Rheological and Thermal Properties of Salecan/Sanxan Composite Hydrogels for Food and Biomedical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Morphological Structure Analysis
2.2. TGA and DSC
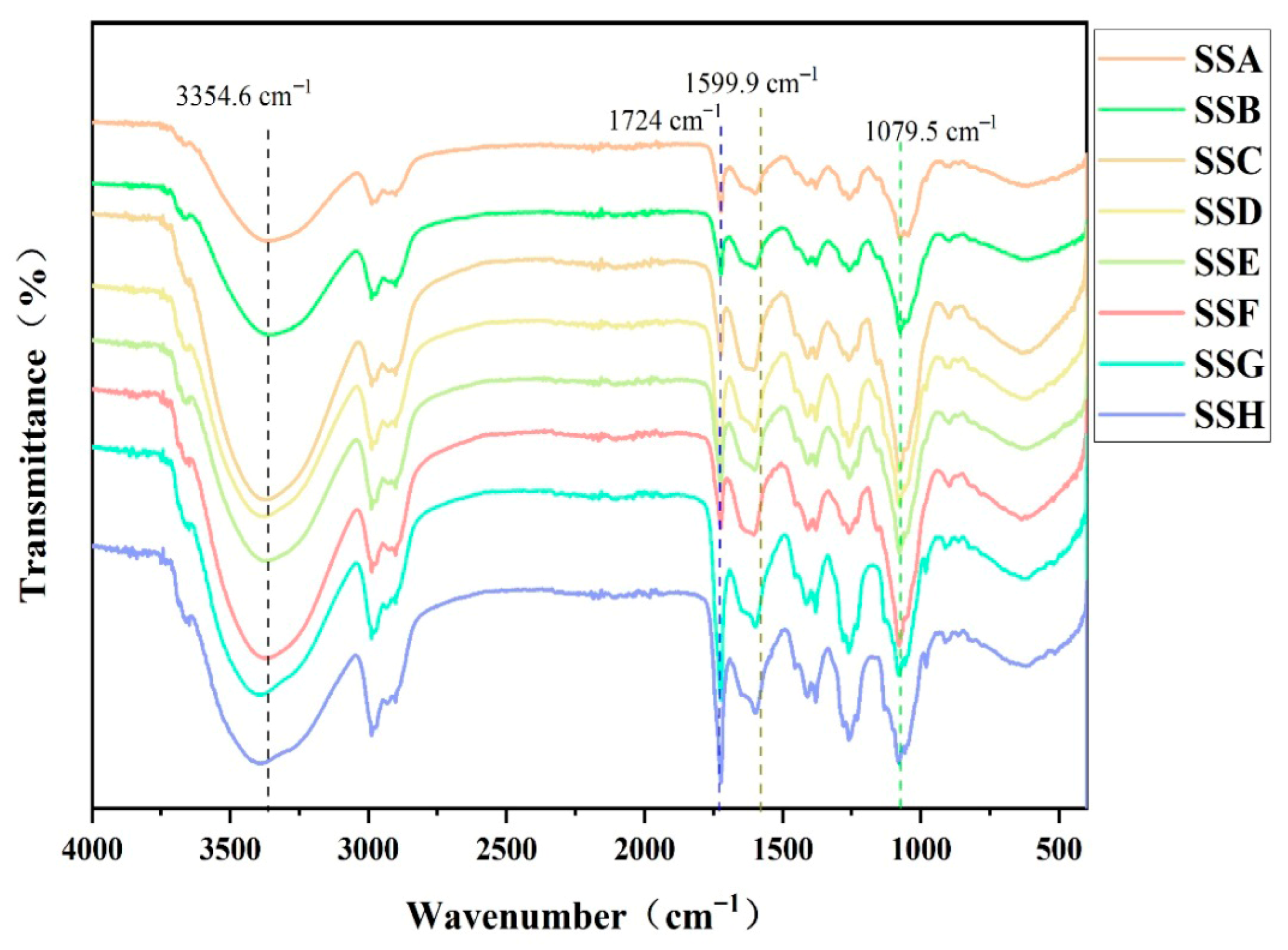
2.3. FTIR
2.4. Rheology
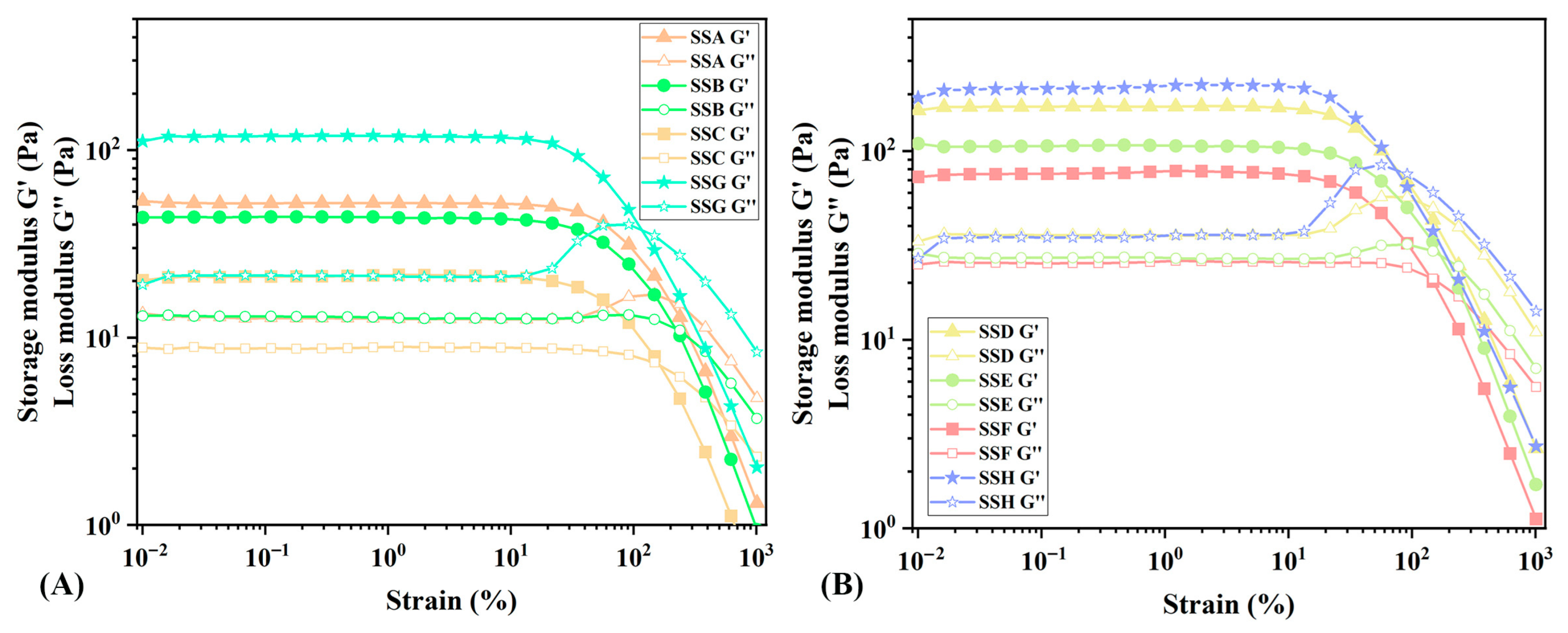
2.4.1. Discussion of Amplitude Sweep (AS)
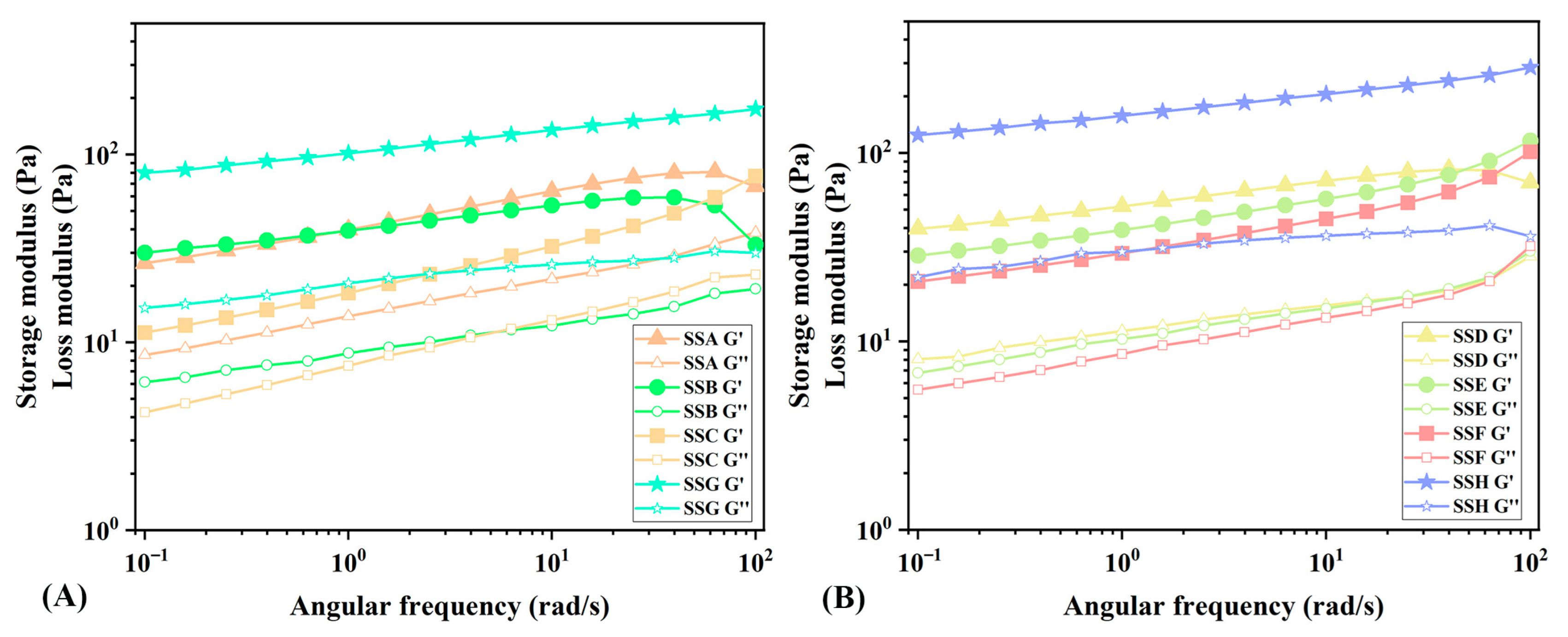
2.4.2. Analysis of Oscillation Frequency Sweep (OFS)
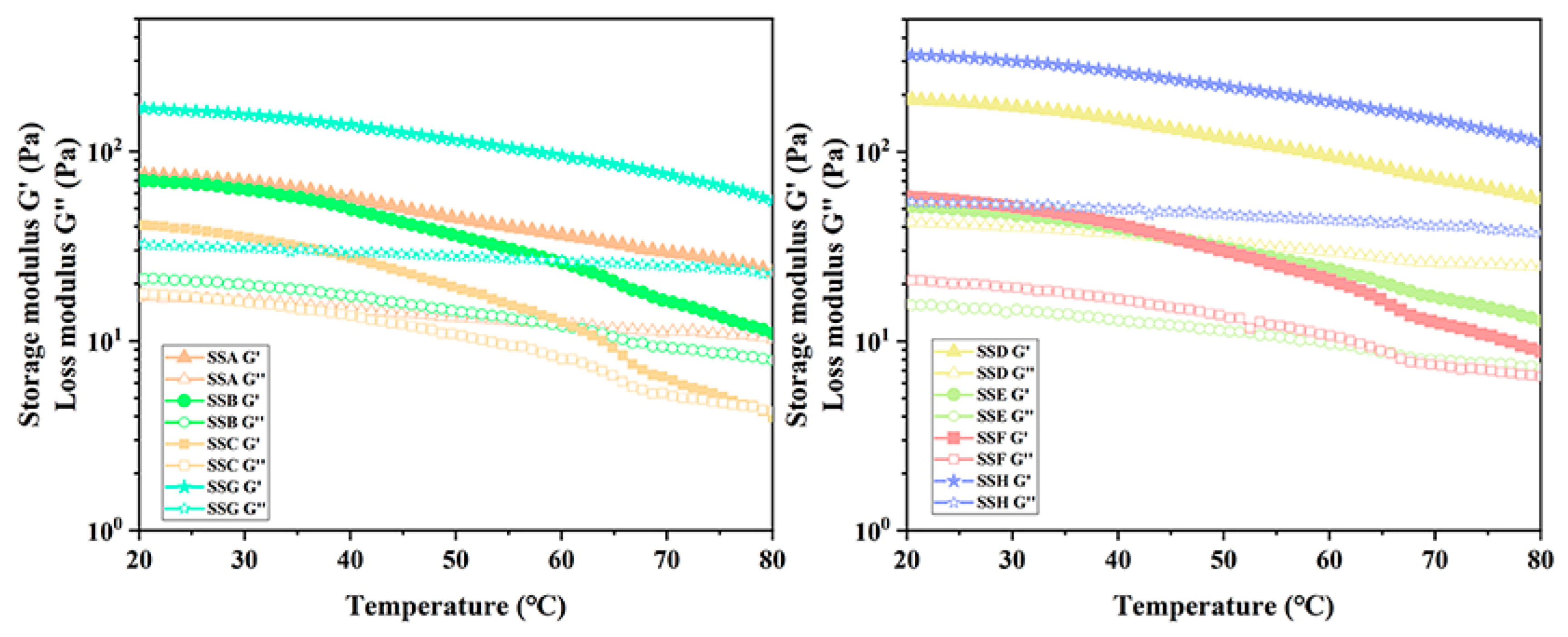
2.4.3. Discussion of Dynamical Temperature Sweep (DTS)
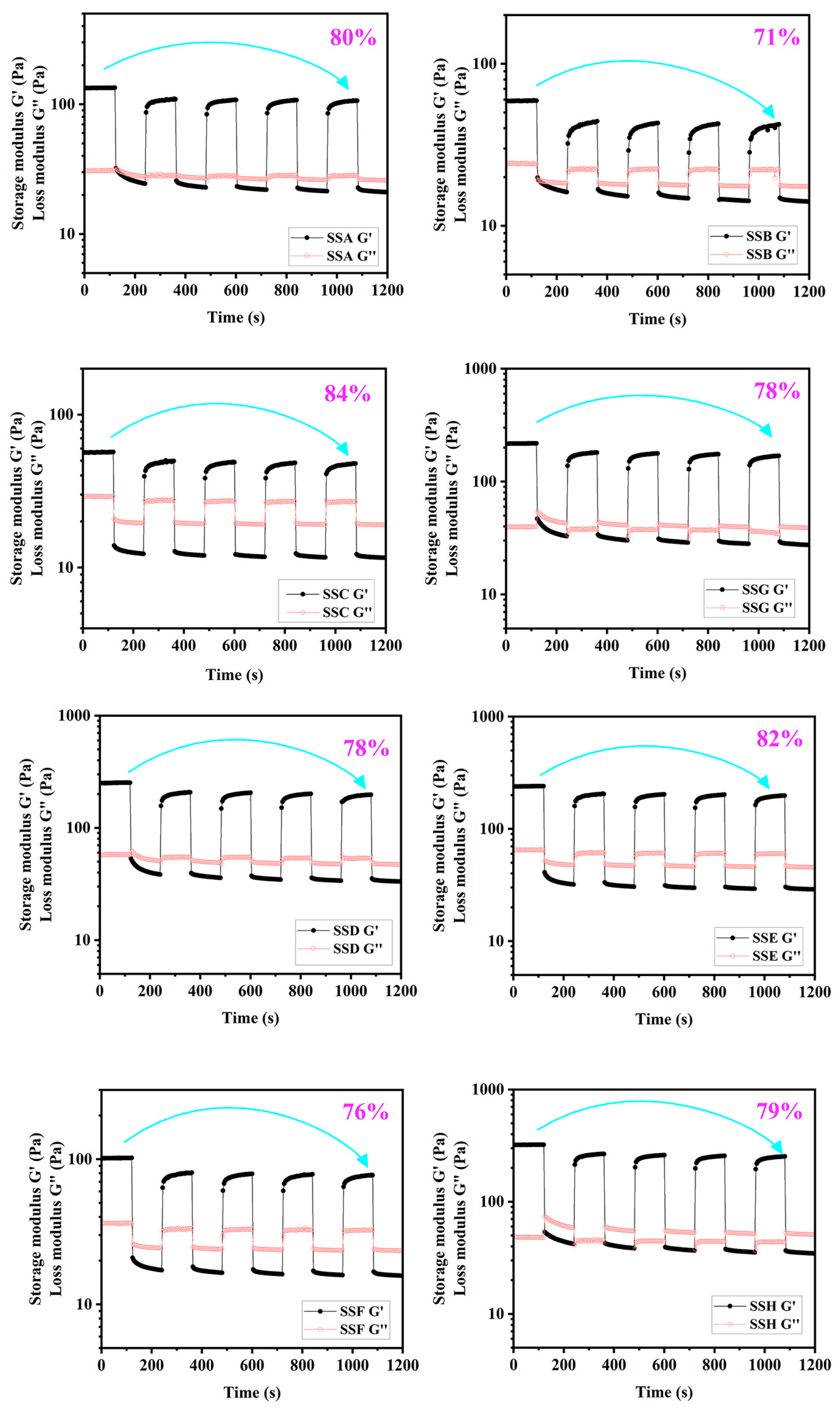
2.4.4. Analysis of Cyclic Strain Time Sweep (CSS)
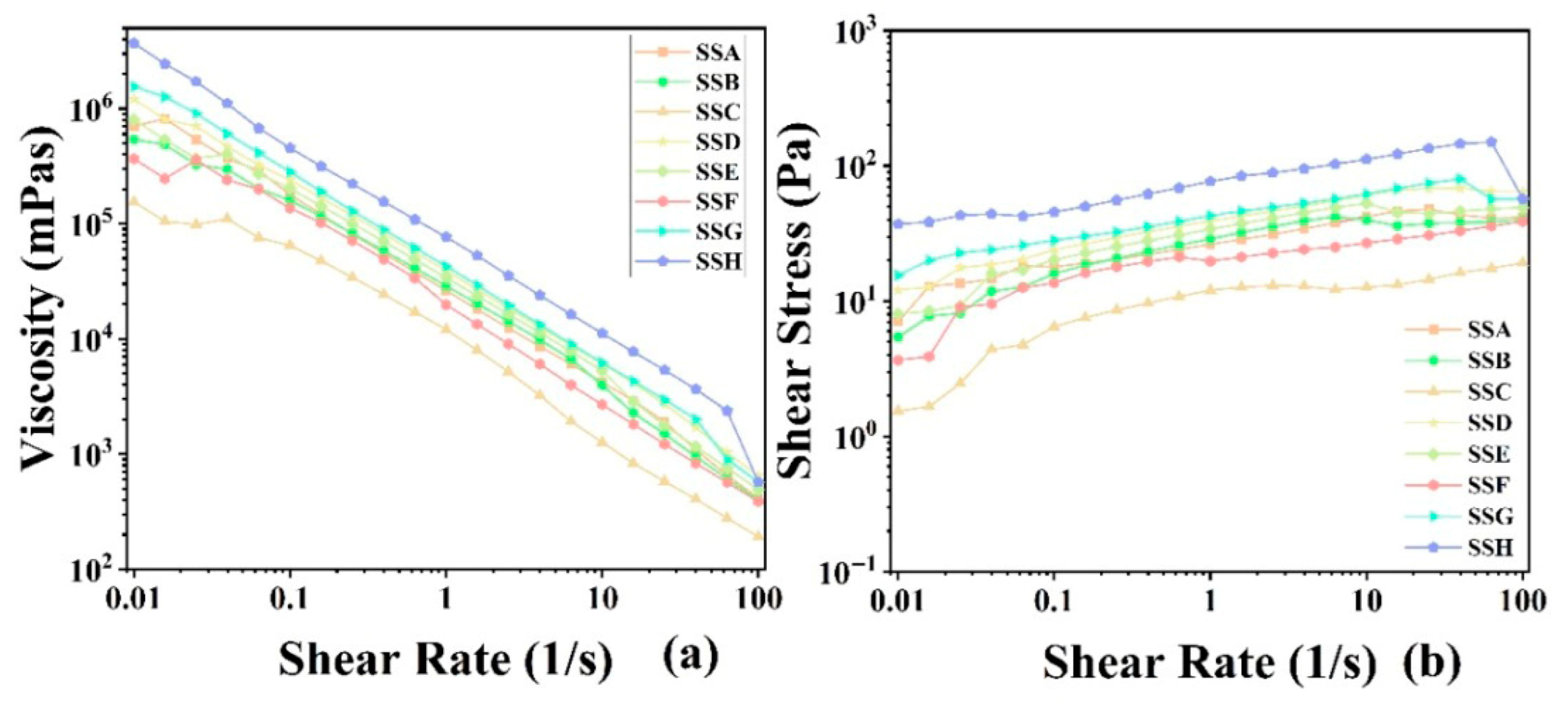
2.4.5. Flow Behavior
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
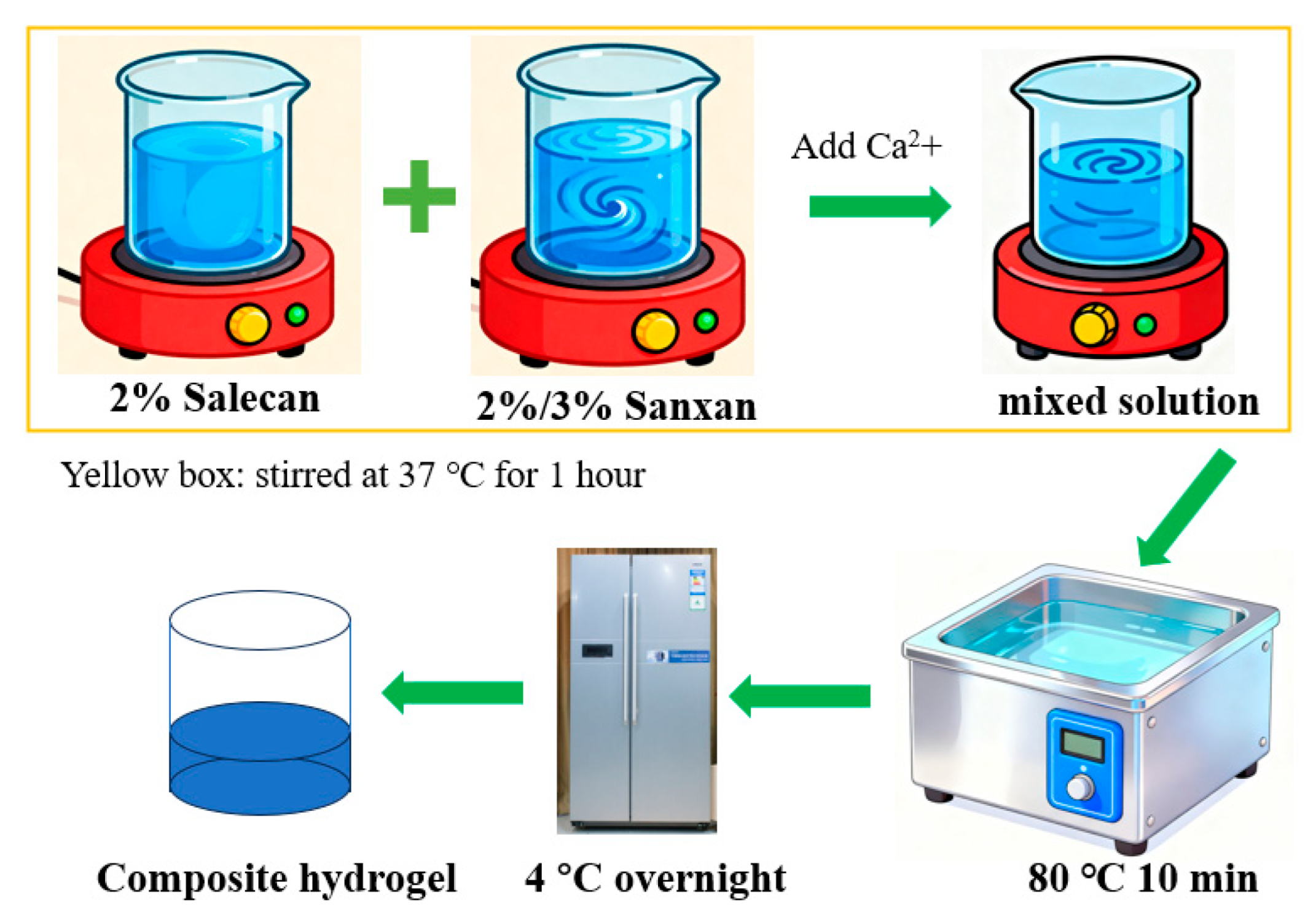
4.2. Hydrogel Design and Preparation
4.3. Morphology
4.4. Thermal Analysis Characterization
4.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
4.6. Rheological Testing—Oscillation Mode
4.6.1. The Amplitude Sweep (AS)
4.6.2. The Oscillation Frequency Sweep (OFS)
4.6.3. The Dynamical Temperature Sweep (DTS)
4.6.4. The Cyclic Strain Time Sweep (CSS)
4.7. Rheological Testing—Rotation Mode
4.8. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Dong, F.; Zou, X.; Liu, W.; Feng, Y. Sodium lignosulfonate doped polyvinyl alcohol-based hydrogel conductive composites based on ion-specific effects with continuously tunable mechanical properties and excellent conductive sensing properties. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 108498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, S.; Arratia, P.E.; Jerolmack, D.J. Origins of complexity in the rheology of Soft Earth suspensions. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Halim, M.S.; Dyson, J.M.; Gong, M.M.; O’Bryan, M.K.; Nosrati, R. Fallopian tube rheology regulates epithelial cell differentiation and function to enhance cilia formation and coordination. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wu, M.; Yang, H.; Li, X.; Ren, M.; Li, G.; Ma, T. Structural and physical properties of sanxan polysaccharide from Sphingomonas sanxanigenens. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 144, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Shi, Z.; Huang, H.; Qu, J.; Dai, X.; Tian, X.; Wei, W.; Li, G.; Ma, T. Network structure and functional properties of transparent hydrogel sanxan produced by Sphingomonas sanxanigenens NX02. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 176, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, J.; Sperl, N.; Sieber, V. A comparison of genes involved in sphingan biosynthesis brought up to date. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 7719–7733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Cheng, R.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Ma, S.; Zhang, W.; Dong, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J. Identification of substituent groups and related genes involved in salecan biosynthesis in Agrobacterium sp. ZX09. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Wei, W.; Shen, J.; Dong, W. Salecan polysaccharide-based hydrogels and their applications: A review. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 2577–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Cheng, P.; Gao, Y.; Wang, D.; Jia, G.; Zhang, P.; Prakash, S.; Wang, Z.; Han, J. Understanding the rheological properties of a novel composite salecan/gellan hydrogels. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Cheng, P.; Prakash, S.; Zhang, P.; Mei, L.; Ji, S.; Wang, Z.; Han, J. Rheological investigation of a versatile salecan/curdlan gel matrix. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 2202–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Cheng, P.; Chu, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Shi, R.; Wang, Z.; Han, J.; Fan, Z. Unveiling the rheological and thermal behavior of a novel Salecan and whey protein isolate composite gel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 271, 132528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. β-glucan Salecan Improves Exercise Performance and Displays Anti-Fatigue Effects through Regulating Energy Metabolism and Oxidative Stress in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Olnood, C.G.; Xu, Y.-J.; Liu, Y. Multiomics analysis revealed the mechanism of the anti-diabetic effect of Salecan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 327, 121694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, P.; Pan, W.; Zhao, J.; Olnood, C.G.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.-J. Salecan confers anti-inflammatory effects in liver injury via regulating gut microbiota and its metabolites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 302, 120418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, W.; Huang, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, F.; Guo, N.; Zhu, G. Gellan gum-quercetin covalent complex prepared by the free radical grafting: Characterization, bioaccessibility and intracellular antioxidant