Abstract
At psychrophilic temperatures (<20 °C), anaerobic digestion produces less methane (CH4). For psychrophilic anaerobic digestion (PAD) to be successful, investigation of cold-adapted microbial consortia involved in methane production is critical. This study aimed to investigate the microbial community driving enhanced methane production from the cold-adaptation process and bioaugmentation of PAD with cold-adapted inoculum (BI). Microbial consortia in cattle manure (CM) and food waste (FW) were adapted and applied during batch PAD of CM and FW to bioaugment methane production at 15 °C. Cold adaptation and PAD with BI resulted in cumulative specific methane yields of 0.874 ± 0.231 and 0.552 ± 0.089 L CH4 g−1 volatile solids, respectively, after 14 weeks, while the absence of BI (control) led to acidification and no methane production during PAD. Following 16S rRNA V4–V5 amplicon sequencing and metagenomic analyses, Methanosarcina was revealed as a key driver of methanogenesis during cold adaptation and PAD bioaugmentation. Furthermore, based on the predictive functional and metabolic analysis of the communities, possible synergies were proposed in terms of substrate production and utilization by the dominant microbial groups. For instance, during methane production, Bacteroides and Methanobrevibacter were possibly involved in a syntrophic relationship, which promoted methanogenesis by Methanosarcina. These findings provide insight into the prospective microbial synergies that can be harnessed and/or regulated in cold-adapted inoculum for the improvement of methane production during PAD.
1. Introduction
Unharnessed methane produced from the decomposition of organic waste such as food waste, animal manure and municipal sewage under anoxic conditions, greatly contributes to the climate crisis [1]. Approximately 40–46% of global methane emissions emanate from the agricultural sector [2]. Conventional agricultural and food production systems often generate millions of tons of biomass energy resources in the form of agricultural waste and livestock manure [3]. In particular, approximately 12 tonnes of crop residue and 121 tonnes of animal manure are produced per annum per South African smallholder farm [4]. Bioenergy in the form of methane derived from anaerobic digestion (AD) of these waste streams has the potential to exceed the energy demands of smallholder households [4]. As a result, the demand for the development of AD technology has increased to harness organic waste for the production of methane as an alternative bioenergy source and a low carbon strategy [5]. Combustion of the methane component of biogas produced from AD can be utilized by smallholder farmers for cooking, heating and lighting purposes, thereby providing access to sustainable bioenergy [6].
Globally, about 84% of farms are operated by smallholder farmers [7]; and millions of smallholder farmers have adopted AD digesters on their farms where food waste and manure are easily accessible for biogas production, particularly in developing countries [8]. Although countries like India and China have installed the largest number of well-developed small-scale digesters (±5–42 million) that have improved the livelihood of their rural communities, the adoption and development of AD technology in African countries has not taken off [4]. In particular, only about 14,000, 11,000, 10,000 and 350 small-scale digesters have been installed in Kenya, Uganda, Ethiopia and South Africa, respectively [9]. Kalina et al. extensively reported on the factors impeding the successful adoption of small-scale digesters in African countries [10]. One prominent factor that affects biogas production and adoption is the low temperatures experienced during winter months [11].
Most small-scale biogas technologies that are adopted use simple, low-cost, unheated digesters that operate at psychrophilic temperatures (below 20 °C) [12]. However, at low temperatures, the AD process often fails to produce methane and conventional solutions include heating systems or insulation, which are expensive and not feasible in rural areas and smallholder farms [11]. Limited studies have investigated the optimization of psychrophilic anaerobic digestion (PAD) compared to mesophilic (20–45 °C) and thermophilic (45–60 °C) AD because the AD process is driven by microorganisms that optimally thrive and metabolize organic substrates to methane at higher temperatures. In most instances, a portion of the energy generated from mesophilic and thermophilic AD is consumed to maintain the high temperatures required to heat the biogas digesters, which often results in minimal net energy production [13]. Therefore, organic waste processing through PAD may be more economical and ecologically beneficial for biogas production, especially in colder regions [3]. However, further investigation on PAD is necessary to optimize methane production during winter months [14].
A drop in temperatures, from 37 °C to 0 °C, can result in a 20–80% reduction in enzymatic activity by mesophilic microorganisms [15]. Low temperature impacts microbial substrate affinity resulting in restricted ability to metabolize substrates that are utilized for growth [16]. In particular, microbial cell membrane fluidity and integrity are physiologically constrained at lower temperatures [16]. The viscosity of the cell membrane increases resulting in reduced movement and diffusion rates of essential nutrients and metabolites that are pertinent to growth and metabolism [13]. More so, faster growing and less cold-sensitive bacteria produce volatile fatty acids (VFAs) during the hydrolysis, acidogenesis and acetogenesis stages of AD, while slow-growing and cold-sensitive methanogens are unable to consume the acidic substrates rapidly enough to produce methane during methanogenesis [13]. This phenomenon results in acidification and reduced buffering capacity in anaerobic digesters, which is a common problem caused by an imbalance in acid consumption and production kinetics [17]. Subsequently, low pH levels from acid accumulation in digesters can create an unstable environment for methanogenic activity by methanogens [3]. Thus, colder temperatures often result in longer AD fermentation cycles and lower methane production due to the impacted performance of cold-sensitive microorganisms.
Cold-adapted microorganisms possess cold-adapted enzymes with lower activation energies and higher membrane structural flexibilities, which allows for better affinity to substrates and higher catalytic rates at low temperatures [18]. Research on stable, cold-tolerant microorganisms driving methane production at psychrophilic temperatures may provide insight into targeted approaches to improving PAD and may pave the way for the development of biogas production on smallholder farms and in colder regions. Previously, 28.3% enhanced methane production during PAD was reported from bioaugmentation with cold-adapted cattle manure inoculum containing acetoclastic Methanosaeta and Methanosarcina as well as fermentative bacteria, Clostridium and Lactobacillus [19]. In another study, bioaugmentation with psychrotolerant inoculum, which was prepared via gradual acclimation of mesophilic inoculum fed with cellulose and natural peptone from 35 to 25 °C in a continuously-stirred tank reactor, was shown to improve PAD of corn starch and cattle manure by 3.4–4.8-fold [20]. The inoculum consisted primarily of Peptococcaceae, Thermovirga and Bacteroidetes, which are fermentative bacteria involved in hydrolysis and acidogenesis as well as butyrate and propionate metabolism during acetogenesis. The archaeal community consisted of acetoclastic methanogens, Methanothrix and Methanosarcina that can metabolize acetate to methane. These cold-adapted microbial groups formed syntrophic relations, which balanced substrate production and consumption, and enhanced psychrophilic methane production.
Liu and colleagues previously reported the core microbial groups involved in PAD of synthetic dairy wastewater with long-chain fatty acids (LCFA) contained acetoclastic Methanosaeta, hydrogenotrophic Methanocorpusculum and bacteria involved in carbohydrate fermentation (Trichococcus, Uncultured Rikenellaceae and Acetobacteroides) [21]. An important finding from the study was that utilization of cold-adapted inoculum enriched with syntrophic bacteria involved in LCFA degradation (uncultured Synergistaceae, uncultured Spirochaetaceae and Smithella) was essential for successful PAD of wastewater containing LCFA. Their study concluded that it was necessary to utilize genome-centric tools to elucidate the microbial community dynamics and their involvement in AD of LCFA. Other studies have indicated that adapting all substrates used for co-digestion to colder temperatures can potentially enhance the PAD of the substrates due to the enrichment of communities with substrate-specific metabolism [13,22]. However, research is rarely published on the dominant and stable indigenous microbial consortia from mixed vegetable food waste and cattle manure after cold acclimatization and the impact of its application for bioaugmentation of methane production on microbial community dynamics and metabolic pathways in PAD.
