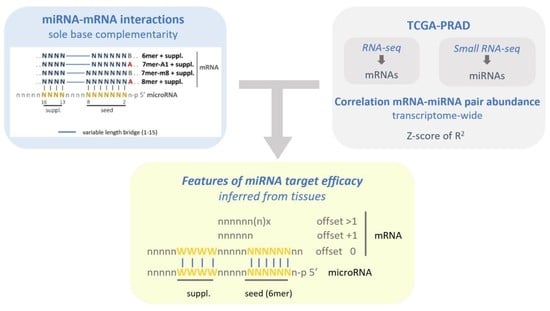
Transcriptome-Wide Analysis of microRNA–mRNA Correlations in Tissue Identifies microRNA Targeting Determinants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
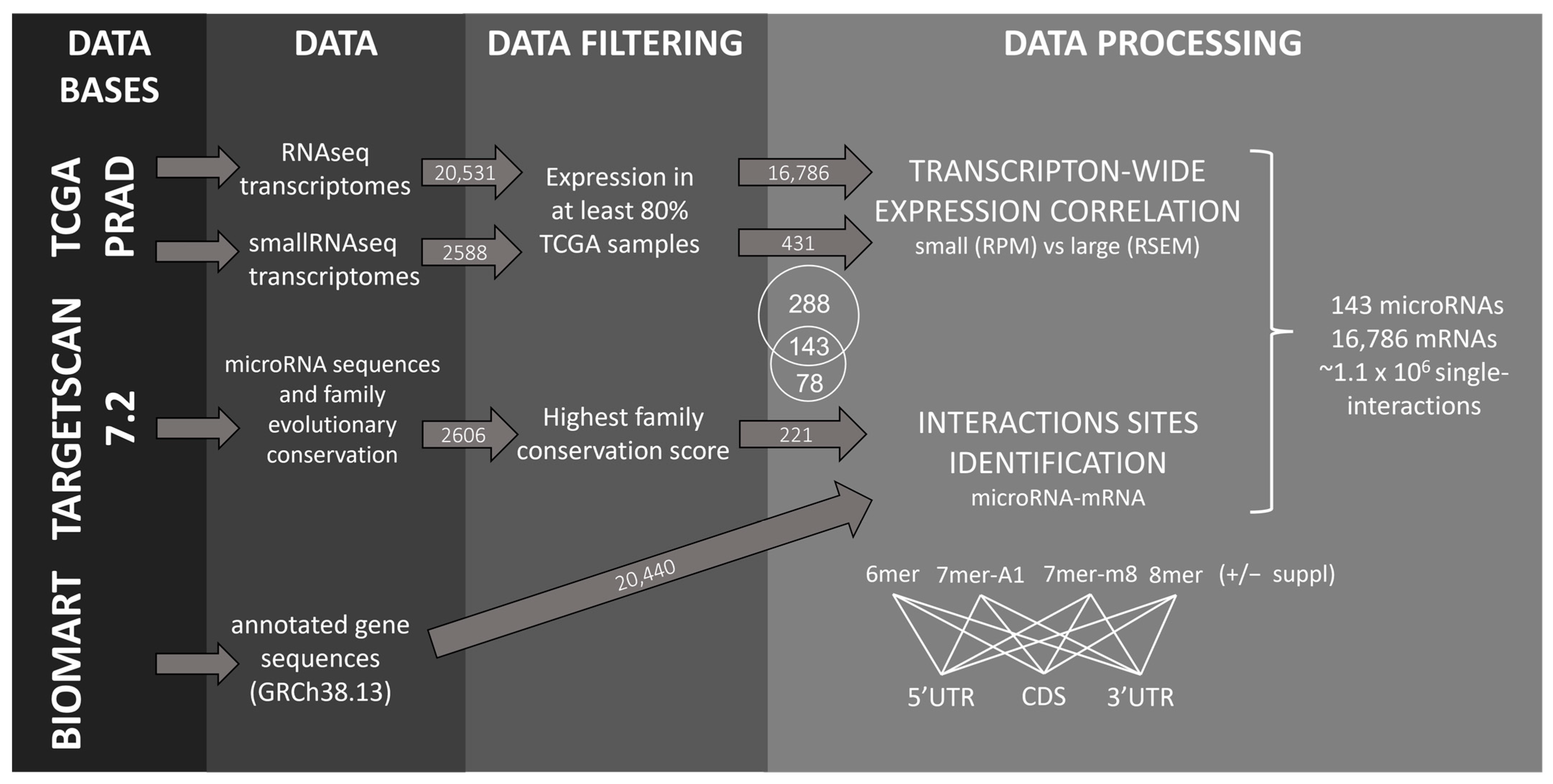
2.1. Identification of microRNA–mRNA Interaction Sites in the PRAD-TCGA Transcriptome Based on Nucleotide Base Complementarity
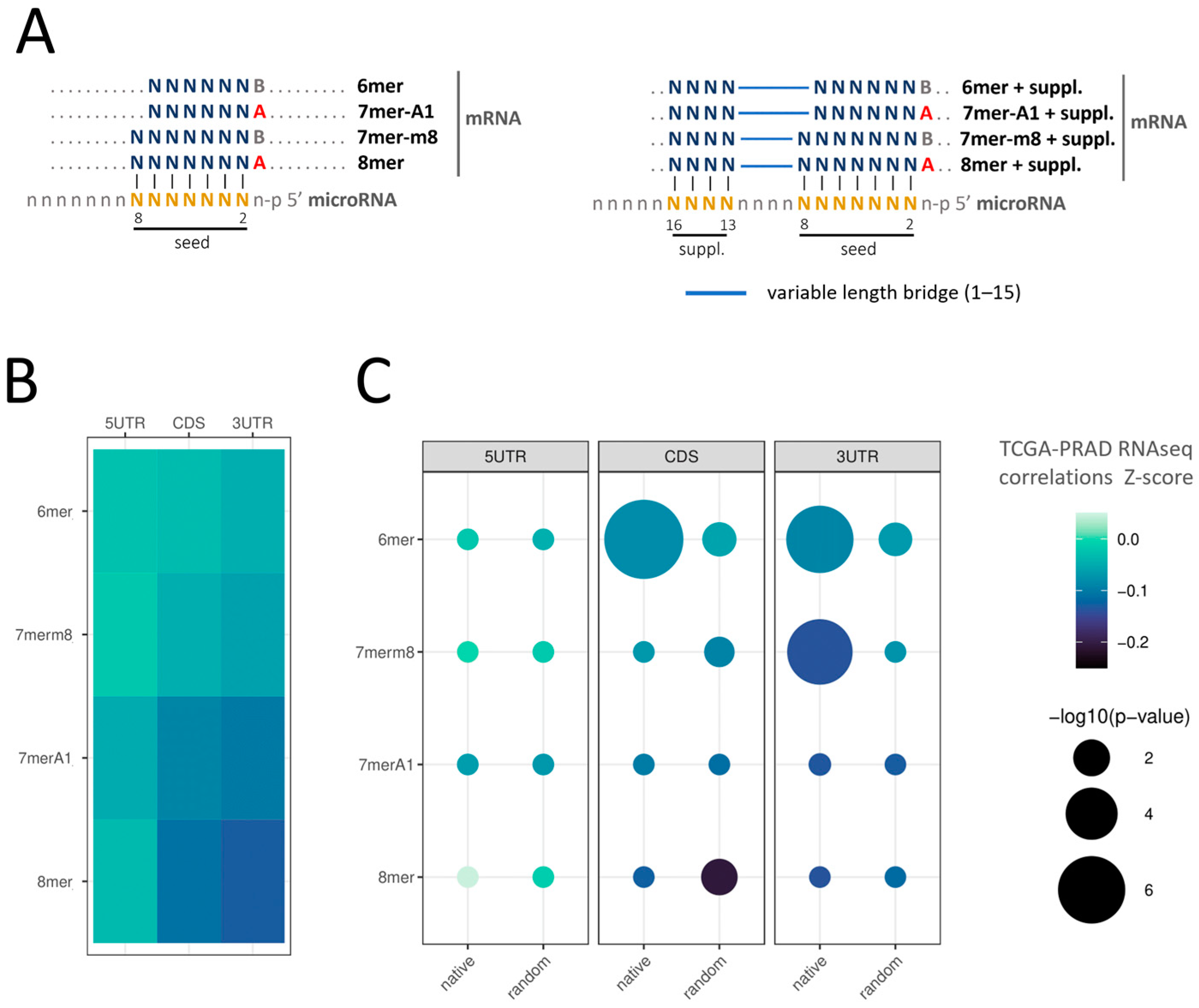
2.2. Validation of microRNA Repressive Mechanisms Using microRNA Activity Inferred from microRNA–mRNA Expression Correlations in PRAD-TCGA
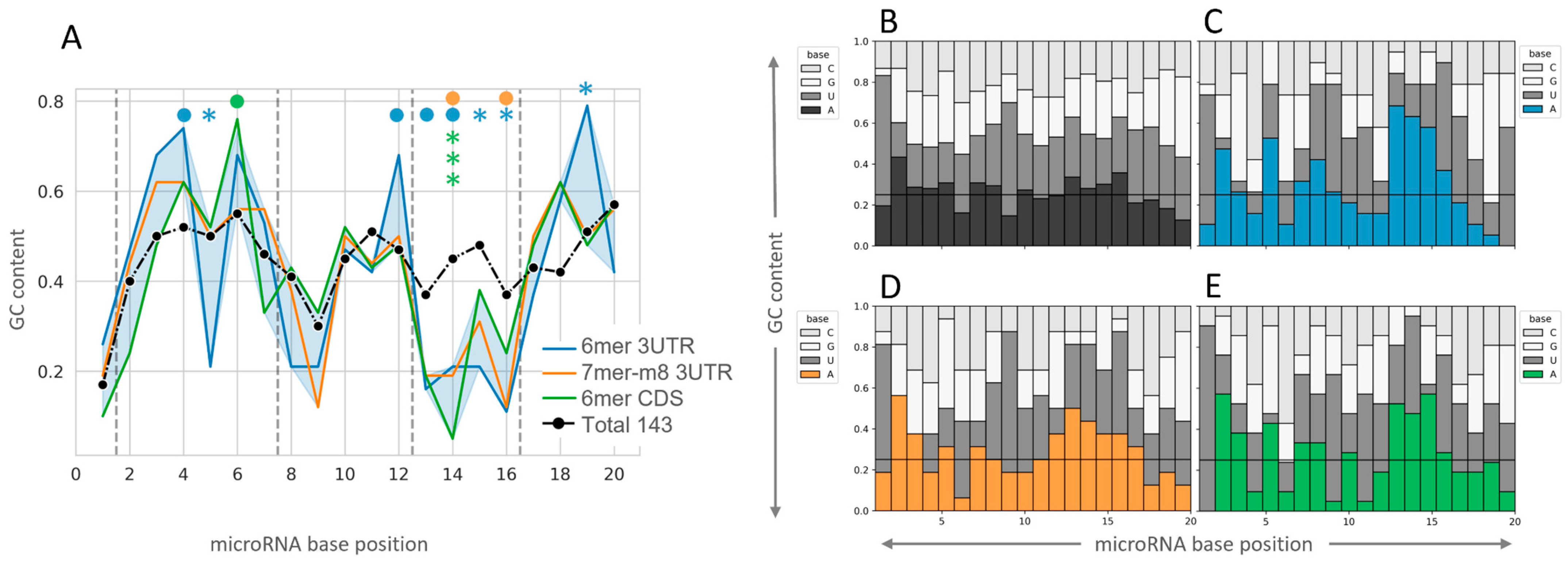
2.3. Insight into the Characteristics of microRNA–mRNA Interaction Involving Beneficial 3′-Supplementary Pairing Regions withdrawn from microRNA–mRNA Correlations
2.4. An Executable Tool to Identify the microRNA–mRNA Seed + Suppl Interactions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. MicroRNAs and mRNAs Transcriptomic Data
4.2. Inference of microRNA Activity from microRNA–mRNA Expression Correlation in the PRAD-TCGA Transcriptomes
4.3. Canonical Seeds and 3′-Supplementary microRNA–mRNA Interactions Identification
4.4. MicroRNA–mRNA Pairs Correlation Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
4.6. Executable Files
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartel, D.P. Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell 2018, 173, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimson, A.; Farh, K.K.H.; Johnston, W.K.; Garrett-Engele, P.; Lim, L.P.; Bartel, D.P. MicroRNA Targeting Specificity in Mammals: Determinants beyond Seed Pairing. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafner, M.; Landthaler, M.; Burger, L.; Khorshid, M.; Hausser, J.; Berninger, P.; Rothballer, A.; Ascano, M.; Jungkamp, A.C.