Improving Haemophilus influenzae Type b Polysaccharide Productivity Through Continuous Culture for Pentavalent Vaccine Manufacturing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganism and Culture Medium
2.2. Media
2.3. Inoculum Preparation
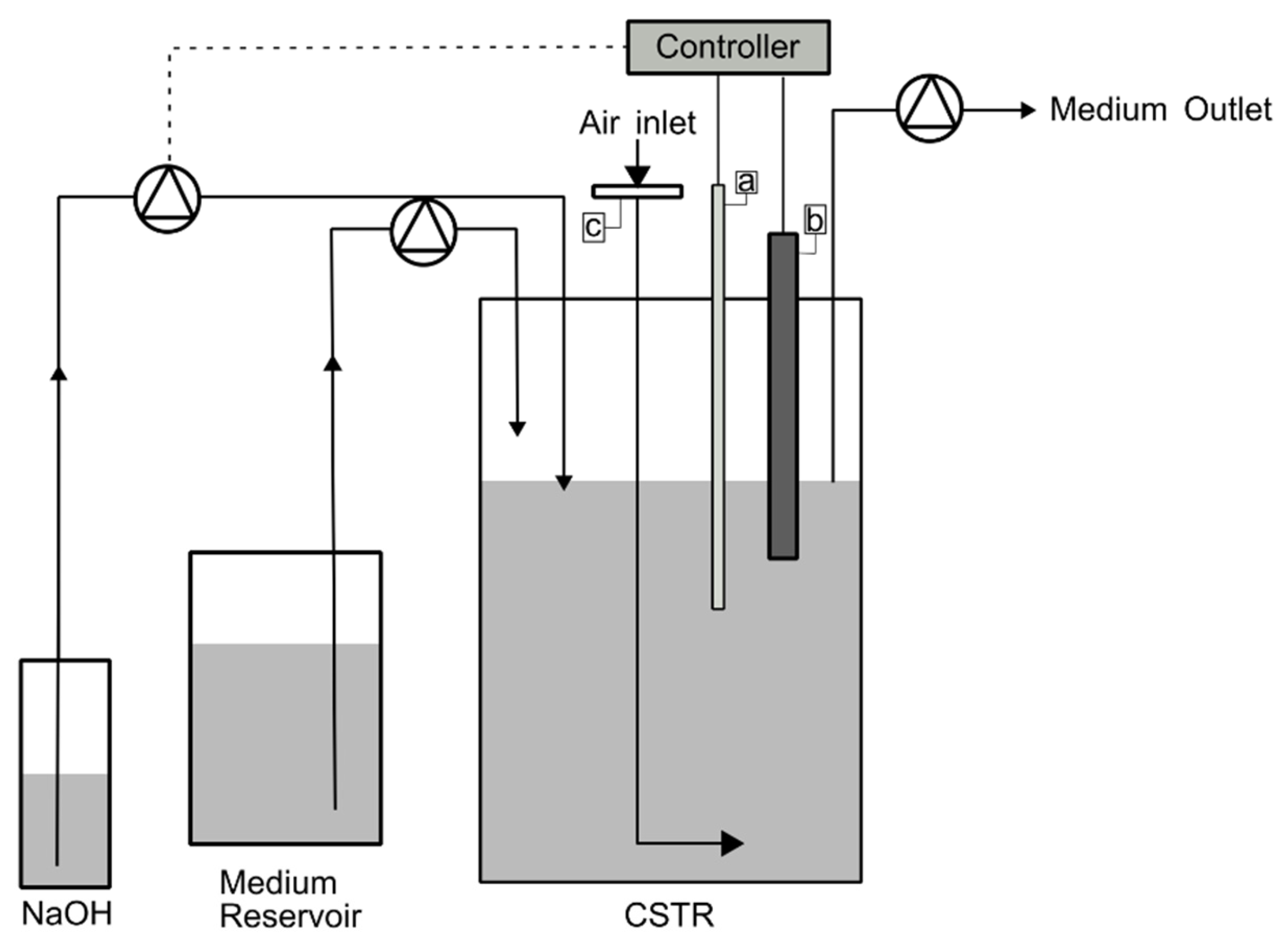
2.4. Culture Conditions and Growth System
2.5. Analytical Methods
2.5.1. Biomass Determination
2.5.2. Analysis of Carbohydrate, Organic Acid and Polysaccharide
Carbohydrate and Organic Acid Determination
Free PRP Determination
Cell-Associated PRP Determination
2.5.3. Molecular Mass Determination
2.6. Kinetic Parameters of Culture
3. Results
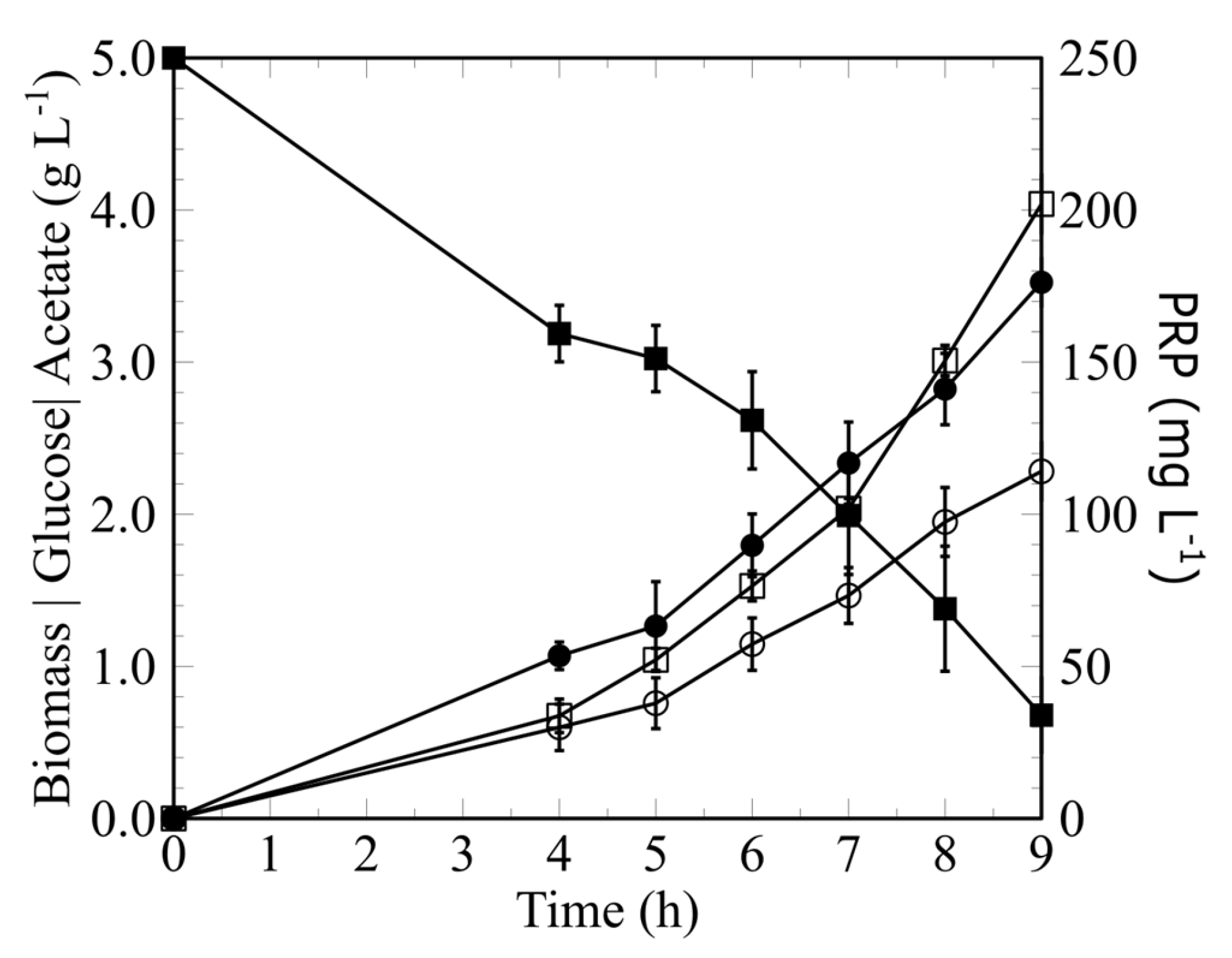
3.1. Fermentative Assay and Batch Experiment
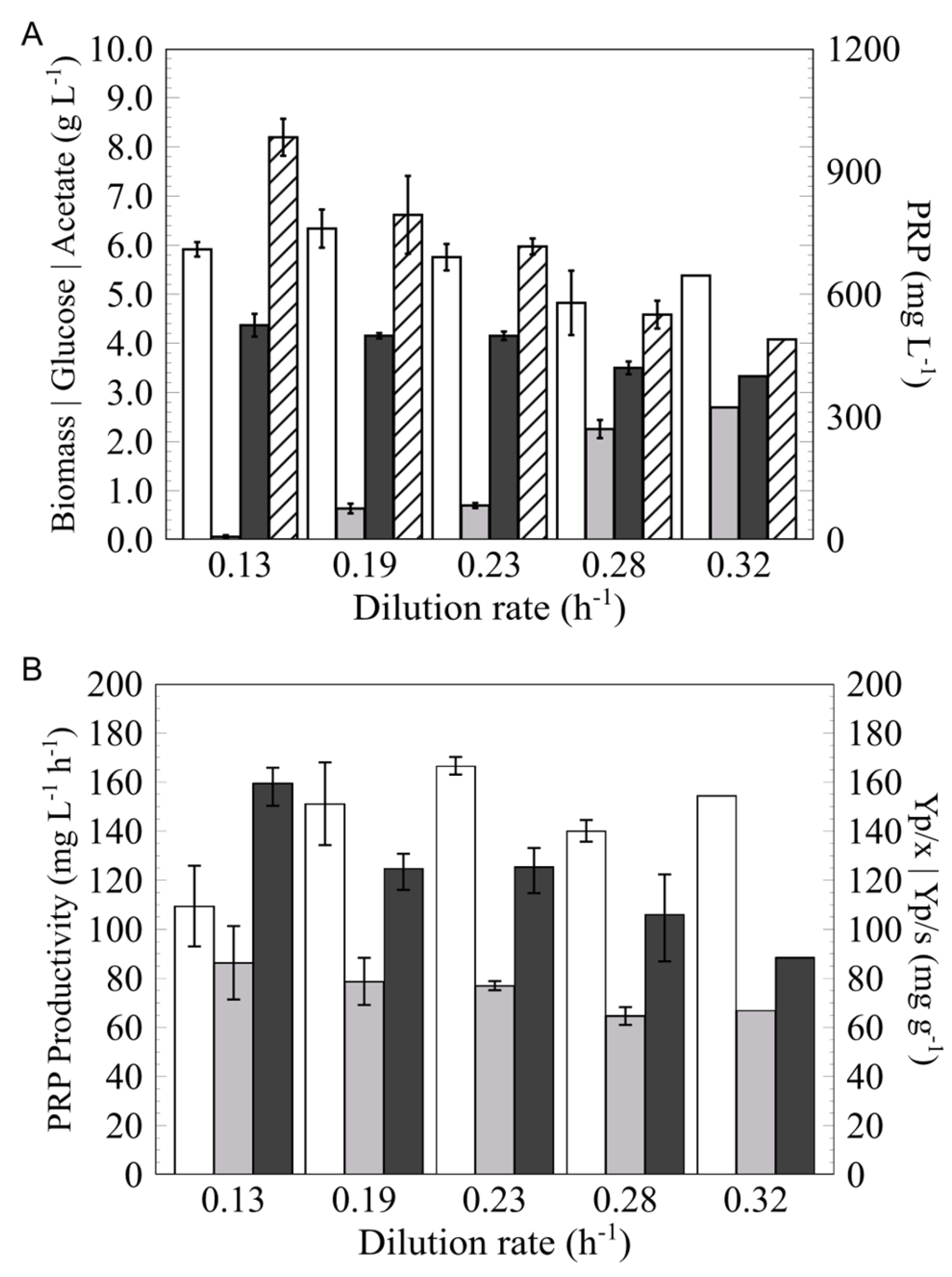
3.2. Determination of the Optimal Dilution Rate (D)
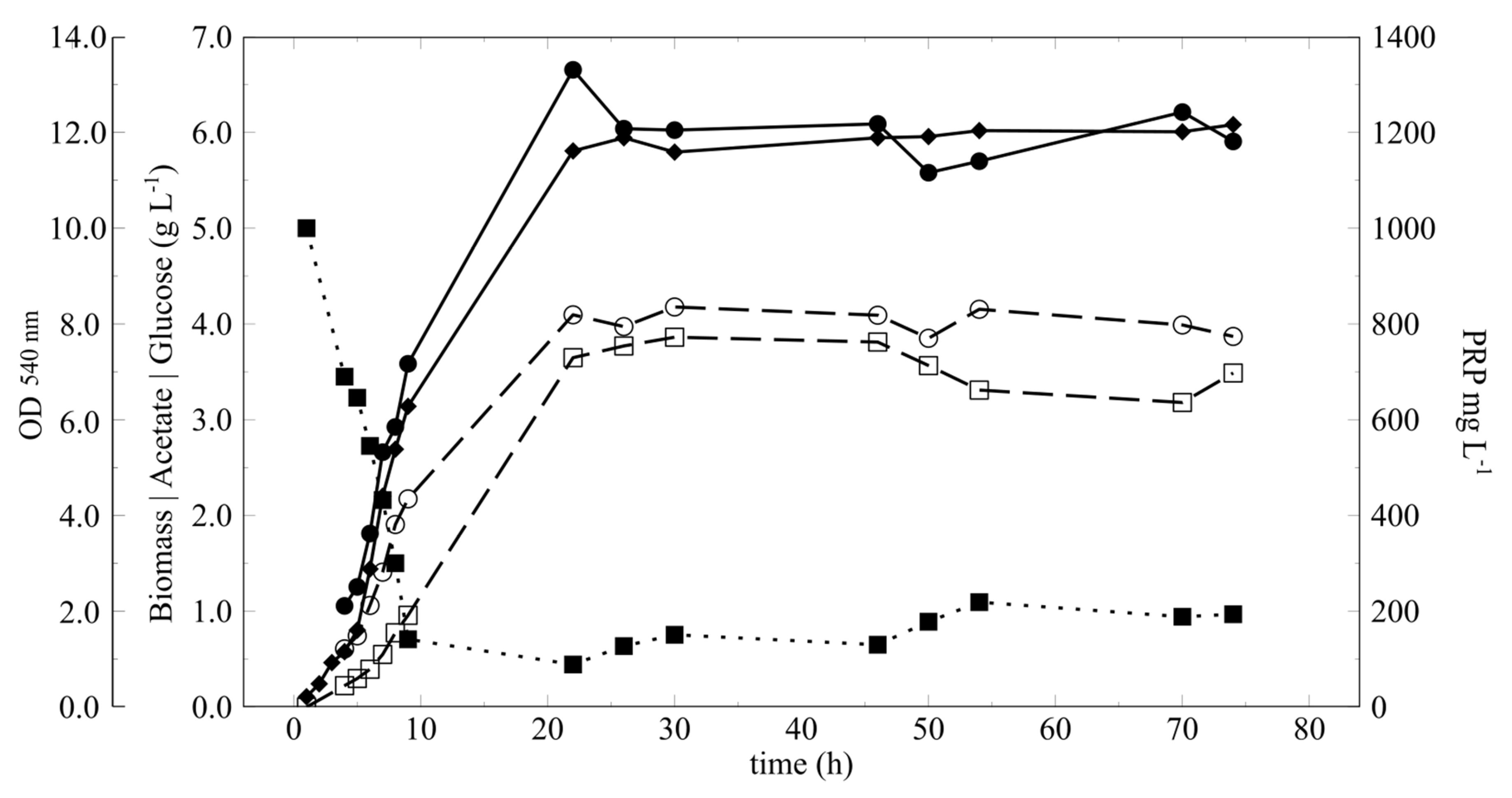
3.3. Cultivation with Fixed D
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Experiments | Dilution (h−1) | Cultivation Time (h) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E01 | 0.13 | 0.19 | - | 52.0 |
| E02 | 0.13 | 0.19 | - | 51.7 |
| E03 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 00.28 | 76.9 |
| E04 | 0.23 | 0.28 | 00.32 | 80.4 |
| E05 | 0.23 | 74.45 | ||
References
- Wenger, J.D.; Hightower, A.W.; Facklam, R.R.; Gaventa, S.; Broome, C.V. Bacterial Meningitis in the United States, 1986: Report of a Multistate Surveillance Study. J. Infect. Dis. 1990, 162, 1316–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Narayanan, S.; Tiefenbach, J.; Lukšić, I.; Ale, B.M.; Adeloye, D.; Rudan, I. Estimating the global and regional burden of meningitis in children caused by Haemophilus influenzae type b: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Glob. Health 2022, 12, 04014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanella, R.C.; Bokermann, S.; Galhardo, M.; Gava, C.; Almeida, S.C.G.; Pereira, G.A.; de Lemos, A.P.S. Trends in serotype distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of invasive Haemophilus influenzae isolates from Brazil, 2009–2021. Int. Microbiol. 