Abstract
The treatment of organic phosphate ester (OPE) pollutants in water is a challenging but highly necessary task. In this study, an advanced oxidation process through light activation of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) involving graphene oxide (GO) as a promoter was developed to degrade OPE in water, taking triphenyl phosphate (TPhP) as an example. The developed “Light+PMS+GO” system demonstrated good convenience, high TPhP degradation efficiency, tolerance in a near-neutral pH, satisfactory re-usability, and a low toxicity risk of degradation products. Under the investigated reaction conditions, viz., the full spectrum of a 300 W Xe lamp, PMS of 200 mg L−1, GO of 4 mg L−1, and TPhP of 10 μmol L−1, the “Light+PMS+GO” system achieved nearly 100% TPhP degradation efficiency during a 15 min reaction duration with a 5.81-fold enhancement in the reaction rate constant, compared with the control group without GO. Through quenching experiments and electron paramagnetic resonance studies, singlet oxygen was identified as the main reactive species for TPhP degradation. Further studies implied that GO could accumulate both oxidants and pollutants on the surface, providing additional reaction sites for PMS activation and accelerating electron transfer, which all contributed to the enhancement of TPhP degradation. Finally, the TPhP degradation pathway was proposed and a preliminary toxicity evaluation of degradation intermediates was conducted. The convenience, high removal efficiency, and good re-usability indicates that the developed “Light+PMS+GO” reaction system has great potential for future applications.
1. Introduction
Since the prohibition of some brominated flame retardants, organic phosphate esters (OPEs), as their substitutes, have been produced and used worldwide. OPEs are widely used as flame retardants, plasticizers, and defoamers in industries such as plastics, furniture, textiles, electronics, construction, vehicles, and petroleum industries [1,2]. As a result of their wide use, OPEs have been detected in the atmosphere, surface water sediments, animals and plants, and even human bodies [2,3,4,5]. Triphenyl phosphate (TPhP), a classical aromatic OPE, has been widely detected in various water environments in recent years [6]. Although the concentrations of TPhP in natural water bodies are not high, it usually poses a higher risk than other OPEs because of its high developmental toxicity, cytotoxicity, and neurotoxicity [7,8]. Hence, to mitigate the biological toxicity and ecological hazards posed by TPhP, it is imperative to devise an economical and eco-friendly treatment approach for the removal of TPhP from contaminated water bodies. Methods such as photocatalysis, Fenton-like reactions, and PMS-based AOPs have been used to remove TPhP from water [9]. Yuan et al. found that 50 μg L−1 of TPhP could be removed after a 30 min treatment by ozone and UV/H2O2 [10]. Song et al. demonstrated that 10 μM TPhP could be quickly degraded with CoFe2O4 and PMS in 6 min [8]. Compared to traditional sewage treatment technologies, advanced oxidation technologies (AOPs) have better degradation effects on TPhP.
Peroxymonosulfate (PMS)-based AOPs can generate sulfate radicals (SO4•−) (E0 = 2.5–3.1 V) possessing a high redox potential and a high selectivity for the oxidation of compounds with benzene rings, compared with hydroxyl radicals (•OH) (E0 = 1.8–2.7 V) [11,12,13,14]. In addition, PMS can also be activated under different conditions to produce reactive oxygen species, such as superoxide radicals and singlet oxygen [15]. The activation of PMS can be achieved through transition metals, alkalis, heat, ultraviolet light, and other methods [13,16,17,18,19]. However, transition metal catalysts (such as Co) are susceptible to leaching, leading to contamination by metal ions. The activation efficiency of alkalis and heat is not satisfactory. Replacing chemical activators with light energy could reduce the risk of secondary pollution. Therefore, light activation of PMS for organic pollutant removal has attracted considerable research attention and demonstrated good removal efficiency.
Graphene oxide (GO) is a “famous star” material, which is also applied in the photocatalysis process, acting as an active sites support, electron transfer mediator, etc. The good electrical conductivity of GO facilitates the rapid transfer of photogenerated electrons, implying that more photogenerated electrons could be involved in the activation process of PMS, which might ultimately serve to improve the photocatalytic efficiency. In studies of the photocatalytic performance of GO, it has often been modified or used as a supporting material in a composite with other semiconductors [20]. Ding et al. discovered that visible light is capable of driving the degradation of ofloxacin by GO-supported titania/zirconia ternary nanocomposites [21]. Jin et al. studied the capacity of Ag3PO4/Fe3O4/GO composites to activate peroxydisulfate for the degradation of p-chlorophenol under visible light irradiation [22]. Sun et al. investigated the capacity of GO-supported TiO2, ZnO, and Ta2O5 composite materials to enhance their responsiveness to both UV and visible light for activating H2O2 and PMS, thereby improving the degradation efficiency of methylene blue [23]. Wang et al. applied GO as both a schwertmannite supporting material and electron transfer mediator, achieving an ideal sulfathiazole degradation result in their developed light/Sch-GO/H2O2 system. However, there are few reports on the sole application of GO in AOP reactions. The capability and activity of GO for PMS activation needs to be further clarified.
Herein, a simple but efficient method involving GO to promote light activation of PMS was developed for the degradation of TPhP. The effects of typical reaction parameters (catalyst dosage, PMS dosage, ions influence, initial solution pH, etc.) on the “Light+PMS+GO” system were studied. The promotional mechanism of GO on PMS activation towards TPhP degradation was primarily proposed based on a material characterization, reactive oxygen species (ROS) quenching experiments, electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR), liquid chromatograph–mass spectrometry (LC-MS), and LSV tests.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Graphene oxide (GO, diameter of 50–200 nm) aqueous dispersion with concentration of 1 mg mL−1 was obtained from Nanjing/Jiangsu XFNANO Materials Tech Co., Ltd. Triphenyl phosphate (TPhP) was of analytical grade and provided by Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd. Potassium salt of peroxymonosulfate (2KHSO5·KHSO4·K2SO4, PMS) was purchased from Adamas-beta. Methanol was obtained from Fisher and supplied as HPLC grade. All other reagents of analytical grade without special descriptions were supplied by Chengdu Kelong Chemical Reagent Company.