This study aimed to elucidate the microbial community dynamics during methane production from the cold adaptation of microorganisms from mixed-vegetable food waste and cattle manure substrates. Furthermore, the effect of the cold-adapted inoculum on methane production and microbial community dynamics at psychrophilic temperatures (15 °C) was investigated in batch PAD trials. Additionally, potential synergistic relationships between the key microbial drivers of methane production were proposed based on the metagenomics analysis conducted. The findings of this study provided better insight into the synergies between microbial communities driving methane production during cold adaptation and PAD as well as a theoretical basis for developing and improving PAD on smallholder farms through cold-adapted microbial intervention.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cold-Adapted Inoculum Preparation
Food waste (FW) composed of mixed vegetables (6 peppers, 10 baby onions, 5 beetroots, 3 cucumbers, 19 carrots, 1 cabbage and a punnet of broccoli and lettuce) was collected from Tshwane Market (Pretoria, South Africa). The vegetables that were collected were deemed no longer fit for retail by the market (Personal communication). The FW was homogenized with a blender and pasteurized at 70 °C for 1 h [23]. Wet cattle manure (CM) was aseptically collected with gloves from the Agricultural Research Council—Animal Production (Pretoria, South Africa). Cattle manure was placed in a sterilized cooler box and transported to the laboratory. The homogenized FW was stored at −20 °C until further use. The cold-adaptation trial (B_Adapt) was conducted in triplicate by incubating a 10% (w/v) 2:1 mixture of CM and FW in high pressure resistant, airtight 1180 mL borosilicate bottles closed with polytetrafluoroethylene coated septa in a working volume of 500 mL. Incubation occurred at 30 °C (1 week), 25 °C (1 week), 20 °C (2 weeks) and 15 °C (10 weeks), successively, with shaking at 100 rpm (Low temperature IncoShake Incubator, Labotec) [19]. Thereafter, the cold-adapted inoculum was stored at 4 °C (termed BI) and used within a month in the PAD batch culture trial.
2.2. Batch Culture Setup
After the cold adaptation trial, psychrophilic anaerobic digestion was conducted in triplicate in batch reactors (366 mL borosilicate bottles closed with polytetrafluoroethylene coated septa) at 15 °C with shaking at 100 rpm (Low temperature IncoShake Incubator, Labotec) for 14 weeks. The experimental batch cultures (B_Inoc) contained 10% (w/v) of CM, FW and BI (i.e., refrigerated cold-adapted inoculum—see Section 2.1), which were mixed in a 2:1:1 (CM:FW:BI) ratio with a working volume of 150 mL. This ratio was applied as it produced the best methane yields in a previous study [19]. The control batch cultures (B_0) contained 10% (w/v) (2:1) CM to FW with no addition of BI. The characteristics of the substrates are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Characteristics of feedstock, cold-adapted inoculum, and digestate.
2.3. Analytical Methods
The total solids (TS) and volatile solids (VS) of the feedstock and BI were characterized according to reported methods [24]. The carbon/nitrogen (C/N) ratio of the feedstock and inoculum was analyzed by the Agricultural Research Council—Natural Resources and Engineering, Arcadia Campus (Pretoria, South Africa) using the Flash 2000 CHNS/O analyzer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The lipid, carbohydrate and protein content of the feedstock were analyzed by the Agricultural Research Council—Animal Production (Pretoria, South Africa) according to reported methods [25]. The pH and VFAs to total alkalinity (FOS/TAC) ratios of the samples were analyzed using the 877 Titrino Plus (Metrohm, Herisau, Switzerland). Methane was measured weekly using an 8610C Gas Chromatograph (GC) (SRI Instruments, Torrance, CA, USA) equipped with a thermal conductivity detector and a HayeSep D packed column. The methane volume was calculated by multiplying the methane percentage by the headspace volume as previously described by Nkuna et al. [26]. The cold adaptation process and PAD trials were terminated after 14 weeks when weekly specific methane yields plateaued and/or reduced. Statistical analysis of variance tests on the accumulative specific methane yields denoted as L CH4 g−1 VS produced from the cold adaptation and PAD trials were conducted using XLSTAT in Excel (Version 2209, Build 16.0.15629.20152) (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA) and SAS9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, CA, USA) [27].
2.4. Kinetics Modelling
The modified Gompertz model (1) was fitted with the observed specific methane yields (mL CH4 g−1 VS—O) obtained over the duration of the trials (days—t) to determine the predicted maximum methane production potential that can be achieved (mL CH4 g−1 VS—P), the maximum methane production rate (mL CH4 g−1 VS d−1—Rm) as well as the lag phase period (in days—λ) [28].
2.5. Next Generation Sequencing of 16S rRNA V4-V5 Amplicons
Extraction of deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) from the feedstock, cold-adapted inoculum as well as inoculum adaptation and batch culture samples (before and after the trials) was conducted in triplicate according to the protocols of the ZymoBIOMICS DNA Miniprep Kit (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, USA). The DNA extracts were standardized to 2 ng/µL, thereafter the triplicate standardized extracts were pooled. The 16S V4–V5 region of the pooled DNA extracts was amplified during polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using the T100 Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) and primers 515F-Y and 915R as described by Fadeev et al. [29] and containing Illumina adapters. The PCR was conducted as follows using OneTaq® 2× Master Mix with Standard Buffer (New England Biolabs Inc., Ipswich, MA, USA): 94 °C for 30 s (initial denaturation), 94 °C for 30 s (denaturation); 55 °C for 30 s (annealing) and 68 °C for 1 min (extension) for 35 cycles; and 68 °C for 5 min (final extension). The PCR products were cleaned, indexed, and sequenced by the Agricultural Research Council—Biotechnology Platform (Onderstepoort, South Africa) using the Illumina MiSeq benchtop system (San Diego, CA, USA).
2.6. Metagenomic Analyses of Sequences
The quality and trimming of the raw sequences were conducted using FastQC [30] and Trimmomatic [31], respectively. The trimmed sequences were then processed using QIIME2™ and DADA2 pipelines [32,33] to produce feature tables of amplicon sequence variants, classify taxonomy, and analyze the beta and alpha diversities of the samples. R (version 3.5.3), RStudio, Tax4Fun2 and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) [34,35,36,37,38,39] were used to determine the predictive pathway and functional capabilities of the microbial communities.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Methane Production
Specific methane yields during cold adaptation and PAD are shown in Figure 1. A high variance in specific methane yields was observed particularly towards the end of the cold adaptation trial. A possible reason for this behavior in the data includes the small size of the dataset (n = 3). No methane production occurred during PAD of B_0. The low pH (5.75) and high FOS/TAC ratio (0.73) obtained after PAD of B_0 suggest that the accumulation of acidic products occurred. Despite the long fermentation cycle, archaea typically grow slower than fermentative bacteria which can result in the accumulation of acidic products [3]. Thus, a possible explanation for the acidic pH levels is the lack of cold-adapted methanogens to convert the acidic substrates to methane. Additionally, methanogens are sensitive to low pH levels and temperatures [3]. As a result, methanogenesis may have been further inhibited, which led to the collapse of the batch reactors. Conversely, the pH and FOS/TAC ratios for B_Adapt and B_Inoc after the trials were 6.5–6.8 and 0.48–0.42, respectively. These results suggest that BI or cold adaptation was necessary for methane production to occur at 15 °C. Higher methane yields can be observed from B_Adapt in the second week onwards compared to B_Inoc, where methane production began in the third week. A small portion of B_Inoc consisted of the cold-adapted inoculum, however, the remaining feedstock was fresh and not cold-adapted, which may have resulted in the observed time lag. Nevertheless, bioaugmentation of methane production occurred due to the addition of BI, which resulted in stable methane yields towards the end of the trial. Additionally, the initial methane yields from B_Adapt can be attributed to the higher temperatures (20–35 °C) at which cold adaptation occurred. However, increase in methane yields from week 4 to 14 was observed from B_Adapt, which peaked in week 13 (0.153 ± 0.040 L CH4 g−1 VS), despite the drop in temperature to 15 °C.