activity. Food Chem. X 2025, 30, 102965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, Q.; Wu, F.; Chen, S.; Su, T.; Qi, X. Adsorption of antibiotics by polydopamine-modified salecan hydrogel: Performance, kinetics and mechanism studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Wang, J.; Jie, Y.; Liu, H.; He, B.; Wang, J. Effects of sanxan on water and ice crystal status of salt free frozen cooked noodles during freeze-thaw cycles. Food Chem. 2024, 448, 139137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; He, B.; Wang, J. Effect of sanxan on the composition and structure properties of gluten in salt-free frozen-cooked noodles during freeze–thaw cycles. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hariri El Nokab, M.; Es Sayed, J.; De Witte, F.; Dewettinck, K.; Elshewy, A.; Zhang, Z.; Van Steenberge, P.H.M.; Wang, T.; Sebakhy, K.O. A comparative analytical study for the different water pools present in alginate hydrogels: Qualitative vs. quantitative approaches. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 154, 110159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, T.; Nakamura, K.; Yoshida, H.; Hatakeyama, H. Phase transition on the water-sodium poly(styrenesulfonate) system. Thermochim. Acta 1985, 88, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Hatakeyama, T.; Hatakeyama, H. Phase transitions of the water-xanthan system. Polymer 1990, 31, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Xu, H.; Huang, D. The investigation on states of water in different hydrophilic polymers by DSC and FTIR. J. Polym. Res. 2011, 18, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roget, S.A.; Piskulich, Z.A.; Thompson, W.H.; Fayer, M.D. Identical Water Dynamics in Acrylamide Hydrogels, Polymers, and Monomers in Solution: Ultrafast IR Spectroscopy and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 14855–14868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, N.; Jyoti; Thakur, M.; Mishra, B.B.; Singh, S.P. Preparation and characterization of biodegradable films based on levan polysaccharide blended with gellan gum. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 31, 103231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Li, X.; Tian, T.; Yang, H.; Quan, G.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H. The pH-responsiveness carrier of sanxan gel beads crosslinked with CaCl2 to control drug release. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 250, 126298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busto, F.; Scalia, A.C.; Gentile, P.; Toniolo, S.; Cometa, S.; Liotino, S.; Cochis, A.; Mastrorilli, P.; De Giglio, E. Gellan gum/tannic acid hydrogels for cartilage repair: The versatile role of tannic acid as green crosslinker conferring antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2025, 10, 100860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Kim, B.; Park, J.D.; Lee, D. Probing metal-carboxylate interactions in cellulose nanofibrils-based hydrogels using nonlinear oscillatory rheology. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 300, 120262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, S.; Biermann, M.; Kara, S.; Jopp, S.; Meyer, J. A novel characterization technique for hydrogels—In situ rheology-Raman spectroscopy for gelation and polymerization tracking. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 6957–6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, G.; Han, J. Rheological insight of polysaccharide/protein based hydrogels in recent food and biomedical fields: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222 Pt B, 1642–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, J.P.; Singhal, R.S. A prebiotic hydrogel based on gellan gum and arabinoxylan from flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum) for advanced probiotic delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 330, 147786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.-Y.; Liao, B.-H.; Huang, W.-L.; Wang, W.-H.; Kankala, R.K.; Wang, S.-B.; Xu, P.-Y.; Chen, A.-Z. Concrete-inspired injectable microspheres/ hydrogel composite system for sustained release stem-cell secretome and long-term soft tissue filling. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 522, 168082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, K.; Kim, S.H.; Ahn, K.H.; Lee, S.J. Large amplitude oscillatory shear as a way to classify the complex fluids. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2002, 107, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, S.; Funami, T.; Nakauma, M.; Asai, I.; Takahashi, R.; Al-Assaf, S.; Ikeda, S.; Nishinari, K.; Phillips, G.O. Molecular structures of gellan gum imaged with atomic force microscopy in relation to the rheological behavior in aqueous systems. 1. Gellan gum with various acyl contents in the presence and absence of potassium. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1148–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Hu, X.; Xu, B.; Bai, C.; Wang, T.; Ma, T.; Song, Y. Effects of different salt ions on the structure and rheological behavior of sulfated cellulose nanocrystal hydrogel. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 151, 109799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhu, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Han, J. Influence of Soybean Dietary Fiber on the properties of Konjac Glucomannan/κ-Carrageenan Corn Oil Composite Gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 129, 107602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xue, C. Rheology and microstructure of heat-induced fluid gels from Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) protein: Effect of pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stading, M.; Hermansson, A.-M. Viscoelastic behaviour of β-lactoglobulin gel structures. Food Hydrocoll. 1990, 4, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross-Murphy, S.B. Rheological Methods. In Physical Techniques for the Study of Food Biopolymers; Ross-Murphy, S.B., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 343–392. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, T.; Wu, Y.; Ni, C.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, J. Rheology and texture analysis of gelatin/dialdehyde starch hydrogel carriers for curcumin controlled release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 283, 119154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Singhal, R.S. Composite hydrogels fabricated from konjac glucomannan and gellan gum: Rheological characterization and their potential application in sustainable agriculture. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 336, 122091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, D.; Yip, R.C.S.; Xie, W.; Chen, H. Injectable Salecan/hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels with antibacterial, rapid self-healing, pH-responsive and controllable drug release capability for infected wound repair. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 347, 122750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamayaro, K.; Mehrkhodavandi, P.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G. Impact of counterion valency on the rheology of sulfonated cellulose nanocrystal hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 302, 120378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Zhou, Z.; Fan, X.; Xu, W.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, C. Small Dop of Comonomer, Giant Shift of Dynamics: α-Methyl-Regulated Viscoelasticity of Poly(methacrylamide) Hydrogels. Giant 2024, 20, 100342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Du, P.; Hsu, Y.