Coccidioidomycosis Osteoarticular Dissemination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
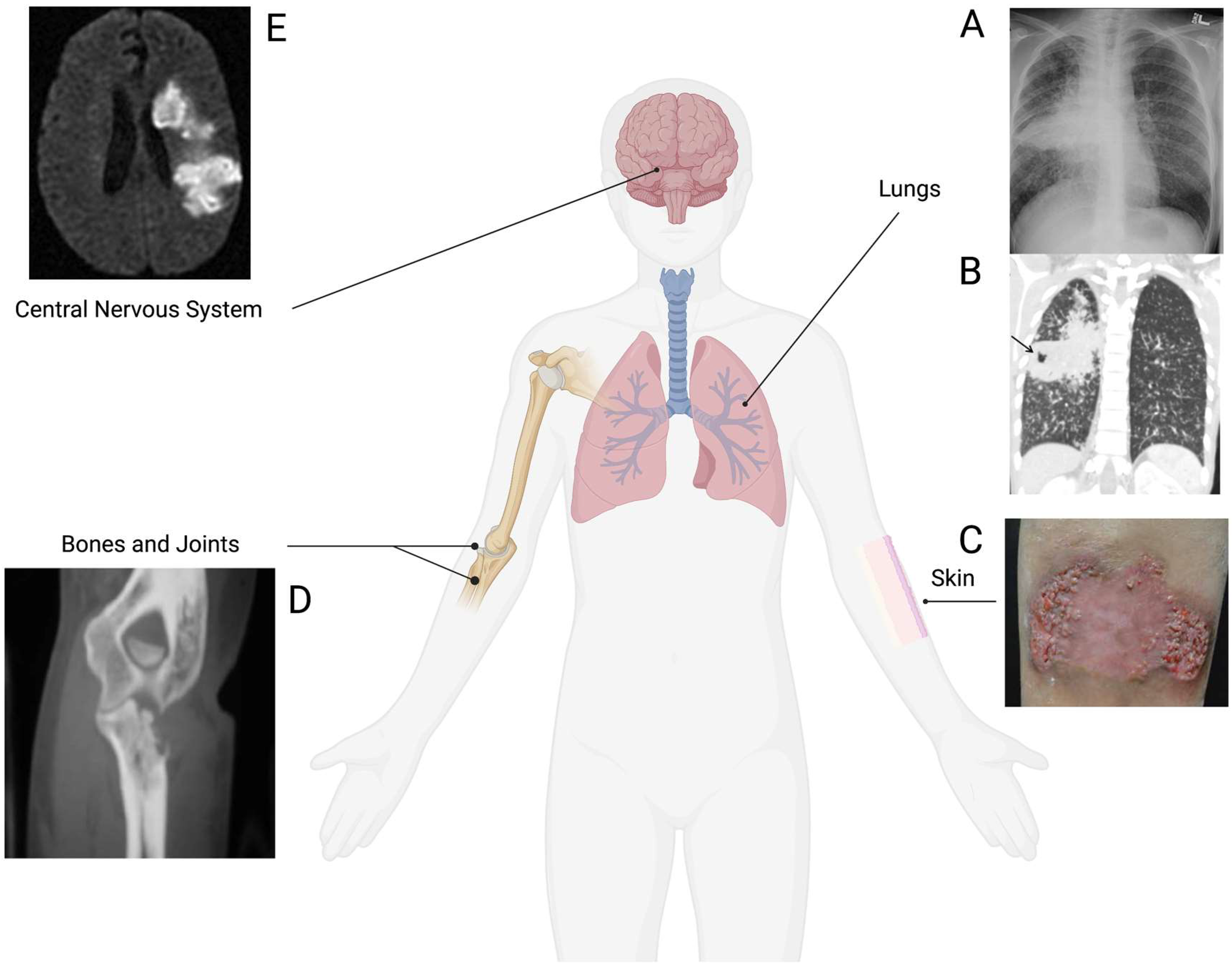
3. Extrapulmonary Coccidioidomycosis
4. Risk Factors for Extrapulmonary Coccidioidomycosis
5. Osteoarticular Coccidioidomycosis
5.1. Clinical Reports
5.2. Diagnosis
5.3. Management of Osteoarticular Coccidioidomycosis
5.4. Animal Studies
5.5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castro-Lopez, N.; Hung, C.Y. Immune Response to Coccidioidomycosis and the Development of a Vaccine. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, S.C.G.; Alanis, J.C.S.; Flores, M.G.; Gonzalez, S.E.G.; Cabrera, L.V.; Candiani, J.O. Coccidioidomycosis and the skin: A comprehensive review. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2015, 90, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutserimpas, C.; Naoum, S.; Raptis, K.; Vrioni, G.; Samonis, G.; Alpantaki, K. Skeletal Infections Caused by Coccidioides Species. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, J.E. State-of-the-art treatment of coccidioidomycosis skeletal infections. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1111, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crum, N.F. Coccidioidomycosis: A Contemporary Review. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2022, 11, 713–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, R.D.; Elliott, S.P.; Taljanovic, M.S. The spectrum and presentation of disseminated coccidioidomycosis. Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bays, D.J.; Thompson, G.R.; Reef, S.; Snyder, L.; Freifeld, A.J.; Huppert, M.; Salkin, D.; Wilson, M.D.; Galgiani, J.N. Natural History of Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis: Examination of the Veterans Affairs–Armed Forces Database. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e3814–e3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coba, A.J.; Sallee, P.K.; Dixon, D.O.; Alkhateb, R.; Anstead, G.M. Pandora’s Box: Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis Associated with Self-Medication with an Unregulated Potent Corticosteroid Acquired in Mexico. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciotti, R.W.; Shekhel, T.A.; Blair, J.E.; Colby, T.V.; Sobonya, R.E.; Larsen, B.T. Surgical Pathology of Skeletal Coccidioidomycosis A Clinical and Histopathologic Analysis of 25 Cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 38, 1672–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odio, C.D.; Marciano, B.E.; Galgiani, J.N.; Holland, S.M. Risk Factors for Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capoor, M.R.; Sen, B.; Varshney, P.; Verghese, M.; Shivaprakash, M.R.; Chakrabarti, A. Coccidioidomycosis masquerading as skeletal tuberculosis: An imported case and review of coccidioidomycosis in India. Trop. Dr. 2014, 44, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammering, J.C.; Iv, M.; Gupta, N.; Pandit, R.; Patel, M.R. Imaging Spectrum of CNS Coccidioidomycosis: Prevalence and Significance of Concurrent Brain and Spinal Disease. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 200, 1334–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, J.D.; Aneke, C.I.; Al-Obaidi, M.M.; Egger, M.; Garcia, L.; Gaines, T.; Hoenigl, M.; Thompson, G.R., III. Race and ethnicity: Risk factors for fungal infections? PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twarog, M.; Thompson, G.R., 3rd. Coccidioidomycosis: Recent Updates. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 36, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.; Brown, J.; Benedict, K.; Park, B.J. Coccidioidomycosis: Epidemiology. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 5, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenstein, N.E.; Emery, K.W.; Werner, S.B.; Kao, A.; Johnson, R.; Rogers, D.; Vugia, D.; Reingold, A.; Talbot, R.; Plikaytis, B.D.; et al. Risk factors for severe pulmonary and disseminated coccidioidomycosis: Kern County, California, 1995–1996. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, A.E.; Prevots, D.R.; Holland, S.M. Hospitalizations Associated with Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis, Arizona and California, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1476–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, F.M.; Gerardi, J.D.; Gholve, P.; Merriott, D.; Hassan, R.M.; McCarty, J. Pediatric Musculoskeletal Coccidioidomycosis in Central California: A Single Center Experience. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2022, 41, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondermeyer Cooksey, G.L.; Nguyen, A.; Vugia, D.; Jain, S. Regional Analysis of Coccidioidomycosis Incidence—California, 2000–2018. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1817–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drutz, D.J.; Huppert, M. Coccidioidomycosis: Factors Affecting the Host-Parasite Interaction. J. Infect. Dis. 1983, 147, 372–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercovitch, R.S.; Catanzaro, A.; Schwartz, B.S.; Pappagianis, D.; Watts, D.; Ampel, N.M. Coccidioidomycosis during pregnancy: A review and recommendations for management. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, E.D. Pregnancy-Associated Depression of Cell-Mediated Immunity. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1984, 6, 814–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, O.; Vera-Cabrera, L.; Rendon, A.; Gonzalez, G.; Bonifaz, A. Coccidioidomycosis. Clin. Dermatol. 2012, 30, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, J.E.; Smilack, J.D.; Caples, S.M. Coccidioidomycosis in Patients With Hematologic Malignancies. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masannat, F.Y.; Ampel, N.M. Coccidioidomycosis in Patients with HIV-1 Infection in the Era of Potent Antiretroviral Therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertz, L.E.; Blair, J.E. Coccidioidomycosis in Rheumatology Patients: Incidence and Potential Risk Factors. Coccidioidomycosis Sixth Int. Symp. 2007, 1111, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santelli, A.C.; Blair, J.E.; Roust, L.R. Coccidioidomycosis in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 964–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, A.P.; Korzeniowska, A.; Aguilar, C.C.; Gu, J.; Karlins, E.; Oler, A.J.; Chen, G.; Reynoso, G.V.; Davis, J.; Chaput, A.; et al. Immunogenetics associated with severe coccidioidomycosis. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e159491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutala, P.J.; Smith, J.W. Coccidioidomycosis in potentially compromised hosts: The effect of immunosuppressive therapy in dissemination. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1978, 275, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, L.; Yocum, D.E.; Ampel, N.M.; Villanueva, I.; Lisse, J.; Gluck, O.; Tesser, J.; Posever, J.; Miller, M.; Araujo, J.; et al. Increased risk of coccidioidomycosis in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonists. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 1959–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.; Ja, S.; Ca, K. Faculty Opinions recommendation of Endemic fungal infections in patients receiving tumour necrosis factor-alpha inhibitor therapy. Drugs 2009, 69, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Blair, J.; Ampel, N.M.; E Hoover, S. Coccidioidomycosis in selected immunosuppressed hosts. Med. Mycol. 2018, 57 (Suppl. S1), S56–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Loo, G.; Bertrand, M.J.M. Death by TNF: A road to inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, D.A.; Shubitz, L.F.; Butkiewicz, C.D.; Trinh, H.T.; Donovan, F.M.; Frelinger, J.A.; Galgiani, J.N. TNFα Blockade Inhibits Both Initial and Continued Control of Pulmonary Coccidioides. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 796114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, J.E.; Wack, E.E.; Mertz, L.E.; Galgiani, J.N. Approach to Management of Coccidioidomycosis in Patients Receiving Inhibitors of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α. Infect. Dis. Clin. Pract. 2017, 25, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelatos, G.; Bamias, G.; Kitas, G.D.; Kollias, G.; Sfikakis, P.P. The second decade of anti-TNF-a therapy in clinical practice: New lessons and future directions in the COVID-19 era. Rheumatol. Int. 2022, 42, 1493–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeyko, L.A.; Taljanovic, M.S.; Dzioba, R.B.; Rapiejko, J.L.; Adam, R.D. Vertebral Coccidioidomycosis: Presentation and Multidisciplinary Management. Am. J. Med. 2012, 125, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellerbrook, L.; Laks, S. Coccidioidomycosis osteomyelitis of the knee in a 23-year-old diabetic patient. Radiol. Case Rep. 2015, 10, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhla, S.G. Complications and Management of a Rare Case of Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis to the Vertebral Spine. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2018, 2018, 8954016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drutz, D.J.; Huppert, M.; Sun, S.H.; McGuire, W.L. Human sex hormones stimulate the growth and maturation of Coccidioides immitis. Infect. Immun. 1981, 32, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crum, N.F.; Lederman, E.R.; Stafford, C.M.; Parrish, J.S.; Wallace, M.R. Coccidioidomycosis—A descriptive survey of a reemerging disease. Clinical characteristics and current controversies. Medicine 2004, 83, 149–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeppa, M.A.; Laorr, A.; Greenspan, A.; McGahan, J.P.; Steinbach, L.S. Skeletal coccidioidomycosis: Imaging findings in 19 patients. Skelet. Radiol. 1996, 25, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crete; Gallmann, W.; Karis, J.; Ross, J. Spinal Coccidioidomycosis: MR Imaging Findings in 41 Patients. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 2148–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgafy, H.; Miller, J.; Meyers, S.; Assaly, R. Disseminated coccidioidomycosis of the spine in an immunocompetent patient. Am. J. Orthop. 2014, 43, E181–E184. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Pervaiz, S.; Sivasubramanian, G. Extensive spinal disease from disseminated coccidioidomycosis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 363, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillsbury, M.M.; Rubio, L.A.; Lucas, C.-H.G.; Babik, J.M. Coccidioidomycosis Presenting with Fever and Back Pain. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 1887–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, D.; Sahasrabudhe, N.; Kim, E. Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis to the Spine—Case Series and Review of Literature. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.; Boken, D.J.; Nelson, C.A.; Totten, V.Y. A Case of Osteomyelitis of the toe caused by Coccidioidomycosis in a 17 year-old with Diabetes Insipidus. IDCases 2017, 9, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbus, W.D.; Bestebreurtje, A.M. Coccidioidomycosis: A Study of 95 Cases of the Disseminated Type with Special Reference to the Pathogenesis of the Disease. Mil. Surg. 1946, 99, 653–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baaj, A.; Martirosyan, N.; Skoch, J.; Zaninovich, O.; Zoccali, C.; Galgiani, J. A paradigm for the evaluation and management of spinal coccidioidomycosis. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2015, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-C.; Calvert, G.; Hanrahan, C.J.; Jones, K.B.; Randall, R.L. Coccidiomycosis infection of the patella mimicking a neoplasm—Two case reports. BMC Med. Imaging 2014, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, D.S.; Kostosky, N.B.; Epstein, A.; Blaydon, S.; Durairaj, V.; Somogyi, M. Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis with Orbital Osteomyelitis and Periorbital Abscess. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 37, e173–e176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraway, N.P.; Fanning, C.V.; Stewart, J.M.; Tarrand, J.J.; Weber, K.L. Coccidioidomycosis osteomyelitis masquerading as a bone tumor. A report of 2 cases. Acta Cytol. 2003, 47, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilde, G.E.; Emery, C.; Lally, J.F. Radiological Reasoning: Miliary Disease, Vertebral Osteomyelitis, and Soft-Tissue Abscesses. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 190 (Suppl. S3), S11–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, N.P.; Taneja, V.; ReyesSacin, C.; Bhanot, R.; Natesan, S.K. Coccidioidomycosis masquerading as malignancy. BMJ Case Rep. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesselius, L.J.; Brooks, R.J.; Gall, E.P. Verterbral coccidiomycosis presenting as pott’s disease.pdf. JAMA 1977, 238, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y. Comparison of Pyogenic Spondylitis and Tuberculous Spondylitis. Asian Spine J. 2014, 8, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endrit, Z.; Vibhu, K.V.; Fassil, B.M. Spinal Metastasis; StatPearls Publishing LLC: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.-M.; Lee, S.; Bae, J. Contiguous Spinal Metastasis Mimicking Infectious Spondylodiscitis. J. Korean Soc. Radiol. 2015, 73, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.A. Infectious Granulomas of Bones and Joints, with Special Reference to Coccidioidal Granuloma. Radiology 1934, 23, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvin, G.J.; Peterfy, C.G. Soft-Tissue Coccidioidomycosis on Mri. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1995, 19, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.H.; Sharma, R.; Kuran, R.; Fong, I.; Heidari, A. Coccidioidomycosis: A review. J. Investig. Med. 2021, 69, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisenberg, S.A. Coccidioides immitis septic knee arthritis. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, M.F.; Shi, A.; Lasco, T.M.; Yoon, L. Disseminated coccidioidomycosis with multifocal musculoskeletal disease involvement. Radiol. Case Rep. 2017, 12, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Patel, K.; De Leon, J.C.; A Buttacavoli, F. Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis of the Knee Joint Requiring Synovectomy and Arthrotomy. J. Orthop. Case Rep. 2021, 11, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuberski, T.; Ianas, V.; Ferguson, T.; Nomura, J.; Johnson, R. Treatment of Prosthetic Joint Infections Associated with Coccidioidomycosis. Infect. Dis. Clin. Pract. 2011, 19, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbeloa-Gutierrez, L.; Kuberski, T.; Johnson, S.M.; Sagastibelza, I.; Alaez, J.I.; Pappagianis, D. Reactivation of coccidioidomycosis: A prosthetic joint infection in Spain. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotchkiss, C.E.; Jeffery, D.A.; Vogel, K.W. Use of Fluconazole-impregnated Beads to Treat Osteomyelitis Caused by Coccidioides in a Pigtailed Macaque (Macaca nemestrina). Comp. Med. 2022, 72, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantz, B.; Selakovich, W.G.; Collins, D.N.; Garvin, K.L. Coccidioidomycosis of the Knee with a 26-Year Follow-up Evaluation: A case report. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1988, 234, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrawi, F.; Heidari, A.; Aljashamy, T.; Mangat, N.; Bhaika, J.; Kaur, S.; Kuran, R.; Johnson, R. Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis Presenting as Polyarticular Septic Arthritis: A Case Report. J. Investig. Med. High Impact Case Rep. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHardy, I.H.; Barker, B.; Thompson, G.R. Review of Clinical and Laboratory Diagnostics for Coccidioidomycosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2023, 61, e0158122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.K.; Shrader, M.W.; Falk, M.N.P.