Figure 1.
Specific methane yields observed during cold-adaptation (B_Adapt) and psychrophilic anaerobic digestion with cold-adapted inoculum (B_Inoc) and without cold-adapted inoculum (B_0). Standard deviation is represented by error bars (n = 3).
The efficiency of methane production during cold adaptation and PAD of B_Inoc was evaluated with the modified Gompertz model (Table 2), which fitted moderately well with the experimental data (R2 = 0.98). The fitted graph is shown in Figure S1. These results suggest that the cold adaptation process was successful and improved the efficiency of methane production under batch psychrophilic conditions, as shown by the reduced lag phase, possibly due to a more stable microbial community. Many studies have reported on the improvement of PAD of different feedstock with the addition of cold-acclimatized biomass [3,21,40].

Table 2.
Kinetic features from the cold adaptation and psychrophilic anaerobic digestion trials using modified Gompertz model.
The cumulative specific methane yields obtained from B_Adapt and B_Inoc were 0.874 ± 0.231 L CH4 g−1 VS and 0.552 ± 0.089 L CH4 g−1 VS, respectively, which were significantly different (p < 0.05). These results were comparable to other recent reports. For instance, Casallas-Ojeda and colleagues reported specific methane yields of 0.562 L CH4 g−1 VS from PAD of cheese whey and dairy manure at 20 °C [41]. In another study, Esparza-Soto et al. reported specific methane yields of 0.20 to 0.27 L CH4 g−1 VS from PAD of waste activated sludge and organic kitchen waste at 20 °C [42].
In the present study, methane yields of 0.081 ± 0.010 L CH4 g−1 VS were obtained on day 70 (week 10) from B_Inoc. On the other hand, Xu et al. reported maximum methane yields from 0.008–0.036 L CH4 g−1 VS by the end of their trial on day 70 during bioaugmentation of PAD (20 °C) of corn starch and CM with the addition of 0–16% mesophilic bioaugmentation seed [3]. In another study, Xu et al. reported maximum methane yields of 0.015–0.073 L CH4 g−1 VS on day 86 (last day) of batch PAD (20 °C) of corn starch and CM with the addition of 0–16% psychrotrophic bioaugmentation seed [20]. In addition, Zhu and Jha et al. reported maximum methane yields of 0.007–0.015 L CH4 g−1 VS on day 84 of dry PAD (15 °C) of CM with cold-adapted CM inoculum [19]. In contrast, the maximum methane yields produced in this study on day 84 (week 12) were 0.074 ± 0.009 L CH4 g−1 VS from B_Inoc. The difference in methane yields between the present study and the other studies may possibly be tied to the resident microbial consortia of the respective feedstocks and inocula. Nonetheless, our results are comparable to the other batch anaerobic co-digestion studies conducted under psychrophilic conditions and showed improved methane production during psychrophilic anaerobic co-digestion of FW and CM with the addition of cold-adapted FW and CM inoculum. Additionally, the results suggest that a direct transition from cold adaptation to PAD or the addition of cold-adapted inoculum to psychrophilic digesters has the potential to improve the efficiency of methane production.
Nevertheless, mesophilic and thermophilic AD cycles typically operate at faster rates due to the higher temperatures [43]. While methane yields and lag phase improved with the addition of BI, further research is required to reduce the duration of the PAD fermentation cycle. Furthermore, semi-continuous or continuous PAD studies can determine the possibility of upscaling methane production under psychrophilic conditions using the cold-adapted inoculum or from the direct transition from cold adaptation to PAD. Such studies may further elucidate the susceptibility of the cold-adapted microbial community to being washed out of reactors.
3.2. Microbial Community Dynamics
3.2.1. Bacterial Community Composition
The bacterial community composition at the genus level for the cold adaptation and PAD trials is shown in Figure 2. Bacteroides and Macellibacteroides (obligate anaerobic genera of Bacteroidota) as well as Acinetobacter (aerobic genus of Proteobacteria), were the primary genera present after B_Adapt and B_Inoc trials from which higher methane production was observed. These genera were reported to have predominant roles in fermentation and acetogenesis during PAD [13,44]. Macellibacteroides are known for the ability to ferment glucose to lactate, butyrate, and iso-butyrate as well as acetate (substrates used by methanogens during acetoclastic methanogenesis) [45]. Two psychrotrophic Bacteroides species, Bacteroides graminisolvens and Bacteroides paurosaccharolyticus, had a relative abundance greater than 10% in B_Adapt and B_Inoc after the trials. These species were reported to have capabilities in metabolizing various saccharides to produce acetate, propionate, and succinate (substrates utilized by acetogens and methanogens) [46,47]. Acinetobacter is an obligate aerobe, however, some species can survive in low oxygen environments [48]. Species of the Acinetobacter genus were unclassified or uncultured, however, previous reports indicate their ability to thrive on short chain fatty acids such as acetate compared to simple carbohydrates [49]. This suggests that Acinetobacter possibly played a functional role in acetogenesis during PAD. Classified bacterial genera arising from only FW, which were present in B_Adapt and B_Inoc but not B_0 after the trials include Comamonas and Strenotrophomonas. Both these genera are versatile in their metabolic capabilities and can adapt to various environmental conditions [50,51] as was evident during cold adaptation and PAD of B_Inoc. After the trials, a higher presence of Bifidobacterium genus (8.4%) was observed in B_Adapt and BI (8.2%) compared to B_Inoc (1.4%). Some species and strains of Bifidobacterium play a role in acetate production [52]. It is possible that this bacterial group could not persist during the PAD of B_Inoc.
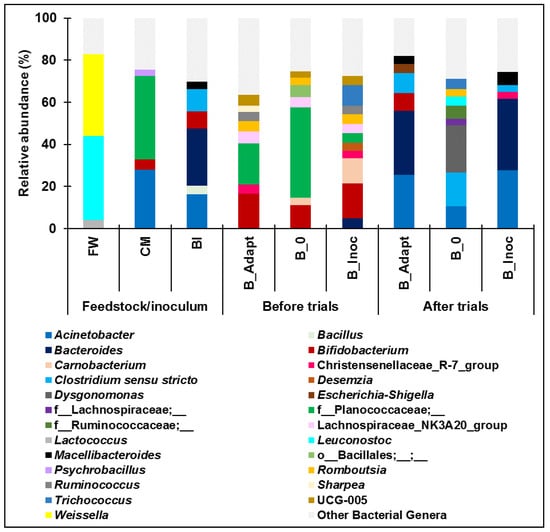
Figure 2.
Bacterial taxonomic classification at genus level (genera with relative abundance < 3% are depicted as Other Bacterial Genera).
