Correlations Between Flavor Profile and Microbial Community Succession in Probiotic-Fermented Burdock Root
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Burdock Roots Fermented Using Lactic Acid Bacteria
2.3. Determination of VFCs
2.4. Determination of Microbial Diversity
2.5. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
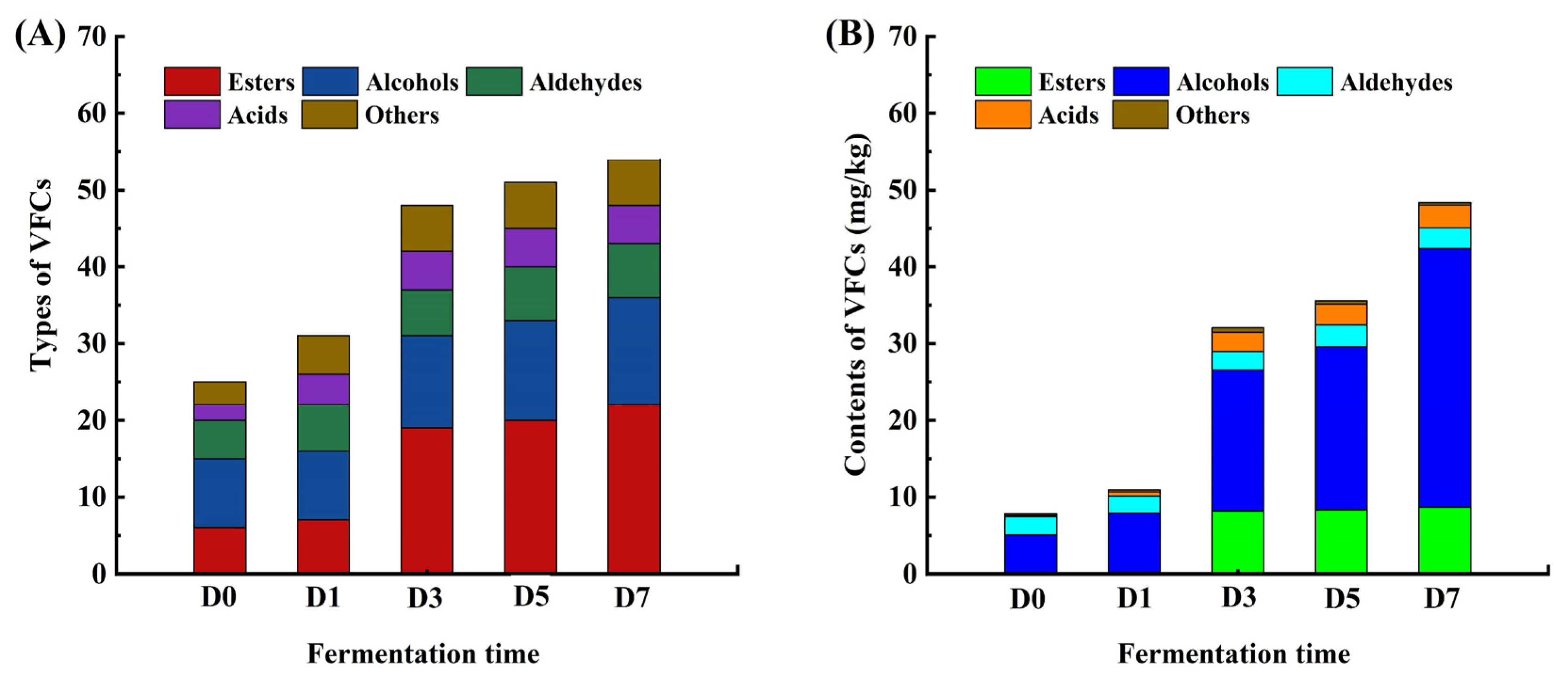
3.1. Dynamic Changes in VFCs During Fermentation
3.2. Analysis of Characteristic VFCs
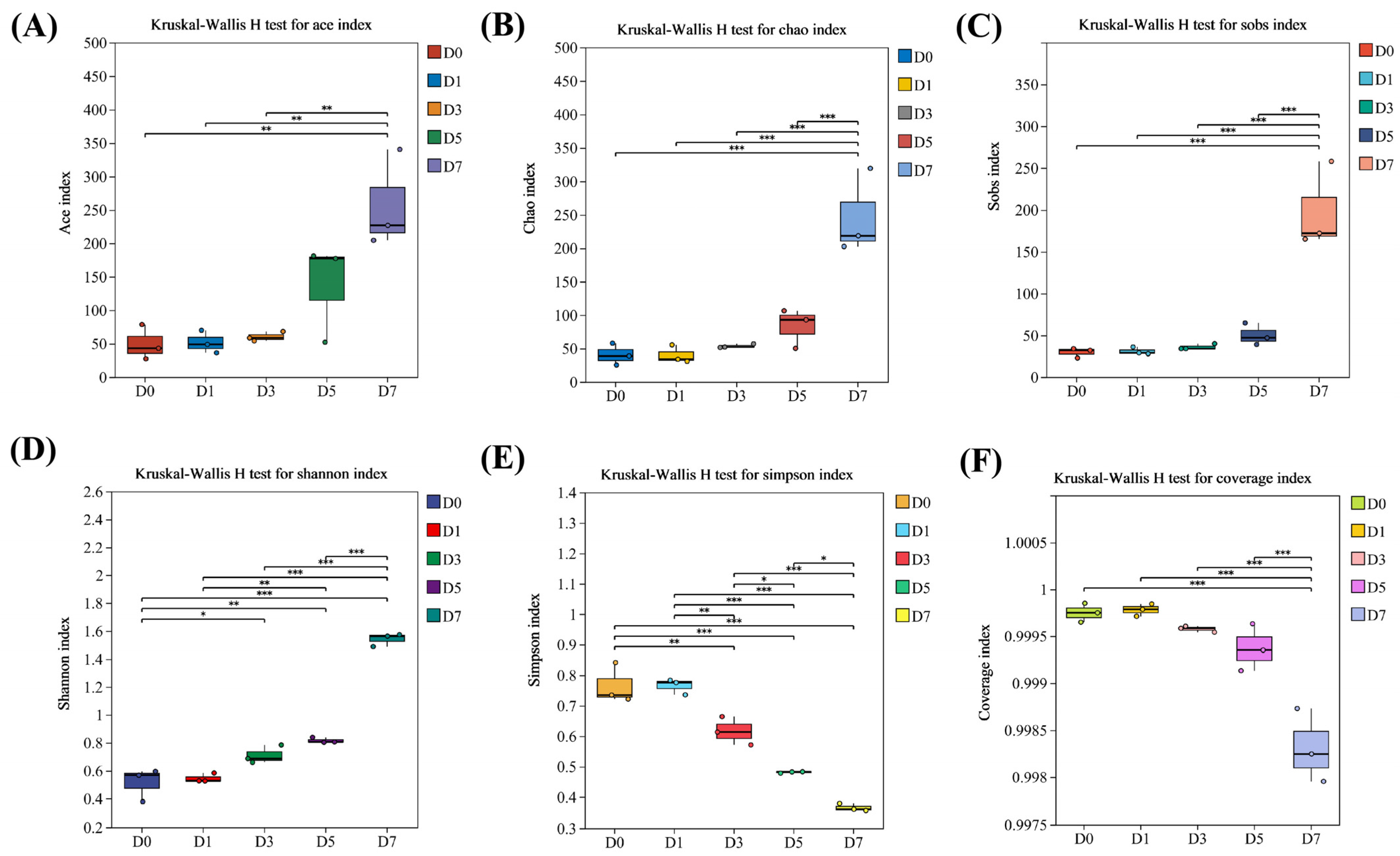
3.3. Alpha Diversity of Bacterial Community
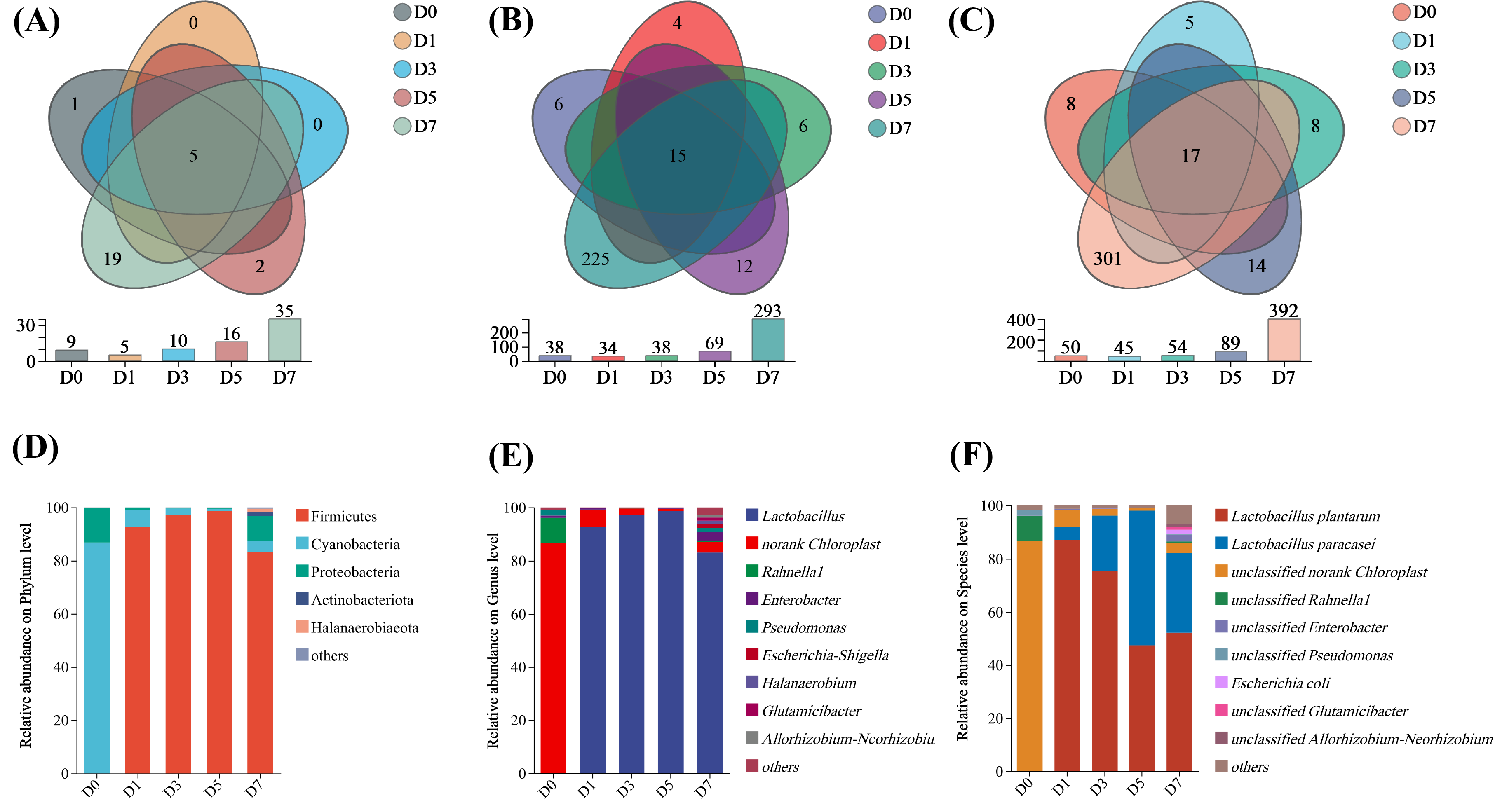
3.4. Overview of Bacterial Community Composition
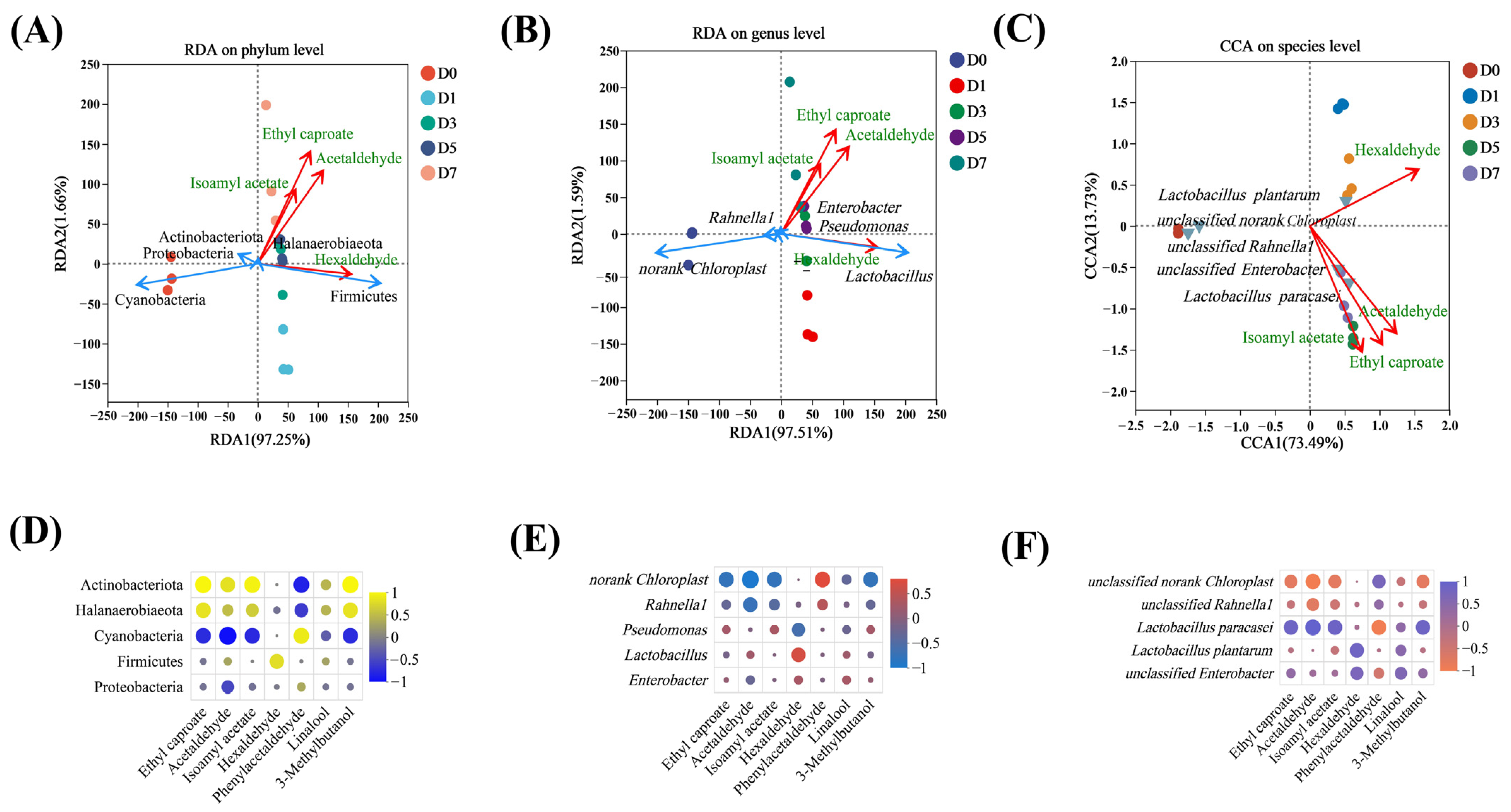
3.5. Correlation Analysis Between Bacteria and Characteristic VFCs
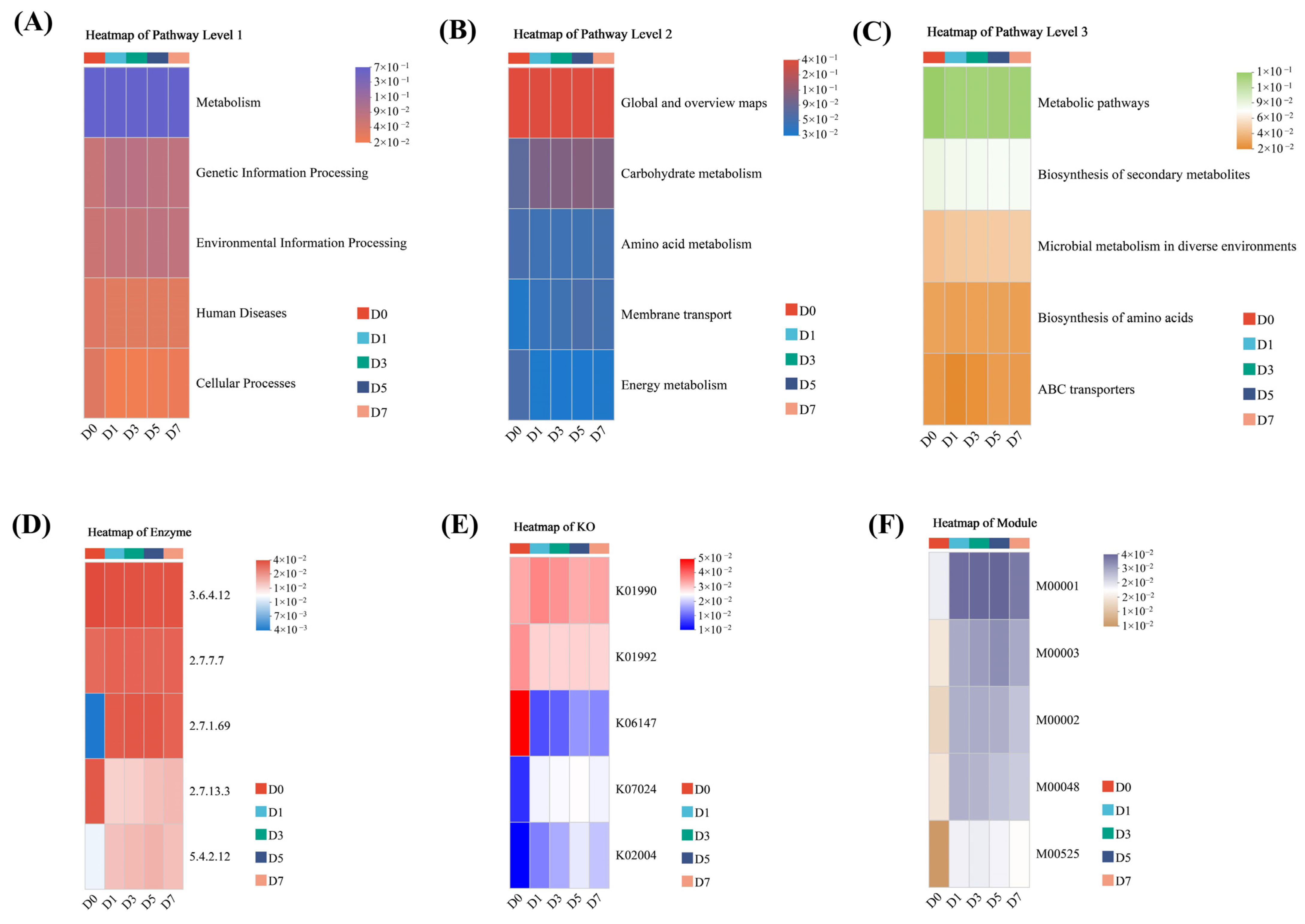
3.6. Function Prediction Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xia, J.; Guo, Z.; Fang, S.; Gu, J.; Liang, X. Effect of drying methods on volatile compounds of burdock (Arctium lappa L.) root tea as revealed by gas chromatography mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Foods 2021, 10, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Herrera-Balandrano, D.D.; Huang, W.; Chai, Z.; Beta, T.; Wang, J.; Feng, J.; Li, Y. Comparison of nutritional and nutraceutical properties of burdock roots cultivated in Fengxian and Peixian of China. Foods 2021, 10, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeili, F.; Hashemiravan, M.; Eshaghi, M.R.; Gandomi, H. Encapsulation of Arctium lappa L. root extracts by spray-drying and freeze-drying using maltodextrin and Gum Arabic as coating agents and it’s application in synbiotic orange-carrot juice. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 2908–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, S.; Sato, M.; Nakamura, A.; Takahashi, H.; Inoue, J.; Takayanagi, S.; Nakamura, M.; Kuda, T. Effects of roasted burdock root tea drink on plasma liver injury indices and faecal microbiota in mice fed a high-fat diet. 3 Biotech 2025, 15, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferracane, R.; Graziani, G.; Gallo, M.; Fogliano, V.; Ritieni, A. Metabolic profile of the bioactive compounds of burdock (Arctium lappa) seeds, roots and leaves. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2010, 51, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cai, Y.Z.; Wong, R.N.; Lee, C.K.; Tang, S.C.; Sze, S.C.