Texture Perception and Chewing of Agar Gel by People with Different Sensitivity to Hardness
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Instrumental Characterization of Agar Gels
2.2. Liking and Perceived Texture of Agar Gels
2.3. Chewing Characteristics of Agar Gels
2.4. Clustering of Hardness Sensitivity
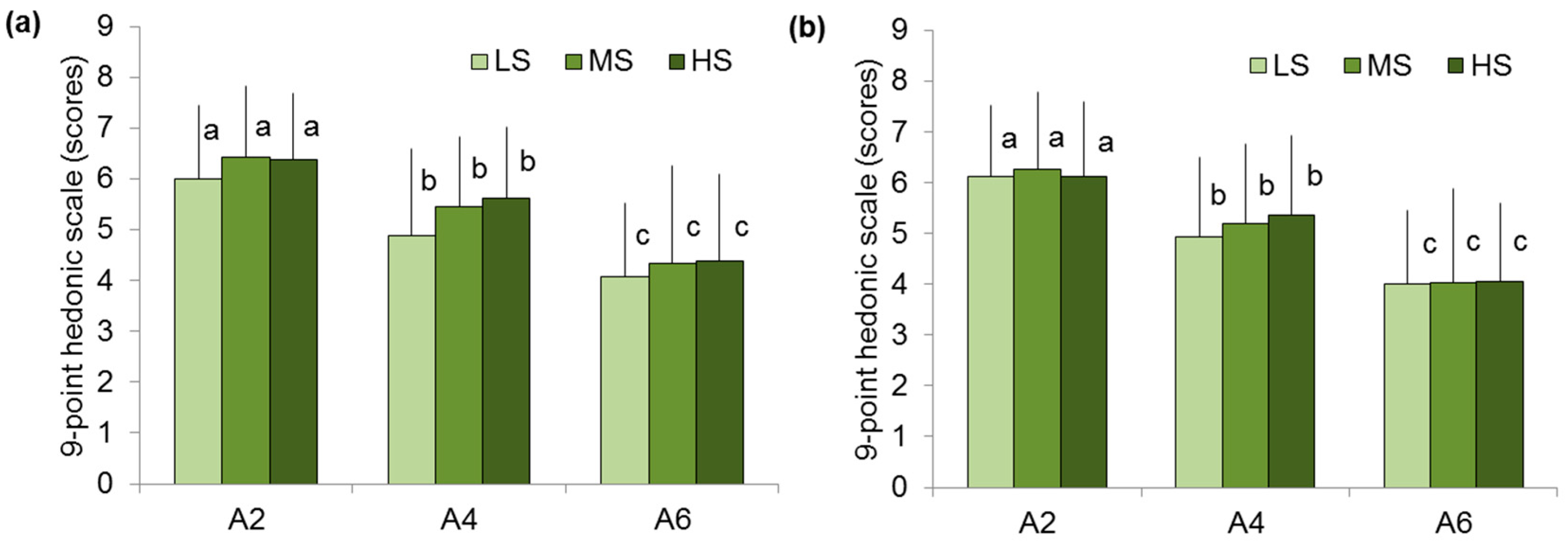
2.5. Sensory Evaluation of Agar Gels in Groups of Different Hardness Sensitivity
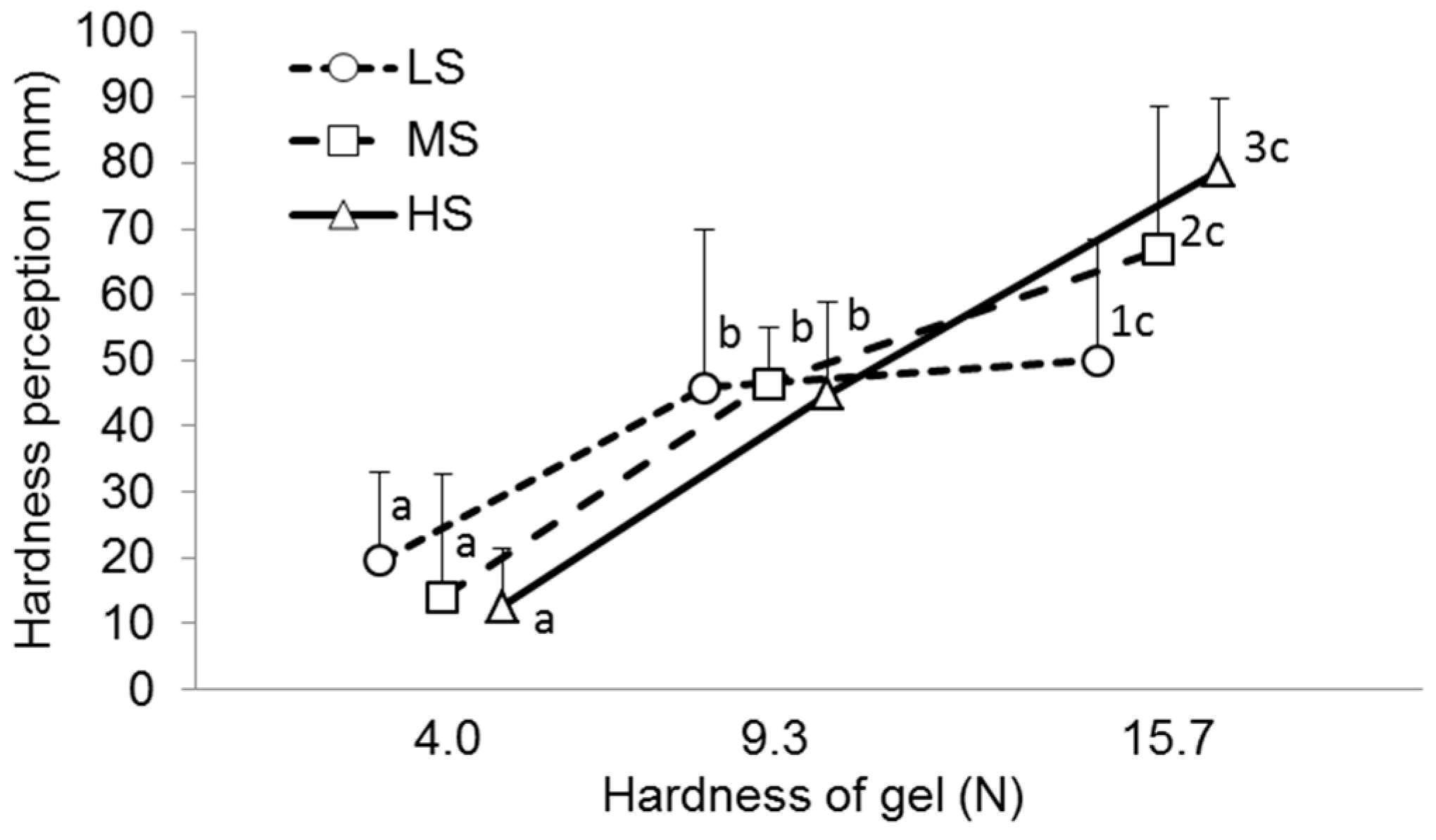
2.6. Chewing Parameters in Groups of Different Hardness Sensitivity
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation and Characterization of Gels
4.2. Participants
4.3. Sensory Analysis and Gel Acceptability Determination
4.4. Hardness Sensitivity Determination
4.5. Chewing Behavior
4.6. Bolus Characterization
4.7. Statistical Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, Y.; Mezzenga, R. Design principles of food gels. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, P.C.; Debnath, S.; Sridhar, K.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Nayak, P.K.; Sharma, M. A Comprehensive review of food hydrogels: Principles, formation mechanisms, microstructure, and its applications. Gels 2023, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lin, S.; Sun, N. Food gel-based systems for efficient delivery of bioactive ingredients: Design to application. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 13193–13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Lu, Y.; Cui, M.; Miao, S.; Gao, Y. Design of gel structures in water and oil phases for improved delivery of bioactive food ingredients. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1651–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Chandra Nath, P.; Kumar Hazarika, T.; Ojha, A.; Kumar Nayak, P.; Sridhar, K. Recent advances in 3D printing properties of natural food gels: Application of innovative food additives. Food Chem. 2024, 432, 137196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devezeaux de Lavergne, M.; van de Velde, F.; Stieger, M. Bolus matters: The influence of food oral breakdown on dynamic texture perception. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 464–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krop, E.M.; Hetherington, M.M.; Miguel, S.; Sarkar, A. The influence of oral lubrication on food intake: A proof-of-concept study. Food Qual. Prefer. 2019, 74, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, D.; van de Velde, F.; Visschers, R.W. The gap between food gel structure, texture and perception. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, F. Vocabularies and terminologies of food texture description and characterization. In Modifying Food Texture; Chen, J., Rosenthal, A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, R.; Luckett, C.R. Aversive textures and their role in food rejection. J. Texture Stud. 2020, 51, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, N.; Zhong, Y.; James, B.; Gant, N.; Hautus, M. Effect of basic structural variation, aimed at increasing perceivable textures in model foods, on the perception of textural complexity. Food Qual. Prefer. 