Donor-Recipient Weight Match in Pediatric Heart Transplantation: Liberalizing Weight Matching with Caution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
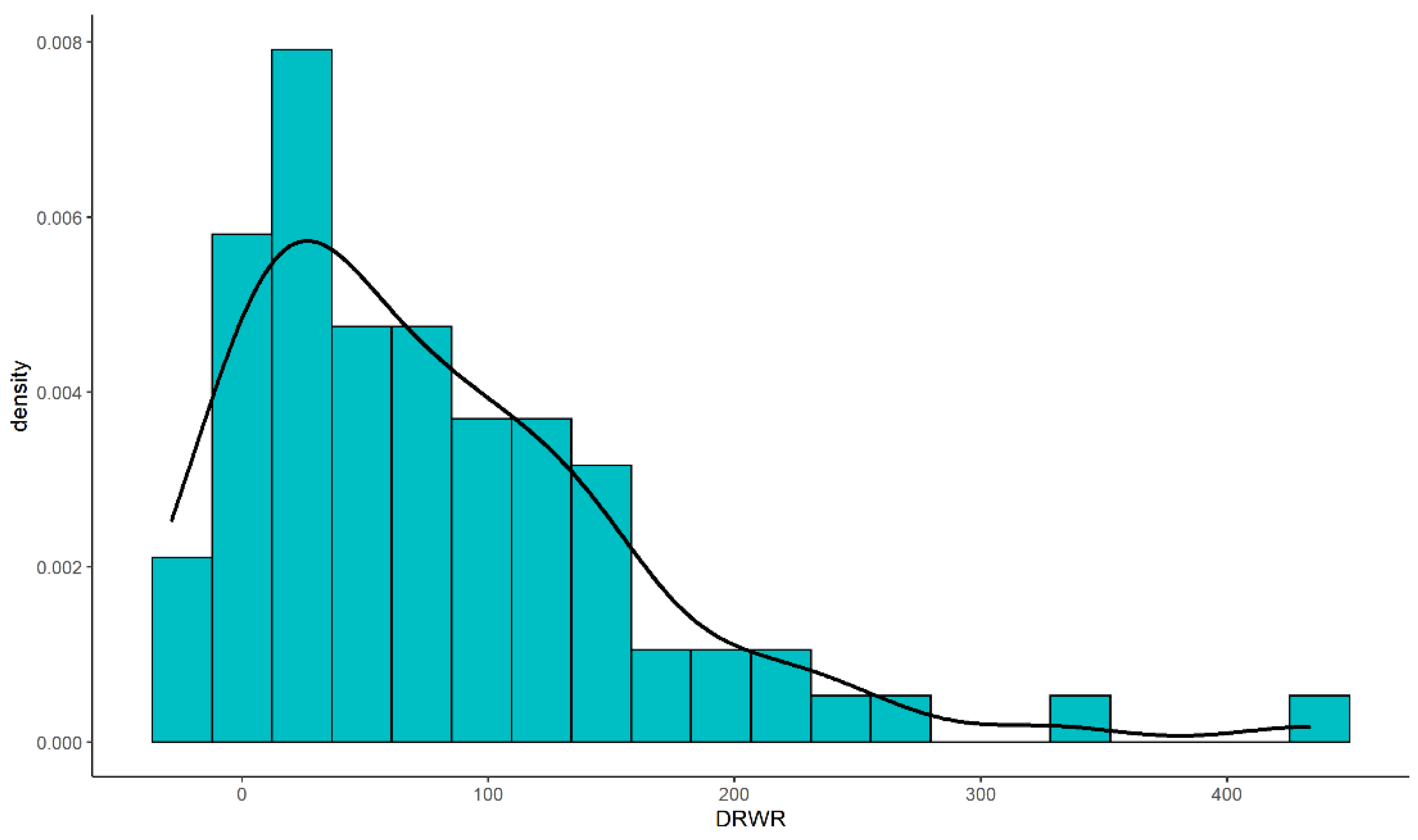
2.2. Donor-Recipient Ratio
2.3. Outcome Measures and Definitions
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
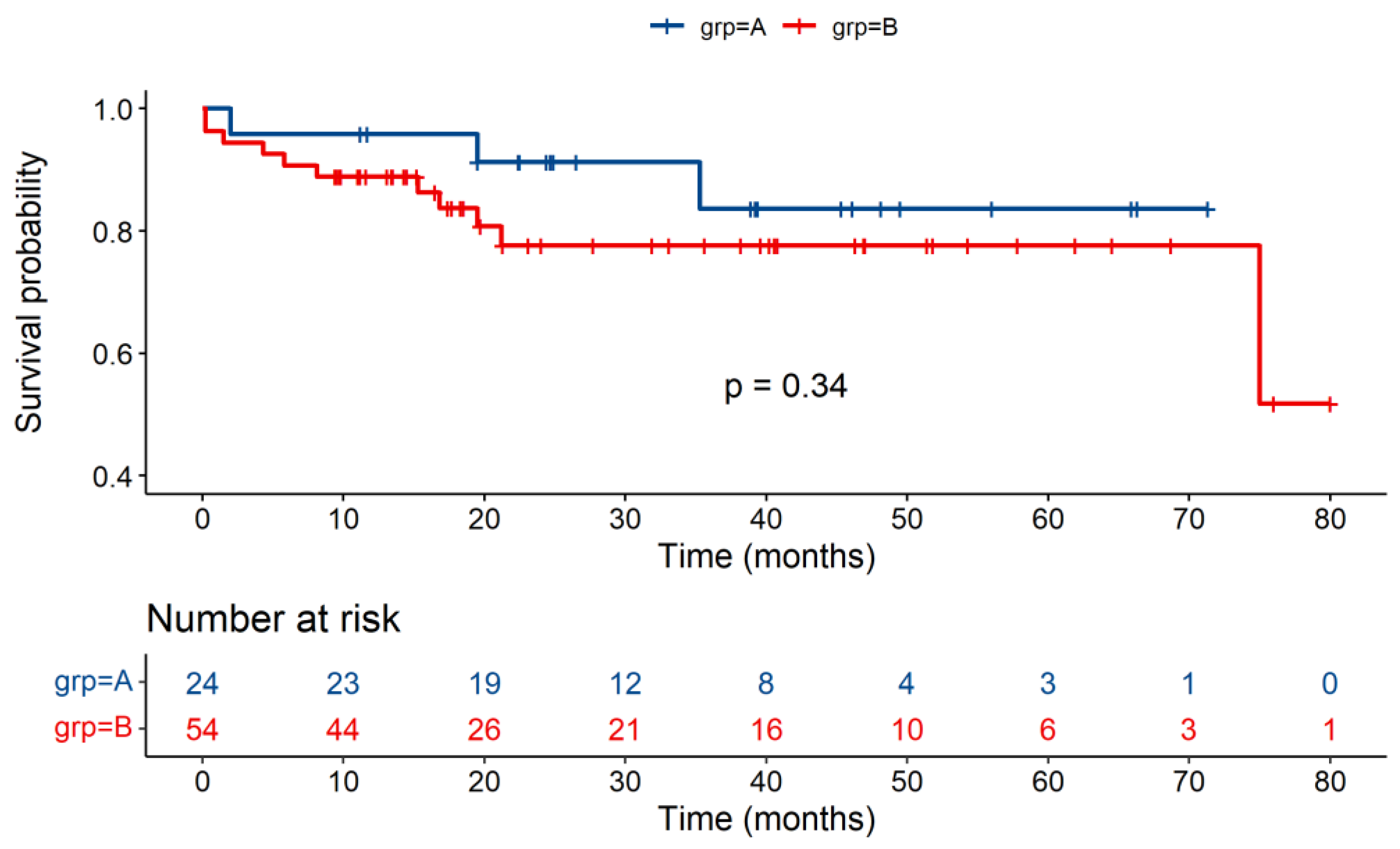
3.2. Post-Transplantation Outcomes
3.3. Detailed Information about Recipients with DRWR > 200%
3.4. Univariate and Multivariate Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. DRWR > 30% Is Feasible in China
4.2. Expansion of the DRWR to Over 200% Is Potentially Risky
4.3. The Outlooks of the Methods to Improve the Utilization of Graft Organ When DRWR > 200% in the Pre-Transplantation Donor-Recipient Size Matching
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khush, K.K.; Cherikh, W.S.; Chambers, D.C.; Harhay, M.O.; Hayes, D.; Hsich, E.; Meiser, B.; Potena, L.; Robinson, A.; Rossano, J.W.; et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-sixth adult heart transplantation report—2019; Focus theme: Donor and recipient size match. J. Heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Heart Transplant. 2019, 38, 1056–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanzo, M.R.; Dipchand, A.; Starling, R.; Anderson, A.; Chan, M.; Desai, S.; Fedson, S.; Fisher, P.; Gonzales-Stawinski, G.; Martinelli, L.; et al. The International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation Guidelines for the care of heart transplant recipients. J. Heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Heart Transplant. 2010, 29, 914–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, R.; Dipchand, A.I.; Davies, R.R.; Miera, O.; Chapman, G.; Conway, J.; Denfield, S.; Gossett, J.G.; Johnson, J.; McCulloch, M.; et al. ISHLT consensus statement on donor organ acceptability and management in pediatric heart transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Heart Transplant. 2020, 39, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanani, M.; Hoskote, A.; Carter, C.; Burch, M.; Tsang, V.; Kostolny, M. Increasing donor-recipient weight mismatch in pediatric orthotopic heart transplantation does not adversely affect outcome. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Assoc. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2012, 41, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Riggs, K.W.; Giannini, C.M.; Szugye, N.; Woods, J.; Chin, C.; Moore, R.A.; Morales, D.L.S.; Zafar, F. Time for evidence-based, standardized donor size matching for pediatric heart transplantation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 158, 1652–1660.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzhauser, L.; Imamura, T.; Bassi, N.; Fujino, T.; Nitta, D.; Kanelidis, A.J.; Narang, N.; Kim, G.; Raikhelkar, J.; Murks, C.; et al. Increasing heart transplant donor pool by liberalization of size matching. J. Heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Heart Transplant. 2019, 38, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.D.; Weiss, E.S.; Nwakanma, L.U.; Russell, S.D.; Baumgartner, W.A.; Shah, A.S.; Conte, J.V. Impact of donor-to-recipient weight ratio on survival after heart transplantation: Analysis of the United Network for Organ Sharing Database. Circulation 2008, 118, S83–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamisier, D.; Vouhé, P.; Le Bidois, J.; Mauriat, P.; Khoury, W.; Leca, F. Donor-recipient size matching in pediatric heart transplantation: A word of caution about small grafts. J. Heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Heart Transplant. 1996, 15, 190–195. [Google Scholar]
- Razzouk, A.J.; Johnston, J.K.; Larsen, R.L.; Chinnock, R.E.; Fitts, J.A.; Bailey, L.L. Effect of oversizing cardiac allografts on survival in pediatric patients with congenital heart disease. J. Heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Heart Transplant. 2005, 24, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christenson, J.T.; Maurice, J.; Simonet, F.; Velebit, V.; Schmuziger, M. Open chest and delayed sternal closure after cardiac surgery. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Assoc. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 1996, 10, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kransdorf, E.P.; Kittleson, M.M.; Benck, L.R.; Patel, J.K.; Chung, J.S.; Esmailian, F.; Kearney, B.L.; Chang, D.H.; Ramzy, D.; Czer, L.S.C.; et al. Predicted heart mass is the optimal metric for size match in heart transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Heart Transplant. 2019, 38, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobashigawa, J.; Zuckermann, A.; Macdonald, P.; Leprince, P.; Esmailian, F.; Luu, M.; Mancini, D.; Patel, J.; Razi, R.; Reichenspurner, H.; et al. Report from a consensus conference on primary graft dysfunction after cardiac transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Heart Transplant. 