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, Y. Comparative analysis of caffeoylquinic acids and lignans in roots and seeds among various burdock (Arctium lappa.) genotypes with high antioxidant activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 4067–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Feng, J.; Huang, W.; Li, Y. Isolation and identification of lactic acid bacteria and their effects on the off-odor of burdocks. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 7485–7494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melkonian, C.; Gottstein, W.; Blasche, S.; Kim, Y.; Abel-Kistrup, M.; Swiegers, H.; Saerens, S.; Edwards, N.; Patil, K.R.; Teusink, B.; et al. Finding functional differences between species in a microbial community: Case studies in wine fermentation and kefir culture. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, R.; Zhou, R.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Lu, L.; Xu, H. The probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum alleviates colitis by modulating gut microflora to activate PPARgamma and inhibit MAPKs/NF-kappaB. Eur. J. Nutr. 2024, 64, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbehat, M.; Mauriello, G.; Altamimi, M. Microencapsulation of probiotics for food functionalization: An update on literature reviews. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, T.J. Functional genomics of the lactic acid bacterium Limosilactobacillus fermentum LAB-1: Metabolic, probiotic and biotechnological perspectives. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Du, J.; Yan, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, L. Dynamic changes in aromas and precursors of edible fungi juice: Mixed lactic acid bacteria fermentation enhances flavor characteristics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 8541–8552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Zeng, B.; Deng, J.; Ren, Z.; Xie, J.; Wei, C. Succession of microbial community structure in fermented grains during the fermentation of strong-flavor Baijiu and its impact on the metabolism of acids, alcohols, and esters. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 33, 3501–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, F.; Li, W.; Chen, X.; Du, B.; Li, X.; Sun, B. Targeted microbial collaboration to enhance key flavor metabolites by inoculating Clostridium tyrobutyricum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the strong-flavor Baijiu simulated fermentation system. Food Res. Int. 2024, 190, 114647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, J.; Dai, M.