2021, 91, 104196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puleo, S.; Valentino, M.; Masi, P.; Di Monaco, R. Hardness sensitivity: Are old, young, female and male subjects all equally sensitive? Food Qual. Prefer. 2021, 90, 104118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cîrstea, N.; Nour, V.; Corbu, A.R.; Codină, G.G. Blackcurrant Pomace Extract as a Natural Antioxidant in Vienna Sausages Reformulated by Replacement of Pork Backfat with Emulsion Gels Based on High Oleic Sunflower and Flaxseed Oils. Gels 2024, 10, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Feng, Y.; Kong, B.; Xia, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Q. Textural and gel properties of frankfurters as influenced by various κ-carrageenan incorporation methods. Meat Sci. 2021, 176, 108483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peh, F.Z.W.; Zhao, L.; Chia, Y.Y.; Ng, C.K.Z.; Du, J. Texture improvement and in vitro digestion modulation of plant-based fish cake analogue by incorporating hydrocolloid blends. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 8, 100775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropciuc, S.; Ghinea, C.; Leahu, A.; Prisacaru, A.E.; Oroian, M.A.; Apostol, L.C.; Dranca, F. Development and characterization of new plant-based ice cream assortments using oleogels as fat source. Gels 2024, 10, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, S.; Nakauma, M.; Funami, T.; Hori, K.; Ono, T. Human physiological responses during swallowing of gel-type foods and its correlation with textural perception. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier, C.; Sulmont-Rossé, C.; Guichard, E. Flavour perception: Aroma, taste and texture interactions. Food 2007, 1, 246–257. [Google Scholar]
- Appleton, K.M.; Newbury, A.; Almiron-Roig, E.; Yeomans, M.R.; Brunstrom, J.M.; de Graaf, K.; Geurts, L.; Kildegaard, H.; Vinoy, S. Sensory and physical characteristics of foods that impact food intake without affecting acceptability: Systematic review and meta-analyses. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2021, 22, e13234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forde, C.G.; Bolhuis, D. Interrelations between food form, texture, and matrix influence energy intake and metabolic responses. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2022, 11, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funami, T.; Nakauma, M. Instrumental food texture evaluation in relation to human perception. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Manei, K.; Jia, L.; Al-Manei, K.K.; Ndanshau, E.L.; Grigoriadis, A.; Kumar, A. Food hardness modulates behavior, cognition, and brain activation: A systematic review of animal and human studies. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y. Perception and measurement of food texture: Solid foods. J. Texture Stud. 2018, 49, 160–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Vickers, Z. Liking of food textures and its relationship with oral physiological parameters and mouth-behavior groups. J. Texture Stud. 2020, 51, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zickgraf, H.F.; Richard, E.; Zucker, N.L.; Wallace, G.L. Rigidity and sensory sensitivity: Independent contributions to selective eating in children, adolescents, and young adults. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 2020, 51, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Cattaneo, C.; Papavasileiou, M.; Methven, L.; Bredie, W. A review on oral tactile acuity: Measurement, influencing factors and its relation to food perception and preference. Food Qual. Prefer. 2022, 100, 104624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olarte Mantilla, S.M.; Shewan, H.M.; Shingleton, R.; Stokes, J.R.; Smyth, H.E. Ability to detect and identify the presence of particles influences consumer acceptance of yoghurt. Food Qual. Prefer. 2020, 85, 103979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bech, A.C.; Waehrens, S.; Bredie, W. Perception and liking of yogurts with different degrees of granularity in relation to ethnicity, preferred oral processing and lingual tactile acuity. Food Qual. Prefer. 2021, 90, 104158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puleo, S.; Miele, N.A.; Cavella, S.; Masi, P.; Di Monaco, R. How sensory sensitivity to graininess could be measured? J. Texture Stud. 2020, 51, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukasewycz, L.; Mennella, J. Lingual tactile acuity and food texture preferences among children and their mothers. Food Qual. Prefer. 2012, 26, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shupe, G.E.; Wilson, A.; Luckett, C.R. The effect of oral tactile sensitivity on texture perception and mastication behavior. J. Texture Stud. 2019, 50, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devezeaux de Lavergne, M.S.M.; Derks, J.A.M.; Ketel, E.C.; de Wijk, R.A.; Stieger, M.A. Eating behaviour explains differences between individuals in dynamic texture perception of sausages. Food Qual. Prefer. 2015, 41, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Estanol, K.; van Bruinessen, M.; Biasioli, F.; Stieger, M. Differences in habitual eating speed lead to small differences in dynamic sensory perception of composite foods. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çakır, E.; Vinyard, C.; Essick, G.; Daubert, C.; Drake, M.; Foegeding, E. Interrelations among physical characteristics, sensory perception and oral processing of protein-based soft-solid structures. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 29, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeltema, M.; Beckley, J.; Vahalik, J. Food texture assessment and preference based on Mouth Behavior. Food Qual. Prefer. 2016, 52, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobies, M.; Kozak, M.; Jurga, S. Studies of gelation process investigated by fast field cycling relaxometry and dynamical rheology: The case of aqueous low methoxyl pectin solution. Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 2004, 25, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghebremedhin, M.; Seiffert, S.; Vilgis, T.A. Physics of agarose fluid gels: Rheological properties and microstructure. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, A.; Chen, J. Dimensions of food texture: A conceptual discussion. J. Texture Stud. 2023, 54, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguayo-Mendoza, M.; Santagiuliana, M.; Ong, X.; Piqueras-Fiszman, B.; Scholten, E.; Stieger, M. How addition of peach gel particles to yogurt affects oral behavior, sensory perception and liking of consumers differing in age. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, K.H.; Kerr, W.L.; Cavender, G.A. The effects of okara ratio and particle size on the physical properties and consumer acceptance of tofu. Foods 2023, 12, 3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Ren, Y.; Huang, L.; Ye, X.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Cao, J.; Liu, X. Quality, thermo-rheology, and microstructure characteristics of cubic fat substituted pork patties with composite emulsion gel composed of konjac glucomannan and soy protein isolate. Gels 2024, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, C.L.; Wagoner, T.B.; Foegeding, E.A. Designing foods for satiety: The roles of food structure and oral processing in satiation and satiety. Food Struct. 2017, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, S.; Smirnov, V.; Khramova, D.; Paderin, N.; Chistiakova, E.; Ptashkin, D.; Vityazev, F. Effect of hogweed pectin on rheological, mechanical, and sensory properties of apple pectin hydrogel. Gels 2023, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, S.; Smirnov, V.; Paderin, N.; Khramova, D.; Chistiakova, E.; Vityazev, F.; Golovchenko, V. Enrichment of agar gel with antioxidant pectin from fireweed: Mechanical and rheological properties, simulated digestibility, and oral processing. Gels 2022, 8, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, S.; Paderin, N.; Khramova, D.; Kvashninova, E.; Patova, O.; Vityazev, F. Swelling, protein adsorption, and biocompatibility in vitro of gel beads prepared from pectin of hogweed Heracleum sosnówskyi Manden. in comparison with gel beads from apple pectin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 8589; International Organization for Standardization (ISO)—Sensory Analysis—General Guidance for the Design of Test Rooms. 2007. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/36385.html (accessed on 3 May 2021).