2.2. Catalytic Degradation Experiments
Catalytic tests were conducted under magnetic stirring in an open cylindrical glass reactor with a cooling water jacket (25 °C). A 300 W Xenon lamp (PLS-SXE300, Perfect Light) was used as the light source. A 400 nm cutoff filter was used with the light source if visible light was needed. During the catalytic experiments, 100 mL of 10 μmol L−1 TPhP solution and a certain volume of GO dispersion were successively added into the reactor without a pH adjustment. After reaching the adsorption–desorption equilibrium by stirring in the dark for 20 min, 20 mg of PMS was added, and the lamp was turned on to initiate the catalytic reaction. At scheduled time intervals, a 500 μL liquid sample was collected, mixed with 500 μL methanol instantly, and filtered with a 0.22 μm syringe filter to remove the GO. The residual TPhP in the filtrate was quantified by a high-performance liquid chromatograph (HPLC, Essentia LC-16, SHIMADZU) equipped with a SHIMSEN Ankylo C-18 column (4.6 × 250 mm, 5 μm) and a UV detector (λ = 210 nm). The mobile phase contained 65% acetonitrile and 35% ultrapure water (v/v), running at a flow rate of 1 mL min−1.
In continuous experiments, after each 20 min reaction cycle, only TPhP was added into the reaction system to maintain the TPhP concentration of 10 μM, while the other reaction conditions, such as light, GO, and PMS, remained unchanged.
To identify the reactive species, quenching experiments and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) measurements were conducted. Methanol (MeOH), tert-butanol (TBA), furfuryl alcohol (FFA), and p-benzoquinone (p-BQ) were utilized to scavenge both SO4•− and •OH, •OH, 1O2, and superoxide radicals (O2•−), respectively [24]. During the photocatalytic process, the generation of SO4•− and •OH, and 1O2 and O2•− in the solution was trapped by 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DMPO), 4-Amino-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine (TEMP), DMPO, and 4-hydroxy-tetramethylpiperidinooxy (TEMPO), respectively, and detected by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy (Bruker EMX PLUS).
When investigating the influence of initial solution pH on the TPhP degradation, 0.1 M NaOH or 0.1 M HCl was used to adjust the solution pH. Environmental water, e.g., river water (Jinjiang river, Chengdu) or effluent from a wastewater treatment plant (Chengdu), was adopted to replace the de-ionized water to investigate the influence of water quality on TPhP degradation.
Liquid chromatograph–mass spectrometry (LC-MS) was used to identify the intermediate degradation products of TPhP. Based on the structural information, the ecotoxicity of TPhP and the intermediate products was determined by the Ecological Structure Activity Relationships (ECOSAR) program.
2.3. Characterization
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was performed on a Thermo-Fischer ESCALAB 250Xi instrument to analyze surface characteristics of the sample before and after the catalytic reaction. The LC-MS samples were analyzed using a Surveyor Plus HPLC System. Separation was carried out on a Hypersil Gold column (150 mm × 2.1 mm, 5 μm; Thermo, Waltham, MA, USA) maintained at 25 °C. The mobile phase consisted of 0.1% (v/v) formic acid (A) and CH3OH (B). The gradient elution program was as follows: 95% A at 0–5 min; 5–8 min, 98–80% A; 8–13 min, 80–40% A; 13–18 min, 40–5% A; 18–23 min, 5% A; and back to 95% A at 23.1 min, with re-conditioning of the column for 7 min. The flow rate was 0.2 mL min−1. The zeta potentials of GO in aqueous solutions with different pHs were tested on a Zetasizer Nano ZS90.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Promoting Effect of GO on Light Activation of PMS for TPhP Degradation
Graphene oxide possesses abundant surface functional groups (-OH, -COOH, -C=O, etc.) and good electron-conducting ability. On the one hand, the oxygen-containing functional group makes GO highly dispersible in an aqueous solution, leading to more contact opportunities for the reactants. On the other hand, accelerated electron transfer can be expected when GO is involved in a PMS activation process. Both facts are favorable for pollutant degradation through a PMS activation-based advanced oxidation process.
As commonly reported, light can activate PMS to generate a series of reactive species, resulting in the degradation of pollutants [15,25]. In this study, after 20 min of light irradiation in the presence of PMS, 72.5% of the TPhP was degraded (“L+PMS” system, Figure 1a). As a control experiment, in the absence of PMS (“L+GO” system), only 10.89% of the TPhP was removed by adsorption after 20 min of reaction. Similarly, in the absence of light (“GO+PMS” system), almost no TPhP was degraded or removed. When GO was introduced into the “L+PMS” system, a remarkable TPhP degradation efficiency was obtained. As displayed in Figure 1a, complete TPhP removal was achieved in 15 min when full-spectrum light was used (“L+GO+PMS” system). Even under only visible light irradiation, the TPhP removal efficiency still reached 90.80% after 20 min reaction (“VL+GO+PMS” system), which was much higher than that of the “L+PMS” system. In terms of reaction rate comparison, as can be seen in Figure 1b, a pseudo-first-order reaction rate constant of 0.3705 min−1 was obtained for the “L+GO+PMS” system, which was 5.81-fold higher than that for the “L+PMS” system (0.0638 min−1). Even under visible light irradiation, the observed reaction rate constant of 0.1194 min−1 was also much higher. Therefore, the promoting effect of GO for the light activation of PMS was confirmed.