2014, 33, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Bock, M.J.; Wollstein, A.; Nguyen, K.; Malerba, S.; Lytrivi, I.D. Donor-recipient height ratio and outcomes in pediatric heart transplantation. Pediatr. Transplant. 2016, 20, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, T.A.; Joseph, S.M.; Lima, B.; Gonzalez-Stawinski, G.V.; Jamil, A.K.; Felius, J.; Qin, H.; Saracino, G.; Rafael, A.E.; Kale, P.; et al. Donor predicted heart mass as predictor of primary graft dysfunction. J. Heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Heart Transplant. 2018, 37, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szugye, N.A.; Lorts, A.; Zafar, F.; Taylor, M.; Morales, D.L.S.; Moore, R.A. Can virtual heart transplantation via 3-dimensional imaging increase the maximum acceptable donor size? J. Heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Heart Transplant. 2019, 38, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shugh, S.B.; Szugye, N.A.; Zafar, F.; Riggs, K.W.; Villa, C.; Lorts, A.; Morales, D.L.S.; Moore, R.A. Expanding the donor pool for congenital heart disease transplant candidates by implementing 3D imaging-derived total cardiac volumes. Pediatr. Transplant. 2020, 24, e13639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plasencia, J.D.; Kamarianakis, Y.; Ryan, J.R.; Karamlou, T.; Park, S.S.; Nigro, J.J.; Frakes, D.H.; Pophal, S.G.; Lagerstrom, C.F.; Velez, D.A.; et al. Alternative methods for virtual heart transplant-Size matching for pediatric heart transplantation with and without donor medical images available. Pediatr. Transplant. 2018, 22, e13290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelson, J.B.; Huang, Y.; Griffis, H.; Huang, J.; Mascio, C.E.; Chen, J.M.; Maeda, K.; Burstein, D.S.; Wittlieb-Weber, C.; Lin, K.Y.; et al. The influence of mechanical Circulatory support on post-transplant outcomes in pediatric patients: A multicenter study from the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) Registry. J. Heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Heart Transplant. 2021, 40, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcliffe, D.L.; Pruitt, E.; Cantor, R.S.; Godown, J.; Lane, J.; Turrentine, M.W.; Law, S.P.; Lantz, J.L.; Kirklin, J.K.; Bernstein, D.; et al. Post-transplant outcomes in pediatric ventricular assist device patients: A PediMACS-Pediatric Heart Transplant Study linkage analysis. J. Heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Heart Transplant. 