c) fragments. The medium containing 1 mg/L 2,4,5-T and 1 mg/L proline gave the highest percentage of milky secondary SEs compared to translucent ones (Table 4). When the secondary SEs were transferred to auxin-free semi-solid medium, they developed into globular, heart-shaped, torpedo-shaped, and well-developed cotyledonary SEs that resembled zygotic SE stages. Tissue browning did not affect the ability to produce SEs. Cotyledon fragments produced up to 202 new secondary SEs on a medium containing 1 mg/L 2,4,5-T and 1 mg/L proline (Table 5).

Figure 2.
Secondary somatic embryogenesis in SUL2. (a) Cotyledonary primary milky SE used as explant for the induction of secondary somatic embryogenesis. (b) Cotyledon fragment isolated from a primary SE with direct secondary SEs; the inset shows an early heart-shaped SE with suspensor-like attaching the SE to the explant. (c) Hypocotyl fragment with direct SEs at cotyledonary stage still attached to it. (d) Direct repetitive SSEs (e–h) Abnormal SEs.

Table 3.
Rate of embryogenic tissue on cotyledon and hypocotyl fragments on modified EM2 medium with or without 2,4,5-T.

Table 4.
Percentage of milky, translucent, and abnormal secondary embryos by auxin 2,4,5-T or proline in secondary somatic embryogenesis.

Table 5.
Total number of SEs of primary SEs, secondary SEs, tertiary SEs, and quaternary SEs of SUL2 clone and relative amount (%) of milky, translucent, and abnormal SEs.
The early stages of secondary SEs showed different developmental paths, such as normal milky or translucent SEs, abnormal SEs, or sometimes those relapsed into calluses. Abnormal SEs were clearly distinguished at the cotyledonary stage, characterized by single, multiple, unusual cotyledon shapes, fused cotyledons or hypocotyls, or the absence of hypocotyls (Figure 2e–h). Normal milky SEs were identified as white and opaque (Figure 3a), with better organization of their meristematic cells (Figure 3c), while the translucent ones were hyperhydric, yellowish (Figure 3b), loosely arranged irregular meristematic cells (Figure 3d).
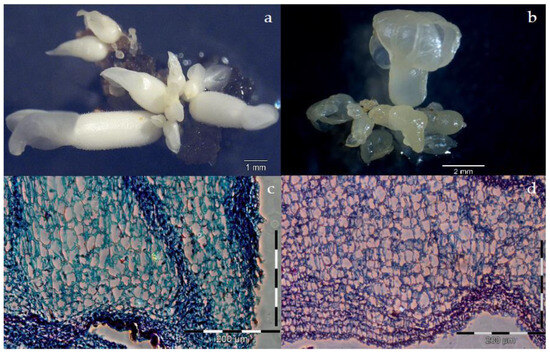
Figure 3.
Secondary SEs derived from cotyledon fragments at different developmental stages. (a) Cluster of milky SEs. (b) Cluster of yellow translucent SEs. Section showing (c) milky and (d) translucent SEs.
In the third and fourth cycles, cotyledons and hypocotyls of milky, translucent, and abnormal SEs were used as explants and cultured on semi-solid medium containing 1 mg/L 2,4,5-T and 1 mg/L proline. After transferring to PGR-free liquid medium, a higher frequency of embryogenic tissue was observed on cotyledon compared with hypocotyl fragments. In the third cycle, cotyledons produced 169 SEs, while hypocotyl fragments produced 53 SEs. In the fourth cycle, cotyledons produced 148 SEs, while hypocotyl fragments produced 62 SEs. These SEs were identified as milky, translucent, and abnormal cotyledon fragments (Figure 4). Table 5 shows the total number of SEs at different stages (primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary) of different explants and the relative percentage distribution of milky, translucent, and abnormal SEs. In primary SEs, petals and staminodes produced the most translucent embryos (46.2% and 40.4%, respectively). In the next stage, secondary somatic embryogenesis produced the highest number of milky embryos from cotyledons (Table S3).
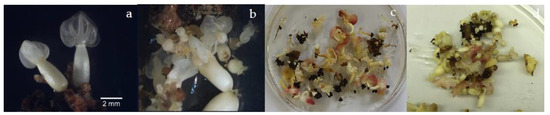
Figure 4.
Tertiary somatic embryogenesis. (a–d) Morphological diversity of tertiary SEs.
