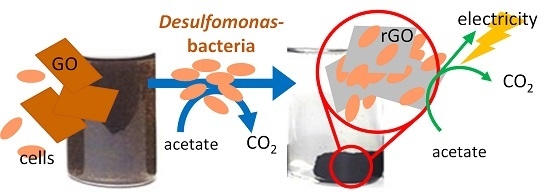
Selective Growth of and Electricity Production by Marine Exoelectrogenic Bacteria in Self-Aggregated Hydrogel of Microbially Reduced Graphene Oxide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
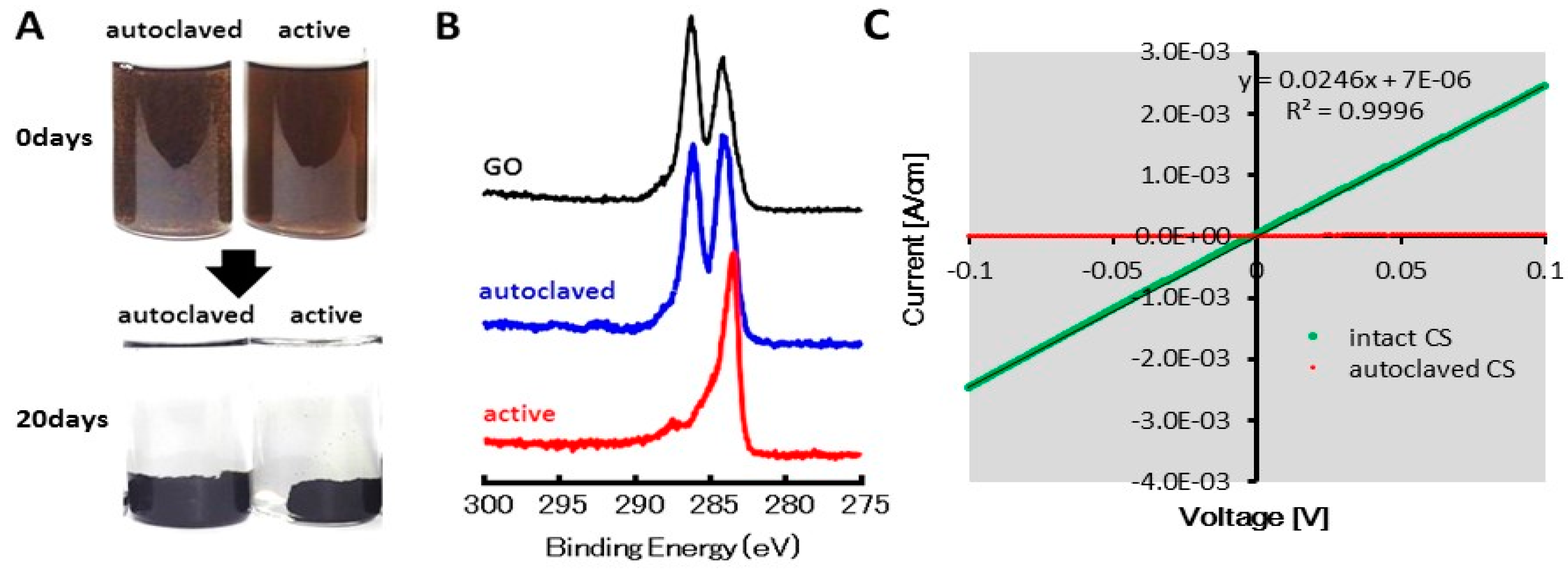
2.1. GO Reduction by the CS Culture, An Enrichment Culture of Marine GORB
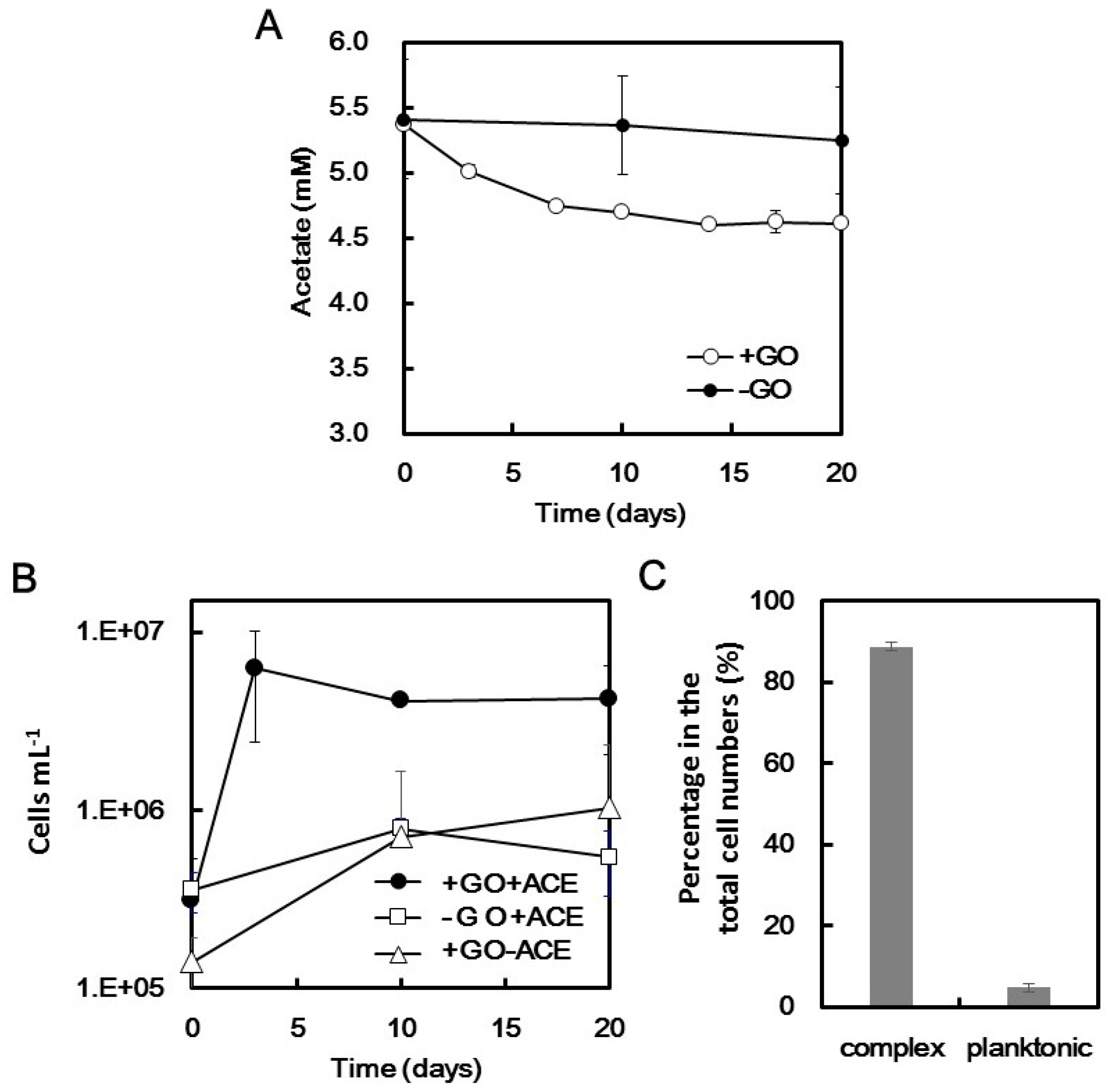
2.2. Microbial Growth Dependent on GO
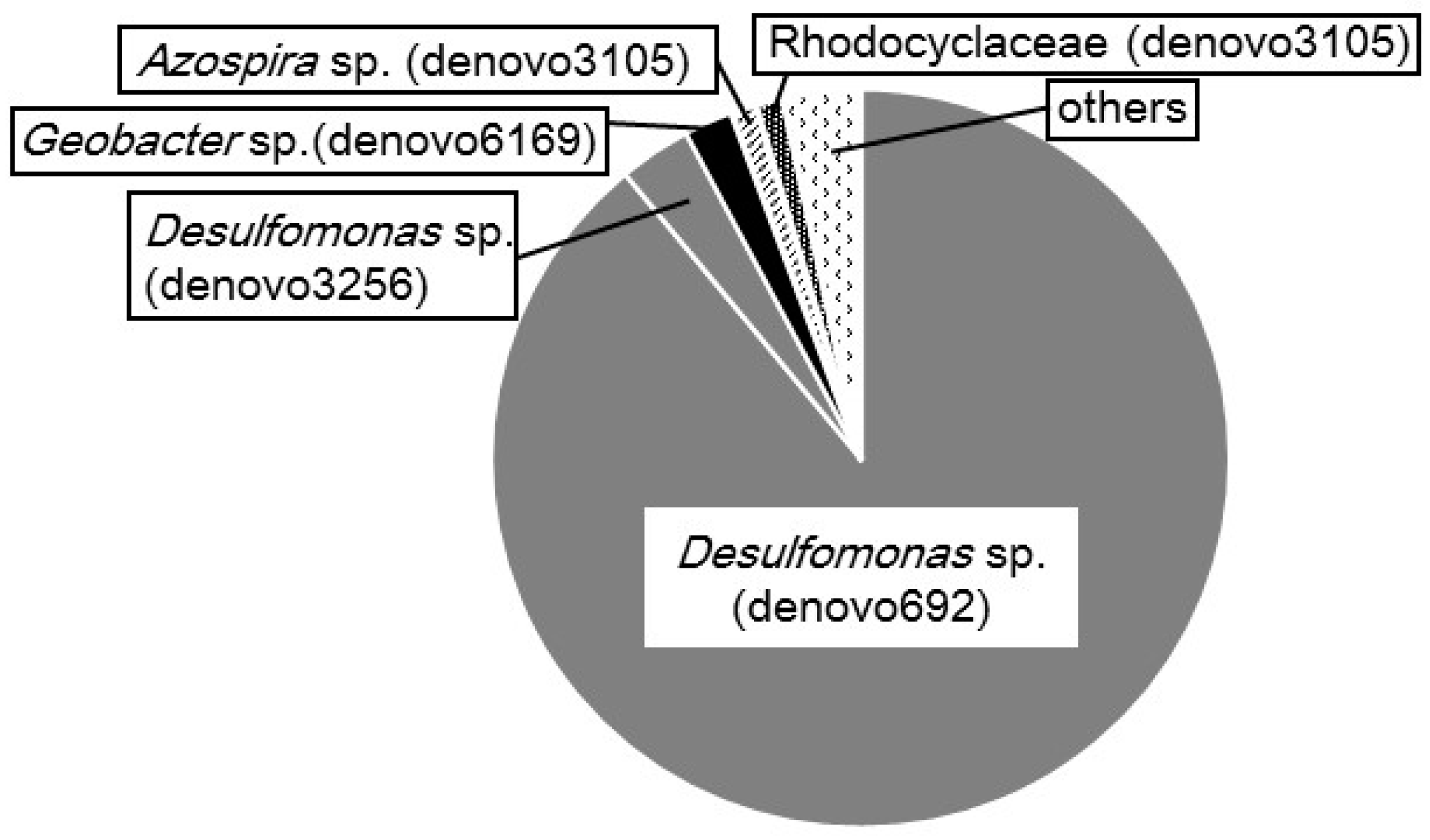
2.3. Microbial Composition in the CS Culture
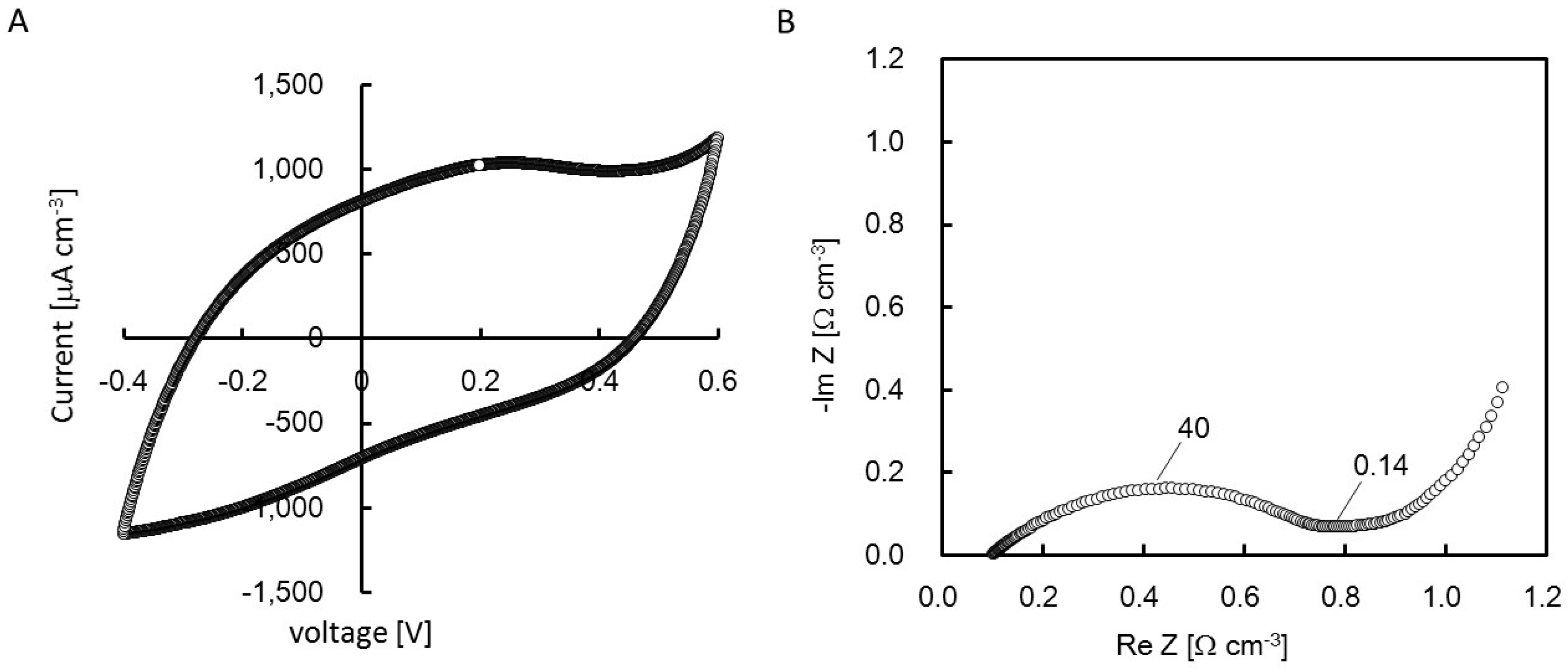
2.4. Cyclic Voltanmetry (CV) and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) of the rGO-CS Complex
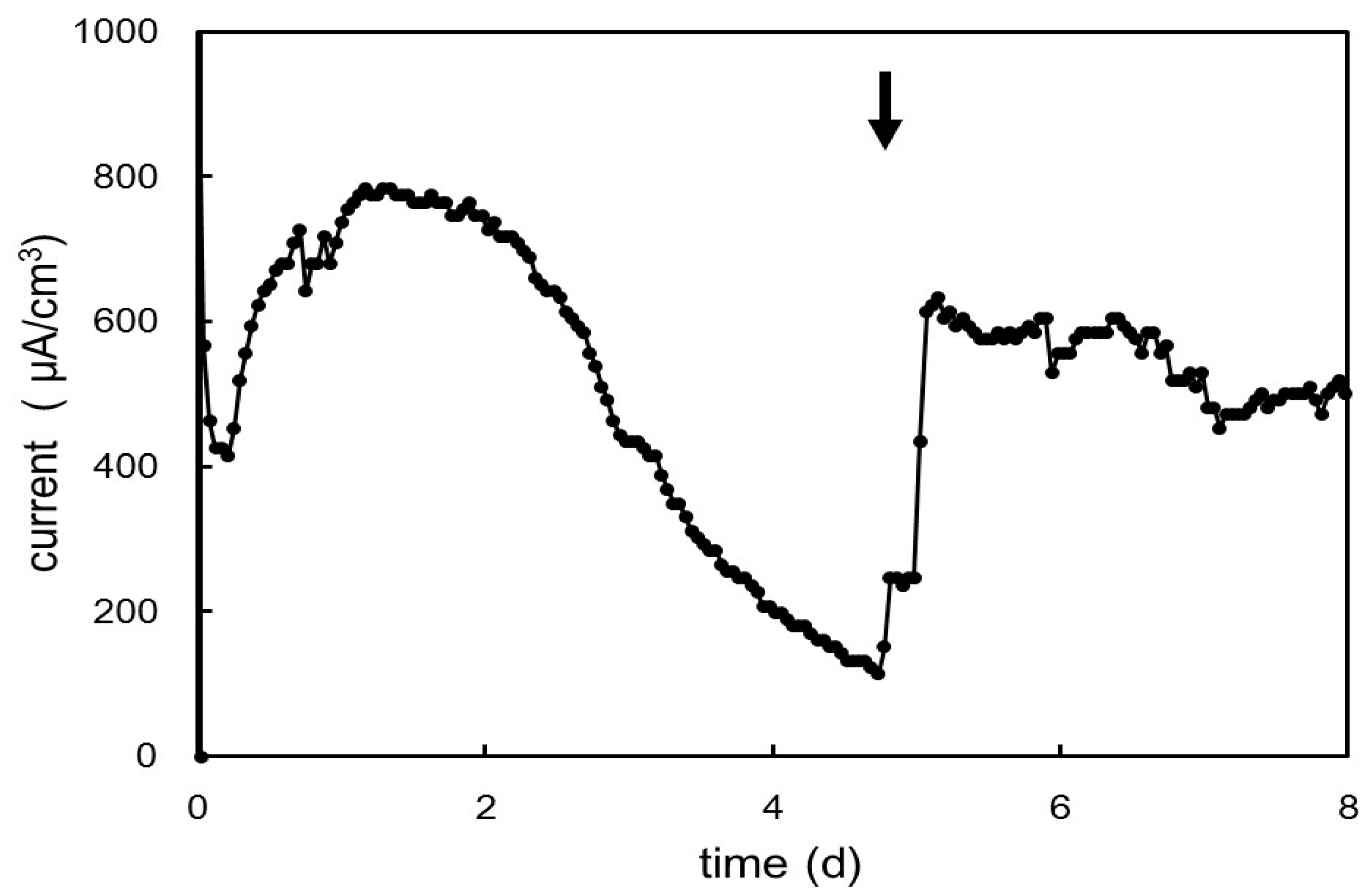
2.5. Electrochemical Cultivation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. GO
4.2. Enrichment of GORB
4.3. XPS and Electric Conductive Analysis
4.4. Phylogenetic Identification of Bacteria in the CS Culture
4.5. Electrochemical Cultivation
4.6. Electrochemical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salas, E.C.; Sun, Z.; Luttge, A.; Tour, J.M. Reduction of graphen oxide via bacterial respiration. ACS Nano 2012, 4, 4852–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Qian, F.; Saltikov, C.W.; Jiao, Y.; Li, Y. Microbial reduction of graphene oxide by Shewanella. Nano Res. 2011, 4, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Escherichia coli bacteria reduce graphene oxide to bactericidal graphene in a self-limiting manner. Carbon 2012, 50, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanra, P.; Kuila, T.; Kim, N.H.; Bae, S.H.; Yu, D.-S.; Lee, J.H. Simultaneous bio-functionalization and reduction of graphene oxide by baker’s yeast. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 183, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, N.; Miyata, Y.; Doi, K.; Goto, Y.; Nagao, Y.; Tero, R.; Hiraishi, A. Graphene oxide-dependent growth and self-aggregation into a hydrogel complex of exoelectrogenic bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2016, 21867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Qian, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Saltikov, C.W.; Gralnick, J.A. Deciphering the electron transport pathway for graphene oxide reduction by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 3662–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, Y.; Yoshida, N. Preliminary evaluation of a microbial fuelcell treating artificial dialysis wastewater using graphene oxide. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1709, 020007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Lin, Y. Graphene and graphene oxide: biofunctionalization and applications in biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 19, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantar-zadeh, K.; Ou, J.Z.; Daeneke, T.; Strano, M.S.; Pumera, M.; Gras, S.L. Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Dichalcogenides in Biosystems. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 5086–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuila, T.; Bose, S.; Khanra, P.; Mishra, A.K.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, J.H. Recent advances in graphene-based biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4637–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Liu, Z.; Welsher, K.; Robinson, J.T.; Goodwin, A.; Zaric, S.; Dai, H. Nano-graphene oxide for cellular imaging and drug delivery. Nano Res. 2008, 1, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roden, E.E.; Lovley, D.R. Dissimilatory Fe (III) reduction by the marine microorganism Desulfomonas acetoxidans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Butler, J.E.; Young, N.D.; Lovley, D.R. Evolution from a respiratory ancestor to fill syntrophic and fermentative niches: Comparative genomics of six Geobacteraceae species. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, D.R.; Holmes, D.E.; Tender, L.M.; Lovley, D.R. Electrode-reducing microorganisms that harvest energy from marine sediments. Science 2002, 295, 483–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, D.; Bond, D.; O’neil, R.; Reimers, C.; Tender, L.; Lovley, D. Microbial communities associated with electrodes harvesting electricity from a variety of aquatic sediments. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 48, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, T.H.; Hofmann, M.; Burcombe, E.; Wei, J.; Jiang, R.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y. Antibacterial activity of graphite, graphite oxide, graphene oxide, and reduced graphene oxide: Membrane and oxidative stress. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6971–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Han, J.W.; Dayem, A.A.; Eppakayala, V.; Kim, J.-H. Oxidative stress-mediated antibacterial activity of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5901–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Toxicity of graphene and graphene oxide nanowalls against bacteria. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5731–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Peng, H.; Wang, X.; Shao, F.; Yuan, Z.; Han, H. Graphene oxide exhibits broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against bacterial phytopathogens and fungal conidia by intertwining and membrane perturbation. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1879–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perreault, F.; de Faria, A.F.; Nejati, S.; Elimelech, M. Antimicrobial properties of graphene oxide nanosheets: why size matters. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7226–7236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpio, I.E.M.; Santos, C.M.; Wei, X.; Rodrigues, D.F. Toxicity of a polymer–graphene oxide composite against bacterial planktonic cells, biofilms, and mammalian cells. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 4746–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E.; Esfandiar, A. Wrapping bacteria by graphene nanosheets for isolation from environment, reactivation by sonication, and inactivation by near-infrared irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 6279–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringeisen, B.R.; Henderson, E.; Wu, P.K.; Pietron, J.; Ray, R.; Little, B.; Biffinger, J.C.; Jones-Meehan, J.M. High power density from a miniature microbial fuel cell using Shewanella oneidensis DSP10. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 2629–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Park, H.S.; Hyun, M.S.; Chang, I.S.; Kim, M.; Kim, B.H. A mediator-less microbial fuel cell using a metal reducing bacterium, Shewanella putrefaciens. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2002, 30, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, G.J.; Mori, S.; Nakamura, R.; Hashimoto, K.; Watanabe, K. Analyses of current-generating mechanisms of Shewanella loihica PV-4 and Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 in microbial fuel cells. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7674–7681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Burgess, J.G. Shewanella electrodiphila sp. nov., a psychrotolerant bacterium isolated from Mid-Atlantic Ridge deep-sea sediments. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 2882–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Obraztova, A.; Stewart, N.; Popa, R.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Tiedje, J.M.; Nealson, K.H.; Zhou, J. Shewanella loihica sp. nov., isolated from iron-rich microbial mats in the Pacific Ocean. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1911–1916. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, A.S.; Paquete, C.M.; Fonseca, B.M.; Louro, R.O. Exploration of the ‘cytochromome’ of Desulfuromonas acetoxidans, a marine bacterium capable of powering microbial fuel cells. Metallomics 2011, 3, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, N.; Ye, L.; Liu, F.; Li, Z.; Katayama, A. Evaluation of biodegradable plastics as solid hydrogen donors for the reductive dechlorination of fthalide by Dehalobacter species. Biores. Technol. 