The Discovery of Acremochlorins O-R from an Acremonium sp. through Integrated Genomic and Molecular Networking
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. General Experimental Procedures
2.2. Fungal Material
2.3. Incubation and Extraction
2.4. Isolation and Purification
2.5. Computation Section
2.6. Antimicrobial Activities
2.7. Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Activity
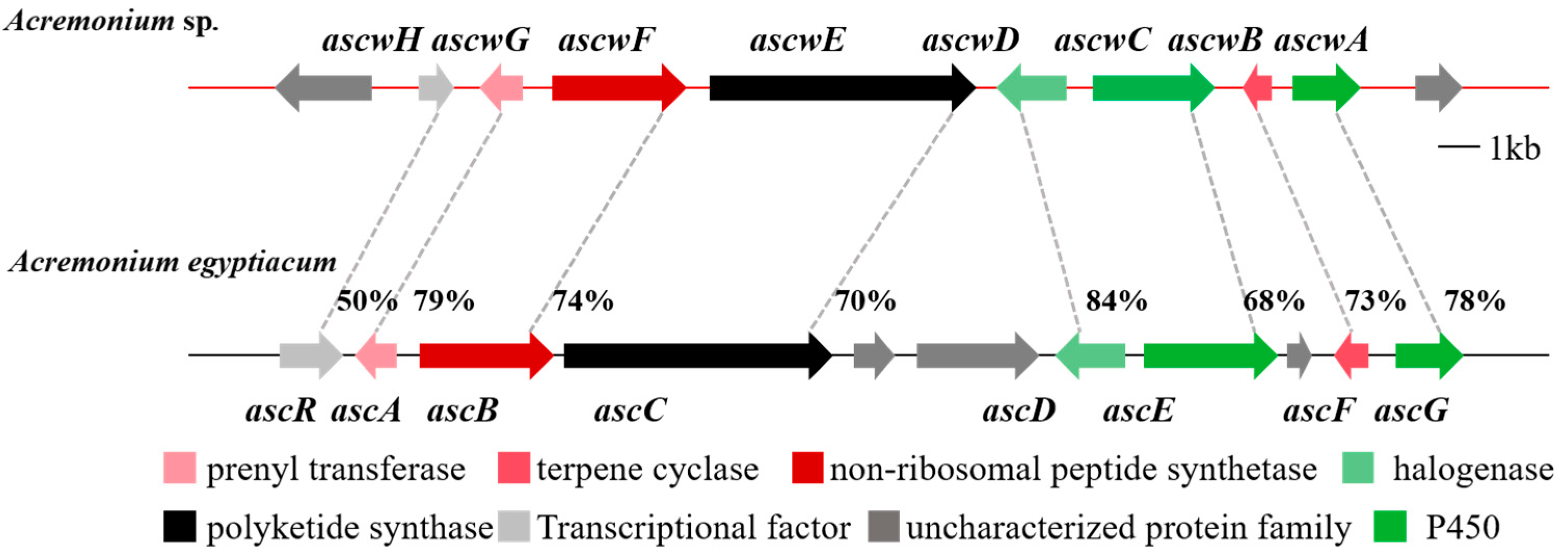
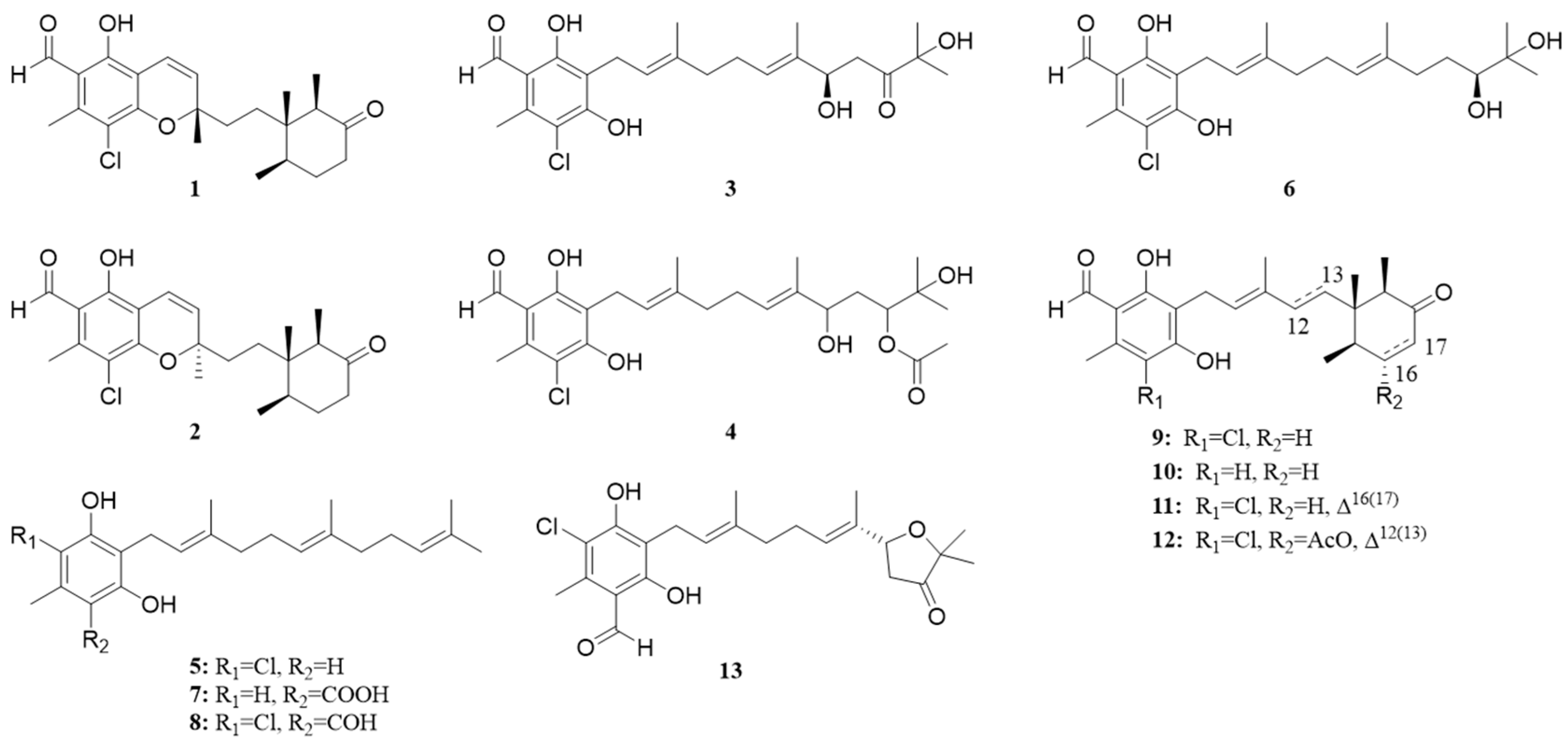
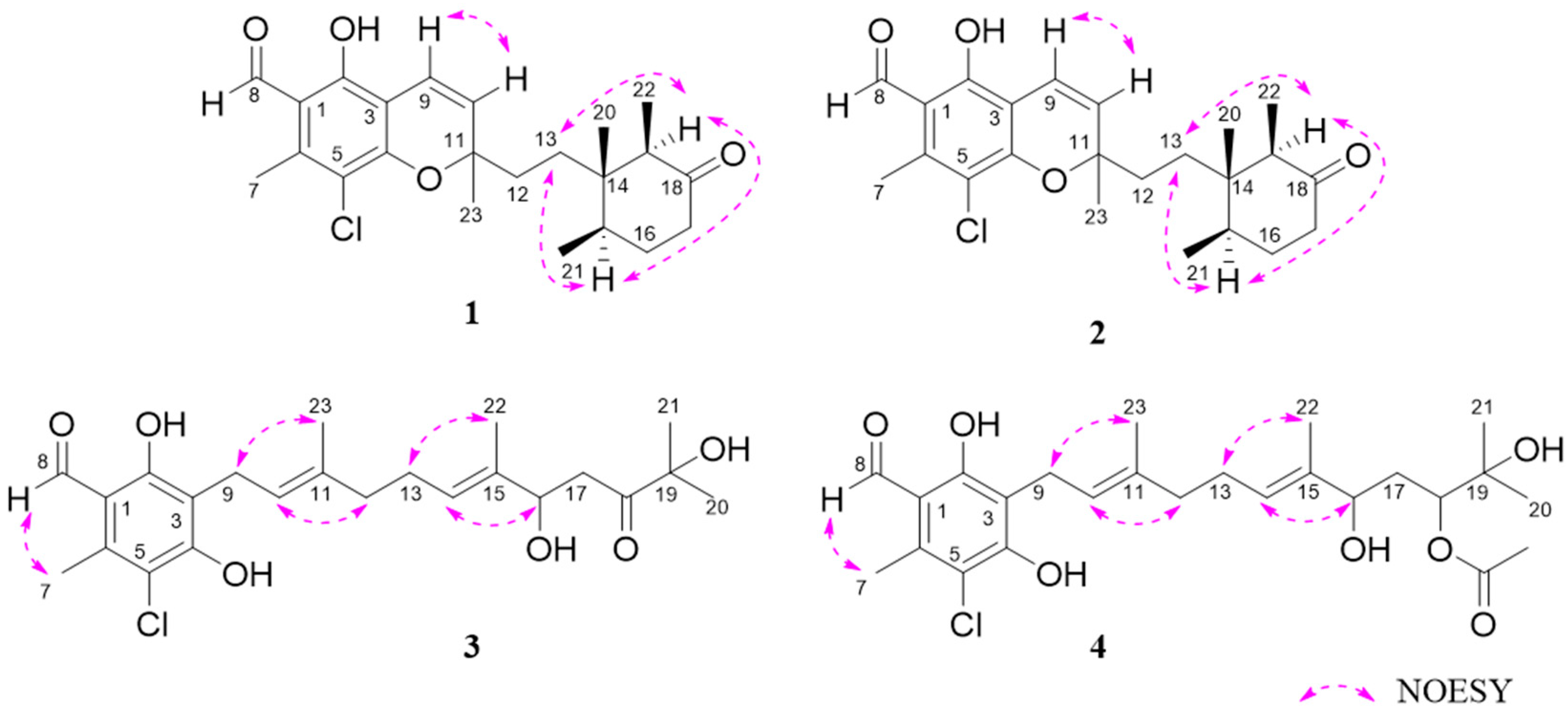
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Araki, Y.; Awakawa, T.; Matsuzaki, M.; Cho, R.; Matsuda, Y.; Hoshino, S.; Shinohara, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Kido, Y.; Inaoka, D.K.; et al. Complete biosynthetic pathways of ascofuranone and ascochlorin in Acremonium egyptiacum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8269–8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Cai, G.; Guo, Y.; Gao, C.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, H.; Liu, K.; Chen, J.; Xiong, X.; et al. Exploring Marine-Derived Ascochlorins as Novel Human Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase Inhibitors for Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 13918–13932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kwak, C.; Lee, S.; Ha, S.; Park, J.; Chung, T.; Ha, K.; Suh, S.; Chang, Y.; Chang, H.W.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Ascochlorin in LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells Is Accompanied with the Down-Regulation of iNOS, COX-2 and Proinflammatory Cytokines Through NF-κB, ERK1/2, and p38 Signaling Pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 117, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Oesker, V.; Wiese, J.; Malien, S.; Schmaljohann, R.; Imhoff, J.F. Spirocyclic drimanes from the marine fungus Stachybotrys sp. strain MF347. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1924–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Yoshida, S.; Koseki, T.; Aboshi, T.; Murayama, T.; Supratman, U.; Shiono, Y. New Metabolites Produced by Cylindrocarpon sp. SY-39 from a Driftwood. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1700493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukai, Y.; Amino, H.; Hirawake, H.; Yabu, Y.; Ohta, N.; Minagawa, N.; Sakajo, S.; Yoshimoto, A.; Nagai, K.; Takamiya, S.; et al. Functional expression of the ascofuranone-sensitive Trypanosoma brucei brucei alternative oxidase in the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. CBPC 1999, 124, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoguro, K.; Ishiyama, A.; Namatame, M.; Nishihara, A.; Furusawa, T.; Masuma, R.; Shiomi, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Yamada, H.; Ōmura, S. Selective and Potent In Vitro Antitrypanosomal Activities of Ten Microbial Metabolites. J. Antibiot. 2008, 61, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Qian, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, G. Filamentous Fungi-Derived Orsellinic Acid-Sesquiterpene Meroterpenoids: Fungal Sources, Chemical Structures, Bioactivities, and Biosynthesis. Planta Med. 2023, 89, 1110–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Dentinger, B.; Nielson, J.; Peterson, R.; Winter, J. Emerimicins V-X, 15-Residue Peptaibols Discovered from an Acremonium sp. through Integrated Genomic and Chemical Approaches. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, M.C.; Maclean, B.; Burke, R.; Amodei, D.; Ruderman, D.L.; Neumann, S.; Gatto, L.; Fischer, B.; Pratt, B.; Egertson, J.; et al. A cross-platform toolkit for mass spectrometry and proteomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 918–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Revision A.1; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bruhn, T.; Schaumlöffel, A.; Hemberger, Y.; Bringmann, G. SpecDis: Quantifying the Comparison of Calculated and Experimental Electronic Circular Dichroism Spectra. Chirality 2013, 25, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Liu, H.; Zhao, X.; Shan, P.; Sun, P.; Xue, J.; Wei, G.; Zhang, H. Meroterpenoids from Daphne genkwa shows promising in vitro antitumor activity via inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in A549 cells. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 140, 106803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Bao, B.; Dang, H.T.; Hong, J.; Lee, H.J.; Yoo, E.S.; Bae, K.S.; Jung, J. Anti-inflammatory sesquiterpenoids from a sponge-derived Fungus Acremonium sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabovyi, G.A.; Mohr, J.T. Total Synthesis of Grifolin, Grifolic Acid, LL-Z1272α, LL-Z1272β, and Ilicicolinic Acid A. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 5010–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zechlin, L.; Wolf, M.; Steglich, W.; Anke, T. Antibiotika aus Basidiomyceten, XII. Cristatsäure, ein modifiziertes Farnesylphenol aus Fruchtkörpern von Albatrellus cristatus. Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1981, 1981, 2099–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, S.; Minato, H.; Katagiri, K. The ilicicolins, antibiotics from Cylindrocladium ilicicola. J. Antibiot. 1971, 24, 653–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, M.; Theoduloz, C.; Rodríguez, J.; Lolas, M.; Schmeda-Hirschmann, G. Bioactive Metabolites from the Fungus Nectria galligena, the Main Apple Canker Agent in Chile. J. Agri. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7701–7708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellestad, G.A.; Evans, R.H., Jr.; Kunstmann, M.P. Some new terpenoid metabolites from an unidentified fusarium species. Tetrahedron 1969, 25, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, A.; Ando, K.; Tamura, G.; Arima, K. Cylindrochlorin, a new antibiotic produced by Cylindrocladium. J. Antibiot. 1970, 23, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sasaki, H.; Hosokawa, T.; Sawada, M.; Ando, K. Isolation and structure of ascofuranone and ascofranol, antibiotics with hypolipidemic activity. J. Antibiot. 