Tuning Pluronic Hydrogel Networks: Effects of Vancomycin Loading on Gelation, Rheological Properties, and Micellar Structures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effects of Vancomycin on Pluronic Gelation and Solubilisation Behaviour
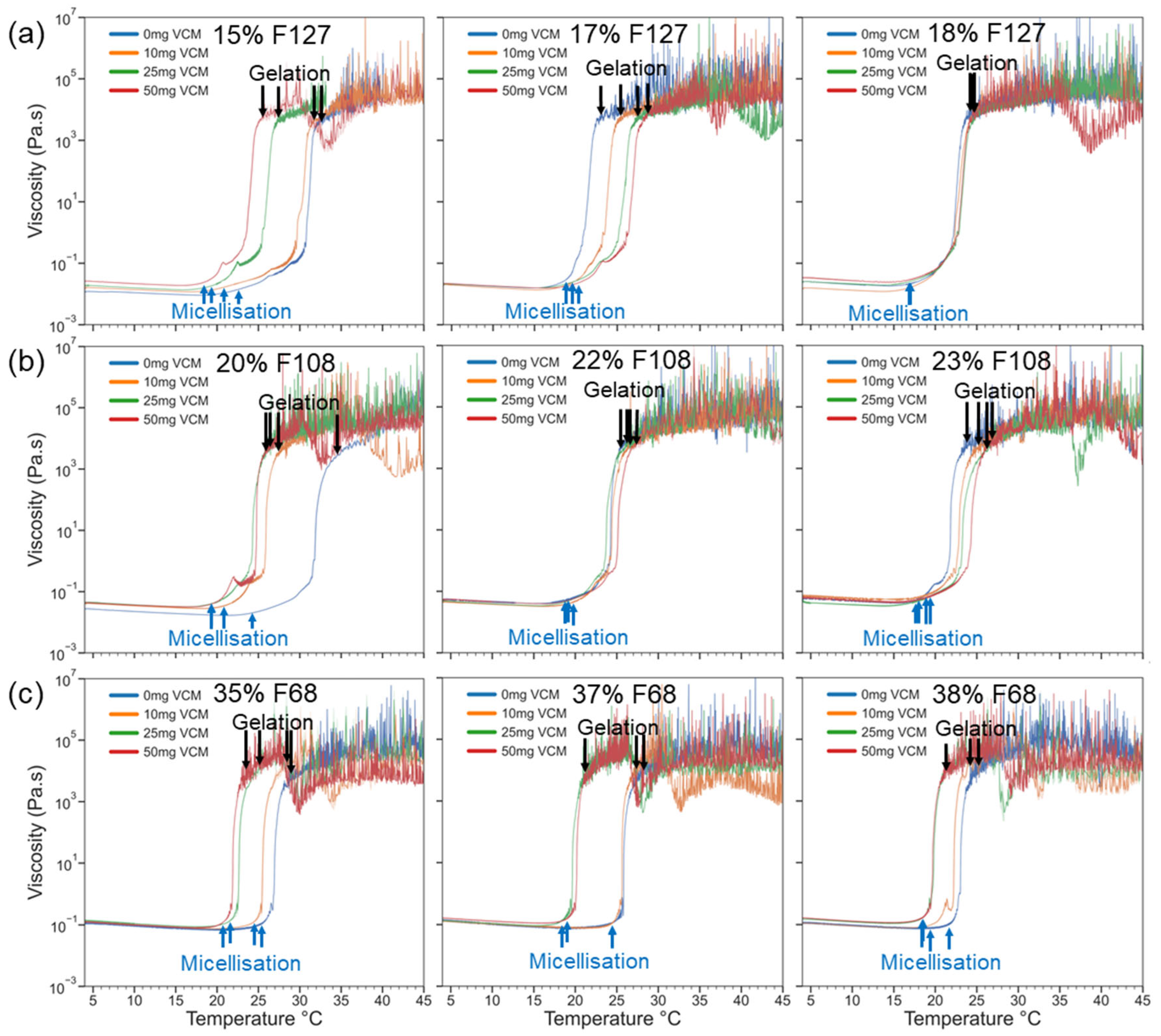
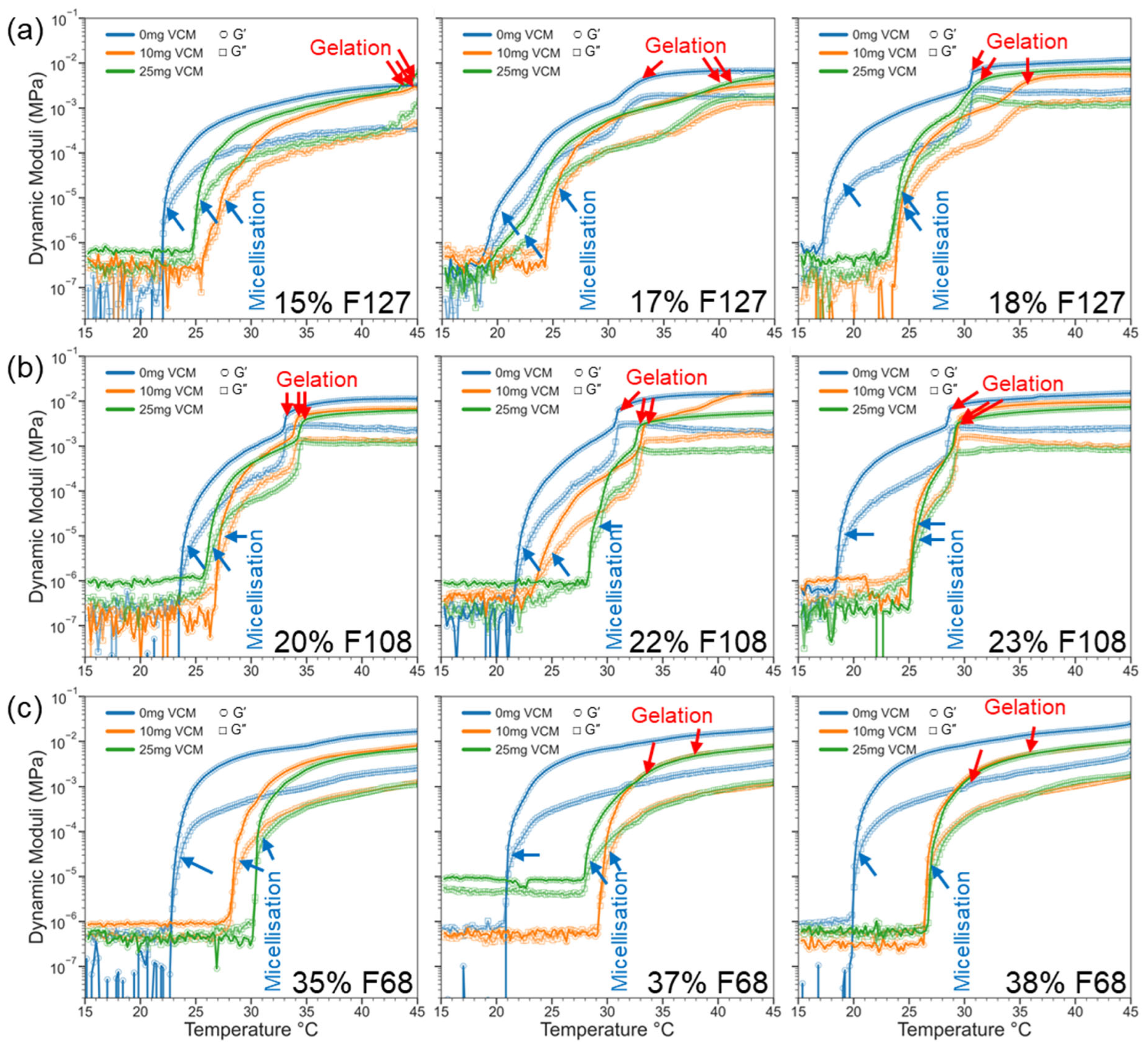
2.2. Micellisation, Gelation, and Viscoelasticity of Pluronic and Pluronic–Vancomycin Hydrogels
2.2.1. Pluronic Hydrogels
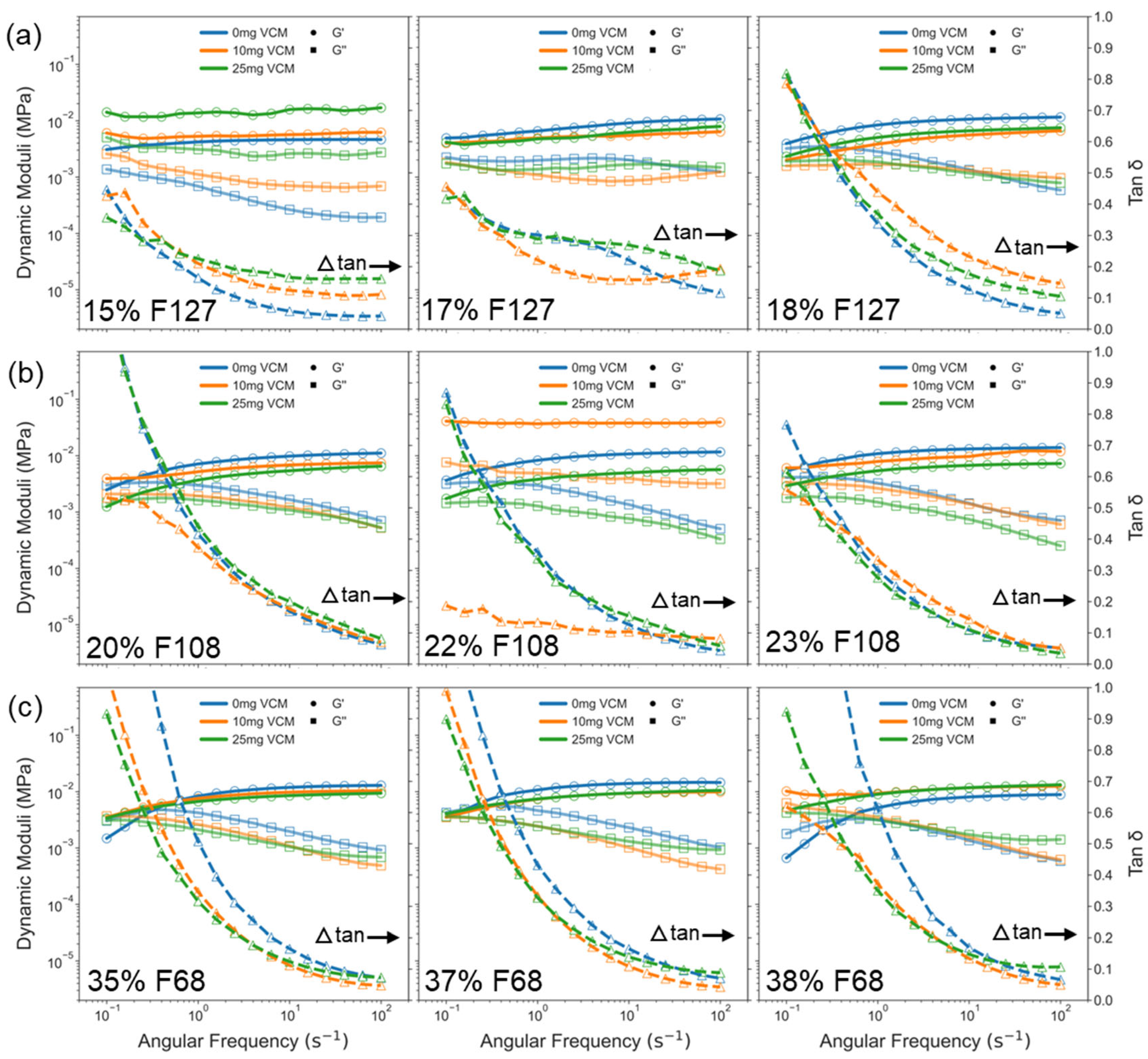
2.2.2. Gelation and Viscoelasticity of Pluronic–Vancomycin Hydrogels
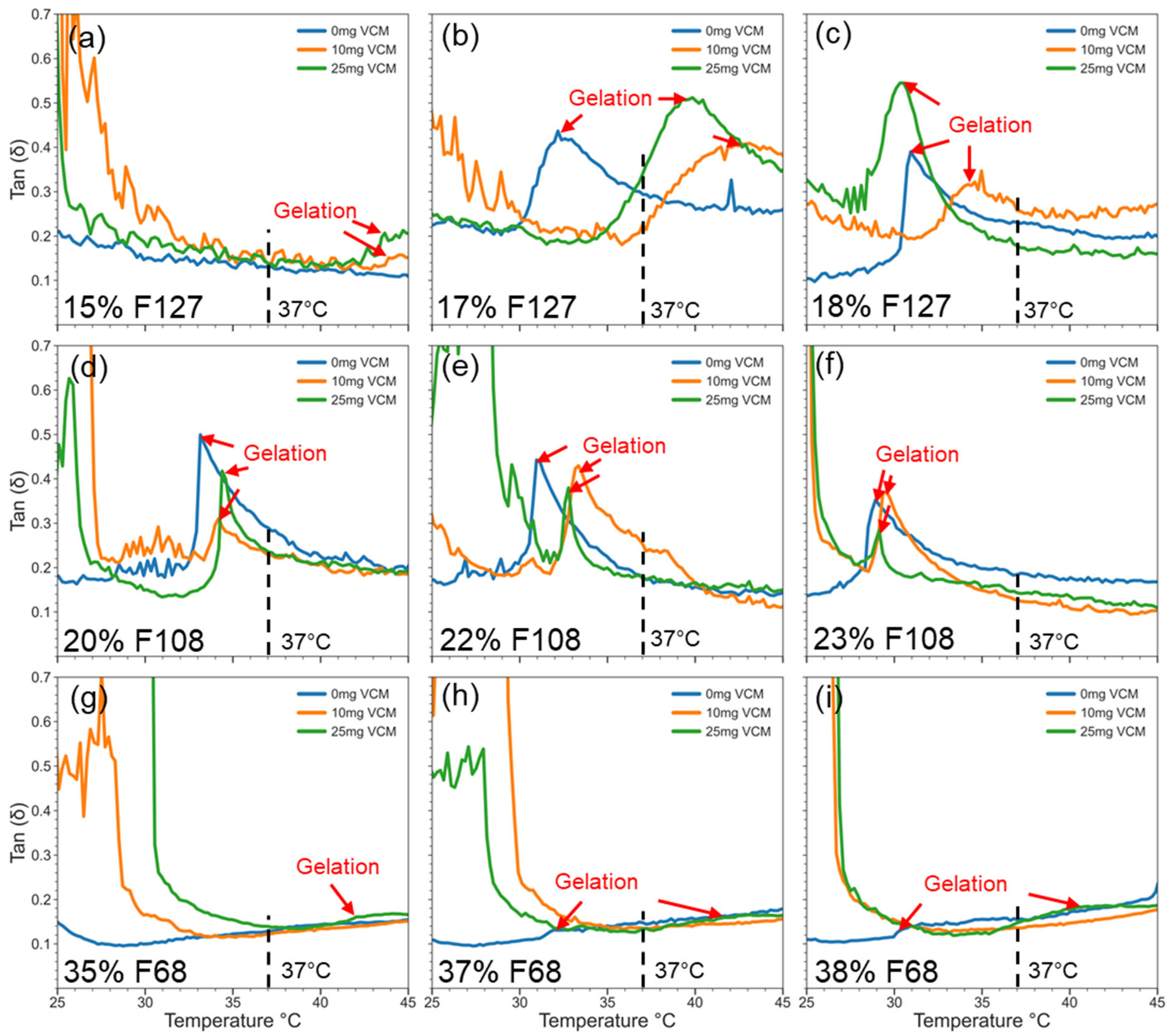
2.2.3. Viscoelasticity of Pluronic–Vancomycin Hydrogels at 37 °C
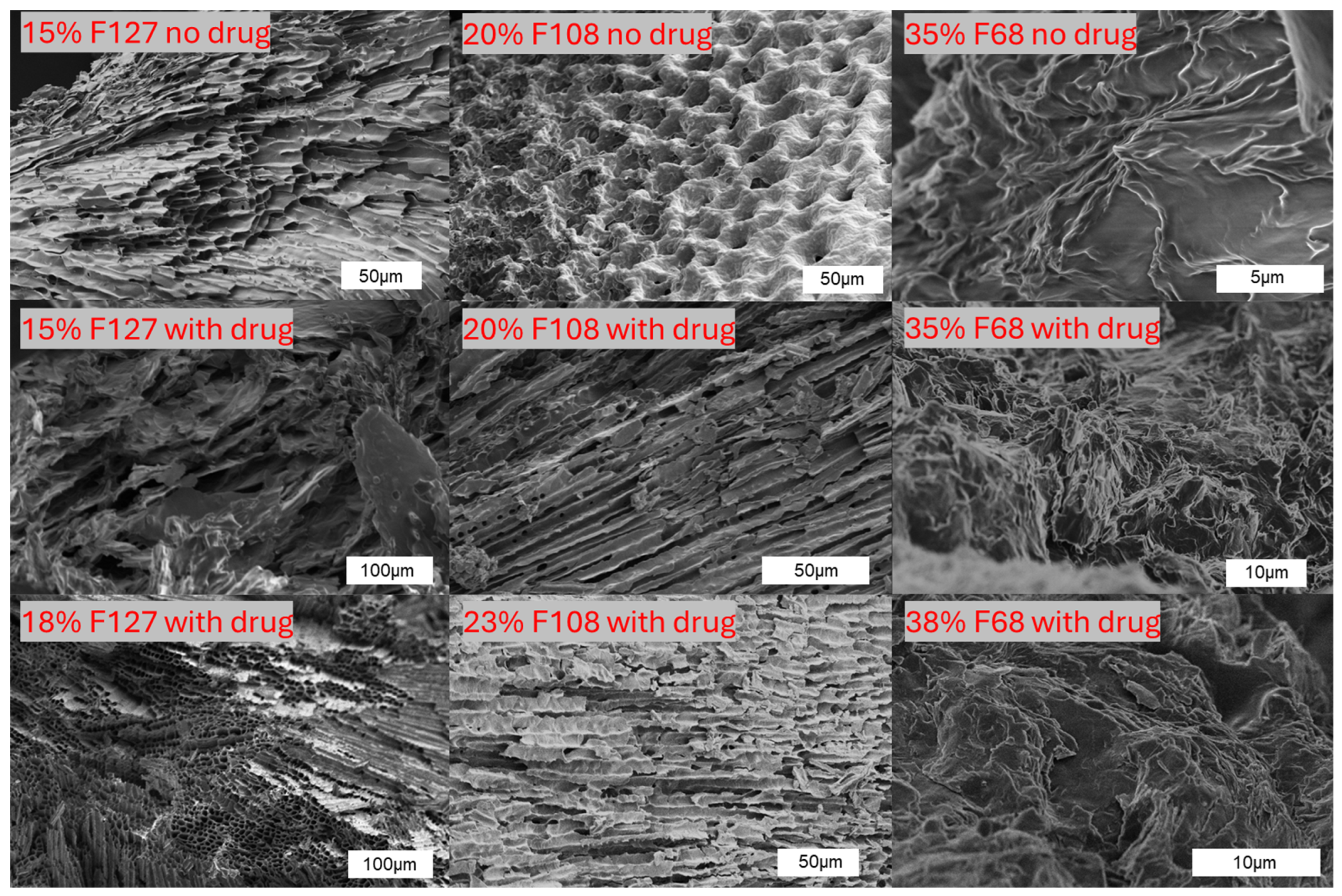
2.3. Microstructural Morphology by SEM
2.4. SAXS Characterisation of Hydrogel Structure
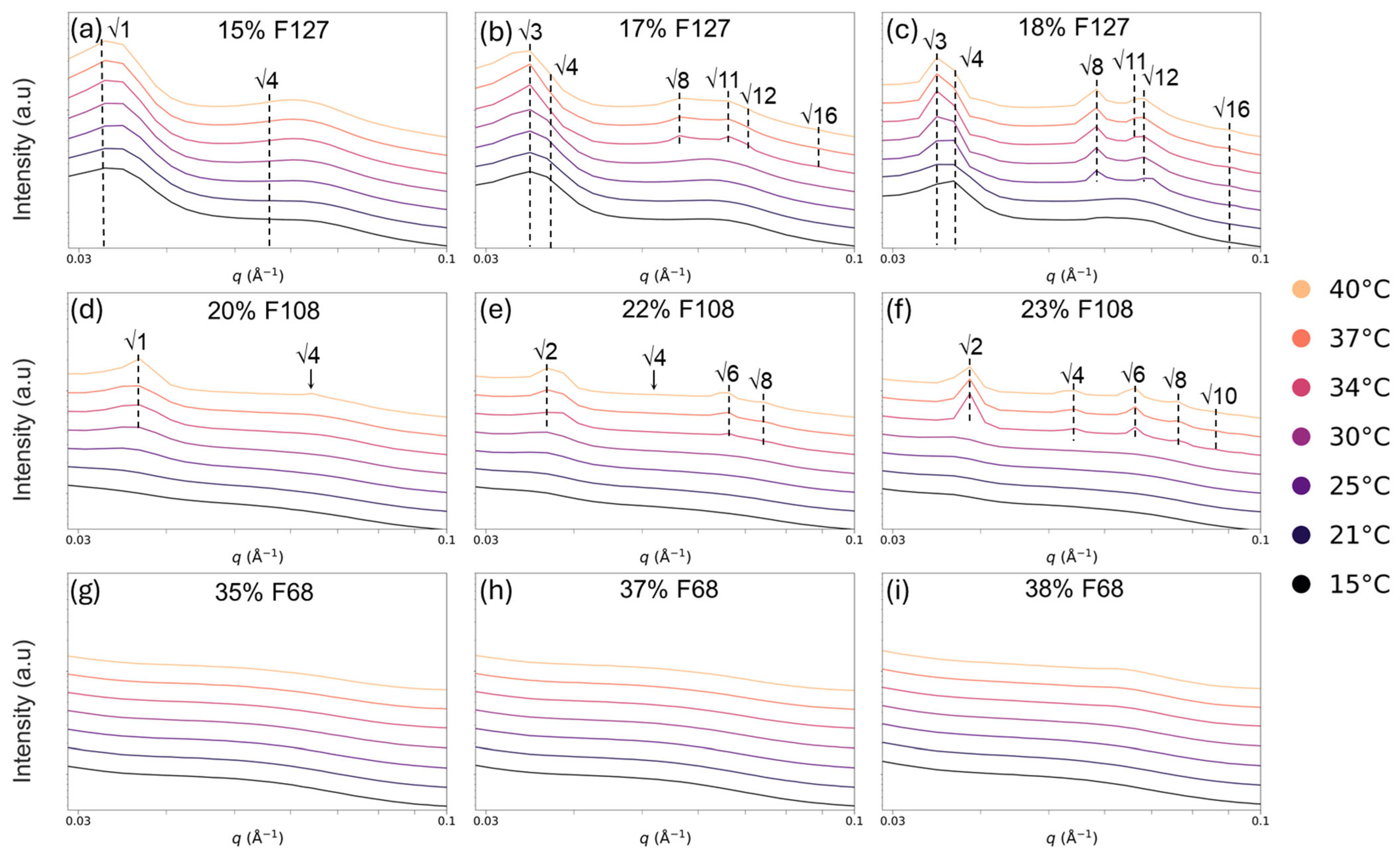
2.4.1. Pluronic Hydrogels: Phase Formation with Temperature and Concentration
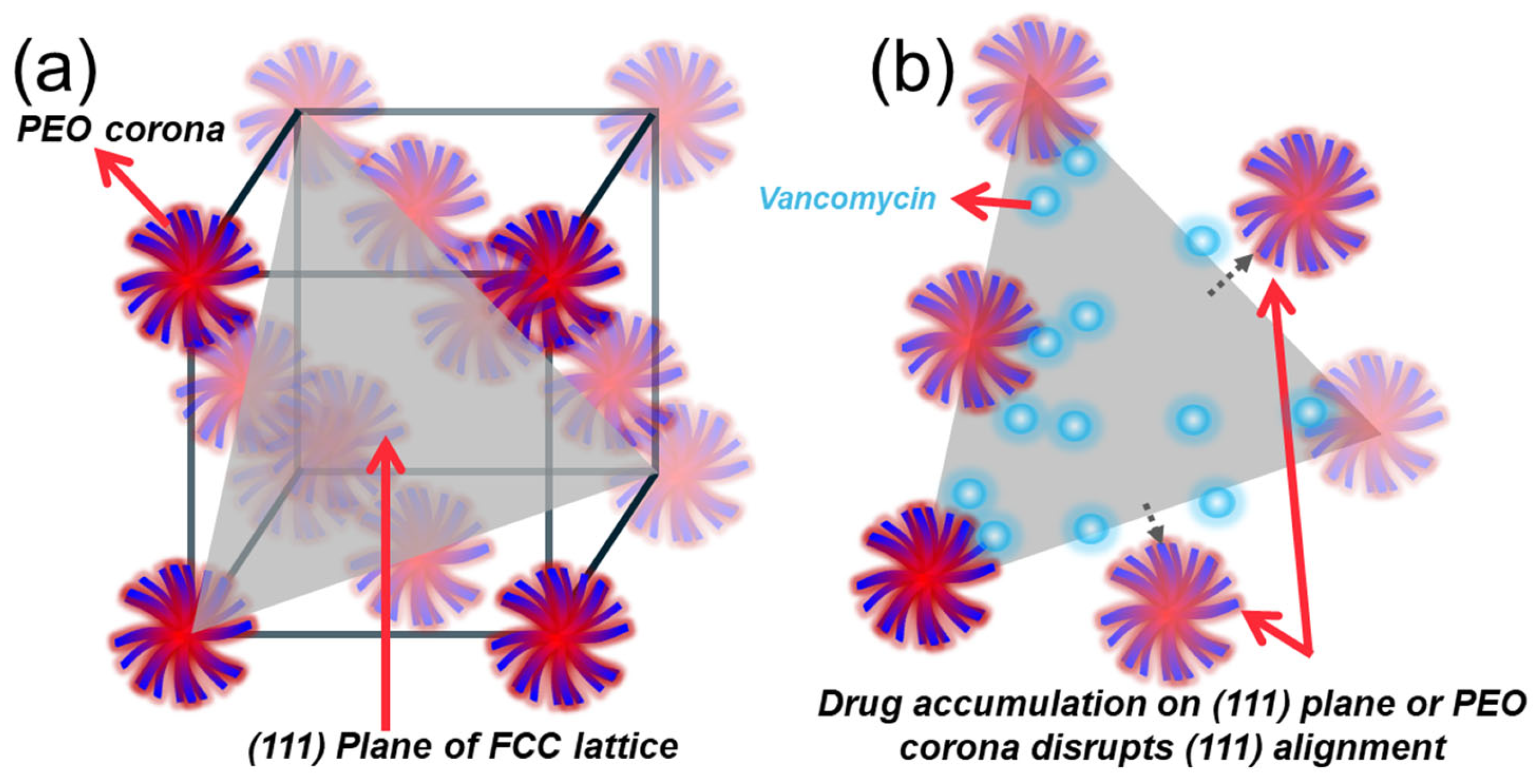
2.4.2. Micellar Organisation of Pluronic–Vancomycin Hydrogels at 37 °C
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Pluronic Hydrogel Preparation
4.2. Rheometric Experiments and Analysis
4.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.4. SAXS Experiments and Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDonald, D.J.; Fitzgerald, R., Jr.; Ilstrup, D. Two-stage reconstruction of a total hip arthroplasty because of infection. JBJS 1989, 71, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, J.R.; Callaway, G.H.; Salvati, E.A.; Pellicci, P.M.; Brause, B.D. Treatment of the infected total hip arthroplasty with a two-stage reimplantation protocol. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1994, 301, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadowska, U.; Brzychczy-Wloch, M.; Pamula, E. Injectable gellan gum-based nanoparticles-loaded system for the local delivery of vancomycin in osteomyelitis treatment. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2016, 27, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, S.L.; Hood, G.A.; Seligson, D. Long-term implantation of gentamicin-polymethylmethacrylate antibiotic beads. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1993, 295, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertazzoni Minelli, E.; Della Bora, T.; Benini, A. Different microbial biofilm formation on polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) bone cement loaded with gentamicin and vancomycin. Anaerobe 2011, 17, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neut, D.; van de Belt, H.; van Horn, J.R.; van der Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J. Residual gentamicin-release from antibiotic-loaded polymethylmethacrylate beads after 5 years of implantation. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1829–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, N.; Werner, S.; Elhaddad, M.; Davies, J.; Firoozabadi, R. Do Antibiotic Beads Need to be Removed? Arch. Bone Jt. Surg. 2020, 8, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darouiche, R.O. Treatment of infections associated with surgical implants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1422–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vugt, T.A.G.; Arts, J.J.; Geurts, J.A.P. Antibiotic-Loaded Polymethylmethacrylate Beads and Spacers in Treatment of Orthopedic Infections and the Role of Biofilm Formation. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akash, M.S.H.; Rehman, K. Recent progress in biomedical applications of Pluronic (PF127): Pharmaceutical perspectives. J. Control. Release 2015, 209, 120–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriky, B.; Kelly, A.; Isreb, M.; Babenko, M.; Mahmoudi, N.; Rogers, S.; Shebanova, O.; Snow, T.; Gough, T. Pluronic F127 thermosensitive injectable smart hydrogels for controlled drug delivery system development. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 565, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.B., Jr.; Shamji, M.F.; Nettles, D.L.; Hwang, P.; Setton, L.A. Sustained release of antibiotics from injectable and thermally responsive polypeptide depots. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 90, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.H.; Kim, J.K.; Song, K.S.; Noh, S.M.; Ghil, S.H.; Yuk, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Prevention of postsurgical tissue adhesion by anti-inflammatory drug-loaded pluronic mixtures with sol–gel transition behavior. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2005, 72, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioffredi, E.; Boffito, M.; Calzone, S.; Giannitelli, S.M.; Rainer, A.; Trombetta, M.; Mozetic, P.; Chiono, V. Pluronic F127 hydrogel characterization and biofabrication in cellularized constructs for tissue engineering applications. Procedia Cirp 2016, 49, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, A.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, X. Ultra-durable cell-free bioactive hydrogel with fast shape memory and on-demand drug release for cartilage regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.D.; Lietman, P.S.; Smith, C.R. Clinical Response to Aminoglycoside Therapy: Importance of the Ratio of Peak Concentration to Minimal Inhibitory Concentration. J. Infect. Dis. 1987, 155, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akash, M.S.H.; Rehman, K.; Sun, H.; Chen, S. Sustained delivery of IL-1Ra from PF127-gel reduces hyperglycemia in diabetic GK-rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grindel, J.M.; Jaworski, T.; Piraner, O.; Emanuele, R.M.; Balasubramanian, M. Distribution, metabolism, and excretion of a novel surface-active agent, purified poloxamer 188, in rats, dogs, and humans. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 1936–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prud’homme, R.K.; Wu, G.; Schneider, D.K. Structure and rheology studies of poly (oxyethylene−oxypropylene−oxyethylene) aqueous solution. Langmuir 1996, 12, 4651–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandridis, P.; Alan Hatton, T. Poly(ethylene oxide) poly(propylene oxide) poly(ethylene oxide) block copolymer surfactants in aqueous solutions and at interfaces: Thermodynamics, structure, dynamics, and modeling. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1995, 96, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naharros-Molinero, A.; Caballo-González, M.Á.; de la Mata, F.J.; García-Gallego, S. Direct and reverse pluronic micelles: Design and characterization of promising drug delivery nanosystems. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picheth, G.F.; Marini, T.C.; Taladriz-Blanco, P.; Shimamoto, G.G.; dos Santos, G.J.V.P.; Meneau, F.; de Oliveira, M.G. Influence of Pluronic F127 microenvironments on the photochemical nitric oxide release from S-nitrosoglutathione. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 544, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.L.; Mensah, L.M.; Love, B.J. The effect of cisplatin on the nanoscale structure of aqueous PEO-PPO-PEO micelles of varying hydrophilicity observed using SAXS. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 3970–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, S.; Di Sarno, A.; D’Apuzzo, M.; Avallone, P.R.; Raccone, E.; Bellissimo, A.; Auriemma, F.; Grizzuti, N.; Pasquino, R. Rheology and morphology of Pluronic F68 in water. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 043113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.C.; Sadhale, Y.; Chilukuri, D.M. Cubic phase gels as drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 47, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi, M.; Pescina, S.; Padula, C.; Santi, P.; Del Favero, E.; Cantù, L.; Nicoli, S. Polymeric micelles in drug delivery: An insight of the techniques for their characterization and assessment in biorelevant conditions. J. Control. Release 2021, 332, 312–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanka, G.; Hoffmann, H.; Ulbricht, W. Phase diagrams and aggregation behavior of poly (oxyethylene)-poly (oxypropylene)-poly (oxyethylene) triblock copolymers in aqueous solutions. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 4145–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulthe, S.S.; Choudhari, Y.M.; Inamdar, N.N.; Mourya, V. Polymeric micelles: Authoritative aspects for drug delivery. Des. Monomers Polym. 2012, 15, 465–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, B.; Cosgrove, T.; Hammouda, B. Pluronic Triblock Copolymer Systems and Their Interactions with Ibuprofen. Langmuir 2009, 25, 6760–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherlund, M.; Malmsten, M.; Holmqvist, P.; Brodin, A. Thermosetting microemulsions and mixed micellar solutions as drug delivery systems for periodontal anesthesia. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 194, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Bhatia, S.R. Effect of anti-inflammatories on Pluronic® F127: Micellar assembly, gelation and partitioning. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 278, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obaidat, R.; Abu Kwiak, A.D.; Hamed, R. Development of combined therapy of metronidazole and ibuprofen using in situ microgels for the treatment of periodontitis. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 71, 103314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.-H.; Wang, Y.; Guo, C.; Liu, H.-Z.; Tang, Y.-L.; Bahadur, P. Oil-Induced Aggregation of Block Copolymer in Aqueous Solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 11140–11148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.-L.; Wei, X.-F.; Liu, H.-Z. Influence of 1-Pentanol on the Micellization of Poly(ethylene oxide)−Poly(propylene oxide)−Poly(ethylene oxide) Block Copolymers in Aqueous Solutions. Langmuir 2003, 19, 2995–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Colby, R.H.; Thiyagarajan, P. Temperature and hydrophobic alcohol-induced structural changes of Pluronics micelles. Phys. B Condensed Matter 2006, 385–386, 685–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, R.; Lindman, B.; Alexandridis, P. Modification of the lyotropic liquid crystalline microstructure of amphiphilic block copolymers in the presence of cosolvents. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 89–90, 351–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Lei, F.; Luo, R.; Fei, Q.; Zheng, Z.; He, N.; Gui, S. Development of a Thermosensitive In-Situ Gel Formulations of Vancomycin Hydrochloride: Design, Preparation, In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 2552–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veyries, M.L.; Couarraze, G.; Geiger, S.; Agnely, F.; Massias, L.; Kunzli, B.; Faurisson, F.; Rouveix, B. Controlled release of vancomycin from Poloxamer 407 gels. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 192, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, P.E.; Wilhelm, M.P. Vancomycin. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1987, 62, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Barrena, E.; Esteban, J.; Medel, F.; Molina-Manso, D.; Ortiz-Pérez, A.; Cordero-Ampuero, J.; Puértolas, J.A. Bacterial adherence to separated modular components in joint prosthesis: A clinical study. J. Orthop. Res. 2012, 30, 1634–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Degen, M.; Grupido, N.; Bendle, S.; Pennartz, P. Effects of molecular weight, temperature and salt on the self assembly of triblock copolymer solutions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 528, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laquintana, V.; Lopedota, A.A.; Ivone, M.; Denora, N.; Franco, M.; Palazzo, G.; Gentile, L. Celecoxib-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex in a chitosan/PEO-PPO-PEO block copolymer matrix: Structural effect and drug release. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 660, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, L. Molecular interactions between PEO–PPO–PEO and PPO–PEO–PPO triblock copolymers in aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 484, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.; Rossella Delpiano, G.; Carucci, C.; Grosso, M.; Dessì, C.; Söderman, O.; Lindman, B.; Monduzzi, M.; Salis, A. Tuning Pluronic F127 phase transitions by adding physiological amounts of salts: A rheology, SAXS, and NMR investigation. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 204, 112714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; He, F.; Chen, S.; Poudel, A.J.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Xiang, F.; Li, S. Preparation and antibacterial activity of thermo-responsive nanohydrogels from qiai essential oil and pluronic F108. Molecules 2021, 26, 5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callan, M.; Jang, E.; Kelly, J.; Nguyen, K.; Marmorat, C.; Rafailovich, M.H. Characterization of Pluronic F 127 for the Controlled Drug Release Vancomycin in the Spinal Column. J. Undergrad. Chem. Eng. Res. 2017, 6, 6–19. [Google Scholar]
- Šturcová, A.; Schmidt, P.; Dybal, J. Role of hydration and water coordination in micellization of Pluronic block copolymers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 352, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupu, A.; Rosca, I.; Gradinaru, V.R.; Bercea, M. Temperature Induced Gelation and Antimicrobial Properties of Pluronic F127 Based Systems. Polymers 2023, 15, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Qiu, H.; Yin, S.; Wang, H.; Li, Y. Polymeric Drug Delivery System Based on