Amino Acid-Based Hydrophobic Cryogels for Efficient Methylene Blue Removal: A Reusable and Eco-Friendly Approach to Dye-Contaminated Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
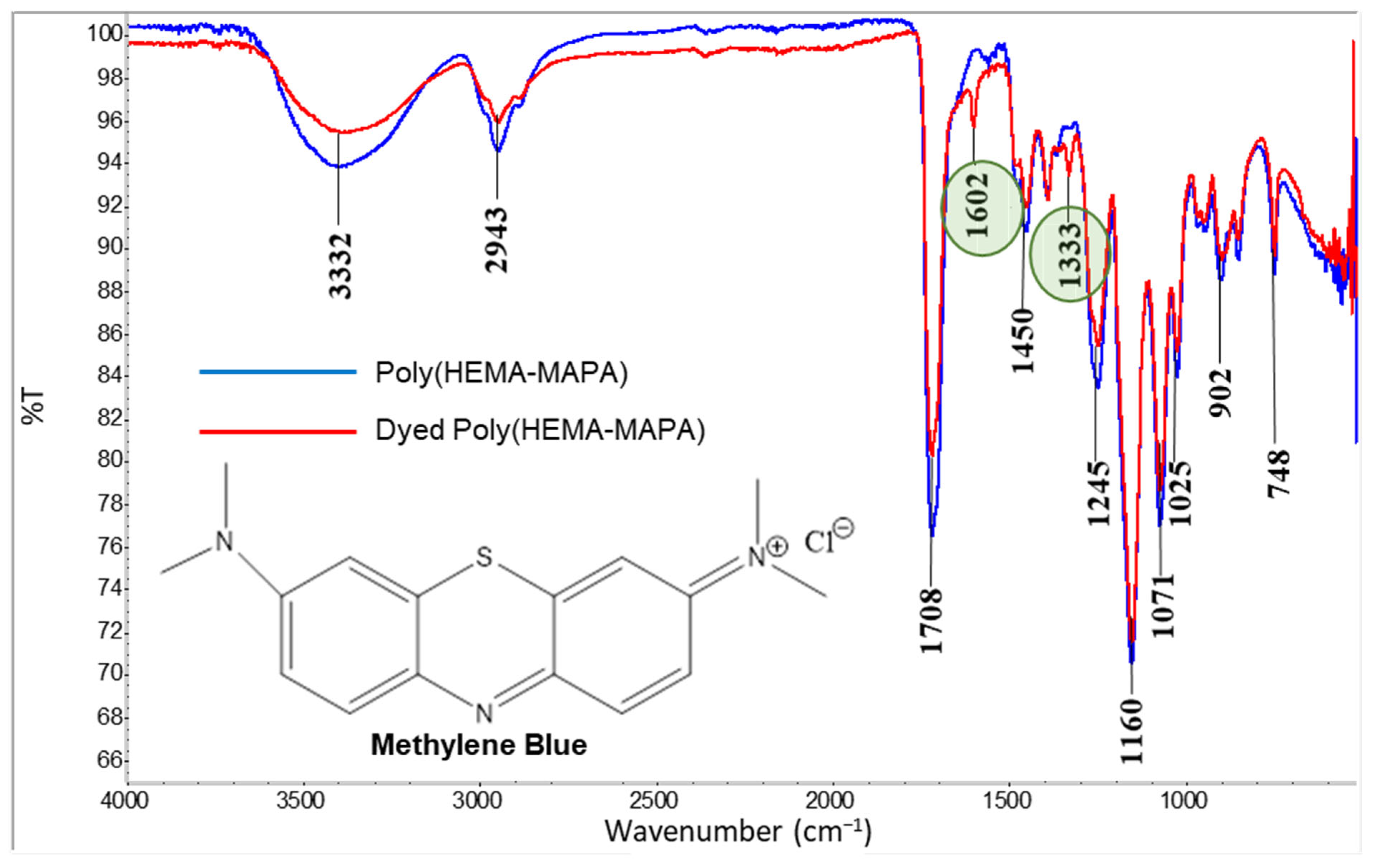
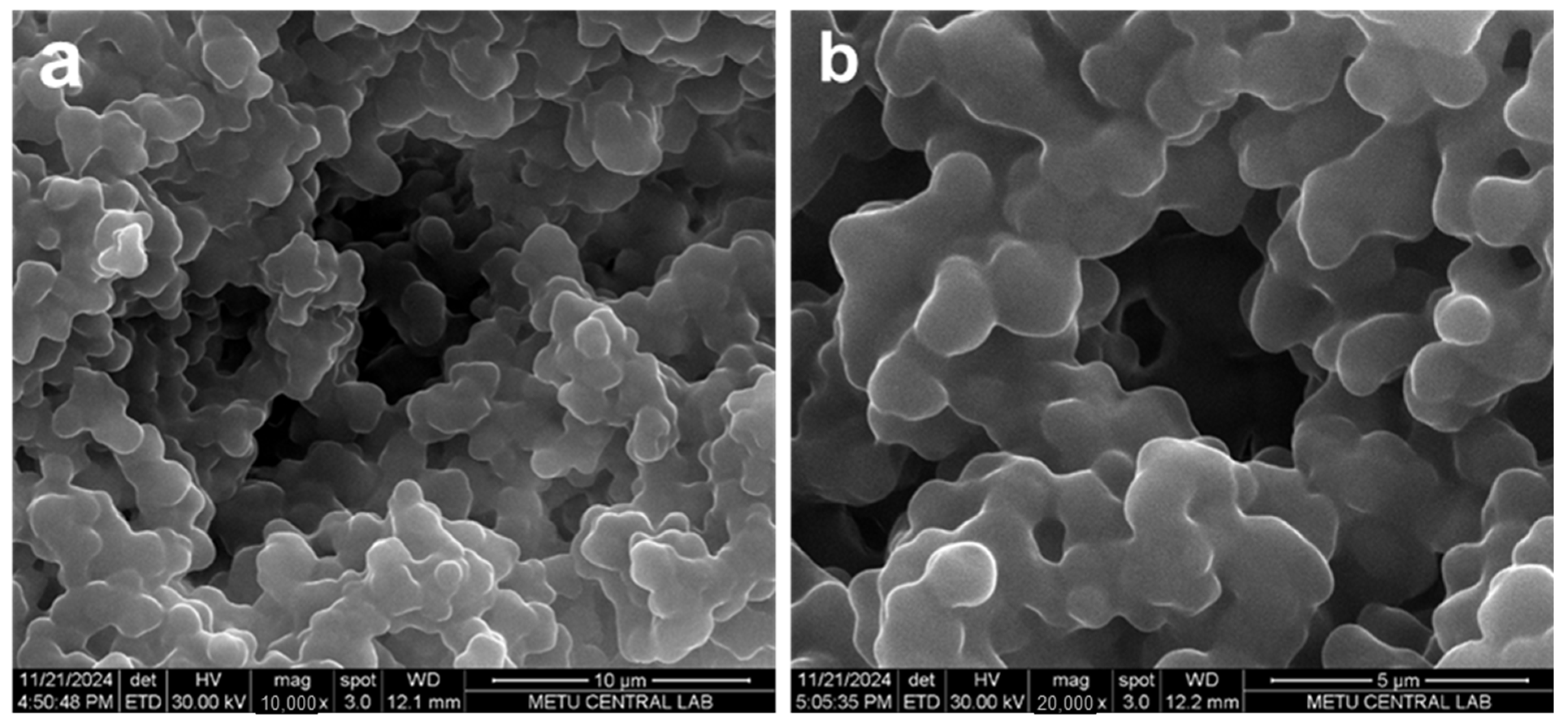
2.1. Characterization
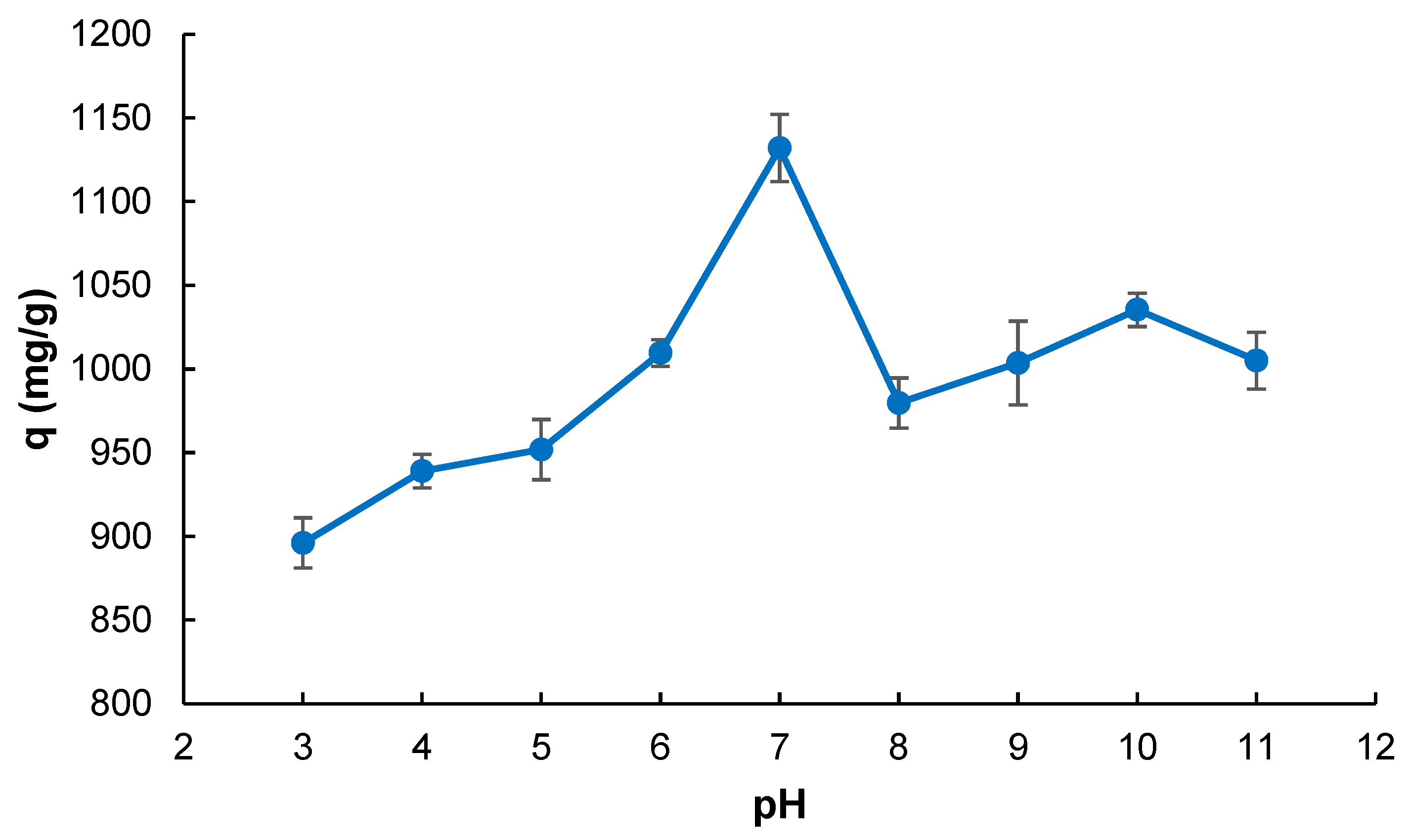
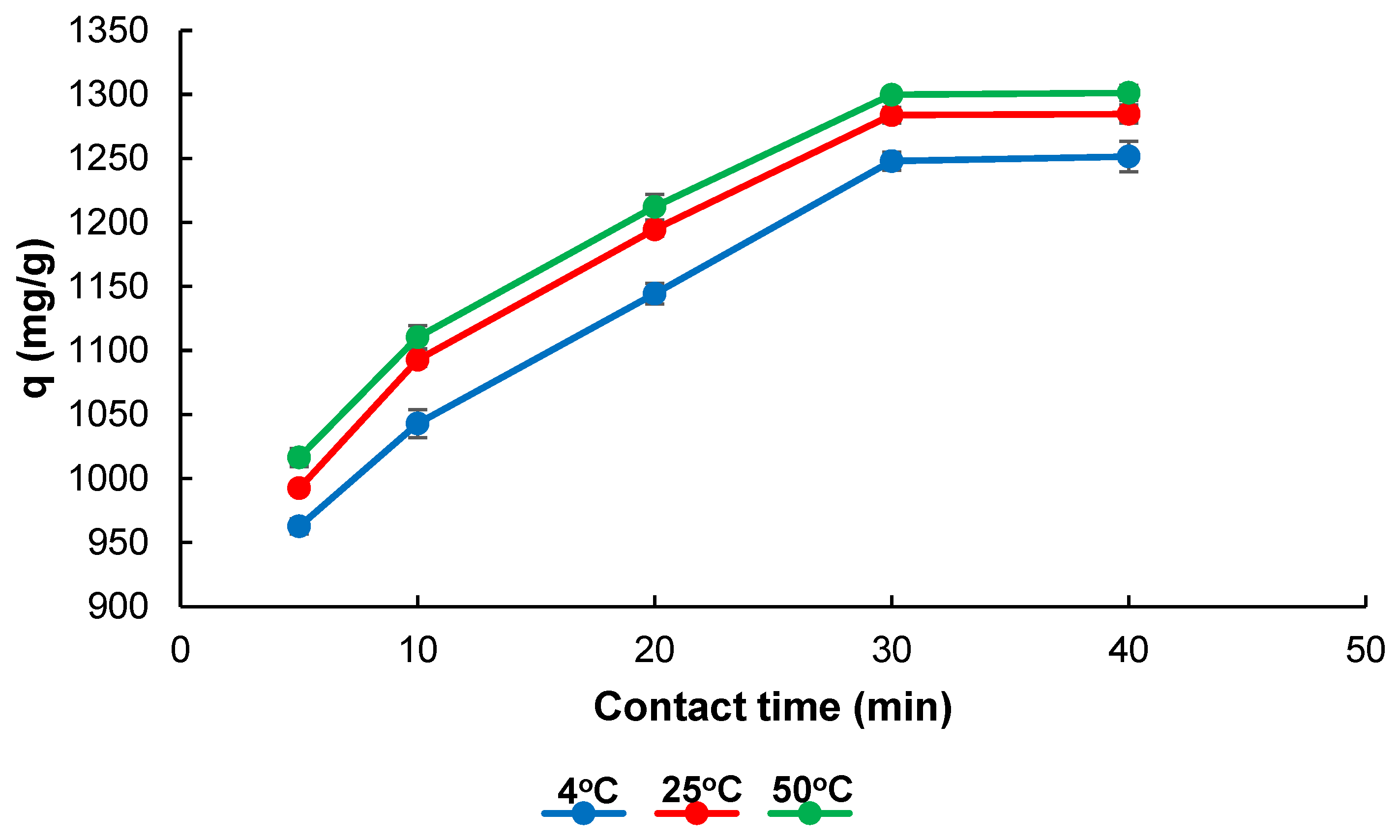
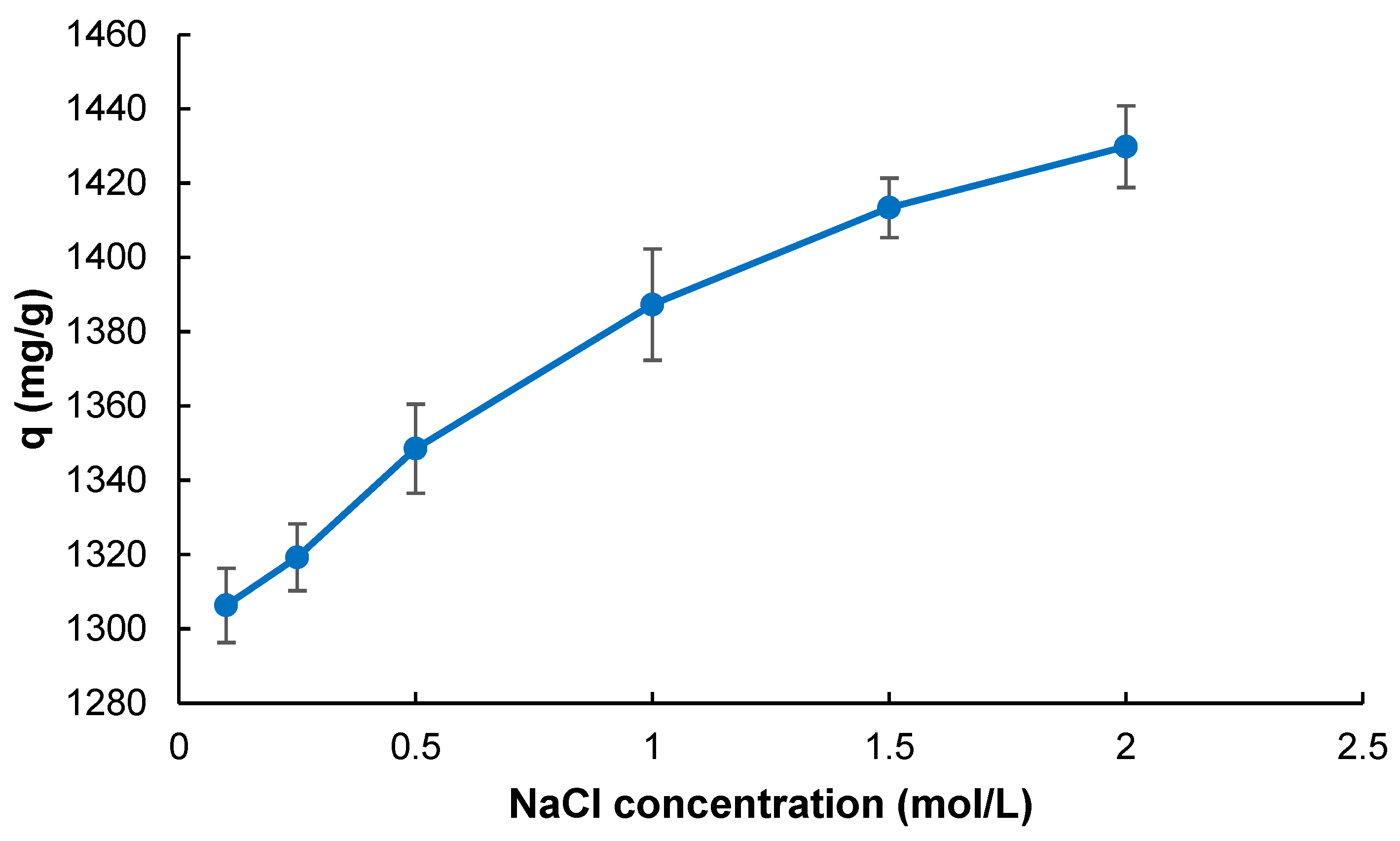
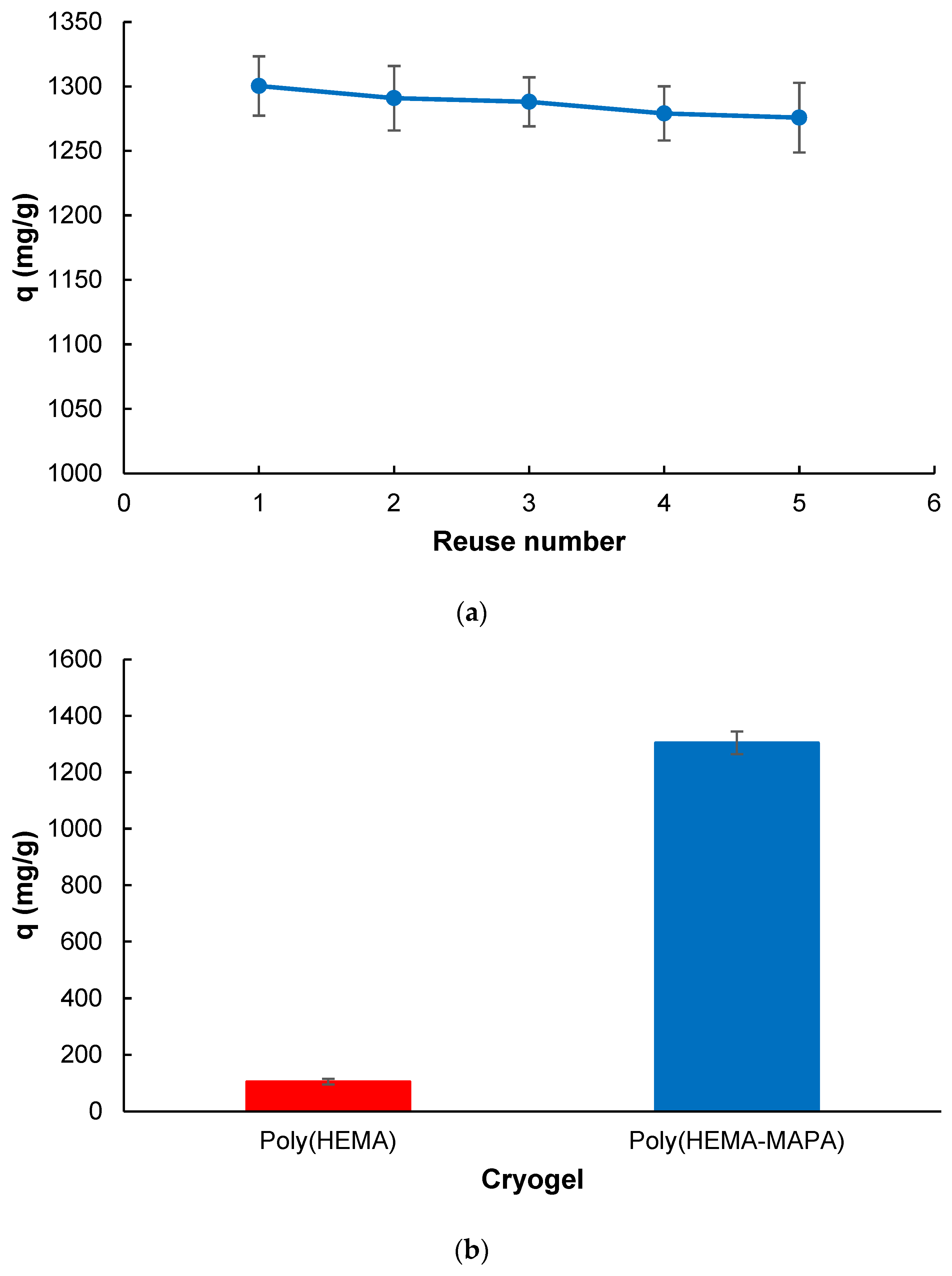
2.2. Adsorption Studies
2.3. Isotherm Studies
2.4. Kinetic Modeling
2.5. Comparison with the Literature
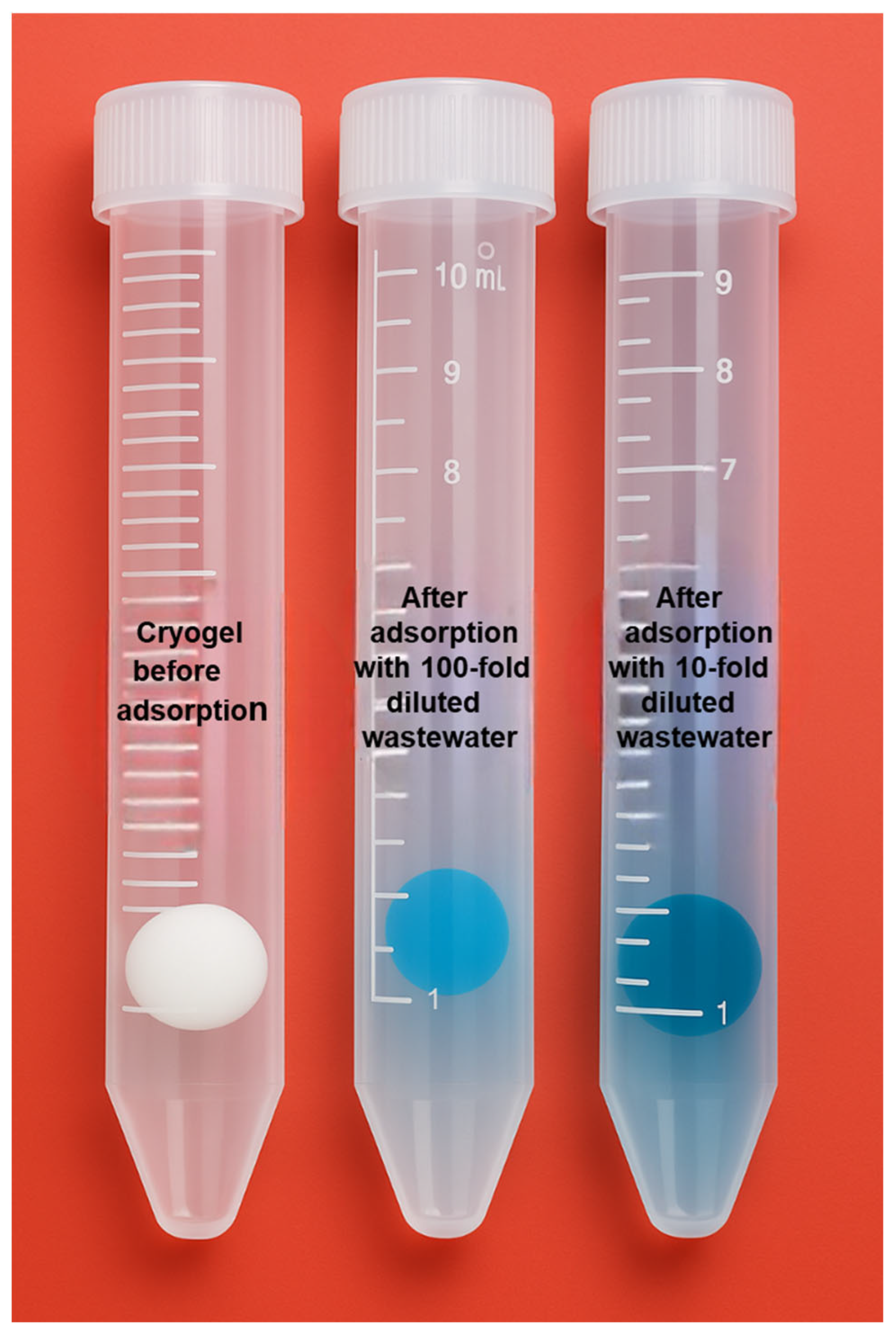
2.6. MB Adsorption from Real Wastewater Sample
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Synthesis of MAPA
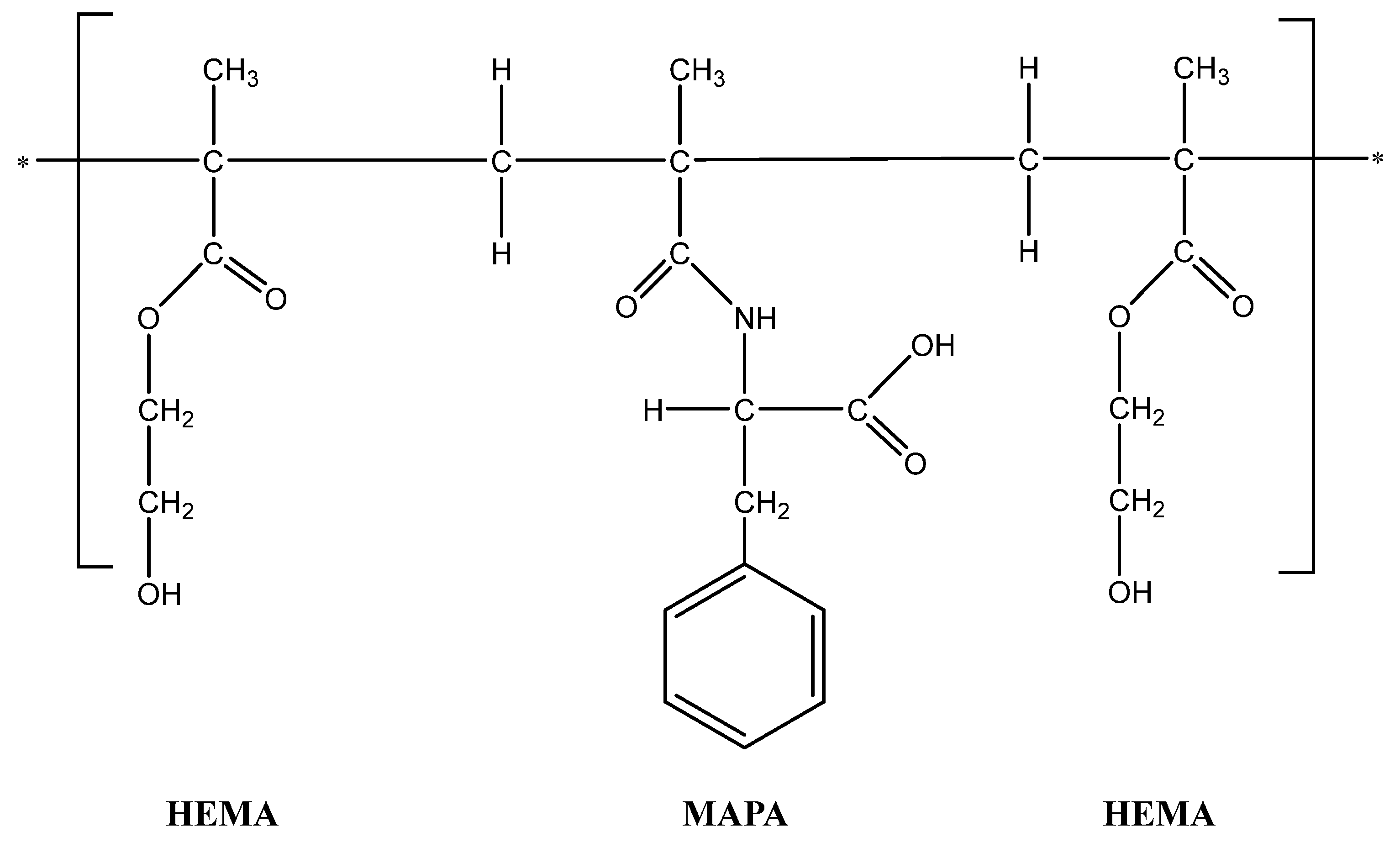
4.2.2. Synthesis of Poly(HEMA-MAPA) Cryogel
4.2.3. Synthesis of Poly(HEMA) Cryogel
4.3. Characterization of Poly(HEMA-MAPA) Cryogel
4.3.1. Swelling Test
4.3.2. Surface Morphology Analysis
4.3.3. FT-IR Spectroscopic Analysis
4.3.4. Elemental Analysis
4.3.5. Specific Surface Area (BET) Analysis
4.3.6. Zeta Potential Analysis
4.4. Adsorption Experiments
4.5. Desorption and Reusability
4.6. Isotherms
- C0 and Ceq are the initial and equilibrium concentrations of MB (mg L−1);
- Qeq and Qmax represent the equilibrium and theoretical maximum adsorption capacities (mg/g);
- θ is the fractional surface coverage;
- b, KF, n, KFH, and nFH are the isotherm constants.
4.7. Adsorption Kinetic Modeling
4.8. Thermodynamic Calculations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Jeevanantham, S.; Karishma, S.; Tajsabreen, B.; Yaashikaa, P.; Reshma, B. Effective water/wastewater treatment methodologies for toxic pollutants removal: Processes and applications towards sustainable development. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Tohamy, R.; Ali, S.S.; Li, F.; Okasha, K.M.; Mahmoud, Y.A.-G.; Elsamahy, T.; Jiao, H.; Fu, Y.; Sun, J. A critical review on the treatment of dye-containing wastewater: Ecotoxicological and health concerns of textile dyes and possible remediation approaches for environmental safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdavi, F.; Ebrahimipour, S.Y.; Hosseini, S.M.A.; Shaghaghian, R.; Fatemi, S.J.; Ramezanpour, S.; Mohamadi, M. Synthesis and application of gadolinium-doped ZnO/silica mesoporous nanocomposite for methylene blue removal. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1318, 139175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peighambardoust, S.J.; Boffito, D.C.; Foroutan, R.; Ramavandi, B. Sono-photocatalytic activity of sea sediment@400/ZnO catalyst to remove cationic dyes from wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 367, 120478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Saied, M.A.; Abualnaja, K.M.; El-Desouky, E.A.; Abdel-Naeem, G.; Eldeeb, E.A.; Elerian, A.F. Sulphonated poly(glycidyl methacrylate-co-styrene)-based adsorbents for the removal of methylene blue (MB) dye from aqueous solutions. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.I.; Soliman, M.M.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Sultan, M.Z.; Kechi, A.; Abdelsalam, N.R.; Abu-Saied, M.; Chowdhury, M. Synthesis and characterization of Graphene Oxide-Ammonium Ferric Sulfate composite for the removal of dyes from tannery wastewater. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 1715–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Zhang, X.; Shao, S.; Xiang, T.; Zhou, S. Covalently crosslinked sodium alginate/poly(sodium p-styrenesulfonate) cryogels for selective removal of methylene blue. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 301, 120356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, I.P.; Novaes, S.D.; Dezotti, R.S.; Oliveira, P.V.; Petri, D.F.S. CTAB-modified carboxymethyl cellulose/bagasse cryogels for the efficient removal of bisphenol A, methylene blue and Cr(VI) ions: Batch and column adsorption studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.; Hwang, S.-W.; Jung, M.; Choi, I.-G.; Yeo, H.; Kwak, H.W. Microwave-assisted utilization of kraft lignin-derived activated carbon for efficient dye removal. Biomass Bioenergy 2024, 186, 107279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, K.; Su, Z.; Zdarta, J.; Jesionowski, T.; Pinelo, M. Synergistic action of laccase treatment and membrane filtration during removal of azo dyes in an enzymatic membrane reactor upgraded with electrospun fibers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 129071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srihanam, P.; Prapasri, A.; Janthar, M.; Leangtanom, P.; Thongsomboon, W. Efficient dye removal using manganese oxide-modified nanocellulosic films from sugarcane bagasse. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 135910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athab, Z.H.; Halbus, A.F.; Mohammed, S.B.; Alesary, H.F.; Hasan, A.S.; Hassan, W.H. Hybrid chitosan/HKUST-1 hydrogel with freezing and thawing modification as sustainable porous material for removal and selective separation of dye mixtures. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Ren, X. Functional chitosan/glycidyl methacrylate-based cryogels for efficient removal of cationic and anionic dyes and antibacterial applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 266, 118129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Peng, X.; Sun, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Zeng, H. Hydrogels for the removal of the methylene blue dye from wastewater: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2665–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatooni, H.; Peighambardoust, S.J.; Foroutan, R.; Mohammadi, R.; Ramavandi, B. Adsorption of methylene blue using sodium carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly (acrylamide-co-methacrylic acid)/Cloisite 30B nanocomposite hydrogel. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 31, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, M.; Cimentepe, M.; Dogan, K.; Necip, A.; Karakoc, V. Advancing drug delivery and antimicrobial activity: Development and molecular docking analysis of quercetin-loaded pHEMA cryogel. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1319, 139271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-S.; Kim, J.-U.; Lee, J.; Ryu, K.M.; Kim, S.-H.; Hwang, N.S. Decellularized brain extracellular matrix based NGF-releasing cryogel for brain tissue engineering in traumatic brain injury. J. Control Release 2024, 368, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Li, Z.; Peng, L.; Wang, X.; Zheng, F.; Su, T.; Huang, Q.; Cao, L.; Zheng, A. Organic-inorganic nHA-Gelatin/Alginate high strength macroporous cryogel promotes bone regeneration. Smart Mater. Med. 2024, 5, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellebois, T.; Canuel, R.; Leclercq, C.C.; Gaiani, C.; Soukoulis, C. Milk protein-based cryogel monoliths as novel encapsulants of probiotic bacteria. Part II: Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG storage stability and bioactivity under in vitro digestion. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 146, 109173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, K.; Bolat, M.; Tatar, D.; Nigiz, C.; Köse, D.A. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial application of silver nanoparticle embedded composite cryogels. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1200, 127060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üzek, R.; Uzun, L.; Şenel, S.; Denizli, A. Nanospines incorporation into the structure of the hydrophobic cryogels via novel cryogelation method: An alternative sorbent for plasmid DNA purification. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andac, M.; Galaev, I.Y.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinted poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) based cryogel for albumin depletion from human serum. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 109, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fito, J.; Abewaa, M.; Mengistu, A.; Angassa, K.; Ambaye, A.D.; Moyo, W.; Nkambule, T. Adsorption of methylene blue from textile industrial wastewater using activated carbon developed from Rumex abyssinicus plant. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, M.; Çakır, O.; Baysal, Z. Adsorption of cellulase on poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacr ethyl methacrylate) cryogels containing phenylalanine. Turk. J. Chem. 2016, 40, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, A.C.; Paul, A.; Rao, G.R. Sol-gel-cum-hydrothermal synthesis of mesoporous Co-Fe@Al2O3−MCM-41 for methylene blue remediation. J. Chem. Sci. 2017, 129, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, G. A novel derivation of collision theory rate constants for a bimolecular reaction. J. Math. Chem. 2011, 49, 1544–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Wang, S.; Lv, H.; Wang, Z.; Han, X.; Zhou, Z.; Pu, J. Porous cellulose nanofiber (CNF)-based aerogel with the loading of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks-8 (ZIF-8) for Cu(II) removal from wastewater. BioResources 2022, 17, 2615–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, N.; Berillo, D. Water uptake as a crucial factor on the properties of cryogels of gelatine cross-linked by dextran dialdehyde. Gels 2021, 7, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savina, I.N.; Ingavle, G.C.; Cundy, A.B.; Mikhalovsky, S.V. A simple method for the production of large volume 3D macroporous hydrogels for advanced biotechnological, medical and environmental applications. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, K. Polychelated cryogels: Hemoglobin adsorption from human blood. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoda-Tandjawa, G.; Dieudé-Fauvel, E.; Girault, R.; Baudez, J.C. Using water activity measurements to evaluate rheological consistency and structure strength of sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widyarani; Sari, Y.W.; Ratnaningsih, E.; Sanders, J.P.; Bruins, M.E. Production of hydrophobic amino acids from biobased resources: Wheat gluten and rubber seed proteins. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 7909–7920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, B.; Burt, K.; Lee, A.; Lingard, K.; Maurer, S.E. Partitioning of amino acids and proteins into decanol using phase transfer agents towards understanding life in non-polar liquids. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taweekarn, T.; Wongniramaikul, W.; Boonkanon, C.; Phanrit, C.; Sriprom, W.; Limsakul, W.; Towanlong, W.; Phawachalotorn, C.; Choodum, A. Starch biocryogel for removal of methylene blue by batch adsorption. Polymers 2022, 14, 5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, B.; Erol, K.; Gökmeşe, E. The effect of the chelator characteristics on insulin adsorption in immobilized metal affinity chromatography. Process Biochem. 2019, 83, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southall, N.T.; Dill, K.A.; Haymet, A.D.J. A view of the hydrophobic effect. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, K.; Yıldız, E.; Alacabey, İ.; Karabörk, M.; Uzun, L. Magnetic diatomite for pesticide removal from aqueous solution via hydrophobic interactions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 33631–33641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kireç, O.; Alacabey, İ.; Erol, K.; Alkan, H. Removal of 17β-estradiol from aqueous systems with hydrophobic microspheres. J. Polym. Eng. 2021, 41, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Zheng, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, R.; Yang, X.; Lin, Z. A novel protein purification scheme based on salt inducible self-assembling peptides. Microb. Cell Fact. 2023, 22, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeroual, S.; Khatib, K.; Belfkira, A.; Ablouh, E.H.; Hanani, Z.; Taourirte, M.; Jalal, R. A novel approach for adsorption of organic dyes from aqueous solutions using a sodium alginate/titanium dioxide nanowire doped with zirconium cryogel beads. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1285230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haleem, A.; Shafiq, A.; Chen, S.Q.; Nazar, M. A comprehensive review on adsorption, photocatalytic and chemical degradation of dyes and nitro-compounds over different kinds of porous and composite materials. Molecules 2023, 28, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragadhita, R.; Nandiyanto, A.B.D. How to calculate adsorption isotherms of particles using two-parameter monolayer adsorption models and equations. Indones. J. Sci. Technol. 2021, 6, 205–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahvecioğlu, K.; Teğin, İ.; Yavuz, Ö.; Saka, C. Phosphorus and oxygen co-doped carbon particles based on almond shells with hydrothermal and microwave irradiation process for adsorption of lead (II) and cadmium (II). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 37946–37960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N. Applying Linear Forms of Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Model for Feasibly Identifying Errors in the Initial Periods of Time-Dependent Adsorption. Water 2023, 15, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, K.; Wu, J.; Li, B.; Wang, W.; Tang, J. Facile preparation of sodium alginate gel beads enhanced by polyamino-modified 3D carbon for efficient remediation of organic dyes in wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 339, 126637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Bao, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. Reverse wood mimetic cryogel based on poly(itaconic acid) for continuous removal of methylene blue from complex water emulsion. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 339, 126533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, F.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, P. Preparation of poly (polyethylene glycol diacrylate -co- maleic anhydride) cryogels and its adsorption performance of cationic dyes. React. Funct. Polym. 2024, 195, 105812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.M.; Ezzat, A.O.; Al-Hussain, S.A.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Tawfeek, A.M.; Hashem, A.I. New crosslinked poly(ionic liquid) cryogels for fast removal of methylene blue from waste water. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 131, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, G.; Kaygusuz, H.; Erim, F.B. Methylene blue removal by alginate–clay quasi-cryogel beads. React. Funct. Polym. 2016, 106, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, D.; Ekti, S.F.; Say, R. N-Acylbenzotriazole mediated synthesis of some methacrylamido amino acids. Lett. Org. Chem. 2007, 4, 585–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarıca, B.; Köse, K.; Uzunoğlu, A.; Erol, K.; Köse, D.A. Isolation of aspartic acid using novel poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-N-methacryloyl-(L)-lysine) cryogels. Chromatographia 2018, 81, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunay Gurer, A.; Aktas, K.; Ozkaleli Akcetin, M.; Erdem Unsar, A.; Asilturk, M. Thermodynamics, and Kinetic Modeling of Methylene Blue onto Novel Carbonaceous Adsorbent Derived from Bitter Orange Peels. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S. Adsorption of Methylene Blue in Water onto Activated Carbon by Surfactant Modification. Water 2020, 12, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Langmuir | ||
| Qmax (mg/g) | b (L/mg) | R2 |
| 1250 | 0.000093 | 0.9706 |
| Freundlich | ||
| KF | 1/n | R2 |
| 0.035 | 1.2312 | 0.6877 |
| Flory–Huggins | ||
| KFH | nFH | R2 |
| 0.00015 | 520.62 | 0.7582 |