2024, 28, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slack, M.P.E. Long Term Impact of Conjugate Vaccines on Haemophilus influenzae Meningitis: Narrative Review. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisel, R.M.; Baker, R.S.; Dorman, D.E. Capsular polymer of Haemophilus influenzae, type b. I. Structural characterization of the capsular polymer of strain Eagan. J. Biol. Chem. 1975, 250, 4926–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilsdorf, J.R. Hib Vaccines: Their Impact on Haemophilus influenzae Type b Disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, S321–S330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienstra, M.S.; Scattergood, E.M.; Sitrin, R.D.; Merck and Co Inc. Process for Removing Bacterial Endotoxin from Gram-Negative Polysaccharides. U.S. Patent 5,039,610, 13 August 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Albani, S.M.F.; da Silva, M.R.; Fratelli, F.; Junior, C.P.C.; Iourtov, D.; Cintra, F.d.O.; Takagi, M.; Cabrera-Crespo, J. Polysaccharide purification from Haemophilus influenzae type b through tangential microfiltration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 116, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, S.; Horiuchi, J.-I.; Yoshida, F. Chemical and Biochemical Kinetics. In Biochemical Engineering, 1st ed.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2015; pp. 27–46. [Google Scholar]
- Cintra, F.d.O.; Takagi, M. Selectiom of a mathematical model for the kinetics of Haemophilus influenzae type b using akaike’s information criterion. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Hierro, A.G.; Moreno-Cid, J.A.; Casey, E. Continuous biomanufacturing for sustainable bioeconomy applications. EFB Bioecon. J. 2024, 4, 100071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogola-Kolling, V.M.R.; Zanardo, R.T.; Carmo, T.S.; Zampoli, N.D.; Figueiredo, D.B.; Gonçalves, V.M. Improved capsular polysaccharide production by Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 14 using continuous cultivation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2014, 91, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerritzen, M.J.; Stangowez, L.; van de Waterbeemd, B.; Martens, D.E.; Wijffels, R.H.; Stork, M. Continuous production of Neisseria meningitidis outer membrane vesicles. