Rapid Diagnosis of Central Nervous System Scedosporiosis by Specific Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction Applied to Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Tissue
Abstract
1. Introduction
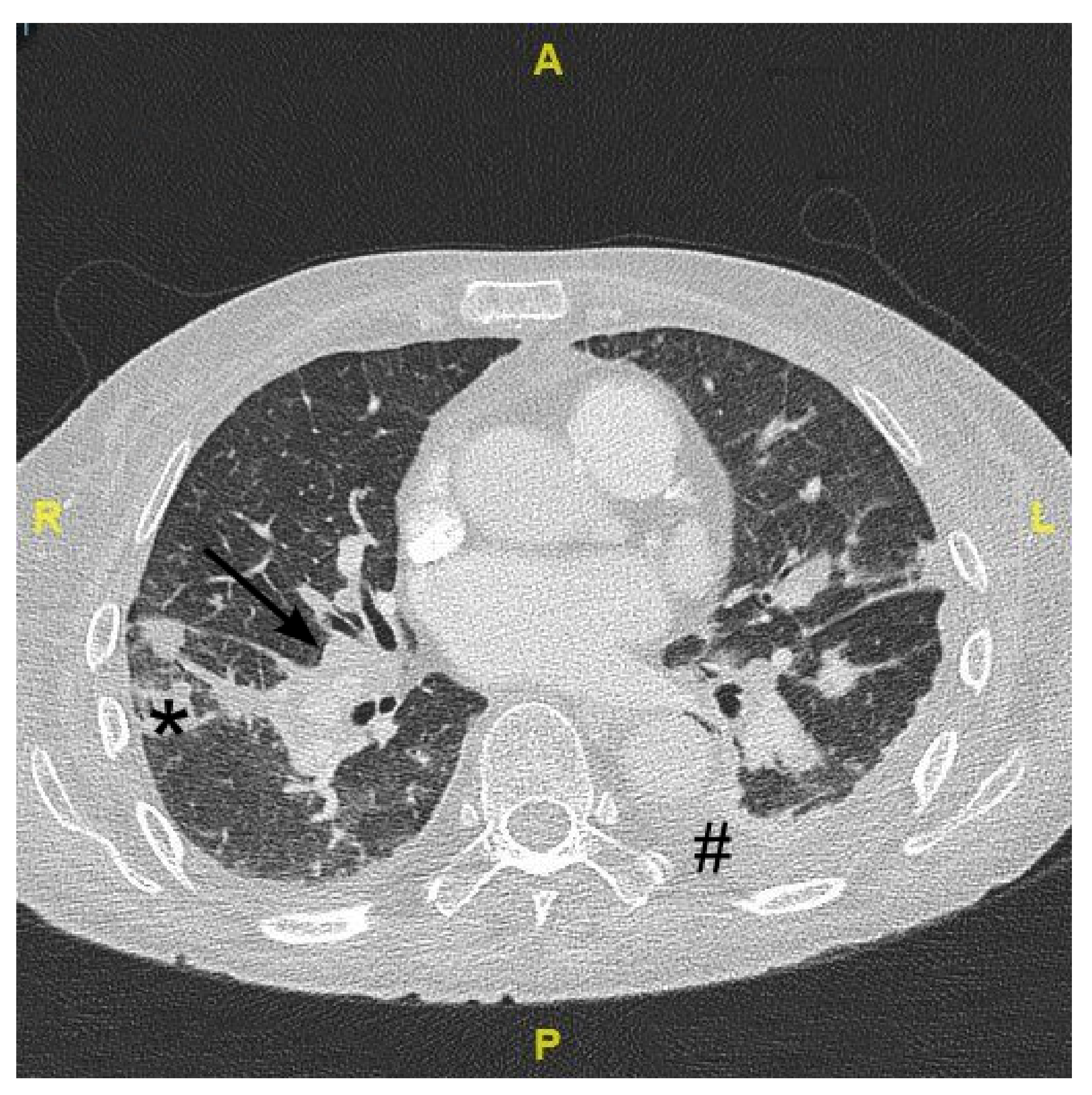
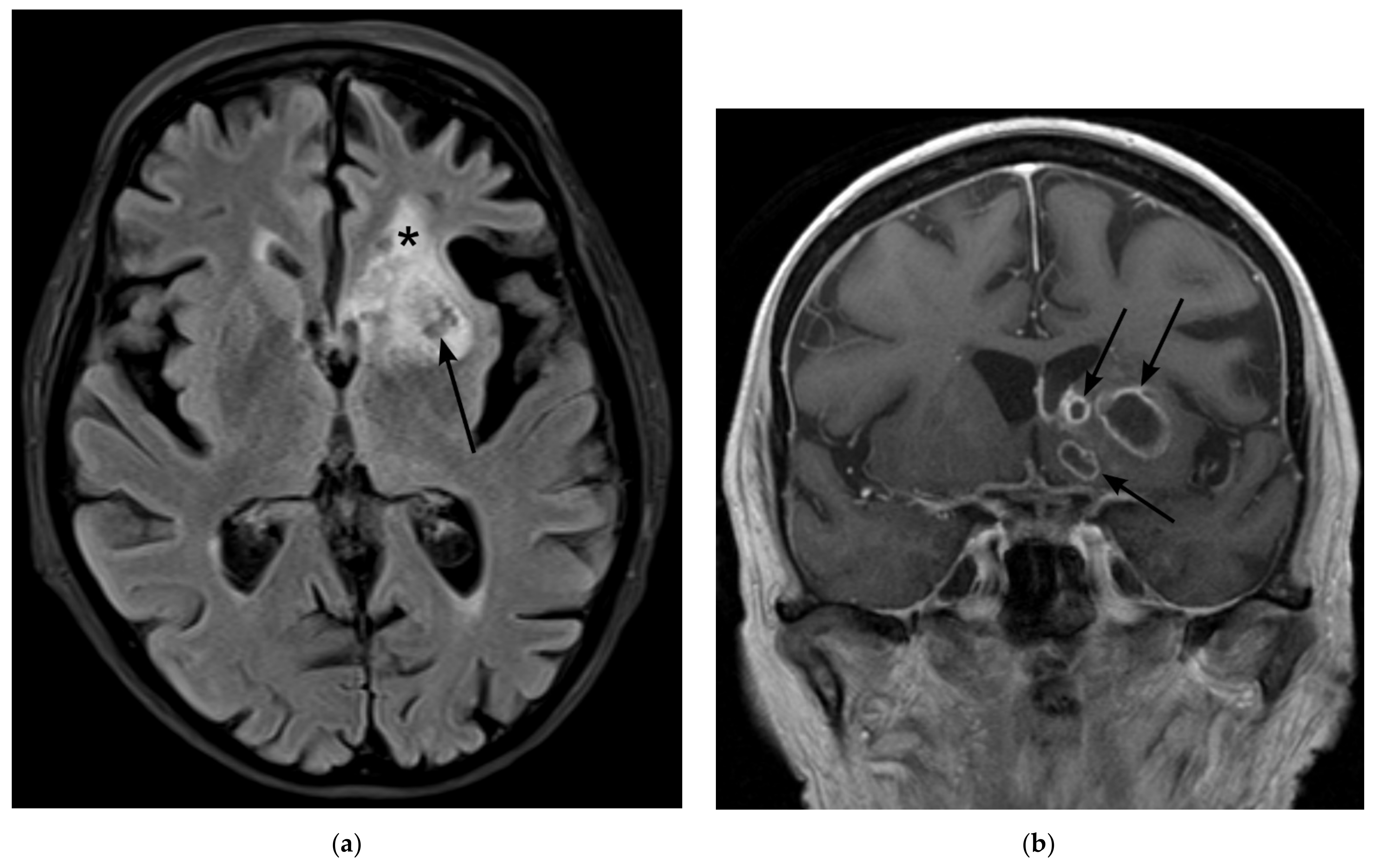
2. Case Presentation
3. Materials and Methods
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Britt, R.H.; Enzmann, D.R. Clinical stages of human brain abscesses on serial CT scans after contrast infusion. Computerized tomographic, neuropathological, and clinical correlations. J. Neurosurg. 1983, 59, 972–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodilsen, J.; Dalager-Pedersen, M.; van de Beek, D.; Brouwer, M.C.; Nielsen, H. Incidence and mortality of brain abscess in Denmark: A nationwide population-based study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.T.; Tsai, C.F.; Wong, Y.S.; Chen, S.C. Epidemiology of brain abscess in Taiwan: A 14-year population-based cohort study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laulajainen-Hongisto, A.; Lempinen, L.; Farkkila, E.; Saat, R.; Markkola, A.; Leskinen, K.; Blomstedt, G.; Aarnisalo, A.A.; Jero, J. Intracranial abscesses over the last four decades; changes in aetiology, diagnostics, treatment and outcome. Infect. Dis. 2016, 48, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, M.C.; Coutinho, J.M.; van de Beek, D. Clinical characteristics and outcome of brain abscess: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology 2014, 82, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troke, P.; Aguirrebengoa, K.; Arteaga, C.; Ellis, D.; Heath, C.H.; Lutsar, I.; Rovira, M.; Nguyen, Q.; Slavin, M.; Chen, S.C.; et al. Treatment of scedosporiosis with voriconazole: Clinical experience with 107 patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamaris, G.A.; Chamilos, G.; Lewis, R.E.; Safdar, A.; Raad, I.I.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Scedosporium infection in a tertiary care cancer center: A review of 25 cases from 1989-2006. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 1580–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzina, W.; Feierl, G.; Haas, D.; Reinthaler, F.F.; Holl, A.; Kleinert, R.; Reichenpfader, B.; Roll, P.; Marth, E. Lethal brain abscess due to the fungus Scedosporium apiospermum (teleomorph Pseudallescheria boydii) after a near-drowning incident: Case report and review of the literature. Med. Mycol. 