Pluronics for Cancer Treatment. Molecules 2021, 26, 3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DesNoyer, J.R.; McHugh, A.J. The effect of Pluronic on the protein release kinetics of an injectable drug delivery system. J. Control. Release 2003, 86, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, K.; Batsberg, W.; Hvidt, S. Effects of PEO−PPO diblock impurities on the cubic structure of aqueous PEO−PPO−PEO pluronics micelles: Fcc and bcc ordered structures in F127. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 1720–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Sprik, R.; Poon, W.C.K.; Eiser, E. Effect of salt on the phase behaviour of F68 triblock PEO/PPO/PEO copolymer. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2006, 18, 4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, R.; Bandyopadhyay, R. Encapsulation of Hydrophobic Drugs in Pluronic F127 Micelles: Effects of Drug Hydrophobicity, Solution Temperature, and pH. Langmuir 2013, 29, 4350–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-F.; Wang, M.-R.; Lin, T.-L.; Yang, C.-H.; Chen, L.-J. Dynamic Behavior of the Structural Phase Transition of Hydrogel Formation Induced by Temperature Ramp and Addition of Ibuprofen. Langmuir 2020, 36, 8929–8938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deiringer, N.; Fischer, F.; Hofsäss, M.; Ranft, M.; Ebert, S. Alteration of gel point of poloxamer 338 induced by pharmaceutical actives and excipients. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2025, 207, 114628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, K.P.; Elliott, G.R.; Robertson, H.; Kumar, A.; Wanless, E.J.; Webber, G.B.; Craig, V.S.; Andersson, G.G.; Page, A.J. Understanding specific ion effects and the Hofmeister series. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 12682–12718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, B.K.; Wang, Q.; Sun, W.; Li, L. Micellization to gelation of a triblock copolymer in water: Thermoreversibility and scaling. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 2014–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Li, J.; Candiloro, Z.P.J.; Cai, X.; Su, Y.; Li, H.; Tran, N.; Zhai, J.; Martin, A.V.; Drummond, C.J.; et al. Alginate-ionic liquid injectable hydrogels supporting protein crystallization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 307, 142166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.; Hocquet, M.; Eon, B.; Sangwan, P.; Ratcliffe, J.; Hinton, T.M.; White, J.; Ozcelik, B.; Reynolds, N.P.; Muir, B.W. Non-lamellar lyotropic liquid crystalline nanoparticles enhance the antibacterial effects of rifampicin against Staphylococcus aureus. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 519, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.; Zhai, J.; Conn, C.E.; Mulet, X.; Waddington, L.J.; Drummond, C.J. Direct Visualization of the Structural Transformation between the Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Lamellar and Bicontinuous Cubic Mesophase. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 3397–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
