Innovative Applications of Hydrogels in Contemporary Medicine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sources of Literature
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- -
- Those published in a language other than English;
- -
- Those without an abstract or full text;
- -
- Editorial comments, letters to the editor, or introductory notes.
2.4. Selection Process
2.5. Data Synthesis
3. Properties and Applications of Hydrogels in Medicine
3.1. Hydrogels in Gynecology
Intravaginal Treatment of Fungal and Bacterial Infections
3.2. Hydrogels in Cardiology
3.3. Hydrogels in Bone and Joint Diseases
3.3.1. Rheumatoid Arthritis
3.3.2. Hydrogels in Rheumatoid Arthritis
3.3.3. Hydrogels as Drug Medium
3.3.4. Hydrogel Lubricating Properties
3.3.5. Tissue Scaffolds
3.3.6. Immunomodulators
3.3.7. Summary
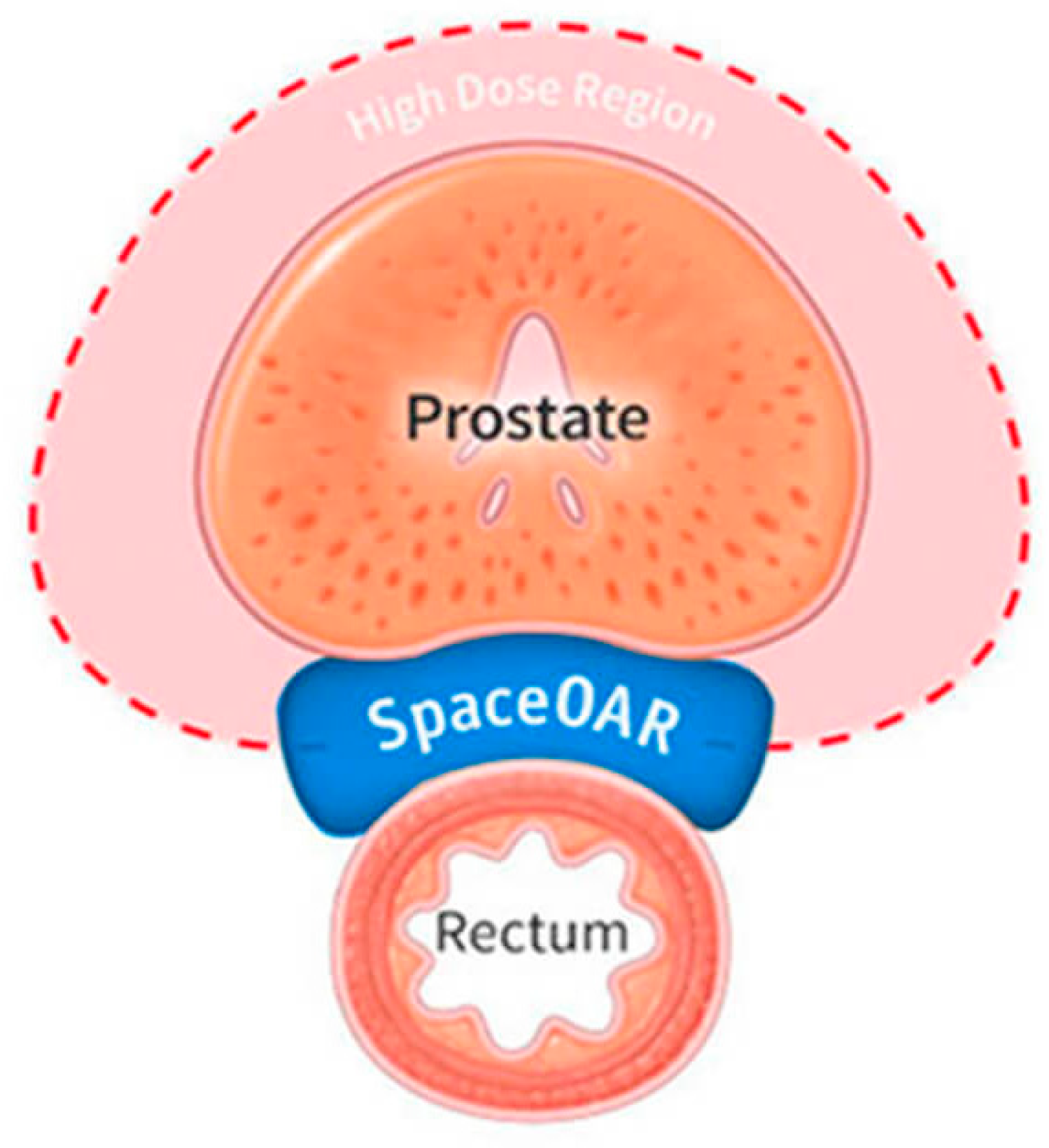
3.4. Hydrogels in Urology
Summary
3.5. Hydrogels in Cancer Therapy/Oncology
3.5.1. Hydrogels as Drug Delivery Systems and Modifiers of Drug Release
3.5.2. Hydrogels as Platforms for Modeling Tumors and Their Microenvironment
3.5.3. Chemoembolic Materials in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
3.5.4. Summary
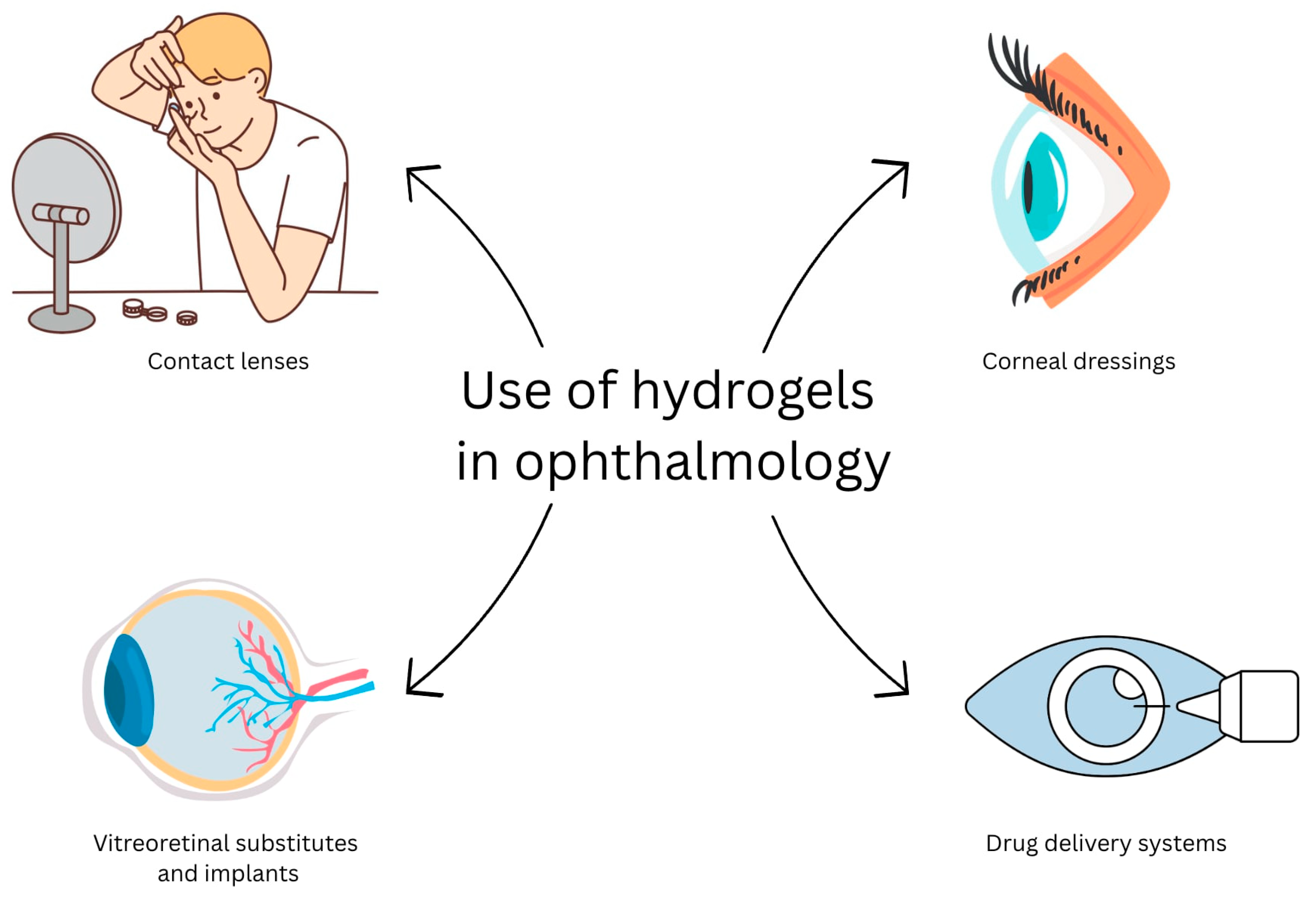
3.6. Hydrogels in Ophthalmology
- ·
- Intended for anterior segment of the eye:
- ○
- Contact lenses;
- ○
- Corneal dressings;
- ○
- Drug delivery systems for the eye surface;
- ○
- Adhesive hydrogels for wound sealing;
- ○
- Intraocular implants (IOLs).
- ·
- Intended for posterior segment of the eye:
- ○
- Vitreous substitutes;
- ○
- Drug delivery systems for the vitreous.
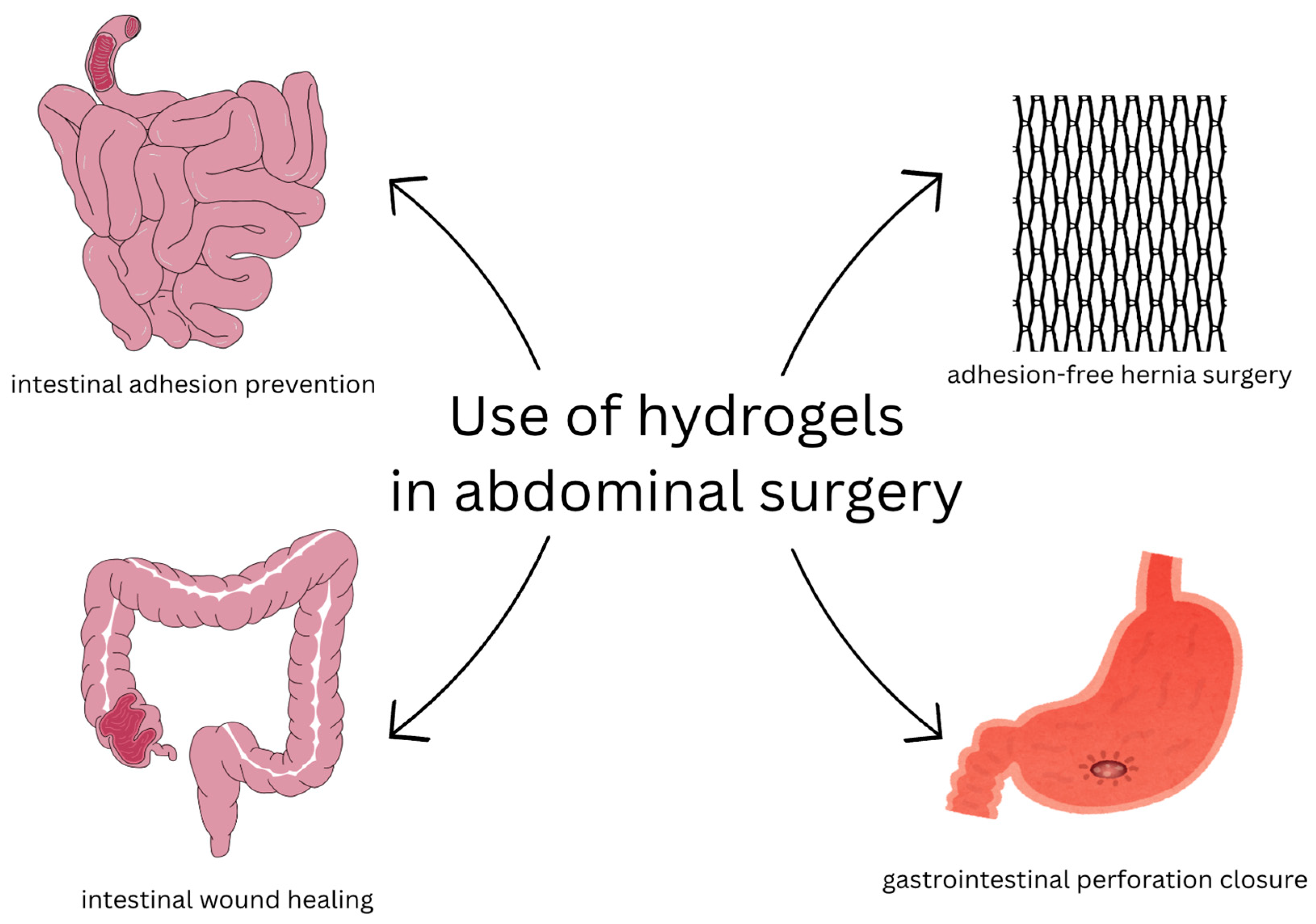
3.7. Hydrogels in Abdominal Surgery
Summary
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HG | Hydrogel |
| PVA | Polyvinyl alcohol |
| pHEMA | Poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| HA | Hyaluronic acid |
| IHD | Ischemic heart disease |
| MI | Myocardial infarctions |
| bFGF | Basic fibroblast growth factor |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| α-CD | α-Cyclodextrin |
| PLL | Poly L-lysine |
| bPANi | Bentonite-polyaniline |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| ACPAs | Anti-citrullinated antibodies |
| HLA | Human leukocyte antigen |
| NSAIDs | Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| DMARDs | Disease-modifying, antirheumatic drugs |
| RF | Rheumatoid factor |
| BMSCs | Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells |
| BMP-2 | Bone morphogenetic protein 2 |
| IONPs | Iron oxide nanoparticles |
| PEG | Poly(ethylene glycol) |
| p-HEMA | Poly(2 hydroxyethyl methacrylate) |
| DOX | Doxorubicin |
| IND | Indomethacin |
| BCNU | Carmustine |
| OS | Overall survival |
| GBM | Glioblastoma multiforme |
| GRPR | Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor |
| PEGDA | Poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| TACE | Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization |
| PCLA | Poly(ε-caprolactone-co-lactide) |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| DED | Dry eye disease |
| SBMA | Zwitterionic sulfobetaine methacrylate |
| HAMA | Hyaluronic acid |
| ZnMSG | Zinc-incorporated mesoporous silica nanogranules |
| GC | Gelatin methacrylate |
| PAA | Polyacrylic acid |
| PPM | Polypropylene mesh |
| BM | Biomaterial |
References
- van Bemmelen, J.M. Das Hydrogel und das krystallinische Hydrat des Kupferoxyds. Z. Für Anorg. Chem. 2004, 5, 466–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Sharma, M.; Devi, M. Hydrogels: An overview of its classifications, properties, and applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 147, 106145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschner, C.M.; Anseth, K.S. Hydrogels in healthcare: From static to dynamic material microenvironments. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichterle, O.; LÍM, D. Hydrophilic Gels for Biological Use. Nature 1960, 185, 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J. Norman Gaylord, 84; helped develop type o f contact lens. N. Y. Times News Serv. Boston Globe 2007. Available online: https://www.bostonglobe.com/2025/10/02/world/manchester-synagogue-stabbing/ (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Lu, H.; Zhang, N.; Ma, M. Electroconductive hydrogels for biomedical applications. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 11, e1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibas, I.; Janik, H. Review: Synthetic Polymer Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Chem. Chem. Technol. 2010, 4, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswathy, S.H.; Narendrakumar, U.; Manjubala, I. Commercial hydrogels for biomedical applications. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmese, L.L.; Thapa, R.K.; Sullivan, M.O.; Kiick, K.L. Hybrid hydrogels for biomedical applications. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2019, 24, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okay, O. General Properties of Hydrogels. In Hydrogel Sensors and Actuators; Series on Chemical Sensors and Biosensors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.A.; Serafin, A.; Collins, M.N. Development of 3D Printable Gelatin Methacryloyl/Chondroitin Sulfate/Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels as Implantable Scaffolds. Polymers 2024, 16, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baishya, G.; Parasar, B.; Limboo, M.; Kumar, R.; Dutta, A.; Hussain, A.; Phukan, M.M.; Saikia, D. Advancements in nanocomposite hydrogels: A comprehensive review of biomedical applications. Discov. Mater. 