Abstract
Head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCCs) are often diagnosed at advanced stages, incurring significant high mortality and morbidity. Several microRNAs (miRs) have been identified as pivotal players in the onset and advancement of HNSCCs, operating as either oncogenes or tumor suppressors. Distinctive miR patterns identified in tumor samples, as well as in serum, plasma, or saliva, from patients have significant clinical potential for use in the diagnosis and prognosis of HNSCCs and as potential therapeutic targets. The aim of this study was to identify previous systematic reviews with meta-analysis data and clinical trials that showed the most promising miRs in HNSCCs, enclosing them into a biomolecular signature to test the prognostic value on a cohort of HNSCC patients according to The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). Three electronic databases (PubMed, Scopus, and Science Direct) and one registry (the Cochrane Library) were investigated, and a combination of keywords such as “signature microRNA OR miR” AND “HNSCC OR LSCC OR OSCC OR oral cancer” were searched. In total, 15 systematic literature reviews and 76 prognostic clinical reports were identified for the study design and inclusion process. All survival index data were extracted, and the three miRs (miR-21, miR-155, and miR-375) most investigated and presenting the largest number of patients included in the studies were selected in a molecular biosignature. The difference between high and low tissue expression levels of miR-21, miR-155, and miR-375 for OS had an HR = 1.28, with 95% CI: [0.95, 1.72]. In conclusion, the current evidence suggests that miRNAs have potential prognostic value to serve as screening tools for clinical practice in HNSCC follow-up and treatment. Further large-scale cohort studies focusing on these miRNAs are recommended to verify the clinical utility of these markers individually and/or in combination.
1. Introduction
Among the main tumors of the head and neck region, oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCCs) represent the sixth malignant tumor in global incidence, with about 700,000 thousand new cases each year [1].
The risk factors most associated with the onset of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) are alcohol and the consumption of smoked or chewed tobacco, and for laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC), positivity to HPV subtypes 16 and 18 was considered a risk factor but with a favorable prognosis [2].
Survival at 5 years after diagnosis remains very low, as only one of two patients survives, and surgical resective therapy can be very debilitating, with a worsening of the quality of life, difficulty in swallowing and speech, and in general due to a perceived deterioration in the relationship with other people [3].
The identification of survival prognostic biomarkers remains a very open topic: In fact, the ability to predict a disease by estimating the clinical trend and survival time remains one of the diagnostic and prognostic objectives to be achieved. In recent decades, several prognostic biomarkers have been investigated in an attempt to create a predictive survival biomolecular signature.
Among the widely studied prognostic and diagnostic biomarkers associated with head and neck cancers, we have the non-coding sequences of RNA messenger (mRNA), and among these, microRNAs (miRNA/miRs) [4]. The latter group is a class of mature, non-coding, single-stranded RNAs with 21–23 nucleotides, which were proposed as promising biomarkers for patients with cancer diagnosis and follow-up [3,5].
Some previous systematic literature reviews have tried to identify individual miRs, aggregating the prognostic survival data of multiple studies, obtaining promising results only in some cases for HNSCCs, such as in the cases of miR-31 [6], miR-21 [7], miR-155 [8], and miR-195 [9].
Other studies tried to identify a biomolecular signature by aggregating miRNAs in HNSCC tissue expression, exploring their use as potential biomarkers for cancer detection and/or prognosis [10,11].
This systematic review aims to identify retrospective and prospective clinical studies investigating the prognostic value of miR expression in HNSCC patients, as well as including data from previous systematic reviews with meta-analyses. From these studies, we selected the most promising miRs, inserting them into a biomolecular signature to test the prognostic value on a cohort of HNSCC patients according to the “The Cancer Genome Atlas” (TCGA) [12].
2. Results
2.1. Study Selection
The following research question guided the selection of the studies: Are there biomolecular signatures consisting of non-coding mRNA sequences (especially miRs) in the scientific literature, whose differential expression in HNSCC tumor tissues was indicative of a different prognosis in patient survival?
The research phase was carried out by consulting and extracting the bibliographic references on three databases, SCOPUS (2455), Science Direct (1367), PubMed (2505), and on a Cochrane Library register (5), providing a total of 6332 articles.
Filters were applied on PubMed and Scopus to selectively include literature reviews and meta-analyses, together with clinical studies. Subsequently, the bibliographic references of Scopus and PubMed were reported on EndNote X8, and the duplicates were removed, while further overlapping of the references were manually removed. The articles obtained were selected by reading the abstract and the title; this phase was also performed for Science Direct and the Cochrane Library, and the articles selected from these two sources were added to those chosen from PubMed and Scopus, and thus 117 potentially eligible records were obtained.
A further search of the gray literature (Google Scholar and Open Gray) and previous systematic reviews did not identify additional manuscripts for inclusion in the present systematic review (Figure 1). Records were independently screened by two authors (M.D. and A.B.), while dubious situations were addressed at the end of the selection by involving a third author (F.S.) to resolve potential conflicts.
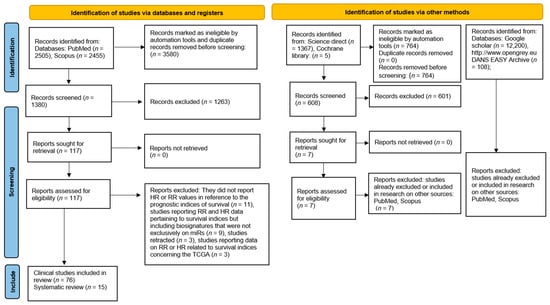
Figure 1.
Flowchart describing the mechanisms of screening miR studies and including several databases and records.
The last update of the literature search was conducted on 13 August 2023.
In total, 76 clinical studies and 15 systematic reviews were included at the end of the inclusion process. We designed our strategy to be optimized for a sensitive and broad search, and the results of this selection are reported in a flowchart (Figure 1).
2.2. Data Characteristics: Systematic Review
The systematic reviews included were the following: Dioguardi et al., 2023 [9]; Dioguardi et al., 2022 [13]; Dioguardi et al., 2022 [14]; Dioguardi et al., 2022 [8]; Dioguardi et. al, 2022 [6]; Dioguardi et al., 2022 [7]; Irimie-Aghiorghiese et al., 2019 [15]; Lubov et al., 2017 [16]; Xie and Wu, 2017 [17]; Wang et al., 2019 [18]; Li et al., 2019 [19]; Qiu et al., 2021 [20]; Huang et al., 2021 [21]; Jamali et al., 2015 [22]; and Troiano et al., 2018 [23]. The selected studies reported the following resulting data: overall survival (OS); disease-free survival (DFS); recurrence-free survival (RFS); cancer-specific survival (CSS); progression-free survival (PFS), and relative risk (RR).
On average, the selected reviews included many studies (≅9.1), with a range from 1 to 36, and the number of included patients ranged from 80 to 1200. Although the systematic review included HNSCCs, two reviews involved only OSCCs, and one study only covered LSCCs. The most reviewed prognostic index was the HR of OS (across different miR tissue expression levels), with thirteen reviews, followed by DFS (six studies), RFS (three studies), CSS (two studies), and PFS (one study). Only one review evaluated the RR of OS.
The miRs subjected to meta-analyses in the 15 systematic reviews were 64 (miR-205, miR-429, miR-21, miR-331-3p, miR-200a, miR-19a, miR-151a, miR-17, miR-18b, miR-324, miR-96, miR-29c, miR-200b, miR-375, miRNA-204, miR−200c, miR-130a, miR-15b, miR-203, miR-195, miR-300, miR-146, miR-155, miR-16-2, miR-10a, miR-100, miR-101, miR-34c, miR-125, miR-149, miR-145, miR-181a, let-7a, miR-494, miR-720, miR-675, miR-137, miR-31, miR-9, miR-424, miR-23a, miR-196b, let-7g, miR-210, miR-20a, miR-126, miR-205, miR-134a, let-7b, miR-153, miR-18a, miR-17a, miR-451, miR-193b, miR-455, miR-372, miR-373, miR29b, miR-1246, miR-196a, miR-181, miR-32, miR-16, and miR-125b).
The microRNAs most reviewed and included in the signatures were miR-21 (in eight revisions including four as a single miR), miR-155 (four times, three of which were within a signature with multiple miRs), and miR-375 (two within a signature). In particular, miR-21 was the most studied and (taken individually) presented an HR of OS ranging from 1.29 [7] to 1.81 [16].
