The Efficacy of Green Synthesized Nanosilver in Reducing the Incidence of Post-Harvest Apple Fruit Brown Rot
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Isolation and Identification of the Fungal Causal Agent of Apple Brown Rot
2.3. Green Synthesis of AgNPs Using Crude Tea Extract
2.4. Characterization of the AgNPs
2.4.1. The Ultraviolet Visible Absorption Spectra
2.4.2. The Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
2.4.3. The Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Analysis
2.4.4. The Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Zeta Potential
2.5. Detection of the In Vitro Antifungal Potency of AgNPs against M. fructigena
2.5.1. The Poisoned Food Technique
2.5.2. The Agar Well Diffusion Assay
2.6. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of the AgNPs
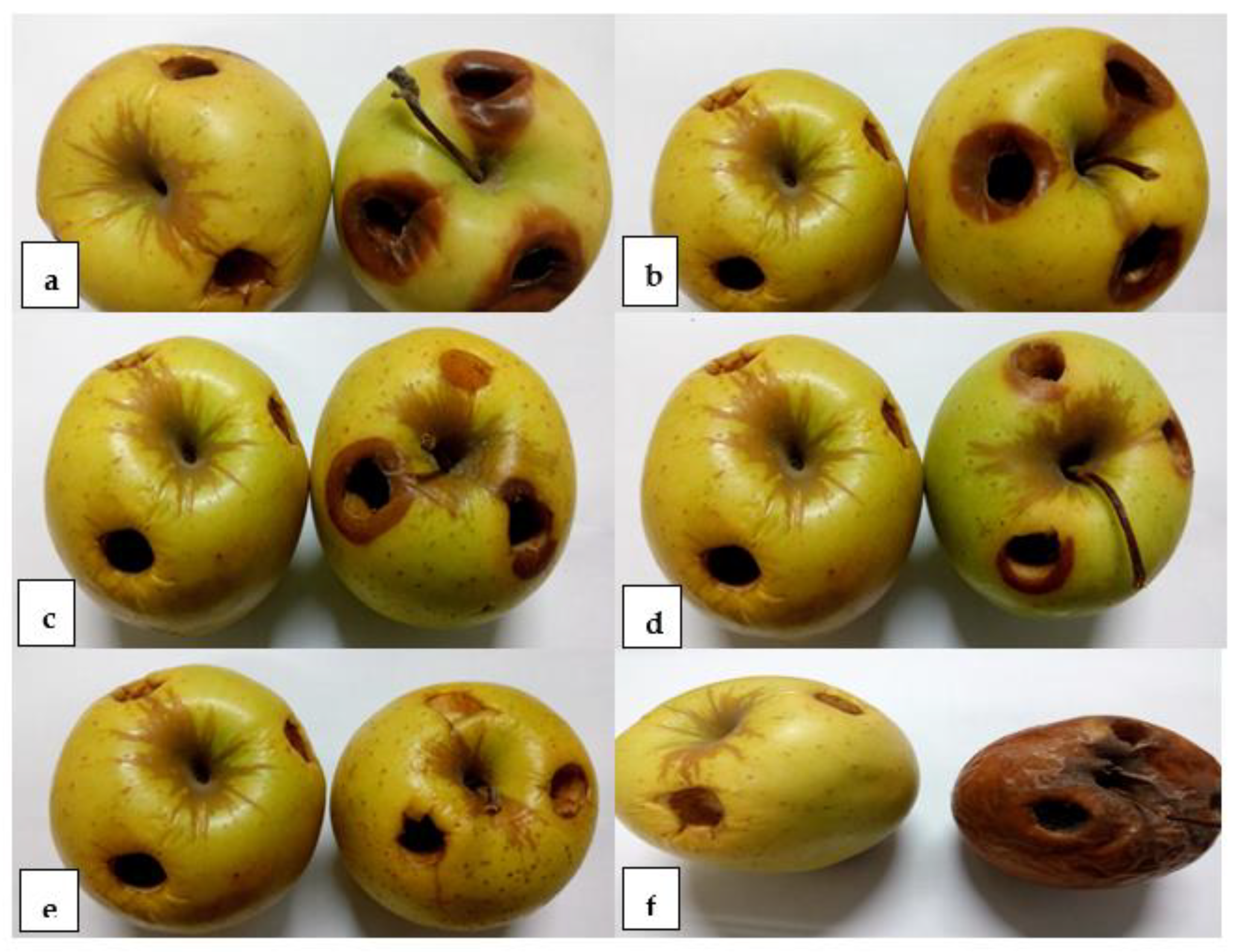
2.7. In Vivo Control of M. fructigena on the Apple Fruits
2.7.1. Preparation of the Apple Fruits and the AgNPs
2.7.2. Inoculation of the Treated M. fructigena into the Wounded Apple Fruits
2.8. Leakage of Proteins and DNA from Conidia of M. fructigena
2.9. Detection of Cytotoxicity of AgNPs
2.9.1. Human Cell Cultures
2.9.2. The Cytotoxicity Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Green Synthesis of the AgNPs
3.2. Characterization of the AgNPs
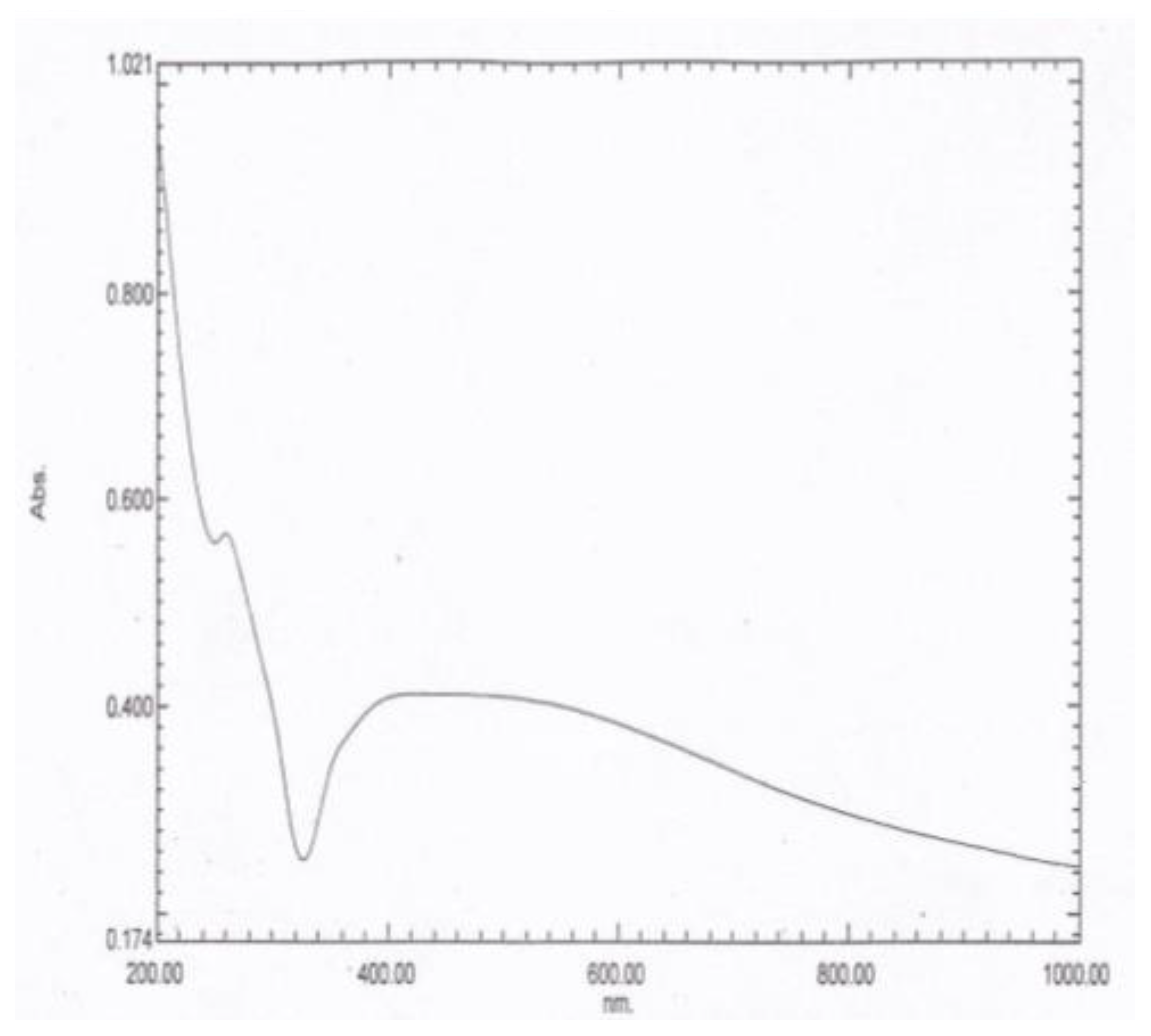
3.2.1. The Ultraviolet Visible (UV–VIS) Absorption Spectra
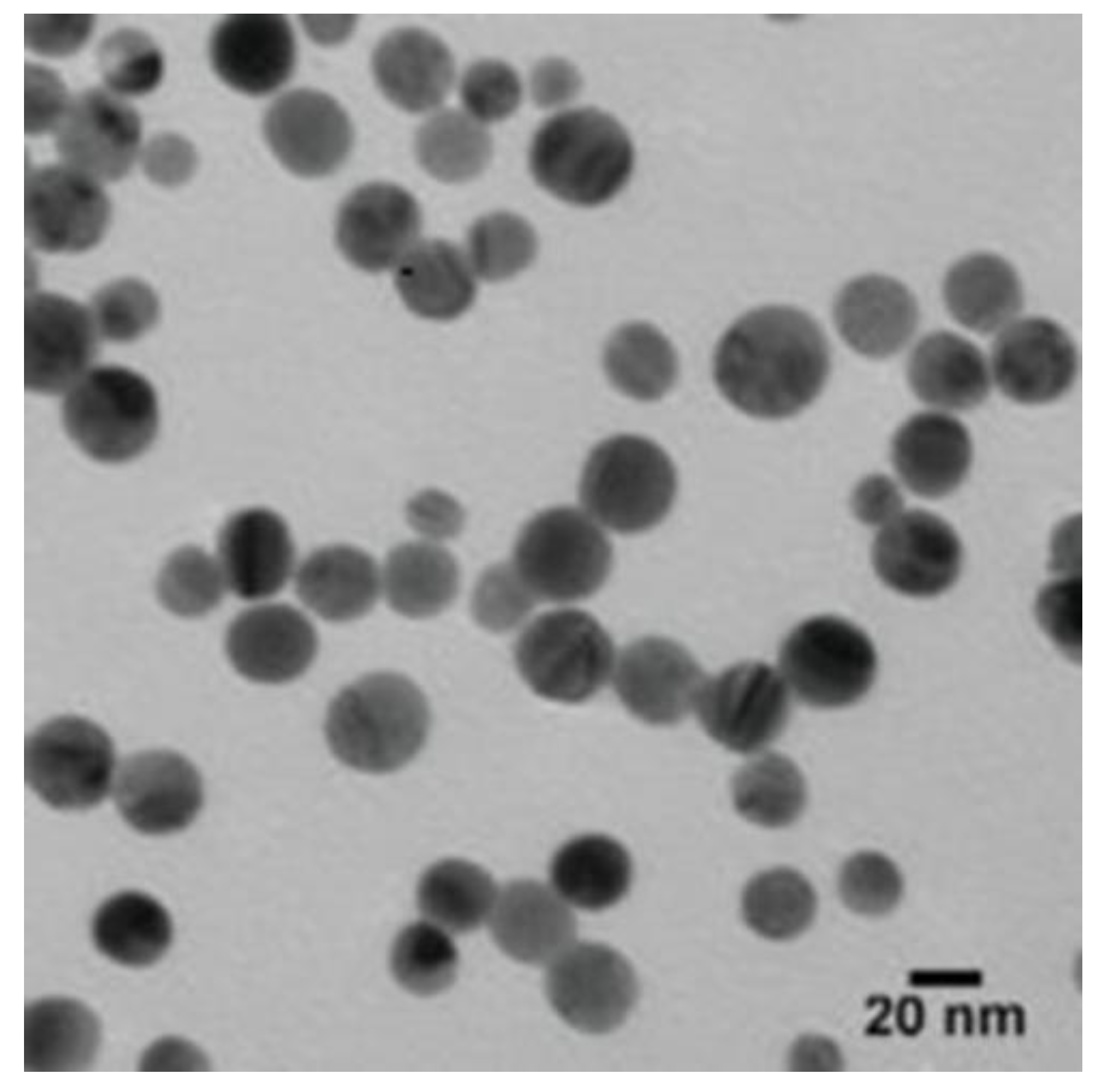
3.2.2. The Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
3.2.3. The Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR)
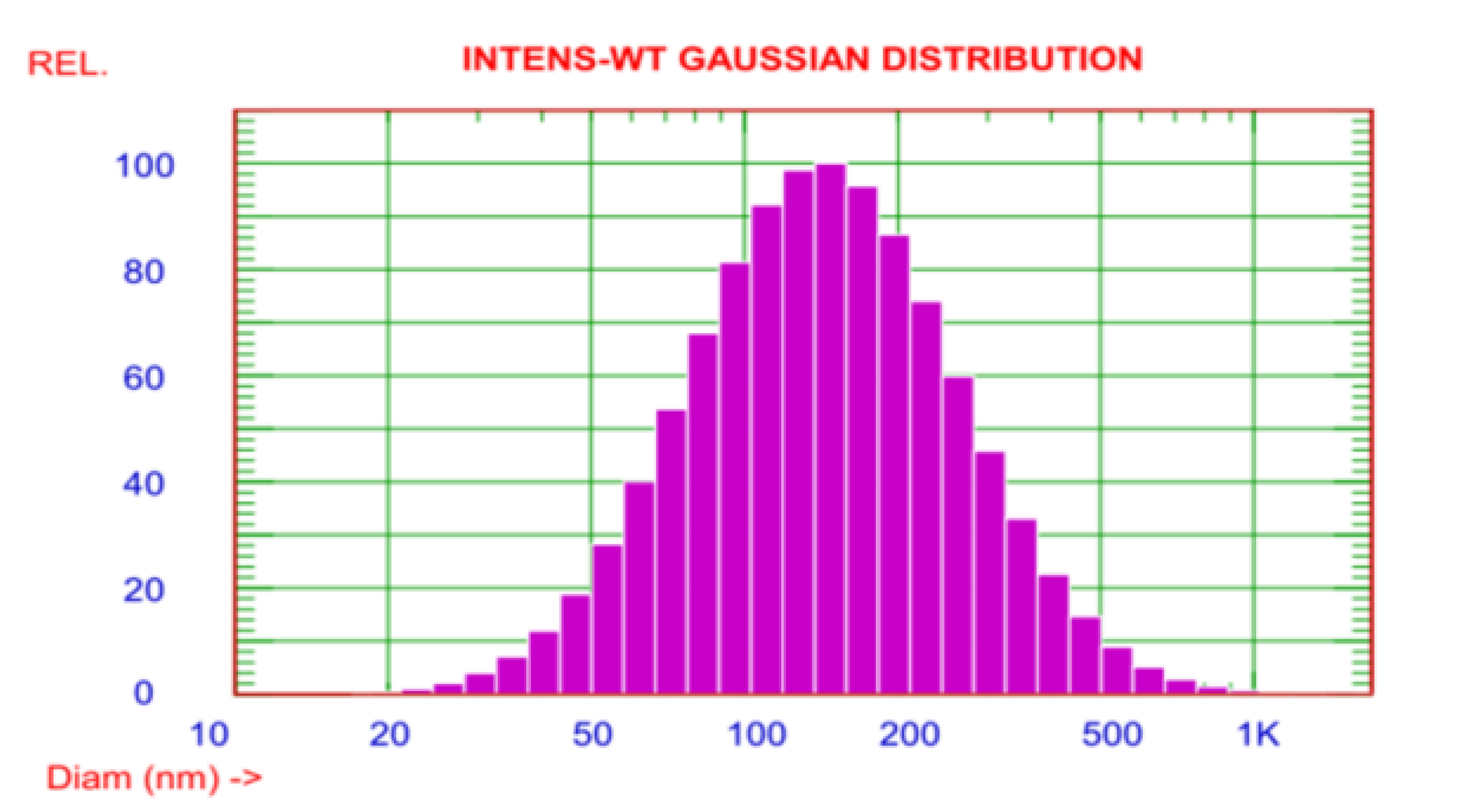
3.2.4. The Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Zeta Potential (ZP)
3.3. The In Vitro Antifungal Efficacy of the AgNPs
3.3.1. Poisoned Food Technique
3.3.2. Agar Well Diffusion Assay
3.4. Determination of MIC of the AgNPs
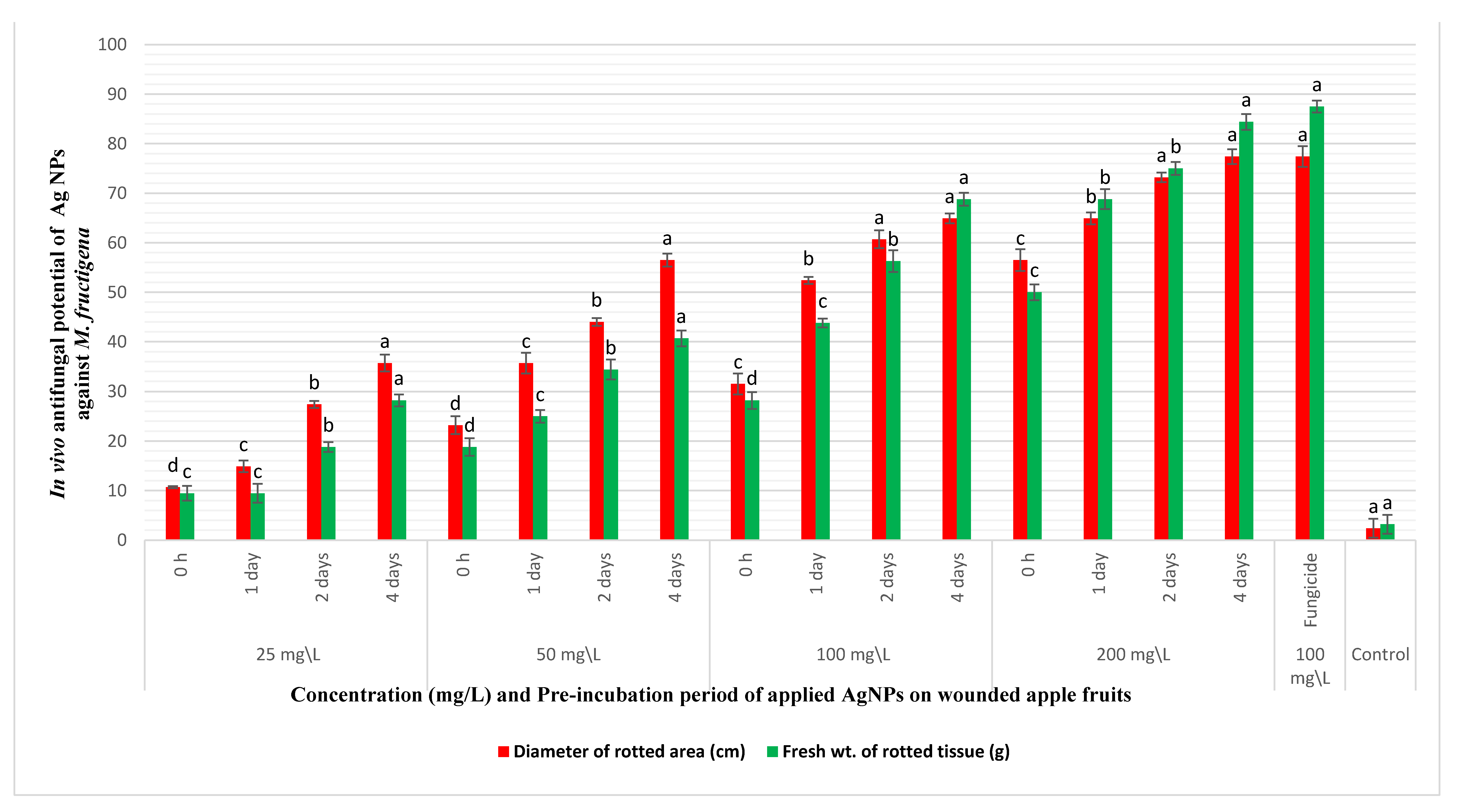
3.5. In Vivo Control of M. fructigena by Coinoculation with AgNPs in Apple Fruit
3.6. Leakage of Proteins and DNA from Conidia of the Treated M. fructigena
3.7. The Cytotoxicity Assay