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 9401–9410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, M.; Cabrera-Crespo, J.; Baruque-Ramos, J.; Zangirolami, T.C.; Raw, I.; Tanizaki, M.M. Characterization of Polysaccharide Production of Haemophilus influenzae Type b and Its Relationship to Bacterial Cell Growth. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2003, 110, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cintra, F.d.O. Mathematical Modeling and Optimization of Exopolysaccharide Production from Haemophilus influenzae Type b. Master’s Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- de Haan, A.; van der Put, R.M.F.; Beurret, M. HPAEC-PAD method for the analysis of alkaline hydrolyzates of Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2013, 27, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, L.; Da Silva, T.; Cintra, F.; Takagi, M. Mathematical model for simultaneous microfiltration and ultrafiltration of Haemophilus influenzae type b to cell separation and polysaccharide recovery. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 481, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawas, F.; Bolgiano, B.; Rigsby, P.; Crane, D.; Belgrave, D.; Corbel, M.J. Evaluation of the saccharide content and stability of the first WHO International Standard for Haemophilus influenzae b capsular polysaccharide. Biologicals 2007, 35, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, J.S.; Moxon, E.R. Capsulation and gene copy number at the cap locus of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J. Bacteriol. 1988, 170, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintra, F.O.; Takagi, M. Comparison among different sample treatment methods for analysis of molecular weight and concentration of exopolysaccharide produced by Haemophilus influenzae type b. In Microbes in Applied Research; WORLD SCIENTIFIC: Singapore, 2012; pp. 513–517. [Google Scholar]