All extracted data are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Main data sources extracted from systematic reviews: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI); The Reporting Recommendations for Tumor Marker Prognostic Studies (REMARK); Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 (QUADAS-2); Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE); The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS); tongue squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC); oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC); oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC); CI (confidence interval); The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA);\ data not reported; overall survival (OS); disease-free survival (DFS); recurrence-free survival (RFS); cancer-specific survival (CSS); progression-free survival (PFS); relative risk (RR).
2.3. Data Characteristics: Clinical study
The clinical studies included in the review were 76: Jung et al., 2012 [24]; Kawakita et al., 2014 [25]; Hedbäck et al., 2014 [26]; Yu et al., 2017 [27]; Supic et al., 2018 [28]; Jakob et al., 2019 [29]; Li et al., 2013 [30]; Zheng et al., 2016 [31]; Li et al., 2009 [32]; Ganci et al., 2016 [33]; Wang et al., 2018 [34]; Qiang et al., 2019 [35]; Tu et al., 2021 [36]; Hess et al., 2017 [37]; Zhao et al., 2018 [38]; Baba et al., 2016 [39]; Shi et al., 2015 [40]; Kim et al., 2018 [41]; Bersani et al., 2018 [42]; Wu et al., 2020 [43]; Shuang et al., 2017 [44]; Ding and Qi, 2019 [45]; Jia et al., 2013 [46]; Qin et al., 2019 [47]; Liu et al., 2013 [48]; Maruyama et al., 2018 [49]; Zhao et al., 2018 [50]; Luo et al., 2019 [51]; Ahn et al., 2017 [52]; Hudcova et al., 2016 [53]; Kang et al., 2021 [54]; Bonnin et al., 2016 [55]; Ganci et al., 2013 [56]; Harris et al., 2012 [57]; Ahmad et al., 2019 [58]; Rajthala et al., 2021 [59]; Song et al., 2020 [60]; Zhao et al., 2018 [61]; Li et al., 2013 [62]; de Jong et al., 2015 [63]; Fang et al., 2019 [64]; He et al., 2017 [65]; Re et al., 2015 [66]; Xu et al., 2016 [67]; Tian et al., 2014 [68]; Zhao et al., 2018 [69]; Guan et al., 2016 [70]; Avissar et al., 2009 [71]; Wu et al., 2014 [72]; Wu, Zhang et al., 2014 [73]; Zhang et al., 2015 [74]; Hu et al., 2015 [75]; Re et al., 2017 [76]; Shen et al., 2012 [77]; Maia et al., 2017 [78]; Ogawa et al., 2012 [79]; Pantazis et al., 2020 [80]; Childs et al., 2009 [81]; Ko et al., 2014 [82]; Arantes et al., 2017 [83]; Chang et al., 2013 [84]; Gee et al., 2010 [85]; Jia et al., 2014 [86]; Liao et al., 2013 [87]; Liu et al., 2013 [88]; Liu, Shen et al., 2013 [89]; Luo et al., 2014 [90]; Peng et al., 2014 [91]; Sasahira et al., 2012 [92]; Tu et al., 2015 [93]; Wu et al., 2014 [94]; Xu et al., 2013 [95]; Zhang et al., 2017 [96]; Jia et al., 2015 [97]; Hu et al., 2014 [98]; and Gu et al., 2018 [99].
The total number of included patients affected by HNSCCs was 6848, with 3295 cases definitely identified as OSCCs and at least 1493 presenting a localization to the tongue, while LSCC was present in 2179 patients.
The most used prognostic indices were OS in 51 studies, DFS in 27 studies, RFS in 12 studies, and CSS in 6 studies. For risk factors, only 13 studies investigated HPV positivity, and 31 studies investigated t-7d, Let-7g, miR-9, miR-15b, miR-17, miR-18a, miR-18b, miR-19, miR-19a, miR-20b, miR-20a, miR-21, miR-22, miR-23a, miR-26a, miR-29b, miR-29c, miR-31, miR-34c, miR-34a, miR-375, miR-331, miR-324, miR-296, miR-205, miR-203, miR-204, miR-210, miR-1246, miR-675, miR-451, miR-452, miR-429, miR-422a, miR-134, miR-126, miR-300, miR-372, miR-373, miR-218, miR-153, miR-155, miR-181a, miR-183, miR-200c, miR-200b, miR-200c, miR-200a, miR-96 miR-195, miR-196a, miR-196a2, miR-196b, miR-197, miR-198, miR-151a, miR-146a, miR-99a, miR-99b, miR-100, miR-101, miR-141, miR-143, miR-145, miR-149, miR-130b, and miR-139.
Among these, the most studied were miR-21 (19 studies), miR-155 (8 studies), and miR-375 (7 studies).
In miR-21, the HR of OS between high and low expression levels ranged from 5.31 95% CI: [1.39–20.38] [24] to 1.1302 95% CI: [0.34–3.757] [98], and in poor OS, it was upregulated, similar to miR-155, while in miR-375, the HR of OS between low and high expression levels ranged from 12.8 95% CI: [3.4–48.6] [57] to 1.32 95% CI: [0.76–2.27] [53], and in case of low survival, it was downregulated. All data related to the clinical studies, as well as the survival data extrapolated from the Kaplan–Meier survival curves, are extensively reported in Table 2 and Table 3.

Table 2.
Data extracted from the 76 studies included, providing information regarding the type of tumor, the location of the tumor, the number of patients with data concerning the average age, the average or maximum follow-up, gender, and the common risk factors in the patients are reported to be smoking, alcohol, and HPV positivity; TNM (T: tumor size; N: regional lymph nodes; M: distant metastasis); pTNM, pathological TNM staging; cTNM, clinical TNM staging; N/A, not available; Ma (male); Fe (female); R (range); y (years); smoking (Sm); alcohol (Alc); SEM (standard error mean); PS (prospective study); RT (retrospective study); HPSCC (hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma); OTSCC (oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma); BOTSCC (base of tongue squamous cell carcinoma); NPC (nasopharyngeal carcinoma). Data are not reported in a clear and explicit manner;\ data not present.

Table 3.
The values of HR (95% confidence interval) and RR for the different prognostic indices of survival are shown in the table; overall survival (OS); disease-free survival (DFS); recurrence-free survival (RFS); cancer-specific survival (CSS); progression-free survival (PFS); relative risk (RR); high versus low expression (H-L); low versus high expression (L-H); infinite (inf).
Analyzing the studies and the systematic reviews performed on the prognostic biomarkers of survival, it becomes clearly evident that the miR that has been most investigated and provides the greatest number of data is miR-21, with 19 clinical studies, followed by miR-155 (8 studies) and miR-375 (7 studies). The other miRs have fewer studies with fewer patients included than miR-21 (1262 patients), miR-155 (706 patients), and miR-375 (572 patients).
For this reason, we decided to use a different cohort (TCGA), which includes about 512 patients, to verify whether a biosignature with a high expression of these three miRs in tumor tissues was correlated with low survival, and significant results were obtained for miR-21 and miR-155, while for miR-375, low survival was associated with low expression.
Using the extracted data shown in Table 1 and Table 2, the three main miRs investigated in the literature (miR-21, miR-155, and miR-375), whose altered expression was investigated in the prognosis of survival in HNSCC patients and included in molecular biosignatures, were then selected. The evaluation was performed through the Kaplan–Meier plotter database portal (https://kmplot.com/analysis/, accessed on 10 May 2023) [100], and HR data were extracted.
The difference between high and low tissue expression levels of the miRs taken into consideration presents an HR of OS = 1.28 95% CI: [0.95, 1.72], log-rank p = 0.1. Moreover, the Kaplan–Meier survival curve generated using the portal is depicted in Figure 2, and the considered follow-up period was 60 months. The median survival in the cohort of patients with low expression was 58.73, while that in patients with high expression was 46.47.
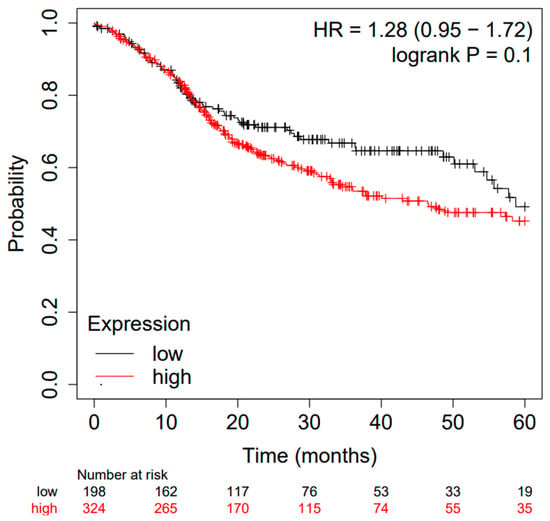
Figure 2.