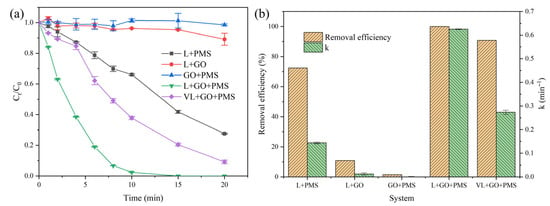
Figure 1.
TPhP degradation efficiency (a) and related pseudo-first-order reaction rate constants (b) in various reaction systems. [TPhP] = 10 μmol L−1; [GO] = 4 mg L−1; [PMS] = 0.2 g L−1; and temperature of 25 °C.
3.2. Identification of Reactive Species and the Mechanism of the GO-Promoting Effect for TPhP Degradation
During the process of metal-free PMS activation, reactive species, including sulfate radicals (SO4•−), hydroxyl radicals (•OH), superoxide radicals (O2•−), and non-radicals of singlet oxygen (1O2), are commonly found, which are responsible for organic pollutant degradation [26,27]. To verify the existence of the above-mentioned reactive species and understand their contributions to TPhP degradation, quenching experiments were conducted, adopting TBA, FFA, p-BQ, and MeOH as scavengers for •OH, 1O2, O2•−, and both SO4•− and •OH, respectively. As depicted in Figure 2a, in the presence of scavengers, TPhP degradation in the “L+GO+PMS” system was strongly inhibited. In addition to TBA, the other scavengers totally inhibited TPhP degradation, manifesting the significant role of 1O2, O2•−, and SO4•−. Actually, O2•− can function as the precursor of 1O2, and SO4•− can also induce the generation of 1O2 [14,24,28]. The other fact to consider is that 1O2 possesses a higher oxidation potential than that of O2•− [29]. Therefore, it was deduced that 1O2 was probably the main reactive oxygen species responsible for TPhP degradation.
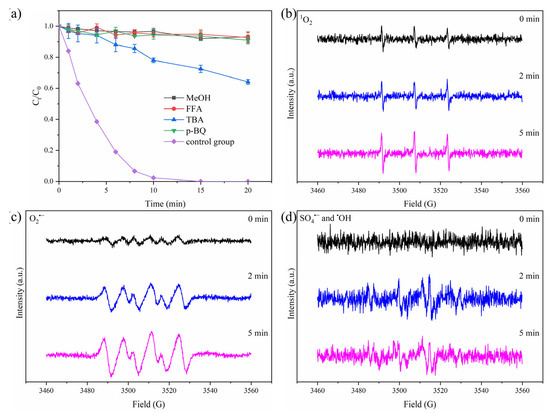
Figure 2.
Effect of scavengers on TPhP degradation (a); in situ EPR spectra for 1O2 (b), O2•− (c), and SO4•− and •OH (d) reactive species detection in the “L+GO+PMS” system. Reaction conditions: [TPhP] = 10 μmol L−1; [GO] = 4 mg L−1; [PMS] = 0.2 g L−1; [MeOH] = 330 mM; [FFA] = 3.5 mM; [TBA] = 330 mM; [p-BQ] = 3.5 mM; and temperature 25 °C.
The EPR measurements provided more evidence of the generation of various reactive species. As presented in Figure 2b,c, the typical signals belonging to TEMP-1O2 and DMPO-O2•− adducts were observed, and the signal intensities were gradually enhanced with an increasing reaction time. In addition to the obvious 1O2 and O2•− signals, weak but still observable signals assigned to DMPO-SO4•− and DMPO-•OH adducts were also found by the EPR measurements (Figure 2d), indicating the generation of SO4•− and •OH radicals in the “L+GO+PMS” system. However, the weak intensities of the SO4•− and •OH radicals might imply their non-significant role in TPhP degradation.
Based on the above quenching experiments and EPR measurements, it seemed that the 1O2-dominated non-radical process was the main contributor to TPhP degradation. During the reaction process, PMS interacted with GO, promoting electron rearrangement and forming metastable PMS. After being excited to a metastable state, the PMS molecules underwent simple redox reactions facilitated by the GO, with the pollutants serving as electron donors and the metastable PMS as electron acceptors. Subsequently, the metastable PMS molecules extracted electrons from the TPhP molecules via the GO, thereby achieving the conversion of TPhP [30]. Studies have demonstrated that N-doped graphene and reduced graphene oxide can readily facilitate electron transfer under ultrasonic conditions, accelerating the self-decomposition (Equation (1)) process of PMS [31,32]. It is highly plausible that analogous processes might also take place during the GO-assisted light activation of PMS (Equations (2) and (3)) [32]. The results of XPS shown in Figure 3a,b also confirm that a certain degree of reduction occurred on the surface of the GO under the illuminated conditions.
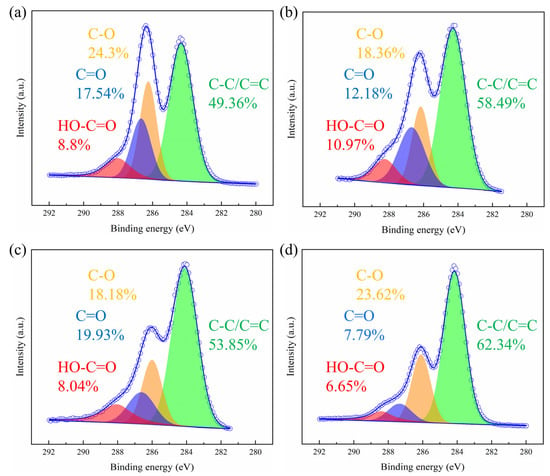
Figure 3.
