Sticking to the Subject: Multifunctionality in Microbial Adhesins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Multiple Activities of Microbial Adhesins
2.1. What Is an Adhesin?
2.2. Biofilms
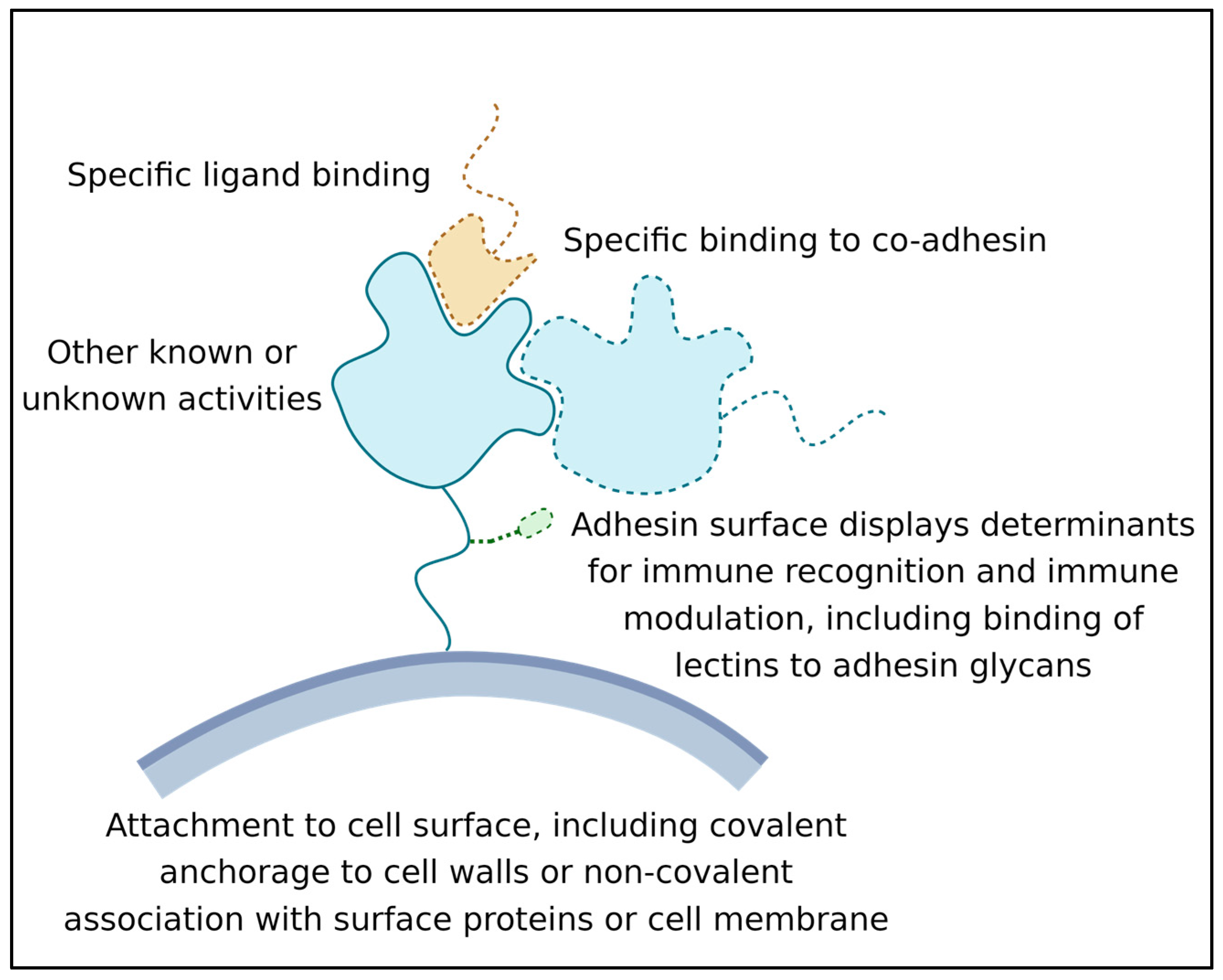
2.3. Multiple Activities of Microbial Adhesins
- Its ability to recognize and bind a ligand or other binding partner. This binding must last long enough for the adhesion to be biologically relevant; often this means that the adhesive bond lasts for hours or even years [15];
- Its attachment to the surface of the expressing cell. Attachment can be through covalent binding to the cell wall, membrane embedment, or association with another wall-attached protein [16];
- Its activity as a surface marker: This activity is crucial in microbe-host interactions, and many adhesins are also immune modulators. Adhesin structures are bound by immune effectors and by other cell signal receptors. This binding leads to the modulation of host responses. In addition, biofilm adhesins mediate microbe–microbe associations, which induce changes in microbial cellular physiology [12,13,17]. This activity can be due to direct signaling between adhesins, or indirect due to adhesin-induced long-term increases in population density [18,19].