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Transcriptome-Wide Identification of RNA-Binding Protein and MicroRNA Target Sites by PAR-CLIP. Cell 2010, 141, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helwak, A.; Kudla, G.; Dudnakova, T.; Tollervey, D. Mapping the Human MiRNA Interactome by CLASH Reveals Frequent Noncanonical Binding. Cell 2013, 153, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.J.; Scheel, T.K.H.; Luna, J.M.; Park, C.Y.; Fak, J.J.; Nishiuchi, E.; Rice, C.M.; Darnell, R.B. MiRNA–Target Chimeras Reveal MiRNA 3′-End Pairing as a Major Determinant of Argonaute Target Specificity. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnall-Levin, M.; Zhao, Y.; Perrimon, N.; Berger, B. Conserved MicroRNA Targeting in Drosophila Is as Widespread in Coding Regions as in 3′UTRs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15751–15756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, D.; Villén, J.; Shin, C.; Camargo, F.D.; Gygi, S.P.; Bartel, D.P. The Impact of MicroRNAs on Protein Output. Nature 2008, 455, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selbach, M.; Schwanhäusser, B.; Thierfelder, N.; Fang, Z.; Khanin, R.; Rajewsky, N. Widespread Changes in Protein Synthesis Induced by MicroRNAs. Nature 2008, 455, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, D.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y. Survey of Computational Algorithms for MicroRNA Target Prediction. Curr. Genom. 2009, 10, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, J.P.; Lovci, M.T.; Huang, J.L.; Yeo, G.W.; Pasquinelli, A.E. Pairing beyond the Seed Supports MicroRNA Targeting Specificity. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Veksler-Lublinsky, I.; Ambros, V. Critical Contribution of 3′ Non-Seed Base Pairing to the in Vivo Function of the Evolutionarily Conserved Let-7a MicroRNA. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, W.E.; Jolly, S.M.; Moore, M.J.; Zamore, P.D.; Serebrov, V. Single-Molecule Imaging Reveals That Argonaute Reshapes the Binding Properties of Its Nucleic Acid Guides. Cell 2015, 162, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu-Gruttadauria, J.; Xiao, Y.; Gebert, L.F.; MacRae, I.J. Beyond the Seed: Structural Basis for Supplementary MicroRNA Targeting by Human Argonaute2. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e101153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlquist, C.; Jeong, D.; Rojas-Muñoz, A.; Kho, C.; Lee, A.; Mitsuyama, S.; Van Mil, A.; Jin Park, W.; Sluijter, J.P.G.; Doevendans, P.A.F.; et al. Inhibition of MiR-25 Improves Cardiac Contractility in the Failing Heart. Nature 2014, 508, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, L.M.; Flores-Jasso, C.F.; Salomon, W.E.; Zamore, P.D. Argonaute Divides Its RNA Guide into Domains with Distinct Functions and RNA-Binding Properties. Cell 2012, 151, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.H.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most Mammalian MRNAs Are Conserved Targets of MicroRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeary, S.E.; Bisaria, N.; Pham, T.M.; Wang, P.Y.; Bartel, D.P. MicroRNA 3′-Compensatory Pairing Occurs through Two Binding Modes, with Affinity Shaped by Nucleotide Identity and Position. Elife 2022, 11, e69803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Macrae, I.J. Robust Differential MicroRNA Targeting Driven by Supplementary Interactions in Vitro. Rna 2020, 26, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting Effective MicroRNA Target Sites in Mammalian MRNAs. Elife 2015, 4, e05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.B.; Lei, H.Q.; Xiong, H.Y.; Fu, X.; Shi, F.; Yang, X.W.; Yang, Y.F.; Liao, G.L.; Feng, Y.P.; Jiang, D.G.; et al. MicroRNA-Regulated Transcriptome Analysis Identifies Four Major Subtypes with Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications in Prostate Cancer. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 4941–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yin, Y.; Deng, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Yin, G.; Yang, J.; Tang, Y. Integrative Analysis of MicroRNA and Gene Interactions for Revealing Candidate Signatures in Prostate Cancer. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Jia, B.