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Sun, B. Simulated fermentation of strong-flavor baijiu through functional microbial combination to realize the stable synthesis of important flavor chemicals. Foods 2023, 12, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Yu, X.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Y. Initial fungal diversity impacts flavor compounds formation in the spontaneous fermentation of Chinese liquor. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 110995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Yang, L.; Chen, C.; Li, J.; Fu, J.; Liu, G.; Kan, Q.; Ho, C.T.; Huang, Q.; Lan, Y.; et al. Applications of multi-omics techniques to unravel the fermentation process and the flavor formation mechanism in fermented foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2024, 64, 8367–8383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bai, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Daglia, M.; Xiao, X.; He, Y. Microbial interactions in food fermentation: Interactions, analysis strategies, and quality enhancement. Foods 2025, 14, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Qin, L.; Liu, N.; Wen, A.; Zeng, H.; Miao, S. Flavor formation by amino acid catabolism in low-salt sufu paste, a Chinese fermented soybean food. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zhou, K.; Ren, J.; Tang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Liu, E.; Wang, Y. Characteristic flavor compounds and bacterial community of different gray sufu, a traditional Chinese fermented soybean curd. Int. J. Food Prop. 2024, 27, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemert, L.J.V. Compilations of Odour Threshold Values in Air, Water and Other Media (Second Enlarged and Revised Edition); Oliemans, Punter & Partners BV: Zeist, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.; Shi, C.; Liu, L.; Han, J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Fu, W.; Gao, H.; Huang, H.; et al. Majorbio Cloud 2024: Update single-cell and multiomics workflows. iMeta 2024, 3, e217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanja, O.; Tomislav, P.I. Relationship between milk microbiota, bacterial load, macronutrients, and human cells during lactation. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huhe; Chen, X.; Hou, F.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, Y. Bacterial and fungal community structures in loess plateau grasslands with different grazing intensities. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 606. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, X.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Gao, C.; Li, S.; Wei, C.; Huang, J.; Tian, Y.; Yuan, J.; Lu, J.; et al. Intratumor microbiome features reveal antitumor potentials of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2156255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, D.; Xu, L.; Wu, M.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, C. Effects of microbial community succession on flavor compounds and physicochemical properties during CS sufu fermentation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 152, 112313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Teh, B.; Sun, C.; Hu, S.; Lu, X.; Boland, W.; Shao, Y. Biodiversity and activity of the gut microbiota across the life history of the insect herbivore spodoptera littoralis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Otify, A.M.; El-Sayed, A.M.; Michel, C.G.; Wessjohann, L.A. Sensory metabolite profiling in a date pit based coffee substitute and in response to roasting as analyzed via mass spectrometry based metabolomics. Molecules 2019, 24, 3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Gallagher, E.D. Ecologically meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia 2001, 129, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, C. Flavor and feeding: Executive summary. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 107, 469–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Liu, C.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Yao, Y. Exploring the flavor formation mechanism under osmotic conditions during soy sauce fermentation in Aspergillus oryzae by proteomic analysis. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R.; Wu, C.; Jin, Y. Effect of fortified daqu on the microbial community and flavor in Chinese strong-flavor liquor brewing process. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, S.; Zhao, N.; Lu, W.; Zhao, F.; Zheng, S.; Wang, W.; Chen, W. Effect of different Lactobacillus species on volatile and nonvolatile flavor compounds in juices fermentation. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2214–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campayo, A.; Serrano De La Hoz, K.; García-Martínez, M.M.; Salinas, M.R.; Alonso, G.L. Spraying ozonated water on bobal grapevines: Effect on wine quality. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ouyang, W.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, H.; Hua, J.; Jiang, Y. Analysis of non-volatile and volatile metabolites reveals the influence of second-drying heat transfer methods on green tea quality. Food Chem. X 2022, 14, 100354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.; Osako, K.; Okamoto, A.; Ohshima, T. Olfactometric characterization of aroma active compounds in fermented fish paste in comparison with fish sauce, fermented soy paste and sauce products. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1027–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Shu, N.; Hou, Q.; Tang, F.; Shan, C.; Yang, X.; Guo, Z. Insights into the aroma profile of sauce-flavor baijiu by GC-IMS combined with multivariate statistical analysis. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2022, 2022, 4614330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerny, M.; Christlbauer, M.; Christlbauer, M.; Fischer, A.; Granvogl, M.; Hammer, M.; Hartl, C.; Hernandez, N.M.; Schieberle, P. Re-investigation on odour thresholds of key food aroma compounds and development of an aroma language based on odour qualities of defined aqueous odorant solutions. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 228, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Deng, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Du, C.; Wang, Q.; Xia, Y.; He, J.; Yuan, W.; Wu, W.; et al. Characteristic changes and potential markers of flavour in raw Pu-erh tea with different ageing cycles analysed by HPLC, HS-SPME-GC-MS, and OAV. Foods 2025, 14, 829. [Google Scholar]
- Farcas, A.C.; Socaci, S.A.; Chis, M.S.; Dulf, F.V.; Podea, P.; Tofana, M. Analysis of fatty acids, amino acids and volatile profile of apple by-products by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Molecules 2022, 27, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Dong, X.; Ren, Y.; Agarwal, M.; Ren, A.; Ding, Z. Profiling real-time aroma from green tea infusion during brewing. Foods 2022, 11, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Chen, W.; Chen, H.; Chen, W.; Zhong, Q. Combination of Lactobacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae DV10 as starter culture to produce mango slurry: Microbiological, chemical parameters and antioxidant activity. Molecules 2019, 24, 4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wan, Y.