XPS C 1s spectra of pristine GO (a), GO under light irradiation for 20 min (b), GO under light irradiation for 20 min in the presence of PMS (c), and GO after TPhP degradation reaction in the “L+GO+PMS” system (d). Reaction conditions: [TPhP] = 10 μmol L−1; [GO] = 4 mg L−1; [PMS] = 0.2 g L−1; and temperature 25 °C.
XPS was used to track the surface functional group changes in the GO during the degradation of TPhP via the “L+GO+PMS” system. Figure 3 displays the C 1s core-level XPS spectra of GO under different conditions. Four components of carboxyl groups (~288.5 eV)—C=O (~287 eV), C–O bonds in hydroxyl and epoxy groups (~286 eV), and C–C/C=C bonds in the graphitic lattice (~284.6 eV)—were deconvoluted from the spectra [33]. We noticed that the oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface of GO changed a lot. In the absence of PMS and TPhP, only light irradiation could have induced the decrease in the oxygen-containing functional groups (C–O, from 24.3% to 18.36%; C=O, from 17.54% to 12.18%) (Figure 3a,b), mainly due to the reduction effect of light irradiation [34]. After adding PMS into the reaction system, the content of the C=O group increased back to its prior level, from 12.18% to 19.93% (Figure 3c). This was because light can trigger PMS activation, leading to the generation of reactive species. Thus, in the absence of pollutant (TPhP), the GO became the target of reactive species, leading to more C=O groups formation by oxidation [35]. After TPhP degradation in the “L+GO+PMS” system, the resulting GO contained fewer C=O and HO-C=O groups than the other treatment groups (Figure 3d). It has been reported that surface functional oxygen-containing groups on biocarbon (e.g., C=O) can act as reactive centers for PMS activation [36,37]. When the PMS molecule attacked the C=O group, a peroxide adduct was formed, which induced a series of reactions and finally led to the generation of 1O2. Meanwhile, the C=O group was consumed, as shown by its decreased content found by XPS. Such a phenomenon has been commonly reported in carbon-based PMS activation processes [38,39,40,41,42].
The beneficial effect of GO on PMS activation also included the enrichment of reactants on the surface of GO. Firstly, considering the graphitic structure of GO and the benzene rings of TPhP, π-π interactions were expected to exist between them, resulting in the preferable adsorption of TPhP on the GO surface. This expectation was confirmed in a previous study, which demonstrated the strong π-π electron-donor–acceptor interactions between TPhP and partially graphitized biocarbon [43]. Secondly, the abundant oxygen-containing functional groups (such as hydroxyl and carboxyl groups) on the surface of GO provided active sites for the process of PMS activation and degrading of pollutants. The undoped sp2 hybridized carbon network possessed abundant free-flowing electrons and unpaired electron edge sites, which could be transferred to the PMS to form a small amount of free radicals [44]. As reported, a negative value for the adsorption energy of PMS on the surface of GO was found, showing that the adsorption process in practical situations is spontaneous and exothermic in nature [45]. Thirdly, GO could have also acted as a bridge in the photocatalytic process to accelerate electron transfer [46]. Therefore, the enrichment of both the oxidant (PMS) and targeted pollutant (TPhP) on the surface of GO shortened the electron transfer pathway, finally promoting TPhP degradation.
Based on the above discussion, it is suggested that the promoting role of GO in the “L+GO+PMS” system for TPhP degradation includes (i) facilitating electron transfer, thus accelerating PMS activation; (ii) providing additional reaction sites (e.g., surface C=O group) for PMS activation; and (iii) enriching PMS and TPhP in a certain region to increase the chances of their reaction, which is illustrated in Figure 4.
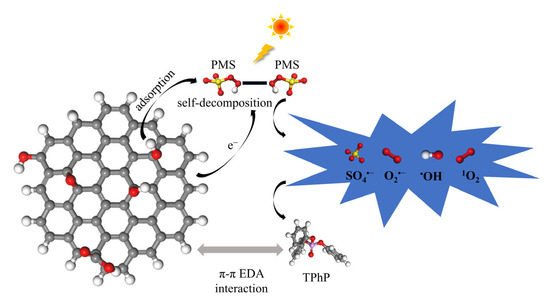
Figure 4.
Schematic illustration of TPhP degradation in the “L+GO+PMS” system.
3.3. Effects of Typical Operation Parameters and Environmental Factors on the Catalytic Degradation of TPhP in the “Light+PMS+GO” System
The effects of environmentally relevant factors, such as the GO dosage, PMS dosage, initial solution pH, co-existing anions and humic acid, and water quality, on TPhP degradation efficiency were considered.
As presented in Figure 5a and Figure S1a in the Supplementary Materials, the GO dosage had an obvious effect on the TPhP degradation in the “Light+PMS+GO” system. Increasing the GO dosage from 2 to 4 mg L−1 significantly improved both the degradation efficiency and reaction rate. Nevertheless, further raising the GO dosage decreased the degradation efficiency, probably attributed to the light penetration barrier of excess GO.
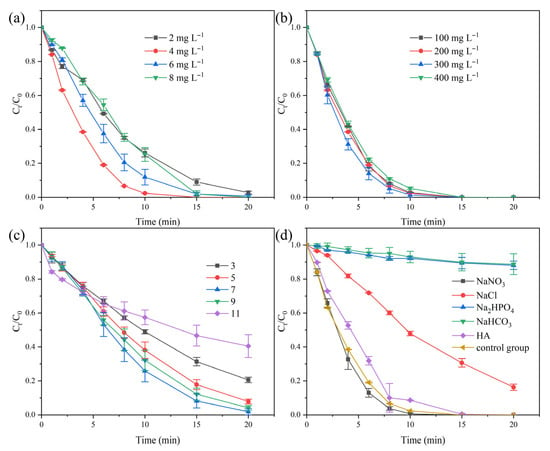
Figure 5.