4. Discussion
4.1. Primary Somatic Embryogenesis
4.1.1. Effect of Types and Concentrations of Auxins
SUL1 and SUL2 demonstrated a positive response in SE production. However, despite their close genetic relationship, there was variation in the productivity of primary SEs. Genotypic variation in somatic embryogenesis occurs between varieties and within varieties in outbreeding crops [39]. Genotype-dependent embryogenic capacity in cocoa is a well-documented phenomenon [12,18,19,20]. A high genotype-specific response was also evident in cocoa secondary SE induction within various genetic groups of Criollo, Forastero, and Trinitario [10]. Different responses between genotypes are likely affected by the concentration and type of endogenous compounds (such as auxin, ethylene, phenols, etc.), by interactions between endogenous and administered PGRs, or differences in the donor flower and/or physiological stage of the flowers [18,24,27].
The study showed that the successful initiation of embryogenic tissue depends on the interaction between the explants and culture medium. In our experiment on primary somatic embryogenesis, calluses derived from staminoids were better for SE production. This result is consistent with previous research on cacao somatic embryogenesis [12,18,40,41]. In contrast, petals were reported to be more embryogenic in certain cocoa genotypes from the Ivory Coast and the Brazilian cocoa clone TSH 565 [42,43].
All cocoa genotypes require a combination of auxin and cytokinin such as 2,4-D and kinetin for the induction of SE. In this study, the most effective combination for primary SE induction was 2 mg/L 2,4-D + 0.25 mg/L KIN. Previous protocols on Ecuadorian cultivars suggested 1 mg/L 2,4-D + 0.25 mg/L KIN as the optimal concentration [12,20,25,44]. It is noteworthy that too high auxin levels negatively affect SE induction in many crops, even in Cocos nucifera, which requires high levels of 2,4-D [45]. In cocoa, the browning and necrosis of explants were observed in most media at an auxin concentration of 3 mg/L.
During the culture process, it is possible for cells within the explant tissue to directly or indirectly differentiate into SEs [46]. In this study, both direct and indirect primary SEs were obtained, specifically from petals cultured with 2 mg/L 2,4-D. Direct SEs formed on petal tissue eventually showed brown discoloration and did not develop further after a few weeks. This could be attributed to several factors, including the accumulation of phenolic compounds in response to environmental stress, inappropriate nutrient levels for sustained proliferation, or any number of unidentified factors [47]. The cocoa plant contains a large number of phenolic compounds [48] that can be oxidized and accumulate at the cut ends of cells when injured. Attempts in this study to protect these SEs from oxidation by transferring them to a new medium were unsuccessful, as the SEs degraded after 2–3 transfers. Direct SEs from staminode and petal explants of cocoa genotypes Sca6 and IMC67 were also successfully obtained, using a modified protocol of Maximova et al. [24] by optimizing the sulfate concentration, but no details were given on further development [20]. Direct SEs were also produced from the SE axis of mature seeds by two different routes: SEs derived from glandular hair-like structures and SEs developed from the internal cotyledonary meristematic zone. However, these SEs also failed to germinate [15]. To date, no reports are acknowledging the generation and further development of direct SEs in cocoa. Because direct SEs are less sensitive to somaclonal variation and offer the advantage of a shorter production period compared with indirect SEs [49], exploring the possibility of inducing direct SEs from petal tissue could contribute to the development of an improved propagation method.
Our indirect primary SE experiments revealed the morphological diversity of calluses and their ability to form SEs. Regardless of color, in this research, friable calluses were essential for SE production. Brown-dark brown calluses do not necessarily indicate their viability. However, in other cases, embryogenic cocoa calluses are typically characterized as granular and friable with a yellowish color [13].
4.1.2. Effect of the Culture System
In this study, liquid medium was more effective for embryogenic expression, resulting in a higher incidence of indirect SEs. High-frequency cacao SEs using shaken liquid Erlenmeyer flasks were reported to produce 1000 to 1500 SEs from 1 g of callus within 5 to 7 weeks [13]. Several researchers have successfully employed a liquid medium to scale up SE production in many plant species, including Norway spruce [50], conifers [51], and coffee [52]. Liquid medium offers many advantages in terms of homogeneous nutrient distribution, enhanced cell movement, improved gas exchange, and the absence of nutrient gradients within the medium and at the cell surface [53].
