Analysis of the Comparative Growth Kinetics of Paenarthrobacter ureafaciens YL1 in the Biodegradation of Sulfonamide Antibiotics Based on Substituent Structures and Substrate Toxicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Bacterial Strain
2.2. Medium and Culture Conditions
2.3. Determination of the Biomass
2.4. Determination of the Degradation Rate of SAs
2.5. Kinetic Analysis of the Degradation of Sulfonamide Antibiotics
2.6. Density Functional Theory (DFT) Method
3. Results and Discussion
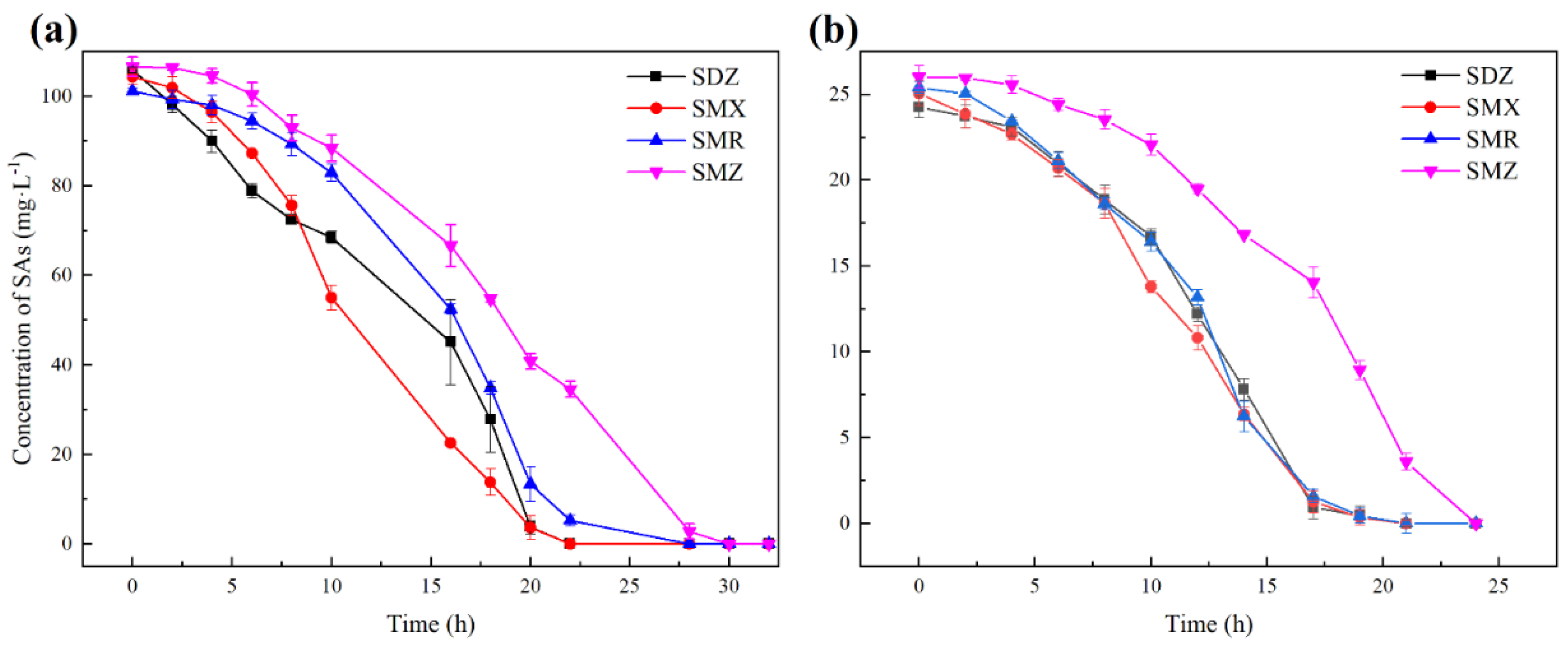
3.1. Substrate Spectrum of Strain YL1
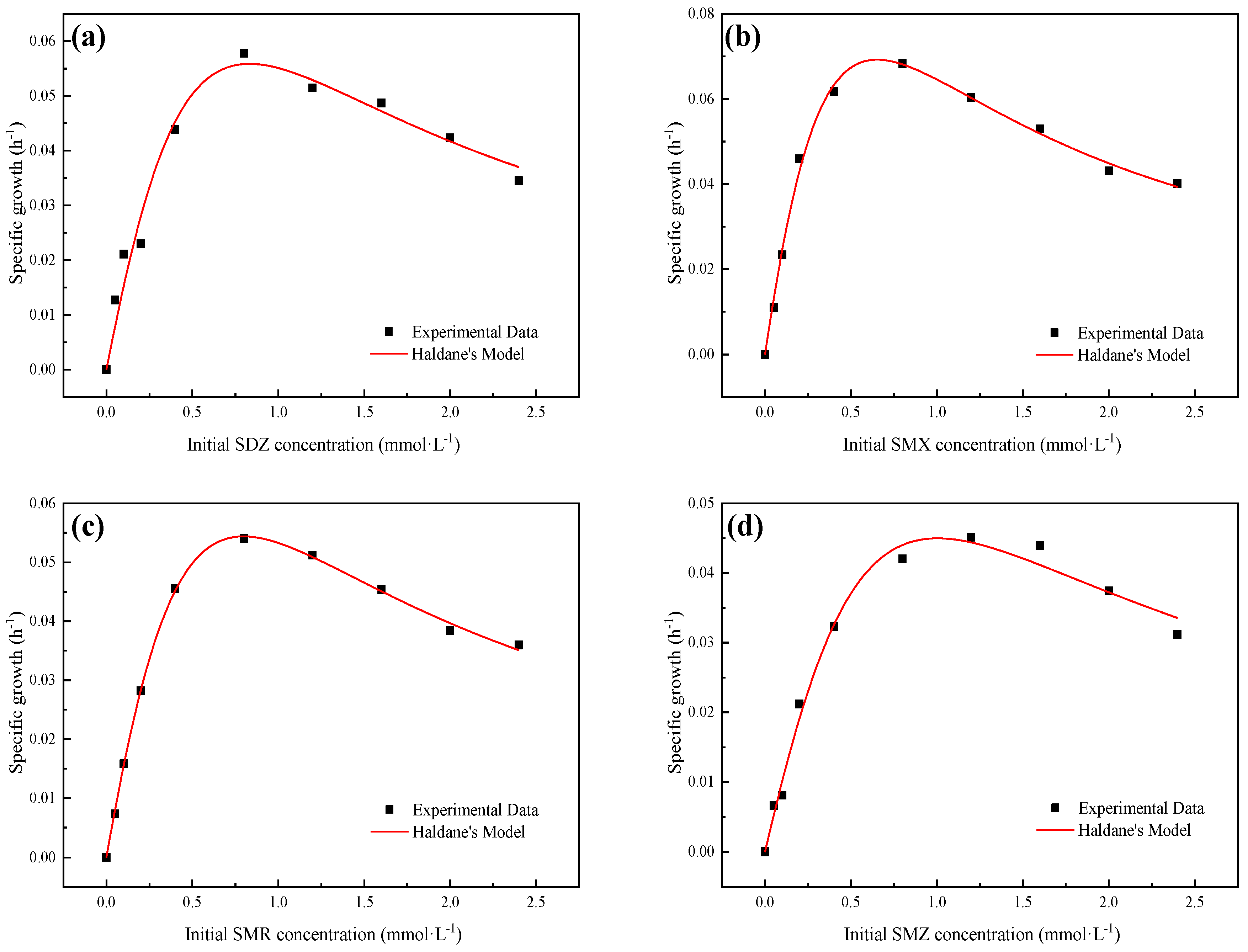
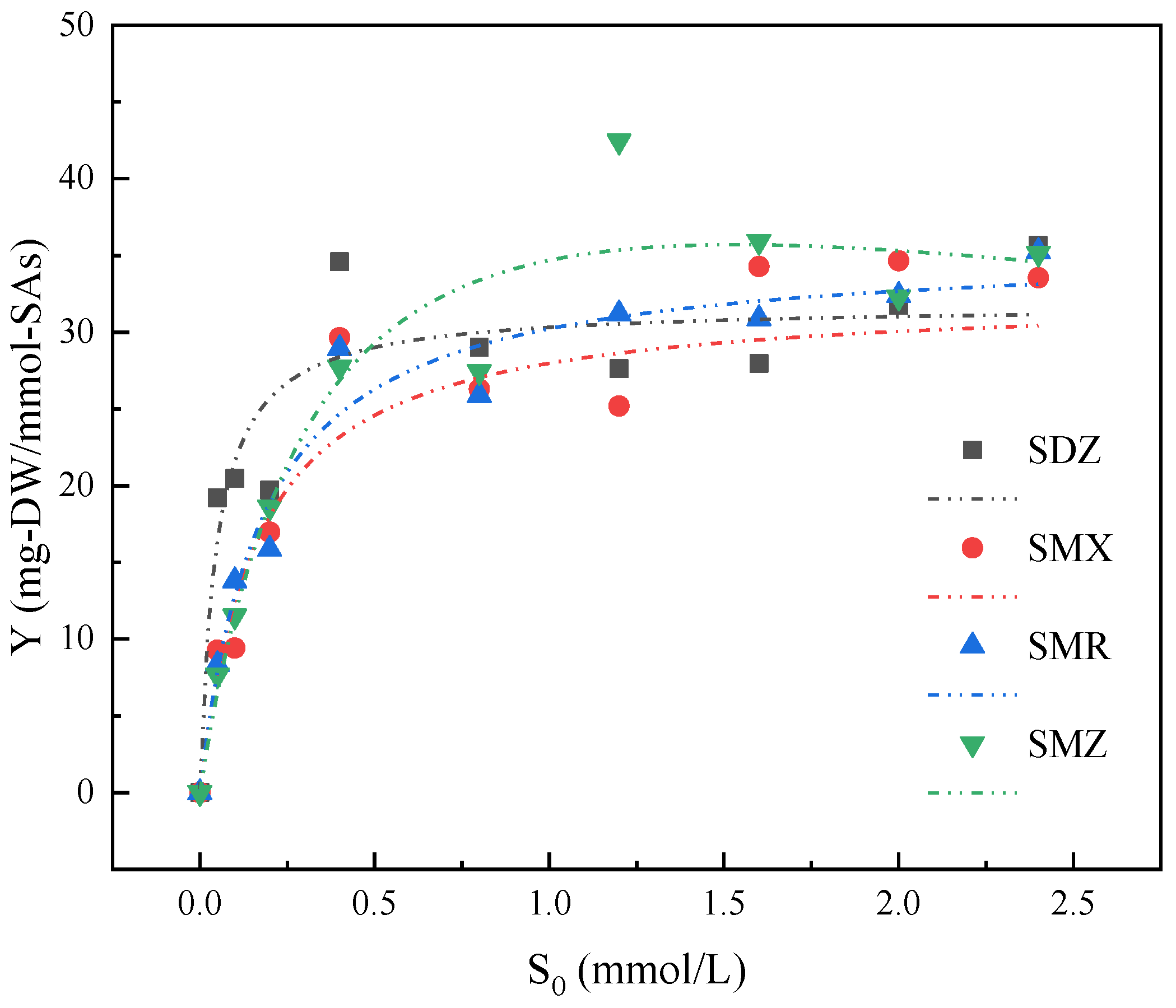
3.2. Growth Kinetics of Strain YL1
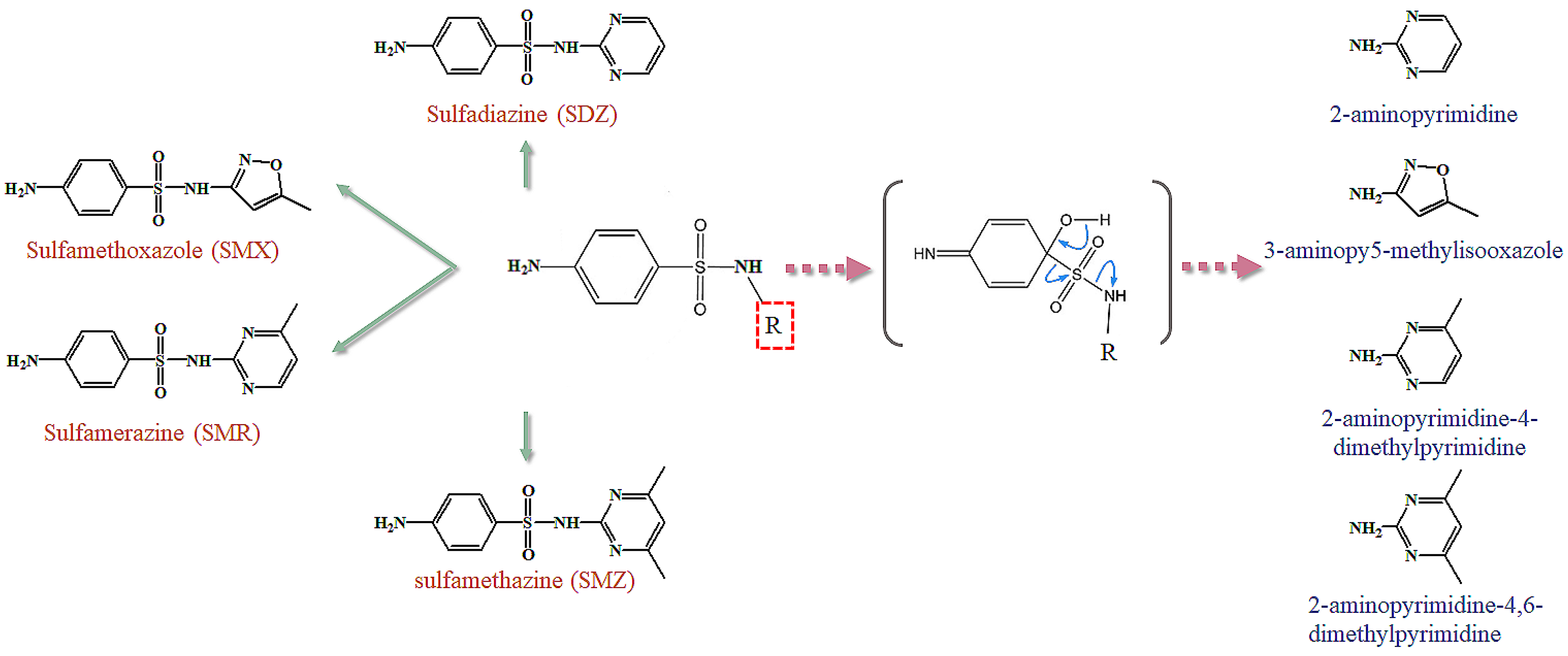
3.3. Effect of the Substitution Groups on the Reactivity of SAs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Yuan, R.; Chen, H.; Wang, F.; Zhou, B. Anaerobic biodegradation of four sulfanilamide antibiotics: Kinetics, pathways and microbiological studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- K’Oreje, K.O.; Kandie, F.J.; Vergeynst, L.; Abira, M.A.; Van Langenhove, H.; Okoth, M.; Demeestere, K. Occurrence, fate and removal of pharmaceuticals, personal care products and pesticides in wastewater stabilization ponds and receiving rivers in the nzoia basin, kenya. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ondarza, P.M.; Haddad, S.P.; Avigliano, E.; Miglioranza, K.S.B.; Brooks, B.W. Pharmaceuticals, illicit drugs and their metabolites in fish from argentina: Implications for protected areas influenced by urbanization. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Ni, B.-J.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, J. Unravelling kinetic and microbial responses of enriched nitrifying sludge under long-term exposure of cephalexin and sulfadiazine. Water Res. 2020, 173, 115592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiki, C.; Rashid, A.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Yu, C.P.; Sun, Q. Dissipation of antibiotics by microalgae: Kinetics, identification of transformation products and pathways. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sella, C.F.; Carneiro, R.B.; Sabatini, C.A.; Sakamoto, I.K.; Zaiat, M. Can different inoculum sources influence the biodegradation of sulfamethoxazole antibiotic during anaerobic digestion? Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 39, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, Y.; Su, X.; Fu, Y.; Ma, F.; Guo, H. Biodiversity, isolation and genome analysis of sulfamethazine-degrading bacteria using high-throughput analysis. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 2020, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of typical antibiotics in the surface waters of seven major rivers, China. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2021, 23, 1088–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S.G.; Ahammad, S.Z. COVID-19 and antimicrobial resistance: A cross-study. Sci Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; An, Z.; Moran, M.J.; Liu, F. Recognition of typical antibiotic residues in environmental media related to groundwater in china (2009–2019). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 122813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hao Ngo, H.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D. Impacts of sulfadiazine on the performance and membrane fouling of a hybrid moving bed biofilm reactor-membrane bioreactor system at different c/n ratios. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 318, 124180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.L.; Lu, Y.X.; Yang, X.L.; Xu, H.; Singh, R.P.; Du, K.X.; Yang, Y.L. Degradation of sulfamethoxazole in low-C/N ratio wastewater by a novel membrane bioelectrochemical reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 305, 123029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, A.; Zhao, B.; Dong, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, P.; Yue, X. Efficient elimination of sulfadiazine in an anaerobic denitrifying circumstance: Biodegradation characteristics, biotoxicity removal and microbial community analysis. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Wang, Y.; Shan, X.; Ma, F.; Guo, H. Harnessing paenarthrobacter ureafaciens yl1 and pseudomonas koreensis yl2 interactions to improve degradation of sulfamethoxazole. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dai, Y.; Tao, R.; Yang, Y. Bibliometric analysis of microbial sulfonamide degradation: Development, hotspots and trend directions. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.H.; Hu, Y.; Liang, D.; Chenga, J.; Chena, Y. Bioaugmentation of moving bed biofilm reactor (mbbr) with achromobacter jl9 for enhanced sulfamethoxazole (smx) degradation in aquaculture wastewater. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J. Biodegradation and metabolic pathway of sulfamethoxazole by a novel strain Acinetobacter sp. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Hu, H.; Li, W.; Hong, X.; Cai, D.; Lin, J.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y. Investigating the biodegradation of sulfadiazine in soil using enterobacter cloacae t2 immobilized on bagasse. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, R.; Deng, Y.; Liu, J.; Fu, W.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Li, B. Genomic characterization, kinetics, and pathways of sulfamethazine biodegradation by Paenarthrobacter sp. A01. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 104961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouju, H.; Ricken, B.; Beffa, T.; Corvini, P.F.; Kolvenbach, B.A. Isolation of bacterial strains capable of sulfamethoxazole mineralization from an acclimated membrane bioreactor. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Li, A.; Cui, D.; Cai, R.; Ma, F.; Wang, Y. Biodegradation and metabolic pathway of sulfamethoxazole by pseudomonas psychrophila ha-4, a newly isolated cold-adapted sulfamethoxazole-degrading bacterium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 4671–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.H.; Hu, Y. Application of a heavy metal-resistant Achromobacter sp. For the simultaneous immobilization of cadmium and degradation of sulfamethoxazole from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 124032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Mao, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, C.; Zhang, T. Aerobic degradation of sulfadiazine by arthrobacter spp.: Kinetics, pathways and genomic characterization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9566–9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegedus, B.; Kos, P.B.; Balint, B.; Maroti, G.; Gan, H.M.; Perei, K.; Rakhely, G. Complete genome sequence of novosphingobium resinovorum sa1, a versatile xenobiotic-degrading bacterium capable of utilizing sulfanilic acid. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 241, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Li, X.; Liu, F.; Fu, W.; Lin, L.; Li, B. Comparison of chemical and biological degradation of sulfonamides: Solving the mystery of sulfonamide transformation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricken, B.; Kolvenbach, B.A.; Bergesch, C.; Benndorf, D.; Kroll, K.; Strnad, H.; Vlcek, C.; Adaixo, R.; Hammes, F.; Shahgaldian, P.; et al. Fmnh2-dependent monooxygenases initiate catabolism of sulfonamides in Microbacterium sp. Strain br1 subsisting on sulfonamide antibiotics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, S.P.; Tan, H.T.; Sudesh, K.; Adnan, R.; Ting, A.S.Y.; Ng, S.L. Phenol and p-nitrophenol biodegradations by acclimated activated sludge: Influence of operational conditions on biodegradation kinetics and responding microbial communities. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Sun, Y.; Li, A.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J. Activation of accumulated nitrite reduction by immobilized pseudomonas stutzeri t13 during aerobic denitrification. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 187, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Hu, X. Biodegradation of 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol via a hydroxyquinol pathway by a gram-negative bacterium, Cupriavidus sp. Strain cnp-8. AMB Express 2018, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, I.; Jasmine, J.; Mukherji, S. Biodegradation of pyrene by a pseudomonas aeruginosa strain rs1 isolated from refinery sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 166, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Xu, L.; Fang, S.; Chen, W.; Hu, X. Microbial degradation kinetics and molecular mechanism of 2,6-dichloro-4-nitrophenol by a cupriavidus strain. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Button, D.K. Nutrient-limited microbial growth kinetics: Overview and recent advances. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1993, 63, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhshi, Z.; Najafpour, G.; Kariminezhad, E.; Pishgar, R.; Mousavi, N.; Taghizade, T. Growth kinetic models for phenol biodegradation in a batch culture of pseudomonas putida. Environ. Technol. 2011, 33, 1835–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Zheng, J.; Xu, J.; Dang, Z.; Zhang, L. Insights into sulfamethazine adsorption interfacial interaction mechanism on mesoporous cellulose biochar: Coupling dft/fot simulations with experiments. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, W.; Yin, R.; Du, J.; Wu, Q.; Luo, H.; Liu, B.; Sseguya, F.; Ren, N. Biochar-induced fe(iii) reduction for persulfate activation in sulfamethoxazole degradation: Insight into the electron transfer, radical oxidation and degradation pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Wei, Z.; Spinney, R.; Zhang, Z.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Gao, L.; Chai, L.; Wang, D.; Xiao, R. Uv direct photolysis of sulfamethoxazole and ibuprofen: An experimental and modelling study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 343, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingerslev, F.; Halling-Sorensen, B. Biodegradability properties of sulfonamides in activated sludge. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2000, 19, 2467–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Ma, X.; Liang, B.; Zhang, L.; Kong, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, A. Complete genome sequences of the antibiotic sulfamethoxazole-mineralizing bacteria Paenarthrobacter sp. P27 and Norcardiodes sp. N27. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.J.M.; Reis, A.C.; Ricken, B.; Kolvenbach, B.A.; Manaia, C.M.; Corvini, P.F.X.; Nunes, O.C. Biodegradation of sulfamethoxazole and other sulfonamides by Achromobacter denitrificans pr1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 280, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedwell, D.B. Effect of low temperature on microbial growth: Lowered affinity for substrates limits growth at low temperature. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1999, 30, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Su, Y.; Liu, N.; Hong, M. Effects of temperature, ph, and salinity on the growth kinetics of Pseudomonas sp. Nb-1, a newly isolated cold-tolerant, alkali-resistant, and high-efficiency nitrobenzene-degrading bacterium. Environ. Technol. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramparo, L.; Suarez-Ojeda, M.E.; Perez, J.; Carrera, J. Kinetics of aerobic biodegradation of dihydroxybenzenes by a p-nitrophenol-degrading activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Guo, W.; Ren, N.; Zeng, L.; Zhu, M. New insight into the substituents affecting the peroxydisulfate nonradical oxidation of sulfonamides in water. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurkan, Y.Y.; Turkten, N.; Hatipoglu, A.; Cinar, Z. Photocatalytic degradation of cefazolin over n-doped tio2 under uv and sunlight irradiation: Prediction of the reaction paths via conceptual dft. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 184, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Liu, J.; Abu-Hamdeh, N.H.; Bezzina, S.; Eshaghi Malekshah, R. Molecular dynamics and quantum simulation of different cationic dyes removal from contaminated water using uio-66 (zr)-(cooh)2 metal–organic framework. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 349, 118085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Pan, J.; Zou, Q.; Wu, M.; Wang, H.; Xu, G. Electron beam irradiation of typical sulfonamide antibiotics in the aquatic environment: Kinetics, removal mechanisms, degradation products and toxicity assessment. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.Y.; Carvalho, G.; Reis, A.C.; Nunes, O.C.; Reis, M.A.M.; Oehmen, A. Impact of biogenic substrates on sulfamethoxazole biodegradation kinetics by achromobacter denitrificans strain pr1. Biodegradation 2017, 28, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Wu, J.; Meng, F.; Liu, J. Natural attenuation of sulfometuron-methyl in seawater: Kinetics, intermediates, toxicity change and ecological risk assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 313, 114980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.-H.; Kuo, T.-H.; Chen, Y.-E.; Huang, C.-H.; Hsu, C.-C.; Lin, A.Y.-C. Substructure reactivity affecting the manganese dioxide oxidation of cephalosporins. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9188–9195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| t·min−1 | Methanol (%) | 0.1% Formic Acid (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 90 |
