Optimization of Fermentation Conditions for Elevating Limonene Production with Engineered Rhodosporidium toruloides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material and Reagents
2.2. Microbial Strain, Media, and Fermentations
2.3. Single-Factor Effects on Limonene Production
2.4. Orthogonal Experiments for Elevating Limonene Production
2.5. Analytical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Limonene Production Stability of Engineered R. toruloides Strains
3.2. The Impacts of Fermentation Parameters on Limonene Production
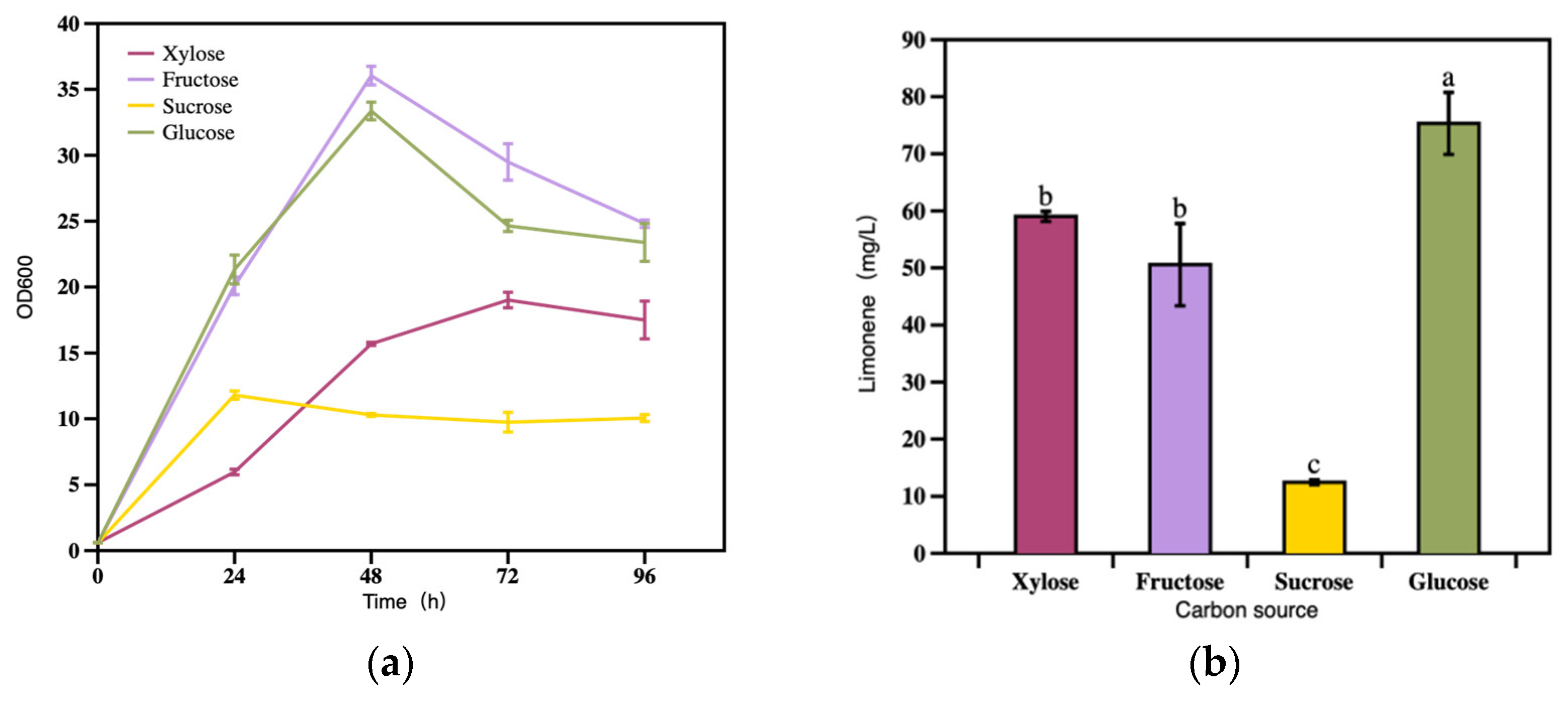
3.2.1. The Effect of Carbon Source on Limonene Production
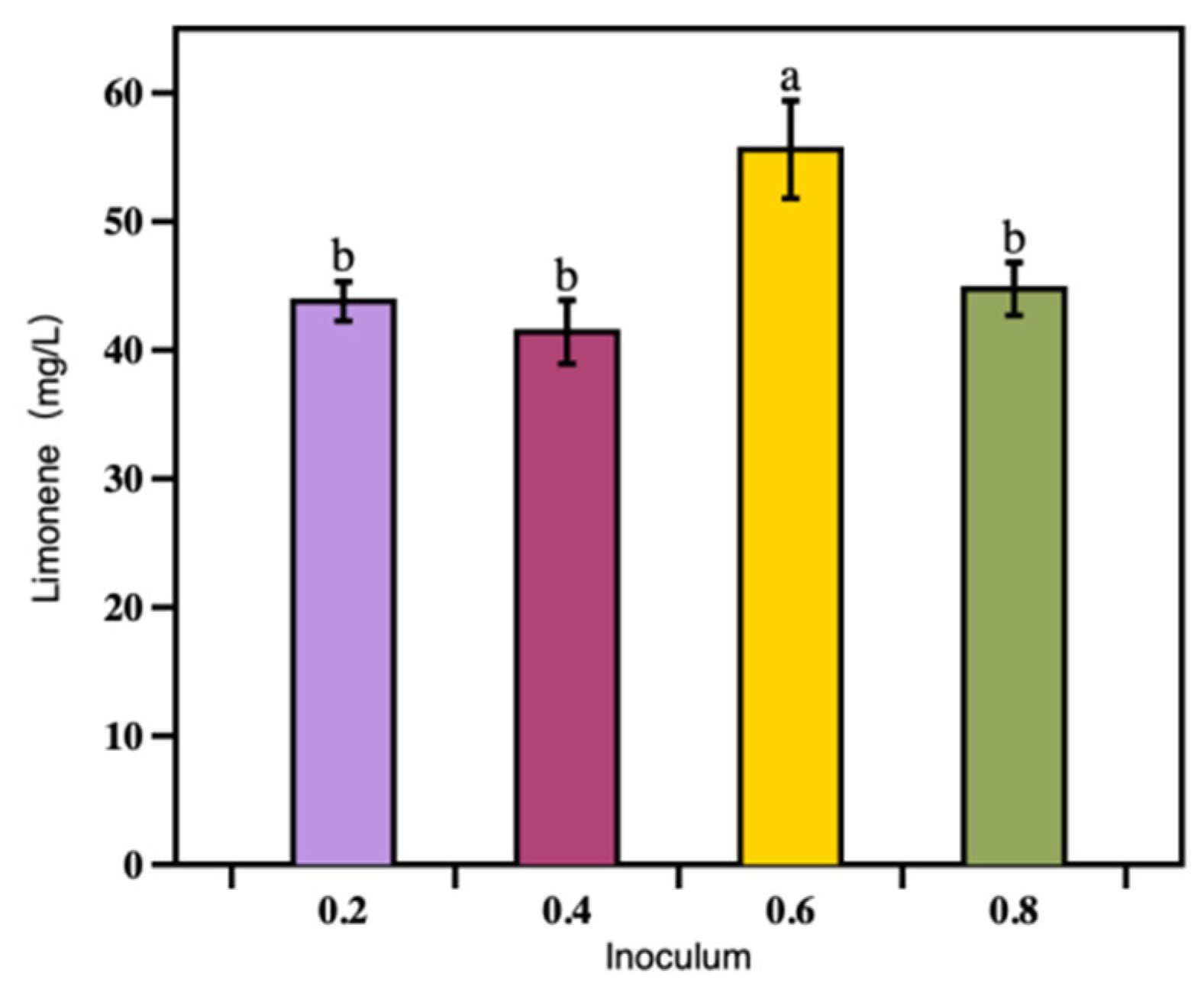
3.2.2. The Effect of Initial Cell Density on Limonene Production
3.2.3. The Effect of Working Volume on Limonene Production
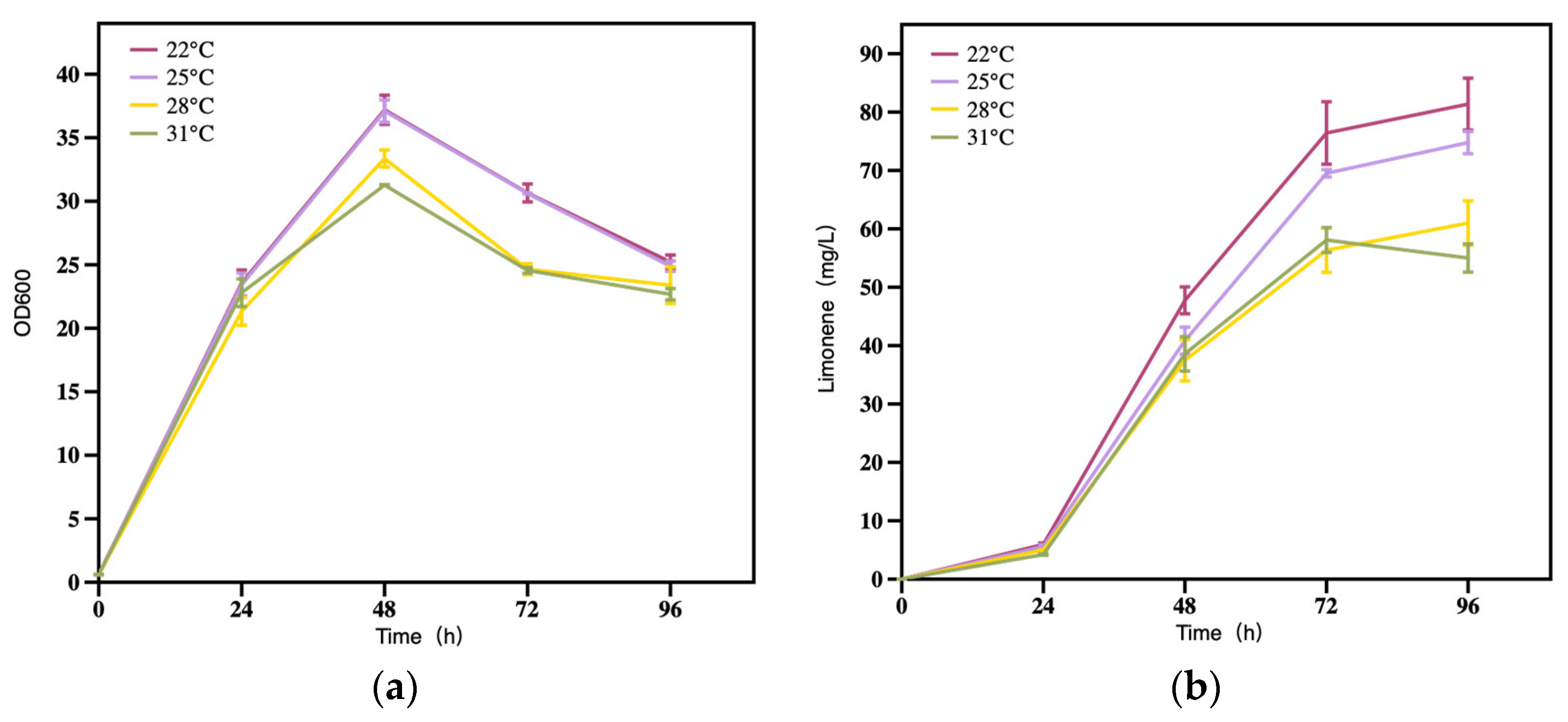
3.2.4. The Effect of Temperature on Limonene Production
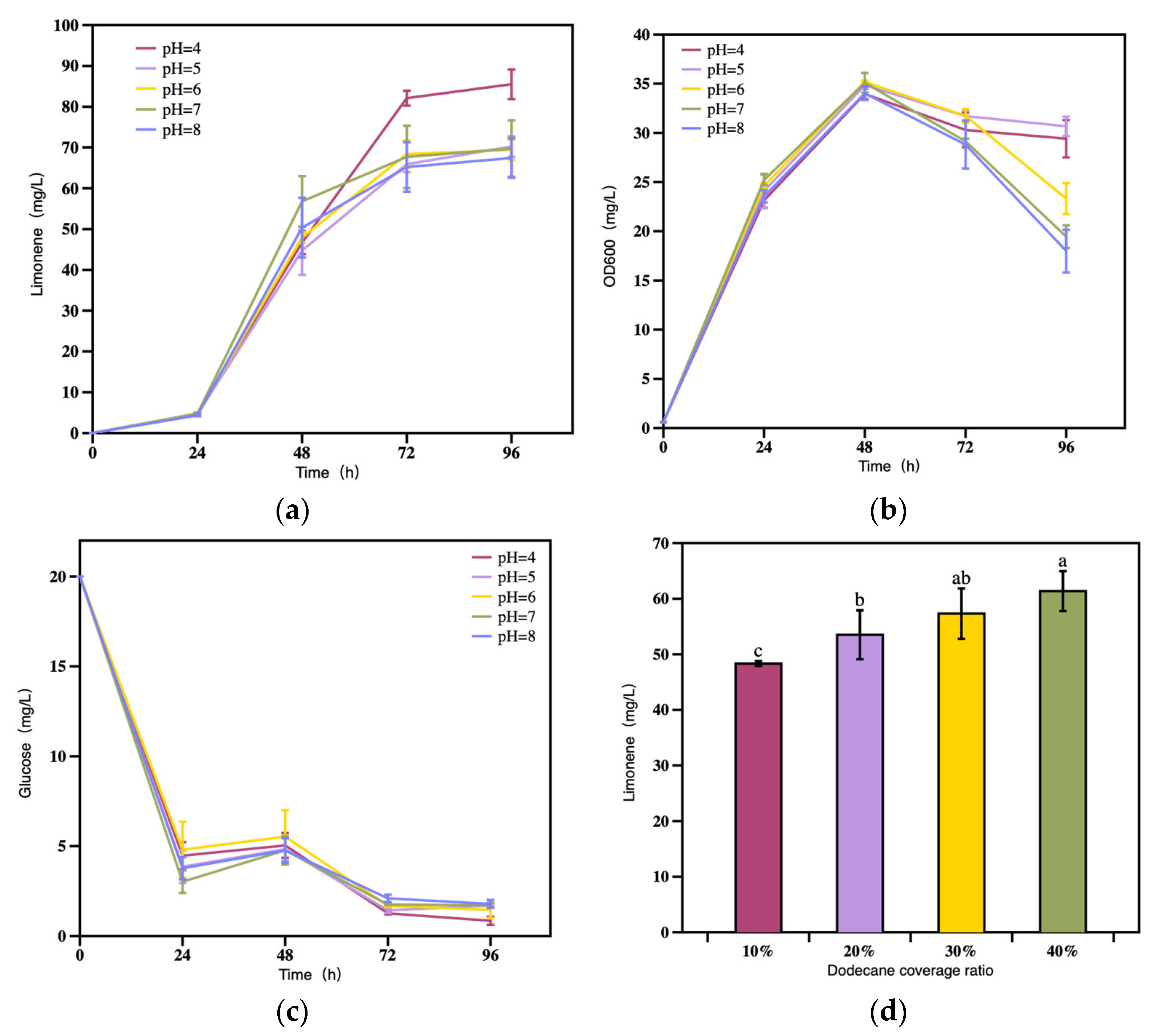
3.2.5. The Effect of Initial pH on Limonene Production
3.2.6. The Effect of Dodecane Coverage Ratio on Limonene Production
3.2.7. The Effect of the Medium on Limonene Production
3.3. Optimization of Limonene Production through Orthogonal Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Ren, Y.; Liu, S.; Jin, G.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Y.J. Microbial production of limonene and its derivatives: Achievements and perspectives. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 44, 107628. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wl, A.; Sw, A.; Mc, B.; Des, A.; Kjlc, D.; Ylac, D. Developing poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan films incorporate with d-limonene: Study of structural, antibacterial, and fruit preservation properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 722–732. [Google Scholar]
