Exploration of Co-Inoculation of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Kazachstania bulderi for Potential Use in Mushroom Pleurotus eryngii Pickle Fermentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganisms and Raw Materials
2.2. Preparation of Fermented Mushrooms
2.3. Microbiological Analyses and pH Measurement
2.4. Determination of Organic Acids
2.5. Determination of Nitrites
2.6. Biogenic Amine Analysis
2.7. Determination of Volatile Flavor Compounds
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dynamics of Microbial Counts and pH during Fermentation
3.2. Organic Acids during Fermentation
3.3. Biogenic Amines in Different Fermented P. eryngii
3.4. Dynamics of Nitrite in Fermentation Process
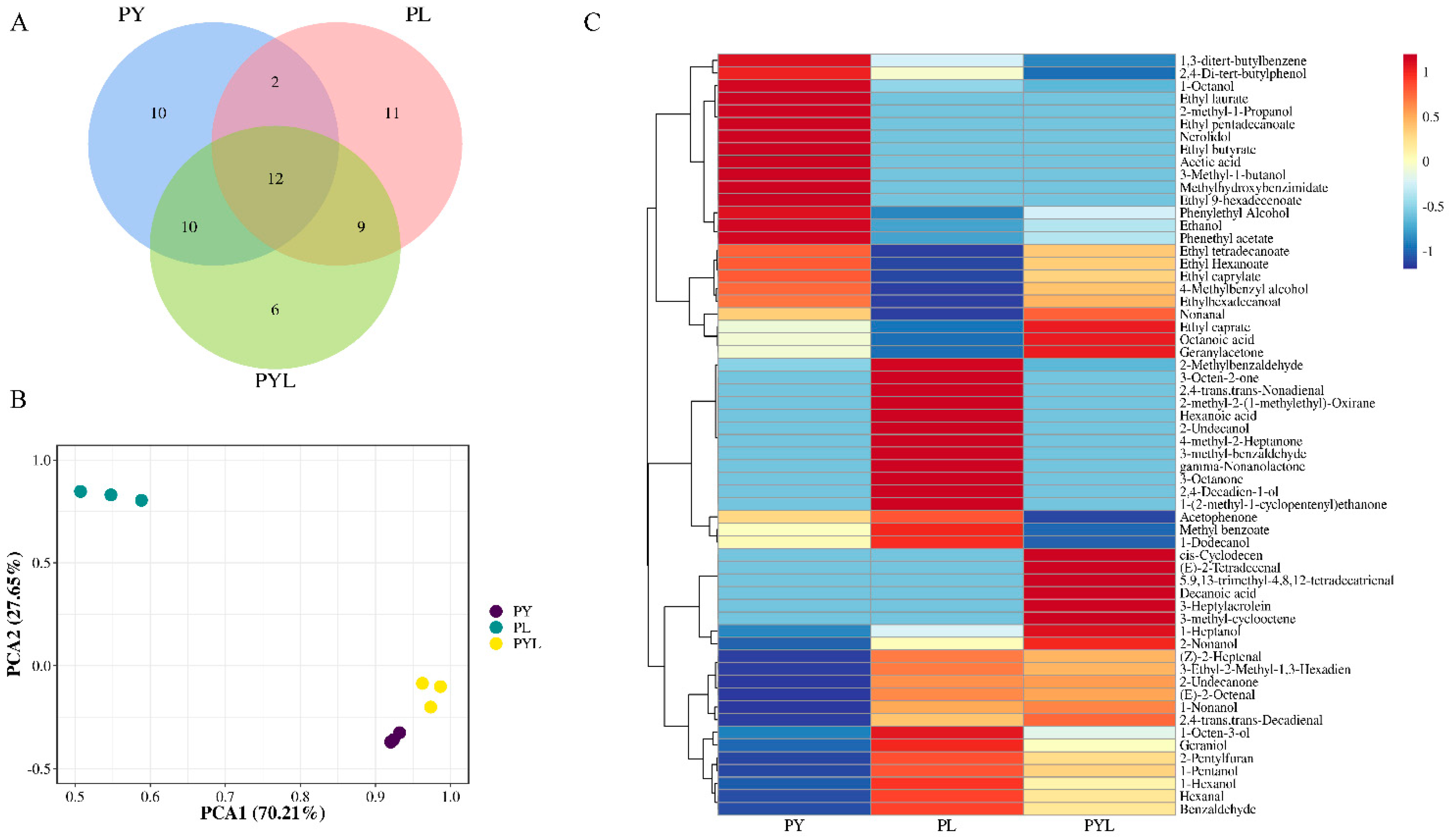
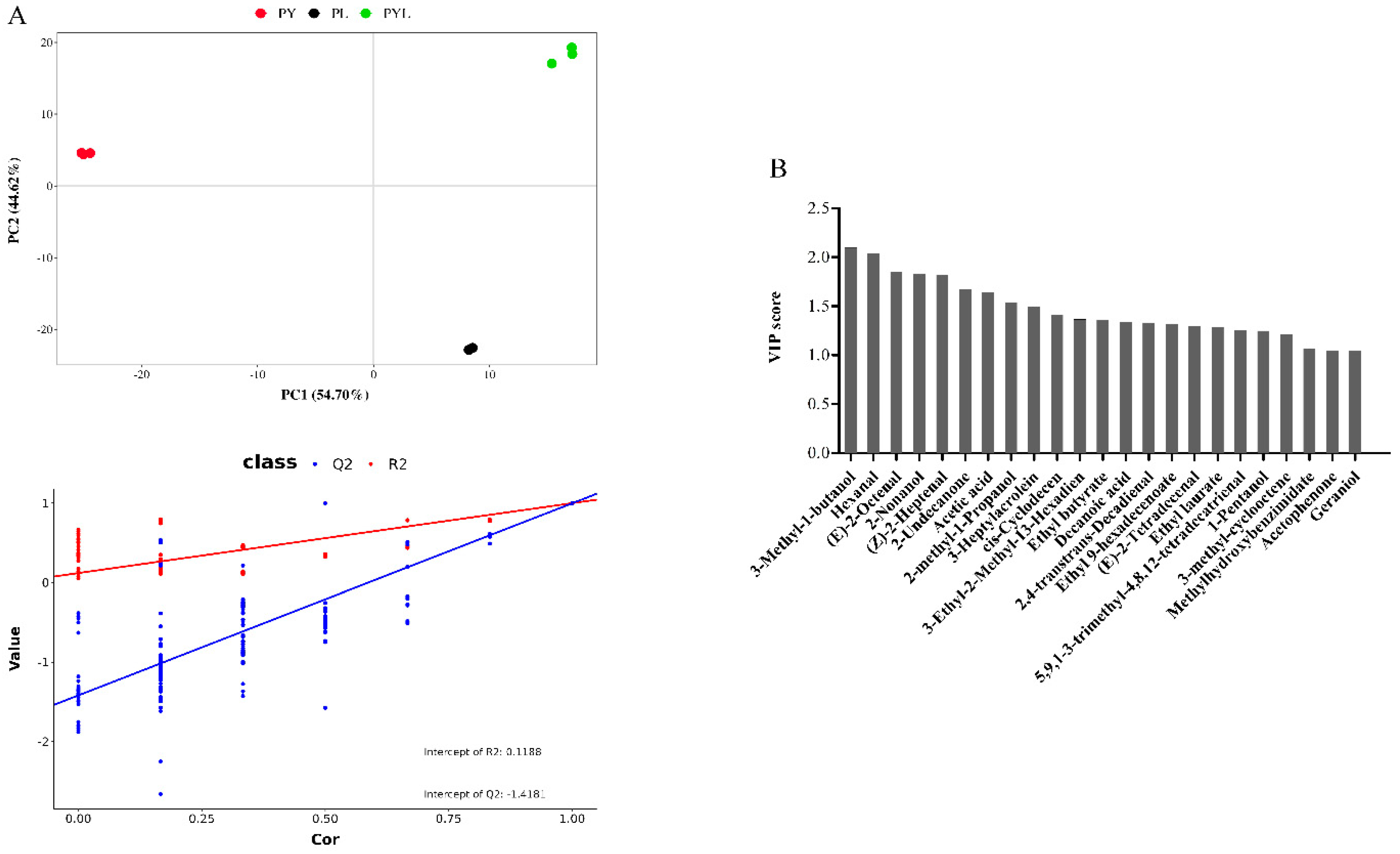
3.5. Volatile Flavor Compounds in Different Fermented P. eryngii
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Qu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, D.; Sun, L.; Tai, G.; Zhou, Y.; et al. β-1,6-glucan from Pleurotus eryngii modulates the immunity and gut microbiota. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 859923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulaka, A.; Mantellou, P.; Stanc, G.M.; Souka, E.; Valavanis, C.; Saxami, G.; Mitsou, E.; Koutrotsios, G.; Zervakis, G.I.; Kyriacou, A.; et al. Genoprotective activity of the Pleurotus eryngii mushrooms following their in vitro and in vivo fermentation by fecal microbiota. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 988517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Xu, Q.; Du, H.; Muinde Kimatu, B.; Su, A.; Yang, W.; Hu, Q.; Xiao, H. Characterization of polysaccharide from Pleurotus eryngii during simulated gastrointestinal digestion and fermentation. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.J.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, A. Extraction, structure and bioactivities of the polysaccharides from Pleurotus eryngii: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 1342–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonsiriwit, A.; Xiao, Y.; Kathuria, A.; Lee, Y.S. Effect of moisture-controlled packaging treatment with acid-modified expanded vermiculite-calcium chloride on the quality of fresh mushrooms (Agaricus bisporus) during low-temperature storage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 3029–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Zhang, P.; Deng, C.; Xu, L.; Yu, M.; Yang, W.; Zhao, R.; Li, B. Effects of Pleurotus eryngii (mushroom) powder and soluble polysaccharide addition on the rheological and microstructural properties of dough. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2113–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Septembre-Malaterre, A.; Remize, F.; Poucheret, P. Fruits and vegetables, as a source of nutritional compounds and phytochemicals: Changes in bioactive compounds during lactic fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2018, 104, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, H.