2.4. Time and Adhesin Activity
2.5. Adhesion Assays
2.6. Characteristics of Adhesin Binding
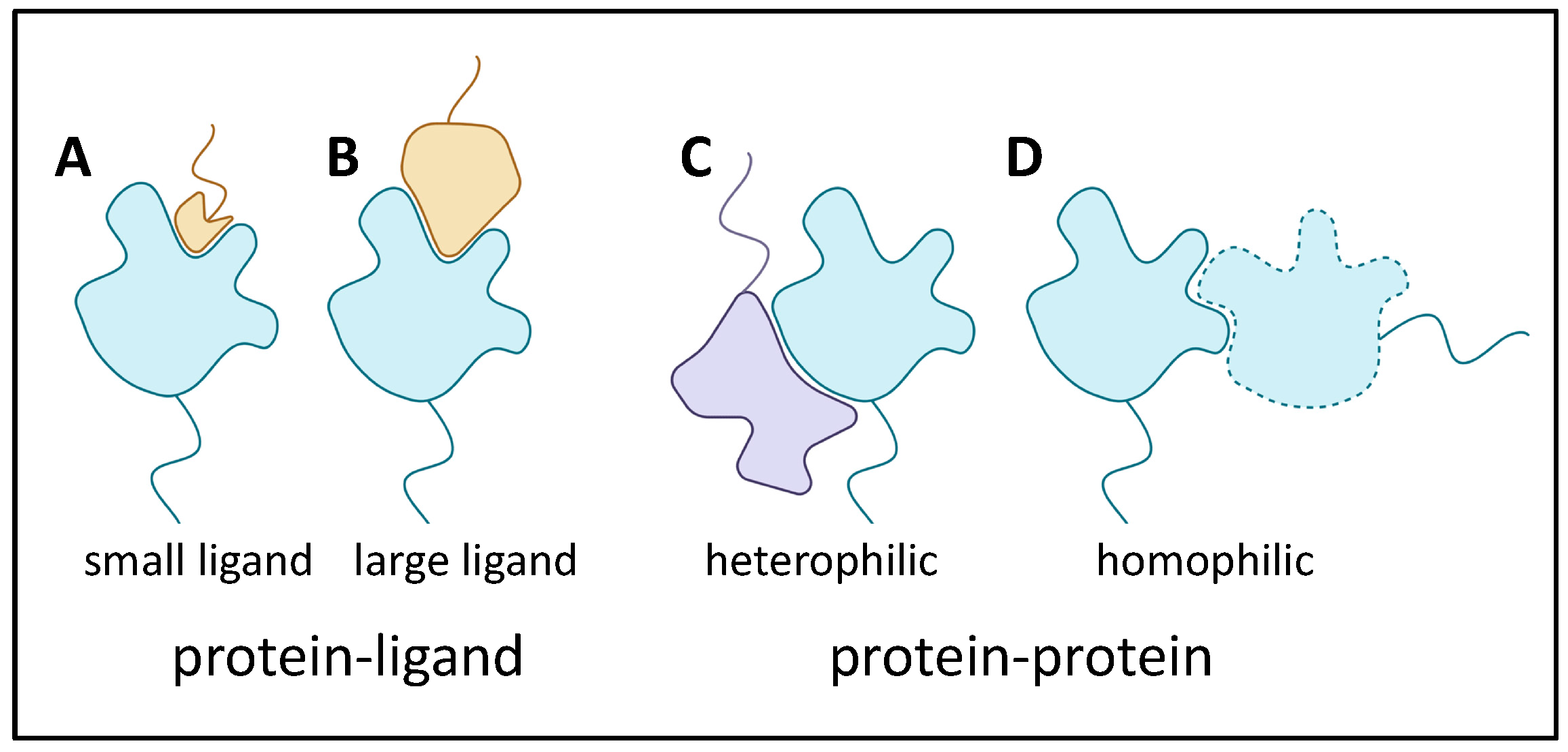
2.6.1. Adhesin Ligands and Partners
2.6.2. Adhesin Bonding
3. Intracellular Proteins That Moonlight as Adhesins
4. Multifunctional Bacterial Adhesins
4.1. Bacillus subtilis TasA
4.2. Pili Adhesins
4.3. MSCRAMMS
5. General Characteristics of Fungal Adhesins
6. Candida albicans Int1
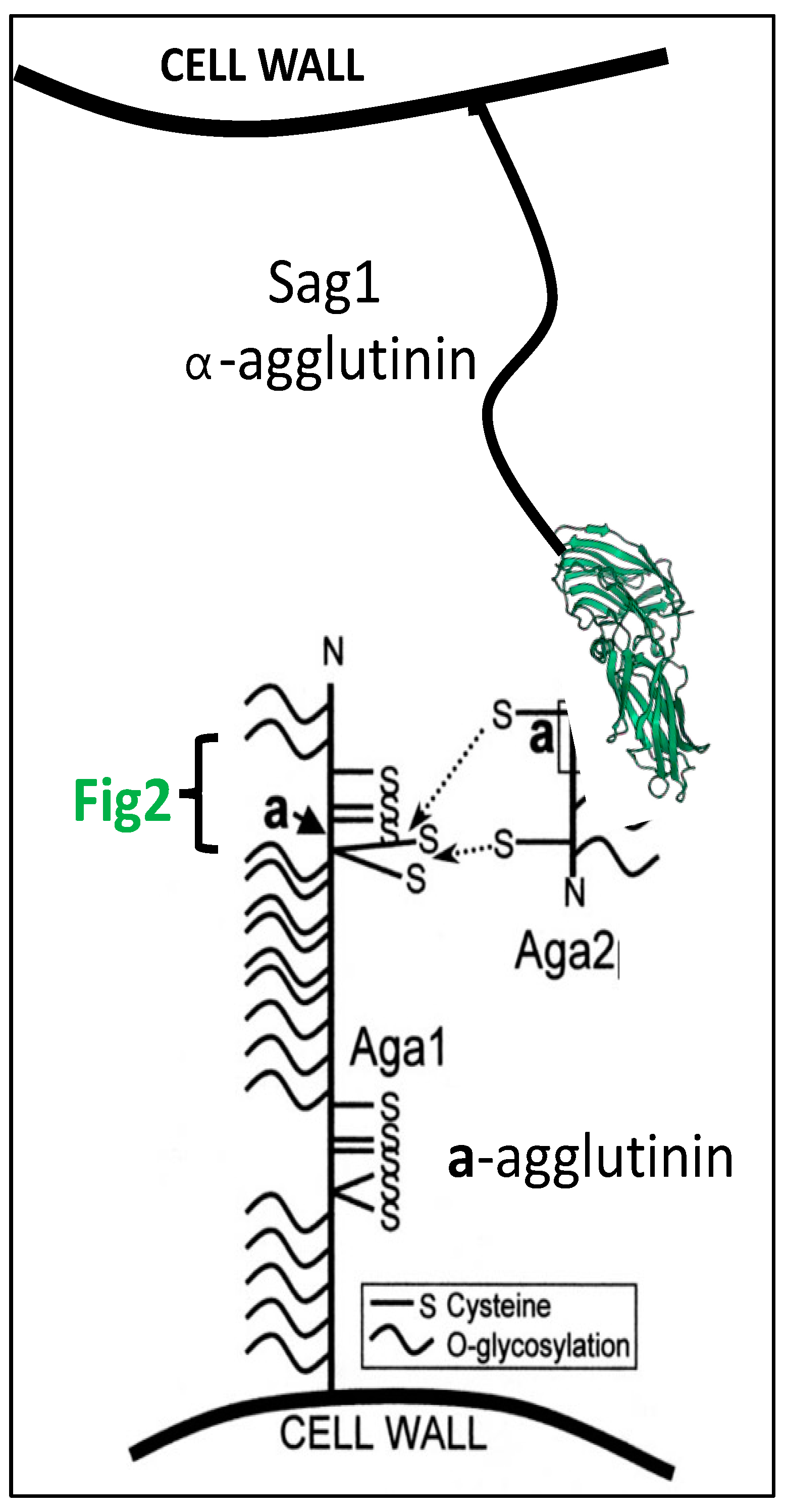
7. Multiple Functions of Yeast Mating Adhesins
Multiple Functions through Indirect Consequences of Adhesion in Mating
8. Multiple Binding Modes and Multiple Functions in Candida adhesins
8.1. Candida glabrata Awp Family Adhesins
8.2. C. albicans Adhesins
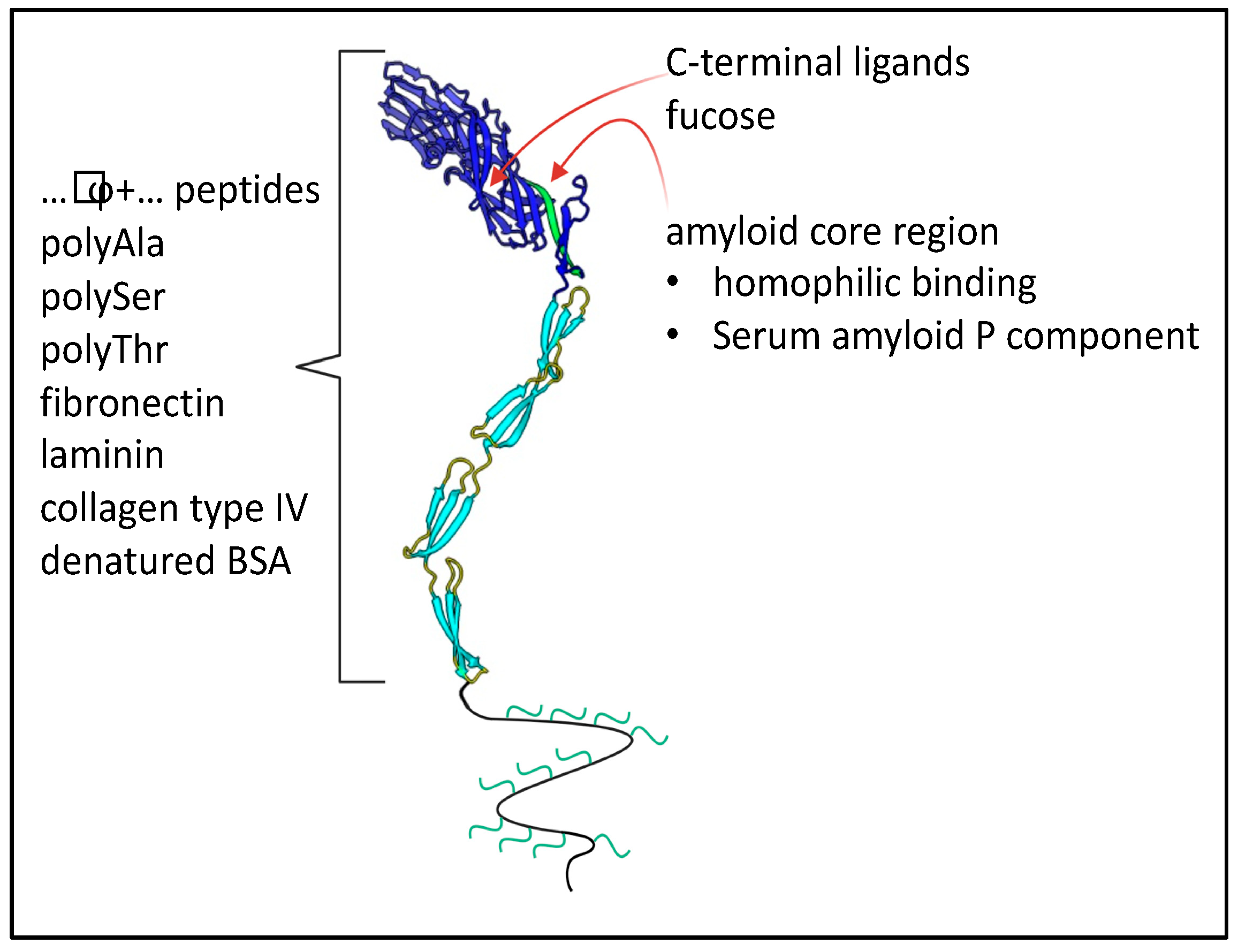
9. C. albicans Als Family Adhesins
9.1. Adhesion-Related Activities of Als Family Proteins
9.2. Unexpected Functions of Als Family Adhesins
10. The Remarkable Similarity of Bacterial MSCRAMMs and Fungal Als Adhesins
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pearce, R.; Huang, X.; Omenn, G.S.; Zhang, Y. De novo protein fold design through sequence-independent fragment assembly simulations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2208275120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, I.E.; Galpern, E.A.; Garibaldi, M.M.; Ferreiro, D.U. Molecular Information Theory Meets Protein Folding. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 8655–8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyna-Beltrán, E.; Iranzo, M.; Calderón-González, K.G.; Mondragón-Flores, R.; Labra-Barrios, M.; Mormeneo, S.; Luna-Arias, J. The Candida albicans ENO1 gene encodes a transglutaminase involved in growth, cell division, morphogenesis, and osmotic protection. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 4304–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, C.; Gerami-Nejad, M.; McClellan, M.; Vandoninck, S.; Longtine, M.S.; Berman, J. Candida albicans Int1p interacts with the septin ring in yeast and hyphal cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 3538–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatty, M.; Laverde Gomez, J.A.; Christie, P.J. The expanding bacterial type IV secretion lexicon. Res. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 620–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez-Beltran, A.; Lopez-Romero, E.; Cuellar-Cruz, M. Identification of proteins involved in the adhesionof Candida species to different medical devices. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 107, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenship, J.R.; Mitchell, A.P. How to build a biofilm: A fungal perspective. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O′Toole, G.; Kaplan, H.B.; Kolter, R. Biofilm formation as microbial development. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2000, 54, 49–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.; Dionne, H.M.; Prabhakar, A.; Mehrotra, A.; Somboonthum, J.; Gonzalez, B.; Edgerton, M.; Cullen, P.J. Aggregate Filamentous Growth Responses in Yeast. mSphere 2019, 4, e00702-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePas, W.H.; Syed, A.K.; Sifuentes, M.; Lee, J.S.; Warshaw, D.; Saggar, V.; Csankovszki, G.; Boles, B.R.; Chapman, M.R. Biofilm formation protects Escherichia coli against killing by Caenorhabditis elegans and Myxococcus xanthus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 7079–7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, S.; Kuttuva Rajarao, G.; Land, C.J.; Dalhammar, G. Biofilm formation and interactions of bacterial strains found in wastewater treatment systems. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 283, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, D.O.; Hengge, R. Bacterial Multicellularity: The Biology of Escherichia coli Building Large-Scale Biofilm Communities. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 75, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palkova, Z.; Vachova, L. Spatially structured yeast communities: Understanding structure formation and regulation with omics tools. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 5613–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vachova, L.; Palkova, Z. Diverse roles of Tup1p and Cyc8p transcription regulators in the development of distinct types of yeast populations. Curr. Genet. 2019, 65, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann, E.I. Endolithic microorganisms in the Antarctic cold desert. Science 1982, 215, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipke, P.N. What We Do Not Know about Fungal Cell Adhesion Molecules. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachova, L.; Stovicek, V.; Hlavacek, O.; Chernyavskiy, O.; Stepanek, L.; Kubinova, L.; Palkova, Z. Flo11p, drug efflux pumps, and the extracellular matrix cooperate to form biofilm yeast colonies. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 194, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bian, Z.; Wang, Y. Biofilm formation and inhibition mediated by bacterial quorum sensing. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 6365–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, N.; Povolotsky, T.L.; Landau, M.; Kolodkin-Gal, I. Emerging roles of functional bacterial amyloids in gene regulation, toxicity, and immunomodulation. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2021, 85, e00062-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, A.; Shimaoka, M.; Phan, U.; Kim, M.; Springer, T.A. Transition from rolling to firm adhesion can be mimicked by extension of integrin alphaLbeta2 in an intermediate affinity state. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 10876–10882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couturier, A.; Virolle, C.; Goldlust, K.; Berne-Dedieu, A.; Reuter, A.; Nolivos, S.; Yamaichi, Y.; Bigot, S.; Lesterlin, C. Real-time visualisation of the intracellular dynamics of conjugative plasmid transfer. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baffi, R.A.; Shenbagamurthi, P.; Terrance, K.; Becker, J.M.; Naider, F.; Lipke, P.N. Different structure-function relationships for α-factor-induced morphogenesis and agglutination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Bacteriol. 1984, 158, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipke, P.N.; Kurjan, J. Sexual agglutination in budding yeasts: Structure, function, and regulation of adhesion glycoproteins. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 56, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimondi, G.; Zanoni, I.; Citterio, S.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P.; Granucci, F. Induction of peripheral T cell tolerance by antigen-presenting B cells. I. Relevance of antigen presentation persistence. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 4012–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrum, A.G.; Palmer, E.; Turka, L.A. Distinct temporal programming of naive CD4+ T cells for cell division versus TCR-dependent death susceptibility by antigen-presenting macrophages. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.