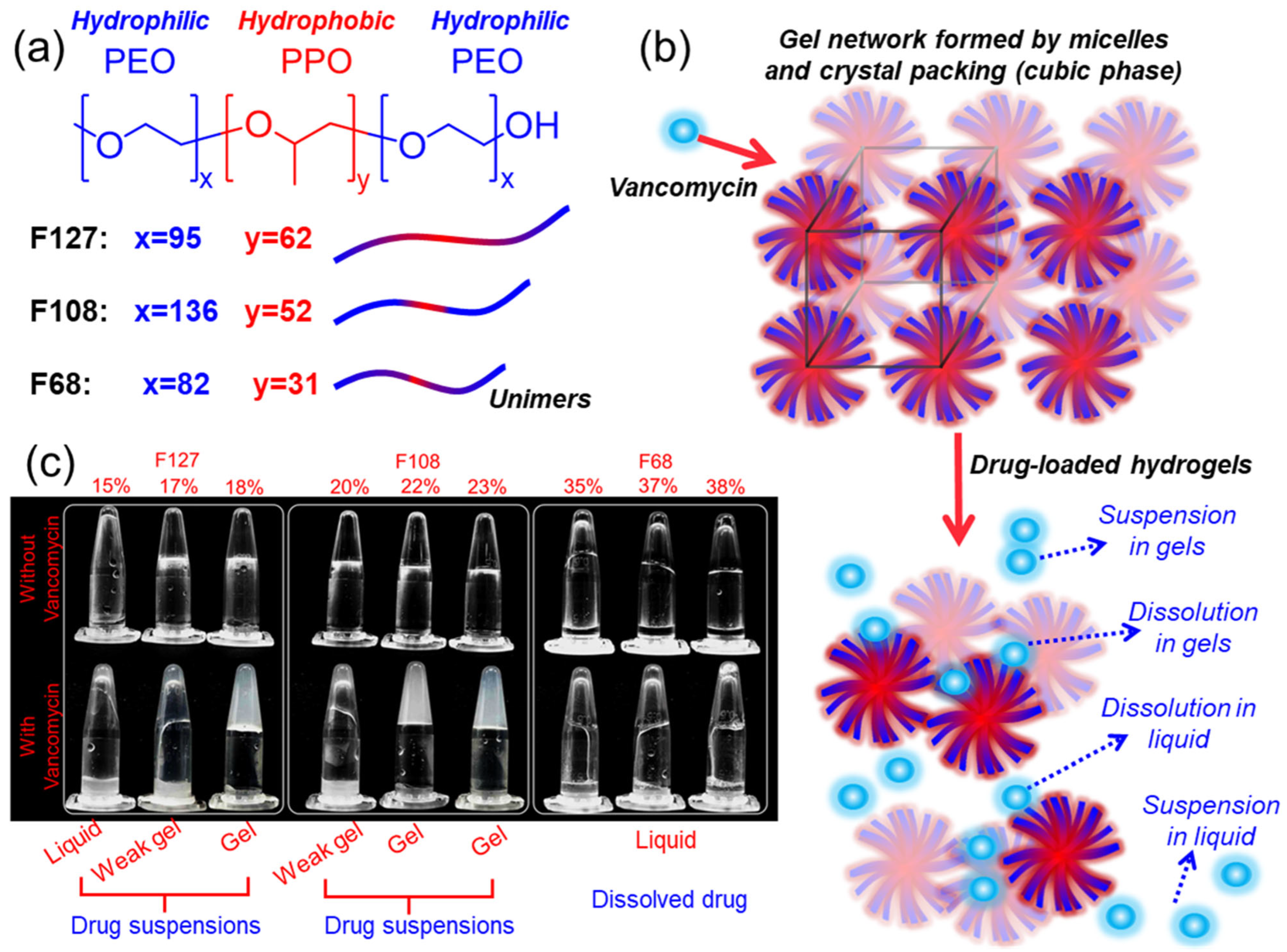


| Polymer in 1 mL of Water (mg) | Polymer Concentration (wt%) | Vancomycin Quantity in 1 mL of Water a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | 25 mg | 50 mg | |||
| wt% | wt% | wt% | |||
| F127 | 175 | 15% | 0.8% | 2.1% | 4.1% |
| 200 | 17% | 0.8% | 2.0% | 4.0% | |
| 225 | 18% | 0.8% | 2.0% | 3.9% | |
| F108 | 250 | 20% | 0.8% | 2.0% | 3.8% |
| 275 | 22% | 0.8% | 1.9% | 3.8% | |
| 300 | 23% | 0.8% | 1.9% | 3.7% | |
| F68 | 550 | 35% | 0.6% | 1.6% | 3.1% |
| 575 | 37% | 0.6% | 1.6% | 3.1% | |
| 600 | 38% | 0.6% | 1.5% | 3.0% | |
| Polymer | Concentration (wt%) | CMT from Flow/Osc (°C) a | CGT from Flow/Osc (°C) b | Tan δ at 37 °C c | Rheology Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F127 | 15% | 22/22 | 33/- | <0.6 | Weak incomplete gelation d |
| 17% | 19/19 | 27/33 | 0.32 | Good gelation, elastic plateau | |
| 18% | 17/17.5 | 25/31 | 0.25 | Strong gel, early gelation | |
| F108 | 20% | 26/24 | 35/33 | 0.45 | Gradual gelation, moderate strength |
| 22% | 20/22 | 26/31 | 0.29 | Strong gel, steady plateau | |
| 23% | 18/19 | 24/29 | 0.27 | Strong gel, stable LVR | |
| F68 | 35% | 26/23.5 | 30/- | <0.6 | Solution state, no clear CGT |
| 37% | 25/21.5 | 28/32 | 0.34 | Weak gel, low-strength network | |
| 38% | 22/20.5 | 26/30.5 | 0.3 | Weak but structured gel |
| Polymer Conc. (wt%) | CMT (°C) of Samples with 0/10/25 mg Vancomycin | CGT (°C) of Samples with 0/10/25 mg Vancomycin | Tan δ at 37 °C (25 mg Vancomycin) | Rheology Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F127 15% | 22/21/19 | 33/32/27.5 | >0.6 | Weak gel, improved by vancomycin |
| F127 17% | 19.0/19.5/19.5 | 24/25.5/27.5 | 0.37 | CGT delayed with vancomycin, moderate strength |
| F127 18% | 17.0/17.0/17.0 | 24/24.5/24.5 | 0.29 | Strong, stable gelation |
| F108 20% | 26/21/19 | 35/27.5/26.5 | 0.35 | CMT/CGT reduced by vancomycin, moderate gel |
| F108 22% | 20/22/22 | 26/26.5/26.5 | 0.27 | Very stable gelation, low interference |
| F108 23% | 18/19/18 | 24/25/26 | 0.25 | Strong gel, minimal change |
| F68 35% | 26/25/22 | 30/28.5/25 | >0.5 | Weak gel, early gelation with vancomycin |
| F68 37% | 25/25/19 | 28/27/21 | 0.33 | Gelation improved, but low strength |
| F68 38% | 22/20/19 | 26/24/21 | 0.3 | Early CGT, still weak gel |