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Ye, W. MiR-93-5p May Be an Important Oncogene in Prostate Cancer by Bioinformatics Analysis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 10463–10483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Li, S.L.; Wang, S.Y. Construction and Analysis of MRNA, MiRNA, LncRNA, and TF Regulatory Networks Reveal the Key Genes Associated with Prostate Cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeshouse, A.; Ahn, J.; Akbani, R.; Ally, A.; Amin, S.; Andry, C.D.; Annala, M.; Aprikian, A.; Armenia, J.; Arora, A.; et al. The Molecular Taxonomy of Primary Prostate Cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 1011–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeary, S.E.; Lin, K.S.; Shi, C.Y.; Pham, T.M.; Bisaria, N.; Kelley, G.M.; Bartel, D.P. The Biochemical Basis of MicroRNA Targeting Efficacy. Science 2019, 366, aav1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, C.B.; Shomron, N.; Sandberg, R.; Hornstein, E.; Kitzman, J.; Burge, C.B. Determinants of Targeting by Endogenous and Exogenous MicroRNAs and SiRNAs. RNA 2007, 13, 1894–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, N.C.; Lim, L.P.; Weinstein, E.G.; Bartel, D.P. An Abundant Class of Tiny RNAs with Probable Regulatory Roles in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Science 2001, 294, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B. Base Composition Characteristics of Mammalian Mirnas. J. Nucleic Acids 2013, 2013, 951570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Nguyen, H.; Lai, T.; Kim, D.R. MiRCancerdb: A Database for Correlation Analysis between MicroRNA and Gene Expression in Cancer. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elton, T.S.; Yalowich, J.C. Experimental Procedures to Identify and Validate Specific MRNA Targets of MiRNAs. EXCLI J. 2015, 14, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, M.J.; Craft, B.; Hastie, M.; Repečka, K.; McDade, F.; Kamath, A.; Banerjee, A.; Luo, Y.; Rogers, D.; Brooks, A.N.; et al. Visualizing and Interpreting Cancer Genomics Data via the Xena Platform. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.H.; Yang, J.H. StarBase v2.0: Decoding MiRNA-CeRNA, MiRNA-NcRNA and Protein–RNA Interaction Networks from Large-Scale CLIP-Seq Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D92–D97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.T.; Lee, C.Y.; Lai, L.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Lu, T.P.; Chuang, E.Y. AnamiR: Integrated Analysis of MicroRNA and Gene Expression Profiling. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, S.M.; Thompson, J.A.; Ufkin, M.L.; Sathyanarayana, P.; Liaw, L.; Congdon, C.B. Common Features of MicroRNA Target Prediction Tools. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Rajewsky, N. The Impact of MiRNA Target Sites in Coding Sequences and in 3′UTRs. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibel, B.; Elkayam, E.; Silletti, S.; Komives, E.A.; Joshua-Tor, L. Target Binding Triggers Hierarchical Phosphorylation of Human Argonaute-2 to Promote Target Release. eLife 2022, 11, e76908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, W.R.; Ober-Reynolds, B.; Jouravleva, K.; Jolly, S.M.; Zamore, P.D.; Greenleaf, W.J. High-Throughput Analysis Reveals Rules for Target RNA Binding and Cleavage by AGO2. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, W. Data Structures for Statistical Computing in Python. In Proceedings of the 9th Python in Science Conference (SCIPY 2010), Austin, TX, USA, 28 June–3 July 2010; Volume 41, pp. 51–56. [Google Scholar]

| Group1 | Group2 | 5’UTR | CDS | 3’UTR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 mer | 7 mer-m8 | n.s. | 6.09 × 10−3 | n.s. |
| 6 mer | 7 mer-A1 | 1.14 × 10−2 | 2.36 × 10−42 | 4.82 × 10−45 |
| 6 mer | 8 mer | n.s. | 1.74 × 10−25 | 9.23 × 10−35 |
| 7 mer-m8 | 8 mer | n.s. | 2.24 × 10−13 | 4.41 × 10−23 |
| 7 mer-A1 | 7 mer-m8 | 2.93 × 10−3 | 3.94 × 10−14 | 9.48 × 10−21 |
| 7 mer-A1 | 8 mer | n.s. | n.s. | 1.24 × 10−2 |
| 6 mer | 6 mer suppl | n.s. | 2.84 × 10−8 | 9.9 × 10−7 |
| 6 mer | 7 mer-m8 suppl | n.s. | n.s. | 3.66 × 10−8 |
| 6 mer | 7 mer-A1 suppl | n.s. | 1.71 × 10−4 | 2.48 × 10−9 |
| 6 mer | 8 mer suppl | n.s. | 1.2 × 10−2 | 3.72 × 10−3 |