-C.; Segal, L.S. Diagnosis and Initial Management of Musculoskeletal Coccidioidomycosis in Children. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2014, 34, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialek, R.; Kern, J.; Herrmann, T.; Tijerina, R.; Cecenas, L.; Reischl, U.; González, G.M. PCR assays for identification of Coccidioides posadasii based on the nucleotide sequence of the antigen 2/proline-rich antigen. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Chen, C.-Y.; Ding, P.-P.; Hu, C.-Z.; Huang, X.-F.; Zhang, X.; Gong, X.; Zhen, P.-L.; Zhang, L. Clinical performance of quantitative PCR for the molecular identification of skeletal tuberculosis from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, V.; Chawla, K.; Acharya, K.; Rao, S.; Rao, S. The role of polymerase chain reaction in the management of osteoarticular tuberculosis. Int. Orthop. 2009, 33, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmes, D.; Schui, D.; Held, J.; Ackermann, S.; Geipel, U.; Emrich, K.; Winkelmann, E.-J.; Rickerts, V. Disseminated coccidioidomycosis: Monitoring of serologic markers for treatment response. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2020, 29, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, G.R., 3rd; Bays, D.J.; Johnson, S.M.; Cohen, S.H.; Pappagianis, D.; Finkelman, M.A. Serum (1→3)-beta-D-glucan measurement in coccidioidomycosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 3060–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, M.M.; Ayazi, P.; Shi, A.; Campanella, M.; Connick, E.; Zangeneh, T.T. The Utility of (1→3)-beta-D-Glucan Testing in the Diagnosis of Coccidioidomycosis in Hospitalized Immunocompromised Patients. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHardy, I.H.; Dinh, B.-T.N.; Waldman, S.; Stewart, E.; Bays, D.; Pappagianis, D.; Thompson, G.R. Coccidioidomycosis Complement Fixation Titer Trends in the Age of Antifungals. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.E.; Saito, M.T.; Beard, R.R.; Kepp, R.M.; Clark, R.W.; Eddie, B.U. Serological tests in the diagnosis and prognosis of coccidioidomycosis. Am. J. Hyg. 1950, 52, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Holley, K.; Muldoon, M.; Tasker, S. Coccidioides immitis Osteomyelitis: A Case Series Review. Orthopedics 2002, 25, 831–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, C.G.; Monroe, S.E.; O’hare, J.E. Coccidioidomycosis and tuberculosis in the same bones. A case report. Ann. Surg. 1951, 133, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassif, E.F.; Maloney, N.; Conley, A.P.; Keung, E.Z. Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis Following COVID-19 Mimicking Metastatic Thoracic Relapse of Well-Differentiated Liposarcoma: A Case Report. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 715939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.; Brown, G.; Barbee, R. Coccidioidomycosis in Patients with Diabetes-Mellitus. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1978, 117, 286. [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani, J.N.; Ampel, N.M.; Blair, J.E.; Catanzaro, A.; Geertsma, F.; Hoover, S.E.; Johnson, R.H.; Kusne, S.; Lisse, J.; Theodore, N.; et al. 2016 Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) Clinical Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, e112–e146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgiani, J.N.; Catanzaro, A.; Cloud, G.A.; Johnson, R.H.; Williams, P.L.; Mirels, L.F.; Nassar, F.; Lutz, J.E.; Stevens, D.A.; Sharkey, P.K.; et al. Comparison of oral fluconazole and itraconazole for progressive, nonmeningeal coccidioidomycosis: A randomized, double-blind trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000, 133, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstead, G.M.; Corcoran, G.; Lewis, J.; Berg, D.; Graybill, J.R. Refractory Coccidioidomycosis Treated with Posaconazole. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 1770–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgiani, J.N.; Ampel, N.M.; Catanzaro, A.; Johnson, R.H.; Stevens, D.A.; Williams, P.L. Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 30, 658–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, E.; Dodds Ashley, E. Antifungal Drug Therapeutic Monitoring: What are the Issues? Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep. 2015, 2, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ashbee, H.R.; Barnes, R.A.; Johnson, E.M.; Richardson, M.D.; Gorton, R.; Hope, W.W. Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) of antifungal agents: Guidelines from the British Society for Medical Mycology. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 1162–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakarla, U.K.; Kalani, M.Y.S.; Sharma, G.K.; Sonntag, V.K.; Theodore, N. Surgical management of coccidioidomycosis of the spine: Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2011, 15, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-H.; Chen, H.-Y.; Chen, J.-C.; Yu, Y.-H.; Chou, Y.-C.; Ueng, S.W.-N.; Liu, S.-J. Resorbable Beads Provide Extended Release of Antifungal Medication: In Vitro and In Vivo Analyses. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiederhold, N.P. Review of the Novel Investigational Antifungal Olorofim. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaver, S.L.; Foy, D.S.; Carter, T.D. Clinical features, treatment, and outcome of dogs with Coccidioides osteomyelitis. J. Am. Veter. Med. Assoc. 2021, 260, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, A.P.; Shubitz, L.F.; Alcott, C.J.; E Sykes, J. Selected Clinical Features of Coccidioidomycosis in Dogs. Med. Mycol. 2019, 57 (Suppl. S1), S67–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbona, N.; Butkiewicz, C.D.; Keyes, M.; Shubitz, L.F. Clinical features of cats diagnosed with coccidioidomycosis in Arizona, 2004–2018. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2020, 22, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macías-Rioseco, M.; Sheley, M.; Ochoa, J.; Carvallo-Chaigneau, F.R.; Uzal, F.A. Coccidioidomycosis in 26 horses in California, USA: Case series and review of the literature. J. Veter. Diagn. Investig. 2022, 34, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.N.; Hodzic, E.; Diab, S.S.; Uzal, F.A. Pathology of coccidioidomycosis in llamas and alpacas. J. Veter. Diagn. Investig. 2018, 30, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capilla, J.; Clemons, K.V.; Stevens, D.A. Animal models: An important tool in mycology. Med. Mycol. 2007, 45, 657–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemons, K.V.; Capilla, J.; Stevens, D.A. Experimental Animal Models of Coccidioidomycosis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1111, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemons, K.V.; Leathers, C.R.; Lee, K.W. Systemic Coccidioides immitis infection in nude and beige mice. Infect. Immun. 1985, 47, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaji, M. Animal Models in Medical Mycology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sass, G.; Larwood, D.J.; Martinez, M.; Chatterjee, P.; Xavier, M.O.; Stevens, D.A. Nikkomycin Z against Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis in a Murine Model of Sustained-Release Dosing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0028521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sass, G.; Larwood, D.J.; Martinez, M.; Shrestha, P.; A Stevens, D. Efficacy of nikkomycin Z in murine CNS coccidioidomycosis: Modelling sustained-release dosing. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 2629–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubitz, L.F.; Trinh, H.T.; Galgiani, J.N.; Lewis, M.L.; Fothergill, A.W.; Wiederhold, N.P.; Barker, B.M.; Lewis, E.R.G.; Doyle, A.L.; Hoekstra, W.J.; et al. Evaluation of VT-1161 for Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis in Murine Infection Models. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 7249–7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shubitz, L.F.; Butkiewicz, C.D.; Trinh, H.T. Modeling Chronic Coccidioidomycosis in Mice. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2667, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubitz, L.F.; Powell, D.A.; Butkiewicz, C.D.; Lewis, M.L.; Trinh, H.T.; Frelinger, J.A.; Orbach, M.J.; Galgiani, J.N. A Chronic Murine Disease Model of Coccidioidomycosis Using Coccidioides posadasii, Strain 1038. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarch-Pérez, C.; Riool, M.; Zaat, S. Current osteomyelitis mouse models, a systematic review. Eur. Cells Mater. 2021, 42, 334–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Su, J.; Hou, Y.; Yao, Z.; Yu, B.; Zhang, X. EGFR/FAK and c-Src signalling pathways mediate the internalisation of Staphylococcus aureus by osteoblasts. Cell. Microbiol. 2020, 22, e13240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuchscherr, L.; Geraci, J.; Löffler, B. Staphylococcus aureus Regulator Sigma B is Important to Develop Chronic Infections in Hematogenous Murine Osteomyelitis Model. Pathogens 2017, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Qin, H.; Jiang, N.; Liu, G.; Wu, H.; Bai, L.; Yu, B.; Zhang, X. G-CSF partially mediates bone loss induced by Staphylococcus aureus infection in mice. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Site Dissemination Frequency | Frequency of Multisite Infection | |
|---|---|---|
| Central nervous system | 34.3% | 19.7% |
| Blood | 21.3% | 6.8% |
| Skeletal-axial | 16.9% | 20.0% |
| Skeletal-peripheral | 15.5% | 18.8% |
| Soft tissue | 7.2% | 0.0% |
| Skin | 7.7% | 5.9% |
| Gastrointestinal tract | 2.4% | 0.0% |
| Genitourinary tract | 1.4% | 0.0% |
| Heart | 0.5% | 0.0% |
| Variables | Vertebral Coccidioidomycosis | Pyogenic Spondylitis | Tuberculous Spondylitis | Spinal Metastasis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location on the spine | Thoracic and lumbar | Thoracic and lumbar | Thoracic | Thoracic and lumbar (and rarely cervical) |
| Associated microorganisms | Coccidioides spp. | Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococci, Enterococci, Escherichia coli, etc. | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | No microorganisms associated |
| Route of spread | Hematogenous | Hematogenous arterial route, direct inoculation from surgery. | Venous, Batson’s paravertebral venous plexus | Venous hematogenous (the most common route), arterial, direct tumor extension, and lymphatic |
| Vertebral bodies | >1 | Few vertebral bodies involved | >1 | Few vertebral bodies involved (some rare cases showed > 5 vertebrae involved on the cervical spine |
| ESP, CRP * | Mildly increased | Markedly increased | Mildly increased | Mildly increased |
| Variables | Itraconazole | Fluconazole | Posaconazole | Amphotericin B |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indication |
|
|
|
|
| Advantage |
|
|
|
|
| Side effects |
|
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moni, B.M.; Wise, B.L.; Loots, G.G.; Weilhammer, D.R. Coccidioidomycosis Osteoarticular Dissemination. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9101002
Moni BM, Wise BL, Loots GG, Weilhammer DR. Coccidioidomycosis Osteoarticular Dissemination. Journal of Fungi. 2023; 9(10):1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9101002
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoni, Benedicte M., Barton L. Wise, Gabriela G. Loots, and Dina R. Weilhammer. 2023. "Coccidioidomycosis Osteoarticular Dissemination" Journal of Fungi 9, no. 10: 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9101002
APA StyleMoni, B. M., Wise, B. L., Loots, G. G., & Weilhammer, D. R. (2023). Coccidioidomycosis Osteoarticular Dissemination. Journal of Fungi, 9(10), 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9101002