-I.; Uyama, H. Smart versatile hydrogels tailored by metal-phenolic coordinating carbon and polypyrrole for soft actuation, strain sensing and writing recognition. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koparipek-Arslan, N.; Kaynak-Uraz, E.; Senses, E. Dynamically bonded cellulose nanocrystal hydrogels: Structure, rheology and fire prevention performance. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 334, 122013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; He, H.; Wu, D.; Lin, D.; Qin, W.; Meng, D.; Yang, R.; Zhang, Q. Rheological and textural properties of acid-induced soybean protein isolate gel in the presence of soybean protein isolate hydrolysates or their glycosylated products. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, C.; Xia, Q.; Pan, D.; Du, L.; He, J.; Sun, Y.; Geng, F.; Cao, J. pH sensitive cold-set hydrogels based on fibrinogen hydrolysates/carrageenan: Insights of rheology, coacervation, microstructure and antioxidant ability. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 147, 109377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yin, J.; Geng, F.; Nie, S. The synergistic gelation of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide (Dendronans) with xanthan gum and its rheological and texture properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 141, 108674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Lan, T.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sui, X. Shear, extensional rheology, and tribology of polysaccharide-thickened soy protein-based liquid systems for dysphagia management. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhou, T.-Q.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, J.-N.; Wang, C.; Lai, B.; Zhang, L.-C.; Wu, H.-T. Rheological characterization of chia seed gum as a thickening agent used for dysphagia management. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 133413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, P.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, M.; Gu, J.; Wang, Z.; Han, J. A novel multifunctional Salecan/κ-carrageenan composite hydrogel with anti-freezing properties: Advanced rheology, thermal analysis and model fitting. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, C.