Calluses in the temporary immersion bioreactor (SETIS) formed only non-embryogenic tissue that was white-brown, hard, and compact. This non-embryogenic tissue proliferation could be attributed to the suboptimal immersion frequency and duration. Because of the limited availability of calluses, the experiment did not explore various immersion cycles but relied on the work of Niemenak et al. [26], who reported that four immersions per day at one minute produced the highest number of SEs compared to one or six immersions. But the tissues were mostly non-embryogenic, even in the most responsive genotype, ‘Scavina6’. Few reports have focused on the production of SEs from cocoa in temporary immersion bioreactors [13].
4.2. Cyclic Somatic Embryogenesis
Cyclic somatic embryogenesis requires cotyledons of primary SEs. An overview of cyclic somatic embryogenesis of the SUL2 clone is shown in Figure 5. Regarding medium composition and culture procedure, the addition of proline and 2,4,5-T improved embryo quality in this study. The induction of secondary SEs has been reported with the inclusion of 2,4-D and BA [12,24] or 2,4,5-T [13,25].
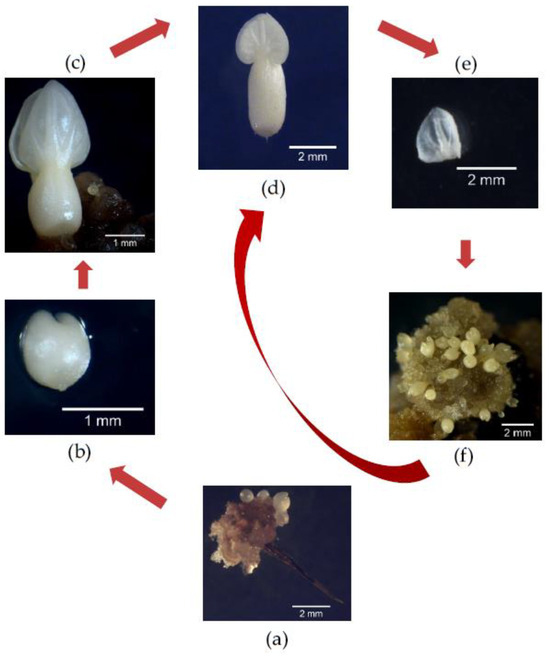
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of cyclic somatic embryogenesis in SUL2. The start involves the formation of embryogenic calluses from staminode-derived tissues, resulting in the production of globular (a), arrow marked), heart (b), torpedo (c), and cotyledonary primary embryos (d). The cotyledonary primary embryo was then fragmented (e) to initiate secondary embryogenic calluses, and then clusters of repetitive secondary embryos were produced (f). Steps (d–f) can be repeated iteratively in a cyclic manner.
As in the primary SEs, the secondary SEs were also formed directly or indirectly through the undifferentiated callus phase. Treatment with 1 mg/L 2,4,5-T led the cotyledon and hypocotyl tissues to become directly competent and determine the change of differentiation pathways. Although the frequency was still low, the direct SEs obtained were similar. SEs obtained by direct embryogenesis are typically less numerous than SEs obtained by indirect embryogenesis. Therefore, the second type is preferred for large-scale propagation. Physical limitations of small explants limit the number of direct SEs produced per culture [54].
The formation of indirect secondary SEs was stimulated by transferring cotyledon and hypocotyl fragments with attached calluses from an auxin-enriched semi-solid medium to PGR-free liquid medium. Auxin stimulated the number of regenerated SEs when the hormone was subsequently removed from the medium. The continuous presence of auxin should be avoided because it may interfere with the further normal development of SEs [55].
Cotyledon fragments were more efficient in secondary SE production than hypocotyl fragments. This was not surprising, as the cut ends of cotyledon provide a wider area for embryogenic tissue initiation. Epidermal cells of the cotyledon showed high embryogenic potential, allowing for cyclic secondary somatic embryogenesis to occur [56]. Some secondary SEs then served as sites for active adventitious SEs capable of directly forming new SEs, particularly at the late cotyledonary stage [17]. The phenomenon of repetitive embryogenesis by direct SE production is common. In the Brazilian cocoa genotype ‘Cenargen 2’, repeated somatic embryogenesis using staminode explants associated with biolistics resulted in stable transgenic cocoa plants [40]. The induction of repetitive somatic embryogenesis has also been successfully demonstrated in several other plant species, including eucalyptus [57], peanut [58], and sunflower [59].