2006, 44, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Caggiano, G.; Cantisani, P.; Rolli, M.; Gianfreda, C.D.; Pizzolante, M.; Montagna, M.T. The importance of a proper aetiological diagnosis in the management of patients with invasive mycoses: A case report of a brain abscess by Scedosporium apiospermum. Mycopathologia 2011, 172, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, C.; Akiyama, M.J.; Torres, J.; Louie, E.; Meehan, S.A. Scedosporium apiospermum infections and the role of combination antifungal therapy and GM-CSF: A case report and review of the literature. Med. Mycol. Case. Rep. 2016, 11, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uenotsuchi, T.; Moroi, Y.; Urabe, K.; Tsuji, G.; Koga, T.; Matsuda, T.; Furue, M. Cutaneous Scedosporium apiospermum infection in an immunocompromised patient and a review of the literature. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2005, 85, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, K.J.; Roilides, E.; Quiroz-Telles, F.; Meletiadis, J.; Antachopoulos, C.; Knudsen, T.; Buchanan, W.; Milanovich, J.; Sutton, D.A.; Fothergill, A.; et al. Infections caused by Scedosporium spp. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 157–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signore, S.C.; Dohm, C.P.; Schutze, G.; Bahr, M.; Kermer, P. Scedosporium apiospermum brain abscesses in a patient after near-drowning—A case report with 10-year follow-up and a review of the literature. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2017, 17, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.G.; Choi, J.G.; Son, B.C. Scedosporium apiospermum: An Emerging Fatal Cause of Fungal Abscess and Ventriculitis after Near-drowning. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2018, 13, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockhart, S.R.; Bialek, R.; Kibbler, C.C.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Jensen, H.E.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Molecular Techniques for Genus and Species Determination of Fungi from Fresh and Paraffin-Embedded Formalin-Fixed Tissue in the Revised EORTC/MSGERC Definitions of Invasive Fungal Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, S109–S113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.S.; Sexton, D.J.; Mick, N.; Nettles, R.; Fowler, V.G., Jr.; Ryan, T.; Bashore, T.; Corey, G.R. Proposed Modifications to the Duke Criteria for the Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 30, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickerts, V.; Khot, P.D.; Myerson, D.; Ko, D.L.; Lambrecht, E.; Fredricks, D.N. Comparison of quantitative real time PCR with Sequencing and ribosomal RNA-FISH for the identification of fungi in Formalin fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue specimens. BMC Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooms, I.; Mugisha, P.; Gambichler, T.; Hadaschik, E.; Esser, S.; Rath, P.-M.; Haase, G.; Wilmes, D.; McCormick-Smith, I.; Rickerts, V. Disseminated Emergomycosis in a Person with HIV Infection, Uganda. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1750–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khot, P.D.; Ko, D.L.; Hackman, R.C.; Fredricks, D.N. Development and optimization of quantitative PCR for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis with bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. BMC Infect. Dis. 2008, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, E.; Hedayati, M.T.; Zoll, J.; Rafati, H.; Ghasemi, M.; Doroudinia, A.; Abastabar, M.; Tolooe, A.; Snelders, E.; Lee, H.A.v.d.; et al. Discrimination of Aspergillosis, Mucormycosis, Fusariosis, and Scedosporiosis in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Specimens by Use of Multiple Real-Time Quantitative PCR Assays. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 2798–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Utsumi, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Nakajima, Y.; Murata, O.; Sasaki, N.; Nitanai, H.; Nagashima, H.; Miyamoto, S.; Yaegashi, J.; et al. Multiple Scedosporium apiospermum abscesses in a woman survivor of a tsunami in northeastern Japan: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2011, 5, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmes, D.; McCormick-Smith, I.; Lempp, C.; Mayer, U.; Schulze, A.B.; Theegarten, D.; Hartmann, S.; Rickerts, V. Detection of Histoplasma DNA from Tissue Blocks by a Specific and a Broad-Range Real-Time PCR: Tools to Elucidate the Epidemiology of Histoplasmosis. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, J.; McCormick Smith, I.; Hartmann, S.; Winkelmann, R.; Wilmes, D.; Cornely, O.; Kessel, J.; Loffler, J.; Rickerts, V. Identification of Aspergillus and Mucorales in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue samples: Comparison of specific and broad-range fungal qPCR assays. Med. Mycol. 2019, 57, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mursch, K.; Trnovec, S.; Ratz, H.; Hammer, D.; Horre, R.; Klinghammer, A.; de Hoog, S.; Behnke-Mursch, J. Successful treatment of multiple Pseudallescheria boydii brain abscesses and ventriculitis/ependymitis in a 2-year-old child after a near-drowning episode. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2006, 22, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tammer, I.; Tintelnot, K.; Braun-Dullaeus, R.C.; Mawrin, C.; Scherlach, C.; Schlüter, D.; König, W. Infections due to Pseudallescheria/Scedosporium species in patients with advanced HIV disease—A diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, e422–e429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao-Martinez, A.F.; Castillo-Mancilla, J.R.; Barron, M.A.; Nichol, A.C. Combination Antifungal Therapy in the Treatment of Scedosporium apiospermum Central Nervous System Infections. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2013, 2013, 589490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Kamili, Q.; Lai, S.; Musher, D.M.; Hamill, R. Cerebral Scedosporium apiospermum infection presenting with intestinal manifestations. Infection 2013, 41, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, N.; Chen, T.C.; Hou, J.K. An unusual cause of diarrhea in an immunocompromised patient. Scedosporium apiospermum colitis and brain abscess. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 519–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.R.; Tenforde, M.W.; Chan, J.D.; Ko, A.; Graham, S.M. Safety and clinical response of intraventricular caspofungin for Scedosporium apiospermum complex central nervous system infection. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2016, 13, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudke, A.Y.; Shaikh, S.T.; Deopujari, C.E.; Sakle, A.S. Scedosporium Apiospermum: Rare Cause of Brain Abscess in an Immunocompetent Patient. Neurol. India 2020, 68, 906–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meletiadis, J.; Meis, J.F.G.M.; Mouton, J.W.; Rodriquez-Tudela, J.L.; Donnelly, J.P.; Verweij, P.E.; Eurofung Network. In Vitro Activities of New and Conventional Antifungal Agents against Clinical Scedosporium Isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauseo, A.M.; Coler-Reilly, A.; Larson, L.; Spec, A. Hope on the Horizon: Novel Fungal Treatments in Development. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiraz, N.; Gulbas, Z.; Akgun, Y.; Uzun, O. Lymphadenitis caused by Scedosporium apiospermum in an immunocompetent patient. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, E59–E61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, R.; Bricker, A.O.; Sahi, H.; Mohammed, T.L. Pseudallescheria boydii (Scedosporium species) in 3 lung transplant recipients: Computed tomography findings and literature review. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2009, 33, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, S.; Kwak, E.J.; Obman, A.; Wagener, M.M.; Kusne, S.; Stout, J.E.; McCurry, K.R.; Singh, N. Prospective assessment of Platelia Aspergillus galactomannan antigen for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in lung transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2004, 4, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, C.; Ruiz-Santana, S.; Saavedra, P.; Castro, C.; Loza, A.; Zakariya, I.; Ubeda, A.; Parra, M.; Macias, D.; Tomas, J.I.; et al. Contribution of Candida biomarkers and DNA detection for the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis in ICU patients with severe abdominal conditions. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, M.L.; Hoff, J.T.; Norman, D.; Edwards, M.S.; Berg, B.O. Nonoperative treatment of brain abscesses in selected high-risk patients. J. Neurosurg. 1980, 52, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, M.C.; Tunkel, A.R.; McKhann, G.M., 2nd; van de Beek, D. Brain abscess. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Literature | Biopsy | Histopathology | Culture | Microscopy of Cultured Material | PCR | Sequencing | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buzina et al., 2006 [8] | + | o | Blood: − BAL:− Biopsy: + | + | Culture: + | Culture: + | |
