Emerging Risk Factors for Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathogenesis of Invasive Aspergillosis
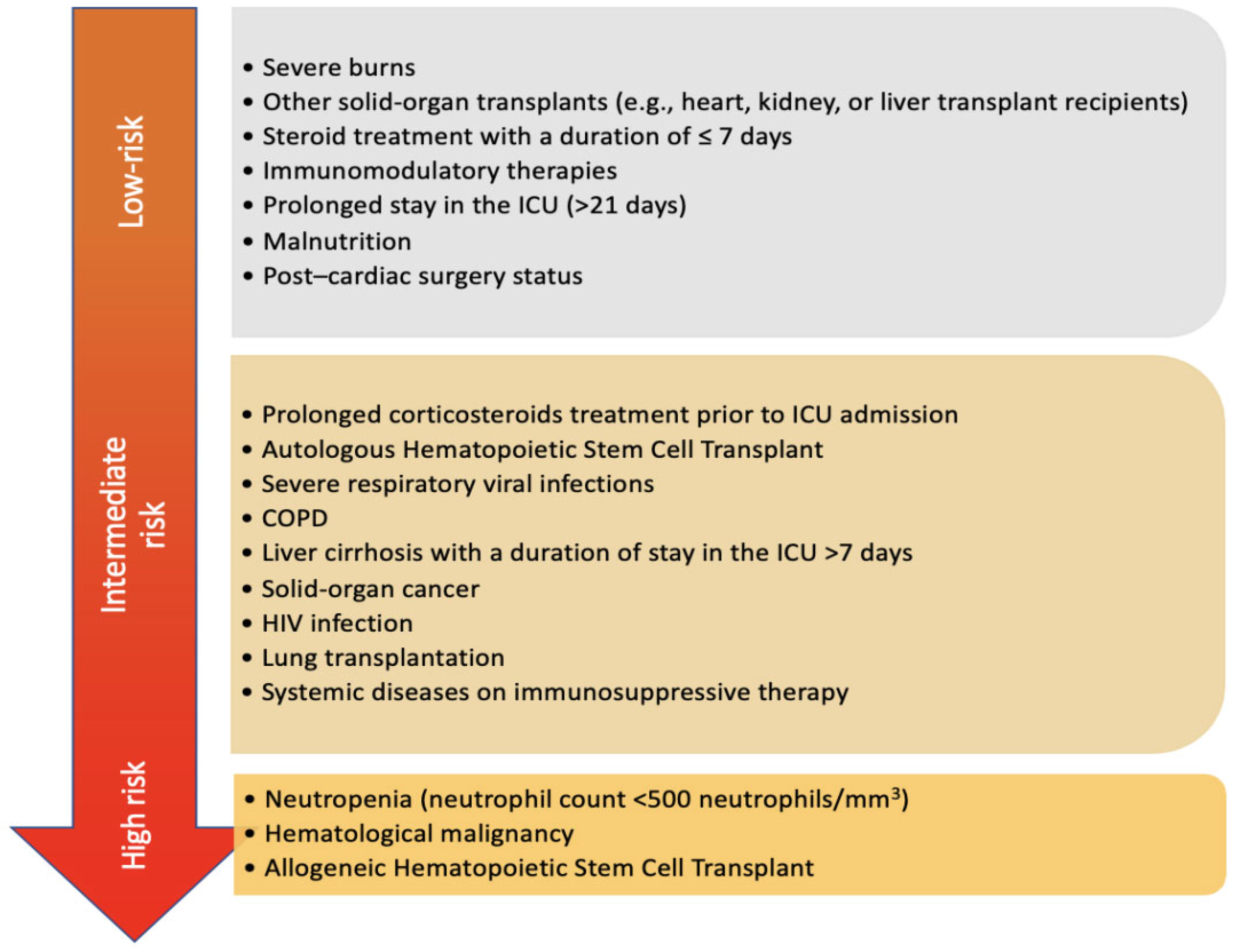
3. Classic Risk Factors of IPA
4. Emerging Risk Factors
4.1. Viral-Associated Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis (VAPA)
4.2. Critical Illness
4.3. Liver Disease
4.4. COPD
4.5. Other Conditions
4.5.1. Solid Malignancies
4.5.2. Immunomodulatory Therapies
4.5.3. CART Cell Therapy
5. Clinical Features
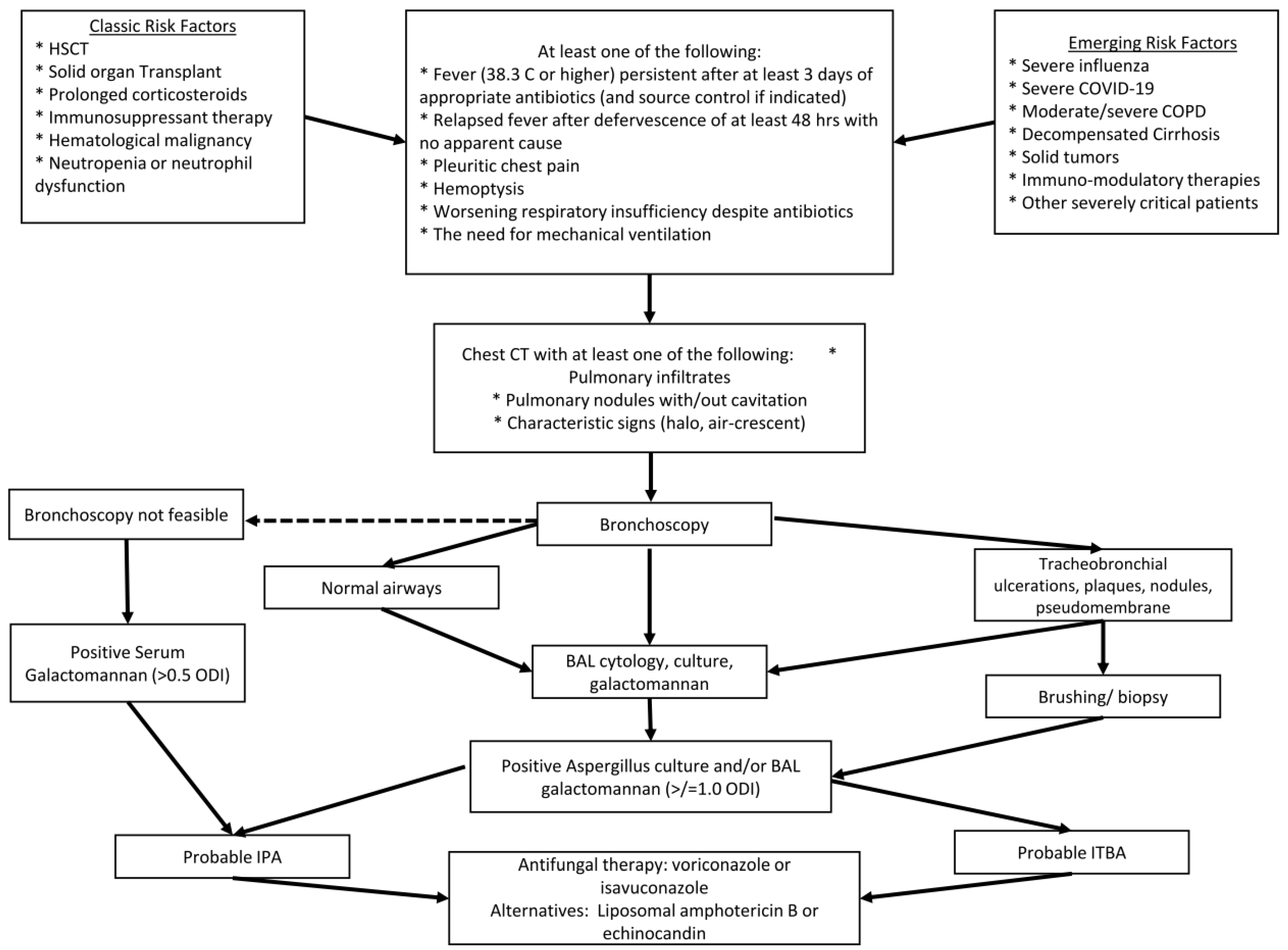
6. Diagnosis
6.1. Test Performance Considerations
6.2. Management Considerations for Emerging Risk Factors of IPA
6.3. Duration of Therapy
6.4. Limitations
6.5. Conclusion and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Latge, J.P.; Chamilos, G. Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillosis in 2019. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 33, e00140-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falvey, D.G.; Streifel, A.J. Ten-year air sample analysis of Aspergillus prevalence in a university hospital. J. Hosp. Infect. 2007, 67, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Kokki, M.H.; Anderson, K.; Richardson, M.D. Sampling of Aspergillus spores in air. J. Hosp. Infect. 2000, 44, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, N.E. Disseminated aspergillosis and moniliasis associated with agranulocytosis and antibiotic therapy. BMJ 1953, 1, 918–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Taplitz, R.A.; Kennedy, E.B.; Bow, E.J.; Crews, J.; Gleason, C.; Hawley, D.K.; Langston, A.A.; Nastoupil, L.J.; Rajotte, M.; Rolston, K.V.; et al. Antimicrobial Prophylaxis for Adult Patients with Cancer-Related Immunosuppression: ASCO and IDSA Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3043–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolle, M.C.; Benet, T.; Thiebaut, A.; Bienvenu, A.L.; Voirin, N.; Duclos, A.; Sobh, M.; Cannas, G.; Thomas, X.; Nicolini, F.E.; et al. Invasive aspergillosis in patients with hematologic malignancies: Incidence and description of 127 cases enrolled in a single institution prospective survey from 2004 to 2009. Haematologica 2011, 96, 1685–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, M.; Peghin, M.; Vena, A. Challenges and Solution of Invasive Aspergillosis in Non-neutropenic Patients: A Review. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2018, 7, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrucchio, G.; Lupia, T.; Lombardo, D.; Stroffolini, G.; Corcione, S.; De Rosa, F.G.; Brazzi, L. Risk factors for invasive aspergillosis in ICU patients with COVID-19: Current insights and new key elements. Ann. Intensive Care 2021, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feys, S.; Carvalho, A.; Clancy, C.J.; Gangneux, J.P.; Hoenigl, M.; Lagrou, K.; Rijnders, B.J.A.; Seldeslachts, L.; Vanderbeke, L.; van de Veerdonk, F.L.; et al. Influenza-associated and COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients. Lancet Respir. Med. 2024, 12, 728–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otu, A.; Kosmidis, C.; Mathioudakis, A.G.; Ibe, C.; Denning, D.W. The clinical spectrum of aspergillosis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Infection 2023, 51, 813–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.J.; Harbeck, R.; Smith, B.; Voelker, D.R.; Mason, R.J. Binding of rat and human surfactant proteins A and D to Aspergillus fumigatus conidia. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 4563–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.J.; Voelker, D.R.; Mason, R.J. Interactions of surfactant proteins A and D with Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 2037–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, T.; Eggleton, P.; Kishore, U.; Strong, P.; Aggrawal, S.S.; Sarma, P.U.; Reid, K.B. Binding of pulmonary surfactant proteins A and D to Aspergillus fumigatus conidia enhances phagocytosis and killing by human neutrophils and alveolar macrophages. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 3171–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Gupta, V.K.; Thiel, S.; Sarma, P.U.; Madan, T. Protective role of mannan-binding lectin in a murine model of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 148, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, T.; Reid, K.B.; Singh, M.; Sarma, P.U.; Kishore, U. Susceptibility of mice genetically deficient in the surfactant protein (SP)-A or SP-D gene to pulmonary hypersensitivity induced by antigens and allergens of Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 6943–6954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumestre-Perard, C.; Lamy, B.; Aldebert, D.; Lemaire-Vieille, C.; Grillot, R.; Brion, J.P.; Gagnon, J.; Cesbron, J.Y. Aspergillus conidia activate the complement by the mannan-binding lectin C2 bypass mechanism. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 7100–7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlanda, C.; Hirsch, E.; Bozza, S.; Salustri, A.; De Acetis, M.; Nota, R.; Maccagno, A.; Riva, F.; Bottazzi, B.; Peri, G.; et al. Non-redundant role of the long pentraxin PTX3 in anti-fungal innate immune response. Nature 2002, 420, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, S.; Boisvieux-Ulrich, E.; Crestani, B.; Houcine, O.; Taramelli, D.; Lombardi, L.; Latge, J.P. Internalization of Aspergillus fumigatus conidia by epithelial and endothelial cells. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 1510–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasylnka, J.A.; Moore, M.M. Uptake of Aspergillus fumigatus Conidia by phagocytic and nonphagocytic cells in vitro: Quantitation using strains expressing green fluorescent protein. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 3156–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balloy, V.; Sallenave, J.M.; Wu, Y.; Touqui, L.; Latge, J.P.; Si-Tahar, M.; Chignard, M. Aspergillus fumigatus-induced interleukin-8 synthesis by respiratory epithelial cells is controlled by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, p38 MAPK, and ERK1/2 pathways and not by the toll-like receptor-MyD88 pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 30513–30521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitz, S.M.; Farrell, T.P. Human neutrophil degranulation stimulated by Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1990, 47, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionakis, M.S.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Glucocorticoids and invasive fungal infections. Lancet 2003, 362, 1828–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annaix, V.; Bouchara, J.P.; Larcher, G.; Chabasse, D.; Tronchin, G. Specific binding of human fibrinogen fragment D to Aspergillus fumigatus conidia. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronchin, G.; Esnault, K.; Renier, G.; Filmon, R.; Chabasse, D.; Bouchara, J.P. Expression and identification of a laminin-binding protein in Aspergillus fumigatus conidia. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadke, A.P.; Mehrad, B. Cytokines in host defense against Aspergillus: Recent advances. Med. Mycol. 2005, 43 (Suppl. 1), S173–S176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrad, B.; Strieter, R.M.; Standiford, T.J. Role of TNF-alpha in pulmonary host defense in murine invasive Aspergillosis. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, B.E.; Park, S.J.; Mooney, J.M.; Mehrad, B. Chemokine-mediated recruitment of NK cells is a critical host defense mechanism in invasive Aspergillosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1862–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochud, P.Y.; Chien, J.W.; Marr, K.A.; Leisenring, W.M.; Upton, A.; Janer, M.; Rodrigues, S.D.; Li, S.; Hansen, J.A.; Zhao, L.P.; et al. Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms and aspergillosis in stem-cell transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1766–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, B.; Ibrahim-Granet, O.; Prevost, M.C.; Gougerot-Pocidalo, M.A.; Sanchez Perez, M.; Van der Meeren, A.; Latge, J.P. Killing of Aspergillus fumigatus by alveolar macrophages is mediated by reactive oxidant intermediates. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 3034–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim-Granet, O.; Philippe, B.; Boleti, H.; Boisvieux-Ulrich, E.; Grenet, D.; Stern, M.; Latge, J.P. Phagocytosis and intracellular fate of Aspergillus fumigatus conidia in alveolar macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagenais, T.R.; Keller, N.P. Pathogenesis of Aspergillus fumigatus in Invasive Aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarember, K.A.; Sugui, J.A.; Chang, Y.C.; Kwon-Chung, K.J.; Gallin, J.I. Human polymorphonuclear leukocytes inhibit Aspergillus fumigatus conidial growth by lactoferrin-mediated iron depletion. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 6367–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamai, Y.; Chiang, L.Y.; Lopes Bezerra, L.M.; Doedt, T.; Lossinsky, A.S.; Sheppard, D.C.; Filler, S.G. Interactions of Aspergillus fumigatus with vascular endothelial cells. Med. Mycol. 2006, 44 (Suppl. 1), S115–S117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergiopoulou, T.; Meletiadis, J.; Roilides, E.; Kleiner, D.E.; Schaufele, R.; Roden, M.; Harrington, S.; Dad, L.; Segal, B.; Walsh, T.J. Host-dependent patterns of tissue injury in invasive pulmonary Aspergillosis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2007, 127, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balloy, V.; Huerre, M.; Latge, J.P.; Chignard, M. Differences in patterns of infection and inflammation for corticosteroid treatment and chemotherapy in experimental invasive pulmonary Aspergillosis. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenguer, J.; Allende, M.C.; Lee, J.W.; Garrett, K.; Lyman, C.; Ali, N.M.; Bacher, J.; Pizzo, P.A.; Walsh, T.J. Pathogenesis of pulmonary Aspergillosis. Granulocytopenia versus cyclosporine and methylprednisolone-induced immunosuppression. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 152, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousha, M.; Tadi, R.; Soubani, A.O. Pulmonary Aspergillosis: A clinical review. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2011, 20, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.E.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Invasive Aspergillosis in glucocorticoid-treated patients. Med. Mycol. 2009, 47 (Suppl. 1), S271–S281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederhold, N.P.; Lewis, R.E.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Invasive Aspergillosis in patients with hematologic malignancies. Pharmacotherapy 2003, 23, 1592–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, K.A.; Carter, R.A.; Boeckh, M.; Martin, P.; Corey, L. Invasive Aspergillosis in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients: Changes in epidemiology and risk factors. Blood 2002, 100, 4358–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Preliminary Estimated Flu Disease Burden 2024–2025 Flu Season. May 2025. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/flu-burden/php/data-vis/2024-2025.html (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID Data Tracker; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2025. Available online: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Vanderbeke, L.; Janssen, N.A.F.; Bergmans, D.; Bourgeois, M.; Buil, J.B.; Debaveye, Y.; Depuydt, P.; Feys, S.; Hermans, G.; Hoiting, O.; et al. Posaconazole for prevention of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill influenza patients (POSA-FLU): A randomised, open-label, proof-of-concept trial. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, F.; Walti, L.N.; Orchanian-Cheff, A.; Husain, S. Risk factors for COVID-19-associated pulmonary Aspergillosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2024, 12, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangneux, J.P.; Dannaoui, E.; Fekkar, A.; Luyt, C.E.; Botterel, F.; De Prost, N.; Tadie, J.M.; Reizine, F.; Houze, S.; Timsit, J.F.; et al. Fungal infections in mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 during the first wave: The French multicentre MYCOVID study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, N.A.F.; Nyga, R.; Vanderbeke, L.; Jacobs, C.; Ergun, M.; Buil, J.B.; van Dijk, K.; Altenburg, J.; Bouman, C.S.C.; van der Spoel, H.I.; et al. Multinational Observational Cohort Study of COVID-19-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis(1). Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2892–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feys, S.; Hoenigl, M.; Gangneux, J.P.; Verweij, P.E.; Wauters, J. Fungal Fog in Viral Storms: Necessity for Rigor in Aspergillosis Diagnosis and Research. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 209, 631–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoletti, M.; Pascale, R.; Cricca, M.; Rinaldi, M.; Maccaro, A.; Bussini, L.; Fornaro, G.; Tonetti, T.; Pizzilli, G.; Francalanci, E.; et al. Epidemiology of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Among Intubated Patients with COVID-19: A Prospective Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e3606–e3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feys, S.; Almyroudi, M.P.; Braspenning, R.; Lagrou, K.; Spriet, I.; Dimopoulos, G.; Wauters, J. A Visual and Comprehensive Review on COVID-19-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CAPA). J. Fungi 2021, 7, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feys, S.; Goncalves, S.M.; Khan, M.; Choi, S.; Boeckx, B.; Chatelain, D.; Cunha, C.; Debaveye, Y.; Hermans, G.; Hertoghs, M.; et al. Lung epithelial and myeloid innate immunity in influenza-associated or COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis: An observational study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 1147–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarden, N.; Sinha, S.; Potts, K.G.; Pernet, E.; Hiroki, C.H.; Hassanabad, M.F.; Nguyen, A.P.; Lou, Y.; Farias, R.; Winston, B.W.; et al. A B1a-natural IgG-neutrophil axis is impaired in viral- and steroid-associated aspergillosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabq6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konig, S.; Schroeder, J.; Nietzsche, S.; Heinekamp, T.; Brakhage, A.A.; Zell, R.; Loffler, B.; Ehrhardt, C. The influenza A virus promotes fungal growth of Aspergillus fumigatus via direct interaction in vitro. Microbes Infect. 