During the cyclic embryogenesis of cocoa, SEs developed asynchronously, and this is often observed [12,13,18,20], as in other plant species such as coffee [52] and date palm [60]. The phenomenon of normal and abnormal SEs has been previously reported [18,24,61]. In this study, the characterization of normal and abnormal SEs in cocoa was based on the criteria of Sondahl et al. [62]. The development of abnormal SEs in cocoa could be associated with epigenetic modification [63]. Abnormal SEs did not necessarily imply that the subsequent growth was an abnormal plant. It was possible to obtain normal plants from these SEs, although their in vitro development was relatively slower than that of the normal type because secondary SEs with abnormal morphology could be reused for callus reduction [24]. Two phenotypically distinct types of normal cotyledonary-shaped SEs were identified: milky white and translucent. Similar types have been reported in other cacao clones [18,43,64], wild cherry [65], rubber [66], and conifers within the Pinaceae [67].
Water-soaked translucent SEs were considered to have limited conversion potential while milky SEs had an enhanced conversion potential [18,24,59,64]. Milky and translucent SEs showed large numbers of differentially regulated proteins through proteomic analysis [56]. Translucent cotyledon SEs contained fewer starch granules in their epidermal cells compared with opaque cotyledons, while torpedo-shaped SEs had the highest levels of proline, protein, and antioxidant enzyme activity during secondary embryogenesis in Persian walnuts [68].
The translucency and malformations in SEs could be a symptom of the reduced accumulation of storage compounds [46,59]. The quality of embryogenic tissue can be improved by supplementing the culture media with proline (Winkelmann, personal communication), but this has not yet been widely used in cocoa. Although this organic nitrogen-containing additive was insufficient to induce secondary SEs, the combination with an auxin-rich condition followed by subculture on a PGR-free medium increased milky SEs. A proline-rich medium not only increased the SEs’ size but also enhanced the production of mature plants [68]. Proline was found to enhance somatic embryogenesis in long-term barley callus [69].
Finally, we observed that the embryogenic potential decreased with prolonged culture because the number of quaternary SEs was lower than the number of tertiary SEs. Prolonged secondary embryogenesis with reduced embryogenic potential was previously reported in the Ecuadorian cocoa genotype EET-103 [56] and other plant species such as olive [70], coffee [71], and pine [72]. A decrease or loss of morphogenic potential during prolonged culture can be attributed to several factors including somaclonal variation that causes genetic or epigenetic variation [73]. The dysfunction or loss of regulatory genetic mechanisms controls the regeneration during subculture [74], alteration in gene expression [75], or changes in hormonal balance or sensitivity to exogenous growth substances [39].
Cyclic secondary somatic embryogenesis is promising for the mass production of clones because it has been shown to effectively improve culture quality and the production of SEs [50]. This potential was confirmed by Garcia et al. [12], who found that secondary SEs increase SE production nearly tenfold on average for all cocoa clones studied. The use of secondary somatic embryogenesis is especially advantageous for gene editing and genetic transformation because it produces true-to-type SEs [62,76]. The secondary SEs produced in each cycle can be harvested for conversion into plantlets or used as an explant source for reintroduction of tertiary SEs. This increases the potential rate of conversion into plantlets (see Figure 5). This cyclic somatic embryogenesis process successfully maintained stable embryogenic cultures for more than a year.