Influences of (a) catalyst dosage, (b) PMS dosage, (c) initial solution pH, and (d) anions and HA on TPhP degradation in “Light+PMS+GO” system. Except for the investigator factor, the other reaction conditions were kept at [TPhP] = 10 μmol L−1; [GO] = 4 mg L−1; [PMS] = 0.2 g L−1; natural solution pH; and temperature 25 °C.
Figure 5b shows that the added amount of PMS (100–400 mg L−1) had little effect on the degradation of TPhP, possibly due to the excess dosage of PMS compared with the concentration of TPhP. Further confirmed by the pseudo-first-order reaction kinetic study (Figure S1b in Supplementary Materials), 300 mg L−1 was a relatively suitable concentration for the “Light+PMS+GO” system, since a slightly high reaction rate constant was obtained.
The initial solution pH was an important factor affecting the TPhP degradation via the “Light+PMS+GO” system. As shown in Figure 5c, under an initial solution pH of 3−11, the TPhP degradation efficiencies varied greatly. Neutral or near-neutral conditions, e.g., pH of 5.0−9.0, were favorable for TPhP degradation, which achieved over a 90% removal efficiency after 20 min of reaction. Actually, due to the commonly reported acidification effect, PMS activation could lead to a decrease in solution pH [47]. A final solution pH of 3.25−3.46 was found with an initial solution pH of 5−9 after 20 min of reaction (Figure S2 in Supplementary Materials). Therefore, near-neutral pH conditions did not affect TPhP degradation much. However, strong acidic or alkaline conditions inhibited TPhP degradation, with a removal efficiency of only 79.4% and 59.8% for an initial pH of 3 and 11, respectively. A similar trend was observed when considering the effect of initial solution pH on the reaction rate constants (Figure S1c in Supplementary Materials). The pKa1 and pKa2 values of PMS were <0 and 9.4, respectively [48]. Therefore, at pH 3−9, HSO5− was the predominant existing species of PMS in the solution. At pH 11, SO52− was the main existing form of PMS. Based on the zeta potential measurement, the GO surface was negatively charged under the investigated solution pH range (Figure S3 in Supplementary Materials). Thus, more negative charges would be present on the GO surface at higher solution pH conditions, since the absolute zeta potential values increased with an increasing solution pH. Due to the electrostatic repulsion between the negative surface raising charge of GO and the negative forms of PMS (HSO5− and SO52−), the TPhP degradation efficiency exhibited a decreasing trend from a neutral to alkaline environment [49]. At neutral pH conditions, PMS was more easily activated by the catalysts [8,50], due to the self-quenching effect of SO4•− under alkaline conditions and the inhibition of SO4•− formation by high concentrations of H+ under acidic conditions. Upon decreasing the solution pH to acidic conditions, the TPhP degradation also showed a decreasing trend. In addition to the above-mentioned reasons, another possible reason was ascribed to the inhibitory effect of Cl−, which was from the HCl used for pH adjustment.
TPhP is found in natural waterbodies, e.g., rivers and lakes [51]. Inorganic anions, including Cl−, NO3−, HPO4−, and HCO3−, are typical co-existing ions in natural waterbodies. Their influence on TPhP degradation should be considered. As shown in Figure 5d, the influences of anions (10 mM) in the “Light+PMS+GO” system were different. The presence of Cl− strongly hindered TPhP degradation, while HPO4− and HCO3− seemed to almost totally suppress TPhP degradation. As commonly reported, anions (Cl−, HPO4−, and HCO3−) can react with the active substance to produce secondary active species with weak oxidation ability, causing a decrease in the TPhP degradation efficiency [49,52]. In contrast, NO3− and the typical organic matter of humic acid (HA) did not affect TPhP degradation much, which is similar to previous studies on the activation of PMS by metal-free catalysts [24]. Consequently, due to the strong inhibition effect of Cl−, HPO4−, and HCO3−, the degradation efficiency of TPhP via the “Light+PMS+GO” system was not ideal in actual water bodies, taking river water and effluent from a wastewater treatment plant as examples (Figure S4 in the Supplementary Materials).
The continuous usability of the “Light+PMS+GO” system was investigated by five successive batches of TPhP degradation, as shown in Figure 6. Since the GO was well dispersed in the aqueous solution and difficult to separate, only fresh TPhP was added into the reaction system after each batch reaction, without adding new PMS or GO. It was observed that even after five successive reaction batches, the TPhP removal efficiency remained over 86%, manifesting the feasibility, facility, and high efficiency of the developed “Light+PMS+GO” advanced oxidation system for TPhP degradation.
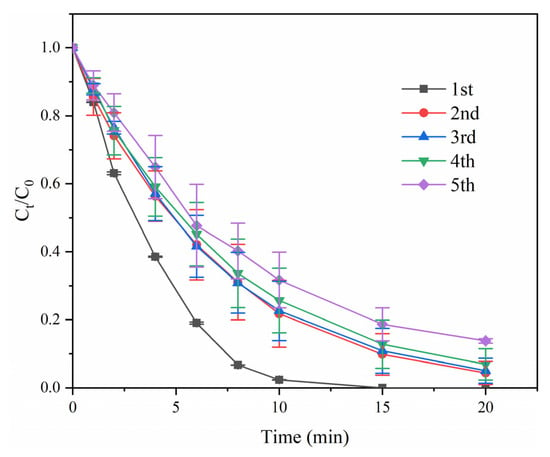
Figure 6.