Kaplan–Meier curve based on miR-21, miR-155, and miR-375 expression levels for overall survival (OS) of patients with HNSCC (TCGA cohort); false discovery rate (FDR): 100%. Kaplan–Meier curves created from a public database and Kaplan–Meier plotter web application (http://kmplot.com/analysis/, accessed on 10 May 2023).
The cut-off value between high and low miR expression levels was automatically generated through the portal (Figure 3), and the cut-off values and the related p-values are present in the the Supplementary Materials (S1).
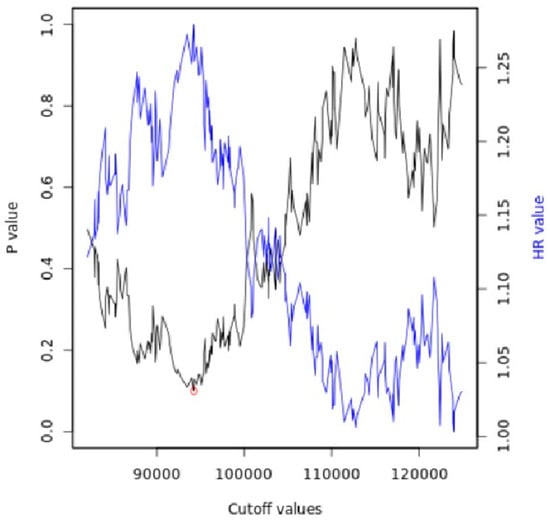
Figure 3.
Automatically generated cut-off plot using the Kaplan–Meier plotter web application, http://kmplot.com/analysis/, accessed on 10 May 2023. Significance vs. cut-off values between the lower and upper quartiles of expression are presented, with the red circle indicating the best cut-off.
The portal to generate and display the Kaplan–Meier plot is used to establish a cut-off value and assign samples to one of the two cohorts, using the best available cut-off value.
To find the best cut-off, the process is repeated using the values of the input variables from the lowest quartile to the upper quartile, and the Cox regression for each setting is calculated [101].
The most significant cut-off value was employed as the optimal threshold to segregate the input data into two groups. Subsequently, the system presents a straightforward visual representation of this analysis, displaying the p-values obtained concerning the selected cut-off values.
In cases where the generated cut-off values were ambiguous (e.g., multiple cut-off values resulted in very low p-values), the value corresponding to the highest hazard ratio was selected.
The calculation of multiple cut-off values led to the generation of multiple assumptions.
Hence, in this setup, the FDR was automatically computed using the Benjamini–Hochberg method to correct for multiple hypothesis testing [102].
Spearman’s correlation and Pearson’s correlation between the expression values of the different miRs investigated (Table 4 and Table 5) were also calculated.

Table 4.
Spearman’s correlations.

Table 5.
Pearson’s correlations among different microRNAs.
All reported data can be reproduced via the Kaplan–Meier plotter portal [101].
Furthermore, additional tests were performed on miR-21, and for the main downregulated miRs described in the literature, the extrapolated data are described in Figure 4.
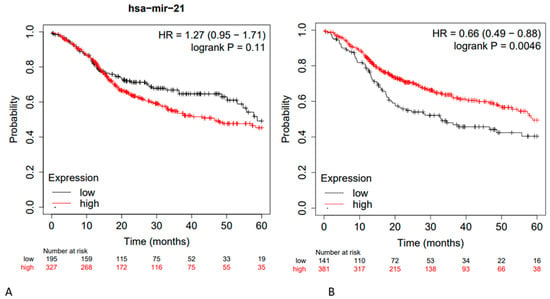
Figure 4.
(A) Kaplan–Meier curve based on miR-21 expression levels for overall survival (OS) of patients with HNSCC (TCGA cohort) FDR: 100%; (B) Kaplan–Meier curve based on hsa-miR-153 (-), hsa-miR-200c (-), hsa-miR-363 (-), hsa-miR-17 (-), hsa-miR-205 (-), hsa-Let-7d (-), hsa-Let -7g (-), hsa-miR-34a (-), hsa-miR-375 (-), hsa-miR-491 (-), hsa-miR-218 (-), and hsa-miR-125b (-); OS HR = 0.66 95% CI: [0.46–0.88]; FDR: over 50%; Kaplan–Meier curves created from public database and Kaplan–Meier plotter web application (http://kmplot.com/analysis/, accessed on 10 May 2023).
Furthermore, the main results related to the resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy administered to patients, in support of resective surgical treatment and in relation to the altered expression of microRNAs, were extracted from the studies, as shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
Data on resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy in relation to altered expression of microRNAs.
2.4. Risk of Bias
The risk of bias for systematic reviews was determined using the ROBIS tool, and for each factor, it was evaluated as “low”, “high”, or “unclear”. The three phases of the evaluation process were as follows: Phase 1: the evaluation of the relevance of the research question (PICO); Phase 2: the identification of critical points of the review process; and Phase 3: the evaluation of the overall risk of bias of the review. All data related to the risk of bias are reported in Table 7.

Table 7.
Risk of bias, ROBIS scale: ok (low); ? (unclear).
The main critical issues related to the individual revisions are as follows:
- ➢
- Irimie-Aghiorghiese et al., 2019 [15]: Study eligibility criteria (?): The protocol number with which the systematic review was registered was not reported. Identification and selection of studies (?): The selection was performed only on two databases (PubMed and Embase), and the number of authors who conducted the research was not specified, nor were the start or end dates in which the review was conducted.
- ➢
- Lubov et al., 2017 [16]: Study eligibility criteria (?): The protocol number with which the systematic review was registered was not reported. Identification and selection of studies (?): The number of authors who selected the articles and the start or end dates of the review were not reported. Data collection and study appraisal (?): The number of authors who performed the data extraction and the methods of data extraction were not stated. The manuscript is both a systematic review and a retrospective study of 100 patients.
- ➢
- Xie and Wu, 2017 [17]: Study eligibility criteria (?): The protocol number with which the systematic review was registered was not reported.
- ➢
- Wang et al., 2019 [18]: Study eligibility criteria (?): The protocol number with which the systematic review was registered was not reported.
- ➢
- Li et al., 2019 [19]: Study eligibility criteria (?): The protocol number with which the systematic review was registered was not reported. Identification and selection of studies (?): The start or end dates of the review were not specified. Data collection and study appraisal (?): The risk of bias was not formally assessed using an appropriate scale or tool. A bioinformatic analysis was also performed.
- ➢
- Huang et al., 2021 [21]: Study eligibility criteria (?): The protocol number with which the systematic review was registered was not reported. Identification and selection of studies (?): The start and end dates of the review were not specified.
- ➢
- Jamali et al., 2015 [22]: Study eligibility criteria (?): The protocol number with which the systematic review was registered was not reported.
- ➢
- Troiano et al., 2018 [23]: Study eligibility criteria (?): The protocol number with which the systematic review was registered was not reported.
- ➢
- Dioguardi et al., 2023 [9]: Synthesis and findings (?): The obtained results were excessively emphasized in the conclusions.
The risk of bias for prognostic studies was assessed using the parameters derived from REMARK. According to the REMARK guidelines, a score ranging from 0 to 3 was considered for each factor (Table 8).

Table 8.
Assessment of the risk of bias; REMARK.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Protocol
The planning of the systematic review was implemented following the guidelines described in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. The drafting of the review manuscript followed the recommendations of PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis) [103], and the protocol was registered on PROSPERO before carrying out the selection of articles and was registered with the registration number CRD42023400856.
3.2. Eligibility Criteria
The search was directed towards the identification of retrospective or prospective clinical studies and bibliographic sources that reported systematic reviews of the literature regarding the role of non-coding RNAs and in particular of miRs, reporting prognostic data of survival in patients with HNSCCs associated with altered expression of a single miR or a signature of miR.
The exclusion criteria were the exclusion of all clinical trials and systematic reviews reporting no data on the use or detection of a molecular biosignature consisting of miRs in HNSCCs, all literature reviews (considered as bibliographic sources only), and studies that did not have an abstract in English.