1973, 26, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Ge, X.; Xua, H.; Ma, K.; Zhang, W.; Zan, Y.; Efferth, T.; Xue, Z.; Hua, X. Phytochemicals with activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Phytomedicine 2022, 100, 154073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos, J.L.; Recio, M.C. Medicinal plants and antimicrobial activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 100, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Compound | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) |
| 1 | 113.6 | 113.6 | 113.7 | 113.7 | ||||
| 2 | 158.9 | 158.9 | 162.3 | 162.3 | ||||
| 3 | 107.9 | 107.9 | 114.5 | 114.5 | ||||
| 4 | 156.3 | 156.3 | 156.5 | 156.6 | ||||
| 5 | 116.2 | 116.2 | 113.3 | 113.4 | ||||
| 6 | 140.8 | 140.8 | 137.8 | 137.8 | ||||
| 7 | 14.7 | 2.60, s | 14.7 | 2.60, s | 14.6 | 2.61, s | 14.6 | |
| 8 | 193.5 | 10.13, s | 193.5 | 10.13, s | 193.5 | 10.14, s | 193.4 | 10.14, s |
| 9 | 116.2 | 6.73, d (10.1) | 116.2 | 6.73, d (10.1) | 22.1 | 3.39, d (7.1) | 22.1 | 3.39, d (7.1) |
| 10 | 126.5 | 5.53, d (10.1) | 126.6 | 5.53, d (10.1) | 121.4 | 5.21, t (7.3) | 121.2 | 5.20, t (7.2) |
| 11 | 82.0 | 82.0 | 136.1 | 136.5 | ||||
| 12 | 34.6 | 1.70, m overlapping | 34.6 | 1.86, m overlapping | 39.1 | 2.04, m | 39.2 | 2.01, m |
| 13 | 30.8 | 1.61, 1.44, m overlapping | 30.8 | 1.57 1.44, m overlapping | 26.1 | 2.16, m | 26.2 | 2.11, m |
| 14 | 43.3 | 43.3 | 128.7 | 5.50, t (7.2) | 127.5 | 5.41, t (7.0) | ||
| 15 | 36.3 | 1.94, m | 36.4 | 1.97, m | 133.1 | 134.3 | ||
| 16 | 31.0 | 1.84, 1.62, m overlapping | 31.0 | 1.84, 1.63, m overlapping | 77.9 | 4.52, m | 80.9 | 4.31, t (7.7) |
| 17 | 41.7 | 2.33, m | 41.7 | 2.33, m | 40.1 | 2.38, m | 37.1 | 1.73, 2.44, m |
| 18 | 213.8 | 213.7 | 218.1 | 79.6 | 4.99, dd (4.4, 7.0) | |||
| 19 | 50.6 | 2.44, q (6.7) | 50.6 | 2.40, q (6.8) | 80.9 | 81.9 | ||
| 20 | 15.6 | 0.58, s | 15.6 | 0.58, s | 24.4 | 1.28, s | 22.8 | 1.22, s |
| 21 | 15.1 | 0.85, d (6.8) | 15.0 | 0.90, d (7.0) | 22.1 | 1.22, s | 25.5 | 1.23, s |
| 22 | 7.5 | 0.93, d (6.7) | 7.6 | 0.88, d (7.1) | 11.3 | 1.63, s | 11.1 | 1.59, s |
| 23 | 27.6 | 1.49, s | 27.5 | 1.49, s | 16.3 | 1.79, s | 16.3 | 1.77, s |
| 1′-OAc | 21.2 | 2.07, s | ||||||
| 2′ | 170.8 | |||||||
| 2-OH | 12.71, s | 12.70, s | 12.69, s | 12.69, s | ||||