- Takagi, M.; Cabrera-Crespo, J.; Zangirolami, T.C.; Raw, I.; Tanizaki, M.M. Improved cultivation conditions for polysaccharide production by H. influenzae type b. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2006, 81, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, J.; Allard, G.; O’toole, L.; Swartz, R.; Licari, P. Development and scale-up of a fed-batch process for the production of capsular polysaccharide from Haemophilus influenzae. J. Biotechnol. 2000, 81, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsang, A.; Tabatabaie, A.; Vaziri, F.; Nejati, M.; Zolfaghari, M.R.; Fateh, A.; Jamnani, F.R.; Bahrmand, A.R.; Siadat, S.D. Optimization of large scale production of Haemophilus influenzae type b polyribosyl-ribitol phosphate. Minerva Biotechnol. Biomol. Res. 2016, 29, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.R.; Portela, C.A.F.; Albani, S.M.F.; de Paiva, P.R.; Tanizaki, M.M.; Zangirolami, T.C. Experimental design and metabolic flux analysis tools to optimize industrially relevant Haemophilus influenzae type b growth medium. Biotechnol. Prog. 2017, 33, 1508–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.R. Cultivation Strategies for the Production of Capsular Polysaccharide by Haemophilus influenzae Type b and Determination of Quality Parameters for the Product. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal de São Carlos, São Carlos, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, D.S.M.P.; Schirra, H.; McEwan, A.G.; Kappler, U. Metabolic versatility in Haemophilus influenzae: A metabolomic and genomic analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, U.; Lasko, D.R.; Fiaux, J.; Hochuli, M.; Glaser, R.; Szyperski, T.; Wüthrich, K.; Bailey, J.E. Metabolic Flux Ratio Analysis of Genetic and Environmental Modulations of Escherichia coli Central Carbon Metabolism. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 6679–6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiteman, M.A.; Altman, E. Overcoming acetate in Escherichia coli recombinant protein fermentations. Trends Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Follens, A.; Veiga-Da-Cunha, M.; Merckx, R.; van Schaftingen, E.; van Eldere, J. acs1 of Haemophilus influenzae Type a Capsulation Locus Region II Encodes a Bifunctional Ribulose 5-Phosphate Reductase– CDP-Ribitol Pyrophosphorylase. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 2001–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillaca-Pullo, O.; Vieira, L.D.; Takagi, M. Scale-Up of Capsular Polysaccharide Production Process by Haemophilus influenzae Type b Using kLa Criterion. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axe, D.D.; Bailey, J.E. Transport of lactate and acetate through the energized cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1995, 47, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, A.J.; McLaggan, D.; Davidson, I.; O’bYrne, C.; Booth, I.R. Perturbation of Anion Balance during Inhibition of Growth of Escherichia coli by Weak Acids. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinhal, S.; Ropers, D.; Geiselmann, J.; de Jong, H. Acetate Metabolism and the Inhibition of Bacterial Growth by Acetate. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ochoa, F.; Gomez, E.; Santos, V.E.; Merchuk, J.C. Oxygen uptake rate in microbial processes: An overview. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 49, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipovsky, J.; Patakova, P.; Paulova, L.; Pokorny, T.; Rychtera, M.; Melzoch, K. Butanol production by Clostridium pasteurianum NRRL B-598 in continuous culture compared to batch and fed-batch systems. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 144, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiong, H.; Chen, Z.; Fu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Chen, N. Effect of fed-batch and chemostat cultivation processes of C. glutamicum CP for L-leucine production. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, J.d.M.; Garcia-Ortega, X.; Montesinos-Seguí, J.L.; Freire, D.M.G.; Valero, F. Continuous operation, a realistic alternative to fed-batch fermentation for the production of recombinant lipase B from Candida antarctica under the constitutive promoter PGK in Pichia pastoris. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 147, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintra, F.d.O.; Takagi, M. Study of the chemical stability of the capsular polysaccharide produced by Haemophilus influenzae type b. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 116, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoiseth, S.K.; Connelly, C.J.; Moxon, E.R. Genetics of spontaneous, high-frequency loss of b capsule expression in Haemophilus influenzae. Infect. Immun. 1985, 49, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, A.; Beurret, M.F. Patents Process for Producing a Capsular Polysaccharide for Use in Conjugate Vaccines. U.S. Patent 7,582,459, 1 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, R.; Dalal, J.; Singh, D.; Kumar, N.; Hanif, S.; Joshi, N.; Chhikara, M. Development and characterization of Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine prepared using different polysaccharide chain lengths. Vaccine 2015, 33, 2646–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Simple Batch | Continuous |
|---|---|---|
| PRP yield based on glucose consumption (YP/S) (mg g−1) | ||
| PRP yield based on cell growth (YP/X) (mg g−1) | ||
| Growth yield coefficient based on glucose consumption (YX/S) (g g−1) | ||
| Acetate yield based on cell growth (YAc/X) (g g−1) | ||
| Acetate yield based on glucose consumption (YAc/S) (g g−1) | ||
| Volumetric Productivity ** (Qp) (mg L−1 h−1) | ||
| Specific Productivity ** (Rp) (mg g−1 h−1) |
| Continuous Cultivation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Bioreactor | Output | |
| Dilution rate (h−1) | 0.23 | |
| Flow rate (L h−1) | 0.184 | |
| PRPfree (mg L−1) | 688 ± 53 | 680 ± 28 |
| Pc (mg L−1) | ND * | 193 ± 18 |
| Pt (mg L−1) | ND | 873 ± 47 |
| % PRPfree | ND | 77.9 ± 2.0 |