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J.; Xu, Y. Dynamic changes in physicochemical properties and microbial diversity during the fermentation of mao-tofu. Foods 2025, 14, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.S.; Noh, J.; Kim, B.; Koh, H.; Lee, D. Refining microbiome diversity analysis by concatenating and integrating dual 16S rRNA amplicon reads. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2025, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, Q.; Zou, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Mao, J.; Zhang, S. A metagenomic analysis of the relationship between microorganisms and flavor development in Shaoxing mechanized huangjiu fermentation mashes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 303, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Lu, Y.; Yu, H.; Chen, Z.; Tian, H. Influence of 4 lactic acid bacteria on the flavor profile of fermented apple juice. Food Biosci. 2019, 27, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cagno, R.; Filannino, P.; Gobbetti, M. Lactic acid fermentation drives the optimal volatile flavor-aroma profile of pomegranate juice. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 248, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y. Novel insight into flavor and quality formation in naturally fermented low-salt fish sauce based on microbial metabolism. Food Res. Int. 2023, 166, 112586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, C.; Tang, Z.; Liu, P.; Ding, W.; Lin, H.; Tang, J. Revealing the formation mechanisms of key flavors in fermented broad bean paste. Food Res. Int. 2024, 177, 113880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Li, P.; Chen, L.; Ma, J.; Guo, H.; Huang, X.; Zhong, R.; Jing, S.; Jiang, L. The formation mechanisms of key flavor substances in stinky tofu brine based on metabolism of aromatic amino acids. Food Chem. 2022, 392, 133253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Ding, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fang, Y.; Yin, L. Metabolic engineering of microorganisms to produce