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Waterhouse, G.I.; Cui, C.; Ruan, Z. Fermentation-enabled wellness foods: A fresh perspective. Food Sci. Hum. Well 2019, 8, 203–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska-Ryś, E.; Skrzypczak, K.; Sławińska, A.; Radzki, W.; Gustaw, W. Lactic acid fermentation of edible mushrooms: Tradition, technology, current state of research: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Xiong, T.; Peng, Z.; Liu, C.; Huang, T.; Yu, H.; Xie, M. Correlation between microbiota and flavours in fermentation of Chinese Sichuan Paocai. Food Res. Int. 2018, 114, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkiene, E.; Zokaityte, E.; Starkute, V.; Mockus, E.; Klupsaite, D.; Lukseviciute, J.; Bogomolova, A.; Streimikyte, A.; Ozogul, F. Biopreservation of wild edible mushrooms (Boletus edulis, Cantharellus, and Rozites caperata) with lactic acid bacteria possessing antimicrobial properties. Foods 2022, 11, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabłońska-Ryś, E.; Sławińska, A.; Radzki, W.; Gustaw, W. Evaluation of the potential use of probiotic strain Lactobacillus plantarum 299v in lactic fermentation of button mushroom fruiting bodies. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2016, 15, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, X.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Khaskheli, S.G.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, W. Characterization of Lactobacillus pentosus as a starter culture for the fermentation of edible oyster mushrooms (Pleurotus spp.). LWT 2016, 68, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Han, M.; Li, H.; Yue, T.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Z. Effects of fermentation with Lactobacillus fermentum 21828 on the nutritional characteristics and antioxidant activity of Lentinus edodes liquid. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 3405–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, F.; Sun, H.; Wu, J.; Zhao, C.; Li, T.; Huang, H.; Fang, Q.; Mu, E.; Wu, R. Investigating the core microbiota and its influencing factors in traditional Chinese pickles. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Ye, Z.; Li, M.; Ren, H.; Cai, S.; Hu, X.; Yi, J. Dynamics of microbial communities, flavor, and physicochemical properties of pickled chayote during an industrial-scale natural fermentation: Correlation between microorganisms and metabolites. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 132004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.S.; Sheikha, A.; Hammami, R.; Kumar, A. Traditionally fermented pickles: How the microbial diversity associated with their nutritional and health benefits? J. Func. Foods 2020, 70, 103971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Xin, X.; Liao, X. Metagenomics reveals the formation mechanism of flavor metabolites during the spontaneous fermentation of potherb mustard (Brassica juncea var. multiceps). Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Xu, Y. A bottom-up strategy for constructing a synthetic microbiome and its application to the design of Pixian Douban starter. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2022, 62, 3913–3931. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, I.; de Sousa Melo, D.; Menezes, A.G.T.; Fonseca, H.C.; de Assis, B.B.T.; Ramos, C.L.; Magnani, M.; Dias, D.R.; Schwan, R.F. Evaluation of potentially probiotic yeasts and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum in co-culture for the elaboration of a functional plant-based fermented beverage. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ni, Y.; Yu, Q.; Fan, L. Evaluation of co-fermentation of L. plantarum and P. kluyveri of a plant-based fermented beverage: Physicochemical, functional, and sensory properties. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Mi, S.; Wang, X.; Mao, K.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Sang, Y. Characterization and discrimination of fermented sweet melon juice by different microbial strains via GC-IMS-based volatile profiling and chemometrics. Food Sci. Hum. Well 2023, 12, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Wu, Y.; Guo, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, X.; Gai, Z. Milk fermentation by monocultures or co-cultures of Streptococcus thermophilus strains. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1097013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Wang, W.; Dou, Z.; Chen, J.; Meng, Y.; Cai, L.; Li, Y. Effects of mixed fermentation of different lactic acid bacteria and yeast on phytic acid degradation and flavor compounds in sourdough. LWT 2023, 174, 114438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Guo, L.; Gu, J.; Mu, G.; Tuo, Y. Screening lactic acid bacteria and yeast strains for soybean paste fermentation in northeast of China. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 4502–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz Rodríguez, L.G.; Mohamed, F.; Bleckwedel, J.; Medina, R.; De Vuyst, L.; Hebert, E.M.; Mozzi, F. Diversity and functional properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from wild fruits and flowers present in Northern Argentina. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Elliston, A.; Le Gall, G.; Colquhoun, I.J.; Collins, S.R.A.; Dicks, J.; Roberts, I.N.; Waldron, K.W. Yeast diversity in relation to the production of fuels and chemicals. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thierry, A.; Baty, C.; Marché, L.; Chuat, V.; Picard, O.; Lortal, S.; Valence, F. Lactofermentation of vegetables: An ancient method of preservation matching new trends. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2023, 139, 104112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofalo, R.; Fusco, V.; Böhnlein, C.; Kabisch, J.; Logrieco, A.F.; Habermann, D.; Cho, G.S.; Benomar, N.; Abriouel, H.; Schmidt-Heydt, M.; et al. The life and times of yeasts in traditional food fermentations. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 60, 3103–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashaolu, T.J.; Khalifa, I.; Mesak, M.A.