| MMPRP (kD) | ND | 134 ± 32 |
| Glucose (g L−1) | 0.85 ± 0.17 | 0.81 ± 0.15 |
| Acetate (g L−1) | 4.02 ± 0.12 | 3.80 ± 0.21 |
| Biomass (g L−1) | 6.03 ± 0.33 | ND * |
| Kinetic Parameters | Batch | Continuous Culture |
|---|---|---|
| PRP (mg L−1) | 202 ± 17 | 688 ± 53 |
| Glucose (g L−1) | 0.11 ± 0.08 | 0.85 ± 0.17 |
| Acetate (g L−1) | 2.28 ± 0.29 | 4.02 ± 0.12 |
| Biomass (g L−1) | 3.53 ± 0.23 | 6.03 ± 0.33 |
| Yp/s (mg g−1) | 46.8 ± 3.3 | 77.7 ± 3.2 |
| Yac/s (g g−1) | 0.63 ± 0.02 | 0.44 ± 0.01 |
| Yp/x (mg g−1) | 57.3 ± 3.0 | 119.0 ± 7.5 |
| Yx/s (g g−1) | 0.82 ± 0.05 | 0.65 ± 0.02 |
| Yac/x (g g−1) | 0.65 ± 0.05 | 0.67 ± 0.03 |
| QpPRP (mg L−1 h−1) | 22.4 ± 1.9 | 164.6 ± 8.9 |
| RpPRP (mg g−1 h−1) | 6.37 ± 0.33 | 27.4 ± 1.7 |
| Qpacetate (g L−1 h−1) | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.93 ± 0.02 |
| Rpacetate (g g−1 h−1) | 0.072 ± 0.005 | 0.153 ± 0.006 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solidade, L.S.; Vieira, L.D.; Takagi, M. Improving Haemophilus influenzae Type b Polysaccharide Productivity Through Continuous Culture for Pentavalent Vaccine Manufacturing. Fermentation 2025, 11, 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11110622
Solidade LS, Vieira LD, Takagi M. Improving Haemophilus influenzae Type b Polysaccharide Productivity Through Continuous Culture for Pentavalent Vaccine Manufacturing. Fermentation. 2025; 11(11):622. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11110622
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolidade, Lucas Santos, Lucas Dias Vieira, and Mickie Takagi. 2025. "Improving Haemophilus influenzae Type b Polysaccharide Productivity Through Continuous Culture for Pentavalent Vaccine Manufacturing" Fermentation 11, no. 11: 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11110622
APA StyleSolidade, L. S., Vieira, L. D., & Takagi, M. (2025). Improving Haemophilus influenzae Type b Polysaccharide Productivity Through Continuous Culture for Pentavalent Vaccine Manufacturing. Fermentation, 11(11), 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11110622