| Mursch et al., 2006 [24] | + | o | CSF: − Biopsy: + | o | o | Culture: + | |
| Caggiano et al., 2011 [9] | + | (+) | Biopsy:+ | + | Molecular analysis of culture was performed but not further specified. | ||
| Nakamura et al., 2011 [21] | o | o | BAL: + | BAL: + | BAL: + | BAL: + | |
| Tammer et al., 2011 [25] | + | (+) | Biopsy: + | + | − | Culture: + | |
| Henao-Martinez et al., 2013 [26] Case 1 | o | o | FESS: + | + | o | o | |
| Henao-Martinez et al., 2013 [26] Case 2 | −/+ | (+) | CSF: + | o | o | o | 1st Biopsy − |
| Lin et al., 2013 [27,28] | + | (+) | Biopsy: + | o | o | o | |
| Wilson et al., 2013 | + | (+) | Biopsy: + Sputum: + | + | Biopsy: + | + | |
| Williams et al., 2016 [29] | + | − | CSF: − Biopsy: + | o | CSF: − Biopsy: + | o | |
| Signore et al., 2017 [13] | −/+ | −/+ | Blood: − Biopsy: + | o | Biopsy: − Blood: − | Tissue: + | 1st Biopsy − |
| Lee et al., 2018 [14] | + | o | Sputum:− CSF:− Biopsy:+ | o | o | o | |
| Sudke et al., 2020 [30] | + | + | Culture + | + | o | o | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lauerer, R.J.; Rosenow, E.; Beschorner, R.; Hempel, J.-M.; Naros, G.; Hofmann, A.; Berger, K.; Sartor-Pfeiffer, J.; Mengel, A.; Ziemann, U.; et al. Rapid Diagnosis of Central Nervous System Scedosporiosis by Specific Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction Applied to Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Tissue. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8010019
Lauerer RJ, Rosenow E, Beschorner R, Hempel J-M, Naros G, Hofmann A, Berger K, Sartor-Pfeiffer J, Mengel A, Ziemann U, et al. Rapid Diagnosis of Central Nervous System Scedosporiosis by Specific Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction Applied to Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Tissue. Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleLauerer, Robert J., Emely Rosenow, Rudi Beschorner, Johann-Martin Hempel, Georgios Naros, Anna Hofmann, Katharina Berger, Jennifer Sartor-Pfeiffer, Annerose Mengel, Ulf Ziemann, and et al. 2022. "Rapid Diagnosis of Central Nervous System Scedosporiosis by Specific Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction Applied to Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Tissue" Journal of Fungi 8, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8010019
APA StyleLauerer, R. J., Rosenow, E., Beschorner, R., Hempel, J.-M., Naros, G., Hofmann, A., Berger, K., Sartor-Pfeiffer, J., Mengel, A., Ziemann, U., Rickerts, V., & Feil, K. (2022). Rapid Diagnosis of Central Nervous System Scedosporiosis by Specific Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction Applied to Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Tissue. Journal of Fungi, 8(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8010019