| 4-OH | 6.43, s | 6.48, s | ||||||
| Strain | S. aureus ATCC29213 | S. aureus MRSA | S. aureus MRCNS | B. cereus | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compounds | |||||
| 1 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | |
| 2 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | |
| 3 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 4 | |
| 4 | 32 | 64 | 32 | 32 | |
| 5 | >128 | >128 | >128 | 16 | |
| 6 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 16 | |
| 7 | 64 | 64 | 32 | 16 | |
| 8 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | |
| 9 | 4 | 16 | 4 | 16 | |
| 11 | >128 | 64 | 32 | 32 | |
| DMSO | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | |
| chloramphenicol | 8 | 8 | 4 | 4 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, G.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Qian, X.; Yang, P.; Cui, L.; Wang, P.; Li, D.; Winter, J.M.; Wu, G. The Discovery of Acremochlorins O-R from an Acremonium sp. through Integrated Genomic and Molecular Networking. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10050365
Cui G, Zhou L, Liu H, Qian X, Yang P, Cui L, Wang P, Li D, Winter JM, Wu G. The Discovery of Acremochlorins O-R from an Acremonium sp. through Integrated Genomic and Molecular Networking. Journal of Fungi. 2024; 10(5):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10050365
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Ge, Luning Zhou, Hanwei Liu, Xuan Qian, Pengfei Yang, Leisha Cui, Pianpian Wang, Dehai Li, Jaclyn M. Winter, and Guangwei Wu. 2024. "The Discovery of Acremochlorins O-R from an Acremonium sp. through Integrated Genomic and Molecular Networking" Journal of Fungi 10, no. 5: 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10050365
APA StyleCui, G., Zhou, L., Liu, H., Qian, X., Yang, P., Cui, L., Wang, P., Li, D., Winter, J. M., & Wu, G. (2024). The Discovery of Acremochlorins O-R from an Acremonium sp. through Integrated Genomic and Molecular Networking. Journal of Fungi, 10(5), 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10050365







