Effect of Inoculation of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Fibrolytic Enzymes on Microbiota in the Terminal and Aerobically Exposed Short-Growing Season Whole-Plant Corn Silage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Corn Silage
2.2. Determination of Microbial Composition in Terminal Silage
2.3. Determination of Microbial Compositions in Aerobically Exposed Silages
2.4. DNA Extraction, Quantification, and Quality Assessment
2.5. Analysis of the Composition of the Bacteria and Fungi Communities by Next-Generation Sequencing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
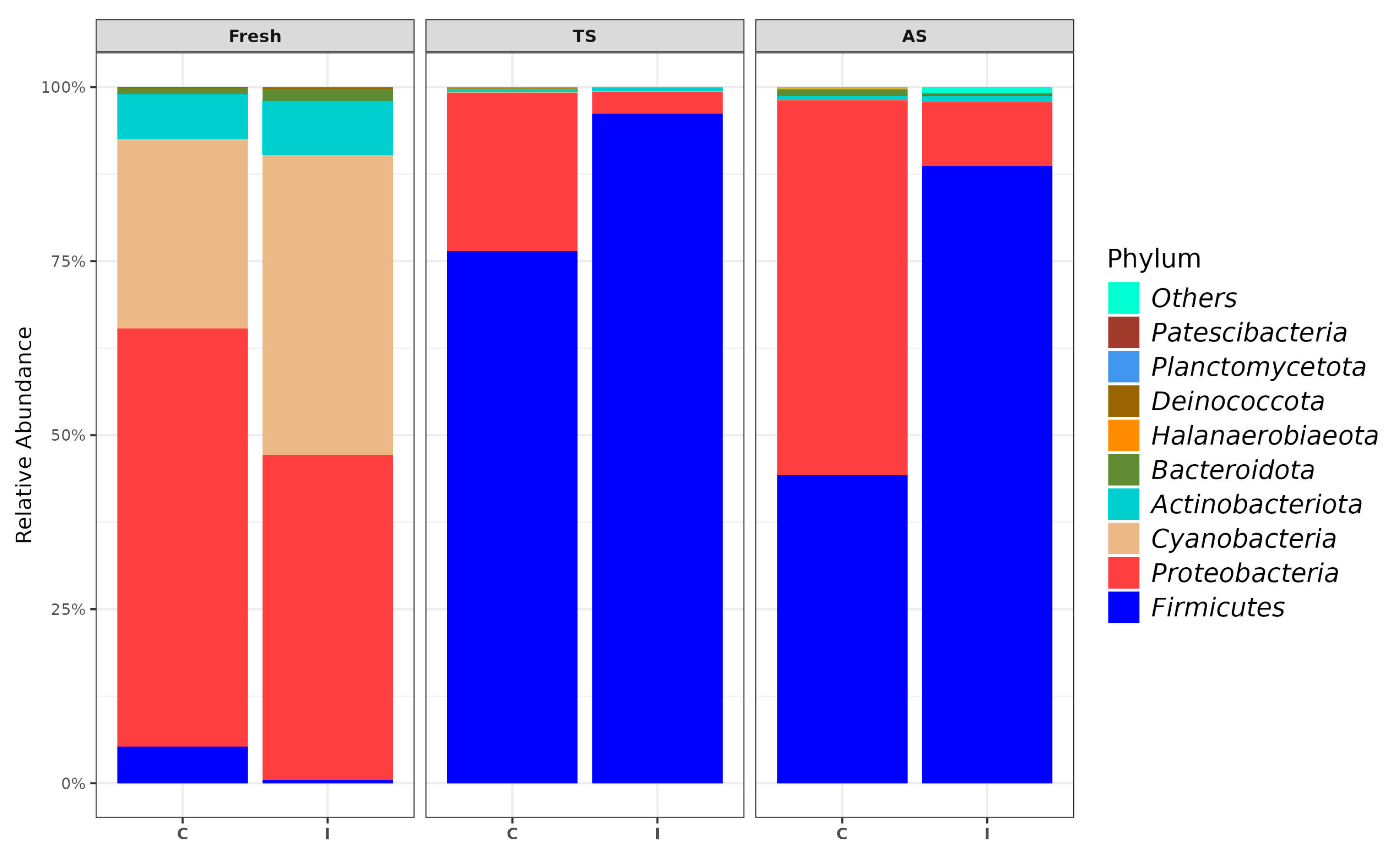
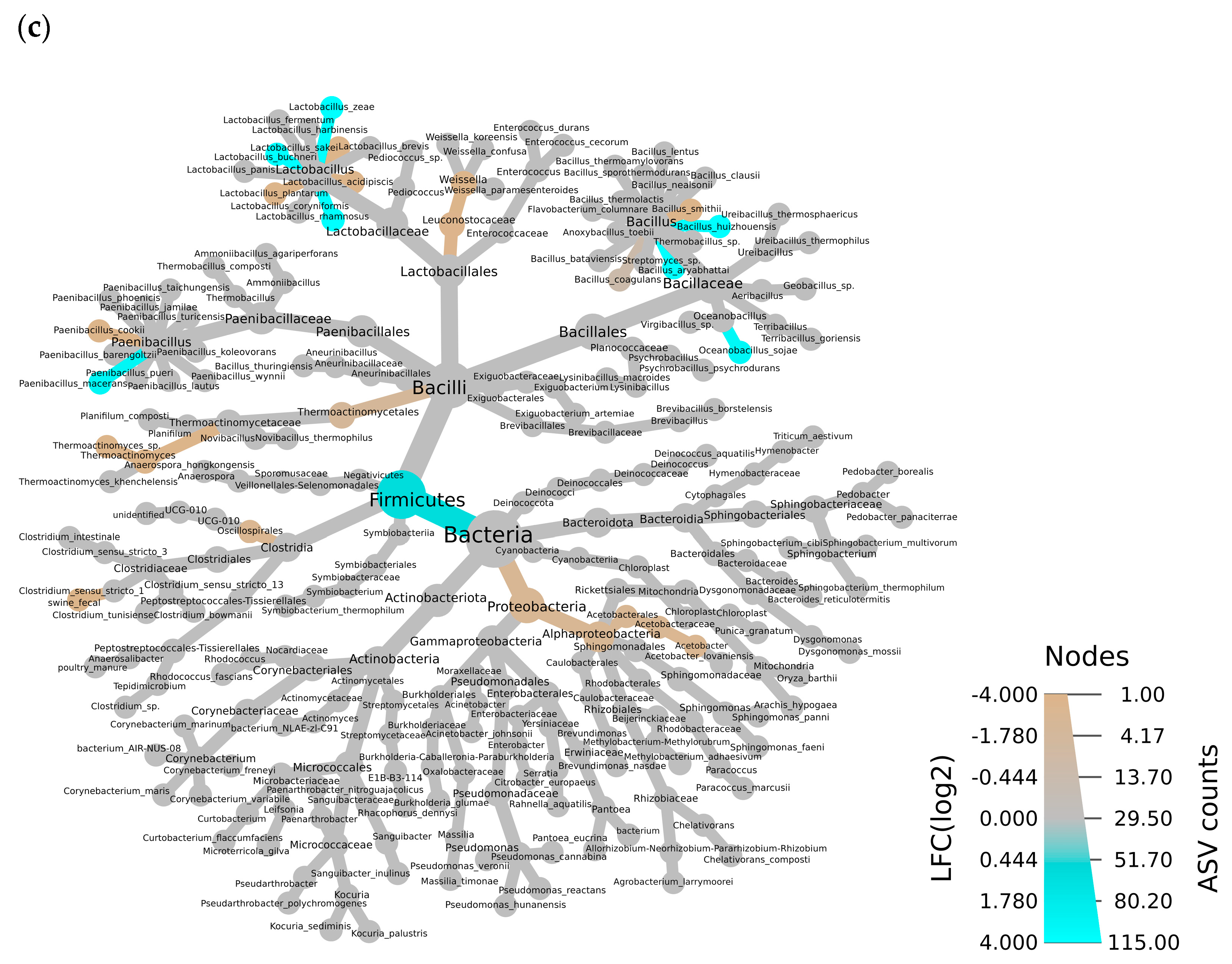
3.1. Bacterial Community in TS and AS
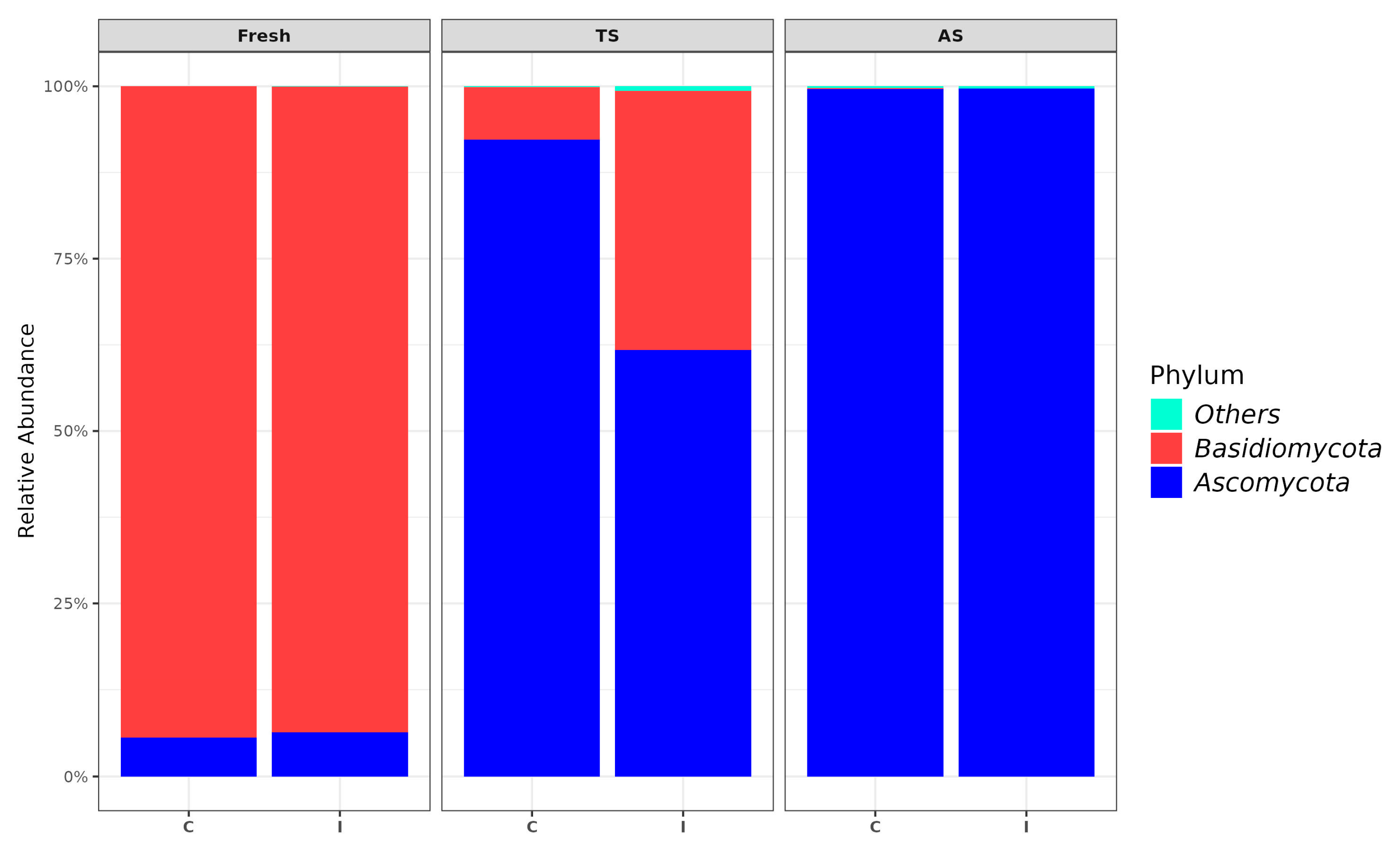
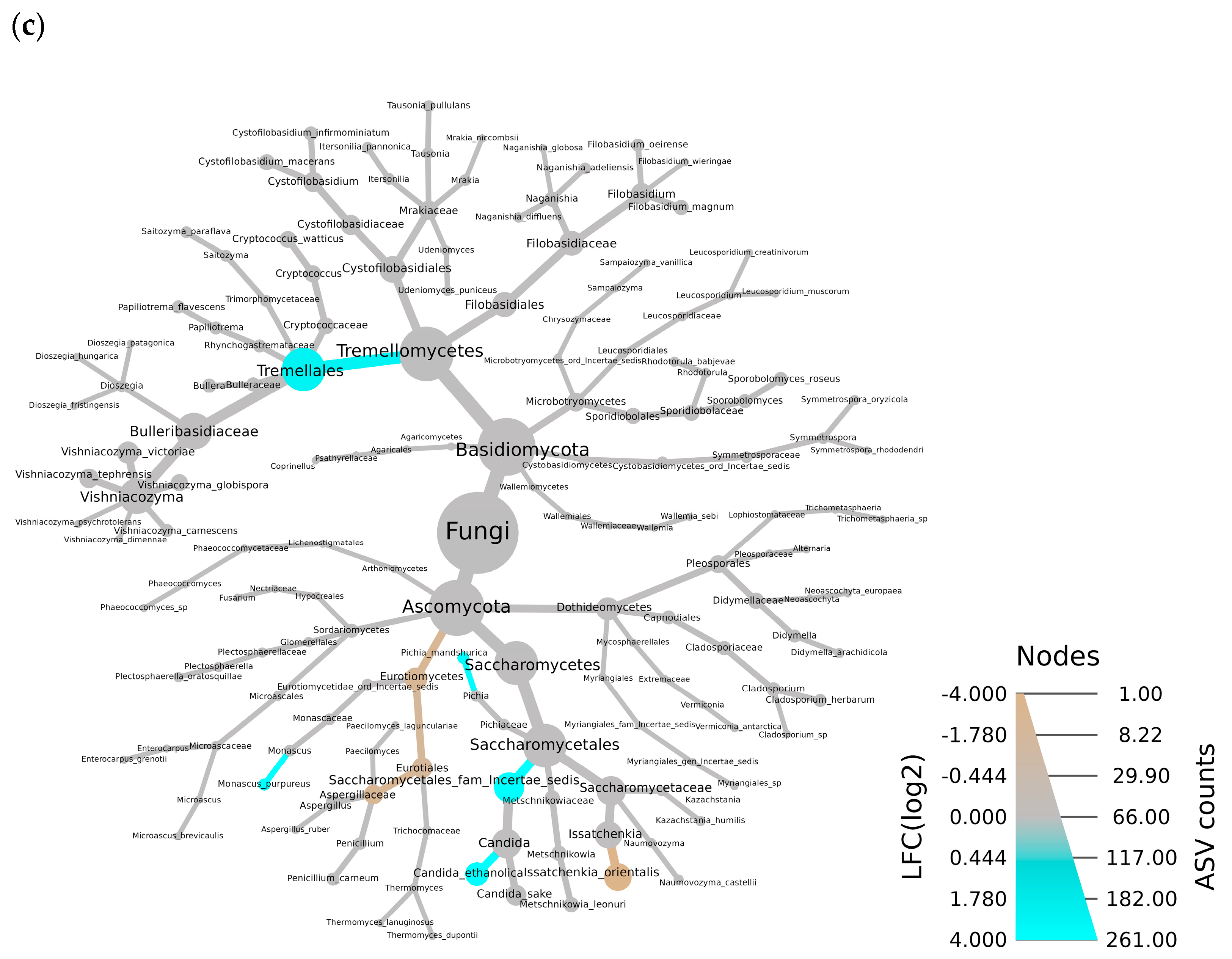
3.2. Fungal Community in TS and AS
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of the Additive on the Bacterial Community in TS and AS
4.2. Effects of the Additive on the Fungal Community in TS and AS
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AS | Aerobically exposed silage |
| ASV | Amplicon sequence variant |
| C | Uninoculated silage |
| cfu | Colony-forming unit |
| DM | Dry matter |
| I | Inoculated silage |
| LAB | Lactic acid bacteria |
| LFC | Log fold change |
| NMDS | Non-metric Multidimensional Scaling |
| OTUs | Operational taxonomic units |
| PERMANOVA | Permutational multivariate analysis of variance |
| RA | Relative abundance |
| TS | Terminal silage |
References
- Muck, R.E.; Nadeau, E.M.G.; McAllister, T.A.; Contreras-Govea, F.E.; Santos, M.C.; Kung, L., Jr. Silage review: Recent advances and future uses of silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3980–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrero, F.; Prencipe, S.; Spadaro, D.; Gullino, M.L.; Cavallarin, L.; Piano, S.; Tabacco, E.; Borreani, G. Increase in aflatoxins due to Aspergillus section Flavi multiplication during the aerobic deterioration of corn silage treated with different bacteria inocula. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1176–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridwan, R.; Abdelbagi, M.; Sofyan, A.; Fidriyanto, R.; Astuti, W.D.; Fitri, A.; Sholikin, M.M.; Rohmatussolihat; Sarwono, K.A.; Jayanegara, A.; et al. A meta-analysis to observe silage microbiome differentiated by the use of inoculant and type of raw material. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1063333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drouin, P.; Tremblay, J.; Renaud, J.; Apper, E. Microbiota succession during aerobic stability of maize silage inoculated with Lentilactobacillus buchneri NCIMB 40788 and Lentilactobacillus hilgardii CNCM-I-4785. MicrobiologyOpen 2021, 10, e1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, É.B.; Liu, X.; Mellinger, C.; Gressley, T.F.; Stypinski, J.D.; Moyer, N.A.; Kung, L., Jr. Effect of dry matter content on the microbial community and on the effectiveness of a microbial inoculant to improve the aerobic stability of corn silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 5024–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Huan, H.; Gu, H.; Xu, N.; Shen, Q.; Ding, C. Dynamics of a microbial community during ensiling and upon aerobic exposure in lactic acid bacteria inoculation-treated and untreated barley silages. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 273, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.J.; Zhao, Y.; Balseca-Paredes, M.A.; Tiezzi, F.; Gutierrez-Rodriguez, E.; Castillo, M.S. Laboratory silo type and inoculation effects on nutritional composition, fermentation, and bacterial and fungal communities of oat silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 1812–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmit, D.H.; Kung, L. A meta-analysis of the effects of Lactobacillus buchneri on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn and grass and small-grain silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 4005–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, E.B.; Smith, M.L.; Savage, R.M.; Polukis, S.A.; Drouin, P.; Kung, L., Jr. Effects of Lactobacillus hilgardii 4785 and Lactobacillus buchneri 40788 on the bacterial community, fermentation and aerobic stability of high-moisture corn silage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, J.; Yang, H.E.; Redman, A.N.; Chevaux, E.; Drouin, P.; McAllister, T.A.; Wang, Y. Effects of a mixture of Lentilactobacillus hilgardii, Lentilactobacillus buchne, Pediococcus pentosaceus and fibrolytic enzymes on silage fermentation, aerobic stability, and growth performance of growing beef cattle. Trans. Anim. Sci. 2022, 6, txac144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhao, M.; Yang, R.; Sun, J.; Yu, Z.; Bai, C.; Xue, Y. Effect of regulation of whole-plant corn silage inoculated with