2013, 130, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanizawa, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Tsuzuki, K.; Nagao, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Tero, R.; Iwasa, S.; Hiraishi, A.; Suda, Y.; Takikawa, H.; et al. Microorganism mediated synthesis of reduced graphene oxide films. J. Phy. Conf. Ser. 2012, 352, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Umeyama, Y.; Yamada, T.; Tero, R.; Hiraishi, A. Enhancement of electricity production by graphene oxide in soil microbial fuel cells and plant microbial fuel cells. Front. Bioeng. Biotech. 2015, 3, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, N.; Iguchi, H.; Yurimoto, H.; Murakami, A.; Sakai, Y. Aquatic plant surface as a niche for methanotrophs. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoshida, N.; Goto, Y.; Miyata, Y. Selective Growth of and Electricity Production by Marine Exoelectrogenic Bacteria in Self-Aggregated Hydrogel of Microbially Reduced Graphene Oxide. C 2016, 2, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/c2020015
Yoshida N, Goto Y, Miyata Y. Selective Growth of and Electricity Production by Marine Exoelectrogenic Bacteria in Self-Aggregated Hydrogel of Microbially Reduced Graphene Oxide. C. 2016; 2(2):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/c2020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoshida, Naoko, Yuko Goto, and Yasushi Miyata. 2016. "Selective Growth of and Electricity Production by Marine Exoelectrogenic Bacteria in Self-Aggregated Hydrogel of Microbially Reduced Graphene Oxide" C 2, no. 2: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/c2020015
APA StyleYoshida, N., Goto, Y., & Miyata, Y. (2016). Selective Growth of and Electricity Production by Marine Exoelectrogenic Bacteria in Self-Aggregated Hydrogel of Microbially Reduced Graphene Oxide. C, 2(2), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/c2020015