| 10 | 50 | 50 |
| 11 | 10 | 90 |
| 12 | 10 | 90 |
| Haldane Model | μmax (1·h−1) | KS (mmol·L−1) | Ki (mmol·L−1) | R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDZ | 0.304 ± 0.287 | 1.858 ± 2.042 | 0.372 ± 0.419 | 0.968 | 0.164 | |
| SMX | 0.311 ± 0.083 | 1.139 ± 0.367 | 0.373 ± 0.121 | 0.995 | 0.273 | |
| SMR | 0.302 ± 0.055 | 1.817 ± 0.383 | 0.351 ± 0.076 | 0.999 | 0.166 | |
| SMZ | 0.285 ± 0.226 | 2.684 ± 2.41 | 0.376 ± 0.351 | 0.989 | 0.106 |
| SDZ | −6.246 | −1.661 | 4.585 |
| SMX | −6.337 | −1.288 | 5.049 |
| SMR | −6.238 | −1.551 | 4.687 |
| SMZ | −6.235 | −1.44 | 4.795 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, L.; Wang, Y.; Xin, J.; Ma, F.; Guo, H. Analysis of the Comparative Growth Kinetics of Paenarthrobacter ureafaciens YL1 in the Biodegradation of Sulfonamide Antibiotics Based on Substituent Structures and Substrate Toxicity. Fermentation 2022, 8, 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120742
Yu L, Wang Y, Xin J, Ma F, Guo H. Analysis of the Comparative Growth Kinetics of Paenarthrobacter ureafaciens YL1 in the Biodegradation of Sulfonamide Antibiotics Based on Substituent Structures and Substrate Toxicity. Fermentation. 2022; 8(12):742. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120742
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Lan, Yingning Wang, Junjie Xin, Fang Ma, and Haijuan Guo. 2022. "Analysis of the Comparative Growth Kinetics of Paenarthrobacter ureafaciens YL1 in the Biodegradation of Sulfonamide Antibiotics Based on Substituent Structures and Substrate Toxicity" Fermentation 8, no. 12: 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120742
APA StyleYu, L., Wang, Y., Xin, J., Ma, F., & Guo, H. (2022). Analysis of the Comparative Growth Kinetics of Paenarthrobacter ureafaciens YL1 in the Biodegradation of Sulfonamide Antibiotics Based on Substituent Structures and Substrate Toxicity. Fermentation, 8(12), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120742