Thus, the reporting data of all clinical trials and meta-analyses on a biomolecular signature consisting of miRs that is prognostic of survival in HNSCCs were considered potentially eligible.
The systematic review involved two reviewers (M.D. and A.B.) and followed the following stages:
- Choice of reviewers (M.D. and A.B.) and a third reviewer (F.S.) as a supervisor in case of conflict regarding the studies to be included, choice of outcomes to identify, choice of databases and k words used, choice of criteria of admissibility, choice of data to be extracted and methods of synthesis and registration of the protocol on PROSPERO;
- Identification of records and selection of studies through databases with the removal of duplicates performed manually or by software (EndNote 8.0), performed independently and subsequently comparison of selected studies and decision of studies to be included;
- Independently performed table data extraction and subsequent data comparison to minimize the risk of error in reporting information.
3.3. Sources of Information, Research, and Selection
The keywords used were microRNA AND HNSCC, LSCC AND MicroRna, OSCC AND MicroRna, and signature microRNA AND HNSCC.
The search was conducted on 3 databases, namely Science Direct, SCOPUS, and PubMed, and one registry, the Cochrane Library. Additionally, Google Scholar (keywords microRNA), gray literature sources such as Open Gray (keywords microRNA), and references from previous systematic reviews on miRs and HNSCCs were searched.
Particularly, the following are all the keywords used in the PubMed search:
Search: (signature microRNA OR miR) AND (HNSCC OR LSCC OR OSCC OR oral cancer) Sort by: Most Recent.
(((“protein domains”[MeSH Terms] OR (“protein”[All Fields] AND “domains”[All Fields]) OR “protein domains”[All Fields] OR “signature”[All Fields] OR “signatures”[All Fields]) AND (“microrna s”[All Fields] OR “micrornas”[MeSH Terms] OR “micrornas”[All Fields] OR “microrna”[All Fields])) OR (“med int rev”[Journal] OR “manag int rev”[Journal] OR “mir”[All Fields])) AND (“hnsccs”[All Fields] OR “squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck”[MeSH Terms] OR (“squamous”[All Fields] AND “cell”[All Fields] AND “carcinoma”[All Fields] AND “head”[All Fields] AND “neck”[All Fields]) OR “squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck”[All Fields] OR “hnscc”[All Fields] OR “LSCC”[All Fields] OR “OSCC”[All Fields] OR (“mouth neoplasms”[MeSH Terms] OR (“mouth”[All Fields] AND “neoplasms”[All Fields]) OR “mouth neoplasms”[All Fields] OR (“oral”[All Fields] AND “cancer”[All Fields]) OR “oral cancer”[All Fields])).
Translations
Signature: “protein domains”[MeSH Terms] OR (“protein”[All Fields] AND “domains”[All Fields]) OR “protein domains”[All Fields] OR “signature”[All Fields] OR “signatures”[All Fields].
microRNA: “microrna’s”[All Fields] OR “micrornas”[MeSH Terms] OR “micrornas”[All Fields] OR “microrna”[All Fields].
miR: “Med Int Rev”[Journal:__jid0017632] OR “Manag Int Rev”[Journal:__jid101593556] OR “mir”[All Fields].
HNSCC: “hnsccs”[All Fields] OR “squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck”[MeSH Terms] OR (“squamous”[All Fields] AND “cell”[All Fields] AND “carcinoma”[All Fields] AND “head”[All Fields] AND “neck”[All Fields]) OR “squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck”[All Fields] OR “hnscc”[All Fields].
Oral cancer: “mouth neoplasms”[MeSH Terms] OR (“mouth”[All Fields] AND “neoplasms”[All Fields]) OR “mouth neoplasms”[All Fields] OR (“oral”[All Fields] AND “cancer”[All Fields]) OR “oral cancer”[All Fields].
The literature search was completed on 20 February 2023.
The data to be extracted included the first author of the study, the publication date, the country in which the research was conducted, the type of squamous cell carcinoma, the number of patients involved in the study, the clinical characteristics of the patients and tumors included in the studies, data on the positivity to the HPV virus and exposure to risk factors such as smoking and alcohol, as well as clinical data on the staging of patients included in the studies and on the average or maximum follow-up, risk of bias tools, the studied miRs, the value or type of risk rate (RR) or hazard rate (HR) for various prognostic survival indices: overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS), progression-free survival (PFS), relapse-free survival (RFS), and cancer-specific survival (CSS).
3.4. Risk of Bias, Bioinformatic Analysis
Furthermore, the data of a cohort of patients with HNSCCs (N ≈ 512) extracted from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database were analyzed to obtain the HR values and associate the prognosis indices with the expression of the signature of miRs created and selected by the authors.
The risk of bias in the individual systematic reviews was assessed by two authors (M.D. and A.B.). The ROBIS (Risk of Bias in Systematic Reviews) was used as an assessment tool specifically developed to assess the risk of bias in systematic reviews. Studies with a high risk of bias were excluded from the review [104].
Clinical studies with the risk of bias were evaluated by two authors (M.D. and A.B.), and the tool used for the assessment of the parameters was derived from the reporting recommendations for prognostic studies of markers (REMARK). Studies with a high risk of bias were excluded from the analysis [105].
4. Discussion
In the last 40 years, a considerable number of new cancer biomarkers have been identified, but only a few have managed to be effectively used in clinical practice.
Many biomarkers pass validation very well, with concordant and reproducible results across trials; nevertheless, these biomarkers lack the capacity to decisively contribute to patient care, except to provide some additional information on prognosis. Therefore, they are considered by clinicians to be not fundamental in the therapeutic choice.
Physicians often show a tendency to overtreat specific patients, rather than relying on prognostic biomarkers that offer less than precise predictions. Using these flawed prognostic biomarkers could result in fewer patients receiving overly aggressive treatments (true positives) but, at the same time, could also increase the chance of not treating some patients who may actually benefit from therapy (false negatives). Therefore, from a clinical point of view, with the exclusion of fraudulent situations and sensationalist discoveries, the prognostic biomarkers detected are not so promising, and their failure is due to their inadequate performance in clinical practice.
Hence, in the process of transitioning a promising biomarker from Phase 1 studies to clinical implementation, meticulous consideration should be given to the study’s design, aiming to mitigate bias in the utilization of sensitive, specific, and precise analytical methodologies. This involves the careful selection of suitable samples, both in terms of quantity and quality, as well as appropriate patient subgroups for the purpose of validation. Furthermore, it is imperative to apply statistically robust and rigorous methods to prevent the occurrence of data overfitting.
The data present in the literature demonstrate how miRs are stable, and the results deriving from the studies are consistent and reproducible, making miRs potential promising biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis [106].
Prognostic biomarkers including miRs could have a significant impact in helping clinicians improve the quality of life and health conditions of HNSCC patients, providing useful information for oncologists in terms of the most appropriate therapeutic choice, according to life expectancy and neoplasm aggressiveness [107].
Knowledge of the prognostic potential of biosignatures could be useful for clinicians after the diagnosis of HNSCCs to define prognosis by formulating predictive models of individualized prognostic risk. Bringing this model back into clinical practice in patients with HNSCCs who have unfavorable prognostic biosignatures (with low RFS or OS), a more or less aggressive therapy or surgical treatment could be recommended, with a tailored therapeutic approach in the context of personalized medicine [108].
The discovery of the miRs’ prognostic value presents critical insights with potential biases that must be taken into consideration before, during, and after the execution of retrospective studies or clinical trials, but also during the data meta-analysis. The choice of variables can significantly affect the results as well as the overall validity of the analysis.
Factors such as sample size, the heterogeneity of patient populations, virus positivity (HPV and EBV), and the choice of statistical analysis can affect the results.
In the context of HNSCCs, taking, for instance, HPV positivity as a variable, the role of papillomavirus as a risk factor in a subset of head and neck cancers [109], mainly oropharyngeal and laryngeal cancers, has been established, with different epidemiological, clinical, and molecular characteristics compared with HNSCCs, starting with HPV positivity, which was associated with distinctly different and more favorable prognostic survival values [110].
Therefore, the inclusion or exclusion of some clinical variables (smoking, alcohol, age, and gender) may alter the results of prognostic values for the associations observed between miR signatures, including the related survival results [111].
