Recycling Oxacillin Residues from Environmental Waste into Graphene Quantum Dots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Instrumentation
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Extraction, Preconcentration and Back Extraction Procedures
2.2.2. Preparation and Optimization of the Graphene Quantum Dots
2.2.3. Kaiser Test Protocol
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Extraction of the Antibiotic from Wastewater
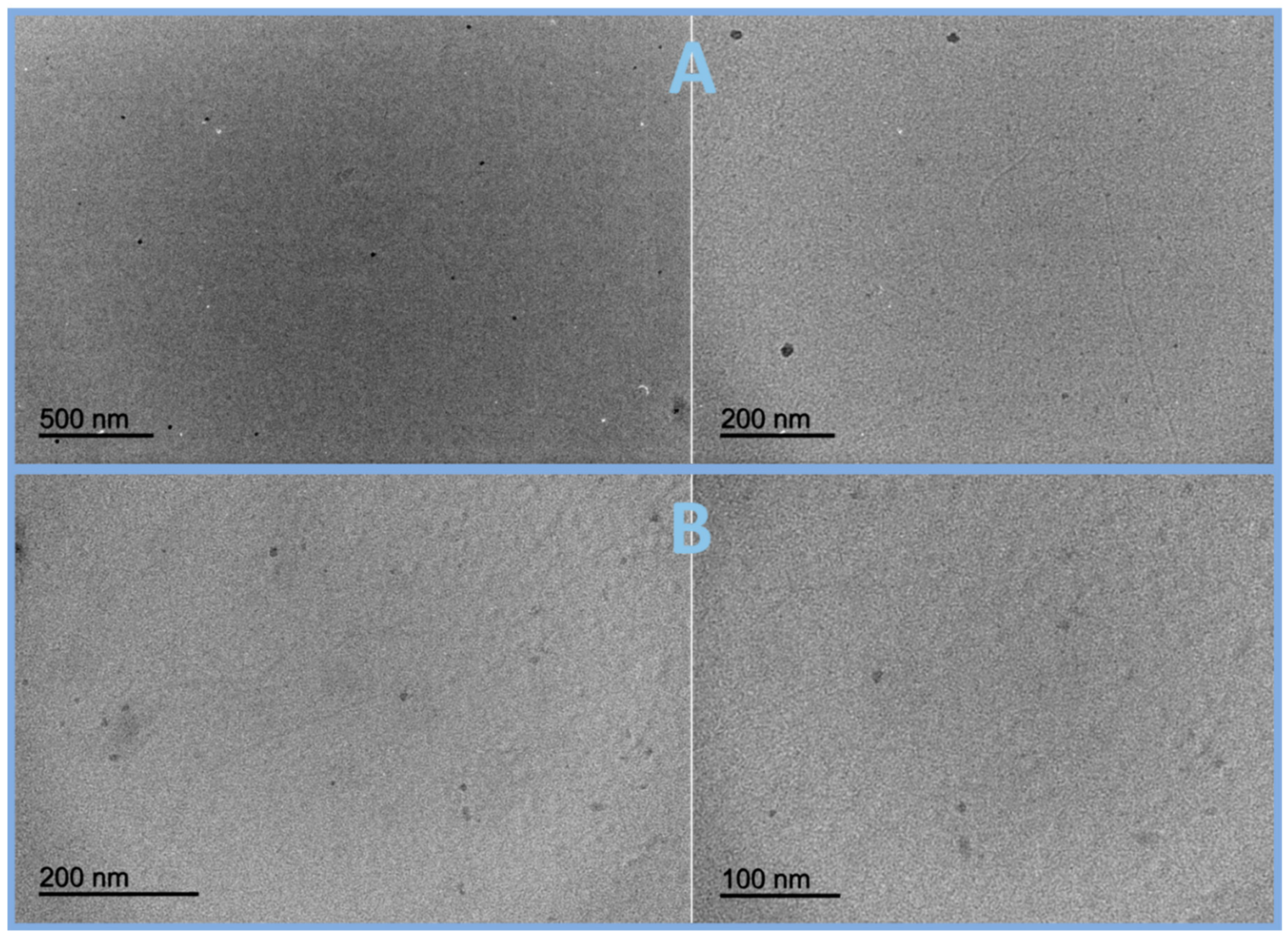
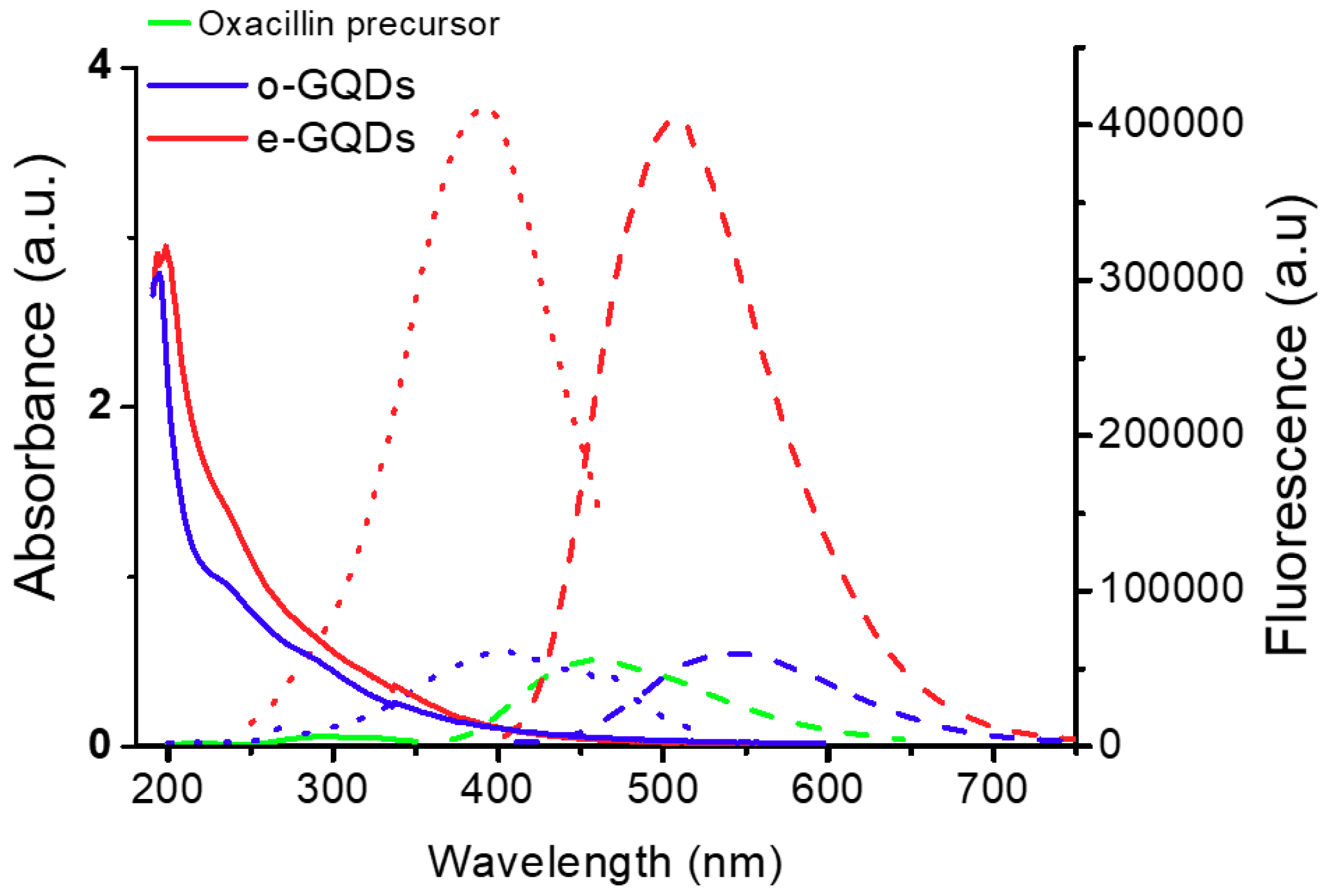
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Two Types of Graphene Quantum Dots, o-GQDs and e-GQDs
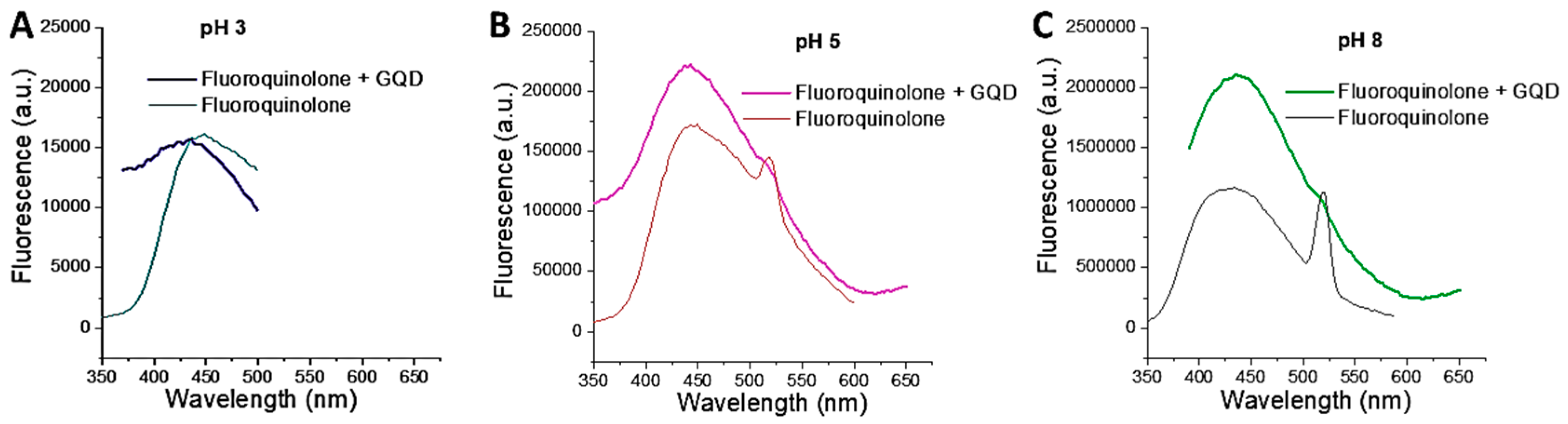
3.3. Interaction and Simple Detection of Fluoroquinolone Based on GQDs as Fluorescent Probes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lobanovska, M.; Pilla, G. Penicillin’s Discovery and Antibiotic Resistance: Lessons for the Future? Yale J. Biol. Med. 2017, 90, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Katzung, B.; Trevor, A. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, 13th ed.; Mcgraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Manyi-Loh, C.; Mamphweli, S.; Meyer, E.; Okoh, A. Antibiotic Use in Agriculture and Its Consequential Resistance in Environmental Sources: Potential Public Health Implications. Molecules 2018, 23, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, I.; Rizzo, L.; McArdell, C.S.; Manaia, C.M.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for the release of antibiotics in the environment: A review. Water Res. 2013, 47, 957–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, J.M.; Yang, S.; Carlson, K.H. Trace determination of b-lactam antibiotics in surface water and urban wastewater using liquid chromatography combined with electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1115, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraldo, A.L.; Erazo-Erazo, E.D.; Flórez-Acosta, O.A.; Serna-Galvis, E.A.; Torres-Palma, R.A. Degradation of the antibiotic oxacillin in water by anodic oxidation with Ti/IrO2 anodes: Evaluation of degradation routes, organic by-products and effects of water matrix components. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, A.; Mert, B.K.; Özengin, N.; Sivrioğlu, Ö.; Yonar, T. Treatment of Antibiotics in Wastewater Using Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs). Phys.-Chem. Wastewater Treat. Resour. Recovery 2017, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, A.; Soriano, M.L.; Carrillo-Carrión, C.; Valcárcel, M. Semiconductor and carbon-based fluorescent nanodots: The need for consistency. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 1311–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarenko, L.A.; Schedin, F.