| 7 mer-m8 | 7 mer-m8 suppl | n.s. | n.s. | 1.74 × 10−6 |
| 7 mer-m8 | 8 mer suppl | n.s. | n.s. | 1.52 × 10−2 |
| 6 mer suppl | 7 mer-m8 | n.s. | 2.84 × 10−3 | 6.92 × 10−4 |
| 6 mer suppl | 8 mer | n.s. | n.s. | 1.74 × 10−3 |
| 7 mer-A1 suppl | 7 mer-m8 | n.s. | 2.20 × 10−2 | 2.43 × 10−7 |
| Group1 | Group2 | 6 mer | 7 mer-A1 | 7 mer-m8 | 8 mer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3UTR | 5UTR | 5.98 × 10−9 | 2.69 × 10−14 | 4.34 × 10−7 | 7.30 × 10−12 |
| 3UTR | CDS | 2.62 × 10−8 | 1.37 × 10−2 | n.s. | n.s. |
| 5UTR | CDS | n.s. | 6.25 × 10−8 | 6.82 × 10−5 | 2.06 × 10−7 |
| Group1 | Group2 | 6 mer suppl | 7 mer-A1 suppl | 7 mer-m8 suppl | 8 mer suppl |
| 3UTR | 5UTR | 2.81 × 10−6 | 3.62 × 10−2 | 1.14 × 10−5 | 1.29 × 10−3 |
| 3UTR | CDS | n.s. | n.s. | 5.11 × 10−3 | n.s. |
| 5UTR | CDS | 7.30 × 10−5 | n.s. | n.s. | 4.49 × 10−3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trinidad-Barnech, J.M.; Fort, R.S.; Trinidad Barnech, G.; Garat, B.; Duhagon, M.A. Transcriptome-Wide Analysis of microRNA–mRNA Correlations in Tissue Identifies microRNA Targeting Determinants. Non-Coding RNA 2023, 9, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9010015
Trinidad-Barnech JM, Fort RS, Trinidad Barnech G, Garat B, Duhagon MA. Transcriptome-Wide Analysis of microRNA–mRNA Correlations in Tissue Identifies microRNA Targeting Determinants. Non-Coding RNA. 2023; 9(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrinidad-Barnech, Juan Manuel, Rafael Sebastián Fort, Guillermo Trinidad Barnech, Beatriz Garat, and María Ana Duhagon. 2023. "Transcriptome-Wide Analysis of microRNA–mRNA Correlations in Tissue Identifies microRNA Targeting Determinants" Non-Coding RNA 9, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9010015
APA StyleTrinidad-Barnech, J. M., Fort, R. S., Trinidad Barnech, G., Garat, B., & Duhagon, M. A. (2023). Transcriptome-Wide Analysis of microRNA–mRNA Correlations in Tissue Identifies microRNA Targeting Determinants. Non-Coding RNA, 9(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9010015