5. Conclusions
By integrating two existing protocols, this study streamlined somatic embryogenesis for SUL2, an important Indonesian cocoa clone, to facilitate the mass production of planting material. It emphasized the efficiency of staminode explants over petal explants in generating primary SEs, especially in liquid medium containing 2,4-D and Kin. Fragmentation of SUL2 cotyledons and culture in supplemented medium significantly increased secondary SE yield, with proline improving SE quality. Cyclic secondary somatic embryogenesis has been explored to enhance SEs, paving the way for mass propagation, potential gene editing, or genetic transformation to address traits such as disease resistance, stress tolerance, and quality improvement of cocoa beans.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae10010024/s1. Table S1. Medium composition used for somatic embryogenesis of elite Indonesian cacao. DKW= Driver and Kuniyuki (1984); MS = Murashige and Skoog; 2,4-D = 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid; 2,4,5-T = 2,4,5-Tricholophenoxyacetic acid. Table S2. Induction of primary somatic embryo on petal and staminode explants on modified IND media with different concentration of 2,4-D on the percentage of callus- producing embryos, the number of callus- producing embryos, and total embryos. Embryogenic response was determined after 8 weeks of culture on INDexp media. Table S3. Percentage of milky, translucent, and abnormal secondary embryos during the maintenance phase of secondary embryogenic calluses.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.U.B.; methodology, M.U.B.; validation, M.U.B. and S.P.O.W.; formal analysis, M.U.B. and S.P.O.W.; investigation, M.U.B.; resources, M.U.B.; data curation, M.U.B. writing—original draft preparation, M.U.B.; writing—review and editing, M.U.B. and S.P.O.W.; visualization, M.U.B.; supervision, S.P.O.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by a Ph.D. research grant from the Directorate General of Higher Education, Research and Technology Ministry of Education, Culture, Research, and Technology of Indonesia.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ruf, F. Indonesia Cocoa Sector Assessment How to Help Indonesian Cocoa Farmers to Re-Invest in Cocoa; UMR Innovation; CIRAD: Paris, France, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, P.; bin Purung, H.; Lambert, S.; Mulia, S.; Nurlaila; Susilo, A.W.; Sulistyowati, E.; Sukamto, S.; Israel, M.; Saftar, A.; et al. Testing local cocoa selections in three provinces in Sulawesi: (i) Productivity and resistance to cocoa pod borer and Phytophthora pod rot (black pod). Crop. Prot. 2015, 70, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICCO in Production Quarterly Bulletin of Cocoa Statistics, Volume XLIX No 1, Cocoa Year 2022/2023. Available online: https://www.icco.org/wp-content/uploads/Production_QBCS-XLIX-No.-1.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2023).
- Panlibuton, H.; Meyer, M. Value Chain Assessment: Indonesia Cocoa. Accelerated Microenterprise Advancement Project (AMAP) Report, USAID. 2004. Available online: https://ei-ado.aciar.gov.au/sites/default/files/Panlibuton-Meyer(2004)ValueChainAssessmentIndoCocoa_USAID_AMAP.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2023).
- Statistical of National Leading Estate Crops Commodity 2020–2022. Directorate General of Estates. Ministry of Agriculture, In-Donesia. Available online: https://ditjenbun.pertanian.go.id/template/uploads/2022/08/STATISTIK-UNGGULAN-2020-2022.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2023).
- Bustami, M.; Werbrouck, S. Somatic embryogenesis in Elite Indonesian cacao Theobroma cacao L. In Step Wise Protocols for Somatic Embryogenesis of Important Woody Plants; Jain, S.M., Gupta, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslimin; Wijayanti, W.; Anshary, A.; Basri, Z.; Cruz, A.F.; Suwastika, I.N.; Shiina, T. Sulawesi cacao (Theobroma cacao, L.) performances under two different agricultural systems in east coast of Central Sulawesi. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 144, 012066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwastika, I.N.; Muslimin, R.; Aisyah, N.; Rahmansyah, M.; Ishizaki, Y.; Basri, Z.; Shiina, T. Genotyping Based on SSR Marker on Local Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) from Central Sulawesi. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximova, S.N.; Young, A.; Pishak, S.; Guiltinan, M.J. Field performance of Theobroma cacao L. plants propagated via somatic embryogenesis. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2008, 44, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masseret, B.; Gianforcaro, M.; Bouquet, J.F.; Brulard, E.; Florin, B. Somatic embryogenesis applied to the creation of a cacao collection. Malays. Cocoa J. 2009, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Issali, A.E.; Traoré, A.; Ngoran, J.A.K.; Koffi, E.K. Relationship between some Phenological Parameters and Somatic embryogenesis in Theobroma cacao L. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 11, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, C.; Corrêa, F.; Findley, S.; Almeida, A.-A.; Costa, M.; Motamayor, J.C.; Schnell, R.; Marelli, J.-P. Optimization of somatic embryogenesis procedure for commercial clones of Theobroma cacao L. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 15, 1936–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, C.; Fillodeau, A.; Brulard, E.; Breton, D.; Maraschin, S.D.F.; Verdier, D.; Simon, M.; Ducos, J.-P. Indirect somatic embryogenesis of Theobroma cacao L. in liquid medium and improvement of embryo-to-plantlet conversion rate. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2018, 54, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esan, E.B. Micropropagation of Cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.). In Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry; High-Tech and Micropropagation II; Bajaj, Y.P.S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; Volume 18, pp. 96–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pence, V.C.; Hasegawa, P.M.; Janick, J. Initiation and Development of Asexual Embryos of Theobroma cacao L. in vitro. Z. Für Pflanzenphysiol. 1980, 98, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez Baez, O.; Bollon, H.; Eskes, A.; Pétiard, V. SEgenèse somatique de cacaoyer Theobroma cacao L. à partir de pièces florales. Comptes Rendus de l’Académie des Sciences. Série 3 Sci. La Vie 1993, 316, 579–584. [Google Scholar]
- Alemanno, L.; Berthouly, M.; Michaux-Ferrière, N. Histology of somatic embryogenesis from floral tissues cocoa. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 1996, 46, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Traore, A.; Maximova, S.; Guiltinan, M.J. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from floral explants of cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) using thidiazuron. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 1998, 34, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traore, A.; Guiltinan, M.J. Effects of Carbon Source and Explant Type on Somatic Embryogenesis of Four Cacao Genotypes. HortScience 2006, 41, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minyaka, E.; Niemenak, N.; Fotso; Sangare, A.; Omokolo, D.N. Effect of MgSO4 and K2SO4 on somatic embryo differentiation in Theobroma cacao L. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2008, 94, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapi, A.; Tahi, M.G.; Adiko, A.; Mahamadou, S.; Mboup, C.M. Field Performance of Cocoa Somaclones Derived from Somatic embryogenesis. J. Plant Sci. Agri. Res. 2020, 4, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Quainoo, A.K.; Dwomo, B.I. The Effect of TDZ and 2, 4-D Concentrations on the Induction of Somatic SE and embryogenesis in Different Cocoa Genotypes. J. Plant Stud. 2012, 1, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiltinan, M.J.; Maximova, S. Integrated System for Vegetative Propagation of Cacao; Protocol Book. Version 2.1. 17 November 2010; American Cacao Research Institute, United States Department of Agriculture, Pennsylvania State University: State College, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Maximova, S.N.; Alemanno, L.; Young, A.; Ferriere, N.; Traore, A.; Guiltinan, M.J. Efficiency, genotypic variability, and cellular origin of primary and secondary somatic embryogenesis of Theobroma cacao L. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2002, 38, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanel, A.; Gire-Bobin, S.; Labbé, G.; Favereau, P.; Álvarez, M.; Rutte, S.; Pétiard, V. In vitro multiplication and plant re-generation of Theobroma cacao L. via stable embryogenic calli. In Proceedings of the 10th IAPTC Congress, Plant Biotechnology 2002 and Beyond, Orlando, FL, USA, 23–28 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Niemenak, N.; Saare-Surminski, K.; Rohsius, C.; Ndoumou, D.O.; Lieberei, R. Regeneration of somatic embryos in Theobroma cacao L. in temporary immersion bioreactor and analyses of free amino acids in different tissues. Plant Cell Rep. 2008, 27, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustami, M.; Werbrouck, S. Comparison of two protocols for somatic embryo induction in a Sulawesi elite Theobroma cacao L. clone. Acta Hortic. 2017, 1155, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehér, A. Somatic embryogenesis—Stress-induced remodeling of plant cell fate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gene Regul. Mech. 2015, 1849, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkle, S.A.; Parrott, W.A.; Flinn, B.S. Morphogenic Aspects of Somatic Embryogenesis. In In Vitro Embryogenesis in Plants; Thorpe, T.A., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 20, pp. 155–203. ISBN 978-94-010-4217-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemenak, N.; Awah, T.M.; Lieberei, R. Establishment of suspension culture in Theobroma cacao and polyamines associated with cacao embryogenesis. Plant Growth Regul. 2012, 67, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanović, M.D.; Ćuković, K.B.; Subotić, A.R.; Dragićević, M.B.; Simonović, A.D.; Filipović, B.K.; Todorović, S.I. Secondary Somatic Embryogenesis in Centaurium erythraea Rafn. Plants 2021, 10, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulecke, W.; McGranahan, G.H.; Leslie, C.A. Somatic embryogenesis in Walnut (Juglans Species). In Somatic Embryogenesis and Synthetic Seed I. Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry; Bajaj, Y.P.S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; Volume 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te-chato, S.; Hilae, A. High-frequency plant regeneration through secondary somatic embryogenesis in oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq. Var. tenera). J. Agric. Technol. 2007, 3, 345–357. [Google Scholar]