- D’Alessio, P.A.; Mirshahi, M.; Bisson, J.F.; Bene, M.C. Skin repair properties of d-Limonene and perillyl alcohol in murine models. Anti Inflamm. Anti Allergy Agents Med. Chem. 2014, 13, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assali, M.; Jaradat, N.; Maqboul, L. The Formation of self-assembled nanoparticles loaded with doxorubicin and D-Limonene for cancer therapy. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 42096–42104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assali, M.; Jaradat, N.; Maqboul, L.; Battista, F.; Remelli, G.; Zanzoni, S.; Bolzonella, D. Valorization of residual orange peels: Limonene recovery, volatile fatty acids, and biogas production. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 6834–6843. [Google Scholar]
- Chubukov, V.; Mingardon, F.; Schackwitz, W.; Baidoo, E.; Mukhopadhyay, A. Acute limonene toxicity in Escherichia coli is caused by limonene hydroperoxide and alleviated by a point mutation in alkyl hydroperoxidase AhpC. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 4690–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Liu, X.; Jiang, G.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Lei, D.; Yuan, Y. Orthogonal engineering of biosynthetic pathway for efficient production of limonene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. ACS Synth. Biol. 2019, 8, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Theodoropoulos, C.; Scrutton, N.S. Techno-economic assessment of microbial limonene production. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 300, 122666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongedijk, E.; Cankar, K.; Buchhaupt, M. Biotechnological production of limonene in microorganisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2016, 100, 2927–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolf, J.; Julsing, M.K.; Rosenthal, K. A gram-scale limonene production process with engineered Escherichia coli. Molecules 2020, 25, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cheng, S.; Cao, J.; Qao, J.; Zhao, G.R. Systematic optimization of limonene production in engineered Escherichia coli. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7087–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qiao, J.; Zhao, G.R. Combinatorial engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for improving limonene production. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 176, 108155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusséaux, S.; Wajn, W.T.; Liu, Y.; Ignea, C.; Kampranis, S.C. Transforming yeast peroxisomes into microfactories for the efficient production of high-value isoprenoids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 31789–31799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, B.; Wei, L.; Lv, Y.; Chen, J.; Hua, Q. Elevating limonene production in oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica via genetic engineering of limonene biosynthesis pathway and optimization of medium composition. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2019, 24, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, A. Engineering the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica to produce limonene from waste cooking oil. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, M.; Ren, Y.; Jin, G.; Tao, Y.; Lyu, L.; Zhao, Z.K.; Yang, X. Engineering Rhodosporidium toruloides for limonene production. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2021, 14, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, T.; Doriano, C. Optimizing scale-up fermentation processes. Trends Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 103–105. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Song, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, J. Rhodotorula toruloides: An ideal microbial cell factory to produce oleochemicals, carotenoids, and other products. World J. Microb. Biol. 2022, 38, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Zhao, Z.K. Effects of biomass hydrolysis by-products on oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 136, S363–S364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiselman, G.M.; Zhuang, X.; Kirby, J.; Tran-Gyamfi, M.B.; Gladden, J.M. Production of ent-kaurene from lignocellulosic hydrolysate in Rhodosporidium toruloides. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaegashi, J.; Kirby, J.; Ito, M.; Sun, J.; Gladden, J.M. Rhodosporidium toruloides: A new platform organism for conversion of lignocellulose into terpene biofuels and bioproducts. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, H.; Bonturi, N.; Kerkhoven, E.; Miranda, E.; Lahtvee, P. C/N ratio and carbon source-dependent lipid production profiling in Rhodotorula toruloides. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2020, 104, 2639–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhao, H.; Shi, S. Engineering oleaginous yeast Rhodotorula toruloides for overproduction of fatty acid ethyl esters. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2021, 14, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galafassi, S.; Cucchetti, D.; Pizza, F.; Franzosi, G.; Bianchi, D.; Compagno, C. Lipid production for second generation biodiesel by the oleaginous yeast Rhodotorula graminis. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 111, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiza, Z.; Maskat, M.Y.; Liew, S.L.; Mamot, S. Fermentation of morinda citrifolia extract by Saccharomyces cerevisiae as affected by substrate concentration, inoculum size, temperature and fermentation time. Int. Food Res. J. 2013, 20, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar]