TPhP degradation in the “Light+PMS+GO” system in the recycle study. Reaction conditions: [TPhP] = 10 μmol L−1; [GO] = 4 mg L−1; [PMS] = 0.2 g L−1; and temperature 25 °C.
3.4. Preliminary Analysis of TPhP Degradation Intermediates and Their Ecotoxicities
LC-MS was used to identify the intermediate degradation products of TPhP in the “Light+PMS+GO” system. Based on the MS spectrum shown in Figure S6 in the Supplementary Materials, a total of eight intermediate products were found, which could be derived from two possible TPhP degradation pathways. As shown in Figure 7, in pathway I, under the attack of •OH/SO4•−, the benzene rings of the TPhP molecules were hydroxylated into a phenol structure, leading to the formation of IP(1) [8,9]. In pathway II, 1O2 played a major role, which induced the hydroxylation and O-functionalization of benzene rings of TPhP, producing IP(2) [53]. Further ring-opening reactions occurred, resulting in the products IP(3)–IP(6). The continuous attacks by the reactive species generated more small organic molecules, metaphosphorous acid, vinyl acetate, etc.
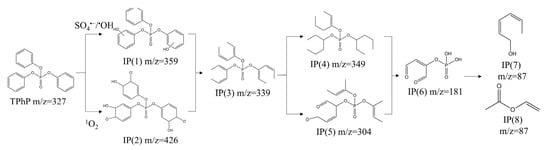
Figure 7.
Proposed degradation pathways of TPhP in “Light+PMS+GO” system.
In the “Light+PMS+GO” catalytic system, TPhP could be degraded. The process produced different intermediates whose toxicities were unknown and worth exploring. The separation of degradation intermediates is relatively difficult, and most of them are not easy to synthesize or commercialize. Thus, the ECOSAR program based on a quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) has been widely used in the field of water treatment to analyze the ecological toxicity of degradation processes [54,55,56]. To assess the ecotoxicities of TPhP and the related degradation intermediates produced in the “Light+PMS+GO” system, the ECOSAR program was adopted. The toxicities were categorized into four classes based on the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals [57,58]. Figure 8 shows that TPhP was recognized as very toxic to three model organisms (fish, daphnia, and green algae) in terms of acute and chronic toxicity. Fortunately, except for the acute and chronic toxicity of IP(3) and IP(4) to the three model organisms and the slightly elevated chronic toxicity of IP(5) to fish, the toxicities of the rest of the intermediates were lower than that of TPhP, probably due to the presence of esters and phosphates. The final toxicities of most of the oxidized ring-opening products were reduced as the reaction proceeded. Thus, the developed “Light+PMS+GO” advanced oxidation system can efficiently degrade TPhP with a low risk of ecotoxicity.
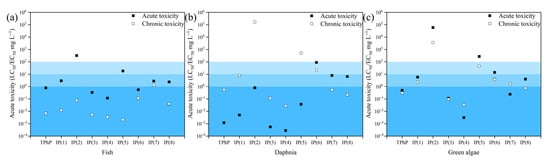
Figure 8.
Predicted acute and chronic toxicity of TPhP and its degradation intermediates to fish (a), daphnia (b), and green algae (c) in “Light+PMS+GO” system using ECOSAR program.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, a simple, efficient, and environmentally friendly method for degrading TPhP has been developed using GO as a promoter in a light-triggered PMS activation system. The involvement of GO in the reaction system accelerated TPhP degradation with a 5.81-fold enhancement in the reaction rate constant. Such a promoting effect could be ascribed to the accumulation of both oxidants and pollutants on the surface of GO through π-π interactions, the additional reaction sites provided by GO, and the good electron transfer ability of GO. Further study identified singlet oxygen generated from PMS activation as the main species responsible for TPhP degradation. The reduced toxicity of TPhP after treatment by the developed “Light+PMS+GO” system was preliminarily verified by the LC-MS results and ECOSAR prediction. This work provides a convenient and highly efficient approach for treating TPhP pollution in water.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/c11030065/s1, Figure S1: Influences of GO dosage (a), PMS dosage (b), pH (c), anions, and HA (d) on the pseudo-first-order reaction rate constant; Figure S2: The final solution pH after the reaction; Figure S3: Zeta potential of GO in aqueous solution with different pH; Figure S4: Influences of water quality on the degradation of TPhP by the “Light+PMS+GO” system; Figure S5: PMS consumption under different conditions; Figure S6: LC-MS spectrogram of the main intermediates of TPhP degradation.