pyruvate and derived compounds. Molecules 2023, 28, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wakai, S.; Sasakura, N.; Tsutsumi, H.; Hata, Y.; Ogino, C.; Kondo, A. Pyruvate metabolism redirection for biological production of commodity chemicals in aerobic fungus Aspergillus oryzae. Metab. Eng. 2020, 61, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de L Agüero, N.; Frizzo, L.S.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Aleu, G.; Rosmini, M.R. Technological characterisation of probiotic lactic acid bacteria as starter cultures for dry fermented sausages. Foods 2020, 9, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardones, W.; Villarroel, C.A.; Krogerus, K.; Tapia, S.M.; Urbina, K.; Oporto, C.I.; O’Donnell, S.; Minebois, R.; Nespolo, R.; Fischer, G.; et al. Molecular profiling of beer wort fermentation diversity across natural Saccharomyces eubayanus isolates. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bai, Y.; Fan, T.P.; Zheng, X.; Cai, Y. Unveiling the multipath biosynthesis mechanism of 2-phenylethanol in proteus mirabilis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 7684–7690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M. Acetyl xylan esterase of Aspergillus ficcum catalyzed the synthesis of peracetic acid from ethyl acetate and hydrogen peroxide. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 112, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| NO. | VFCs | Thresholds (μg/kg) | Contents (mg/kg) | OAVs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ethyl caproate | 0.00065 | 1.273 | 1.95 × 106 |
| 2 | Acetaldehyde | 0.021 | 1.892 | 9.01 × 104 |
| 3 | Isoamyl acetate | 0.0035 | 0.236 | 6.75 × 104 |
| 4 | Hexaldehyde | 0.0069 | 0.352 | 5.10 × 104 |
| 5 | Phenylacetaldehyde | 0.004 | 0.078 | 1.96 × 104 |
| 6 | Linalool | 0.0053 | 0.081 | 1.54 × 104 |
| 7 | 3-Methylbutanol | 0.735 | 8.480 | 1.15 × 104 |
| 8 | Ethyl heptanoate | 0.019 | 0.167 | 8.76 × 103 |
| 9 | Ethyl caprate | 0.0725 | 0.616 | 8.50 × 103 |
| 10 | Nonyl aldehyde | 0.0036 | 0.027 | 7.47 × 103 |
| 11 | 2-Amylfuran | 0.0059 | 0.036 | 6.13 × 103 |
| 12 | 2-Nonanol | 0.07 | 0.357 | 5.11 × 103 |
| 13 | Ethyl caprylate | 0.0193 | 0.086 | 4.44 × 103 |
| 14 | Hexyl acetate | 0.08 | 0.308 | 3.85 × 103 |
| 15 | 2-Methylbutanol | 1.2 | 3.572 | 2.98 × 103 |
| 16 | 2-Undecanone | 0.007 | 0.016 | 2.29 × 103 |
| 17 | 1-Hexanol | 1.21 | 2.602 | 2.15 × 103 |