Overall, the bacterial composition results suggest that Bacteroides, Macellibacteroides and Acinetobacter were the key bacteria driving PAD of B_Inoc (15 °C). Higher methane production from B_Adapt and B_Inoc possibly resulted from the conversion of available acetate produced by the dominant bacterial groups to methane by acetoclastic methanogens. Dysgonomonas (22.6%) was the dominant genus in B_0 after PAD. Dysgonomonas play a key role in the bioconversion of polysaccharides during biofuel production [53]. The relative abundance of the Dysgonomonas genus was composed of Dysgonomonas gadei (1%), Dysgonomonas alginatilytica (0.4%), and Dysgonomonas capnocytophagoides (0.2%) while the remaining Dysgonomonas species (21%) were either unclassified or uncultured. The identified Dysgonomonas species are capable of metabolizing saccharides to produce acids such as lactic, propionic, and succinic acids [54]. Furthermore, B_0 was composed of a higher relative abundance of Clostridium sensu stricto genera (16%) compared to B_Adapt (9.3%) and B_Inoc (3.3%), after the trials. Clostridium sensu stricto species are capable of metabolizing various substrates to produce acids (e.g., butyric acid, acetic acid, lactic acid, succinic acid) and alcohols (e.g., butanol, ethanol, acetone) [55,56]. Highly acidic environments were found to be less conducive to the growth of methanogens compared to environments with elevated concentrations of weakly basic and dissociated ions of acid products such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate [57]. These results suggest that Dysgonomonas and Clostridium sensu stricto species were the microbial drivers of the acidification and collapse during the PAD of the B_0 batch reactor.
3.2.2. Archaeal Community Composition
The archaeal composition from the feedstock, BI, and trials are shown in Figure 3. The archaeal community originated from CM as no archaea were identified in FW. Methanobrevibacter (>90%) and Methanosphaera (<7%) from the Euryarchaeota phylum were the dominant genera before cold adaptation and PAD. After the trials, Methanosarcina (>50%) and Methanobrevibacter (<50%) dominated the archaeal communities in B_Adapt and B_Inoc, suggesting that these methanogens adapted to colder temperatures. Insignificant change in archaeal community composition was observed in B_0 after PAD from which no cold-adapted inoculum was added, and no methane was produced. These results indicate that the other methanogens could not thrive in the cold and acidic environment.
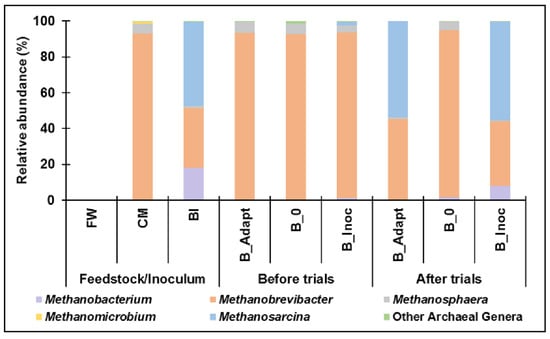
Figure 3.
Archaeal taxonomic classification at genus level (Relative abundance < 1% are depicted as Other Archaeal Genera).
Methanosarcina is metabolically diverse as it possesses all three methanogenesis pathways (methylotrophic, hydrogenotrophic and acetoclastic) where they can utilize methylamines, methanol, hydrogen/carbon dioxide (H2/CO2), and acetate as sources for methane production [58]. In contrast, Methanobrevibacter are hydrogenotrophic methanogens that predominantly utilize H2/CO2 for methane production and acetate for cell synthesis [13,59]. This suggests that a shift occurred towards acetoclastic and/or methylotrophic methanogenesis as the major pathways involved in methane production under psychrophilic, anaerobic conditions. Other reports have suggested similarly acetoclastic methanogenesis being the major pathway during PAD as it is the more thermodynamically favorable pathway under psychrophilic conditions [13,22,60].
Another observation included the higher presence of Methanobrevibacter arboriphilus (4% and 1%) and hydrogenotrophic Methanobacterium (17.9% and 8.1%) in BI and B_Inoc, respectively, compared to B_Adapt (0%) (after cold adaptation/PAD). In addition to Methanosarcina, ten species of Methanobacterium and only one known Methanobrevibacter species, M. arboriphilus, were found to contain genes involved in homoacetogenesis which includes the acetyl-CoA pathway (Module M00422) on the KEGG Pathway database [34,35,36]. This pathway involves the conversion of H2/CO2 to acetyl-CoA which can be further metabolized to produce methane via acetoclastic methanogenesis [61]. Furthermore, M. arboriphilus was previously found to produce acetate and propionate from cysteine, although many hydrogenotrophic methanogens utilize acetate as a carbon source for cell synthesis [59].
Storage conditions (4 °C) of the cold-adapted inoculum (BI) after cold adaptation (B_Adapt) possibly promoted the proliferation of Methanobacterium and M. arboriphilus, which resulted in the shift in archaeal community composition when comparing B_Adapt and B_Inoc, after the trials. A previous study reported similar findings where storage time and temperature of inoculum used for AD impacted the microbial community and its methanogenic activity [62].
3.2.3. Microbial Diversity
Alpha diversity encompasses species richness (number of species in a sample based on abundance which can be estimated with Chao1 and Ace indices) as well as evenness (distribution of individuals among species within a sample that can be estimated with Pielou, Simpson and Shannon indices) [63,64]. The low diversity in terms of species richness and evenness was observed in the feedstock, B_Adapt and B_Inoc (after the trials) as well as B_0 (before PAD) (Table S1). Furthermore, species richness and evenness decreased after cold adaptation and PAD of B_Inoc. Psychrophilic environments are niche environments in which cold adaptable or specific microbial groups can survive and thrive [13]. A previous study supports the results observed herein [65].
In contrast, higher species richness and evenness were observed after PAD of B_0. Based on the results thus far, psychrophilic conditions are conducive to the growth of fermentative bacterial groups as opposed to methanogenic archaeal groups when cold-adapted inoculum or gradual cold adaptation processes are not available. Furthermore, saturation of community function and interaction is probable with increasing diversity and competition between diverse microbial groups [66]. This is particularly evident for B_0 after PAD, whereby diverse and dominant fermentative bacterial genera that could withstand the psychrophilic conditions hindered the transition from fermentative stages to methanogenesis (Figure 2). On the other hand, less species richness and evenness from cold adaptation and PAD of B_Inoc possibly sustained synergistic interactions between species with different functions involved in methane production.
Weighted UniFrac is a beta diversity distance metric that separates environmental samples based on significant differences between phylogenetic lineages of the microbial sequences and their relative abundances obtained per sample [67]. The differences between microbial community structures determined with weighted UniFrac beta diversity metrics are shown in Figure 4. Food waste had the most dissimilar microbial community compared to the other samples indicating that it had the least impact on the other microbial communities. Cattle manure and digestate arising from B_0 (after PAD) clustered together in terms of microbial community structure. Major shifts in microbial community structures between the feedstock and BI are evident. As expected, the microbial communities in B_Adapt, B_Inoc and B_0 before the trials clustered closely together indicating their similarity. Subsequently, B_Adapt, BI and B_Inoc were more similar than B_0 after the trials indicating that BI influenced the microbial community structure of digestate arising from PAD of B_Inoc. In essence, the shift in community structures can be attributed to the adaptation of resident feedstock microbial communities to the digestion process as well as the addition of the inoculum microbial community to B_Adapt and B_Inoc. Similar results were obtained in another study that showed the shift in community due to inoculum addition [68]. Hence, these results correspond to the methane production, microbial taxonomic classification and alpha diversity results obtained thus far.