Author Contributions
Y.L.: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing—original draft; Y.X.: Investigation and Methodology; X.W.: Conceptualization, Methodology, and Supervision; Y.W.: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, and Writing—reviewing and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (grant number 2023YFS0361) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 22178227).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the project administration support from Yongkui Zhang, Sichuan University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the Data Availability Statement. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
References
- Marklund, A.; Andersson, B.; Haglund, P. Screening of organophosphorus compounds and their distribution in various indoor environments. Chemosphere 2003, 53, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Liu, F.; Sun, B.; Liu, W.; Wu, J.; Wu, Y. Bioaccumulation and Potential Endocrine Disruption Risk of Legacy and Emerging Organophosphate Esters in Cetaceans from the Northern South China Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 4368–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundkvist, A.M.; Olofsson, U.; Haglund, P. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in marine and fresh water biota and in human milk. J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.-L.; Li, D.-Q.; Zhuo, M.-N.; Liao, Y.-S.; Xie, Z.-Y.; Guo, T.-L.; Li, J.-J.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Liang, Z.-Q. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers: Sources, occurrence, toxicity and human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 196, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Huang, W.; Yu, W.; Tang, S.; Yin, H. Metagenomic insights into the mechanisms of triphenyl phosphate degradation by bioaugmentation with Sphingopyxis sp. GY. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2023, 263, 115261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tang, J.; Xie, Z.; Mi, W.; Chen, Y.; Wolschke, H.; Tian, C.; Pan, X.; Luo, Y.; Ebinghaus, R. Occurrence and spatial distribution of organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in 40 rivers draining into the Bohai Sea, north China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 198, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y.; Kong, D.; Wu, Q.; Hong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Leung, J.Y.S. Occurrence, composition and biological risk of organophosphate esters (OPEs) in water of the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 14852–14862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Lv, W. Degradation of triphenyl phosphate (TPhP) by CoFe2O4-activated peroxymonosulfate oxidation process: Kinetics, pathways, and mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 681, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Feng, Y.; Liu, G.; Lv, W. Degradation of the flame retardant triphenyl phosphate by ferrous ion-activated hydrogen peroxide and persulfate: Kinetics, pathways, and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X. Removal of organophosphate esters from municipal secondary effluent by ozone and UV/H2O2 treatments. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhang, Y.; Si, F.; Yao, C.; Du, M.; Hussain, I.; Kim, H.; Huang, S.; Lin, Z.; Hayat, W. Persulfate non-radical activation by nano-CuO for efficient removal of chlorinated organic compounds: Reduced graphene oxide-assisted and CuO (0 0 1) facet-dependent. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.C.; Zhao, Z.; Hoag, G.E.; Dahmani, A.; Block, P.A. Degradation of volatile organic compounds with thermally activated persulfate oxidation. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, P.; Yang, S.; Rehman, S.; Ahmed, Z.; Zhu, N.; Dang, Z.; Liu, Z. A photo-switch for peroxydisulfate non-radical/radical activation over layered CuFe oxide: Rational degradation pathway choice for pollutants. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 261, 118232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Lin, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, H. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by base: Implications for the degradation of organic pollutants. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Activation of persulfate (PS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruton, T.A.; Sedlak, D.L. Treatment of perfluoroalkyl acids by heat-activated persulfate under conditions representative of in situ chemical oxidation. Chemosphere 2018, 206, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, L.; Lu, J.; Ferronato, C.; Chovelon, J.-M. Photodegradation of sulfasalazine and its human metabolites in water by UV and UV/peroxydisulfate processes. Water Res. 2018, 133, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Fernandez, J.; Rodriguez, S.; Dominguez, C.M.; Lominchar, M.A.; Lorenzo, D.; Romero, A. Abatement of chlorinated compounds in groundwater contaminated by HCH wastes using ISCO with alkali activated persulfate. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wei, S.; Ma, X.; Gao, Z.; Huang, W.; Wang, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J. Core–shell CoTiO3@MnO2 heterostructure for the photothermal degradation of tetracycline. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 3551–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Mallapur, S.; Reddy, M.; Singh, J.K.; Lee, D.-E.; Park, T. An Overview on Graphene-Metal Oxide Semiconductor Nanocomposite: A Promising Platform for Visible Light Photocatalytic Activity for the Treatment of Various Pollutants in Aqueous Medium. Molecules 2020, 25, 5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Li, J.; Guo, M.; Ji, H.; Li, P.; Liu, W.; Tressel, J.; Gao, S.; Wang, Q.; Chen, S. Visible light-driven degradation of ofloxacin by graphene oxide-supported titania/zirconia ternary nanocomposites. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 155, 111001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Zhu, L.; Xu, X.; Yu, X.; Qu, X.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wei, Q. Synergistic pollutant degradation by Ag3PO4/Fe3O4/graphene oxide visible light–persulfate coupled system: Mechanism elucidation and performance optimization. Catal. Commun. 2023, 177, 106643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, S. A comparative study of reduced graphene oxide modified TiO2, ZnO and Ta2O5 in visible light photocatalytic/photochemical oxidation of methylene blue. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 146, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhan, J.; Ma, J.; Wang, Z.; Han, B.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z. Metal-free catalysts with local fluorination regulation for peroxymonosulfate activation: Nearly 100% singlet oxygen production for selective degradation of aqueous organic pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berruti, I.; Oller, I.; Polo-López, M.I. Direct oxidation of peroxymonosulfate under natural solar radiation: Accelerating the simultaneous removal of organic contaminants and pathogens from water. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Chen, D.; Liang, Y.; Wang, W.; Lin, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Ou, J.Z. Understanding the active sites and associated reaction pathways of metal-free carbocatalysts in persulfate activation and pollutant degradation. Environ. Sci. Nano 2024, 11, 1368–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Chen, F.; Yao, F.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Yi, K.; Hou, L.; Li, X.; Wang, D. Recent advances in photo-activated sulfate radical-advanced oxidation process (SR-AOP) for refractory organic pollutants removal in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, M.; Drazic, G.; Tavares, P.B.