The meta-analysis size of the sample can also be addressed by performing a trial sequential analysis (TSA) to verify the power of the results as a function of the sample, with an effect achieved in terms of RR [112].
In addition, some laboratory study phases can be biased, making the detection of biomolecular signatures in biological samples difficult. In fact, possible biases can be identified in the sample selection (e.g., fresh tissue, fixed tissue, and biological fluids), RNA extraction, and sample quality control. In addition, miR profiling can also be affected by variability in the technical platform (instruments and software), which is an important source of bias that affects not least the data analysis [113].
In addition, the results of tissue miR expression seem to be influenced by the tissue preservation technique (frozen or in formalin); in fact, to reduce the heterogeneity of the data, it is recommended to aggregate data during a meta-analysis by conducting a subgroup analysis also based on the category of tissue preservation [114].
The difficulty in determining the prognostic value of miRs is due to the complexity of biological systems and the multiple roles of miRs in the regulation of gene expression. It is important to remember that microRNA expression patterns can vary between different cancer types, and even within subtypes of the same cancer, making it difficult to establish universal prognostic markers [113].
Furthermore, many miR biosignatures are currently being developed using algorithms and machine learning based on the search for associations between expression and disease outcomes. Therefore, causality is often not considered, and algorithms can generate signatures that are not biologically expressive, despite their statistical significance [115].
In this context, the execution of systematic reviews with the inclusion of Phase 2 prognostic studies can lead to improvement in these studies by better highlighting the most reliable and predictable results while not overlooking data without statistical significance or evidence (publication bias). The present systematic review aims to refine the design, execution, and reporting of Phase 2 studies [116,117] and provide useful knowledge in guiding Phase 3 clinical studies aimed toward finding a prognostic model [118].
Jamail et al. indicated that the over- or underexpression of some miRs was related to the survival of patients with HNSCCs, reporting that the elevated expressions of miR-21, miR-18a, miR-134a, miR-210, miR-181a, miR-19a, and miR-155 were associated with a reduction in the survival of patients with HNSCCs, while the decreased expression of miR-153, miR-200c, miR-363, miR-203, miR-17, miR-205, miR-Let-7d, Let-7g, miR-34a, miR-126a, miR-375, miR-491-p5, miR-218, miR-451, and miR-125b was associated with a poor survival prognosis [22].
These results agree with the findings of Huang et al. (2021) [21], who provide evidence in their review of LSCC suggesting that miRNA-100, miR155, miR-21, miR-34a, miR-195, and miR-let-7 are potential tumor biomarkers.
In light of the data reported in the medical literature, and from the preliminary research conducted in the field [6,7,8,9,13,14,119], we carried out our review after registering it on Prospero, which was written following the indications of PRISMA. A meta-analysis of the data was not carried out due to the excessive heterogeneity of data and histological subtypes of HNSCCs, and thus a TCGA analysis was instead used to test possible microRNA biosignatures that emerged from the data extraction and qualitative analysis of the studies.
In this systematic review, we identified 64 miRs from 15 systematic reviews, whose altered expression was correlated with prognostic indices. The miRs mainly investigated were miR-21, miR-155, and miR-375. HR values for OS in miR-21 ranged from 1.29 to 1.72, and these values were 1.59 for miR 375 and 1.40 for miR-155 (considering only the results of meta-analyses reporting HR values aggregated for individual miRs); the HR values for several miR panels ranged from 2.65 to 1.10 (Table 1).
By selecting the three miRs that, based on our research, were the most investigated in HNSCCs, and performing a survival analysis using these three miRs on the patient cohorts present in the TCGA, an HR of OS equal to 1.28 was found. From these preliminary data, it is evident that the existing results in the literature are still insufficient to clearly define a prognostic microRNA biosignature, and the retrospective statistical analyses performed using the TCGA in an attempt to further validate the findings do not fully achieve this purpose. In fact, by considering only miR-21, three meta-analyses report an aggregate HR value of about 1.7 as the difference between high and low expression levels, while using the TGCA, considering a follow-up period of 60 months, miR-21 presented an HR (high and low expression) equal to 1.27 95% CI: [0.95, 1.71] (Figure 4). Considering instead the HR data of miR-21, miR-155, and miR-375 using the TCGA and combining them in a single prognostic signature, the value of HR was 1.28 95% CI: [0.95, 1.72].
The performance of miRs is more or less superimposable if we consider the miRs that are reportedly downregulated in the literature during HNSCCs; for instance, Jamali et al. (2015) [22] and Wang et al. (2019) [18] revealed that hsa-miR-153 (-), hsa-miR-200c (-), hsa-miR-363 (-), hsa-miR-17 (-), hsa-miR-205 (-), hsa-Let-7d (-), hsa-Let -7g (-), hsa-miR-34a (-), hsa-miR-375 (-), hsa-miR-491 (-), hsa-miR-218 (-), hsa-miR-125b (-), and hsa-mir-375 (-) were downregulated, with an HR = 0.66 95% CI: [0.46–0.88] (Figure 4). Considering the HR between low and high expression levels, an HR of 1.51 was observed. These results are largely reproducible using the Kaplan–Meier portal except for subsequent updates of the latter.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we can state that although prognostic survival biomarkers have been identified that possess a discrete potential consisting of a miR signature, in the current state of knowledge for head and neck tumors, there are no studies that fully validate the results. Nevertheless, it is crucial to emphasize that additional validation is necessary before we can definitively establish their practicality. While some miRNA studies have revealed noteworthy findings related to their influence on patient survival, the limited number of studies that have been agregaded to derive these results diminishes their relevance in clinical contexts. Hence, there is a clear need for more extensive and long-term patient studies that specifically investigate these miRs.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ncrna9050054/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.D., A.Q.N. and G.T.; methodology, M.D., G.I. and A.B.; software, F.S., M.D. and D.S.; validation, F.S., M.D. and A.B.; formal analysis, M.D.; investigation, M.D. and G.A.C.; data curation, M.D. and G.I.; bibliographic arch research, G.I. and A.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.D. and A.B.; writing—review and editing, M.D. and A.B.; visualization, L.L.M., M.D. and E.L.; supervision, L.L., L.L.M., G.T. and M.D.; critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content, M.D., E.L. and A.B.; project administration, M.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received REFIN (Research for Innovation) funding: Title project: Analysis of Non-Coding RNA as Biomarkers in Patients with Squamous Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity; Project Code: (UNIFG222–CUP D74I19003340002).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marur, S.; D’Souza, G.; Westra, W.H.; Forastiere, A.A. HPV-associated head and neck cancer: A virus-related cancer epidemic. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringash, J. Survivorship and Quality of Life in Head and Neck Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3322–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, K.; Wu, J.; Lee, B.W.; Farah, C.S. MicroRNAs in Head and Neck Cancer. Int. J. Dent. 2013, 2013, 650218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashooa, R.K.; Nabi, A.Q. The miR-146a-5p and miR-125b-5p levels as biomarkers for early prediction of Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Gene 2022, 34, 201129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; Spirito, F.; Sovereto, D.; Alovisi, M.; Aiuto, R.; Garcovich, D.; Crincoli, V.; Laino, L.; Cazzolla, A.P.; Caloro, G.A.; et al. The Prognostic Role of miR-31 in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis with Trial Sequential Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; Spirito, F.; Sovereto, D.; Alovisi, M.; Troiano, G.; Aiuto, R.; Garcovich, D.; Crincoli, V.; Laino, L.; Cazzolla, A.P.; et al. MicroRNA-21 Expression as a Prognostic Biomarker in Oral Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; Spirito, F.; Sovereto, D.; La Femina, L.; Campobasso, A.; Cazzolla, A.P.; Di Cosola, M.; Zhurakivska, K.; Cantore, S.; Ballini, A.; et al. Biological Prognostic Value of miR-155 for Survival Outcome in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas: Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis. Biology 2022, 11, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; Spirito, F.; Caloro, G.A.; Lo Muzio, L.; Cantore, S.; Ballini, A.; Scacco, S.; Malcangi, A.; Sembronio, S.; Cascardi, E.; et al. Is the Non-Coding RNA miR-195 a Biodynamic Marker in the Pathogenesis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma? A Prognostic Meta-Analysis. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subha, S.T.; Chin, J.W.; Cheah, Y.K.; Mohtarrudin, N.; Saidi, H.I. Multiple microRNA signature panel as promising potential for diagnosis and prognosis of head and neck cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Jia, Y.; Yang, B. Identification of a novel necroptosis-associated miRNA signature for predicting the prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Open Med. 2022, 17, 1682–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomczak, K.; Czerwińska, P.; Wiznerowicz, M. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): An immeasurable source of knowledge. Contemp. Oncol. 2015, 19, A68–A77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dioguardi, M.; Cantore, S.; Sovereto, D.; La Femina, L.; Spirito, F.; Caloro, G.A.; Caroprese, M.; Maci, M.; Scacco, S.; Lo Muzio, L.; et al. Does miR-197 Represent a Valid Prognostic Biomarker in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC)? A Systematic Review and Trial Sequential Analysis. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dioguardi, M.; Cantore, S.; Sovereto, D.; La Femina, L.; Caloro, G.A.; Spirito, F.; Scacco, S.; Di Cosola, M.; Lo Muzio, L.; Troiano, G.; et al. Potential Role of miR-196a and miR-196b as Prognostic Biomarkers of Survival in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis. Life 2022, 12, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimie-Aghiorghiesei, A.I.; Pop-Bica, C.; Pintea, S.; Braicu, C.; Cojocneanu, R.; Zimța, A.-A.; Gulei, D.; Slabý, O.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Prognostic Value of MiR-21: An Updated Meta-Analysis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC). J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubov, J.; Maschietto, M.; Ibrahim, I.; Mlynarek, A.; Hier, M.; Kowalski, L.P.; Alaoui-Jamali, M.A.; da Silva, S.D. Meta-analysis of microRNAs expression in head and neck cancer: Uncovering association with outcome and mechanisms. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 55511–55524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wu, J. MicroRNA-21 as prognostic molecular signatures in oral cancer: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 10, 9848–9856. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Xu, L.; Li, L.; Ren, S.; Tang, J.; Zhang, M.; Xu, M. The microRNA-375 as a potentially promising biomarker to predict the prognosis of patients with head and neck or esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 276, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-w.; Gao, L.; Dang, Y.-w.; Li, P.; Li, Z.-y.; Chen, G.; Luo, D.-z. Protective potential of miR-146a-5p and its underlying molecular mechanism in diverse cancers: A comprehensive meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.; Song, Y.; Rao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, D.; Pang, W.; Ren, J.; Zhao, Y. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of MicroRNAs in Metastasis and Recurrence of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 711171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Gu, M.; Tang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Luo, J.; Li, Z. Systematic review and meta-analysis of prognostic microRNA biomarkers for survival outcome in laryngeal squamous cell cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamali, Z.; Asl Aminabadi, N.; Attaran, R.; Pournagiazar, F.; Ghertasi Oskouei, S.; Ahmadpour, F. MicroRNAs as prognostic molecular signatures in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Oncol. 2015, 51, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troiano, G.; Mastrangelo, F.; Caponio, V.C.A.; Laino, L.; Cirillo, N.; Lo Muzio, L. Predictive Prognostic Value of Tissue-Based MicroRNA Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.M.; Phillips, B.L.; Patel, R.S.; Cohen, D.M.; Jakymiw, A.; Kong, W.W.; Cheng, J.Q.; Chan, E.K.L. Keratinization-associated miR-7 and miR-21 regulate tumor suppressor reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs (RECK) in oral cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 29261–29272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakita, A.; Yanamoto, S.; Yamada, S.; Naruse, T.; Takahashi, H.; Kawasaki, G.; Umeda, M. MicroRNA-21 promotes oral cancer invasion via the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway by targeting DKK2. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2014, 20, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedbäck, N.; Jensen, D.H.; Specht, L.; Fiehn, A.M.K.; Therkildsen, M.H.; Friis-Hansen, L.; Dabelsteen, E.; Von Buchwald, C. miR-21 expression in the tumor stroma of oral squamous cell carcinoma: An independent biomarker of disease free survival. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.H.; Tu, H.F.; Wu, C.H.; Yang, C.C.; Chang, K.W. MicroRNA-21 promotes perineural invasion and impacts survival in patients with oral carcinoma. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2017, 80, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supic, G.; Zeljic, K.; Rankov, A.D.; Kozomara, R.; Nikolic, A.; Radojkovic, D.; Magic, Z. miR-183 and miR-21 expression as biomarkers of progression and survival in tongue carcinoma patients. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2018, 22, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, M.; Mattes, L.M.; Küffer, S.; Unger, K.; Hess, J.; Bertlich, M.; Haubner, F.; Ihler, F.; Canis, M.; Weiss, B.G.; et al. MicroRNA expression patterns in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Hsa-mir-99b-3p and hsa-mir-100-5p as novel prognostic markers for oral cancer. Head Neck 2019, 41, 3499–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L. Abnormal expression of STAT3 and miRNA-21 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Chin. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 40, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Li, N.; Jia, X.; Peng, C.; Luo, L.; Deng, Y.; Yin, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, H.; Lu, M.; et al. MYCN-mediated miR-21 overexpression enhances chemo-resistance via targeting CADM1 in tongue cancer. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, H.; Sun, L.; Yang, M.; Pan, C.; Chen, W.; Wu, D.; Lin, Z.; Zeng, C.; Yao, Y.; et al. MiR-21 indicates poor prognosis in tongue squamous cell carcinomas as an apoptosis inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3998–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganci, F.; Sacconi, A.; Manciocco, V.; Sperduti, I.; Battaglia, P.; Covello, R.; Muti, P.; Strano, S.; Spriano, G.; Fontemaggi, G.; et al. MicroRNA expression as predictor of local recurrence risk in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2016, 38 (Suppl. 1), E189–E197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-L.; Li, H.-X.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Su, Y.-L.; Lian, J.-S.; Li, T.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.-N.; Jin, N.; Liu, X.-F. MiR-31 is a potential biomarker for diagnosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 4339–4345. [Google Scholar]
- Qiang, H.; Zhan, X.; Wang, W.; Cheng, Z.; Ma, S.; Jiang, C. A Study on the Correlations of the miR-31 Expression with the Pathogenesis and Prognosis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2019, 34, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.-F.; Liu, C.-J.; Hung, W.-W.; Shieh, T.-M. Co-upregulation of miR-31 and its host gene lncRNA MIR31HG in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Dent. Sci. 2022, 17, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, A.K.; Müer, A.; Mairinger, F.D.; Weichert, W.; Stenzinger, A.; Hummel, M.; Budach, V.; Tinhofer, I. MiR-200b and miR-155 as predictive biomarkers for the efficacy of chemoradiation in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 77, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; Ji, W. YB-1 promotes laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma progression by inducing miR-155 expression via c-Myb. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, O.; Hasegawa, S.; Nagai, H.; Uchida, F.; Yamatoji, M.; Kanno, N.I.; Yamagata, K.; Sakai, S.; Yanagawa, T.; Bukawa, H. MicroRNA-155-5p is associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis and poor prognosis. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2016, 45, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.-J.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Zhou, Z.-T.; Ma, J.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Bao, Z.-X.; Jiang, W.-W. MicroRNA-155 in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Overexpression, localization, and prognostic potential. Head Neck 2015, 37, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Yang, J.M.; Ahn, S.H.; Jeong, W.J.; Chung, J.H.; Paik, J.H. Potential Oncogenic Role and Prognostic Implication of MicroRNA-155-5p in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 5193–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bersani, C.; Mints, M.; Tertipis, N.; Haeggblom, L.; Näsman, A.; Romanitan, M.; Dalianis, T.; Ramqvist, T. MicroRNA-155, -185 and -193b as biomarkers in human papillomavirus positive and negative tonsillar and base of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2018, 82, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Duan, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, P.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, H. MiR-155-5p promotes oral cancer progression by targeting chromatin remodeling gene ARID2. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 122, 109696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L. MicroRNA-195 inhibits growth and invasion of laryngeal carcinoma cells by directly targeting DCUN1D1. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2155–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Qi, Z. Clinical significance of miRNA-195 expression in patients with laryngeal carcinoma. J. Buon 2019, 24, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, L.-f.; Wei, S.-b.; Gong, K.; Gan, Y.-h.; Yu, G.