Lactobacillus buchneri or Bacillus licheniformis regarding the dynamics of bacterial and fungal communities on aerobic stability. Plants 2024, 13, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, A.; Fancello, F.; Ghilardelli, F.; Zara, S.; Froldi, F.; Spanghero, M. Effects of several lactic acid bacteria inoculants on fermentation and mycotoxins in corn silage. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2021, 277, 114962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, C.L.S.; Carvalho, B.F.; Pinto, J.C.; Duarte, W.F.; Schwan, R.F. The use of Lactobacillus species as starter cultures for enhancing the quality of sugar cane silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, B.F.; Sales, G.F.C.; Schwan, R.F.; Ávila, C.L.S. Criteria for lactic acid bacteria screening to enhance silage quality. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, J.; Huaxin, N.; Andrada, E.; Yang, H.-E.; Chavaux, E.; Drouin, P.; McAllister, T.A.; Wang, Y. Effects of inoculation of corn silage with Lactobacillus hilgardii and Lactobacillus buchneri on silage quality, aerobic stability, nutrient digestibility, and growth performance of growing beef cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, P.; Tremblay, J.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F. Dynamic succession of microbiota during ensiling of whole plant corn following inoculation with Lactobacillus buchneri and Lactobacillus hilgardii alone or in combination. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, E.B.; Costa, D.M.; Santos, E.M.; Moyer, K.; Hellings, E.; Kung, L. The effects of Lactobacillus hilgardii 4785 and Lactobacillus buchneri 40788 on the microbiome, fermentation, and aerobic stability of corn silage ensiled for various times. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 10678–10698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, F.; Tabacco, E.; Piano, S.; Casale, M.; Borreani, G. Temperature during conservation in laboratory silos affects fermentation profile and aerobic stability of corn silage treated with Lactobacillus buchneri, Lactobacillus hilgardii, and their combination. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 1696–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuderi, R.A.; Drouin, P.; Apper, E. Inoculation with heterofermentative strains Lentilactobacillus buchneri CNCM 40788 and Lentilactobacillus hilgardii CNCM I-4785 either alone or combined improves fermentation and aerobic stability of ensiled triticale (X-triticosecale). AIMS Agri. Food. 2023, 8, 914–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriola, K.G.; Vyas, D.; Kim, D.; Agarussi, M.C.N.; da Silva, V.P.; Flores, M.; Jiang, Y.; Yanlin, X.; Pech-Cervantes, A.A.; Ferraretto, L.F.; et al. Effect of Lactobacillus hilgardii, Lactobacillus buchneri, or their combination on the fermentation and nutritive value of sorghum silage and corn silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 9664–9675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyader, J.; Baron, V.S.; Beauchemin, K.A. Corn forage yield and quality for silage in short growing season areas of the Canadian prairies. Agronomy 2018, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, D.J.; McGinn, S.M.; Beauchemin, K.A. Climate change impacts on corn heat unit for the Canadian prairie provinces. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 1852–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.D.; Lee, S.B.; Taylor, J.W. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; Chapter 38; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5264–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, S.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA and “All-species Living Tree Project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D643–D648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, R.H.; Larsson, K.; Taylor, A.F.S.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Jeppesen, T.S.; Schigel, D.; Kennedy, P.; Picard, K.; Glöckner, F.O.; Tedersoo, L.; et al. The UNITE database for molecular identification of fungi: Handling dark taxa and parallel taxonomic classifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D259–D264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Henry, M.; Stevens, H.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Packag. version 2.4-1. 2016. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Ding, Z.; Su, R.; Wang, M.; Cheng, M.; Xie, D.; Guo, X. Storage temperature is more effective than lactic acid bacteria inoculations in manipulating fermentation and bacterial community diversity, co-occurrence and functionality of the whole-plant corn silage. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e00101–e00122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, P.; da Silva, É.B.; Scuderi, R.A.; Tremblay, J.; Castex, M.; Apper, E. Effects of an inoculant containing Lentilactobacillus hilgardii (CNCM-I-4785) on the microbiome, fermentation, and aerobic stability of corn silage stored for long term at different incubation temperatures. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2024, 104, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikmeyer, F.G.; Köfinger, P.; Poschenel, A.; Jünemann, S.; Zakrzewski, M.; Heinl, S.; Mayrhuber, E.; Grabherr, R.; Pühler, A.; Schwab, H.; et al. Metagenome analyses reveal the influence of the inoculant Lactobacillus buchneri CD034 on the microbial community involved in grass ensiling. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 167, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarvey, J.A.; Franco, R.B.; Palumbo, J.D.; Hnasko, R.; Stanker, L.; Mitloehner, F.M. Bacterial population dynamics during the ensiling of Medicago sativa (alfalfa) and subsequent exposure to air. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharechahi, J.; Kharazian, Z.A.; Sarikhan, S.; Jouzani, G.S.; Aghdasi, M.; Salekdeh, G.H. The dynamics of the bacterial communities developed in maize silage. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1663–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Shuai, Y.; Feng, G.; Ran, Q.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Microbial communities and natural fermentation of corn silages prepared with farm bunker-silo in Southwest China. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xu, D.; Li, F.; Bai, J.; Su, R. Current approaches on the roles of lactic acid bacteria in crop silage. Microb. Biotechnol. 2023, 16, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ma, J.; Sa, R.; Sui, H.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Zhu, X.; Wu, B.; Hu, Z.; Niu, H. Effects of lactic acid bacteria inoculants on the nutrient composition, fermentation quality, and microbial diversity of whole-plant soybean-corn mixed silage. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1347293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoelstra, S.F.; Courtin, M.G.; Beers, J.A.C.V. Acetic acid bacteria can initiate aerobic deterioration of whole crop maize silage. J. Agric. Sci. 1988, 111, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, K.; Zhu, Y.; Han, D.; Yu, Y. Regulatory mechanisms of acetic acid, ethanol and high temperature tolerances of acetic acid bacteria during vinegar production. Microb. Cell Fact. 2024, 23, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Ran, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, X. Succession of microbial communities of corn silage inoculated with heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria from ensiling to aerobic exposure. Fermentation 2021, 7, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.