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Qiao, S.; Jiao, B.; Ma, L.; Fu, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. Stabilization of capsanthin in physically-connected hydrogels: Rheology property, self-recovering performance and syringe/screw-3D printing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 319, 121209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, S.; Annapure, U.S. Impact of atmospheric pressure cold plasma on the rheological and gelling properties of high methoxyl apple pectin. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 129, 107639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
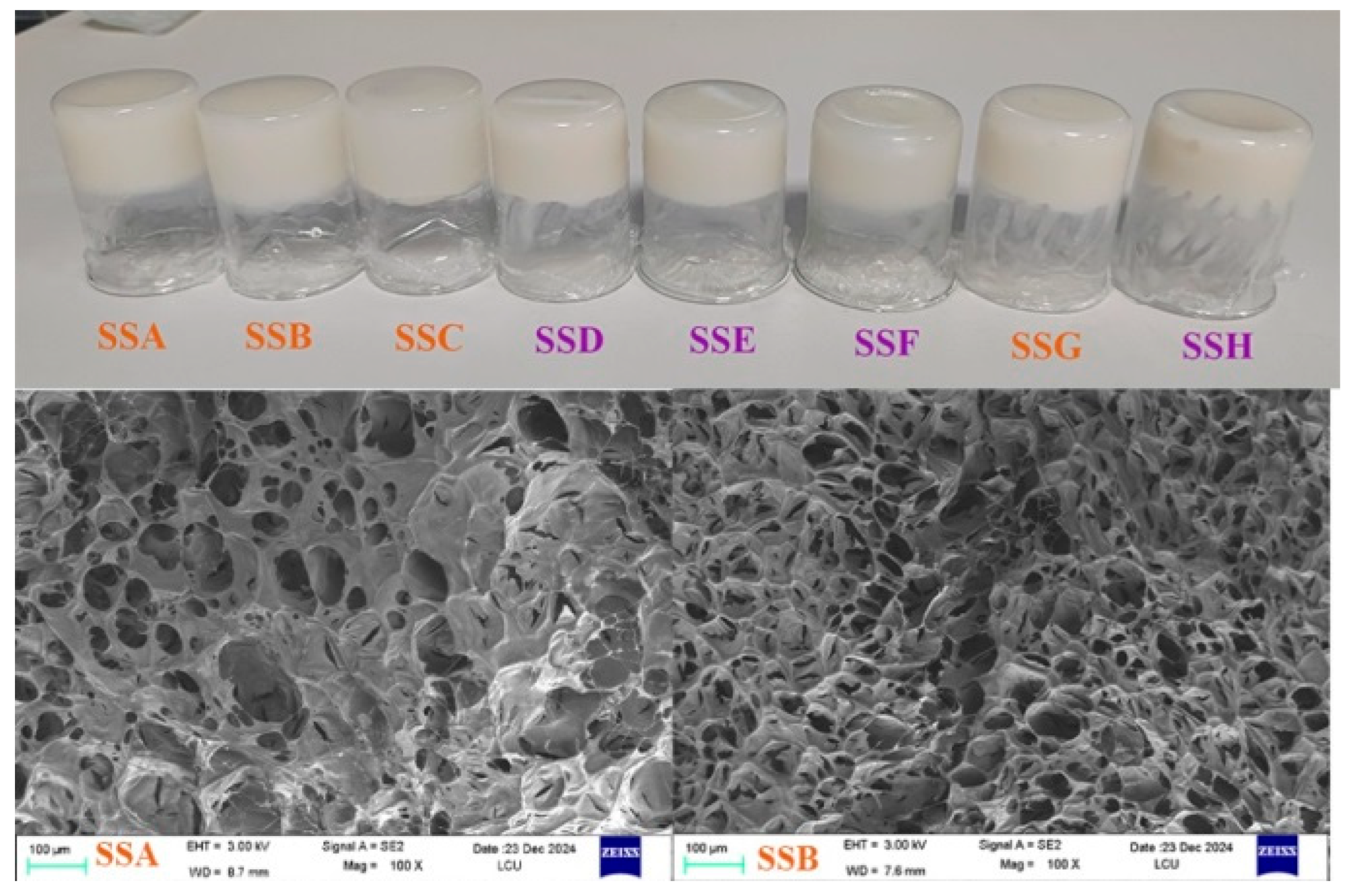
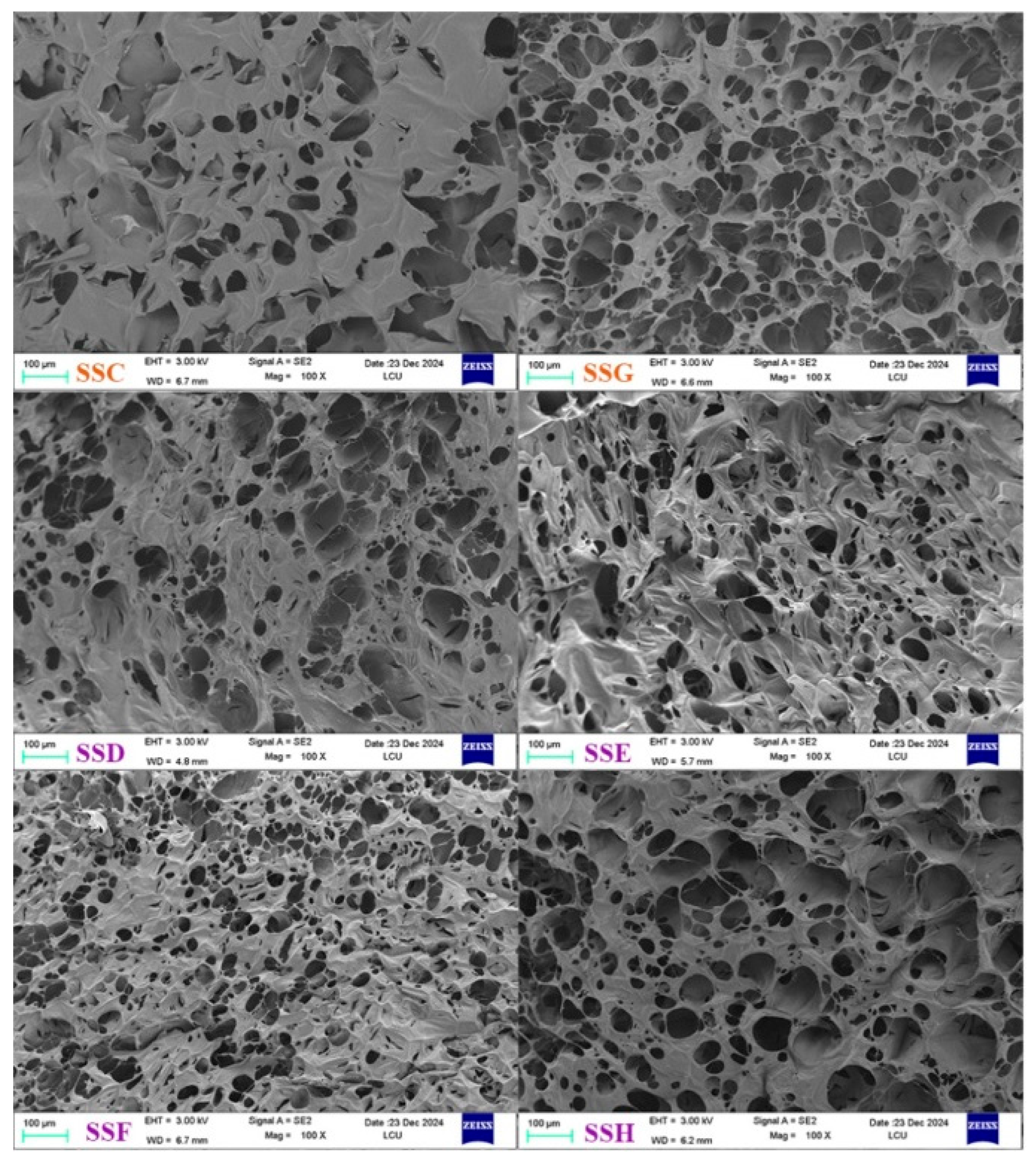
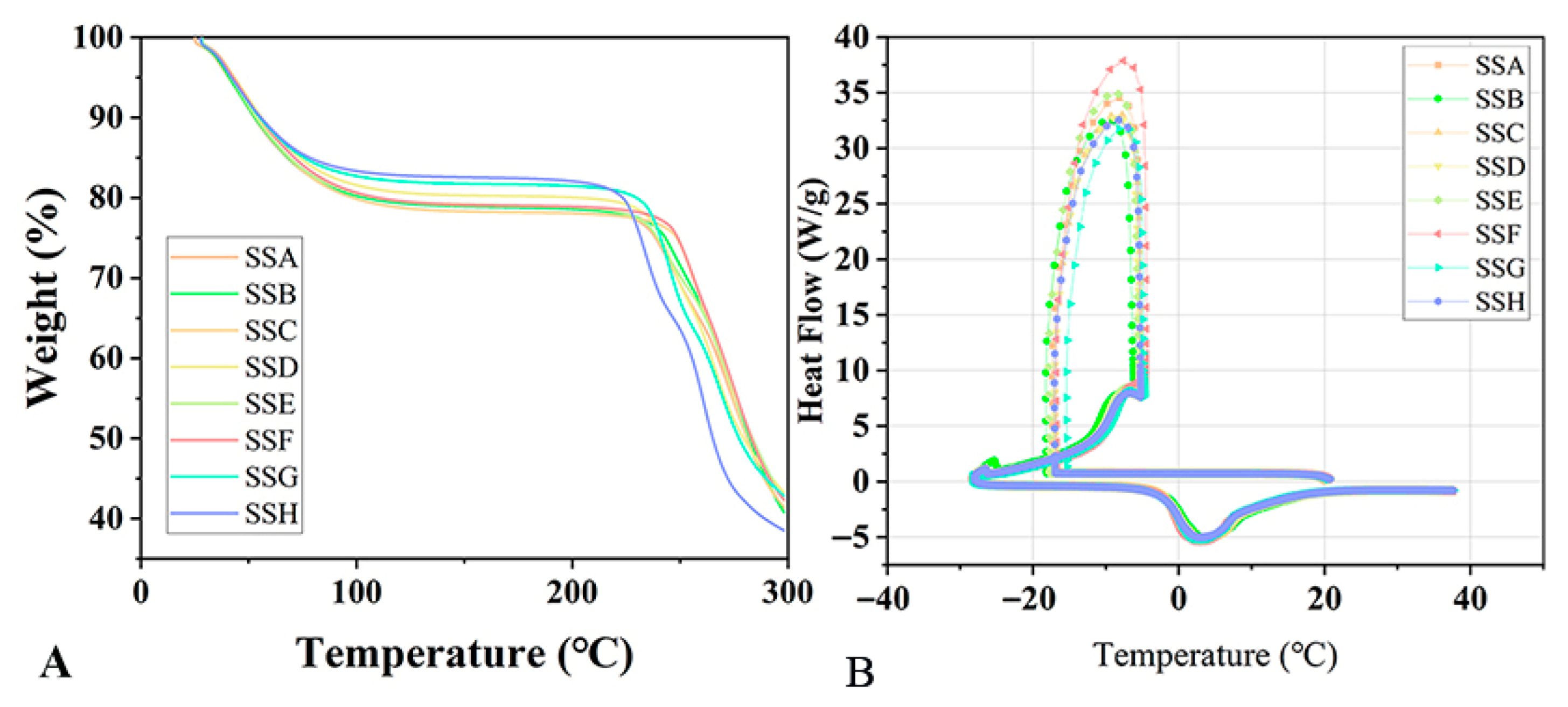
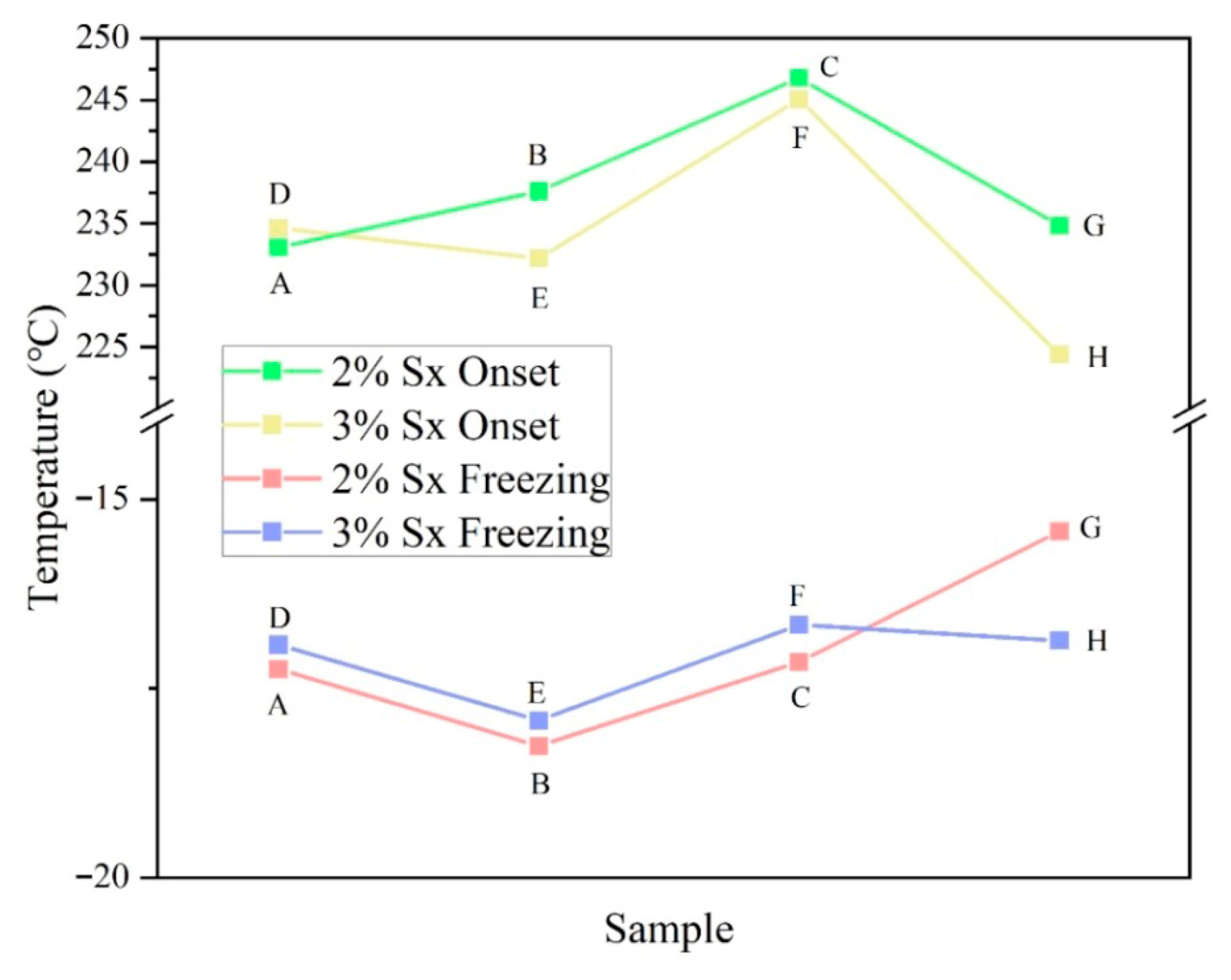

| SSs Sample | Tm (℃) | Enthalpy (J/g) |
|---|---|---|
| SSA | 3.13 | 308.38 |
| SSB | 3.98 | 315.68 |
| SSC | 3.24 | 315.30 |
| SSD | 3.44 | 315.76 |
| SSE | 3.27 | 308.53 |
| SSF | 2.51 | 314.70 |
| SSG | 3.08 | 310.57 |
| SSH | 2.98 | 309.11 |
| SSs | Yield Point | Flow Point | Flow Transition Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| (τy, Pa) | (τf, Pa) | (τf/τy) | |
| SSA | 11.139 | 47.228 | 4.24 |
| SSB | 5.908 | 35.639 | 6.03 |
| SSC | 4.730 | 15.939 | 3.37 |
| SSD | 22.779 | 97.283 | 4.27 |
| SSE | 14.186 | 65.161 | 4.59 |
| SSF | 10.446 | 43.174 | 4.13 |
| SSG | 15.638 | 67.283 | 4.3 |
| SSH | 29.236 | 90.483 | 3.09 |
| Samples | G’ = a’ωb’ | G’’ = a’’ωb’’ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a’ | b’ | R2 | a’’ | b’’ | R2 | |
| Low frequency (0.1–1 rad s−1) | ||||||
| SSA | 39.566 | 0.179 | 0.999 | 13.743 | 0.209 | 0.989 |
| SSB | 39.084 | 0.116 ∆ | 0.997 | 8.666 | 0.151 | 0.989 |
| SSC | 18.209 # | 0.212 ∆∆ | 0.999 | 7.480 | 0.249 | 0.999 |
| SSD | 51.980 ## | 0.121 | 0.998 | 11.373 | 0.156 | 0.987 |
| SSE | 38.937 | 0.137 | 0.999 | 10.359 | 0.183 | 0.996 |
| SSF | 29.181 | 0.149 | 0.998 | 8.530 | 0.194 | 0.996 |
| SSG | 101.248 | 0.105 | 0.998 | 20.395 | 0.133 | 0.989 |
| SSH | 157.228 | 0.103 | 0.996 | 30.374 | 0.135 | 0.963 |
| High frequency (1–100 rad s−1) | ||||||
| SSA | 42.258 | 0.169 | 0.971 | 12.972 | 0.227 | 0.987 |
| SSB | 40.616 | 0.111 | 0.960 | 8.321 | 0.179 | 0.978 |
| SSC | 15.062 * | 0.338 †† | 0.970 | 7.456 | 0.250 | 0.991 |
| SSD | 54.701 ** | 0.106 † | 0.946 | 11.242 | 0.143 | 0.974 |
| SSE | 35.952 | 0.211 | 0.973 | 10.063 | 0.178 | 0.984 |
| SSF | 26.711 | 0.235 | 0.975 | 8.264 | 0.213 | 0.983 |
| SSG | 102.595 | 0.116 | 0.998 | 21.609 | 0.076 | 0.968 |
| SSH | 156.4 | 0.119 | 0.998 | 31.004 | 0.066 | 0.973 |
| Sample Label | lnA | Ea (J·mol−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSA | 2.64 | 16,815.1 | 0.988 |
