Roles of Three FgPel Genes in the Development and Pathogenicity Regulation of Fusarium graminearum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Strains, Media, and Culture Conditions
2.2. Sequential Analysis
2.3. Phylogenetic Tree Construction and Physicochemical Characterization of FgPels
2.4. Generation of the Knockout Mutants
2.5. qRT-PCR Assays
2.6. Effect of Variation in pH and Pectin Concentration on Mycelial Growth
2.7. Asexual Reproduction of Mutants
2.8. Determination of Pathogenicity on Wheat at Flowering Stage and Pathogenicity Experiment of Corn Silk Inoculation
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Analysis of F. graminearum FgPel Gene and Generation of the Gene Mutation
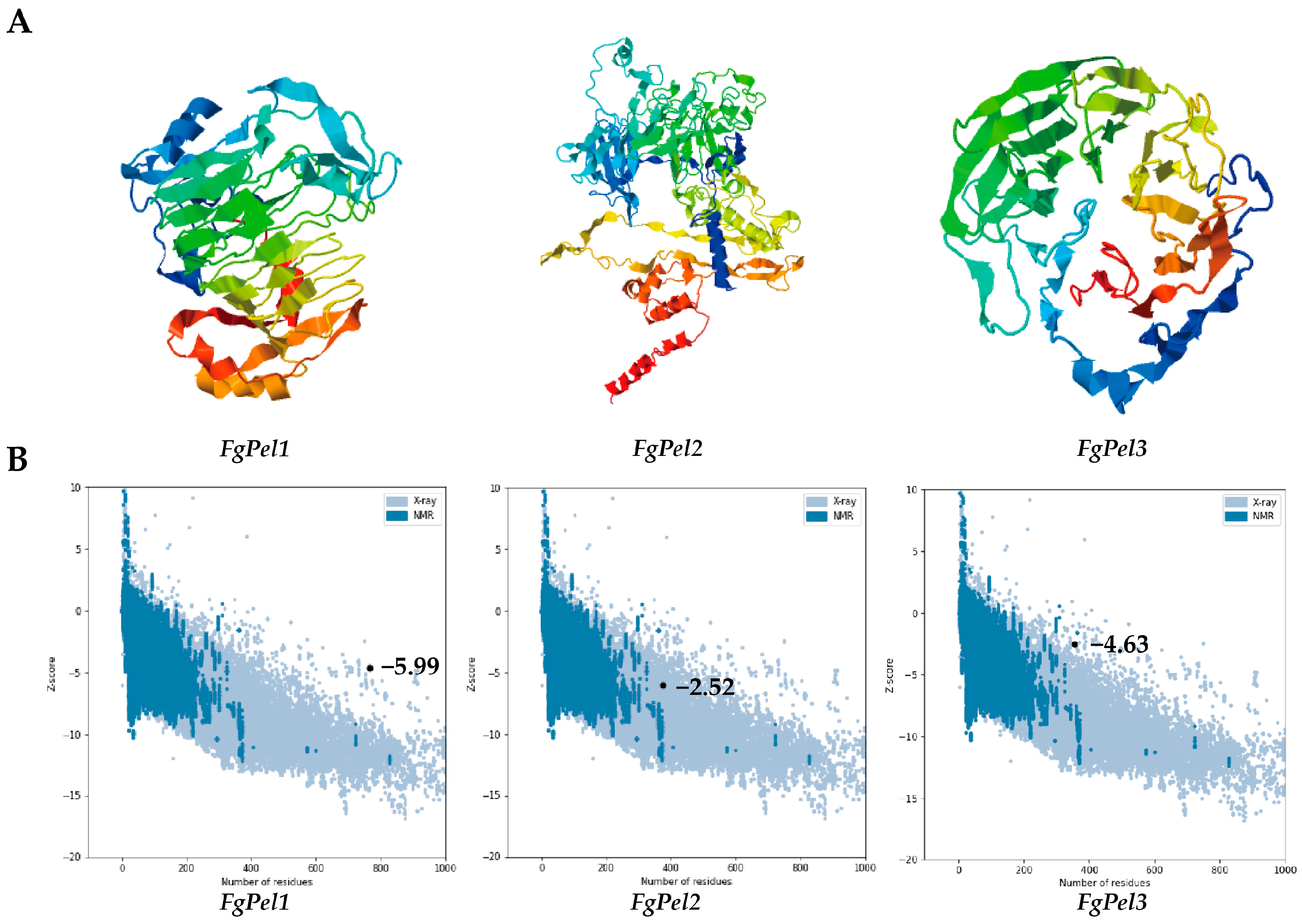
3.2. Prediction of the Gene Tertiary Structure and Characterization of Physicochemical Properties
3.3. The Generation of Three FgPel Gene Deletion Mutants
3.4. The Mutual Regulation of Pectinase Genes FgPel1, FgPel2, and FgPel3 and Their Expression Changes during the Infection Process
3.5. The Utilization of Different Concentrations of Pectin and Growth Characteristics of Mutant Strains at Different pH Values
3.6. Pectin Cleavage Genes Are Not Involved in Mycelial and Conidia Growth
3.7. Effect of the Gene Deletion Mutants on F. graminearum Virulence
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McMullen, M.; Jones, R.; Gallenberg, D. Scab of wheat and barley: A re-emerging disease of devastating impact. Plant Dis. 1997, 81, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, G.; Shaner, G. Management and resistance in wheat and barley to Fusarium head blight. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2004, 42, 135–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, R.S.; Kistler, H.C. Heading for disaster: Fusarium graminearum on cereal crops. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2004, 5, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shude, S.; Yobo, K.S.; Mbili, N.C. Progress in the management of Fusarium head blight of wheat: An overview. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2020, 116, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, L.E.; Stein, J.M. Epidemiology of Fusarium head blight on small-grain cereals. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 119, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dweba, C.; Figlan, S.; Shimelis, H.; Motaung, T.; Sydenham, S.; Mwadzingeni, L.; Tsilo, T. Fusarium head blight of wheat: Pathogenesis and control strategies. Crop Prot. 2017, 91, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’mello, J.P.F.; Placinta, C.M.; Macdonald, A.M.C. Fusarium mycotoxins: A review of global implications for animal health, welfare and productivity. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 1999, 80, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, P.A.; Lipps, P.E.; Hershman, D.E.; McMullen, M.P.; Draper, M.A.; Madden, L. Efficacy of triazole-based fungicides for Fusarium head blight and deoxynivalenol control in wheat: A multivariate meta-analysis. Phytopathology 2008, 98, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, I.; Friberg, H.; Steinberg, C.; Persson, P. Fungicide effects on fungal community composition in the wheat phyllosphere. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, J.; Haber, S. Overview of some recent research developments in Fusarium head blight of wheat. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2013, 35, 149–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhugga, K.S. Plant Golgi cell wall synthesis: From genes to enzyme activities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1815–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibeaut, D.M.; Carpita, N.G. Biosynthesis of plant cell wall polysaccharides. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doblin, M.S.; Pettolino, F.; Bacic, A. Plant cell walls: The skeleton of the plant world. Funct. Plant Biol. 2010, 37, 357–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keegstra, K. Plant cell walls. Plant Physiol. 2010, 154, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, B.L.; O’Neill, M.A.; Mohnen, D. Pectins: Structure, biosynthesis, and oligogalacturonide-related signaling. Phytochemistry 2001, 57, 929–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpita, N.C. Structure and biogenesis of the cell walls of grasses. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1996, 47, 445–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruben, B.S.; Zhou, M.; Wiebenga, A.; Ballering, J.; Overkamp, K.M.; Punt, P.J.; de Vries, R.P. Aspergillus niger RhaR, a regulator involved in L-rhamnose release and catabolism. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5531–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Rodríguez, M.C.; Orchard, J.; Seymour, G.B. Pectate lyases, cell wall degradation and fruit softening. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 2115–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Yadav, P.K.; Yadav, D.; Yadav, K.D.S. Pectin lyase: A review. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayani, R.S.; Saxena, S.; Gupta, R. Microbial pectinolytic enzymes: A review. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 2931–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, A.; Casanova, F.; Loehrer, M.; Jordine, A.; Bohnert, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Schaffrath, U. Gene deletion and constitutive expression of the pectate lyase gene 1 (MoPL1) lead to diminished virulence of Magnaporthe oryzae. J. Microbiol. 2022, 60, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shieh, M.T.; Brown, R.L.; Whitehead, M.P.; Cary, J.W.; Cotty, P.J.; E Cleveland, T.; A Dean, R. Molecular genetic evidence for the involvement of a specific polygalacturonase, P2c, in the invasion and spread of Aspergillus flavus in cotton bolls. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3548–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, X.; Dong, Y.; Qiu, D. A Verticillium dahliae pectate lyase induces plant immune responses and contributes to virulence. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paccanaro, M.C.; Sella, L.; Castiglioni, C.; Giacomello, F.; Martínez-Rocha, A.L.; D’oVidio, R.; Schäfer, W.; Favaron, F. Synergistic effect of different plant cell wall–degrading enzymes is important for virulence of Fusarium graminearum. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2017, 30, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonkers, W.; Rodrigues, C.D.A.; Rep, M. Impaired colonization and infection of tomato roots by the Δ frp1 mutant of Fusarium oxysporum correlates with reduced CWDE gene expression. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamnioti, P.; Gurr, S.J. Magnaporthe grisea cutinase2 mediates appressorium differentiation and host penetration and is required for full virulence. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2674–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Wang, G.; Jiang, W.; Sun, H.; Deng, Y.; Chen, H. The CHY-type zinc finger protein FgChy1 regulates polarized growth, pathogenicity, and microtubule assembly in fusarium graminearum. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2021, 34, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Li, H.; Luo, X.; Li, H.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Teng, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zuo, Z.; Ren, J. IBS 2.0: An upgraded illustrator for the visualization of biological sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W420–W426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, R.; Roy, A.; Xu, D.; Poisson, J.; Zhang, Y. The I-TASSER Suite: Protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, C.; Nigam, A.; Singh, R. Computational-approach understanding the structure-function prophecy of Fibrinolytic Protease RFEA1 from Bacillus cereus RSA1. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiederstein, M.; Sippl, M.J. ProSA-web: Interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35 (Suppl. S2), W407–W410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server; Humana Publication: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.; Zhu, Q.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.; Fan, X.; Yu, X.; He, F.; Xu, H.; Liang, Y.; Yu, J. Differential roles of three FgPLD genes in regulating development and pathogenicity in Fusarium graminearum. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2017, 109, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Sanjarian, F.; Safaie, N.; Mousavi, A.; Khaniki, G.B. A modified method for transformation of Fusarium graminearum. J. Crop Prot. 2013, 2, 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, J.; Wu, M.; Zhou, S. FgEaf6 regulates virulence, asexual/sexual development and conidial septation in Fusarium graminearum. Curr. Genet. 