| Temp (°C) | F127-15% | F127-17% | F127-18% | F108-20% | F108-22% | F108-23% | F68-35% | F68-37% | F68-38% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | Less ordered | Less ordered | Less ordered | Solution | Solution | Solution | Solution | Solution | Solution |
| 20 | Less ordered | Less ordered | FCC (311 *) | Solution | Solution | Solution | Solution | Solution | Solution |
| 25 | Less ordered | Less ordered | FCC (307) | Less ordered | Less ordered | Less ordered | Solution | Solution | Solution |
| 30 | Less ordered | Less ordered | FCC (308) | Less ordered | Less ordered | Less ordered | Solution | Solution | Solution |
| 35 | Less ordered | FCC (318) | FCC (309) | Less ordered | Hex (171) | BCC (237) | Solution | Solution | Solution |
| 37 | Less ordered | FCC (319) | FCC (310) | Less ordered | Hex (170) | BCC (234) | Solution | Solution | Solution |
| 40 | Less ordered | FCC (316) | FCC (318) | Hex (172) | BCC (240) | BCC (241) | Solution | Solution | Solution |
| Temp (°C) | F127-15% | F127-17% | F127-18% | F108-20% | F108-22% | F108-23% | F68-35% | F68-37% | F68-38% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 mg | Less Ordered | FCC | FCC | Less Ordered | Hex | BCC | Less Ordered | Less Ordered | Less Ordered |
| 10 mg | Less Ordered | FCC | FCC | Less Ordered | BCC | BCC | Less Ordered | Less Ordered | Less Ordered |
| 25 mg | Less Ordered | Less Ordered | FCC | Less Ordered | Less Ordered | BCC | Less Ordered | Less Ordered | Less Ordered |
| 50 mg | Less Ordered | Less Ordered | FCC | Less Ordered | BCC | BCC | Less Ordered | Less Ordered | Less Ordered |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaffney, M.J.; Han, Q.; Fox, K.; Tran, N. Tuning Pluronic Hydrogel Networks: Effects of Vancomycin Loading on Gelation, Rheological Properties, and Micellar Structures. Gels 2025, 11, 688. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090688
Gaffney MJ, Han Q, Fox K, Tran N. Tuning Pluronic Hydrogel Networks: Effects of Vancomycin Loading on Gelation, Rheological Properties, and Micellar Structures. Gels. 2025; 11(9):688. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090688
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaffney, Michael J., Qi Han, Kate Fox, and Nhiem Tran. 2025. "Tuning Pluronic Hydrogel Networks: Effects of Vancomycin Loading on Gelation, Rheological Properties, and Micellar Structures" Gels 11, no. 9: 688. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090688
APA StyleGaffney, M. J., Han, Q., Fox, K., & Tran, N. (2025). Tuning Pluronic Hydrogel Networks: Effects of Vancomycin Loading on Gelation, Rheological Properties, and Micellar Structures. Gels, 11(9), 688. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090688