4. Discussion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, D.; Sharma, R.R. Postharvest diseases of fruits and vegetables and their management. In Sustainable Pest Management; Prasad, D., Ed.; Data Publishing House: New Delhi, India, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Thilakarathna, S.H.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. Flavonoid bioavailability and attempts for bioavailability enhancement. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3367–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, J.L.; Lloyd, B. Health benefits of fruits and vegetables. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.D.; Park, M.Y.; Jeon, B.J.; Kim, B.S. Disease control efficacy of 32,33-didehydrorofamycoin produced by Streptomyces rectiviolaceus strain DY46 against gray mold of tomato fruit. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Hernandez, S.; Reyes-Pérez, J.J.; Chiquito-Contreras, R.G.; Rincon-Enriquez, G.; Cerdan-Cabrera, C.R.; Hernandez-Montiel, L.G. Biocontrol of Postharvest Fruit Fungal Diseases by Bacterial Antagonists: A Review. Agronomy 2019, 9, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, P.; Murugan, M.; Pitchaikani, S.; Venkatachalam, P.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V.; Kandasamy, S.; Shakila, H. Synthesis and characterization of bioactive silver nanoparticles from red marine macroalgae Chondrococcus Hornemannii. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, T.J.; Wick, P.; Manser, P. In vitro cytotoxicity of oxide nanoparticles: Comparison to asbestos, silica, and the effect of particle solubility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4374–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho Bernardo, W.L.; Boriollo, M.F.G.; Tonon, C.C.; da Silva, J.J.; Cruz, F.M.; Martins, A.L.; Hofling, J.F.; Spolidorio, D.M.P. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles and extracts of Syzygium cumini flowers and seeds: Periodontal, cariogenic and opportunistic pathogens. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 125, 105101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanamangai, B.M.; Ponmurugan, P.; Jeeva, S.E.; Manjukarunambika, K.; Elango, V.; Hemalatha, K.; Kakati, J.P.; Mohanraj, R.; Prathap, S. Biosynthesised silver and copper nanoformulation as foliar spray to control bird’s eye spot disease in tea plantations. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, P.; Dhoke, S.K.; Khanna, A.S. Effect of Nano-ZnO particle suspension on growth of mung (Vigna radiata) and Gram (Cicer arietinum) seedlings using plant agar method. J. Nanotechnol. 2011, 2011, 696535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.A.; Salari, S.; Hadizadeh, S. Evaluation of Antifungal Effect of Silver nanoparticles against Microsporum canis, Trichophyton mentagrophytes and Microsporum gypseum. Iran. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 13, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejad, M.S.; Khatami, M.; Bonjar, G.H.S. Extracellular synthesis gold nano-triangles using biomass of Streptomyces microflavus. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 10, 33–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Yan, M.; Duan, H.; Bi, Y.; Cheng, X.; Yu, H. Synergistic Antifungal Activity of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles and Epoxiconazole against Setosphaeria turcica. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020, 9535432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madbouly, A.K.; Abo Elyousr, K.A.M.; Ismail, I.M. Biocontrol of Monilinia fructigena, causal agent of brown rot of apple fruit, by using endophytic yeasts. Biol. Control 2020, 144, 104239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, W.; Chen, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Lu, M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by waste tea extract and degradation of organic dye in the absence and presence of H2O2. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 423, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgorban, A.M.; El-Samawaty, A.M.; Yassin, M.A.; Sayed, S.R.; Adil, S.F.; Elhindi, K.M.; Bakri, M.; Bakri, M. Antifungal silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2016, 30, 5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandalakshmi, K.; Venugobal, J.; Ramasamy, V. Characterization of silver nanoparticles by green synthesis method using Pedalium murex leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponmurugan, P.; Manjukarunambika, K.; Elango, V.; Gnanamangai, B.M. Antifungal activity of biosynthesised copper nanoparticles evaluated against red root-rot disease in tea plants. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2016, 11, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvioni, L.; Galbiati, E.; Collico, V.; Alessio, G.; Avvakumova, S.; Corsi, F.; Tortora, P.; Prosperi, D.; Colombo, M. Negatively charged silver nanoparticles with potent antibacterial activity and reduced toxicity for pharmaceutical preparations. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2517–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgorban, A.M.; El-Samawaty, A.M.; Abd-Elkader, O.H.; Yassin, M.A.; Sayed, S.R.M.; Khan, M.; Adil, S.F. Bioengineered silver nanoparticles using Curvularia pallescens and its fungicidal activity against Cladosporium fulvum. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 1522–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, J.G.; Martín, A.; Fernández-Baldo, M.A.; Berni, E.; Camí, G.; Duránb, N.; Rabaa, J.; Sanz, M.I. Production of silver nanoparticles using yeasts and evaluation of their antifungal activity against phytopathogenic fungi. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azrad, M.; Tkhawkho, L.; Isakovich, N.; Nitzan, O.; Peretz, A. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli: Comparison between E-test and a broth dilution method. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2018, 17, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahima, I.R.; Abo-Elyousr, K.A.M. Using of endophytic Saccharomycopsis fibuligera and thyme oil for management of gray mold rot of guava fruits. Biol. Control 2017, 110, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, N.M.; Abd El-Ghany, M.N.; Rodríguez-Couto, S. Antifungal and anti-mycotoxin efficacy of biogenic silver nanoparticles produced by Fusarium chlamydosporum and Penicillium chrysogenum at non-cytotoxic doses. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mioc, M.; Pavel, I.Z.; Ghiulai, R.; Coricovac, D.E.; Farcaş, C.; Mihali, C.V.; Oprean, C.; Serafim, V.; Popovici, R.A.; Dehelean, C.A.; et al. The Cytotoxic Effects of Betulin-Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles as Stable Formulations in Normal and Melanoma Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán, N.; Seabra, A.B. Biogenic synthesized Ag/Au nanoparticles: Production, characterization, and applications. Curr. Nanosci. 2018, 14, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saada, N.S.; Abdel-Maksoud, G.; Abd El-Aziz, M.S.; Youssef, A.M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles, characterization, and use for sustainable preservation of historical parchment against microbial biodegradation. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 32, 101948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-González, M.; Talavera-Rojas, M.; Soriano-Vargas, E.; Rodríguez-González, V. Practical mediated-assembly synthesis of silver nanowires using commercial Camellia sinensis extracts and their antibacterial properties. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 2133–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, S.; Poulose, E.K. Silver nanoparticles: Mechanism of antimicrobial action, synthesis, medical applications, and toxicity effects. Int. Nano Lett. 2012, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabra, A.B.; Manosalva, N.; Lima, B.A.; Pelegrino, M.T.; Brocchi, M.O.; Rubilar, O.; Durán, N. Antibacterial activity of nitric oxide releasing silver nanoparticles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 838, 012031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, P.; Vaseeharan, B.; Das, J.; Pandian, K.; Pachaiappan, R. Greener approach for synthesis of antibacterial silver nanoparticles using aqueous solution of neem gum (Azadirachta indica L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 66, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankura, K.P.; Maity, D.; Mollick, M.M.R.; Mondal, D.; Bhowmick, B.; Bain, M.K.; Chakraborty, A.; Sarkar, J.; Acharya, K.; Chattopadhya, D. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of dextran stabilized silver nano-particles in aqueous medium. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.L.; El-sayed, M.A. Gold and silver nanoparticles in sensing and imaging: Sensitivity of plasmon response to size, shape, and metal composition. J. Phy. Chem. B 2006, 110, 19220–19225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajitha, B.; Reddy, Y.A.K.; Reddy, P.S. Biogenic nano-scale silver particles by Tephrosia purpurea leaf extract and their inborn antimicrobial activity. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2014, 121, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendra, C.; Murali, M.; Manasa, G.; Ponnamma, P.; Abhilash, M.R.; Lakshmeesha, T.R.; Satish, A.; Amruthesh, K.N.; Sudarshana, M.S. Antibacterial and antimitotic potential of bio-fabricated zinc oxide nanoparticles of Cochlospermum religiosum (L.). Microb. Pathog. 2017, 110, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, S.S.; de Araujo-Nobre, A.R.; Mafud, A.C.; Guimarães, M.A.; Alves, M.M.M.; Plácido, A.; Carvalho, F.A.A.; Arcanjo, D.D.R.; Mascarenhas, Y.; Costa, F.G.; et al. Silver nanoparticle stabilized by hydrolyzed collagen and natural polymers: Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial-antifungal evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Vidyasagar, G.M. Green synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles by using Sterculia foetida L. young leaves aqueous extract. Int. J. Green Chem. Bioprocess 2014, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rubina, M.S.; Vasil’kov, A.Y.; Naumkin, A.V.; Shtykova, E.V.; Abramchuk, S.S.; Alghuthaymi, M.A.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan–copper nanocomposites and their fungicidal activity against two sclerotia-forming plant pathogenic fungi. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2017, 7, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocate, K.P.; Reisa, G.F.; de Souza, P.C.; Juniora, A.G.O.; Duránb, N.; Nakazatoa, G.; Furlaneto, M.C.; Almeidaa, R.S.; Panagio, L.A. Antifungal activity of silver nanoparticles and simvastatin against toxigenic species of Aspergillus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 291, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Lin, L.; Wei, A.; Sepulveda, M.S. Protein Corona Analysis of Silver Nanoparticles Exposed to Fish Plasma. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoimenov, P.K.; Klinger, R.L.; Marchin, G.L.; Klabunde, K. Metal oxide nanoparticles as bactericidal agents. Langmuir 2004, 18, 6679–6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudadhe, J.A.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A.; Marcato, P.D.; Durán, N.; Rai1, M. Preparation of an agar-silver nanoparticles (A-AgNP) film for increasing the shelf-life of fruits. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2014, 8, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, F.; Jia, W.; Hou, X. Silver nanoparticles biologically synthesized using tea leaf extracts and their use for extension of fruit shelf life. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordenave, N.; Grelier, S.; Coma, V. Hydrophobization and antimicrobial activity of chitosan and paper-based packaging material. Biomacromolecules 2011, 11, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Media | Percentage (%) Reduction of Radial Growth of M. fructigena | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg AgNPs/L | 50 mg AgNPs/L | 100 mg AgNPs/L | 200 mg AgNPs/L | Nystatin 100 mg/L | Control | |||||||||||||
| 0 h | 1 d | 2 d | 4 d | 0 h | 1 d | 2 d | 4 d | 0 h | 1 d | 2 d | 4 d | 0 h | 1 d | 2 d | 4 d | |||
| PDA | 17.9 d ± 0.45 | 22.2 c ± 0.52 | 25.5 b ± 0.48 | 33.1 a ± 1 | 32.5 c ± 0.6 | 42.9 b ± 1.3 | 46.1 b ± 0.59 | 64.6 a ± 0.39 | 47.2 d ± 0.72 | 59.2 c ± 0.49 | 64.6 b ± 0.47 | 76.6 a ± 1.5 | 67.9 c ± 0.47 | 82 b ± 0.61 | 91.8 a ± 1.4 | 96.1 a ± 0.7 | 98.3 a ± 1 | 0 |