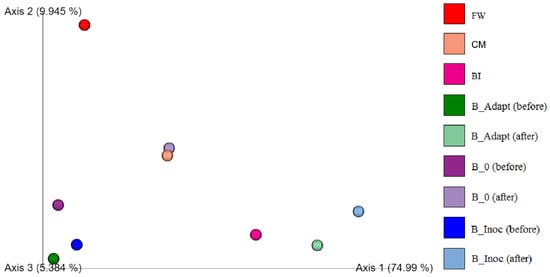
Figure 4.
Weighted UniFrac beta diversity analysis of microbial communities from feedstock, cold adaptation, and psychrophilic (15 °C) anaerobic digestion trials.
3.2.4. Predicted Functional Capabilities
The distinctive functional capabilities of the microbial communities associated with acetoclastic, hydrogenotrophic and methylotrophic methanogenesis as well as homoacetogenesis before and after cold adaptation and PAD were predicted with Tax4Fun2 and KEGG (pathway modules M00567, M00357, M00356, M00563, M00377). The predicted relative abundance of the associated genes is shown in Table S2. Higher representation of predicted functional genes encoding key enzymes associated with acetoclastic methanogenesis and homoacetogenesis were observed across all groups (Figure 5). Autotrophic microorganisms utilize acetyl-CoA, which is produced by using carbon sources such as acetate and CO2, in prokaryotic carbon fixation pathways for cell synthesis [59]. Acetyl-CoA forms a key component of the homoacetogenesis and acetoclastic pathways, which may explain the higher relative abundance of genes involved in these pathways across all samples. A previous report indicated acetoclastic methanogenesis as the dominant pathway at low temperatures possibly due to the increased production of acetate by enhanced homoacetogenesis [69]. After cold adaptation and PAD of B_Inoc, all four pathways were observed (Figure 5), including an increase in functional capabilities associated with methylotrophic methanogenesis compared to before digestion as well as B_0 after PAD. These results suggest that methylotrophic methanogenesis also played an important role in methane production under psychrophilic conditions. Yun et al. reported similar results which showed a distinct presence of functional genes involved in methylotrophic methanogenesis during PAD [70]. Additionally, Figure S2 indicated that the B_Adapt and B_Inoc microbial communities had a higher involvement in the metabolism of amino acids, propionate and butyrate, while B_0 displayed higher predicted capabilities in starch and sucrose metabolism after the trials. These results suggest that the substrates possibly produced from the dominant fermentative and acetogenic bacteria (Bacteroides, Acinetobacter and Macellibacteroides and Clostridium sensu stricto) from B_Adapt and B_Inoc could be utilized by Methanosarcina and Methanobrevibacter for methane production. Conversely, the lower predicted capabilities in VFA metabolism by the microbial community from B_0 corroborates the notion that acidification occurred due to the accumulation of VFAs, which affected Methanosarcina growth and subsequently methanogenesis.
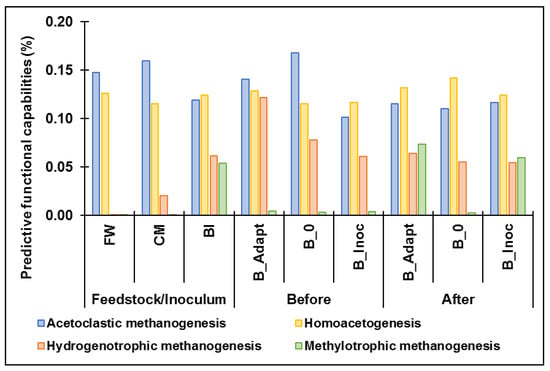
Figure 5.
Predictive key functional capabilities of the microbial communities in acetoclastic, methylotrophic (using methylamines or methanol) and hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis and homoacetogenesis (reductive acetyl-CoA or Wood-Ljungdahl) pathways (based on KEGG Pathway Modules; see Table S2).
3.2.5. Possible Synergistic Dynamics between Core Microbial Groups
The possible roles and synergies between the core microbial groups during cold adaptation and PAD are summarized in Figure 6. In a recent study conducted by Catlette et al., a metabolic syntrophic partnership was shown to form between Bacteroides and Methanobrevibacter [71]. Furthermore, acetate and formate were shown to display inhibitory effects on Bacteroides, although these are products produced during fermentation by Bacteroides. The products were consumed by Methanobrevibacter for growth, which subsequently prevented the inhibition of Bacteroides. Furthermore, Methanobrevibacter benefitted from the altered synthesis of metabolites produced by Bacteroides and the metabolic efficiency of Bacteroides was greater in the presence of Methanobrevibacter indicating a mutualistic synergy between the microbial groups [71]. This synergistic relationship was observed in previous AD studies [72,73].
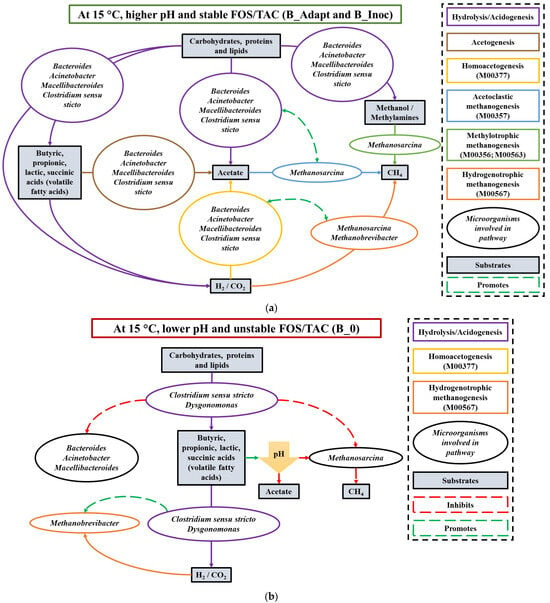
Figure 6.
Possible roles and synergistic relationships between dominant bacteria and archaea in acidogenesis, acetogenesis and methanogenesis during (a) cold adaptation and psychrophilic anaerobic digestion with inoculum (at higher pH) and (b) during psychrophilic anaerobic digestion without inoculum (at lower pH). H2/CO2—hydrogen/carbon dioxide; CH4—methane; FOS/TAC—ratio of volatile fatty acids to total alkalinity. Predicted genes associated with the KEGG pathway modules (M00377; M00357; M00567; M00356; M00563) can be found in Table S2.
In other studies, co-cultures of Clostridium and Methanosarcina were found to enhance psychrophilic and mesophilic methane production from various substrates including cellulose, xylose, sugar beet pulp and cattle manure [74,75,76]. Many Clostridium species were reported as fermentative, acetogens that produce acetate, formate, H2/CO2, butyrate, and lactate, among other fermentation end products from the metabolism of various substrates under psychrophilic conditions [74]. These products generated through homoacetogenesis can be directly utilized by Methanosarcina and/or Methanobrevibacter for methane production thus overcoming rate-limiting steps during PAD.