-y. Prognostic implications of micoRNA miR-195 expression in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Yan, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, Q.; Shi, J.; Lu, E.; Chen, W.; et al. Exosomal miR-196a derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts confers cisplatin resistance in head and neck cancer through targeting CDKN1B and ING5. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Tsai, M.M.; Tu, H.F.; Lui, M.T.; Cheng, H.W.; Lin, S.C. miR-196a overexpression and miR-196a2 gene polymorphism are prognostic predictors of oral carcinomas. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20 (Suppl. 3), S406–S414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Nishihara, K.; Umikawa, M.; Arasaki, A.; Nakasone, T.; Nimura, F.; Matayoshi, A.; Takei, K.; Nakachi, S.; Kariya, K.-I.; et al. MicroRNA-196a-5p is a potential prognostic marker of delayed lymph node metastasis in early-stage tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 2349–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; Ji, W. miR-196b is a prognostic factor of human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and promotes tumor progression by targeting SOCS2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 501, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Sun, G.; Sun, J.W. MiR-196b affects the progression and prognosis of human LSCC through targeting PCDH-17. Auris Nasus Larynx 2019, 46, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, H.; Yang, J.M.; Kim, H.; Chung, J.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Jeong, W.J.; Paik, J.H. Clinicopathologic implications of the miR-197/PD-L1 axis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 66178–66194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudcova, K.; Raudenska, M.; Gumulec, J.; Binkova, H.; Horakova, Z.; Kostrica, R.; Babula, P.; Adam, V.; Masarik, M. Expression profiles of miR-29c, miR-200b and miR-375 in tumour and tumour-adjacent tissues of head and neck cancers. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 12627–12633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y. MicroRNA-198 suppresses tumour growth and metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting CDK4. Int. J. Oncol. 2021, 59, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnin, N.; Armandy, E.; Carras, J.; Ferrandon, S.; Battiston-Montagne, P.; Aubry, M.; Guihard, S.; Meyronet, D.; Foy, J.P.; Saintigny, P.; et al. MiR-422a promotes loco-regional recurrence by targeting NT5E/CD73 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 44023–44038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganci, F.; Sacconi, A.; Bossel Ben-Moshe, N.; Manciocco, V.; Sperduti, I.; Strigari, L.; Covello, R.; Benevolo, M.; Pescarmona, E.; Domany, E.; et al. Expression of TP53 mutation-associated microRNAs predicts clinical outcome in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 3082–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, T.; Jimenez, L.; Kawachi, N.; Fan, J.B.; Chen, J.; Belbin, T.; Ramnauth, A.; Loudig, O.; Keller, C.E.; Smith, R.; et al. Low-level expression of miR-375 correlates with poor outcome and metastasis while altering the invasive properties of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, P.; Sana, J.; Slavik, M.; Gurin, D.; Radova, L.; Gablo, N.A.; Kazda, T.; Smilek, P.; Horakova, Z.; Gal, B.; et al. MicroRNA-15b-5p Predicts Locoregional Relapse in Head and Neck Carcinoma Patients Treated With Intensity-modulated Radiotherapy. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2019, 16, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajthala, S.; Dongre, H.; Parajuli, H.; Min, A.; Nginamau, E.S.; Kvalheim, A.; Lybak, S.; Sapkota, D.; Johannessen, A.C.; Costea, D.E. Combined In Situ Hybridization and Immunohistochemistry on Archival Tissues Reveals Stromal microRNA-204 as Prognostic Biomarker for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhang, N.; Cao, L.; Xiao, D.; Ye, X.; Luo, E.; Zhang, Z. Down-regulation of miR-200c associates with poor prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 25, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; Ji, W. MYO5A inhibition by miR-145 acts as a predictive marker of occult neck lymph node metastasis in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 3619–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Tian, L.; Ren, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Ge, J.; Wu, S.; Sun, Y.; Liu, M.; Xiao, H. MicroRNA-101 is a potential prognostic indicator of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and modulates CDK8. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, M.C.; Ten Hoeve, J.J.; Grénman, R.; Wessels, L.F.; Kerkhoven, R.; Te Riele, H.; van den Brekel, M.W.; Verheij, M.; Begg, A.C. Pretreatment microRNA Expression Impacting on Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Predicts Intrinsic Radiosensitivity in Head and Neck Cancer Cell Lines and Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 5630–5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, R.; Huang, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhang, J.; Ji, X. Downregulation of miR-29c-3p is associated with a poor prognosis in patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Diagn. Pathol. 2019, 14, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.Y.; Liu, H.J.; Guo, Q.; Sheng, J.L. Reduced miR-300 expression predicts poor prognosis in patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 760–764. [Google Scholar]
- Re, M.; Çeka, A.; Rubini, C.; Ferrante, L.; Zizzi, A.; Gioacchini, F.M.; Tulli, M.; Spazzafumo, L.; Sellari-Franceschini, S.; Procopio, A.D.; et al. MicroRNA-34c-5p is related to recurrence in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, E306–E312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lin, Y.P.; Yang, D.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, H.F. Clinical Significance of miR-149 in the Survival of Patients with Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biomed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8561251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Li, M.; Ge, J.; Guo, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, M.; Xiao, H. MiR-203 is downregulated in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and can suppress proliferation and induce apoptosis of tumours. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 5953–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; Ji, W. miR-181a targets GATA6 to inhibit the progression of human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 1741–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.F.; Zhang, D.J.; Wen, L.J.; Xin, D.; Liu, Y.; Yu, D.J.; Su, K.; Zhu, L.; Guo, Y.Y.; Wang, K. Overexpression of lncRNA H19/miR-675 promotes tumorigenesis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 13, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avissar, M.; McClean, M.D.; Kelsey, K.T.; Marsit, C.J. MicroRNA expression in head and neck cancer associates with alcohol consumption and survival. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 2059–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Jia, S.; Xu, P. MicroRNA-9 as a novel prognostic biomarker in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 5523–5528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.Y.; Zhang, T.H.; Qu, L.M.; Feng, J.P.; Tian, L.L.; Zhang, B.H.; Li, D.D.; Sun, Y.N.; Liu, M. MiR-19a is correlated with prognosis and apoptosis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating TIMP-2 expression. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.W.; Liu, N.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.X.; Sun, Y.Y.; Qiu, G.B.; Fu, W.N. High microRNA-23a expression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma is associated with poor patient prognosis. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Huang, J.J.; Xu, W.H.; Jin, X.J.; Li, J.P.; Tang, Y.J.; Huang, X.F.; Cui, H.J.; Sun, G.B.; Li, R.L.; et al. MiR-21/miR-375 ratio is an independent prognostic factor in patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 1775–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Re, M.; Magliulo, G.; Gioacchini, F.M.; Bajraktari, A.; Bertini, A.; Çeka, A.; Rubini, C.; Ferrante, L.; Procopio, A.D.; Olivieri, F. Expression Levels and Clinical Significance of miR-21-5p, miR-let-7a, and miR-34c-5p in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 3921258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhan, G.; Ye, D.; Ren, Y.; Cheng, L.; Wu, Z.; Guo, J. MicroRNA-34a affects the occurrence of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting the antiapoptotic gene survivin. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 2473–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, D.; de Carvalho, A.C.; Horst, M.A.; Carvalho, A.L.; Scapulatempo-Neto, C.; Vettore, A.L. Expression of miR-296-5p as predictive marker for radiotherapy resistance in early-stage laryngeal carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Saiki, Y.; Shiga, K.; Chen, N.; Fukushige, S.; Sunamura, M.; Nagase, H.; Hashimoto, S.; Matsuura, K.; Saijo, S.; et al. miR-34a is downregulated in cis-diamminedichloroplatinum treated sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma patients with poor prognosis. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantazis, T.L.; Giotakis, A.I.; Karamagkiolas, S.; Giotakis, I.; Konstantoulakis, M.; Liakea, A.; Misiakos, E.P. Low expression of miR-20b-5p indicates favorable prognosis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma, especially in patients with non-infiltrated regional lymph nodes. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2020, 41, 102563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, G.; Fazzari, M.; Kung, G.; Kawachi, N.; Brandwein-Gensler, M.; McLemore, M.; Chen, Q.; Burk, R.D.; Smith, R.V.; Prystowsky, M.B.; et al. Low-level expression of microRNAs let-7d and miR-205 are prognostic markers of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, Y.H.; Won, H.S.; Sun, D.S.; An, H.J.; Jeon, E.K.