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Yang, R.; Hill, E.W.; Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K. Chaotic Dirac billiard in graphene quantum dots. Science 2008, 320, 356–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez-Martínez, S.; Valcárcel, M. Graphene quantum dots in analytical science. Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 72, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Guo, S. Chemically doped fluorescent carbon and graphene quantum dots for bioimaging, sensor, catalytic and photoelectronic applications. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 2532–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, N.; Qu, L. Graphene quantum dots: An emerging material for energy-related applications and beyond. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 8869–8890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rui, M.; Song, J.; Shen, Z.; Zeng, H. Carbon and graphene quantum dots for optoelectronic and energy devices: A review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4929–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Dissanayake, S. Large-scale and controllable synthesis of graphene quantum dots from rice husk biomass: A comprehensive utilization strategy. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 1434–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryawanshi, A.; Biswal, M.; Mhamane, D.; Gokhale, R.; Patil, S.; Guin, D.; Ogale, S. Large scale synthesis of graphene quantum dots (GQDs) from waste biomass and their use as an efficient and selective photoluminescence on-off-on probe for Ag+ ions. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11664–11670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.; Moon, K.; Jeong, S.; Koh, W.-G.; Lee, K. Converting Waste Papers to Fluorescent Carbon Dots in the Recycling Process without Loss of Ionic Liquids and Bioimaging Applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4510–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Miao, Y.; Li, D.; Yan, G. Preparation of graphene oxide quantum dots from waste toner, and their application to a fluorometric DNA hybridization assay. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Singh, S.K.; Mobin, S.M. Bioinspired carbon dots: From rose petals to tunable emissive nanodots. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 1290–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Palomero, C.; Soriano, M.L.; Benítez-Martínez, S.; Valcárcel, M. Photoluminescent sensing hydrogel platform based on the combination of Nanocellulose and S,N-codoped Graphene Quantum Dots. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 245, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresco-Cala, B.; Soriano, M.L.; Sciortino, A.; Cannas, M.; Messina, F.; Cárdenas, S. One-pot synthesis of graphene quantum dot and simultaneous nanostructured self-assembly via a novel microwave-assisted method: Impact on triazines removal and efficiency monitoring. RSC. Adv. 2018, 8, 29939–29946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Tang, L.; Teng, K.S.; Lau, S.P. Graphene quantum dots from chemistry to applications. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 10, 221–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B. The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots, and polymer dots): Current state and future perspective. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sk, M.A.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Huang, L.; Lim, K.H.; Chen, P. Revealing the Tunable Photoluminescence Properties of Graphene Quantum Dots. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 6954–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweetman, M.J.; Hickey, S.M.; Brooks, D.A.; Hayball, J.D.; Plush, S.E. A practical guide to prepare and synthetically modify graphene quantum dots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Zheng, M.; Li, J.; Xie, Z.; Sun, Z. Tailoring color emissions from N-doped graphene quantum dots for bioimaging applications. Light Sci. Appl. 2015, 4, e364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Dai, L.; Li, L.-S. Nitrogen-Doped Colloidal Graphene Quantum Dots and Their Size-Dependent Electrocatalytic Activity for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 18932–18935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh, A.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Shadjou, N.; de la Guardia, M. Electrochemical biosensing using N-GQDs: Recent advances in analytical approach. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 105, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh, A.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Shadjou, N.; de la Guardia, M. Optical bio(sensing) using nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots: Recent advances and future challenges. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 108, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.T.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, R.; Ryan, C.; Pota, K.; Green, K.; Coffer, J.L.; Naumov, A.V. Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots: Optical properties modification and photovoltaic applications. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Kaur, M.; Sharma, V.K. Nitrogen-doped graphene and graphene quantum dots: A review on synthesis and applications in energy, sensors and environment. Adv. Coll. Interface Sci. 2018, 259, 44–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Qiu, J.; Zhu, H.; Liu, X. Achieving stem cell imaging and osteogenic differentiation by using nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, B.; Rao, Z.; Zhang, B.; Gong, J.R. Strong two-photon-induced fluorescence from photostable, biocompatible nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for cellular and deep-tissue imaging. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2436–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druart, S.; Kopelent-Frank, H. A rapid capillary electrophoretic assay for selective quantitation of oxacillin in the presence of its degradation products. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2005, 28, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea-Corbacho, A.; Gutiérrez, S.; Quiroga, J.M. Removal of emerging contaminants from wastewater through pilot plants using intermittent sand/coke filters for its subsequent reuse. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Tang, S.; Meng, Q.; Li, Y.; Shi, C.; Hu, R.; et al. Graphene quantum dots with controllable surface oxidation, tunable fluorescence and up-conversion emission. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 2717–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Run n° | GQD Sample (mg) | Amine Content Found (µmol/g) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.0 | 14.03 |
| 2 | 3.9 | 12.52 |
| 3 | 4.2 | 16.35 |
| λexc (nm) | τ1 (ns) | %Rel | τ2 (ns) | %Rel | τ3 (ns) | %Rel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 | 0.22 | 14 | 1.33 | 49 | 4.71 | 37 |
| 440 | 0.34 | 21 | 1.89 | 47 | 5.43 | 32 |
| 475 | 0.20 | 17 | 1.62 | 45 | 5.10 | 39 |
| λexc (nm) | τ1 (ns) | %Rel | τ2 (ns) | %Rel | τ3 (ns) | %Rel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 390 | 0.14 | 1 | 1.25 | 50 | 6.3 | 49 |
| 415 | 0.34 | 19 | 1.83 | 50 | 5.94 | 31 |
| 435 | 0.10 | 9 | 1.25 | 45 | 4.64 | 46 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soriano, M.L.; Cárdenas, S. Recycling Oxacillin Residues from Environmental Waste into Graphene Quantum Dots. C 2019, 5, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/c5040068
Soriano ML, Cárdenas S. Recycling Oxacillin Residues from Environmental Waste into Graphene Quantum Dots. C. 2019; 5(4):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/c5040068
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoriano, Maria Laura, and Soledad Cárdenas. 2019. "Recycling Oxacillin Residues from Environmental Waste into Graphene Quantum Dots" C 5, no. 4: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/c5040068
APA StyleSoriano, M. L., & Cárdenas, S. (2019). Recycling Oxacillin Residues from Environmental Waste into Graphene Quantum Dots. C, 5(4), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/c5040068