-Z.; Balyan, R.; Brzostek, J.; Zhao, X.; Gascoigne, N.R.J. Time required for commitment to T cell proliferation depends on TCR affinity and cytokine response. EMBO Rep. 2023, 24, e54969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean-Pierre, V.; Boudet, A.; Sorlin, P.; Menetrey, Q.; Chiron, R.; Lavigne, J.-P.; Marchandin, H. Biofilm Formation by Staphylococcus aureus in the Specific Context of Cystic Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Naganuma, T.; Nakai, R.; Imura, S.; Tsujimoto, M.; Convey, P. Microbiomic Analysis of Bacteria Associated with Rock Tripe Lichens in Continental and Maritime Antarctic Regions. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipke, P.N.; Klotz, S.A.; Dufrene, Y.F.; Jackson, D.N.; Garcia-Sherman, M.C. Amyloid-Like beta-Aggregates as Force-Sensitive Switches in Fungal Biofilms and Infections. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 82, e00035-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dranginis, A.M.; Rauceo, J.R.; Coronado, J.E.; Lipke, P.N. A biochemical guide to yeast adhesins: Glycoproteins for social and antisocial occasions. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, G.I. Models for the specific adhesion of cells to cells. Science 1978, 200, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C. Kinetics and mechanics of cell adhesion. J. Biomech. 2000, 33, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajra, K.M.; Fearon, E.R. Cadherin and catenin alterations in human cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002, 34, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvizu-Rubio, V.; García-Carnero, L.C.; Mora-Montes, H. Moonlighting proteins in medically relevant fungi. PeerJ 2022, 10, e14001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.J.; Chirico, W.J.; Lipke, P.N. Through the back door: Unconventional protein secretion. Cell Surf. 2020, 6, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staab, J.F.; Bradway, S.D.; Fidel, P.L.; Sundstrom, P. Adhesive and mammalian transglutaminase substrate properties of Candida albicans Hwp1. Science 1999, 283, 1535–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staab, J.F.; Bahn, Y.S.; Tai, C.H.; Cook, P.F.; Sundstrom, P. Expression of transglutaminase substrate activity on Candida albicans germ tubes through a coiled, disulfide-bonded N-terminal domain of Hwp1 requires C-terminal glycosylphosphatidylinositol modification. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 40737–40747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopeckova, M.; Pavkova, I.; Stulik, J. Diverse Localization and Protein Binding Abilities of Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase in Pathogenic Bacteria: The Key to its Multifunctionality? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkowska-Kuleta, J.; Smolarz, M.; Seweryn-Ozog, K.; Satala, D.; Zawrotniak, M.; Wronowska, E.; Bochenska, O.; Kozik, A.; Nobbs, A.H.; Gogol, M.; et al. Proteinous components of neutrophil extracellular traps are arrested by the cell wall proteins of Candida albicans during fungal infection, and can be used in the host invasion. Cells 2021, 10, 2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkowska-Kuleta, J.; Wronowska, E.; Satala, D.; Zawrotniak, M.; Bras, G.; Kozik, A.; Nobbs, A.H.; Rapala-Kozik, M. Als3-mediated attachment of enolase on the surface of Candida albicans cells regulates their interactions with host proteins. Cell Microbiol. 2021, 23, e13297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghrayeb, M.; Hayet, S.; Lester-Zer, N.; Levi-Kalisman, Y.; Chai, L. Fibrilar polymorphism of the bacterial extracellular matrix protein tasa. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, D.; Aguilar, C.