- Lardet, L.; Dessailly, F.; Carron, M.-P.; Montoro, P.; Monteuuis, O. Influences of aging and cloning methods on the capacity for somatic embryogenesis of a mature Hevea brasiliensis genotype. Tree Physiol. 2008, 29, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driver, J.A.; Kuniyuki, A.H. In Vitro Propagation of Paradox Walnut Rootstock. HortScience 1984, 19, 507–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etienne, H.; Berthouly, M. Temporary immersion systems in plant micropropagation. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2002, 69, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A Revised Medium for Rapid Growth and Bioassays with Tobacco Tissue Cultures. Physiol. Plant 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchtler, H.; Waldrop, F.S.; Conner, H.M.; Terry, M.S. Carnoy fixation: Practical and theoretical considerations. Histochem. 1968, 16, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhojwani, S.S.; Razdan, M.K. Plant tissue culture: Theory and Practice, a Revised Edition. In Studies in Plant Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.O.; Barros, E.V.S.A.; Tinoco, A.C.M.B.; Aragao, F.J.L. Repetitive somatic embryogenesis in cacao and optimization of gene expression by particle bombardment. J. Plant Biotechnol. 2002, 4, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.; Furtek, D. Development of an in vitro regeneration system for Theobroma cacao from mature tissues. Plant Sci. 2003, 164, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issali, A.E.; Traore, A.; Koffi, E.K.; N’goran, J.A.K.; Sangare, A. Characterization of callogenic and embryogenic abilities of some genotypes of cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.) under selection in the Cote d’Ivoire. Biotechnology 2008, 7, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- da Silva, T.R.; Cidade, L.C.; Alvim, F.C.; Cascardo, J.C.d.M.; Costa, M.G.C. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in elite clones of Theobroma cacao. Pesqui. Agropecuária Bras. 2008, 43, 1433–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutchouang, R.P.; Tchouatcheu, N.; Niemenak, N. Influence of the position of flowers buds on the tree on somatic embryogenesis of cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.). Int. J. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 8, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Magnaval, C.; Noirot, M.; Verdeil, J.; Blattes, A.; Huet, C.; Grosdemange, F.; Beulé, T.; Buffard-Morel, J. Specific nutritional requirements of coconut calli (Cocos nucifera L.) during somatic embryogenesis induction. J. Plant Physiol. 1997, 150, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelmann, T. Somatic Versus Zygotic embryogenesis: Learning from seeds. Maria Antonietta Germanà and Maurizio Lambardi. In In Vitro embryogenesis in Higher Plants, Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1359, pp. 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.G.; Maheswaran, G. Somatic embryogenesis: Factors Influencing Coordinated Behaviour of Cells as an embryogenic Group. Ann. Bot. 1986, 57, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.S.; Fu, C.H.; Su, P.; Xu, X.P.; Yuan, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, C.F.; Yu, L.J. Mechanisms and effective control of physiological browning phenomena in plant cell cultures. Physiol. Plant. 2016, 156, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstman, A.; Bemer, M.; Boutilier, K. A transcriptional view on somatic embryogenesis. Regeneration 2017, 4, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbatenko, O.; Hakman, I. Desiccation-Tolerant Somatic Embryos of Norway Spruce (Picea abies) Can Be Produced in Liquid Cultures and Regenerated into Plantlets. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2001, 162, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Arnold, S.; Sabala, I.; Bozhkov, P.; Dyachok, J.; Filonova, L. Developmental pathways of somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2002, 69, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducos, J.-P.; Lambot, C.; Pétiard, V. Bioreactors for Coffee Mass Propagation by Somatic embryogenesis. Int. J. Plant Dev. Biol. 2007, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Collin, H.A.; Edwards, S. Plant Cell Culture; BIOS Scientific Publisher: Oxford, UK; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wann, S.R. Somatic Embryogenesis in Woody Species in Horticultural Reviews Volume 10; Janick, J., Ed.; Purdue University, Timber Press: Portland, OR, USA, 1988; pp. 153–177. [Google Scholar]