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, H.H.; Kang, J.H.; Jung, C.K. Human papillomavirus-stratified analysis of the prognostic role of miR-21 in oral cavity and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Pathol. Int. 2014, 64, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arantes, L.M.; Laus, A.C.; Melendez, M.E.; de Carvalho, A.C.; Sorroche, B.P.; De Marchi, P.R.; Evangelista, A.F.; Scapulatempo-Neto, C.; de Souza Viana, L.; Carvalho, A.L. MiR-21 as prognostic biomarker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients undergoing an organ preservation protocol. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 9911–9921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.C.; Yang, Y.J.; Li, Y.J.; Chen, S.T.; Lin, B.R.; Wu, T.S.; Lin, S.K.; Kuo, M.Y.; Tan, C.T. MicroRNA-17/20a functions to inhibit cell migration and can be used a prognostic marker in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, H.E.; Camps, C.; Buffa, F.M.; Patiar, S.; Winter, S.C.; Betts, G.; Homer, J.; Corbridge, R.; Cox, G.; West, C.M.; et al. hsa-mir-210 is a marker of tumor hypoxia and a prognostic factor in head and neck cancer. Cancer 2010, 116, 2148–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.-F.; Wei, S.-B.; Gan, Y.-H.; Guo, Y.; Gong, K.; Mitchelson, K.; Cheng, J.; Yu, G.-Y. Expression, regulation and roles of miR-26a and MEG3 in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 2282–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Wang, J.; Ouyang, S.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M. Expression and clinical significance of microRNA-1246 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Jiang, N.; Guo, R.; Jiang, W.; He, Q.M.; Xu, Y.F.; Li, Y.Q.; Tang, L.L.; Mao, Y.P.; Sun, Y.; et al. MiR-451 inhibits cell growth and invasion by targeting MIF and is associated with survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Shen, W.G.; Peng, S.Y.; Cheng, H.W.; Kao, S.Y.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, K.W. miR-134 induces oncogenicity and metastasis in head and neck carcinoma through targeting WWOX gene. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; McCarthy, J.B.; She, X.; Zhang, W.; Ma, J.; et al. miR-18a promotes malignant progression by impairing microRNA biogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.C.; Liao, C.T.; Peng, C.H.; Cheng, A.J.; Chen, S.J.; Huang, C.G.; Hsieh, W.P.; Yen, T.C. MicroRNAs MiR-218, MiR-125b, and Let-7g predict prognosis in patients with oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasahira, T.; Kurihara, M.; Bhawal, U.K.; Ueda, N.; Shimomoto, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Kirita, T.; Kuniyasu, H. Downregulation of miR-126 induces angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis by activation of VEGF-A in oral cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, H.F.; Chang, K.W.; Cheng, H.W.; Liu, C.J. Upregulation of miR-372 and -373 associates with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis of oral carcinomas. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, E365–E370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.W.; Chuang, C.Y.; Lin, W.L.; Sung, W.W.; Cheng, Y.W.; Lee, H. Paxillin promotes tumor progression and predicts survival and relapse in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma by microRNA-218 targeting. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Z. Downregulation of miR-153 contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis in human epithelial cancer. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Hou, D.; Shi, Q.; Yang, S.; Li, Q. MicroRNA-375 Inhibits Growth and Enhances Radiosensitivity in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Targeting Insulin Like Growth Factor 1 Receptor. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 2105–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lyu, M.; Zhang, C.; Meng, Z.; Gan, Y.; Yu, G. miR-375 inhibits cell growth and correlates with clinical outcomes in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2061–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Huang, J.J.; Xu, W.H.; Jin, X.J.; Li, J.P.; Tang, Y.J.; Huang, X.F.; Cui, H.J.; Sun, G.B. miR-21 and miR-375 microRNAs as candidate diagnostic biomarkers in squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx: Association with patient survival. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2014, 6, 604–613. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Liu, H.; Kong, F.; Ye, J.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, N.; Yin, J.; Zheng, G.; He, Z. miR-22/KAT6B axis is a chemotherapeutic determiner via regulation of PI3k-Akt-NF-kB pathway in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Győrffy, B. Discovery and ranking of the most robust prognostic biomarkers in serous ovarian cancer. Geroscience 2023, 45, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lánczky, A.; Győrffy, B. Web-Based Survival Analysis Tool Tailored for Medical Research (KMplot): Development and Implementation. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e27633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2009, 339, b2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiting, P.; Savović, J.; Higgins, J.P.; Caldwell, D.M.; Reeves, B.C.; Shea, B.; Davies, P.; Kleijnen, J.; Churchill, R. ROBIS: A new tool to assess risk of bias in systematic reviews was developed. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2016, 69, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauerbrei, W.; Taube, S.E.; McShane, L.M.; Cavenagh, M.M.; Altman, D.G. Reporting Recommendations for Tumor Marker Prognostic Studies (REMARK): An Abridged Explanation and Elaboration. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozniak, T.; Shcharbin, D.; Bryszewska, M. Circulating microRNAs in Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamorro Petronacci, C.M.; García García, A.; Padín Iruegas, E.; Rivas Mundiña, B.; Lorenzo Pouso, A.I.; Pérez Sayáns, M. Identification of Prognosis Associated microRNAs in HNSCC Subtypes Based on TCGA Dataset. Medicina 2020, 56, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahabi, M.; Blandino, G.; Di Agostino, S. MicroRNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A possible challenge as biomarkers, determinants for the choice of therapy and targets for personalized molecular therapies. Transl. Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 3090–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzio, L.L.; Ballini, A.; Cantore, S.; Bottalico, L.; Charitos, I.A.; Ambrosino, M.; Nocini, R.; Malcangi, A.; Dioguardi, M.; Cazzolla, A.P.; et al. Overview of Candida albicans and Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection Agents and their Biomolecular Mechanisms in Promoting Oral Cancer in Pediatric Patients. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 7312611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supic, G.; Stefik, D.; Ivkovic, N.; Sami, A.; Zeljic, K.; Jovic, S.; Kozomara, R.; Vojvodic, D.; Stosic, S. Prognostic impact of miR-34b/c DNA methylation, gene expression, and promoter polymorphism in HPV-negative oral squamous cell carcinomas. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, R.; Majumder, M.; Janakiraman, H.; Ogretmen, B.; Kato, M.; Erkul, E.; Hill, E.; Atkinson, C.; Barth, J.; Day, T.A.; et al. Smoking-induced control of miR-133a-3p alters the expression of EGFR and HuR in HPV-infected oropharyngeal cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miladinovic, B.; Mhaskar, R.; Hozo, I.; Kumar, A.; Mahony, H.; Djulbegovic, B. Optimal information size in trial sequential analysis of time-to-event outcomes reveals potentially inconclusive results because of the risk of random error. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 66, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, J.; Psarianos, P.; Bruce, J.; Yip, K.; Liu, F.-f. The complexity of microRNAs in human cancer. J. Radiat. Res. 2016, 57, rrw009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How, C.; Pintilie, M.; Bruce, J.P.; Hui, A.B.; Clarke, B.A.; Wong, P.; Yin, S.; Yan, R.; Waggott, D.; Boutros, P.C.; et al. Developing a prognostic micro-RNA signature for human cervical carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Patnaik, S.; Dixit, A. Predictive models for stage and risk classification in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). PeerJ 2020, 8, e9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauman, J.E.; Austin, M.C.; Schmidt, R.; Kurland, B.F.; Vaezi, A.; Hayes, D.N.; Mendez, E.; Parvathaneni, U.; Chai, X.; Sampath, S.; et al. ERCC1 is a prognostic biomarker in locally advanced head and neck cancer: Results from a randomised, phase II trial. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 2096–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psyrri, A.; Lee, J.W.; Pectasides, E.; Vassilakopoulou, M.; Kosmidis, E.K.; Burtness, B.A.; Rimm, D.L.; Wanebo, H.J.; Forastiere, A.A. Prognostic biomarkers in phase II trial of cetuximab-containing induction and chemoradiation in resectable HNSCC: Eastern cooperative oncology group E2303. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3023–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Li, C.X.; Guo, C.; Zhu, H. MicroRNA model that can predict the prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma based on bioinformatics analysis. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2020, 38, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; Caloro, G.A.; Laino, L.; Alovisi, M.; Sovereto, D.; Crincoli, V.; Aiuto, R.; Coccia, E.; Troiano, G.; Lo Muzio, L. Circulating miR-21 as a Potential Biomarker for the Diagnosis of Oral Cancer: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2020, 12, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).