| 18 | 1-Octen-3-ol | 0.0425 | 0.067 | 1.58 × 103 |
| 19 | 2-Heptenal | 0.032 | 0.045 | 1.41 × 103 |
| 20 | 2-Heptanone | 0.14 | 0.197 | 1.41 × 103 |
| 21 | Ethyl benzoate | 0.06 | 0.079 | 1.31 × 103 |
| 22 | Ethyl acetate | 3.29 | 3.028 | 9.20 × 102 |
| 23 | 2-Undecanol | 0.0248 | 0.014 | 5.67 × 102 |
| 24 | Hexylenic aldehyde | 0.0887 | 0.049 | 5.56 × 102 |
| 25 | Isobutyl alcohol | 4.8776 | 2.629 | 5.39 × 102 |
| 26 | Benzaldehyde | 0.75089 | 0.286 | 3.81 × 102 |
| 27 | 1-Propanol | 8.5056 | 2.605 | 3.06 × 102 |
| 28 | Benzeneethanol | 1 | 0.264 | 2.64 × 102 |
| 29 | Lactic acid | 9 | 1.562 | 1.74 × 102 |
| 30 | Ethyl palmitate | 2 | 0.278 | 1.39 × 102 |
| 31 | Octanoic acid | 3.0 | 0.300 | 99.9 |
| 32 | Phenethyl acetate | 0.24959 | 0.018 | 72.6 |
| 33 | Ethanol | 150 | 9.816 | 65.4 |
| 34 | Hexanoic acid | 3.0 | 0.190 | 63.2 |
| 35 | 2,3-Butanediol | 67.5 | 2.953 | 43.8 |
| 36 | Ethyl laurate | 3.15 | 0.098 | 31.2 |
| 37 | Decanoic acid | 2.595 | 0.079 | 30.3 |
| 38 | Benzyl alcohol | 8.7731 | 0.198 | 22.6 |
| 39 | Tetradecane | 1 | 0.017 | 16.5 |
| 40 | Acetic acid | 50 | 0.811 | 16.2 |
| 41 | Methyl palmitate | 2 | 0.011 | 5.7 |
| 42 | Ethyl lactate | 150 | 0.197 | 1.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, C.; Yuan, H.; Shi, S.; Xu, M.; Shi, W.; Yu, N.; Hou, J.; Wang, Y. Correlations Between Flavor Profile and Microbial Community Succession in Probiotic-Fermented Burdock Root. Fermentation 2025, 11, 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11110604
Xie C, Yuan H, Shi S, Xu M, Shi W, Yu N, Hou J, Wang Y. Correlations Between Flavor Profile and Microbial Community Succession in Probiotic-Fermented Burdock Root. Fermentation. 2025; 11(11):604. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11110604
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Chunzhi, Heng Yuan, Shuxin Shi, Mengying Xu, Wenting Shi, Nannan Yu, Jinhui Hou, and Yu Wang. 2025. "Correlations Between Flavor Profile and Microbial Community Succession in Probiotic-Fermented Burdock Root" Fermentation 11, no. 11: 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11110604
APA StyleXie, C., Yuan, H., Shi, S., Xu, M., Shi, W., Yu, N., Hou, J., & Wang, Y. (2025). Correlations Between Flavor Profile and Microbial Community Succession in Probiotic-Fermented Burdock Root. Fermentation, 11(11), 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11110604