2018, 37, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.S.; Emerson, D.; Megna, D.; Arabia, F.A. Total artificial heart: Surgical technique in the patient with normal cardiac anatomy. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2020, 9, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | All Patients | Group A DRWR ≤ 30% | Group B DRWR > 30% | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numbers | n = 78 | n = 24 | n = 54 | |
| Recipient sex (%) | 0.925 | |||
| Male | 40 (51.3%) | 13 (54.2%) | 27 (50.0%) | |
| Female | 38 (48.7%) | 11 (45.8%) | 27 (50.0%) | |
| Recipient age, year | 9.74 (4.70) | 12.9 (3.67) | 8.35 (4.46) | <0.001 |
| Recipient weight, kg | 30.0 [17.1; 42.5] | 48.5 [39.5; 53.0] | 24.2 [14.0; 33.0] | <0.001 |
| Recipient blood type (%) | 0.356 | |||
| A | 21 (26.9%) | 9 (37.5%) | 12 (22.2%) | |
| B | 29 (37.2%) | 6 (25.0%) | 23 (42.6%) | |
| AB | 25 (32.1%) | 8 (33.3%) | 17 (31.5%) | |
| O | 3 (3.85%) | 1 (4.17%) | 2 (3.70%) | |
| Donor age, years (%) | 18.5 [11.0; 30.2] | 18.5 [12.8; 24.5] | 18.5 [8.50; 31.8] | 0.828 |
| Donor sex (%) | 0.651 | |||
| Male | 50 (64.1%) | 14 (58.3%) | 36 (66.7%) | |
| Female | 28 (35.9%) | 10 (41.7%) | 18 (33.3%) | |
| Donor weight, kg (%) | 50.0 [35.2; 60.0] | 50.0 [40.0; 55.0] | 50.0 [31.2; 60.0] | 0.493 |
| DRWR (%) | 63.7 [16.8; 122] | 5.80 [−9.10; 13.6] | 98.5 [60.7; 140] | <0.001 |
| DRAR | 1.81 [1.33; 2.73] | 1.39 [1.00; 1.68] | 2.20 [1.44; 3.50] | <0.001 |
| Sex identical match (%) | 34 (43.6%) | 9 (37.5%) | 25 (46.3%) | 0.634 |
| Blood-type identical match (%) | 40 (51.3%) | 12 (50.0%) | 28 (51.9%) | 1 |
| Diagnosis (%) | 0.001 | |||
| DCM | 57 (73.1%) | 11 (45.8%) | 46 (85.2%) | |
| CAD | 2 (2.56%) | 2 (8.33%) | 0 (0.00%) | |
| VHD | 4 (5.13%) | 3 (12.5%) | 1 (1.85%) | |
| CHD | 14 (17.9%) | 7 (29.2%) | 7 (13.0%) | |
| Others | 1 (1.28%) | 1 (4.17%) | 0 (0.00%) | |
| Cardiac surgery history (%) | 18 (23.1%) | 9 (37.5%) | 9 (16.7%) | |
| Cold ischemia time, minutes | 354 [320; 375] | 348 [322; 374] | 364 [320; 375] | 0.439 |
| Preoperative IABP (%) | 1 (1.28%) | 1 (4.17%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0.308 |
| Preoperative ECMO (%) | 5 (6.41%) | 1 (4.17%) | 4 (7.41%) | 1 |
| Preoperative dopamine (%) | 46 (59.0%) | 15 (62.5%) | 31 (57.4%) | 0.863 |
| Preoperative ACEI (%) | 32 (41.0%) | 9 (37.5%) | 23 (42.6%) | 0.863 |
| Preoperative ARB (%) | 7 (8.97%) | 5 (20.8%) | 2 (3.70%) | 0.026 |