2020, 66, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zou, S.; Dong, H. The ADP-ribosylation factor-like small GTPase FgArl1 participates in growth, pathogenicity and DON production in Fusarium graminearum. Fungal Biol. 2020, 124, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, S.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Gu, Q.; Yin, Y.; Ma, Z. The microtubule end-binding protein FgEB1 regulates polar growth and fungicide sensitivity via different interactors in Fusarium graminearum. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1791–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Xu, J.R.; Wang, G. Deletion of FgHOG1 is suppressive to the mgv1 mutant by stimulating Gpmk1 activation and avoiding intracellular turgor elevation in Fusarium graminearum. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, R.H.; Kosugi, A. Cellulosomes: Plant-cell-wall-degrading enzyme complexes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, A.K.; Yadav, S.; Kumar, M.; Anand, G.; Yadav, D. Molecular biology of microbial pectate lyase: A review. Br. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 13, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, N.; Espeso, E.A.; Prusky, D. Virulence regulation of phytopathogenic fungi by pH. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Huang, Z.; Duan, Z.; Zhu, L.; Di, R.; Bao, Y.; Powell, C.A.; Hu, Q.; Chen, B.; Zhang, M.; et al. Pectate lyase from Fusarium sacchari induces plant immune responses and contributes to virulence. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e00165-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, R.A.; Timberlake, W.E. Regulation of the Aspergillus nidulans pectate lyase gene (pelA). Plant Cell 1989, 1, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, P.; Deng, Y.; Situ, J.; He, Z.; Zhou, W.; Li, M.; Xi, P.; Liang, X.; Kong, G.; et al. A plant cell death-inducing protein from litchi interacts with Peronophythora litchii pectate lyase and enhances plant resistance. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Tan, M.Q.; Wang, D.; Zhang, D.D.; Chen, J.Y. Functional analyses of pectin lyase family 1 gene VdPL1-4 in Verticillium dahliae. Plant Prot. 2022, 49, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Strain | Accession Numbers | Number of Amino Acids | SP (aa) | Molecular Weight | Isoelectric Point (PI) | Instability Index | Fat Factor | Relative Average Hydrophilicity (GRAY) | Total Anionic Residue Number (Asp + Glu) | Total Cationic Residue (Arg + Lys) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FgPel1 | NC_026475.1 | 375 | 1–18 | 39,816.88 | 9.03 | 24.21 | 78.03 | −0.171 | 25 | 33 |
| FgPel2 | NC_026474.1 | 355 | NO | 36,785.35 | 4.27 | 41.25 | 58.54 | −0.386 | 49 | 23 |
| FgPel3 | NC_026476.1 | 766 | 1–18 | 79,828.43 | 4.25 | 46.73 | 55.52 | −0.592 | 134 | 55 |
| Strains | Conidiation (106 Conidia/mL) |
|---|---|
| PH-1 | 1.04 ± 0.12 a |
| ΔFgPel1 | 1.19 ± 0.16 a |
| ΔFgPel2 | 0.92 ± 0.01 a |
| ΔFgPel3 | 1.04 ± 0.22 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, L.; Xu, X.; Dong, Y.; Jin, Y.; Rashad, Y.M.; Ma, D.; Gu, A. Roles of Three FgPel Genes in the Development and Pathogenicity Regulation of Fusarium graminearum. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10100666
Cai L, Xu X, Dong Y, Jin Y, Rashad YM, Ma D, Gu A. Roles of Three FgPel Genes in the Development and Pathogenicity Regulation of Fusarium graminearum. Journal of Fungi. 2024; 10(10):666. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10100666
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Lu, Xiao Xu, Ye Dong, Yingying Jin, Younes M. Rashad, Dongfang Ma, and Aiguo Gu. 2024. "Roles of Three FgPel Genes in the Development and Pathogenicity Regulation of Fusarium graminearum" Journal of Fungi 10, no. 10: 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10100666
APA StyleCai, L., Xu, X., Dong, Y., Jin, Y., Rashad, Y. M., Ma, D., & Gu, A. (2024). Roles of Three FgPel Genes in the Development and Pathogenicity Regulation of Fusarium graminearum. Journal of Fungi, 10(10), 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10100666








