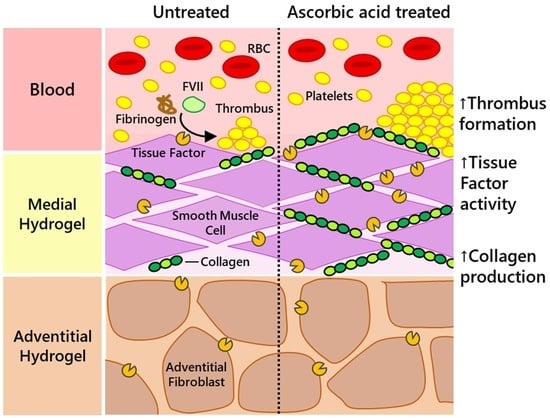
Developing Biomimetic Hydrogels of the Arterial Wall as a Prothrombotic Substrate for In Vitro Human Thrombosis Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
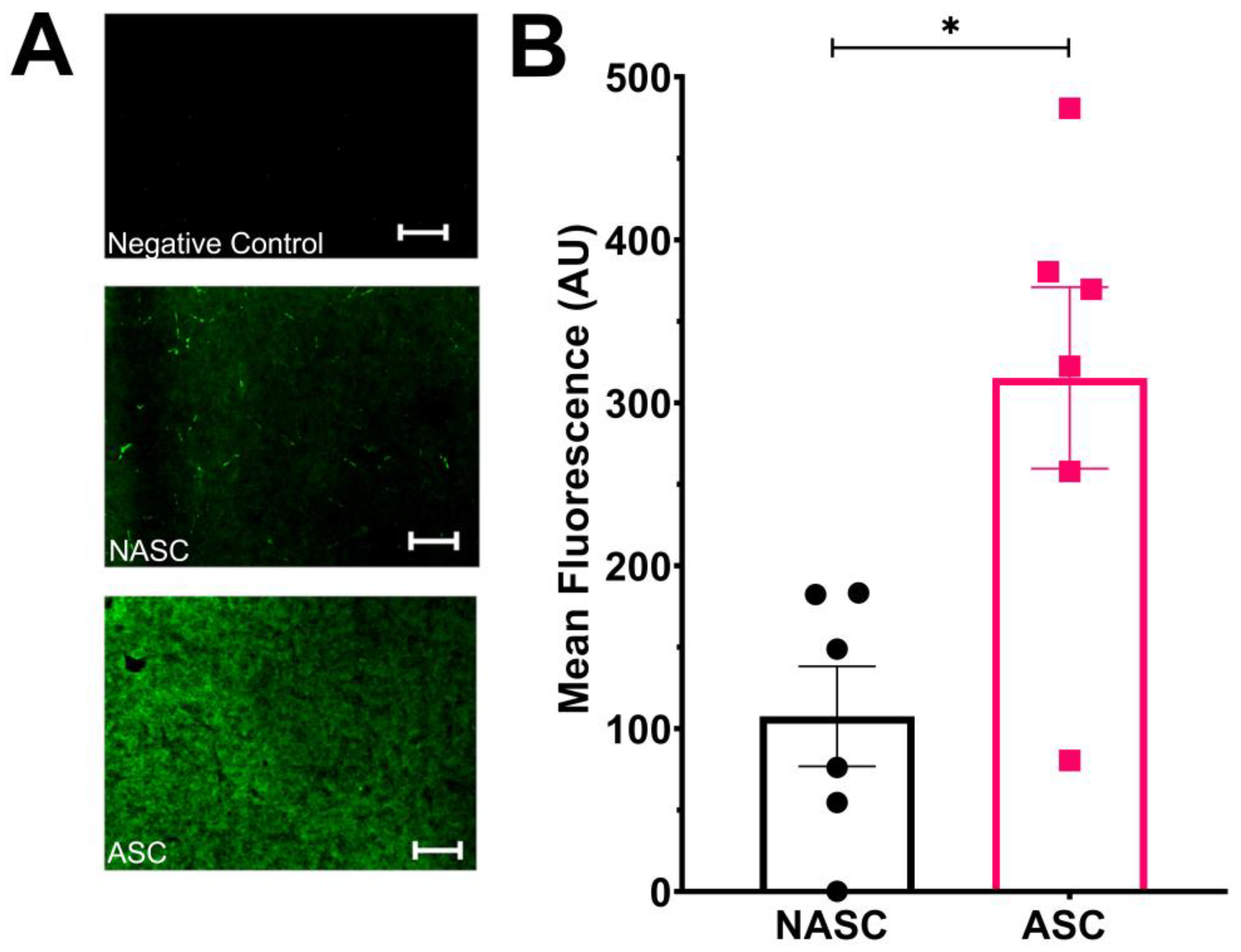
2.1. Ascorbic Acid Supplementation Enhances the Rate of Type I Collagen Deposition in Tissue-Engineered Medial Layer Hydrogels
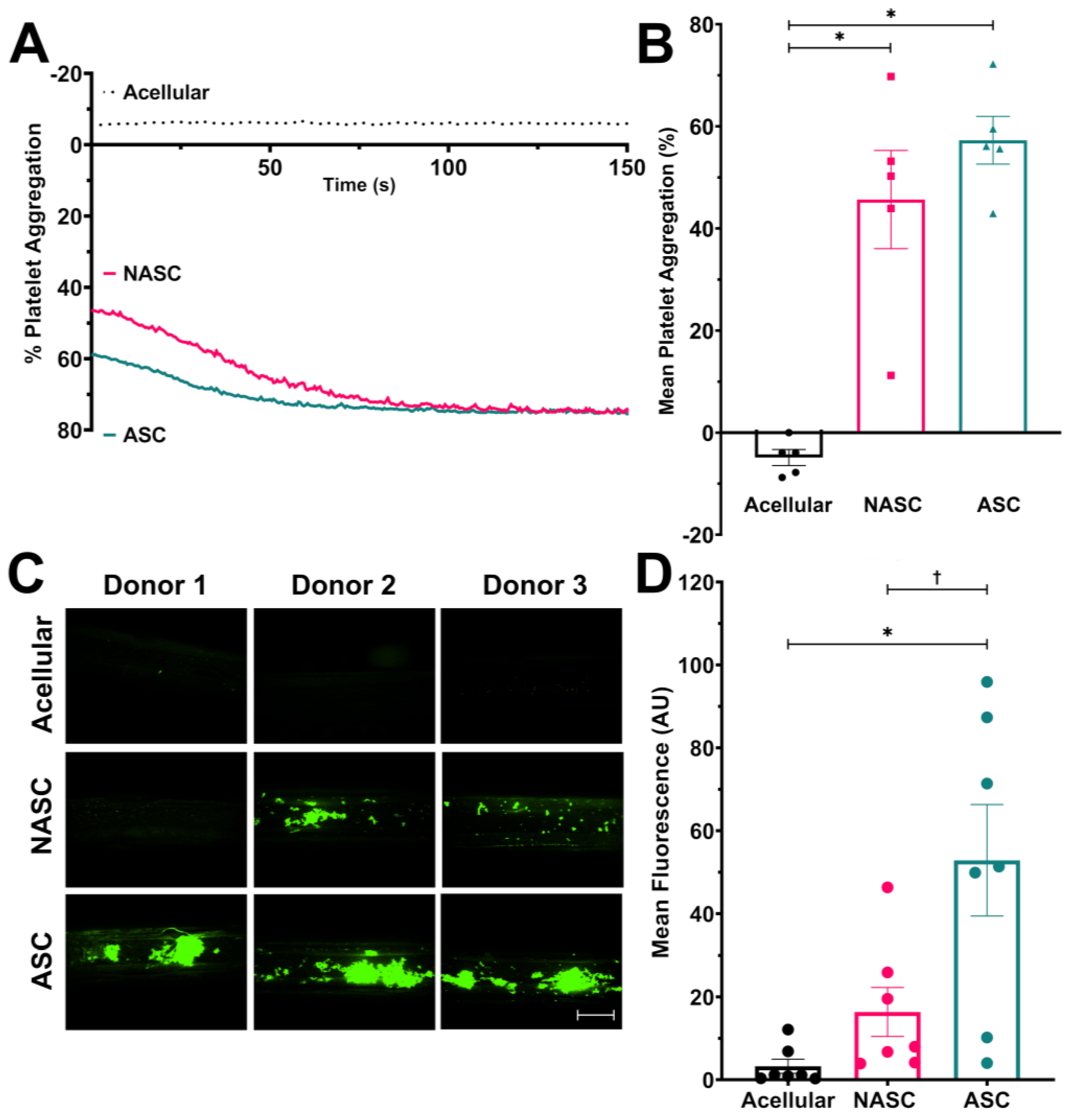
2.2. Increased Neo-Collagen Production Improves the Pro-Aggregatory Capacity of the Medial Layer Hydrogel under Physiological Flow Conditions but Not under Non-Physiological Stirring
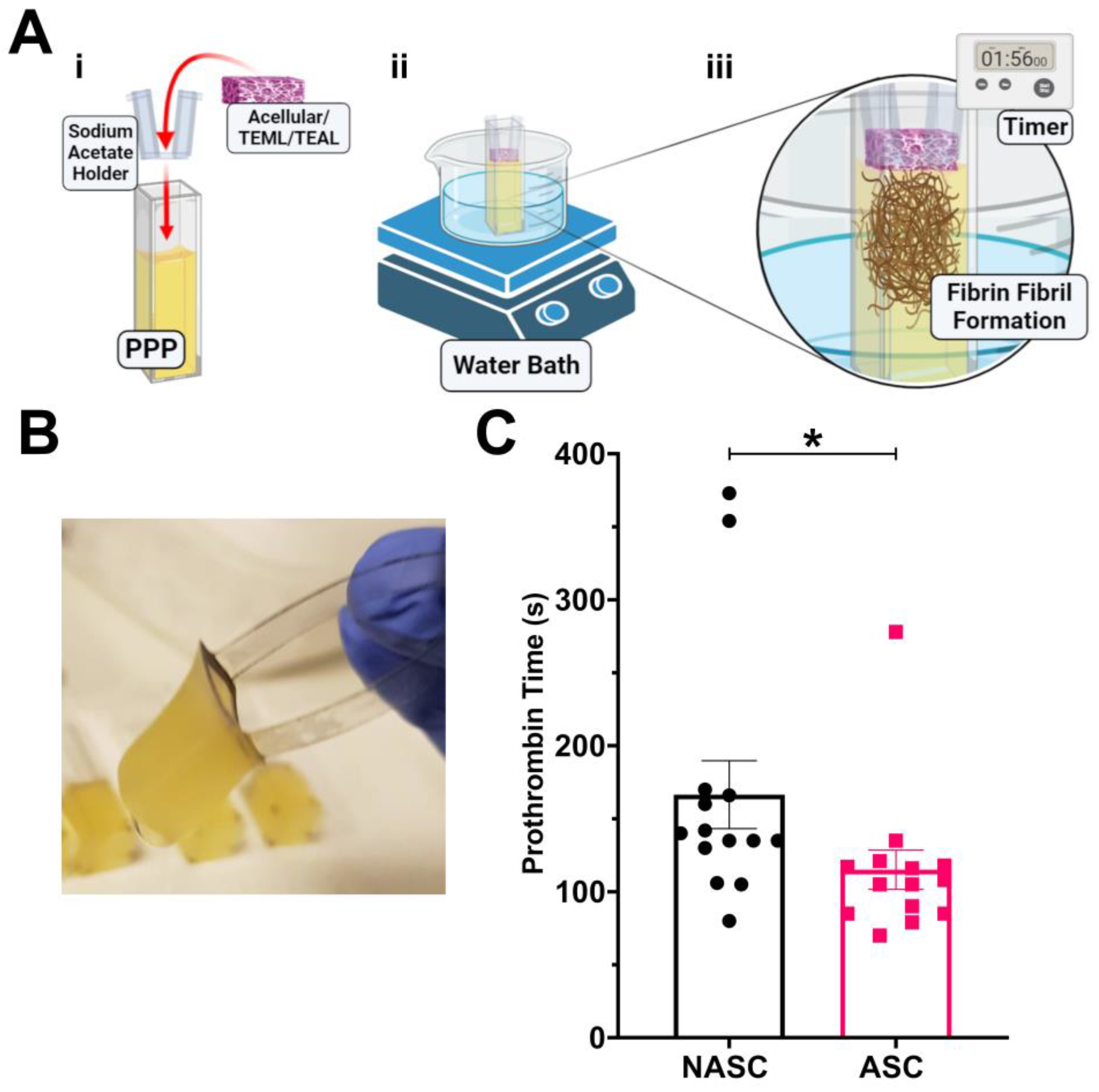
2.3. Ascorbic Acid Supplementation Enhances the Procoagulant Properties of the TEML Hydrogels
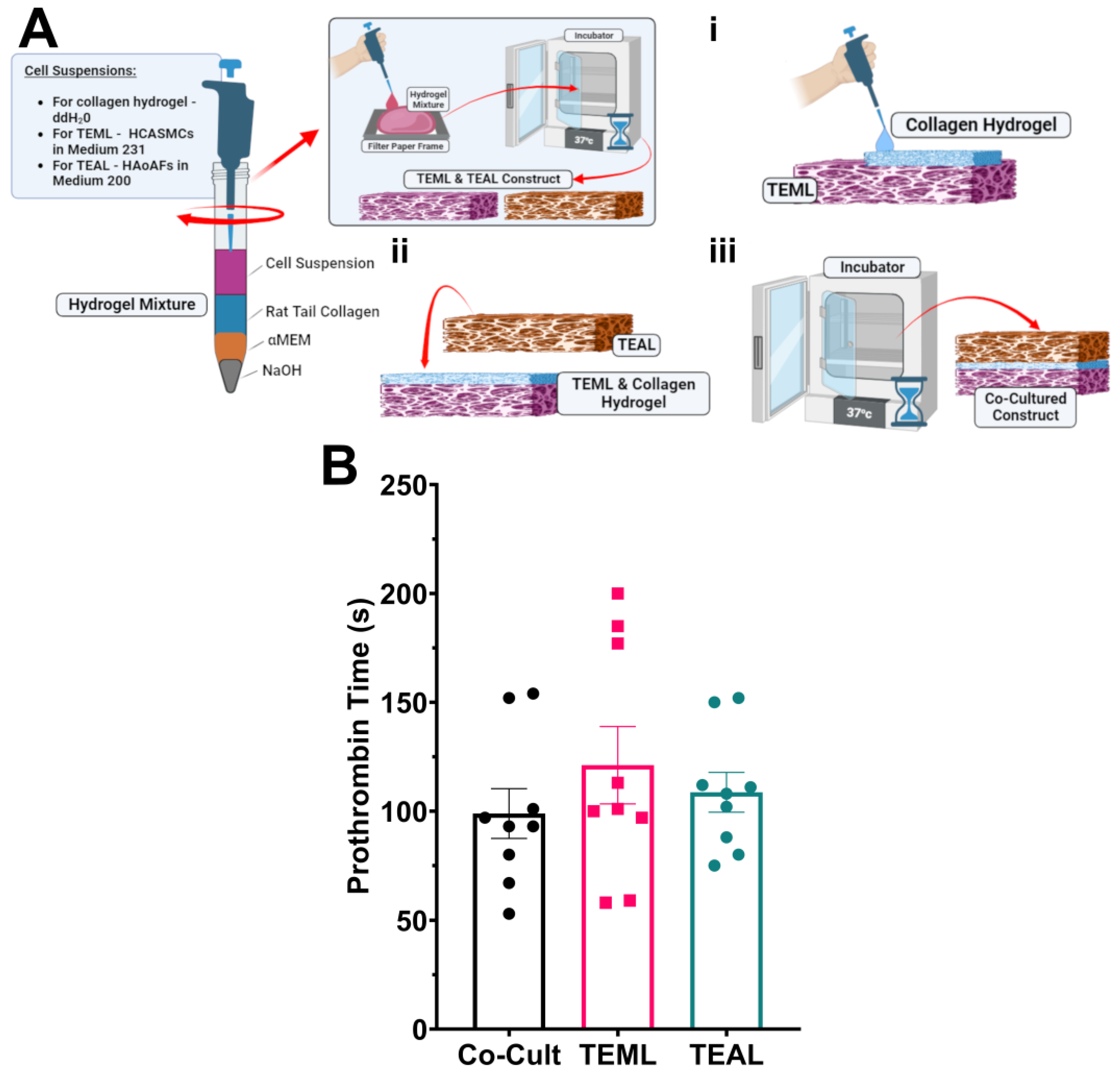
2.4. The TEML Hydrogels Trigger the Extrinsic Pathway of the Coagulation Cascade
2.5. Ascorbic Acid Supplementation Enhances the Tissue Factor Activity of the TEML Hydrogels
2.6. Ascorbic Acid Supplementation Did Not Enhance the Tissue Factor Activity of Adventitial Fibroblasts
2.7. An Adventitial Layer Is Not Required to Trigger Blood Coagulation
2.8. Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. D Culture of Primary HCASMCs and HAoAFs
4.3. Construction of 3D Tissue-Engineered Medial and Adventitial Layers
4.4. Preparation of Platelet-Poor Plasma and Washed Human Platelet Samples
4.5. Immunofluorescent Staining of Human Type I Collagen
4.6. Light Transmission Aggregometry
4.7. Parallel Flow Chamber Experiments
4.8. Prothrombin Assays
4.9. Tissue Factor Activity of TEML and TEAL