- ISO 11036; International Organization for Standardization (ISO)—Sensory Analysis—Methodology-Texture Profile. 2020. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/76668.html (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Lawless, H.T.; Heymann, H. Sensory Evaluation of Food. Principles and Practices, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 149–177. [Google Scholar]
- Choy, J.Y.M.; Goh, A.T.; Chatonidi, G.; Ponnalagu, S.; Wee, S.M.M.; Stieger, M.; Forde, C.G. Impact of food texture modifications on oral processing behaviour, bolus properties and postprandial glucose responses. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandalari, G.; Parker, M.L.; Grundy, M.M.; Grassby, T.; Smeriglio, A.; Bisignano, C.; Raciti, R.; Trombetta, D.; Baer, D.J.; Wilde, P.J. Understanding the effect of particle size and processing on almond lipid bioaccessibility through microstructural analysis: From mastication to faecal collection. Nutrients 2018, 10, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Jamovi Project. Jamovi (Version 2.3). 2024. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org (accessed on 11 November 2024).


| Parameter | Agar Gel | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A2 | A4 | A6 | |
| Density (mg/mm3) | 1.08 ± 0.03 a | 1.12 ± 0.07 a | 1.12 ± 0.06 a |
| Water content (%) | 85.1 ± 0.1 a | 82.5 ± 0.1 b | 79.9 ± 0.2 c |
| pH | 4.17 ± 0.03 a | 4.27 ± 0.05 b | 4.26 ± 0.02 b |
| G’LVE (Pa) | 31,156 ± 1052 a | 133,519 ± 11,681 b | 168,248 ± 40,533 c |
| G″LVE (Pa) | 2455 ± 1010 a | 15,506 ± 7665 b | 20,050 ± 13,911 c |
| Tan [δ]LVE | 0.080 ± 0.036 a | 0.120 ± 0.067 ab | 0.164 ± 0.079 b |
| k’ (Pa·s) | 35,720 ± 1455 a | 144,006 ± 11,551 b | 144,909 ± 113,361 b |
| k″ (Pa·s) | 1645 ± 94 a | 8477 ± 761 b | 10,529 ± 4519 b |
| η·s | 5605 ± 304 a | 22,426 ± 1481 b | 29,241 ± 15,693 b |
| Viscosity K (Pa·s) | 5605 | 24,143 | 22,948 |
| Parameter | Agar Gel | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A2 | A4 | A6 | |
| Hardness (N) | 4.03 ± 0.26 a | 9.35 ± 0.68 b | 15.71 ± 1.21 c |
| Cohesiveness | 0.25 ± 0.09 a | 0.24 ± 0.04 a | 0.25 ± 0.07 a |
| Springiness | 0.98 ± 0.05 a | 1.02 ± 0.08 ab | 1.04 ± 0.10 b |
| Adhesiveness (N×s) | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.01 b | 0.03 ± 0.01 b |
| Gumminess | 1.03 ± 0.46 a | 2.21 ± 0.37 b | 3.99 ± 1.17 c |
| Parameter | Agar Gel | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A2 | A4 | A6 | |
| Overall liking (score) | 6.3 ± 1.4 a | 5.4 ± 1.5 b | 4.3 ± 1.7 c |