-H.; Huang, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, M.-Z.; Yin, H.-Y.; Yang, F.; Chen, C.; Hao, J. Characterization of mycotoxins and microbial community in whole-plant corn ensiled in different silo types during aerobic exposure. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1136022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yang, Z.; Huan, H.; Gu, H.; Xu, N.; Ding, C. Impact of molasses and microbial inoculants on fermentation quality, aerobic stability, and bacterial and fungal microbiomes of barley silage. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshri, J.; Chen, Y.; Pinto, R.; Kroupitski, Y.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Sela Saldinger, S. Microbiome dynamics during ensiling of corn with and without Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant. Appli. Microb. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 4025–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, L.A.; Smiley, B.; Schmidt, M.G. Comparative denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of fungal communities associated with whole plant corn silage. Can. J. Microbiol. 2001, 47, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; da Silva, E.B.; Li, J.; Kung, L., Jr. Effect of homo-fermentative lactic acid bacteria inoculants on fermentation characteristics and bacterial and fungal communities in alfalfa silage. Fermentation 2022, 8, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tan, Z.; Wu, G.; Wang, L.; Qin, G.; Wang, Y.; Pang, H. Microbial community and fermentation characteristic of whole-crop wheat silage treated by lactic acid bacteria and Artemisia argyi during ensiling and aerobic exposure. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1004495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.C.; Golt, C.; Joerger, R.D.; Mechor, G.D.; Mourão, G.B.; Kung, L. Identification of the major yeasts isolated from high moisture corn and corn silages in the United States using genetic and biochemical methods. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhao, M.; Pan, G.; Zhang, H.; Yang, R.; Sun, J.; Yu, Z.; Bai, C.; Xue, Y. Effects of Bacillus subtilis or Lentilactobacillus buchneri on aerobic stability, and the microbial community in aerobic exposure of whole plant corn silage. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1177031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.W.; Teng, K.L.; Cao, Y.H.; Shi, W.X.; Xuan, Z.Y.; Zhou, J.H.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, J. Effects of Lactobacillus hilgardii 60TS-2, with or without homofermentative Lactobacillus plantarum B90, on the aerobic stability, fermentation quality and microbial community dynamics in sugarcane top silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 312, 123600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ding, W.; Ke, W.; Li, F.; Zhang, P.; Guo, X. Modulation of metabolome and bacterial community in whole crop corn silage by inoculating homofermentative Lactobacillus plantarum and heterofermentative Lactobacillus buchneri. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolci, P.; Tabacco, E.; Cocolin, L.; Borreani, G. Microbial dynamics during aerobic exposure of corn silage stored under oxygen barrier or polyethylene films. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7499–7507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tan, Z.; Gu, L.; Ma, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, G.; Qin, G.; Wang, Y.; Pang, H. Variation of microbial community and fermentation quality in corn silage treated with lactic acid bacteria and Artemisia argyi during aerobic exposure. Toxins 2022, 14, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, V.A.; Pereyra, C.M.; Keller, L.A.M.; Dalcero, A.M.; Rosa, C.A.R.; Chiacchiera, S.M.; Cavaglieri, L.R. Fungi and mycotoxins in silage: An overview. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 115, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cai, X.; Shao, T.; Yangzong, Z.; Wang, W.; Ma, P.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Gallo, A.; Yuan, X. Effects of bacterial inoculants on the microbial community, mycotoxin contamination, and aerobic stability of corn silage infected in the field by toxigenic fungi. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2022, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Der Bedrosian, M.C.; Nestor, K.E.; Kung, L. The effects of hybrid, maturity, and length of storage on the composition and nutritive value of corn silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 5115–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, P.C.; Esser, N.M.; Shaver, R.D.; Coblentz, W.K.; Scott, M.P.; Bodnar, A.L.; Schmidt, R.J.; Charley, R.C. Influence of ensiling time and inoculation on alteration of the starch-protein matrix in high-moisture corn. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 2465–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irawan, A.; Sofyan, A.; Ridwan, R.; Hassim, H.A.; Respati, A.N.; Wardani, W.W.; Sadarman; Astuti, W.D.; Jayanegara, A. Effects of different lactic acid bacteria groups and fibrolytic enzymes as additives on silage quality: A meta-analysis. Biores. Technol. Rep. 2021, 14, 100654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraretto, L. Ensiling Time Affects Silage Quality. Hay and Forage Grower. 2016. Available online: https://hayandforage.com/article-476-ensiling-time-affects-silage-quality.html (accessed on 15 July 2025).




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Nair, J.; Chevaux, E.; McAllister, T.A.; Wang, Y. Effect of Inoculation of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Fibrolytic Enzymes on Microbiota in the Terminal and Aerobically Exposed Short-Growing Season Whole-Plant Corn Silage. Fermentation 2025, 11, 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11090530
Li C, Nair J, Chevaux E, McAllister TA, Wang Y. Effect of Inoculation of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Fibrolytic Enzymes on Microbiota in the Terminal and Aerobically Exposed Short-Growing Season Whole-Plant Corn Silage. Fermentation. 2025; 11(9):530. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11090530
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chunli, Jayakrishnan Nair, Eric Chevaux, Tim A. McAllister, and Yuxi Wang. 2025. "Effect of Inoculation of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Fibrolytic Enzymes on Microbiota in the Terminal and Aerobically Exposed Short-Growing Season Whole-Plant Corn Silage" Fermentation 11, no. 9: 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11090530
APA StyleLi, C., Nair, J., Chevaux, E., McAllister, T. A., & Wang, Y. (2025). Effect of Inoculation of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Fibrolytic Enzymes on Microbiota in the Terminal and Aerobically Exposed Short-Growing Season Whole-Plant Corn Silage. Fermentation, 11(9), 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11090530