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Farag, M.A. A comprehensive review of the role of microorganisms on texture change, flavor and biogenic amines formation in fermented meat with their action mechanisms and safety. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 63, 3538–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świder, O.; Roszko, M.Ł.; Wójcicki, M.; Szymczyk, K. Biogenic amines and free amino acids in traditional fermented vegetables-dietary risk evaluation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 856–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA scientific opinion on risk based control of biogenic amine formation in fermented foods. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2393. [CrossRef]
- Al-Habsi, M.; Chamoto, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Nomura, N.; Zhang, B.; Sugiura, Y.; Sonomura, K.; Maharani, A.; Nakajima, Y.; Wu, Y.; et al. Spermidine activates mitochondrial trifunctional protein and improves antitumor immunity in mice. Science 2022, 378, eabj3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofer, S.J.; Simon, A.K.; Bergmann, M.; Eisenberg, T.; Kroemer, G.; Madeo, F. Mechanisms of spermidine-induced autophagy and geroprotection. Nat. Aging 2022, 2, 1112–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Li, C.; He, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Ho, C. Research advances on biogenic amines in traditional fermented foods: Emphasis on formation mechanism, detection and control methods. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bover-Cid, S.; Izquierdo-Pulido, M.; Vidal-Carou, M.C. Mixed starter cultures to control biogenic amine production in dry fermented sausages. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 1556–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Jover, T.; Izquierdo-Pulido, M.; Veciana-Nogués, M.T.; Mariné-Font, A.; Vidal-Carou, M.C. Biogenic amine and polyamine contents in meat and meat products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 2098–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laranjo, M.; Potes, M.E.; Elias, M. Role of starter cultures on the safety of fermented meat products. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maijala, R.; Eerola, S.; Lievonen, S.; Hill, P.; Hirvi, T. Formation of biogenic amines during ripening of dry sausages as affected by starter culture and thawing time of raw materials. J. Food Sci. 1995, 60, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xu, Z. Evaluation of nitrite, ethyl carbamate, and biogenic amines in four types of fermented vegetables. Foods 2021, 10, 3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, E.; González-Montelongo, R.; Giraldez, T.; Alvarez de la Rosa, D.; Siverio, J.M. Molecular components of nitrate and nitrite efflux in yeast. Eukaryot. Cell 2014, 13, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Zeng, X.; Kong, L.; Sun, X.; Shi, J.; Wu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Pan, D. Research progress of nitrite metabolism in fermented meat products. Foods 2023, 12, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.L.M.; Bueno, A.V.I.; Osmari, M.P.; Machado, J.; Nussio, L.G.; Jobim, C.C.; Daniel, J.L.P. Effects of obligate heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria alone or in combination on the conservation of sugarcane silage. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 643879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saerens, S.M.; Delvaux, F.; Verstrepen, K.J.; Van Dijck, P.; Thevelein, J.M.; Delvaux, F.R. Parameters affecting ethyl ester production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae during fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Huang, K.; Yu, H.; Tian, H. The diversity of microbial communities in Chinese milk fan and their effects on volatile organic compound profiles. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 2581–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorn, D.; Nguyen, T.K.; Ho, P.H.; Tan, R.; Licandro, H.; Waché, Y. Screening of lactic acid bacteria for their potential use as aromatic starters in fermented vegetables. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 350, 109242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Wang, X.; Wan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Zhu, Q. Correlation and difference between core micro-organisms and volatile compounds of Suan Rou from six regions of China. Foods 2022, 11, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 2760-2014; National Food Safety Standard—Standard for Uses of Food Additives. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republication of China: Beijing, China, 2014.


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gou, X.; Zhang, W.; Luo, X.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, S.; He, R.; Hua, R.; Wu, S.; Sun, D. Exploration of Co-Inoculation of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Kazachstania bulderi for Potential Use in Mushroom Pleurotus eryngii Pickle Fermentation. Fermentation 2024, 10, 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10080428
Gou X, Zhang W, Luo X, Zhou P, Zhang S, He R, Hua R, Wu S, Sun D. Exploration of Co-Inoculation of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Kazachstania bulderi for Potential Use in Mushroom Pleurotus eryngii Pickle Fermentation. Fermentation. 2024; 10(8):428. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10080428
Chicago/Turabian StyleGou, Xuelei, Weisi Zhang, Xiaoli Luo, Pei Zhou, Shasha Zhang, Rong He, Rong Hua, Surui Wu, and Dafeng Sun. 2024. "Exploration of Co-Inoculation of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Kazachstania bulderi for Potential Use in Mushroom Pleurotus eryngii Pickle Fermentation" Fermentation 10, no. 8: 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10080428
APA StyleGou, X., Zhang, W., Luo, X., Zhou, P., Zhang, S., He, R., Hua, R., Wu, S., & Sun, D. (2024). Exploration of Co-Inoculation of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Kazachstania bulderi for Potential Use in Mushroom Pleurotus eryngii Pickle Fermentation. Fermentation, 10(8), 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10080428