2024, 26, 105264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.Y.; Lee, H.M.; Burke, A.; Li Bassi, G.; Torres, A.; Fraser, J.F.; Fanning, J.P. Prevalence, Risk Factors, Clinical Features, and Outcome of Influenza-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Critically Ill Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Chest 2024, 165, 540–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group, R.C.; Horby, P.; Lim, W.S.; Emberson, J.R.; Mafham, M.; Bell, J.L.; Linsell, L.; Staplin, N.; Brightling, C.; Ustianowski, A.; et al. Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, C.; Han, J.; Yau, L.; Reiss, W.G.; Kramer, B.; Neidhart, J.D.; Criner, G.J.; Kaplan-Lewis, E.; Baden, R.; Pandit, L.; et al. Tocilizumab in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 Pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergun, M.; Bruggemann, R.J.M.; Alanio, A.; Delliere, S.; van Arkel, A.; Bentvelsen, R.G.; Rijpstra, T.; van der Sar-van der Brugge, S.; Lagrou, K.; Janssen, N.A.F.; et al. Aspergillus Test Profiles and Mortality in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0122921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meersseman, W.; Vandecasteele, S.J.; Wilmer, A.; Verbeken, E.; Peetermans, W.E.; Van Wijngaerden, E. Invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients without malignancy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, B.D.; Lamoth, F.; Heussel, C.P.; Prokop, C.S.; Desai, S.R.; Morrissey, C.O.; Baddley, J.W. Guidance on Imaging for Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis and Mucormycosis: From the Imaging Working Group for the Revision and Update of the Consensus Definitions of Fungal Disease from the EORTC/MSGERC. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, S79–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnacho-Montero, J.; Amaya-Villar, R.; Ortiz-Leyba, C.; Leon, C.; Alvarez-Lerma, F.; Nolla-Salas, J.; Iruretagoyena, J.R.; Barcenilla, F. Isolation of Aspergillus spp. from the respiratory tract in critically ill patients: Risk factors, clinical presentation and outcome. Crit. Care 2005, 9, R191–R199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taccone, F.S.; Van den Abeele, A.M.; Bulpa, P.; Misset, B.; Meersseman, W.; Cardoso, T.; Paiva, J.A.; Blasco-Navalpotro, M.; De Laere, E.; Dimopoulos, G.; et al. Epidemiology of invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients: Clinical presentation, underlying conditions, and outcomes. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortorano, A.M.; Dho, G.; Prigitano, A.; Breda, G.; Grancini, A.; Emmi, V.; Cavanna, C.; Marino, G.; Morero, S.; Ossi, C.; et al. Invasive fungal infections in the intensive care unit: A multicentre, prospective, observational study in Italy (2006–2008). Mycoses 2012, 55, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Lin, T.; Zhang, R.; Li, M.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, X. Invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddley, J.W.; Stephens, J.M.; Ji, X.; Gao, X.; Schlamm, H.T.; Tarallo, M. Aspergillosis in Intensive Care Unit (ICU) patients: Epidemiology and economic outcomes. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGettigan, B.; Hernandez-Tejero, M.; Malhi, H.; Shah, V. Immune Dysfunction and Infection Risk in Advanced Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2025, 168, 1085–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, E. The impact of bacterial infections on survival of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. Ann. Hepatol. 2013, 13, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albillos, A.; Lario, M.; Alvarez-Mon, M. Cirrhosis-associated immune dysfunction: Distinctive features and clinical relevance. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1385–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniades, C.G.; Wendon, J.; Vergani, D. Paralysed monocytes in acute on chronic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tritto, G.; Bechlis, Z.; Stadlbauer, V.; Davies, N.; Frances, R.; Shah, N.; Mookerjee, R.P.; Such, J.; Jalan, R. Evidence of neutrophil functional defect despite inflammation in stable cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkovic, I.A.; Williams, R. Abnormalities of neutrophil phagocytosis, intracellular killing and metabolic activity in alcoholic cirrhosis and hepatitis. Hepatology 1986, 6, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmer, T.; Brandl, A.; Rasch, S.; Baires, G.B.; Schmid, R.M.; Huber, W.; Mayr, U. Prevalence and outcome of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients with liver cirrhosis: An observational study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levesque, E.; Ait-Ammar, N.; Dudau, D.; Clavieras, N.; Feray, C.; Foulet, F.; Botterel, F. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in cirrhotic patients: Analysis of a 10-year clinical experience. Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prattes, J.; Hoenigl, M.; Krause, R.; Buzina, W.; Valentin, T.; Reischies, F.; Koidl, C.; Zollner-Schwetz, I. Invasive aspergillosis in patients with underlying liver cirrhosis: A prospective cohort study. Med. Mycol. 2017, 55, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeurissen, S.; Vogelaers, D.; Sermijn, E.; Van Dycke, K.; Geerts, A.; Van Vlierberghe, H.; Colle, I. Invasive aspergillosis in patients with cirrhosis, a case report and review of the last 10 years. Acta Clin. Belg. 2013, 68, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, M.; Massetti, A.P.; Russo, A.; Vullo, V.; Venditti, M. Invasive aspergillosis in patients with liver disease. Med. Mycol. 2011, 49, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.; Singh, S.; Syal, A.; Pradhan, P.; Singh, M.; Singh, M. Invasive aspergillosis is a critical determinant of mortality in cirrhosis: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Med. Mycol. 2021, 59, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Mohamad, B.; Soubani, A.O. Epidemiology and Inpatient Outcomes of Invasive Aspergillosis in Patients with Liver Failure and Cirrhosis. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, E.E.; McDonald, C.S.; Vestbo, J.; Denning, D.W. The global impact of Aspergillus infection on COPD. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinea, J.; Torres-Narbona, M.; Gijon, P.; Munoz, P.; Pozo, F.; Pelaez, T.; de Miguel, J.; Bouza, E. Pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Incidence, risk factors, and outcome. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, L.; Huang, W.J.; Wang, L.X.; Li, W.F.; Yuan, W.F. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A case control study from China. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Chen, L.; Hu, G.; Mei, H. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and the diagnostic value of combined serological tests. Ann. Saudi Med. 2010, 30, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulpa, P.; Dive, A.; Sibille, Y. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 30, 782–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.J.; Schranz, J.; Teutsch, S.M. Aspergillosis case-fatality rate: Systematic review of the literature. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.; Niederman, M.S.; Fein, A.M.; Pai, P.B. Nonresolving pneumonia in steroid-treated patients with obstructive lung disease. Am. J. Med. 1992, 93, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, T.; Uddin, M.; Khalil, A.; Lohia, P.; Porter, L.; Regmi, N.; Weinberger, J.; Koul, P.A.; Soubani, A.O. Mortality outcomes associated with invasive aspergillosis among acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patient population. Respir. Med. 2022, 191, 106720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Ye, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, K.; Zhong, J.; Chen, B.; Su, X. A risk-predictive model for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarakoon, P.; Soubani, A. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with COPD: A report of five cases and systematic review of the literature. Chron. Respir. Dis. 2008, 5, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leav, B.A.; Fanburg, B.; Hadley, S. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis associated with high-dose inhaled fluticasone. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barouky, R.; Badet, M.; Denis, M.S.; Soubirou, J.L.; Philit, F.; Guerin, C. Inhaled corticosteroids in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and disseminated aspergillosis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2003, 14, 380–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandachi, D.; Wilson Dib, R.; Fernandez-Cruz, A.; Jiang, Y.; Chaftari, A.M.; Hachem, R.; Raad, I. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with solid tumours: Risk factors and predictors of clinical outcomes. Ann. Med. 2018, 50, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Li, M.; Jiang, M.; Zou, L.Q.; Luo, F.; Jiang, Y. Clinical characteristics of 45 patients with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: Retrospective analysis of 1711 lung cancer cases. Cancer 2009, 115, 5018–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltolini, C.; Ripa, M.; Andolina, A.; Brioschi, E.; Cilla, M.; Petrella, G.; Gregorc, V.; Castiglioni, B.; Tassan Din, C.; Scarpellini, P. Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Complicated by Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection During Pembrolizumab Immunotherapy for Metastatic Lung Adenocarcinoma: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Mycopathologia 2019, 184, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyi, C.; Hellmann, M.D.; Wolchok, J.D.; Chapman, P.B.; Postow, M.A. Opportunistic infections in patients treated with immunotherapy for cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2014, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, N.; Fujita, K.; Nakatani, K.; Mio, T. Acute progression of aspergillosis in a patient with lung cancer receiving nivolumab. Respirol. Case Rep. 2018, 6, e00289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Castillo, M.; Romero, F.A.; Arguello, E.; Kyi, C.; Postow, M.A.; Redelman-Sidi, G. The Spectrum of Serious Infections Among Patients Receiving Immune Checkpoint Blockade for the Treatment of Melanoma. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 1490–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiodras, S.; Samonis, G.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Fungal infections complicating tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade therapy. Mayo. Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salliot, C.; Dougados, M.; Gossec, L. Risk of serious infections during rituximab, abatacept and anakinra treatments for rheumatoid arthritis: Meta-analyses of randomised placebo-controlled trials. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.C.; Sterner, R.M. CAR-T cell therapy: Current limitations and potential strategies. Blood. Cancer J. 2021, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, W.; Samanta, P.; Haidar, G. Invasive Fungal Infections after Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T-Cell Therapy: State of the Evidence and Future Directions. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Romero, F.A.; Taur, Y.; Sadelain, M.; Brentjens, R.J.; Hohl, T.M.; Seo, S.K. Cytokine Release Syndrome Grade as a Predictive Marker for Infections in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated with Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.A.; Li, D.; Hay, K.A.; Green, M.L.; Cherian, S.; Chen, X.; Riddell, S.R.; Maloney, D.G.; Boeckh, M.; Turtle, C.J. Infectious complications of CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor-modified T-cell immunotherapy. Blood 2018, 131, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, J.S.; Aleissa, M.M.; Beluch, K.; Gonzalez-Bocco, I.H.; Marty, F.M.; Manne-Goehler, J.; Koo, S.; Hammond, S.P.; Jacobson, C.A. Low incidence of invasive fungal disease following CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 4821–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, J.S.; Kampouri, E.; Friedman, D.Z.; McCarty, T.; Thompson, G.R., 3rd; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Vazquez, J.; Baddley, J.W.; Hammond, S.P. The Burden of Invasive Fungal Disease Following Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy and Strategies for Prevention. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2024, 11, ofae133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estella, A.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Nunez, M.R.; Garcia, C.G.; Pesaresi, L.M.; Escors, A.A.; Prieto, M.D.L.; Calvo, J.M.S. Microbiological diagnosis of pulmonary invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia: A bronchoalveolar study. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2023, 22, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, R.E.; Schlamm, H.T.; Oestmann, J.W.; Stark, P.; Durand, C.; Lortholary, O.; Wingard, J.R.; Herbrecht, R.; Ribaud, P.; Patterson, T.F.; et al. Imaging findings in acute invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: Clinical significance of the halo sign. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; White, P.L.; Backx, M.; Gangneux, J.P.; Reizine, F.; Koehler, P.; Bentvelsen, R.G.; Cuestas, M.L.; Fakhim, H.; Jung, J.I.; et al. CT findings of COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis: A systematic review and individual patient data analysis. Clin. Imaging 2022, 90, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, J.D.; Nam, H.H.; Hoenigl, M. Invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients: Review of definitions and diagnostic approaches. Mycoses 2021, 64, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, J.P.; Chen, S.C.; Kauffman, C.A.; Steinbach, W.J.; Baddley, J.W.; Verweij, P.E.; Clancy, C.J.; Wingard, J.R.; Lockhart, S.R.; Groll, A.H.; et al. Revision and Update of the Consensus Definitions of Invasive Fungal Disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer and the Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaggi, T.K.; Agarwal, R.; Tiew, P.Y.; Shah, A.; Lydon, E.C.; Hage, C.A.; Waterer, G.W.; Langelier, C.R.; Delhaes, L.; Chotirmall, S.H. Fungal lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 64, 2400803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoth, F.; Lewis, R.E.; Walsh, T.J.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Navigating the Uncertainties of COVID-19-Associated Aspergillosis: A Comparison with Influenza-Associated Aspergillosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderbeke, L.; Jacobs, C.; Feys, S.; Resendiz-Sharpe, A.; Debaveye, Y.; Hermans, G.; Humblet-Baron, S.; Lagrou, K.; Meersseman, P.; Peetermans, M.; et al. A Pathology-based Case Series of Influenza- and COVID-19-associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis: The Proof Is in the Tissue. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 208, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrich, W.C.; Lamoth, F. Viral-associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis: Have We Finally Overcome the Debate of Colonization versus Infection? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 208, 230–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitis, M.; Ziakas, P.D.; Zacharioudakis, I.M.; Zervou, F.N.; Caliendo, A.M.; Mylonakis, E. PCR in diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis: A meta-analysis of diagnostic performance. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 3731–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, P.; Bassetti, M.; Chakrabarti, A.; Chen, S.C.A.; Colombo, A.L.; Hoenigl, M.; Klimko, N.; Lass-Florl, C.; Oladele, R.O.; Vinh, D.C.; et al. Defining and managing COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis: The 2020 ECMM/ISHAM consensus criteria for research and clinical guidance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, e149–e162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, P.E.; Rijnders, B.J.A.; Bruggemann, R.J.M.; Azoulay, E.; Bassetti, M.; Blot, S.; Calandra, T.; Clancy, C.J.; Cornely, O.A.; Chiller, T.; et al. Review of influenza-associated pulmonary aspergillosis in ICU patients and proposal for a case definition: An expert opinion. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1524–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blot, S.I.; Taccone, F.S.; Van den Abeele, A.M.; Bulpa, P.; Meersseman, W.; Brusselaers, N.; Dimopoulos, G.; Paiva, J.A.; Misset, B.; Rello, J.; et al. A clinical algorithm to diagnose invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.L.; Wingard, J.R.; Bretagne, S.; Loffler, J.; Patterson, T.F.; Slavin, M.A.; Barnes, R.A.; Pappas, P.G.; Donnelly, J.P. Aspergillus Polymerase Chain Reaction: Systematic Review of Evidence for Clinical Use in Comparison with Antigen Testing. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, M.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Agvald-Ohman, C.; Akova, M.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Arikan-Akdagli, S.; Azoulay, E.; Blot, S.; Cornely, O.A.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; et al. Invasive Fungal Diseases in Adult Patients in Intensive Care Unit (FUNDICU): 2024 consensus definitions from ESGCIP, EFISG, ESICM, ECMM, MSGERC, ISAC, and ISHAM. Intensive Care Med. 2024, 50, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeflang, M.M.; Debets-Ossenkopp, Y.J.; Wang, J.; Visser, C.E.; Scholten, R.J.; Hooft, L.; Bijlmer, H.A.; Reitsma, J.B.; Zhang, M.; Bossuyt, P.M.; et al. Galactomannan detection for invasive aspergillosis in immunocompromised patients. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD007394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, M.; He, Q.; Li, P.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.; Su, X. Diagnostic Value of Galactomannan Antigen Test in Serum and Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Samples from Patients with Nonneutropenic Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2153–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, A.; Porcher, R.; Sulahian, A.; de Bazelaire, C.; Chagnon, K.; Raffoux, E.; Vekhoff, A.; Cornet, M.; Isnard, F.; Brethon, B.; et al. The strategy for the diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis should depend on both the underlying condition and the leukocyte count of patients with hematologic malignancies. Blood 2012, 119, 1831–1837, quiz 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Tang, L.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, P.; Huang, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Fan, X. Systematic review and meta-analysis of detecting galactomannan in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for diagnosing invasive aspergillosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengoli, C.; Cruciani, M.; Barnes, R.A.; Loeffler, J.; Donnelly, J.P. Use of PCR for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbert, S.; Gauthier, L.; Joly, I.; Brossas, J.Y.; Uzunov, M.; Touafek, F.; Brun, S.; Mazier, D.; Datry, A.; Gay, F.; et al. Aspergillus PCR in serum for the diagnosis, follow-up and prognosis of invasive aspergillosis in neutropenic and nonneutropenic patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 562.e1–562.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Alexander, B.D.; Kett, D.H.; Vazquez, J.; Pappas, P.G.; Saeki, F.; Ketchum, P.A.; Wingard, J.; Schiff, R.; Tamura, H.; et al. Multicenter clinical evaluation of the (1-->3) beta-D-glucan assay as an aid to diagnosis of fungal infections in humans. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, F.M.; Koo, S. Role of (1-->3)-beta-D-glucan in the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis. Med. Mycol. 2009, 47 (Suppl. 1), S233–S240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachem, R.Y.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Chemaly, R.F.; Jiang, Y.; Reitzel, R.; Raad, I. Utility of galactomannan enzyme immunoassay and (1,3) beta-D-glucan in diagnosis of invasive fungal infections: Low sensitivity for Aspergillus fumigatus infection in hematologic malignancy patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, S.; Bryar, J.M.; Page, J.H.; Baden, L.R.; Marty, F.M. Diagnostic performance of the (1-->3)-beta-D-glucan assay for invasive fungal disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persat, F.; Ranque, S.; Derouin, F.; Michel-Nguyen, A.; Picot, S.; Sulahian, A. Contribution of the (1-->3)-beta-D-glucan assay for diagnosis of invasive fungal infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obayashi, T.; Negishi, K.; Suzuki, T.; Funata, N. Reappraisal of the serum (1-->3)-beta-D-glucan assay for the diagnosis of invasive fungal infections--a study based on autopsy cases from 6 years. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2008, 46, 1864–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vlieger, G.; Lagrou, K.; Maertens, J.; Verbeken, E.; Meersseman, W.; Van Wijngaerden, E. Beta-D-glucan detection as a diagnostic test for invasive aspergillosis in immunocompromised critically ill patients with symptoms of respiratory infection: An autopsy-based study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3783–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledoux, M.P.; Herbrecht, R. Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, T.F.; Thompson, G.R., 3rd; Denning, D.W.; Fishman, J.A.; Hadley, S.; Herbrecht, R.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Marr, K.A.; Morrison, V.A.; Nguyen, M.H.; et al. Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Aspergillosis: 2016 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, e1–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbrecht, R.; Denning, D.W.; Patterson, T.F.; Bennett, J.E.; Greene, R.E.; Oestmann, J.W.; Kern, W.V.; Marr, K.A.; Ribaud, P.; Lortholary, O.; et al. Voriconazole versus amphotericin B for primary therapy of invasive aspergillosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissot, F.; Agrawal, S.; Pagano, L.; Petrikkos, G.; Groll, A.H.; Skiada, A.; Lass-Florl, C.; Calandra, T.; Viscoli, C.; Herbrecht, R. ECIL-6 guidelines for the treatment of invasive candidiasis, aspergillosis and mucormycosis in leukemia and hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients. Haematologica 2017, 102, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, A.J.; Aguado, J.M.; Arikan-Akdagli, S.; Denning, D.W.; Groll, A.H.; Lagrou, K.; Lass-Florl, C.; Lewis, R.E.; Munoz, P.; Verweij, P.E.; et al. Diagnosis and management of Aspergillus diseases: Executive summary of the 2017 ESCMID-ECMM-ERS guideline. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24 (Suppl. 1), e1–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groll, A.H.; Townsend, R.; Desai, A.; Azie, N.; Jones, M.; Engelhardt, M.; Schmitt-Hoffman, A.H.; Bruggemann, R.J.M. Drug-drug interactions between triazole antifungal agents used to treat invasive aspergillosis and immunosuppressants metabolized by cytochrome P450 3A4. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2017, 19, e12751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutboul, F.; Alberti, C.; Leblanc, T.; Sulahian, A.; Gluckman, E.; Derouin, F.; Ribaud, P. Invasive aspergillosis in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients: Increasing antigenemia is associated with progressive disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elkhapery, A.; Fatima, M.; Soubani, A.O. Emerging Risk Factors for Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis: A Narrative Review. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11080555
Elkhapery A, Fatima M, Soubani AO. Emerging Risk Factors for Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis: A Narrative Review. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(8):555. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11080555
Chicago/Turabian StyleElkhapery, Ahmed, Mariam Fatima, and Ayman O. Soubani. 2025. "Emerging Risk Factors for Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis: A Narrative Review" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 8: 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11080555
APA StyleElkhapery, A., Fatima, M., & Soubani, A. O. (2025). Emerging Risk Factors for Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis: A Narrative Review. Journal of Fungi, 11(8), 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11080555