- Parrott, W.A. Auxin-stimulated somatic embryogenesis from immature cotyledons of white clover. Plant Cell Rep. 1991, 10, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinga, L.A.P.; Fraga, H.P.d.F.; Vieira, L.D.N.; Guerra, M.P. Epigenetics of long-term somatic embryogenesis in Theobroma cacao L.: DNA methylation and recovery of embryogenic potential. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2017, 131, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, G.; Park, Y.-S.; Silva, S.; Neves, L.; Araújo, C.; Santos, C. Factors affecting maintenance, proliferation, and germination of secondary somatic embryos of Eucalyptus globulus Labill. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2008, 95, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, E.L.; Magbanua, Z.V.; Parrott, W.A. A protocol for repetitive somatic embryogenesis from mature peanut epicotyls. Plant Cell Rep. 2000, 19, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasic, D.; Alibert, G.; Skoric, D. Protocols for efficient repetitive and secondary somatic embryogenesis in Helianthus maximiliani (Schrader). Plant Cell Rep. 2001, 20, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldin, A.F.Z.; Ibrahim, H.A. Some biochemical changes and activities of antioxidant enzymes in developing date palm somatic and zygotic embryos in vitro. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2015, 60, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; de Almeida, A.-A.F.; Costa, M.; Britto, D.; Valle, R.; Royaert, S.; Marelli, J.-P. Abnormalities in somatic embryogenesis caused by 2,4-D: An overview. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult. 2019, 137, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondahl, M.R.; Sereduk, T.B.; Chen, Z.; Bellato, C.M.; Liu, S.J.; Bragin, C.H. Somatic Embryogenesis and Plant Re-Generation of cacao. US Patent #5.312.801, 17 May 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, C.; de Almeida, A.-A.F.; Costa, M.; Britto, D.; Correa, F.; Mangabeira, P.; Silva, L.; Silva, J.; Royaert, S.; Marelli, J.-P. Single-base resolution methylomes of somatic embryogenesis in Theobroma cacao L. reveal epigenome modifications associated with somatic embryo abnormalities. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, C.; Fillodeau, A.; Brulard, E.; Verdier, D.; Simon, M.; Landmann, A.; Lausanne, F.; Fontanel, A.; Ducos, J.P.; Buchwalder, A.; et al. Nestlé Cocoa Plan: Cocoa propagation by somatic embryogenesis. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference of the IUFRO Unit 2.09.02 on Woody Plant Production Integrating Genetic and Vegetative Propagation Technologies, Vitoria-Gasteiz, Spain, 8–12 September 2014; Park, Y.S., Bonga, J.M., Eds.; pp. 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Garin, E.; Grenier, E.; March, G.G.-D. Somatic embryogenesis in wild cherry (Prunus avium). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 1997, 48, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cailloux, F.; Julien-Guerrier, J.; Linossier, L.; Coudret, A. Long-term somatic embryogenesis and maturation of somatic embryos in Hevea brasiliensis. Plant Sci. 1996, 120, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atree, S.M.; Fowke, L.C. Micropropagation Through Somatic embryogenesis in Conifers. In Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry; High-Tech and Micro-Propagation I; Bajaj, Y.P.S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; Volume 17, pp. 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jariteh, M.; Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Niknam, V.; Mirmasoumi, M.; Vahdati, K. Developmental changes of protein, proline and some antioxidant enzymes activities in somatic and zygotic embryos of Persian walnut (Juglans regia L.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2015, 122, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengel, Z.; Jelaska, S. The effect of L-proline on somatic embryogenesis in long-term callus culture of Hordeum Vulgare. Acta Bot. Croat. 1986, 45, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Bradaï, F.; Pliego-Alfaro, F.; Sánchez-Romero, C. Long-term somatic embryogenesis in olive (Olea europaea L.): Influence on regeneration capability and quality of regenerated plants. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 199, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landey, R.B.; Cenci, A.; Guyot, R.; Bertrand, B.; Georget, F.; Dechamp, E.; Herrera, J.-C.; Aribi, J.; Lashermes, P.; Etienne, H. Assessment of genetic and epigenetic changes during cell culture ageing and relations with somaclonal variation in Coffea arabica. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult. 2015, 122, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton, D.; Harvengt, L.; Trontin, J.-F.; Bouvet, A.; Favre, J.-M. Long-term subculture randomly affects morphology and subsequent maturation of early somatic embryos in maritime pine. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2006, 87, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.M.; Brar, D.S.; Ahloowalia, B.S. (Eds.) Somaclonal Variation and Induced Mutations in Crop Improvement, vol. 32. In Current Plant Science and Biotechnology in Agriculture; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.F.; Hall, M.A.; De Klerk, G.J. (Eds.) Plant Propagation by Tissue Culture, 3rd ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 355–401. [Google Scholar]
- Dunstan, D.I.; Bethune, T.D. Variability in maturation and germination from white spruce somatic embryos, as affected by age and use of solid or liquid culture. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 1996, 32, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.-Y.; Wetten, A.; Adu-Gyamfi, R. Use of secondary somatic embryos promotes genetic fidelity in cryopreservation of cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.). Agric. Food Sci. 2008, 18, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).