| CMA | 17.8 c ± 0.73 | 21.2 b ± 0.53 | 22.3 b ± 1.2 | 28 a ± 0.8 | 23.5 c ± 1.5 | 26.8 b ± 0.65 | 29.1 b ± 0.71 | 33.6 a ± 1.4 | 34.7 c ± 0.89 | 40.3 ab ± 0.79 | 51.6 b ± 1.6 | 62.8 a ± 0.58 | 62.8 d ± 1.6 | 74 c ± 0.79 | 84.1 b ± 0.89 | 92 a ± 0.76 | 97.6 a ± 1.2 | 0 |
| MEA | 17.8 c ± 0.8 | 24.6 b ± 1.6 | 28 b ± 0.41 | 31.3 a ± 0.76 | 22.3 c ± 0.7 | 24.6 c ± 0.97 | 29.1 b ± 1.4 | 34.7 a ± 0.91 | 31.3 d ± 1.7 | 34.7 c ± 0.92 | 41.4 b ± 0.79 | 48.2 a ± 1.3 | 63.9 d ± 0.93 | 70.7 c ± 1.4 | 77.4 b ± 0.98 | 88.6 a ± 1.4 | 97.6 a ± 1.6 | 0 |
| % Increase in Diameter of Inhibition Zone | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg AgNPs/L | 50 mg AgNPs/L | 100 mg AgNPs/L | 200 mg AgNPs/L | Nystatin (100 mg/L) |
| 13.6 a (±0.8) | 23.4 b (±1.2) | 46.2 c (±0.5) | 59.1 d (±1.1) | 61.4 d (±0.7) |
| Human Cell Lines | Percentage (%) of Cell Viability | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | Fungicide (50 mg/L) | Control (0.5% DMSO) | |||||||
| 15 mg/L | 25 mg/L | 50 mg/L | 15 mg/L | 25 mg/L | 50 mg/L | 15 mg/L | 25 mg/L | 50 mg/L | |||
| HaCaT | 110 a | 112 ab | 115 b | 120 a | 110 b | 105 c | 100 a | 102 a | 105 b | 26 a | 100 a |
| 1BR3 | 98 a | 96 b | 95 b | 98 a | 95 b | 80 c | 100 a | 85 b | 70 c | 21 a | 100 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madbouly, A.K. The Efficacy of Green Synthesized Nanosilver in Reducing the Incidence of Post-Harvest Apple Fruit Brown Rot. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7060473
Madbouly AK. The Efficacy of Green Synthesized Nanosilver in Reducing the Incidence of Post-Harvest Apple Fruit Brown Rot. Journal of Fungi. 2021; 7(6):473. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7060473
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadbouly, Adel Kamel. 2021. "The Efficacy of Green Synthesized Nanosilver in Reducing the Incidence of Post-Harvest Apple Fruit Brown Rot" Journal of Fungi 7, no. 6: 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7060473
APA StyleMadbouly, A. K. (2021). The Efficacy of Green Synthesized Nanosilver in Reducing the Incidence of Post-Harvest Apple Fruit Brown Rot. Journal of Fungi, 7(6), 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7060473






