Inhibition of Dopamine Activity and Response of Rhipicephalus microplus Challenged with Metarhizium anisopliae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rhipicephalus microplus Ticks
2.2. Metarhizium anisopliae and Fungal Suspension
2.3. Antagonist SCH 23390
2.4. In Vitro Phagocytic Assay
2.5. Inoculation Treatments in Rhipicephalus microplus Females
2.6. Survival and Biological Parameters of Rhipicephalus microplus
2.7. Quantification of Hemocytes
2.8. Dopamine Detection in Hemocytes of Rhipicephalus microplus
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phagocytic Index of Rhipicephalus microplus Hemocytes Challenged with Metarhizium anisopliae and the Antagonist
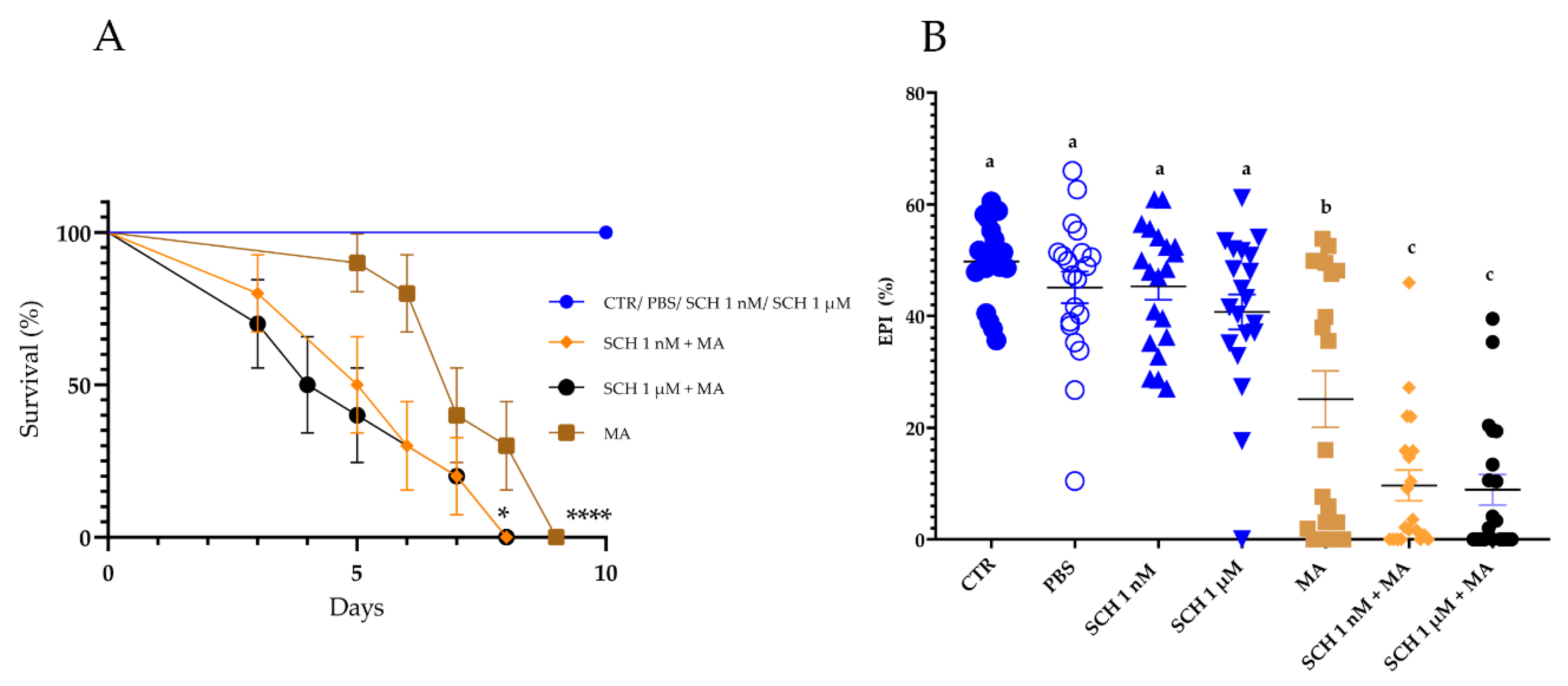
3.2. Survival and Biological Parameters of Rhipicephalus microplus Females
3.3. Quantification of Hemocytes
3.4. Dopamine Detection in R. microplus Hemocytes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bahia, M.; Silva, J.D.S.; Gontijo, I.S.; Cordeiro, M.D.; Santos, P.N.D.; Silva, C.B.D.; Nicolino, R.R.; Mota, D.A.; Silva, J.B.; Fonseca, A.H. Characterization of cattle tick fever in calves from the northwestern region of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2020, 29, e017119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klafke, G.M.; Castro-Janer, E.; Mendes, M.C.; Namindome, A.; Schumaker, T.T.S. Applicability of in vitro bioassays for the diagnosis of ivermectin resistance in Rhipicephalus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 184, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higa, L.; De, O.S.; Garcia, M.V.; Barros, J.C.; Koller, W.W.; Andreotti, R. Evaluation of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) resistance to different acaricide formulations using samples from Brazilian properties: Ixodidae resistance to different acaricide formulations using samples from Brazilian properties. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2016, 25, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adehan, S.B.; Biguezoton, A.; Adakal, H.; Assogba, M.N.; Zoungrana, S.; Gbaguidi, A.M.; Aretas, T.; Souleymane, K.; Louis, A.; Hamade, K.; et al. Acaricide resistance of Rhipicephalus microplus ticks in Benin. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 11, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, M.G.; Nogueira, M.R.; Marciano, A.F.; Perinotto, W.M.; Coutinho-Rodrigues, C.J.; Scott, F.B.; Angelo, I.C.; Prata, M.C.; Bittencourt, V.R. Metarhizium anisopliae for controlling Rhipicephalus microplus ticks under field conditions. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 223, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciano, A.F.; Mascarin, G.M.; Franco, R.F.F.; Golo, P.S.; Jaronski, S.T.; Fernandes, É.K.K.; Bittencourt, V.R. Innovative granular formulation of Metarhizium robertsii microsclerotia and blastospores for cattle tick control. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maina, U.M.; Galadima, I.B.; Gambo, F.M.; Zakaria, D. A review on the use of entomopathogenic fungi in the management of insect pests of field crops. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2018, 6, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Feitosa, A.P.S.; Alves, L.C.; Chaves, M.M.; Veras, D.L.; Silva, E.M.; Alliança, A.S.S.; França, I.R.S.; Gonçalves, G.G.A.; Lima-Filho, J.L. Hemocytes of Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2015, 52, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorotti, J.; Urbanová, V.; Gôlo, P.S.; Bittencourt, V.R.E.P.; Kopáček, P. The role of complement in the tick cellular immune defense against the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium robertsii. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2022, 126, 104234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, P.; Vitari, G.; Rezende, A.; Couto, J.; Antunes, S.; Domingos, A.; Peckle, M.; Massard, C.; Araujo, F.; Santos, H. Characterization of the Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus Sialotranscriptome Profile in Response to Theileria equi Infection. Pathogens 2021, 10, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorotti, J.; Gôlo, P.S.; Marciano, A.F.; Camargo, M.G.; Angelo, I.C.; Bittencourt, V.R.E.P. Disclosing hemolymph collection and inoculation of Metarhizium blastospores into Rhipicephalus microplus ticks towards invertebrate pathology studies. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 148, e59899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelo, I.C.; Gôlo, P.S.; Camargo, M.G.; Kluck, G.E.G.; Folly, E.; Bittencourt, V.R.E.P. Haemolymph protein and lipid profile of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus infected by fungi. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2010, 57, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogaça, A.C.; Sousa, G.; Pavanelo, D.B.; Esteves, E.; Martins, L.A.; Urbanová, V.; Kopáček, P.; Daffre, S. Tick immune system: What is known; the interconnections; the gaps; and the challenges. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 628054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D. Innate immunity in ticks: A review. J. Acarol. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 15, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pereira, L.S.; Oliveira, P.L.; Barja-Fidalgo, C.; Daffre, S. Production of reactive oxygen species by hemocytes from the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. Exp. Parasitol. 2001, 99, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayne, C.J. Phagocytosis and non-self-recognition in invertebrates. BioScience 1990, 40, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovičková, B.; Václav, H. Ontogeny of tick hemocytes: A comparative analysis of Ixodes ricinus and Ornithodoros moubata. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2005, 35, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitosa, A.P.S.; Chaves, M.M.; Veras, D.L.; de Deus, D.M.V.; Portela, N.C.; Araújo, A.R.; Alves, L.C.; Brayner, F.A. Assessing the cellular and humoral immune response in Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato (Acari: Ixodidae) infected with Leishmania infantum (Nicolle; 1908). Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.F.; Xu, G.; Stanley, D.; Huang, J.; Ye, G.Y. Dopamine modulates hemocyte phagocytosis via a D1-like receptor in the rice stem borer, Chilo suppressalis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, T.A.; Fiorotti, J.; Mesquita, E.; Meirelles, L.N.; Camargo, M.G.; Coutinho-Rodrigues, C.J.B.; Marciano, A.F.; Bittencourt, V.R.E.P.; Gôlo, P.S. How Dopamine Influences Survival and Cellular Immune Response of Rhipicephalus microplus Inoculated with Metarhizium anisopliae. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Dong, C.; Tian, Z.; Mao, N.; Wang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jian, G.X.; Luo, L. Altered immunity in crowded Mythimna separata is mediated by octopamine and dopamine. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šimo, L.; Koči, J.; Kim, D.; Park, Y. Invertebrate specific D1-like dopamine receptor in control of salivary glands in the black-legged tick Ixodes scapularis. J. Comp. Neurol. 2014, 522, 2038–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, Q.; Thakur, M.; Smith, A.A.; Kitsou, C.; Yang, X.; Pal, U. Borrelia burgdorferi protein interactions critical for microbial persistence in mammals. Cell. Microbiol. 2019, 21, e12885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, J.M.; Ejendal, K.F.; Avramova, L.V.; Garland-Kuntz, E.E.; Giraldo-Calderón, G.I.; Brust, T.F.; Hill, C.A. A “genome-to-lead” approach for insecticide discovery: Pharmacological characterization and screening of Aedes aegypti D1-like dopamine receptors. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, J.M.; Ejendal, K.F.; Watts, V.J.; Hill, C.A. Molecular and pharmacological characterization of two D1-like dopamine receptors in the Lyme disease vector, Ixodes scapularis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejendal, K.F.K.; Meyer, J.M.; Brust, T.F.; Avramova, L.V.; Hill, C.A.; Watts, V.J. Discovery of antagonists of tick dopamine receptors via chemical library screening and comparative pharmacological analyses Ixodes scapularis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, E.; Marciano, A.F.; Corval, A.R.C.; Fiorotti, J.; Corrêa, T.A.; Quinelato, S.; Bittencourt, V.R.E.P.; Gôlo, P.S. Efficacy of a native isolate of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae against larval tick outbreaks under semifield conditions. BioControl 2020, 65, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustard, J.A.; Blenau, W.; Hamilton, I.S.; Ward, V.K.; Ebert, P.R.; Mercer, A.R. Analysis of two D1-like dopamine receptors from the honey bee Apis mellifera reveals agonist-independent activity. Mol. Brain Res. 2003, 113, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brayner, F.A.; Araújo, H.R.C.; Cavalcanti, M.G.S.; Alves, L.C.; Peixoto, C.A. Ultrastructural characterization of the hemocytes of Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae). Micron 2005, 36, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.F. Ovoposition of Boophilus microplus (Canestrini) (Acarida: Ixodidae) I. Influence of tick size on egg production. Acarologia 1974, 16, 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- Drummond, R.O.; Gladney, W.J.; Whetstone, T.M.; Ernst, S.E. Laboratory testing of insecticides for control of the winter tick. J. Econ. Entomol. 1971, 64, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zekeya, N.; Mbega, E.R.; Ndossi, H. Susceptibility of different species of ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) to an entomopathogenic fungus in Tanzania. J. Anim. Sci. Res. 2020, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafarchia, C.; Pellegrino, R.; Romano, V.; Friuli, M.; Demitri, C.; Pombi, M.; Benelli, G.; Otranto, D. Delivery and effectiveness of entomopathogenic fungi for mosquito and tick control: Current knowledge and research challenges. Acta Trop. 2022, 234, 106627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorotti, J.; Menna-Barreto, R.F.S.; Gôlo, P.S.; Coutinho-Rodrigues, C.J.B.; Bitencourt, R.O.B.; Spadacci-Morena, D.D.; Angelo, I.C.; Bittencourt, V.R.E.P. Ultrastructural and cytotoxic effects of Metarhizium robertsii infection on Rhipicephalus microplus hemocytes. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bório, V.S.; Corrêa, T.A.; Fiorotti, J.; Mesquita, E.; Meirelles, L.N.; Camargo, M.G.; Bittencourt, V.R.E.P.; Golo, P.S. Inhibition of Dopamine Activity and Response of Rhipicephalus microplus Challenged with Metarhizium anisopliae. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121312
Bório VS, Corrêa TA, Fiorotti J, Mesquita E, Meirelles LN, Camargo MG, Bittencourt VREP, Golo PS. Inhibition of Dopamine Activity and Response of Rhipicephalus microplus Challenged with Metarhizium anisopliae. Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(12):1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121312
Chicago/Turabian StyleBório, Victória Silvestre, Thaís Almeida Corrêa, Jéssica Fiorotti, Emily Mesquita, Laura Nóbrega Meirelles, Mariana Guedes Camargo, Vânia Rita Elias Pinheiro Bittencourt, and Patrícia Silva Golo. 2022. "Inhibition of Dopamine Activity and Response of Rhipicephalus microplus Challenged with Metarhizium anisopliae" Journal of Fungi 8, no. 12: 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121312
APA StyleBório, V. S., Corrêa, T. A., Fiorotti, J., Mesquita, E., Meirelles, L. N., Camargo, M. G., Bittencourt, V. R. E. P., & Golo, P. S. (2022). Inhibition of Dopamine Activity and Response of Rhipicephalus microplus Challenged with Metarhizium anisopliae. Journal of Fungi, 8(12), 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121312