| Temperature (K) | ΔG° (kJ·mol−1) | ΔH° (kJ·mol−1) | ΔS° (J·mol−1·K−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 277 | –17.89 | ||
| 298 | –22.02 | +36.57 | +196.6 |
| 323 | –26.93 |
| Pseudo-First-Order | ||
| qe (mg/g) | k1 (L mg−1) | R2 |
| 1066.1 | 0.168 | 0.8546 |
| Pseudo-Second-Order | ||
| qe (mg/g) | k2 (g−1 mg−1 min−1) | R2 |
| 1250.0 | 0.000356 | 0.9985 |
| Cryogel | Method | Isotherm Model | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Equilibrium Time (min) | MB Concentration (mg L−1) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly(itaconic acid) | Batch study | Langmuir | 172.4 | above 400 | 500 | [47] |
| AlgMA/PNaSS | Batch study | Freundlich | 2300 | 480 | 192 | [7] |
| Poly(PEGDA-co-MA) | Continuous study | Langmuir | 447.7 | 60 | 1000 | [48] |
| Poly(ionic liquids) | Batch study | Freundlich | 1228.8 | 10 | 500 | [49] |
| SA/clay quasi | Batch study | Freundlich | 181.8 | 240 | 50 | [50] |
| Poly(HEMA-MAPA) | Batch study | Langmuir | 1304.6 | 30 | 2000 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sofuoğlu, M.; Kuyucu, A.E.; Erol, K.; Gökmeşe, F. Amino Acid-Based Hydrophobic Cryogels for Efficient Methylene Blue Removal: A Reusable and Eco-Friendly Approach to Dye-Contaminated Wastewater Treatment. Gels 2025, 11, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060411
Sofuoğlu M, Kuyucu AE, Erol K, Gökmeşe F. Amino Acid-Based Hydrophobic Cryogels for Efficient Methylene Blue Removal: A Reusable and Eco-Friendly Approach to Dye-Contaminated Wastewater Treatment. Gels. 2025; 11(6):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060411
Chicago/Turabian StyleSofuoğlu, Merve, Ali Ender Kuyucu, Kadir Erol, and Faruk Gökmeşe. 2025. "Amino Acid-Based Hydrophobic Cryogels for Efficient Methylene Blue Removal: A Reusable and Eco-Friendly Approach to Dye-Contaminated Wastewater Treatment" Gels 11, no. 6: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060411
APA StyleSofuoğlu, M., Kuyucu, A. E., Erol, K., & Gökmeşe, F. (2025). Amino Acid-Based Hydrophobic Cryogels for Efficient Methylene Blue Removal: A Reusable and Eco-Friendly Approach to Dye-Contaminated Wastewater Treatment. Gels, 11(6), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060411