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Silva, A.M.T. Metal-free graphene-based catalytic membrane for degradation of organic contaminants by persulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.R.M.; Valenzuela, L.; Rosal, R.; Ruotolo, L.A.M.; Nogueira, F.G.E.; Bahamonde, A. Peroxymonosulfate activation by Co3O4 coatings for imidacloprid degradation in a continuous flow-cell reactor under simulated solar irradiation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawle, R.; Giannakopoulos, S.; Frontistis, Z.; Mantzavinos, D. Peroxymonosulfate enhanced photoelectrocatalytic degradation of 17α-ethinyl estradiol. Catal. Today 2023, 413–415, 114026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Zhang, C.; Duan, X.; Sun, H.; Liu, S.; Tade, M.O.; Wang, S. An insight into metal organic framework derived N-doped graphene for the oxidative degradation of persistent contaminants: Formation mechanism and generation of singlet oxygen from peroxymonosulfate. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherifi, Y.; Addad, A.; Vezin, H.; Barras, A.; Ouddane, B.; Chaouchi, A.; Szunerits, S.; Boukherroub, R. PMS activation using reduced graphene oxide under sonication: Efficient metal-free catalytic system for the degradation of rhodamine B, bisphenol A, and tetracycline. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 52, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharie-Butucel, D.; Potara, M.; Craciun, A.M.; Boukherroub, R.; Szunerits, S.; Astilean, S. Revealing the structure and functionality of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide/pyrene carboxylic acid interfaces by correlative spectral and imaging analysis. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 16038–16046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Subrahmanyam, K.S.; Rao, C.N.R. Graphene produced by radiation-induced reduction of graphene oxide. Int. J. Nanosci. 2011, 10, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, G.; Ang, H.M.; Tadé, M.O.; Wang, S. Reduced Graphene Oxide for Catalytic Oxidation of Aqueous Organic Pollutants. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 5466–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Sun, H.; Wang, S. Metal-Free Carbocatalysis in Advanced Oxidation Reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Tan, J.; Pan, G.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Direct conversion of wet sewage sludge to carbon catalyst for sulfamethoxazole degradation through peroxymonosulfate activation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Tong, W.; Li, Y.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wen, Z.; Feng, S.; Wang, X.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; et al. Hydrothermal route-enabled synthesis of sludge-derived carbon with oxygen functional groups for bisphenol A degradation through activation of peroxymonosulfate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.-C.; Jiang, J.; Huang, G.-X.; Yu, H.-Q. Sludge biochar-based catalysts for improved pollutant degradation by activating peroxymonosulfate. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 8978–8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Tian, J.; Yang, F.; Duan, X.; Gao, S.; Shi, W.; Luo, X.; Cui, F.; Luo, S.; Wang, S. Identification and Regulation of Active Sites on Nanodiamonds: Establishing a Highly Efficient Catalytic System for Oxidation of Organic Contaminants. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ao, Z.; Sun, H.; Duan, X.; Wang, S. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by carbonaceous oxygen groups: Experimental and density functional theory calculations. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 198, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, K.; Li, M.; Lu, D.; Meng, X.; Deng, J.; Kong, D.; Ding, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y. Bioinspired Coordination Micelles Integrating High Stability, Triggered Cargo Release, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 2017, 9, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Dai, L.; Huang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Waste baijiu distillers’ grains-derived biochar for efficient removal of organophosphate esters from water through adsorption. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 221, 119402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Duan, X.; Sun, H.; Kang, J.; Zhang, H.; Tade, M.O.; Wang, S. Facile synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene via low-temperature pyrolysis: The effects of precursors and annealing ambience on metal-free catalytic oxidation. Carbon 2017, 115, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Chen, R.; Khan, A.; Zhao, W.; Lin, J.; Hu, R.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, S. Modulating electronic structure of Fe site by adjacent Cu site through orbital coupling in Cu-Fe2O3 catalyst derived from Fenton sludge quenching. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L. Self-assembling TiO2 on aminated graphene based on adsorption and catalysis to treat organic dyes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 539, 147889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Cao, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y. Peroxymonosulfate enhanced visible light photocatalytic degradation bisphenol A by single-atom dispersed Ag mesoporous g-C3N4 hybrid. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 211, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shao, Y.; Gao, N.; Chu, W.; Chen, J.; Lu, X.; Zhu, Y.; An, N. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by Al2O3-based CoFe2O4 for the degradation of sulfachloropyridazine sodium: Kinetics and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 189, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Treatment of bisphenol pollutant in water by N,P-co-doped carbon nanosheet: Fast degradation, toxicity elimination and reaction mechanism investigation. Environ. Pollut 2023, 327, 121586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anipsitakis, G.P.; Dionysiou, D.D. Radical Generation by the Interaction of Transition Metals with Common Oxidants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 3705–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelaki, I.; Voutsa, D. Organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs): A review on analytical methods and occurrence in wastewater and aquatic environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qian, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, J.; Shen, S.; Tang, J.; Ding, Y.; Zhi, S.; Zhang, K.; Yang, L.; et al. Efficient degradation of sulfamethoxazole in various waters with peroxymonosulfate activated by magnetic-modified sludge biochar: Surface-bound radical mechanism. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 319, 121010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Xie, H.B.; Chen, J. Atmospheric chemical reactions of alternatives of polybrominated diphenyl ethers initiated by OH: A case study on triphenyl phosphate. Sci Total Environ. 2016, 571, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, B.; Cao, Q.; Deng, S.; Yu, G. Ozonation of trimethoprim in aqueous solution: Identification of reaction products and their toxicity. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2863–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.-F.; Cao, M.; Xu, D.-Y.; Ren, H.-Y.; Zhao, M.-X.; Huang, Z.-X.; Ruan, W.-Q. Degradation of phenazone in aqueous solution with ozone: Influencing factors and degradation pathways. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Li, X.; Fu, K.; Gu, Z.; Shi, J.; Deng, H. Overlooked role of secondary radicals in the degradation of beta-blockers and toxicity change in UV/chlorine process. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dai, L.; He, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. A novel biomineralization regulation strategy to fabricate schwertmannite/graphene oxide composite for effective light-assisted oxidative degradation of sulfathiazole. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 312, 123314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Gu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, H. Co single-atom confined in N-doped hollow carbon sphere with superb stability for rapid degradation of organic pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).