The Prognostic Potential of Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein 1 for Cardiovascular Complications in Peripheral Artery Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Recruitment
2.4. Baseline Characteristics
2.5. Quantification of Plasma Protein Concentrations
2.6. Follow-Up and Outcomes
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events
3.3. Plasma Concentrations of Growth Factors
3.4. Associations Between Growth Factors and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events
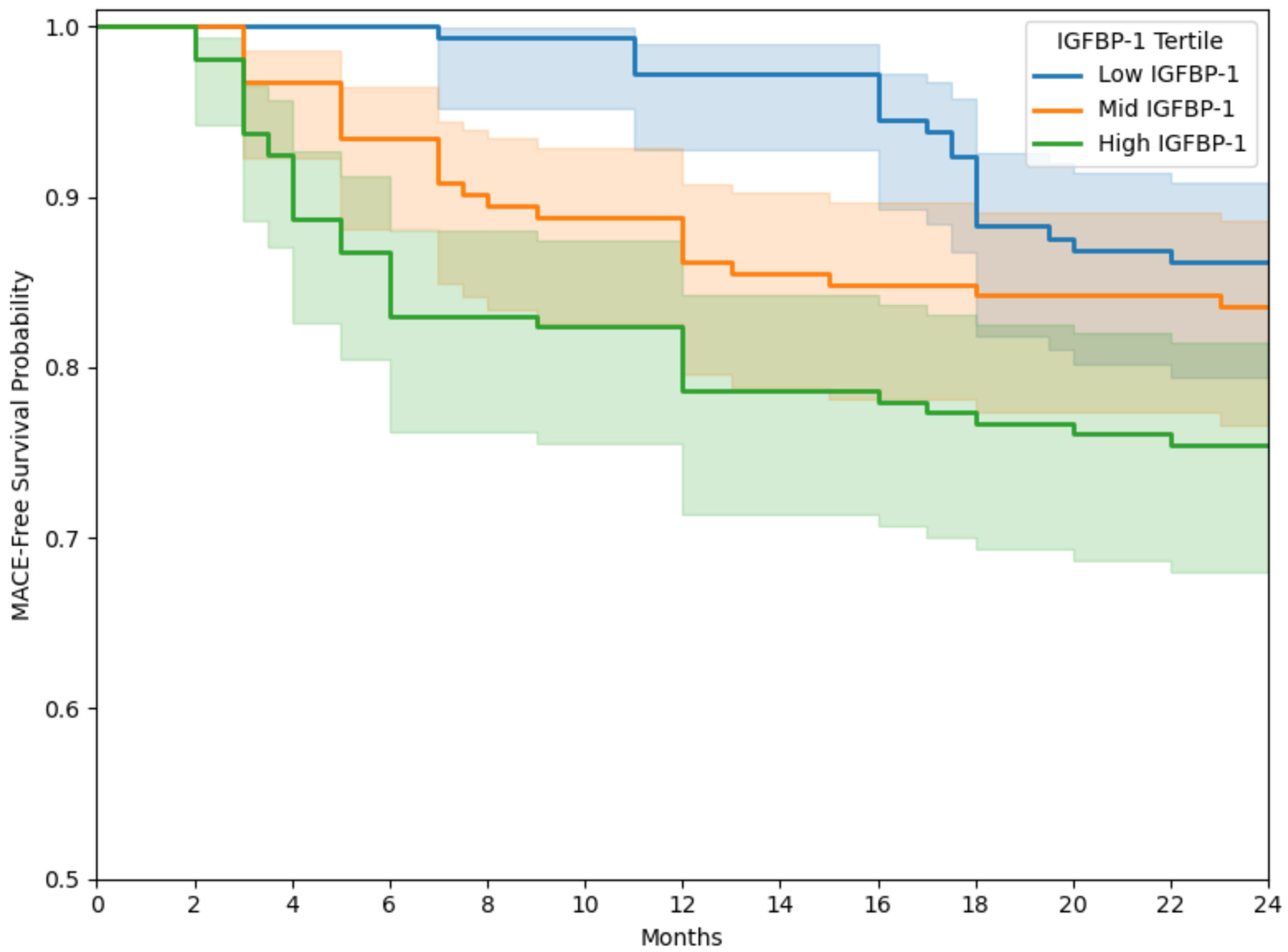
3.5. Kaplan–Meier Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Findings
4.2. Comparison with the Existing Literature
4.3. Explanation of Findings
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olin, J.W.; Sealove, B.A. Peripheral Artery Disease: Current Insight Into the Disease and Its Diagnosis and Management. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, 678–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horváth, L.; Németh, N.; Fehér, G.; Kívés, Z.; Endrei, D.; Boncz, I. Epidemiology of Peripheral Artery Disease: Narrative Review. Life 2022, 12, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenon, S.M.; Vittinghoff, E.; Owens, C.D.; Conte, M.S.; Whooley, M.; Cohen, B.E. Peripheral Artery Disease and Risk of Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: Insights from the Heart and Soul Study. Vasc. Med. 2013, 18, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikary, D.; Barman, S.; Ranjan, R.; Stone, H. A Systematic Review of Major Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Growing Global Health Concern. Cureus 2022, 14, e30119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, C.; Astin, F. A Multidisciplinary Approach to Prevention. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2017, 24, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shaikh, F.; Zamzam, A.; Syed, M.H.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. A Machine Learning Algorithm for Peripheral Artery Disease Prognosis Using Biomarker Data. iScience 2024, 27, 109081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zamzam, A.; Syed, M.H.; Jahanpour, N.; Jain, S.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. Urinary Fatty Acid Binding Protein 3 Has Prognostic Value in Peripheral Artery Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 875244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zamzam, A.; Syed, M.H.; Jahanpour, N.; Jain, S.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. Urinary Cystatin C Has Prognostic Value in Peripheral Artery Disease. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Djahanpour, N.; Zamzam, A.; Syed, M.H.; Jain, S.; Arfan, S.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. The Prognostic Capability of Inflammatory Proteins in Predicting Peripheral Artery Disease Related Adverse Events. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 1073751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, W.L.; Leavitt, L.; Varacallo, M.A. Physiology, Growth Factor. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Diehl, C.; Song, R.J.; Sawyer, D.B.; Wollert, K.C.; Mitchell, G.F.; Cheng, S.; Vasan, R.S.; Xanthakis, V. Circulating Growth Factors and Cardiac Remodeling in the Community: The Framingham Heart Study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 329, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domouzoglou, E.M.; Naka, K.K.; Vlahos, A.P.; Papafaklis, M.I.; Michalis, L.K.; Tsatsoulis, A.; Maratos-Flier, E. Fibroblast Growth Factors in Cardiovascular Disease: The Emerging Role of FGF21. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 309, H1029–H1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangogiannis, N.G. Transforming Growth Factor-β in Myocardial Disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 19, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florek, K.; Mendyka, D.; Gomułka, K. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Its Role in the Cardiovascular System. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewitt, M.S.; Boyd, G.W. Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-1 (IGFBP-1) as a Biomarker of Cardiovascular Disease. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Liu, Y.; Pan, H.; Feng, Y.; Lu, X.; Gan, L.; Wan, J.; Ye, J. Insights into Bone Morphogenetic Proteins in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1125642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Shibayama, C.; Gil-Cruz, C.; Cadosch, N.; Lütge, M.; Cheng, H.-W.; De Martin, A.; Frischmann, K.; Joachimbauer, A.; Onder, L.; Papadopoulou, I.; et al. Bone Morphogenic Protein-4 Availability in the Cardiac Microenvironment Controls Inflammation and Fibrosis in Autoimmune Myocarditis. Nat. Cardiovasc. Res. 2024, 3, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceelen, D.C.H.; Bracun, V.; van Essen, B.J.; Voors, A.A.; de Boer, R.A.; ter Maaten, J.M.; Masson, S.; Kastner, P.; Lang, C.C.; Suthahar, N. Circulating Bone Morphogenetic Protein 10 as a Novel Marker of Atrial Stress and Remodelling in Heart Failure. Heart 2025, 111, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Nassereldine, R.; Shaikh, F.; Younes, H.; AbuHalimeh, B.; Zamzam, A.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. Inflammatory Protein Panel: Exploring Diagnostic Insights for Peripheral Artery Disease Diagnosis in a Cross-Sectional Study. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, G.S.; Moons, K.G.M.; Dhiman, P.; Riley, R.D.; Beam, A.L.; Calster, B.V.; Ghassemi, M.; Liu, X.; Reitsma, J.B.; van Smeden, M.; et al. TRIPOD+AI Statement: Updated Guidance for Reporting Clinical Prediction Models That Use Regression or Machine Learning Methods. BMJ 2024, 385, e078378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, F.; Janzer, S.F. Peripheral Vascular Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Grundy, S.M.; Stone, N.J.; Bailey, A.L.; Beam, C.; Birtcher, K.