- Pursell, M.R.; Mendes-Tatsis, M.A.; Stuckey, D.C. Effect of fermentation broth and biosurfactants on mass transfer During liquid–liquid extraction. Biotech. Bioeng. 2004, 80, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arino, J. Integrative responses to high pH stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Omics. 2010, 14, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra-Cardona, A.; Canadell, D.; Arino, J. Coordinate responses to alkaline pH stress in budding yeast. Microb. Cell. 2015, 2, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.S.; Miranda, S.M.; Lopes, M.; Belo, I. Factors affecting microbial lipids production by Yarrowia lipolytica strains from volatile fatty acids: Effect of co-substrates, operation mode and oxygen. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 331, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakov, T.; Kane, P.M. Regulation of vacuolar proton-translocating ATPase activity and assembly by extracellular pH. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 23771–23778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagtap, S.; Bedekar, A.; Liu, J.; Jin, S.; Rao, C.V. Production of galactitol from galactose by the oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides IFO0880. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, T.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Campbell, K.; Nielsen, J.; Chen, Y. Rewiring carbon metabolism in yeast for high level production of aromatic chemicals. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Level | Medium Volume (mL) | Temperature (°C) | pH | Dodecane Coverage Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 | 22 | 4 | 20 |
| 2 | 50 | 25 | 5 | 30 |
| 3 | 75 | 28 | 6 | 40 |
| Number | A | B | C | D | Limonene (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 | 22 | 4 | 20 | 114.2 |