| SSB | 0.92 | 25,655.3 | 0.966 |
| SSC | 3.54 | 30,997.1 | 0.949 |
| SSD | 3.39 | 17,298.9 | 0.972 |
| SSE | 1.29 | 19,345.8 | 0.964 |
| SSF | 1.36 | 26,335.4 | 0.956 |
| SSG | 4.23 | 14,923.6 | 0.961 |
| SSH | 4.97 | 14,688.3 | 0.965 |
| Sample | PL | HB | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K (Pa·s) | n | R2 | τ0 (Pa) | K (Pa·s) | n | R2 | |
| SSA | 24.652 | 0.130 ∆ | 0.921 | 6.225 | 17.895 | 0.167 | 0.885 |
| SSB | 22.990 | 0.142 | 0.875 | 4.830 | 17.602 | 0.174 | 0.841 |
| SSC | 9.344 # | 0.159 | 0.873 | 1.003 | 8.160 | 0.177 | 0.853 |
| SSD | 36.613 ## | 0.152 | 0.918 | 11.412 | 24.109 | 0.205 | 0.865 |
| SSE | 32.523 | 0.232 ∆∆ | 0.976 | 6.548 | 24.954 | 0.297 | 0.952 |
| SSF | 18.902 | 0.158 | 0.939 | 2.158 | 16.662 | 0.151 | 0.900 |
| SSG | 41.804 | 0.177 | 0.998 | 11.633 | 29.740 | 0.218 | 0.982 |
| SSH | 74.839 | 0.175 | 0.994 | 30.570 | 41.042 | 0.245 | 0.950 |
| Label | Sx(W/V) | Sal(W/V) | Sx: Sal a | Final Polymer Concentration Ratio (Sx:Sal) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSA | 2% | 2% | 2:1 | 1.33%:0.67% |
| SSB | 2% | 2% | 1:1 | 1%:1% |
| SSC | 2% | 2% | 1:2 | 0.67%:1.33% |
| SSD | 3% | 2% | 2:1 | 2%:0.67% |
| SSE | 3% | 2% | 1:1 | 1.5%:1% |
| SSF | 3% | 2% | 1:2 | 1%:1.33% |
| SSG | 2% | - | - | 2%:0 |
| SSH | 3% | - | - | 3%:0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Zhang, G.; Yan, X.; Han, J.; Cao, X.; Xu, Y.; Fan, Z. Rheological and Thermal Properties of Salecan/Sanxan Composite Hydrogels for Food and Biomedical Applications. Gels 2025, 11, 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100839
Zhang X, Yang H, Zhang G, Yan X, Han J, Cao X, Xu Y, Fan Z. Rheological and Thermal Properties of Salecan/Sanxan Composite Hydrogels for Food and Biomedical Applications. Gels. 2025; 11(10):839. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100839
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiusheng, Haihong Yang, Guangming Zhang, Xiaoxue Yan, Jun Han, Xuesong Cao, Yan Xu, and Zhiping Fan. 2025. "Rheological and Thermal Properties of Salecan/Sanxan Composite Hydrogels for Food and Biomedical Applications" Gels 11, no. 10: 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100839
APA StyleZhang, X., Yang, H., Zhang, G., Yan, X., Han, J., Cao, X., Xu, Y., & Fan, Z. (2025). Rheological and Thermal Properties of Salecan/Sanxan Composite Hydrogels for Food and Biomedical Applications. Gels, 11(10), 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100839