| Preoperative BB (%) | 28 (35.9%) | 12 (50.0%) | 16 (29.6%) | 0.14 |
| Variables | All Patients | Group A DRWR ≤ 30% | Group B DRWR > 30% | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | n = 78 | n = 24 | n = 54 | |
| Early Postoperative Data | ||||
| Pneumonia (%) | 44 (56.4%) | 12 (50.0%) | 32 (59.3%) | 0.607 |
| Neurological complications (%) | 6 (7.69%) | 2 (8.33%) | 4 (7.41%) | 1 |
| Acute renal injury (%) | 1 (1.28%) | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (1.85%) | 1 |
| Liver injury (%) | 9 (11.5%) | 0 (0.00%) | 9 (16.7%) | 0.05 |
| Sepsis (%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | - |
| LOPH, days | 44.5 [33.2; 66.2] | 36.0 [29.0; 43.5] | 53.5 [39.2; 72.8] | 0.002 |
| In-hospital death (%) | 5 (6.41%) | 1 (4.17%) | 4 (7.41%) | 1 |
| Long-Term Postoperative Data | ||||
| Death (%) | 14 (17.9%) | 3 (12.5%) | 11 (20.4%) | 0.531 |
| Length of survival, months | 23.6 [14.4; 45.9] | 30.9 [22.4; 46.6] | 19.6 [13.2; 40.8] | 0.075 |
| Survival | Group A | Group B | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-year survival% | 95.8 | 88.9 | 0.33 |
| 3-year survival% | 83.7 | 77.6 | 0.34 |
| 5-year survival% | 83.7 | 77.6 | 0.34 |
| Overall survival% | 83.7 | 51.8 | 0.34 |
| Patients | Patient A | Patient B | Patient C | Patient D | Patient E | Patient F | Patient G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis | DCM | DCM | DCM | DCM | DCM | DCM | DCM |
| Recipient sex | female | female | female | male | male | male | female |
| Recipient age, year(s) | 1 | 6 | 5 | 10 | 1 | 8 | 4 |
| Recipient weight, kg | 8.3 | 14 | 14.5 | 28 | 7.5 | 16 | 14 |
| Recipient blood type | AB | AB | AB | B | A | A | B |
| Donor age, years | 8 | 10 | 33 | 35 | 13 | 18 | 32 |
| Donor sex | male | male | male | male | female | female | female |
| Donor weight, kg | 25 | 60 | 50 | 90 | 40 | 50 | 50 |
| DRWR (%) | 201.2 | 328.6 | 244.8 | 221.4 | 433.3 | 212.5 | 257.1 |
| DRAR | 8 | 1.67 | 6.6 | 3.5 | 13 | 2.25 | 8 |
| Cold ischemia time, minutes | 370 | 345 | 365 | 394 | 394 | 348 | 498 |
| Blood-type identical match | √ | √ | |||||
| Cardiac surgery history | |||||||
| Preoperative IABP | |||||||
| Preoperative ECMO | √ | √ | |||||
| Preoperative dopamine | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Preoperative ACEI | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Preoperative ARB | √ | √ | |||||
| Preoperative BB | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| RBC, 1012 | 4.94 | 4.16 | 2.15 | 4.27 | 4.32 | 5.92 | 4.02 |