| 2 | 25 | 25 | 6 | 30 | 146.5 |
| 3 | 25 | 28 | 5 | 40 | 193.0 |
| 4 | 50 | 22 | 6 | 40 | 358.1 |
| 5 | 50 | 25 | 5 | 20 | 115.7 |
| 6 | 50 | 28 | 4 | 30 | 199.5 |
| 7 | 75 | 22 | 5 | 30 | 235.1 |
| 8 | 75 | 25 | 4 | 40 | 298.8 |
| 9 | 75 | 28 | 6 | 20 | 322.3 |
| K1 | 453.7 | 707.4 | 612.5 | 552.3 | |
| K2 | 673.3 | 561.0 | 543.7 | 581.0 | |
| K3 | 856.2 | 714.7 | 827.0 | 849.9 | |
| k1 | 151.2 | 235.8 | 204.2 | 184.1 | |
| k2 | 224.4 | 187.0 | 181.2 | 193.7 | |
| k3 | 285.4 | 238.2 | 275.7 | 283.3 | |
| R | 134.2 | 51.2 | 94.4 | 99.2 | |
| Major factor | ADCB | ||||
| Optimal combination | A3D3C3B3 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, D.; Gao, Q.; Zheng, X.; Liu, S.; Qi, Q.; Wang, X.; Yang, X. Optimization of Fermentation Conditions for Elevating Limonene Production with Engineered Rhodosporidium toruloides. Fermentation 2023, 9, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9050431
Zhao D, Gao Q, Zheng X, Liu S, Qi Q, Wang X, Yang X. Optimization of Fermentation Conditions for Elevating Limonene Production with Engineered Rhodosporidium toruloides. Fermentation. 2023; 9(5):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9050431
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Di, Qidou Gao, Xiaochun Zheng, Sasa Liu, Qingsheng Qi, Xue Wang, and Xiaobing Yang. 2023. "Optimization of Fermentation Conditions for Elevating Limonene Production with Engineered Rhodosporidium toruloides" Fermentation 9, no. 5: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9050431
APA StyleZhao, D., Gao, Q., Zheng, X., Liu, S., Qi, Q., Wang, X., & Yang, X. (2023). Optimization of Fermentation Conditions for Elevating Limonene Production with Engineered Rhodosporidium toruloides. Fermentation, 9(5), 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9050431