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Amyloid fibers provide structural integrity to Bacillus subtilis biofilms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2230–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaszczyk, M.; Pradhan, B.; Remaut, H. The Biosynthesis and Structures of Bacterial Pili. Bact. Cell Walls Membr. 2019, 92, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligthart, K.; Belzer, C.; de Vos, W.M.; Tytgat, H.L.P. Bridging Bacteria and the Gut: Functional Aspects of Type IV Pili. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignolet, J.; Panis, G.; Viollier, P.H. More than a Tad: Spatiotemporal control of Caulobacter pili. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 42, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sønderby, T.V.; Najarzadeh, Z.; Otzen, D.E. Functional Bacterial Amyloids: Understanding Fibrillation, Regulating Biofilm Fibril Formation and Organizing Surface Assemblies. Molecules 2022, 27, 4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBenedictis, E.P.; Liu, J.; Keten, S. Adhesion mechanisms of curli subunit CsgA to abiotic surfaces. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.J. The MSCRAMM Family of Cell-Wall-Anchored Surface Proteins of Gram-Positive Cocci. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossart, P.; Jonquieres, R. Sortase, a universal target for therapeutic agents against Gram-positive bacteria? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5013–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, T.B.; Fink, G.R. Bakers′ yeast, a model for fungal biofilm formation. Science 2001, 291, 878–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauvais, A.; Loussert, C.; Prevost, M.C.; Verstrepen, K.; Latge, J.P. Characterization of a biofilm-like extracellular matrix in FLO1-expressing Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. FEMS Yeast Res. 2009, 9, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.; Starr, I.; Jamalzadeh, S.; Muniz, O.; Kumar, A.; Gokcumen, O.; Ferkey, D.M.; Cullen, P.J. Filamentation Regulatory Pathways Control Adhesion-Dependent Surface Responses in Yeast. Genetics 2019, 212, 667–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willaert, R.G.; Kayacan, Y.; Devreese, B. The Flo Adhesin Family. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraushaar, T.; Bruckner, S.; Veelders, M.; Rhinow, D.; Schreiner, F.; Birke, R.; Pagenstecher, A.; Mosch, H.U.; Essen, L.O. Interactions by the Fungal Flo11 Adhesin Depend on a Fibronectin Type III-like Adhesin Domain Girdled by Aromatic Bands. Structure 2015, 23, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyx, C.; Schiavone, M.; Teste, M.A.; Dague, E.; Sieczkowski, N.; Julien, A.; Francois, J.M. The dual role of amyloid-beta-sheet sequences in the cell surface properties of FLO11-encoded flocculins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. eLife 2021, 10, e68592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zara, S.; Bakalinsky, A.T.; Zara, G.; Pirino, G.; Demontis, M.A.; Budroni, M. FLO11-based model for air-liquid interfacial biofilm formation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2934–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, C.A.; Bendel, C.M.; McClellan, M.; Hauser, M.; Becker, J.M.; Berman, J.; Hostetter, M.K. Linkage of adhesion, filamentous growth, and virulence in Candida albicans to a single gene, INT1. Science 1998, 279, 1355–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana-Munoz, S.; Duenas-Santero, E.; Arnaiz-Pita, Y.; Del Rey, F.; Correa-Bordes, J.; Vazquez de Aldana, C.R. The anillin-related Int1 protein and the Sep7 septin collaborate to maintain cellular ploidy in Candida albicans. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2257–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ding, X.; Akram, N.; Xue, S.; Luo, S. Fused in Sarcoma: Properties, Self-Assembly and Correlation with Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2019, 24, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hostetter, M.K. The iC3b receptor of Candida albicans and its roles in pathogenesis. Vaccine 2008, 26 (Suppl. S8), 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.M.; Wang, L.; Pike, J.; Jue, C.K.; Zhao, H.; de Nobel, H.; Kurjan, J.; Lipke, P.N. Delineation of functional regions within the subunits of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell adhesion molecule a-agglutinin. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 15768–15775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellaro, C.; Baldermann, C.; Rachel, R.; Tanner, W. Mating type-specific cell-cell recognition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Cell wall attachment and active sites of a- and alpha-agglutinin. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 4737–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-H.; Hoyer, L.L. Assessing Als3 Peptide-Binding Cavity and Amyloid-Forming Region Contributions to Candida albicans Invasion of Human Oropharyngeal Epithelial Cells. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Dougherty, S.D.; Erdman, S.E. Conserved WCPL and CX4C domains mediate several mating adhesin interactions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 2009, 182, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Bennett, D.; Erdman, S.E. Maintenance of mating cell integrity requires the adhesin Fig2p. Eukaryot. Cell 2002, 1, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieber, B.; Coronas-Serna, J.; Martin, S.G. A focus on yeast mating: From pheromone signaling to cell-cell fusion. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 133, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huberman, L.B.; Murray, A.W. A model for cell wall dissolution in mating yeast cells: Polarized secretion and restricted diffusion of cell wall remodeling enzymes induces local dissolution. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, P.G.; Lionakis, M.S.; Arendrup, M.C.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Kullberg, B.J. Invasive candidiasis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 18026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, B.; Peñas, A.D.L.; Castaño, I.; Van Dijck, P. Adhesins in Candida glabrata. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reithofer, V.; Fernández-Pereira, J.; Alvarado, M.; de Groot, P.; Essen, L.-O. A novel class of Candida glabrata cell wall proteins with β-helix fold mediates adhesion in clinical isolates. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, L.L. The ALS gene family of Candida albicans. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyer, L.L.; Cota, E. Candida albicans Agglutinin-Like Sequence (Als) Family Vignettes: A Review of Als Protein Structure and Function. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, I.; Silva-Dias, A.; Rocha, R.; Teixeira-Santos, R.; Coelho, C.; Gonçalves, T.; Santos, M.A.S.; Pina-Vaz, C.; Solis, N.V.; Filler, S.G.; et al. Candida albicans CUG mistranslation is a mechanism to create cell surface variation. mBio 2013, 4, e00285-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, N.E.; Lipke, P.N.; Pilling, D.; Gomer, R.H.; Klotz, S.A. Serum Amyloid P Component Binds Fungal Surface Amyloid and Decreases Human Macrophage Phagocytosis and Secretion of Inflammatory Cytokines. MBio 2019, 10, e00218-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Sherman, M.C.; Lundgren, T.; Sobonya, R.; Lipke, P.N.; Klotz, S.A. A Unique Biofilm in Human Deep Mycoses: Fungal Amyloid is bound by Host Serum Amyloid P Component. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2015, 2015, 15009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, S.A.; Bradley, N.; Lipke, P.N. Blocking Serum Amyloid-P Component from Binding to Macrophages and Augmenting Fungal Functional Amyloid Increases Macrophage Phagocytosis of Candida albicans. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellaro, C.; Hauser, K.; Mrsa, V.; Watzele, M.; Watzele, G.; Gruber, C.; Tanner, W. Saccharomyces cerevisiae a- and alpha-agglutinin: Characterization of their molecular interaction. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 4081–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Qiu, W.G.; Lipke, P.N. Accelerated and adaptive evolution of yeast sexual adhesins. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 3127–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-H.; Schliep, K.; Isenhower, A.; Rodriguez-Bobadilla, R.; Vuong, V.M.; Fields, C.J.; Hernandez, A.G.; Hoyer, L.L. Using Genomics to Shape the Definition of the Agglutinin-Like Sequence (ALS) Family in the Saccharomycetales. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 794529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, P.S.; Yan, R.; Taylor, J.D.; Burchell, L.; Jones, R.; Hoyer, L.L.; Matthews, S.J.; Simpson, P.J.; Cota, E. Structural basis for the broad specificity to host-cell ligands by the pathogenic fungus Candida albicans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15775–15779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, S.A.; Gaur, N.K.; Lake, D.F.; Chan, V.; Rauceo, J.; Lipke, P.N. Degenerate peptide recognition by Candida albicans adhesins Als5p and Als1p. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 2029–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, A.T.; Ramsook, C.B.; Otoo, H.N.; Tan, C.; Soybelman, G.; Rauceo, J.M.; Gaur, N.K.; Klotz, S.A.; Lipke, P.N. Structure and function of glycosylated tandem repeats from Candida albicans Als adhesins. Eukaryot. Cell 2010, 9, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauceo, J.M.; De Armond, R.; Otoo, H.; Kahn, P.C.; Klotz, S.A.; Gaur, N.K.; Lipke, P.N. Threonine-Rich Repeats Increase Fibronectin Binding in the Candida albicans Adhesin Als5p. Eukaryot. Cell 2006, 5, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipke, P.N.; Mathelie-Guinlet, M.; Viljoen, A.; Dufrene, Y.F. A New Function for Amyloid-Like Interactions: Cross-Beta Aggregates of Adhesins form Cell-to-Cell Bonds. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, C.J.; Mitchell, A.P. Microbial biofilms: E pluribus unum. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, C.J.; Schneider, H.A.; Nett, J.E.; Sheppard, D.C.; Filler, S.G.; Andes, D.R.; Mitchell, A.P. Complementary adhesin function in C. albicans biofilm formation. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, N.; Schwartz-Perov, S.; Landau, M.; Lipke, P.N. Structure and Conservation of Amyloid Spines From the Candida albicans Als5 Adhesin. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 926959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourer, T.; El Ghalid, M.; Pehau-Arnaudet, G.; Kauffmann, B.; Loquet, A.; Brûlé, S.; Cabral, V.; D’enfert, C.; Bachellier-Bassi, S. The Pga59 cell wall protein is an amyloid forming protein involved in adhesion and biofilm establishment in the pathogenic yeast Candida albicans. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2023, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X. ALS1 Deletion Increases the Proportion of Small Cells in a Candida albicans Culture Population: Hypothesizing a Novel Role for Als1. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 895068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, S.A.; Gaur, N.K.; De Armond, R.; Sheppard, D.; Khardori, N.; Edwards, J.E.; Lipke, P.; El-Azizi, M. Candida albicans Als proteins mediate aggregation with bacteria and yeasts. Med. Mycol. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Hum. Anim. Mycol. 2007, 45, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, Q.T.; Lin, J.; Solis, N.V.; Eng, M.; Swidergall, M.; Wang, F.; Li, S.; Gaffen, S.L.; Chou, T.-F.; Filler, S.G. The Globular C1q Receptor Is Required for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Signaling during Candida albicans Infection. mBio 2021, 12, e02716-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, Q.T.; Myers, C.L.; Fu, Y.; Sheppard, D.C.; Yeaman, M.R.; Welch, W.H.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Edwards, J.E., Jr.; Filler, S.G. Als3 is a Candida albicans invasin that binds to cadherins and induces endocytosis by host cells. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, D.L.; Scheres, N.; Willems, H.M.E.; Bode, C.S.; Krom, B.P.; Shirtliff, M.E. The host immune system facilitates disseminated Staphylococcus aureus disease due to phagocytic attraction to Candida albicans during coinfection: A case of bait and switch. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00137-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpak-Amikam, Y.; Lapidus, T.; Isaacson, B.; Duev-Cohen, A.; Levinson, T.; Elbaz, A.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Osherov, N.; Bachrach, G.; Hoyer, L.L.; et al. Candida albicans evades NK cell elimination via binding of Agglutinin-Like Sequence proteins to the checkpoint receptor TIGIT. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, D.C.; Yeaman, M.R.; Welch, W.H.; Phan, Q.T.; Fu, Y.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Filler, S.G.; Zhang, M.; Waring, A.J.; Edwards, E.J., Jr. Functional and structural diversity in the Als protein family of Candida albicans. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30480–30489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.X.; El-Kirat-Chatel, S.; Joseph, I.G.; Jackson, D.N.; Ramsook, C.B.; Dufrene, Y.F.; Lipke, P.N. Force Sensitivity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Flocculins. mSphere 2016, 1, e00128-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.J. Surface Proteins of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lipke, P.N.; Ragonis-Bachar, P. Sticking to the Subject: Multifunctionality in Microbial Adhesins. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9040419
Lipke PN, Ragonis-Bachar P. Sticking to the Subject: Multifunctionality in Microbial Adhesins. Journal of Fungi. 2023; 9(4):419. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9040419
Chicago/Turabian StyleLipke, Peter N., and Peleg Ragonis-Bachar. 2023. "Sticking to the Subject: Multifunctionality in Microbial Adhesins" Journal of Fungi 9, no. 4: 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9040419
APA StyleLipke, P. N., & Ragonis-Bachar, P. (2023). Sticking to the Subject: Multifunctionality in Microbial Adhesins. Journal of Fungi, 9(4), 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9040419