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palta, S.; Saroa, R.; Palta, A. Overview of the coagulation system. Indian J. Anaesth. 2014, 58, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlman, R.L. Mouse models of human disease: An evolutionary perspective. Evol. Med. Public. Health 2016, 2016, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooley, B.C. Murine arterial thrombus induction mechanism influences subsequent thrombodynamics. Thromb. Res. 2015, 135, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whinna, H.C. Overview of murine thrombosis models. Thromb. Res. 2008, 122, S64–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westrick, R.J.; Winn, M.E.; Eitzman, D.T. Murine models of vascular thrombosis (Eitzman series). Arterioscl. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 2079–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, S.M.; Reeve, J.L.; Myers, D.D.; Fay, W.P. Murine thrombosis models. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 92, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denis, C.V.; Dubois, C.; Brass, L.F.; Heemskerk, J.W.M.; Lenting, P.J. Towards standardization of in vivo thrombosis studies in mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 1641–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fay, W.; Eitzman, D.; Shapiro, A.; Madison, E.; Ginsburg, D. Platelets inhibit fibrinolysis in vitro by both plasminogen activator inhibitor-1-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Blood 1999, 83, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinides, S.; Schäfer, K.; Thinnes, T.; Loskutoff, D.J. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 and Its Cofactor Vitronectin Stabilize Arterial Thrombi After Vascular Injury in Mice. Circulation 2001, 103, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechler, B.; Gachet, C.; Léon, C. Comparison of arterial thrombosis models. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 1, 238–246. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenwaelder, S.M.; Jackson, S.P. Ferric chloride thrombosis model: Unraveling the vascular effects of a highly corrosive oxidant. Blood 2015, 126, 2652–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sashindranath, M.; Sales, E.; Daglas, M.; Freeman, R.; Samson, A.L.; Cops, E.J.; Medcalf, R.L. The mode of anesthesia influences outcome in mouse models of arterial thrombosis. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 3, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, M.V.; Gros, R.; Hackam, D.G. Translation of Cardiovascular Animal Models to Human Randomized Trials. Am. J. Cardiol. 2020, 137, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, N.K.R.; Mannino, R.G.; Lam, W.A.; Jain, A. Thrombosis-on-a-chip: Prospective impact of microphysiological models of vascular thrombosis. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 5, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.A. Thrombosis-on-a-Chip: A New Way to Model a Complex Process. Blood 2017, 130 (Suppl. 1), SCI-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, J.; Peaudecerf, F.J.; Masters, N.A.; Neeves, K.B.; Goldstein, R.E.; Harper, M.T. An “occlusive thrombosis-on-a-chip” microfluidic device for investigating the effect of anti-thrombotic drugs. Lab A Chip 2021, 21, 4104–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Oklu, R.; Albadawi, H. Bioengineered in vitro models of thrombosis: Methods and techniques. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2017, 7 (Suppl. 3), S329–S335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provenzale, I.; Brouns, S.L.N.; van der Meijden, P.E.J.; Swieringa, F.; Heemskerk, J.W.M. Whole Blood Based Multiparameter Assessment of Thrombus Formation in Standard Microfluidic Devices to Proxy In Vivo Haemostasis and Thrombosis. Micromachines 2019, 10, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poventud-Fuentes, I.; Kwon, K.W.; Seo, J.; Tomaiuolo, M.; Stalker, T.J.; Brass, L.F.; Huh, D. A Human Vascular Injury-on-a-Chip Model of Hemostasis. Small 2021, 17, 2004889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, F.I.; Harper, A.G.S.; Yang, Y. A Real-Time Monitoring System to Assess the Platelet Aggregatory Capacity of Components of a Tissue-Engineered Blood Vessel Wall. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2016, 22, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njoroge, W.; Hernández, A.C.H.; Musa, F.I.; Butler, R.; Harper, A.G.S.; Yang, Y. The Combination of Tissue-Engineered Blood Vessel Constructs and Parallel Flow Chamber Provides a Potential Alternative to In Vivo Drug Testing Models. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Bell, J.; Juliao, S.; Li, L.; May, J.M. Ascorbic Acid Uptake and Regulation of Type I Collagen Synthesis in Cultured Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. J. Vasc. Res. 2008, 46, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.M.; LuValle, P.A.; Zoia, O.; Quaglino, D.; Giro, M. Ascorbate Differentially Regulates Elastin and Collagen Biosynthesis in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells and Skin Fibroblasts by Pretranslational Mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, T.A.; Morrissey, J.H.; Edgington, T.S. Selective Cellular Expression of Tissue Factor in Human Tissues. Implications for Disorders of Hemostasis and Thrombosis. Am. J. Pathol. 1989, 134, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, J.N.; Smith, K.M.; Schwartz, S.M.; Gordon, D. Localization of Tissue Factor in the Normal Vessel Wall and in the Atherosclerotic Plaque. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 2839–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, S.P.; Mackman, N. Intrinsic Pathway of Coagulation and Thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackman, N.; Tilley, R.E.; Key, N.S. Role of the Extrinsic Pathway of Blood Coagulation in Hemostasis and Thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 1687–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, R.; Dave, J.M.; Chandran, R.R.; Misra, A.; Sheikh, A.Q.; Greif, D.M. Vascular Cells in Blood Vessel Wall Development and Disease. Adv. Pharmacol. 2017, 78, 323–350. [Google Scholar]
- Murad, S.; Grove, D.; Lindberg, K.A.; Reynolds, G.; Sivarajah, A.; Pinnell, S.R. Regulation of collagen synthesis by ascorbic acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 2879–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schecter, A.D.; Giesen, P.L.; Taby, O.; Rosenfield, C.L.; Rossikhina, M.; Fyfe, B.S.; Kohtz, D.S.; Fallon, J.T.; Nemerson, Y.; Taubman, M.B. Tissue factor expression in human arterial smooth muscle cells. TF is present in three cellular pools after growth factor stimulation. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 2276–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schecter, A.D.; Spirito, R.; Rossikhina, M.; Giesen, P.L.; Bogdanov, V.; Fallon, J.T.; Fisher, E.A.; Schnapp, L.M.; Nemerson, Y.; Taubman, M.B. Release of active tissue factor by human arterial smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schünbeck, U.; Funke-Kaiser, H.; Holzmeister, J.; Henke, S.; Mach, F.; Sukhova, G.K.; Libby, P. CD40 ligation induces tissue factor expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, P.; Golino, P.; Calabrò, P.; Calì, G.; Ragni, M.; De Rosa, S.; Cimmino, G.; Pacileo, M.; Forte, L.; De Palma, R.; et al. C-reactive protein induces tissue factor expression and promotes smooth muscle and endothelial cell proliferation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 68, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackman, N.; Taubman, M.B. Does tissue factor expression by vascular smooth muscle cells provide a link between C-reactive protein and cardiovascular disease? Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 601–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durante, W.; Liao, L.; Reyna, S.V.; Peyton, K.J.; Schafer, A.I. Physiological cyclic stretch directs L-arginine transport and metabolism to collagen synthesis in vascular smooth muscle. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.Y.M.; Glagov, S.; Mathews, M.B. Cyclic stretching stimulates synthesis of matrix components by arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro. Science 1976, 191, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumpio, B.E.; Banes, A.J.; Link, W.G.; Johnson, G. Enhanced collagen production by smooth muscle cells during repetitive mechanical stretching. Arch. Surg. 1988, 123, 1233–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, K.; Sakai, J.; Watanabe, T.; Ohyama, T.; Karino, T. Improved arterial wall model by coculturing vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2007, 43, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, E.; Bienkowski, R.S.; Coltoff-Schiller, B.; Goldfischer, S.; Blumenfeld, O.O. Changes in the components of extracellular matrix and in growth properties of cultured aortic smooth muscle cells upon ascorbate feeding. J. Cell. Biol. 1982, 92, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannino, R.G.; Qiu, Y.; Lam, W.A. Endothelial cell culture in microfluidic devices for investigating microvascular processes. Biomicrofluidics 2018, 12, 042203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coenen, D.M.; Mastenbroek, T.G.; Cosemans, J.M.E.M. Platelet interaction with activated endothelium: Mechanistic insights from microfluidics. Blood 2017, 130, 2819–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P.F.; Albers, H.J.; Linssen, J.E.A.; Middelkamp, H.H.T.; van der Hout, L.; Passier, R.; van den Berg, A.; Malda, J.; van der Meer, A.D. Mimicking arterial thrombosis in a 3D-printed microfluidic in vitro vascular model based on computed tomography angiography data. Lab A Chip 2017, 17, 2785–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbar, J.; Yang, Y.; Harper, A.G.S. Developing human tissue engineered arterial constructs to simulate human in vivo thrombus formation. Platelets 2023, 34, 2153823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ranjbar, J.; Njoroge, W.; Gibbins, J.M.; Roach, P.; Yang, Y.; Harper, A.G.S. Developing Biomimetic Hydrogels of the Arterial Wall as a Prothrombotic Substrate for In Vitro Human Thrombosis Models. Gels 2023, 9, 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9060477
Ranjbar J, Njoroge W, Gibbins JM, Roach P, Yang Y, Harper AGS. Developing Biomimetic Hydrogels of the Arterial Wall as a Prothrombotic Substrate for In Vitro Human Thrombosis Models. Gels. 2023; 9(6):477. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9060477
Chicago/Turabian StyleRanjbar, Jacob, Wanjiku Njoroge, Jonathan M. Gibbins, Paul Roach, Ying Yang, and Alan G. S. Harper. 2023. "Developing Biomimetic Hydrogels of the Arterial Wall as a Prothrombotic Substrate for In Vitro Human Thrombosis Models" Gels 9, no. 6: 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9060477
APA StyleRanjbar, J., Njoroge, W., Gibbins, J. M., Roach, P., Yang, Y., & Harper, A. G. S. (2023). Developing Biomimetic Hydrogels of the Arterial Wall as a Prothrombotic Substrate for In Vitro Human Thrombosis Models. Gels, 9(6), 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9060477