| Texture liking (score) | 6.2 ± 1.5 a | 5.2 ± 1.6 b | 4.0 ± 1.7 c |
| Parameter | Agar Gel | r with Overall Liking | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A2 | A4 | A6 | ||
| Hardness (mm) | 15 ± 10 a | 46 ± 20 b | 66 ± 20 c | −0.42 * |
| Brittleness (mm) | 61 ± 28 a | 50 ± 22 b | 46 ± 25 b | 0.19 * |
| Springiness (mm) | 32 ± 23 a | 47 ± 25 b | 59 ± 35 c | −0.06 |
| Adhesiveness (mm) | 24 ± 20 a | 25 ± 19 a | 24 ± 22 a | 0.16 * |
| Chewiness (mm) | 14 ± 12 a | 33 ± 21 b | 50 ± 26 c | −0.40 * |
| Moisture (mm) | 70 ± 17 a | 43 ± 20 b | 24 ± 17 c | 0.44 * |
| Swallowability (mm) | 79 ± 19 a | 66 ± 23 b | 51 ± 25 c | 0.48 * |
| Parameter | Gels | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A2 | A4 | A6 | |
| Temporal characteristics | |||
| Chewing time (s) | 14 ± 8 a | 21 ± 10 b | 25 ± 12 c |
| Chewing cycle number (times) | 19 ± 8 a | 29 ± 12 b | 34 ± 14 c |
| Chewing cycle time (ms) | 754 ± 219 a | 723 ± 163 a | 745 ± 175 a |
| Amplitude characteristics of masseter muscle | |||
| Maximal amplitude (mcV) | 719 ± 508 a | 910 ± 634 b | 1016 ± 713 c |
| Mean amplitude (mcV) | 25 ± 19 a | 32 ± 22 b | 36 ± 24 c |
| Area amplitude (mV·ms) | 415 ± 357 a | 725 ± 531 b | 945 ± 781 c |
| Amplitude characteristics of temporalis muscle | |||
| Maximal amplitude (mcV) | 596 ± 409 a | 699 ± 436 b | 765 ± 468 c |
| Mean amplitude (mcV) | 21 ± 13 a | 25 ± 14 b | 28 ± 14 c |
| Area amplitude (mV·ms) | 358 ± 321 a | 586 ± 451 b | 758 ± 559 c |
| Amplitude characteristics of suprahyoid muscles * | |||
| Maximal amplitude (mcV) | 668 ± 316 a | 782 ± 409 b | 825 ± 409 c |
| Mean amplitude (mcV) | 32 ± 14 a | 35 ± 15 b | 36 ± 15 c |
| Area amplitude (mV·ms) | 545 ± 319 a | 802 ± 474 b | 985 ± 628 c |
| Activity index | |||
| Masseter/temporalis m. (%) | 7 ± 21 a | 10 ± 20 b | 10 ± 20 b |
| Masseter/suprahyoid m. (%) | −15 ± 27 a | −6 ± 27 b | −3 ± 26 c |
| Parameter | Sensitivity Group | Agar Gel | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A2 | A4 | A6 | ||
| Temporal characteristics | ||||
| Chewing cycle number (times) | LS | 20 ± 7 a | 29 ± 11 b | 36 ± 14 c |
| MS | 18 ± 6 a | 29 ± 12 b | 32 ± 13 c | |
| HS | 22 ± 9 a | 30 ± 14 b | 36 ± 17 c | |
| Chewing time (s) | LS | 14.8 ± 7.4 a | 21.3 ± 9.2 b | 26.3 ± 10.8 c |
| MS | 12.5 ± 5.1 a | 19.1 ± 7.9 b | 22.6 ± 8.6 c | |
| HS | 17 ± 11.7 a | 22.6 ± 14 b | 27.1 ± 17.8 c | |
| Amplitude characteristics of masseter muscle | ||||
| Maximal amplitude (mcV) | LS | 774 ± 729 a | 997 ± 795 b | 1116 ± 988 b |