| PLT, 109 | 404 | 327 | 97 | 270 | 314 | 281 | 257 |
| WBC, 109 | 7.77 | 5.68 | 6.42 | 9.29 | 3.89 | 11.52 | 12.22 |
| Neut (%) | 83.8 | 58.8 | 77.88 | 50.81 | 20.82 | 64.93 | 57.69 |
| Lym (%) | 50.8 | 36.62 | 10.9 | 39.4 | 64.27 | 23.78 | 35.68 |
| ALT, U/L | 12 | 15 | 909 | 10 | 26 | 32 | 29 |
| AST, U/L | 36 | 24 | 1557 | 23 | 64 | 49 | 37 |
| Tbil, mmol/L | 10.3 | 7.7 | 23.1 | 8.9 | 9.3 | 20 | 9.8 |
| SCr, μmol/L | 26.3 | 52.1 | 33.8 | 50.1 | 33.1 | 48.7 | 41.3 |
| BUN, μmol/L | 3.5 | 9.7 | 6.63 | 5.8 | 5.27 | 5.92 | 7.3 |
| Early Postoperative Data | Patient A | Patient B | Patient C | Patient D | Patient E | Patient F | Patient G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pneumonia (%) | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| Neurological complications (%) | |||||||
| Acute renal injury (%) | |||||||
| Liver injury (%) | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| Sepsis (%) | |||||||
| In-hospital death | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| LOPH, days | 54 | 51 | 41 | 77 | 6 | 46 | 7 |
| Death | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| Cause of death | Malignant arrhythmia | Systemic infection | Acute rejection |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, M.; Xu, L.; Yu, W.; Qian, X.; Rao, Z.; Tu, J.; Dong, N.; Li, F. Donor-Recipient Weight Match in Pediatric Heart Transplantation: Liberalizing Weight Matching with Caution. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd9050148
Chen M, Xu L, Yu W, Qian X, Rao Z, Tu J, Dong N, Li F. Donor-Recipient Weight Match in Pediatric Heart Transplantation: Liberalizing Weight Matching with Caution. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2022; 9(5):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd9050148
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ming, Li Xu, Wenjing Yu, Xingyu Qian, Zhenqi Rao, Jingrong Tu, Nianguo Dong, and Fei Li. 2022. "Donor-Recipient Weight Match in Pediatric Heart Transplantation: Liberalizing Weight Matching with Caution" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 9, no. 5: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd9050148
APA StyleChen, M., Xu, L., Yu, W., Qian, X., Rao, Z., Tu, J., Dong, N., & Li, F. (2022). Donor-Recipient Weight Match in Pediatric Heart Transplantation: Liberalizing Weight Matching with Caution. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 9(5), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd9050148