2024, 4, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothawade, S.N.; Pande, V.V. Polymers in Modern Medicine—Part 2; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angaria, N.; Saini, S.; Hussain, M.S.; Sharma, S.; Singh, G.; Khurana, N.; Kumar, R. Natural polymer-based hydrogels: Versatile biomaterials for biomedical applications. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2024, 73, 1550–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Annaka, M.; Ilmain, F.; Ishii, K.; Kokufuta, E.; Suzuki, A.; Tokita, M. Phase Transitions of Gels. In Mechanics of Swelling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 683–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosiak, J.M.; Yoshii, F. Hydrogels and their medical applications. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 1999, 151, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulanski, P.; Rosiak, J.M. The use of radiation technique in the synthesis of polymeric nanogels. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 1999, 151, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosiak, J.M.; Ulański, P. Synthesis of hydrogels by irradiation of polymers in aqueous solution. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 1999, 55, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lee, B.P. Recent Developments in Tough Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Gels 2018, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Du, Q.; Li, C.; Ding, C.; Chen, J.; He, Y.; Duan, T.; Feng, Q.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Q. Functionalized human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and injectable HA/Gel hydrogel synergy in endometrial repair and fertility recovery. Acta Biomater. 2023, 167, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Zhou, H.; Liang, X.; He, S.; Sun, X.; Guan, Y.; Song, Y. Thermo-sensitive ε-polylysine-heparin-poloxamer hydrogel-encapsulated BMSCs promote endometrial regeneration. Mater. Today Bio. 2025, 31, 101580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, J.; Karolewicz, B. Hydrożele: Właściwości i Zastosowanie w Technologii Postaci Leku. II. Możliwości Zastosowania Hydrożeli Jako Nośników Substancji Leczniczej. Available online: https://www.dbc.wroc.pl/Content/2174/304_Plut.pdf (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Chen, J.; Geng, L.; Song, X.; Li, H.; Giordan, N.; Liao, Q. Evaluation of the Efficacy and Safety of Hyaluronic Acid Vaginal Gel to Ease Vaginal Dryness: A Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled, Open-Label, Parallel-Group, Clinical Trial. J. Sex. Med. 2013, 10, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molteni, B.; D’Antuono, A.; Bandini, P.; Sintini, G.; Barcellona, E.; Agnello, A.; Milani, M. Efficacy and tolerability of a new chlorhexidine-based vaginal gel in vaginal infections. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2004, 20, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthis, A.H.C.; Kilchenmann, S.; Murdeu, M.; LeValley, P.J.; Wolf, M.; Meyer, C.; Cipolato, O.; Tibbitt, M.W.; Rosendorf, J.; Liska, V.; et al. Reversible Mechanical Contraception and Endometriosis Treatment Using Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2310301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, O.; Bhardwaj, R.D.; Bernard, S.; Zdunek, S.; Barnabé-Heider, F.; Walsh, S.; Zupicich, J.; Alkass, K.; Buchholz, B.A.; Druid, H.; et al. Evidence for Cardiomyocyte Renewal in Humans. Science 2009, 324, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, G.A.; Johnson, C.; Abajobir, A.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abera, S.F.; Abyu, G.; Ahmed, M.; Aksut, B.; Alam, T.; Alam, K.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases for 10 Causes, 1990 to 2015. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchel, J.F.; McKay, R.G. Treatment of acute stent thrombosis with local urokinase therapy using catheter-Based, drug delivery systems: A case report. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Diagn. 2005, 34, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, G.L.; Thomas, C.N.; Hanson, S.R.; Barry, J.J.; King, S.B.; Scott, N.A. Inhibition of Platelet-Dependent Thrombosis by Local Delivery of Heparin with a Hydrogel-Coated Balloon. Circulation 1995, 92, 1697–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellke, F.W.; Laham, R.J.; Edelman, E.R.; Pearlman, J.D.; Simons, M. Therapeutic Angiogenesis with Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor: Technique and Early Results. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1998, 65, 1540–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Suto, N.; Okubo, T.; Mikuniya, A.; Hanada, H.; Yagihashi, S.; Fujita, M.; Okumura, K. Intramyocardial Delivery of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor-Impregnated Gelatin Hydrogel Microspheres Enhances Collateral Circulation to Infarcted Canine Myocardium. Jpn. Circ. J. 2001, 65, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbern, J.C.; Lee, R.T. Heart regeneration: 20 years of progress and renewed optimism. Dev. Cell 2022, 57, 424–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocker, A.J.; Cavasin, M.; Johnson, N.R.; Shandas, R.; Park, D. Sulfonated Thermoresponsive Injectable Gel for Sequential Release of Therapeutic Proteins to Protect Cardiac Function after Myocardial Infarction. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 3883–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, T.; Liu, S.; Guo, B.; Huang, W.; Wu, Y. 3D bioprinting in cardiac tissue engineering. Theranostics 2021, 11, 7948–7969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Chen, J.; Bao, R.; Tan, B.; Cui, Y.; Fan, G.; Wang, W.; et al. Paintable and Rapidly Bondable Conductive Hydrogels as Therapeutic Cardiac Patches. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1704235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Xie, J.; Wei, H.; Yu, C.Y. Hydrogel-based cardiac patches for myocardial infarction therapy: Recent advances and challenges. Mater. Today Bio 2024, 29, 101331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Oyama, K.; Tsujita, K.; Yasuda, S.; Kobayashi, Y. Treatment strategies of acute myocardial infarction: Updates on revascularization, pharmacological therapy, and beyond. J. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacca, M. Cardiac Regeneration After Myocardial Infarction: An Approachable Goal. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2020, 22, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasumarthi, K.B.S.; Nakajima, H.; Nakajima, H.O.; Soonpaa, M.H.; Field, L.J. Targeted Expression of Cyclin D2 Results in Cardiomyocyte DNA Synthesis and Infarct Regression in Transgenic Mice. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.J.; Yang, X.; Don, C.W.; Minami, E.; Liu, Y.W.; Weyers, J.J.; Mahoney, W.M.; Van Biber, B.; Cook, S.M.; Palpant, N.J.; et al. Human embryonic-stem-cell-derived cardiomyocytes regenerate non-human primate hearts. Nature 2014, 510, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabisonia, K.; Prosdocimo, G.; Aquaro, G.D.; Carlucci, L.; Zentilin, L.; Secco, I.; Ali, H.; Braga, L.; Gorgodze, N.; Bernini, F.; et al. MicroRNA therapy stimulates uncontrolled cardiac repair after myocardial infarction in pigs. Nature 2019, 569, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singelyn, J.M.; Sundaramurthy, P.; Johnson, T.D.; Schup-Magoffin, P.J.; Hu, D.P.; Faulk, D.M.; Wang, J.; Mayle, K.M.; Bartels, K.; Salvatore, M.; et al. Catheter-Deliverable Hydrogel Derived From Decellularized Ventricular Extracellular Matrix Increases Endogenous Cardiomyocytes and Preserves Cardiac Function Post-Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Jin, R.; Chen, L.; Dang, M.; Cao, H.; Dong, Y.; Cai, B.; Bai, G.; Gooding, J.J.; et al. Injectable hydrogel with MSNs/microRNA-21-5p delivery enables both immunomodification and enhanced angiogenesis for myocardial infarction therapy in pigs. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabd6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, W.; Zhao, X.; Xian, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, N.; Xu, F.J.; Wang, C. Natural Melanin/Alginate Hydrogels Achieve Cardiac Repair through ROS Scavenging and Macrophage Polarization. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2100505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yue, Z.; Shi, M.; Jiang, L.; Chen, S.; Yao, M.; Yu, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhang, H.; Yao, F.; et al. An Intrapericardial Injectable Hydrogel Patch for Mechanical–Electrical Coupling with Infarcted Myocardium. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 16234–16248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.R.; Aghaei-Ghareh-Bolagh, B.; Gao, X.; Nikkhah, M.; Jung, S.M.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, S.M.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Tang, X.; et al. Layer-by-Layer Assembly of 3D Tissue Constructs with Functionalized Graphene. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 6136–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shu, Y.; Hao, T.; Wang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Duan, C.; Sun, H.; Lin, Q.; Wang, C. A chitosan–glutathione based injectable hydrogel for suppression of oxidative stress damage in cardiomyocytes. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 9071–9081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Shen, S.; Yin, W.; Ye, G.; Wang, L.; Hou, H.; Qiu, X. A tunable self-healing ionic hydrogel with microscopic homogeneous conductivity as a cardiac patch for myocardial infarction repair. Biomaterials 2021, 273, 120811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lee, R.J.; Tao, L. First-in-human transcatheter endocardial alginate-hydrogel implantation for the treatment of heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Fan, L.; Peng, N.; Yin, Y.; Mu, D.; Wang, J.; Meng, R.; Xie, J. Galunisertib-Loaded Gelatin Methacryloyl Hydrogel Microneedle Patch for Cardiac Repair after Myocardial Infarction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 40491–40500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Li, Z.; Huang, K.; Caranasos, T.G.; Rossi, J.S.; Cheng, K. Minimally invasive delivery of therapeutic agents by hydrogel injection into the pericardial cavity for cardiac repair. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, S.-G.; Kim, B.-s.; Park, S.; Sundaram, M.N.; Kim, B.-g.; Kim, C.-Y.; Hwang, N.S. Paintable Decellularized-ECM Hydrogel for Preventing Cardiac Tissue Damage. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2307353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherif, H.M.; Nekolla, S.G.; Saraste, A.; Reder, S.; Yu, M.; Robinson, S.; Schwaiger, M. Simplified Quantification of Myocardial Flow Reserve with flurpiridaz F 18: Validation with Microspheres in a Pig Model. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Marques, T. Connecting different heart diseases through intercellular communication. Biol. Open 2021, 10, bio058777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jugdutt, B.I. Prevention of ventricular remodelling post myocardial infarction: Timing and duration of therapy. Can. J. Cardiol. 1993, 9, 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Weil, B.R.; Neelamegham, S. Selectins and Immune Cells in Acute Myocardial Infarction and Post-infarction Ventricular Remodeling: Pathophysiology and Novel Treatments. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, J.W.; Borg, T.K.; Covell, J.W. Structure and Mechanics of Healing Myocardial Infarcts. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 7, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, N.J.R.; Sofrenovic, T.; Kuraitis, D.; Ahmadi, A.; McNeill, B.; Deng, C.; Rayner, K.J.; Zhong, Z.; Ruel, M.; Suuronen, E.J. Timing underpins the benefits associated with injectable collagen biomaterial therapy for the treatment of myocardial infarction. Biomaterials 2015, 39, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leor, J.; Tuvia, S.; Guetta, V.; Manczur, F.; Castel, D.; Willenz, U.; Petnehazy, O.; Landa, N.; Feinberg, M.S.; Konen, E.; et al. Intracoronary injection of in situ forming alginate hydrogel reverses left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in Swine. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.S.; Avazmohammadi, R.; Rodell, C.B.; Hsu, E.W.; Burdick, J.A.; Gorman, J.H.; Gorman, R.C.; Sacks, M.S. How hydrogel inclusions modulate the local mechanical response in early and fully formed post-infarcted myocardium. Acta Biomater. 2020, 114, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dileep, D.; Syed, T.A.; Sloan, T.F.W.; Dhandapany, P.S.; Siddiqi, K.; Sirajuddin, M. Cardiomyocyte orientation recovery at micrometer scale reveals long-axis fiber continuum in heart walls. EMBO J. 2023, 42, e113288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschenhagen, T.; Didié, M.; Heubach, J.; Ravens, U.; Zimmermann, W.-H. Cardiac tissue engineering. Transpl. Immunol. 2002, 9, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfer, A.; Bursac, N. Frame-Hydrogel Methodology for Engineering Highly Functional Cardiac Tissue Constructs. In Cardiac Regeneration; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, C.L.; Roche, E.T.; Ruiz-Hernandez, E.; Schenke-Layland, K.; Walsh, C.J.; Duffy, G.P. Drug and cell delivery for cardiac regeneration. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 84, 85–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, M.S.; Travas-Sejdic, J.; Malmström, J. Modulation of hydrogel stiffness by external stimuli: Soft materials for mechanotransduction studies. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 7578–7596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, N.; Luo, Q.; Yang, Y.; Shao, N.; Nie, T.; Deng, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Y.; Hu, K.; et al. Injectable pH Responsive Conductive Hydrogel for Intelligent Delivery of Metformin and Exosomes to Enhance Cardiac Repair after Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2410590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Lin, Q.; Tang, H.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, X. Fabrication of Temperature- and Alcohol-Responsive Photonic Crystal Hydrogel and Its Application for Sustained Drug Release. Langmuir 2022, 38, 3785–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshosaz, J.; Masoudi, S.; Mehdikhani, M.; Hashemi Beni, B.; Farsaei, S. Atorvastatin lipid nanocapsules and gold nanoparticles embedded in injectable thermo-gelling hydrogel scaffold containing adipose tissue extracellular matrix for myocardial tissue regeneration. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 13, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regato-Herbella, M.; Morhenn, I.; Mantione, D.; Pascuzzi, G.; Gallastegui, A.; Caribé dos Santos Valle, A.B.; Moya, S.E.; Criado-Gonzalez, M.; Mecerreyes, D. ROS-Responsive 4D Printable Acrylic Thioether-Based Hydrogels for Smart Drug Release. Chem. Mater. 2023, 36, 1262–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Lei, C.; Liu, H.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, C.Y.; Wei, H. A ROS-Responsive Liposomal Composite Hydrogel Integrating Improved Mitochondrial Function and Pro-Angiogenesis for Efficient Treatment of Myocardial Infarction. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, e2200990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, C.; Xie, X.; Cui, W.; Zuo, K. Tissue-Penetrating Ultrasound-Triggered Hydrogel for Promoting Microvascular Network Reconstruction. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2401368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Liu, S.; Qin, S.; Yang, J.; Yue, T.; Ye, B.; Tang, Y.; Feng, J.; Hou, J.; Danzeng, D. Injectable hydrogel-based combination therapy for myocardial infarction: A systematic review and Meta-analysis of preclinical trials. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2024, 24, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, N.; Linke, A.; Süselbeck, T.; Müller-Ehmsen, J.; Vermeersch, P.; Schoors, D.; Rosenberg, M.; Bea, F.; Tuvia, S.; Leor, J. Intracoronary Delivery of Injectable Bioabsorbable Scaffold (IK-5001) to Treat Left Ventricular Remodeling After ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2014, 7, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Gui, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, F.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, N.; Chen, W.; Xu, C.; Yang, H.; et al. Black-Phosphorus-Reinforced Injectable Conductive Biodegradable Hydrogel for the Delivery of ADSC-Derived Exosomes to Repair Myocardial Infarction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 58286–58298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Song, H.; Zhou, J.; Peng, Z.; Yin, W.; Fan, X.; Yang, K.; et al. A Novel Conductive Polypyrrole-Chitosan Hydrogel Containing Human Endometrial Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Facilitated Sustained Release for Cardiac Repair. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2024, 13, e2304207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeso, L.; Eufrásio-da-Silva, T.; Deveci, E.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Orive, G. Latest progress of self-healing hydrogels in cardiac tissue engineering. Biomed. Microdevices 2024, 26, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, A.M. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis. Am. Fam. Physician 2011, 84, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Lassere, M.N.; Rappo, J.; Portek, I.J.; Sturgess, A.; Edmonds, J.P. How many life years are lost in patients with rheumatoid arthritis? Secular cause-specific and all-cause mortality in rheumatoid arthritis, and their predictors in a long-term Australian cohort study. Intern. Med. J. 2013, 43, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaurasia, N.; Singh, A.; Singh, I.L.; Singh, T.; Tiwari, T. Cognitive dysfunction in patients of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2020, 9, 2219–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, A.F.; Bungau, S.G. Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Overview. Cells 2021, 10, 2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Nossent, J.; Pavlos, N.J.; Xu, J. Rheumatoid arthritis: Pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res. 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Ren, F.; Zhang, J.; Song, W.; Ren, L. New Dawn in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Advanced Insight into Polymer Hydrogel Research. Gels 2025, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, R.S.; Chen, P.Y.; Fang, J.H.; Chen, Y.Y.; Chang, C.W.; Lu, Y.J.; Hu, S.H. Adaptable Microporous Hydrogels of Propagating NGF-Gradient by Injectable Building Blocks for Accelerated Axonal Outgrowth. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Liu, Y.; Xie, H.; An, H.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Chai, W. Hydrogels for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Front Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1014543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, M.; Wong, L.K.; Zia, A.W.; Wu, H. Development of biomedical hydrogels for rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 19, 100887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Zhao, J.; Tao, B.; Yang, Y.; Duan, Q.; Gao, P.; He, T.; Liu, S.; Feng, Q.; Zhao, P.; et al. Regulation of rheumatoid arthritis microenvironment via a self-healing injectable hydrogel for improved inflammation elimination and bone repair. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 36, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, M.; Gao, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, P.; Wang, W.; Feng, Z.; Gao, J. Hyaluronic-Acid-Nanomedicine Hydrogel for Enhanced Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Mediating Macrophage-Synovial Fibroblast Cross-Talk. Biomater. Res. 2024, 28, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshabrawy, H.A.; Abo Dena, A.S.; Sobhy, M.H.; El-Sherbiny, I.M. Integrating 3D-printed hydrogels and polymeric nanofibers in a double-layered transdermal patch for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 40187–40197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Conde, B.R.; Brewer, E.; Lowman, A.; Peppas, N.A. Complexation Hydrogels as Oral Delivery Vehicles of Therapeutic Antibodies: An in Vitro and ex Vivo Evaluation of Antibody Stability and Bioactivity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 10197–10205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.D. The normal synovium. Open Rheumatol. J. 2011, 5, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, S.; Li, B.; Lin, J.; Lu, X.; Xie, C. Injectable bioadhesive and lubricating hydrogel with polyphenol mediated single atom nanozyme for rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngadimin, K.D.; Stokes, A.; Gentile, P.; Ferreira, A.M. Biomimetic hydrogels designed for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 4246–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Feng, Y.; Lin, Q.; Li, Z.; Liu, H. Enhanced osseointegration of three-dimensional supramolecular bioactive interface through osteoporotic microenvironment regulation. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4779–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedberg, H. Catheter induced urethral inflammatory reaction and urinary tract infection. An experimental and clinical study. Scand J. Urol. Nephrol. Suppl. 1989, 124, 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Bazira, P.J. Anatomy of the kidney and ureter. Surg. Oxf. 2022, 40, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wnętrzak, I.; Didkowska, J.; Sosnowski, R.; Czajkowski, M.; Sigorski, D.; Małkiewicz, B.; Marczyński, P.; Jaskulski, J.; Kania, P.; Ostrowski, A.; et al. Urogenital Cancer Epidemiology in Poland (1980–2020): A Narrative Review. Cancers 2025, 17, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, A.; Wang, C.; Ni, S.; Meng, Y.; Wang, T.; Yue, Z.; Yang, K.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Guo, P.; et al. Intravesical Mucoadhesive Hydrogel Induces Chemoresistant Bladder Cancer Ferroptosis through Delivering Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in a Three-Tier Strategy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 52374–52384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- What Is SpaceOAR Hydrogel? Available online: https://www.spaceoar.com/us/en/home.html?hl=pl-PL (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Harvey, M.; Ong, W.L.; Chao, M.; Udovicich, C.; McBride, S.; Bolton, D.; Eastham, J.; Perera, M. Comprehensive review of the use of hydrogel spacers prior to radiation therapy for prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2023, 131, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurowiak, J.; Kaczmarek-Pawelska, A.; Mackiewicz, A.G.; Bedzinski, R. Analysis of the Degradation Process of Alginate-Based Hydrogels in Artificial Urine for Use as a Bioresorbable Material in the Treatment of Urethral Injuries. Processes 2020, 8, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Meng, Q.; Yu, J. Preparation of a Photocured Biocompatible Hydrogel for Urethral Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 3519–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.S.; Andrews, G.P.; Hamill, T.; Gilmore, B.F. Fatty Acid-Containing p(HEMA) Hydrogels; A Promising Coating Platform to Reduce Encrustation on Urinary Catheters. Polymers 2025, 17, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Zhong, W.; Chai, M.; Shi, X. Dynamic compliance penis enlargement patch. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 42, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA: A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganti, A.K.; Pearce, A.; Haas, M.; Viney, R.; Pearson, S.-A.; Haywood, P.; Brown, C.; Ward, R. Incidence and severity of self-reported chemotherapy side effects in routine care: A prospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L. Nanoparticle-Hydrogel: A Hybrid Biomaterial System for Localized Drug Delivery. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 44, 2049–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhail, A.S.; Morhard, R.; Mauda-Havakuk, M.; Kassin, M.; Arrichiello, A.; Wood, B.J. Hydrogel drug delivery systems for minimally invasive local immunotherapy of cancer. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 202, 115083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Song, S.; Zhao, H.; Yuan, Y. Platinum-based drugs and hydrogel: A promising anti-tumor combination. Drug Deliv. 2023, 30, 2287966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, M.; Betts, D.; Suh, A.; Bui, K.; Kim, L.; Cho, H. Hydrogel-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Molecules 2015, 20, 20397–20408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lin, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, R.; Wang, C.; Zhao, C.; Lu, L.; Zhou, C.; Tian, J.; et al. Temperature- and pH-responsive injectable chitosan hydrogels loaded with doxorubicin and curcumin as long-lasting release platforms for the treatment of solid tumors. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1043939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, C.; Tian, Y.; Tang, Y.; Tang, M.; Yang, D.; Chen, F.; Ghaffarlou, M.; Tu, Y.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Li, Y. Hydrogel-based platforms for site-specific doxorubicin release in cancer therapy. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashby, L.S.; Smith, K.A.; Stea, B. Gliadel wafer implantation combined with standard radiotherapy and concurrent followed by adjuvant temozolomide for treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: A systematic literature review. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 14, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rurarz, B.P.; Urbanek, K.A.; Karczmarczyk, U.; Raczkowska, J.; Habrowska-Górczyńska, D.E.; Kozieł, M.J.; Kowalska, K.; Kadłubowski, S.; Sawicka, A.; Maurin, M.; et al. Towards Cancer Nanoradiopharmaceuticals—Radioisotope Nanocarrier System for Prostate Cancer Theranostics Based on Radiation-Synthesized Polymer Nanogels. Cancers 2023, 15, 5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qi, L.; Cai, Y.; Gao, X. Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor (GRPR) as a novel biomarker and therapeutic target in prostate cancer. Ann. Med. 2024, 56, 2320301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuwatfa, W.H.; Pitt, W.G.; Husseini, G.A. Scaffold-based 3D cell culture models in cancer research. J. Biomed. Sci. 2024, 31, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loessner, D.; Holzapfel, B.M.; Clements, J.A. Engineered microenvironments provide new insights into ovarian and prostate cancer progression and drug responses. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 79–80, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.H.; Siah, K.W.; Lo, A.W. Estimation of clinical trial success rates and related parameters. Biostatistics 2019, 20, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.M.; Lewis, D.; Gerecht, S. Bioinspired Hydrogels to Engineer Cancer Microenvironments. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 19, 109–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, J.; Mahajan, V.; Welzel, P.B.; Werner, C.; Taubenberger, A. Precision Hydrogels for the Study of Cancer Cell Mechanobiology. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2023, 12, e2202514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwag, H.R.; Serbo, J.V.; Korangath, P.; Sukumar, S.; Romer, L.H.; Gracias, D.H. A Self-Folding Hydrogel In Vitro Model for Ductal Carcinoma. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2016, 22, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rape, A.; Ananthanarayanan, B.; Kumar, S. Engineering strategies to mimic the glioblastoma microenvironment. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 79–80, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubenberger, A.V. In vitro microenvironments to study breast cancer bone colonisation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 79–80, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-P.; Zhang, J.-L.; Zou, Y.; Wu, Y.-L. Recent Advances on Polymeric Beads or Hydrogels as Embolization Agents for Improved Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization (TACE). Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lym, J.S.; Nguyen, Q.V.; Ahn, D.W.; Huynh, C.T.; Jae, H.J.; Kim, Y.I.; Lee, D.S. Sulfamethazine-based pH-sensitive hydrogels with potential application for transcatheter arterial chemoembolization therapy. Acta Biomater. 2016, 41, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Deng, X.; Tan, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Li, Q.; Zhou, J.; Xiao, Z.; Li, J. Idarubicin-loaded degradable hydrogel for TACE therapy enhances anti-tumor immunity in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mater. Today Bio 2024, 29, 101343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partyka, O.W.M. Epidemiologia chorób narządu wzroku oraz infrastruktura okulistyki w Polsce. Przegląd Epidemiol. Epidemiol. Rev. 2015, 69, 905–908. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Applications and Recent Developments of Hydrogels in Ophthalmology. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 5968–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhof, S.; Goepferich, A.M.; Brandl, F.P. Hydrogels in ophthalmic applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 95, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haworth, K.; Travis, D.; Leslie, L.; Fuller, D.; Pucker, A.D. Silicone hydrogel versus hydrogel soft contact lenses for differences in patient-reported eye comfort and safety. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 2023, CD014791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, P.; Tiwari, A.; Chowdhury, S.K.; Vohra, M.; Gour, A.; Waghmare, N.; Bhutani, U.; Kamalnath, S.; Sangwan, B.; Rajput, J.; et al. Kuragel: A biomimetic hydrogel scaffold designed to promote corneal regeneration. iScience 2024, 27, 109641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Han, Z. Injectable hydrogels for ophthalmic applications. J. Control. Release 2017, 268, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinberg, T.T.; Tzekov, R.T.; Stein, L.; Ravi, N.; Kaushal, S. Vitreous Substitutes: A Comprehensive Review. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2011, 56, 300–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhou, L.; Lu, X.; Gao, Q. A Novel Vitreous Substitute of Using a Foldable Capsular Vitreous Body Injected with Polyvinylalcohol Hydrogel. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, srep01838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulbay, M.; Wu, K.Y.; Truong, D.; Tran, S.D. Smart molecules in ophthalmology: Hydrogels as responsive systems for ophthalmic applications. Smart Mol. 2024, 2, e20230021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Han, Y.; Liu, Z. Advances in adhesive hydrogels applied for ophthalmology: An overview focused on the treatment. Theranostics 2025, 15, 915–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Wei, C.; Li, R.; Wu, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Photothermal conversion hydrogel based mini-eye patch for relieving dry eye with long-term use of the light-emitting screen. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5125–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osada, H.; Takahashi, K.; Fujii, T.K.; Tsunoda, I.; Satoh, K. The Effect of Cross-Linked Hyaluronate Hydrogel on the Reduction of Post-Surgical Adhesion Reformation in Rabbits. J. Int. Med. Res. 1999, 27, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, M.; Feng, J.; Zhou, J. A “Janus” Zwitterionic Hydrogel Patch for Tissue Repair and Prevention of Post-Operative Adhesions. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2024, 14, e2404082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, S.; Dawit, H.; Hussain, Z.; Ullah, S.; Ullah, I.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Pei, R. Harnessing bi-layered supramolecular Janus tissue-adhesive/anti-adhesive fibrous hydrogel for efficient hemostasis, wound healing, and suppressing postoperative tissue adhesion. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, J.; Chen, S.; Guo, W.; Chen, T.; Liu, X. A Janus adhesive hydrogel sheet for preventing postoperative tissue adhesion of intestinal injuries. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 4416–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Yu, L.; Qin, M.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Zheng, W.; Li, Z.; Ouyang, J.; et al. Photocurable injectable Janus hydrogel with minimally invasive delivery for all-in-one treatment of gastric perforations and postoperative adhesions. Theranostics 2023, 13, 5365–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Wu, X.; Han, M.; Peng, R.; Zhao, R.; Qin, M.; Li, T.; Yin, J.; Yu, L.; et al. A Sprayable Janus Hydrogel as an Effective Bioadhesive for Gastrointestinal Perforation Repair. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2408479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, R.T.; Kavalukas, S.L.; Barbul, A. Intra-abdominal adhesions: Anatomy, physiology, pathophysiology, and treatment. Curr. Probl. Surg. 2015, 52, 271–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela, M.F.; Stephen, J.; Lekshmi, M.; Ojha, M.; Wenzel, N.; Sanford, L.M.; Hernandez, A.J.; Parvathi, A.; Kumar, S.H. Bacterial Resistance to Antimicrobial Agents. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.-L.; Deng, F.-S.; Chuang, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-H. Antimicrobial Actions and Applications of Chitosan. Polymers 2021, 13, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, H.; Mori, T.; Fujinaga, T. Topical formulations and wound healing applications of chitosan. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 52, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, N.; Shinde, S.D.; Jadhav, G.S.; Adsare, D.R.; Rao, K.; Kachhia, M.; Maingle, M.; Patil, S.P.; Arya, N.; Sahu, B. Peptide-Chitosan Engineered Scaffolds for Biomedical Applications. Bioconjug. Chem. 2021, 32, 448–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranaz, I.; Alcántara, A.R.; Civera, M.C.; Arias, C.; Elorza, B.; Heras Caballero, A.; Acosta, N. Chitosan: An Overview of Its Properties and Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sizílio, R.H.; Galvão, J.G.; Trindade, G.G.G.; Pina, L.T.S.; Andrade, L.N.; Gonsalves, J.K.M.C.; Lira, A.A.M.; Chaud, M.V.; Alves, T.F.R.; Arguelho, M.L.P.M.; et al. Chitosan/pvp-based mucoadhesive membranes as a promising delivery system of betamethasone-17-valerate for aphthous stomatitis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 190, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ways, T.M.M.; Lau, W.M.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Chitosan and Its Derivatives for Application in Mucoadhesive Drug Delivery Systems. Polymers 2018, 10, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Li, H.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Du, Y. Water-solubility of chitosan and its antimicrobial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 63, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Sun, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, C.; Zou, M.; Ju, R.; Feng, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; et al. Study on repair of abdominal wall defect rats with hernia mesh coated with chitosan-based photosensitive hydrogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | TOTAL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gynecology | 8 | 14 | 23 | 16 | 26 | 87 |
| Myocardial infarction | 65 | 64 | 74 | 73 | 87 | 363 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 19 | 22 | 17 | 27 | 45 | 131 |
| Urology | 55 | 60 | 86 | 83 | 111 | 395 |
| Oncology | 38 | 49 | 51 | 59 | 78 | 275 |
| Ophthalmology | 134 | 170 | 150 | 148 | 207 | 809 |
| Abdominal surgery | 12 | 18 | 28 | 28 | 56 | 142 |
| TOTAL | 331 | 397 | 429 | 434 | 610 | 2202 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rybicki, M.; Czajkowska, K.; Grochowska, A.; Białas, B.; Dziatosz, M.; Karolczak, I.; Kot, J.; Wach, R.A.; Kłosiński, K.K. Innovative Applications of Hydrogels in Contemporary Medicine. Gels 2025, 11, 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100798
Rybicki M, Czajkowska K, Grochowska A, Białas B, Dziatosz M, Karolczak I, Kot J, Wach RA, Kłosiński KK. Innovative Applications of Hydrogels in Contemporary Medicine. Gels. 2025; 11(10):798. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100798
Chicago/Turabian StyleRybicki, Maciej, Karolina Czajkowska, Agata Grochowska, Bartłomiej Białas, Michał Dziatosz, Igor Karolczak, Julia Kot, Radosław Aleksander Wach, and Karol Kamil Kłosiński. 2025. "Innovative Applications of Hydrogels in Contemporary Medicine" Gels 11, no. 10: 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100798
APA StyleRybicki, M., Czajkowska, K., Grochowska, A., Białas, B., Dziatosz, M., Karolczak, I., Kot, J., Wach, R. A., & Kłosiński, K. K. (2025). Innovative Applications of Hydrogels in Contemporary Medicine. Gels, 11(10), 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11100798