| MS | 732 ± 452 a | 949 ± 583 b | 1076 ± 626 c | |
| HS | 646 ± 335 a | 762 ± 544 ab | 822 ± 514 b | |
| Area amplitude (mV·ms) | LS | 432 ± 519 a | 733 ± 671 b | 1043 ± 1158 c |
| MS | 416 ± 274 a | 770 ± 496 b | 968 ± 616 c | |
| HS | 398 ± 310 a | 641 ± 449 b | 816 ± 598 c | |
| Amplitude characteristics of temporalis muscle | ||||
| Maximal amplitude (mcV) | LS | 584 ± 381 a | 686 ± 417 b | 789 ± 483 c |
| MS | 608 ± 435 a | 752 ± 474 b | 800 ± 475 c | |
| HS | 588 ± 405 a | 621 ± 387 ab | 681 ± 451 b | |
| Area amplitude (mV·ms) | LS | 353 ± 260 a | 586 ± 347 b | 813 ± 522 c |
| MS | 349 ± 257 a | 610 ± 463 b | 780 ± 602 c | |
| HS | 379 ± 453 a | 544 ± 523 b | 670 ± 529 c | |
| Amplitude characteristics of suprahyoid muscles | ||||
| Maximal amplitude (mcV) | LS | 743 ± 326 a | 873 ± 464 ab | 946 ± 444 b |
| MS | 642 ± 302 a | 786 ± 400 b | 782 ± 371 b | |
| HS | 643 ± 329 a | 692 ± 362 a | 782 ± 426 b | |
| Area amplitude (mV·ms) | LS | 600 ± 309 a | 867 ± 488 b | 1087 ± 519 c |
| MS | 512 ± 281 a | 781 ± 429 b | 917 ± 531 c | |
| HS | 547 ± 386 a | 775 ± 540 b | 1000 ± 842 c | |
| Parameter | Sensitivity Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| LS | MS | HS | |
| Saliva incorporation rate (g/min) | 4.0 ± 3.2 a | 4.7 ± 2.5 a | 5.1 ± 3.3 a |
| Saliva uptake (g/g) | 1.29 ± 0.96 a | 1.34 ± 1.4 a | 1.12 ± 1.14 a |
| Bolus particle size < 1.6 mm (%) | 79 ± 14 a | 82 ± 13 a | 78 ± 16 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smirnov, V.; Khramova, D.; Chistiakova, E.; Zueva, N.; Vityazev, F.; Velskaya, I.; Popov, S. Texture Perception and Chewing of Agar Gel by People with Different Sensitivity to Hardness. Gels 2025, 11, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11010005
Smirnov V, Khramova D, Chistiakova E, Zueva N, Vityazev F, Velskaya I, Popov S. Texture Perception and Chewing of Agar Gel by People with Different Sensitivity to Hardness. Gels. 2025; 11(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmirnov, Vasily, Daria Khramova, Elizaveta Chistiakova, Natalya Zueva, Fedor Vityazev, Inga Velskaya, and Sergey Popov. 2025. "Texture Perception and Chewing of Agar Gel by People with Different Sensitivity to Hardness" Gels 11, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11010005
APA StyleSmirnov, V., Khramova, D., Chistiakova, E., Zueva, N., Vityazev, F., Velskaya, I., & Popov, S. (2025). Texture Perception and Chewing of Agar Gel by People with Different Sensitivity to Hardness. Gels, 11(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11010005