Enhanced activity of homoacetogens under psychrophilic conditions can promote successful competition for common substrates with fermentative bacteria and hydrogenotrophic methanogens [77]. Additionally, a previous report indicated the conversion of acetate to H2/CO2 during syntrophic acetate oxidation (SAO) was only thermodynamically favorable at higher temperatures and the acetogens involved in SAO were outcompeted by Methanosarcina in terms of energy sharing [78]. Although Methanobrevibacter were previously found to thrive at lower temperatures [79,80] as evident after cold adaptation and PAD, methanogenesis by Methanobrevibacter (the only dominant methanogen in B_0) may have been inhibited due to acidic substrates produced by fermentative bacterial groups. Furthermore, the dominance of Methanobrevibacter during reduced biogas yield and lower temperatures was similarly reported in a previous study [81]. Therefore, it is proposed that synergistic relationships between Bacteroides, Methanobrevibacter, Methanosarcina and Clostridium sensu stricto genera may have provided better dynamics for methane production during cold adaptation and PAD of B_Inoc compared to B_0.
The absence of Bacteroides and Methanosarcina (0%) in B_0 after PAD further suggests that without the cold-adapted inoculum and the synergistic relationship with Methanobrevibacter and Clostridium sensu stricto genera, respectively, during AD under psychrophilic conditions, no methane production could occur. In the presence of dominant Methanobrevibacter, homoacetogens such as Clostridiaceae, Lachnospiraceae and Ruminococcaceae were found to inhabit a ruminal environment [82]. Furthermore, in the absence of methanogenesis and under acidic conditions, homoacetogenesis possibly outcompeted hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis. This phenomenon was similarly observed for B_0 after PAD (Figure 5). Additionally, homoacetogens can outcompete hydrogenotrophic methanogens by utilizing H2/CO2 for acetate production at low temperatures which can be utilized subsequently during acetoclastic methanogenesis for methane production [83].
Recently, Xu et al. indicated that Methanosarcina had a low affinity for acetate in VFA-stressed batch PAD reactors, despite its competitive capabilities in PAD [20]. Hence, an optimal ratio between Methanosarcina (63%) and acetate degrader, Methanothrix (35%) as well as an observed upregulation of Bacteroidetes fermentative bacteria, possibly promoted a balance between the acidogenesis and methanogenesis stages. Comparatively, in this study, an approximate 1:1 ratio of Methanosarcina and Methanobrevibacter was observed during enhanced methane production. Methanobrevibacter possibly played a role in consuming VFAs produced by upregulated Bacteroides and the other fermentative bacteria, which may have promoted methanogenesis by Methanosarcina. A constructed co-culture study investigating the effect of the core cold-adapted microbial groups on PAD may elucidate the validity of the proposed synergistic relationships driving methane production. Furthermore, metabolomics, transcriptomics and proteomics investigation as well as characterization of unclassified archaeal methanogens may provide better insight into the microbial community dynamics of PAD.
4. Conclusions
This study investigated the cold adaptation of microbial consortia in cattle manure and vegetable food waste. The inoculum was further evaluated for its potential to enhance methane production at psychrophilic temperatures from co-digestion of cattle manure and food waste. The microbial community analyses confirmed that the application of cold-adapted inoculum enhanced PAD efficiency and methane production by favoring the growth of metabolically stable microorganisms at colder temperatures. However, further development to enhance methane production rates, which can be comparable to mesophilic and thermophilic digesters is warranted. Furthermore, this study identified possible microbial synergies driving methane production under psychrophilic conditions during anaerobic digestion. Investigation into the synergistic relationships between methanogens and bacteria which can determine possible targeted approaches to enhancing methanogenesis during PAD is recommended. Moreover, it will pave the way for a more competitive trajectory for efficient methane production on small-scale farms and in cold regions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation10070370/s1, Figure S1. Fitted Modified Gompertz Model for (a) B_Adapt and (b) B_Inoc; Table S1. Alpha diversity in feedstock, cold-adapted inoculum, and digestate samples.; Table S2. Predicted relative abundance of unique genes associated with the different methanogenesis and homoacetogenesis pathways.; Figure S2. Heatmap of relative gene abundance of microbial community predicted functions after cold adaptation and psychrophilic anaerobic digestion trials in relation to hydrolysis/acidogenesis and acetogenesis pathways.
Author Contributions
H.R.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Writing—Original draft preparation, Visualization, Investigation, Project administration. B.N.: Writing—Reviewing and Editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition. M.S.D.: Writing—Reviewing and Editing, Supervision. N.C.: Formal analysis. M.M.: Writing—Reviewing and Editing, Supervision. A.R.: Conceptualization, Writing—Reviewing and Editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of South Africa (NRF; Grant numbers 128307 and 121924). Opinions expressed and conclusions reached are those of the authors and not necessarily endorsed by the NRF.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw sequence data was deposited into the SRA (Sequence Read Archive) via NCBI (National Centre for Biotechnology Information) under the BioProject accession number: PRJNA996176. The raw sequences can be openly accessed via the following link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/PRJNA996176 (accessed on 17 July 2024). Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Agricultural Research Council—Animal Production (Pretoria, South Africa) and Tshwane Market for providing access to the cattle manure and food waste. This work forms part of a PhD thesis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Rama, H.; Akindolire, M.; Obi, L.; Bello-Akinosho, M.; Ndaba, B.; Dhlamini, M.S.; Maaza, M.; Roopnarain, A. Anaerobic Digestion: Climate Change Mitigation through Sustainable Organic Waste Valorization. In Handbook of Nature-Based Solutions to Mitigation and Adaptation to Climate Change; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1–19. ISBN 978-3-030-98067-2. [Google Scholar]
- Searchinger, T.; Herrero, M.; Yan, X.; Wang, J.; Dumas, P.; Beauchemin, K.; Kebreab, E. Opportunities to Reduce Methane Emissions from Global Agriculture; Princeton University: Princeton, NJ, USA; Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y. Bioaugmentation Improves Batch Psychrophilic Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cattle Manure and Corn Straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolessa, A.; Zantsi, S.; Louw, T.M.; Greyling, J.C.; Goosen, N.J. Estimation of Biomass Feedstock Availability for Anaerobic Digestion in Smallholder Farming Systems in South Africa. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 142, 105798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, T.; Tauseef, S.M.; Abbasi, S.A. Anaerobic Digestion for Global Warming Control and Energy Generation—An Overview. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 3228–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopnarain, A.; Rama, H.; Ndaba, B.; Bello-Akinosho, M.; Bamuza-Pemu, E.; Adeleke, R. Unravelling the Anaerobic Digestion ‘Black Box’: Biotechnological Approaches for Process Optimization. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 152, 111717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, V.; Ramankutty, N.; Mehrabi, Z.; Jarvis, L.; Chookolingo, B. How Much of the World’s Food Do Smallholders Produce? Glob. Food Secur. 2018, 17, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, C.H.; Triolo, J.M.; Sommer, S.G. Predicting Methane Production in Simple and Unheated Biogas Digesters at Low Temperatures. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SANEDI; UJ-TRCTI; UJ-PEETS; SABIA. Sector Development Plan for the Micro-Digester Sector in South Africa: Pathways to Growth and Sustainability by 2030; SANEDI: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2022; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kalina, M.; Ogwang, J.Ò.; Tilley, E. From Potential to Practice: Rethinking Africa’s Biogas Revolution. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2022, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nape, K.M.; Magama, P.; Moeletsi, M.E.; Tongwane, M.I.; Nakana, P.M.; Mliswa, V.K.; Motsepe, M.; Madikiza, S. Introduction of Household Biogas Digesters in Rural Farming Households of the Maluti-a-Phofung Municipality, South Africa. J. Energy South. Afr. 2019, 30, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Herrero, J.; Castro, L.; Jaimes-Estévez, J.; Grijalva, M.; Gualatoña, M.; Aldás, M.B.; Escalante, H. Biomethane Potential Test Applied to Psychrophilic Conditions: Three Issues about Inoculum Temperature Adaptation. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 20, 101279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akindolire, M.A.; Rama, H.; Roopnarain, A. Psychrophilic Anaerobic Digestion: A Critical Evaluation of Microorganisms and Enzymes to Drive the Process. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 161, 112394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Jiménez, L.M.; Pérez-Vidal, A.; Torres-Lozada, P. Research Trends and Strategies for the Improvement of Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste in Psychrophilic Temperatures Conditions. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struvay, C.; Feller, G. Optimization to Low Temperature Activity in Psychrophilic Enzymes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 11643–11665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedwell, D.B. Effect of Low Temperature on Microbial Growth: Lowered Affinity for Substrates Limits Growth at Low Temperature. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1999, 30, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi-Borazjani, S.A.; Capela, I.; Tarelho, L.A.C. Over-Acidification Control Strategies for Enhanced Biogas Production from Anaerobic Digestion: A Review. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 143, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Ma, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, Q.; Tian, C.; Fang, Y.; Zhong, R.; Chen, G.; Zhang, S. Advances in Cold-Adapted Enzymes Derived from Microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1152847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Jha, A.K. Psychrophilic Dry Anaerobic Digestion of Cow Dung for Methane Production: Effect of Inoculum. ScienceAsia 2013, 39, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yan, M.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y. Bioaugmentation with Cold-Tolerant Methanogenic Culture to Boost Methane Production from Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cattle Manure and Corn Straw at 20 °C. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 466, 143183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Ramiro-Garcia, J.; Paulo, L.M.; Braguglia, C.M.; Gagliano, M.C.; O’Flaherty, V. Psychrophilic and Mesophilic Anaerobic Treatment of Synthetic Dairy Wastewater with Long Chain Fatty Acids: Process Performances and Microbial Community Dynamics. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 380, 129124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, B.R.; Rouissi, T.; Brar, S.K.; Surampalli, R.Y. Critical Insights into Psychrophilic Anaerobic Digestion: Novel Strategies for Improving Biogas Production. Waste Manag. 2021, 131, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariunbaatar, J.; Panico, A.; Frunzo, L.; Esposito, G.; Lens, P.N.L.; Pirozzi, F. Enhanced Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste by Thermal and Ozonation Pretreatment Methods. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhuba, M.; Roopnarain, A.; Moeletsi, M.E.; Adeleke, R. Metagenomic Insights into the Microbial Community and Biogas Production Pattern during Anaerobic Digestion of Cow Dung and Mixed Food Waste. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsabisa, M.G.; Bala, A.; Tripathy, S.; Digashu, M.M.; Rautenbach, F.; Dassarma, B.; Erhabor, J.O.; Braga, F.C.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Tang, M.; et al. Study on South African Indigenous Teas—Antioxidant Potential, Nutritional Content, and Hypoxia-Induced Cyclooxygenase Inhibition on U87 MG Cell Line. Molecules 2022, 27, 3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkuna, R.; Roopnarain, A.; Adeleke, R. Effects of Organic Loading Rates on Microbial Communities and Biogas Production from Water Hyacinth: A Case of Mono- and Co-digestion. J Chem. Tech Biotech 2019, 94, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institute, Inc. SAS/STAT User’s Guide, SAS 9.4 for Windows, 5th ed.; SAS Institute, Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Obi, L.U.; Roopnarain, A.; Tekere, M.; Adeleke, R.A. Bioaugmentation Potential of Inoculum Derived from Anaerobic Digestion Feedstock for Enhanced Methane Production Using Water Hyacinth. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadeev, E.; Cardozo-Mino, M.G.; Rapp, J.Z.; Bienhold, C.; Salter, I.; Salman-Carvalho, V.; Molari, M.; Tegetmeyer, H.E.; Buttigieg, P.L.; Boetius, A. Comparison of Two 16S rRNA Primers (V3–V4 and V4–V5) for Studies of Arctic Microbial Communities. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 637526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data 2010. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M. Toward Understanding the Origin and Evolution of Cellular Organisms. Protein Sci. 2019, 28, 1947–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG for Taxonomy-Based Analysis of Pathways and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D587–D592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wemheuer, F.; Taylor, J.A.; Daniel, R.; Johnston, E.; Meinicke, P.; Thomas, T.; Wemheuer, B. Tax4Fun2: Prediction of Habitat-Specific Functional Profiles and Functional Redundancy Based on 16S rRNA Gene Sequences. Environ. Microbiome 2020, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, C.; Hughes, D.; Mahony, T.; Cysneiros, D.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Smith, C.J.; O’Flaherty, V. Cold Adaptation and Replicable Microbial Community Development during Long-Term Low-Temperature Anaerobic Digestion Treatment of Synthetic Sewage. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casallas-Ojeda, M.; Cabeza, I.; Sanchez, N.; Caicedo-Concha, D.M.; Astals, S. Cheese Whey and Dairy Manure Anaerobic Co-Digestion at Psychrophilic Conditions: Technical and Environmental Evaluation. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esparza-Soto, M.; Alcaraz-Ibarra, S.; Lucero-Chavez, M.; Jimenez-Moleon, M.D.C.; Mier-Quiroga, M.D.L.A.; Fall, C. Enhancing Kitchen Waste Minimization and Energy Generation at 20 °C: A Psychrophilic Anaerobic Co-digestion Study. J. Chem. Tech. Biotech. 2024, 99, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meegoda, J.; Li, B.; Patel, K.; Wang, L. A Review of the Processes, Parameters, and Optimization of Anaerobic Digestion. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, A.; Liu, H.; Varrone, C.; Shyryn, A.; Defemur, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Yue, X. New Insight into Waste Activated Sludge Acetogenesis Triggered by Coupling Sulfite/Ferrate Oxidation with Sulfate Reduction-Mediated Syntrophic Consortia. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabari, L.; Gannoun, H.; Cayol, J.-L.; Hedi, A.; Sakamoto, M.; Falsen, E.; Ohkuma, M.; Hamdi, M.; Fauque, G.; Ollivier, B.; et al. Macellibacteroides Fermentans Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., a Member of the Family Porphyromonadaceae Isolated from an Upflow Anaerobic Filter Treating Abattoir Wastewaters. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 2522–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, T.; Ueki, A.; Kaku, N.; Watanabe, K.; Ueki, K. Bacteroides Graminisolvens Sp. Nov., a Xylanolytic Anaerobe Isolated from a Methanogenic Reactor Treating Cattle Waste. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, A.; Abe, K.; Ohtaki, Y.; Kaku, N.; Watanabe, K.; Ueki, K. Bacteroides Paurosaccharolyticus Sp. Nov., Isolated from a Methanogenic Reactor Treating Waste from Cattle Farms. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulami, D.; Schauss, T.; Eisenberg, T.; Blom, J.; Schwengers, O.; Bender, J.K.; Wilharm, G.; Kämpfer, P.; Glaeser, S.P. Acinetobacter Stercoris Sp. Nov. Isolated from Output Source of a Mesophilic German Biogas Plant with Anaerobic Operating Conditions. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2021, 114, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Hao, O.J.; Wang, N.S. Acinetobacter Isolates from Different Activated Sludge Processes: Characteristics and Neural Network Identification. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1997, 23, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.P.; Monchy, S.; Cardinale, M.; Taghavi, S.; Crossman, L.; Avison, M.B.; Berg, G.; Van Der Lelie, D.; Dow, J.M. The Versatility and Adaptation of Bacteria from the Genus Stenotrophomonas. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zaiden, N.; Cao, B. The Core- and Pan-Genomic Analyses of the Genus Comamonas: From Environmental Adaptation to Potential Virulence. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, S.M.; Munoz-Munoz, J.; Van Sinderen, D. Plant Glycan Metabolism by Bifidobacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 609418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridges, C.M.; Gage, D.J. Development and Application of Aerobic, Chemically Defined Media for Dysgonomonas. Anaerobe 2021, 67, 102302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstad, T.; Olsen, I.; Eribe, E.R.; Falsen, E.; Collins, M.D.; Lawson, P.A. Dysgonomonas Gen. Nov. to Accommodate Dysgonomonas Gadei Sp. Nov., an Organism Isolated from a Human Gall Bladder, and Dysgonomonas Capnocytophagoides (Formerly CDC Group DF-3). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 2189–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alou, M.T.; Ndongo, S.; Frégère, L.; Labas, N.; Andrieu, C.; Richez, M.; Couderc, C.; Baudoin, J.-P.; Abrahão, J.; Brah, S.; et al. Taxonogenomic Description of Four New Clostridium Species Isolated from Human Gut: ‘Clostridium Amazonitimonense’, ‘Clostridium Merdae’, ‘Clostridium Massilidielmoense’ and ‘Clostridium Nigeriense’. New Microbes New Infect. 2018, 21, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberato, V.; Benevenuti, C.; Coelho, F.; Botelho, A.; Amaral, P.; Pereira, N.; Ferreira, T. Clostridium Sp. as Bio-Catalyst for Fuels and Chemicals Production in a Biorefinery Context. Catalysts 2019, 9, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Yanagawa, K.; Prasitwuttisak, W.; Goel, R.; Watanabe, R.; Harada, H.; Liu, B.; Terashima, M.; Yasui, H. Kinetics for the Methanogen’s Death in the Acidic Environments. J. Wat. Environ. Tech. 2023, 21, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopnarain, A.; Akindolire, M.A.; Rama, H.; Ndaba, B. Casting Light on the Micro-Organisms in Digestate: Diversity and Untapped Potential. Fermentation 2023, 9, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetten, M.S.M.; Stams, A.J.M.; Zehnder, A.J.B. Acetate Threshold Values and Acetate Activating Enzymes in Methanogenic Bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1990, 73, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, S.; Saha, S.; Kurade, M.B.; Salama, E.-S.; El-Dalatony, M.M.; Ha, G.-S.; Chang, S.W.; Jeon, B.-H. Perspective on Anaerobic Digestion for Biomethanation in Cold Environments. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 103, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurth, J.M.; Op Den Camp, H.J.M.; Welte, C.U. Several Ways One Goal—Methanogenesis from Unconventional Substrates. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 6839–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagen, L.H.; Vivekanand, V.; Pope, P.B.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Horn, S.J. The Effect of Storage Conditions on Microbial Community Composition and Biomethane Potential in a Biogas Starter Culture. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 5749–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, L. The Relation between Evenness and Diversity. Diversity 2010, 2, 207–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-R.; Shin, J.; Guevarra, R.B.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Seol, K.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, H.B.; Isaacson, R.E. Deciphering Diversity Indices for a Better Understanding of Microbial Communities. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 2089–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Ma, F.; Ma, W.; Wang, P.; Zhao, G.; Lu, X. Influence of Temperature on Biogas Production Efficiency and Microbial Community in a Two-Phase Anaerobic Digestion System. Water 2019, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Polz, M.F.; Alm, E.J. Interactions in Self-Assembled Microbial Communities Saturate with Diversity. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1602–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Lladser, M.E.; Knights, D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R. UniFrac: An Effective Distance Metric for Microbial Community Comparison. ISME J. 2011, 5, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Keating, C.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Hassard, F. Molecular Insights Informing Factors Affecting Low Temperature Anaerobic Applications: Diversity, Collated Core Microbiomes and Complexity Stability Relationships in LCFA-Fed Systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeown, R.M.; Scully, C.; Enright, A.-M.; Chinalia, F.A.; Lee, C.; Mahony, T.; Collins, G.; O’Flaherty, V. Psychrophilic Methanogenic Community Development during Long-Term Cultivation of Anaerobic Granular Biofilms. ISME J. 2009, 3, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, H.; Liang, B.; He, Z.; Li, M.; Zong, S.; Wang, Z.; Ge, B.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.; Wang, A. Insights into Methanogenesis of Mesophilic-Psychrophilic Varied Anaerobic Digestion of Municipal Sludge with Antibiotic Stress. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 331, 117278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catlett, J.L.; Carr, S.; Cashman, M.; Smith, M.D.; Walter, M.; Sakkaff, Z.; Kelley, C.; Pierobon, M.; Cohen, M.B.; Buan, N.R. Metabolic Synergy between Human Symbionts Bacteroides and Methanobrevibacter. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01067-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catlett, J.L.; Catazaro, J.; Cashman, M.; Carr, S.; Powers, R.; Cohen, M.B.; Buan, N.R. Metabolic Feedback Inhibition Influences Metabolite Secretion by the Human Gut Symbiont Bacteroides Thetaiotaomicron. mSystems 2020, 5, e00252-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, B.S.; Hansen, E.E.; Manchester, J.K.; Coutinho, P.M.; Henrissat, B.; Fulton, R.; Latreille, P.; Kim, K.; Wilson, R.K.; Gordon, J.I. Genomic and Metabolic Adaptations of Methanobrevibacter Smithii to the Human Gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10643–10648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akila, G.; Chandra, T.S. Stimulation of Biomethanation by Clostridium Sp. PXYL1 in Coculture with a Methanosarcina Strain PMET1 at Psychrophilic Temperatures: Stimulation of Biomethanation by Coculture. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Ng, S.-K.; Jia, Y.; Cai, M.; Lee, P.K.H. Physiological and Molecular Characterizations of the Interactions in Two Cellulose-to-Methane Cocultures. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, H.; Okazaki, F.; Tamaru, Y. Biomethane Production from Sugar Beet Pulp under Cocultivation with Clostridium Cellulovorans and Methanogens. AMB Express 2019, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsyurbenko, O.R. Trophic Interactions in the Methanogenic Microbial Community of Low-Temperature Terrestrial Ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2005, 53, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyksma, S.; Jansen, L.; Gallert, C. Syntrophic Acetate Oxidation Replaces Acetoclastic Methanogenesis during Thermophilic Digestion of Biowaste. Microbiome 2020, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Sihvonen, M.; Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Mikola, A.; Vahala, R. Microbial Ecology of Full-Scale Wastewater Treatment Systems in the Polar Arctic Circle: Archaea, Bacteria and Fungi. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, A.D.; Evans, P.; Parameswaran, P. Long-Term Microbial Community Dynamics in a Pilot-Scale Gas Sparged Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor Treating Municipal Wastewater under Seasonal Variations. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 310, 123425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciotola, R.; Martin, J.; Castańo, J.; Lee, J.; Michel, F. Microbial Community Response to Seasonal Temperature Variation in a Small-Scale Anaerobic Digester. Energies 2013, 6, 5182–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karekar, S.; Stefanini, R.; Ahring, B. Homo-Acetogens: Their Metabolism and Competitive Relationship with Hydrogenotrophic Methanogens. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, C.; Angelidaki, I.; Lv, N.; Ning, J.; Cai, G.; Zhu, G. Deep Insights into the Network of Acetate Metabolism in Anaerobic Digestion: Focusing on Syntrophic Acetate Oxidation and Homoacetogenesis. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).