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Braun, L.T.; de Ferranti, S.; Faiella-Tommasino, J.; Forman, D.E.; et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, e285–e350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison, H.C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, e127–e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, C.; Baweja, M.; Crews, D.C.; Eneanya, N.D.; Gadegbeku, C.A.; Inker, L.A.; Mendu, M.L.; Miller, W.G.; Moxey-Mims, M.M.; Roberts, G.V.; et al. A Unifying Approach for GFR Estimation: Recommendations of the NKF-ASN Task Force on Reassessing the Inclusion of Race in Diagnosing Kidney Disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2022, 79, 268–288.E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luminex Assays, Multiplex Immunoassays. Available online: https://www.bio-techne.com/ (accessed on 6 May 2023).
- MAGPIX® System | xMAP Instrument | Luminex Corporation. Available online: https://www.luminexcorp.com/magpix-system/ (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- Luminex Assays—CA. Available online: www.thermofisher.com/ca/en/home/life-science/antibodies/immunoassays/procartaplex-assays-luminex.html (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- xPONENT® Software for xMAP® Instruments, version 4.3; Luminex Corporation: Austin, TX, USA, 2025.
- Thygesen, K.; Alpert, J.S.; Jaffe, A.S.; Chaitman, B.R.; Bax, J.J.; Morrow, D.A.; White, H.D. The Executive Group on behalf of the Joint European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA)/World Heart Federation (WHF) Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction (2018). Circulation 2018, 138, e618–e651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, R.L.; Kasner, S.E.; Broderick, J.P.; Caplan, L.R.; Connors, J.J.; Culebras, A.; Elkind, M.S.V.; George, M.G.; Hamdan, A.D.; Higashida, R.T.; et al. An Updated Definition of Stroke for the 21st Century: A Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2013, 44, 2064–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornik, H.L.; Aronow, H.D.; Goodney, P.P.; Arya, S.; Brewster, L.P.; Byrd, L.; Chandra, V.; Drachman, D.E.; Eaves, J.M.; Ehrman, J.K.; et al. 2024 ACC/AHA/AACVPR/APMA/ABC/SCAI/SVM/SVN/SVS/SIR/VESS Guideline for the Management of Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2024, 149, e1313–e1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelani, Q.-U.-A.; Petrov, M.; Martinez, S.C.; Holmvang, L.; Al-Shaibi, K.; Alasnag, M. Peripheral Arterial Disease in Women: An Overview of Risk Factor Profile, Clinical Features, and Outcomes. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2018, 20, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, K.F.; Wang, Z.; Janes, H.; McClelland, R.L.; Psaty, B.M.; Pepe, M.S. Net Reclassification Indices for Evaluating Risk-Prediction Instruments: A Critical Review. Epidemiology 2014, 25, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pencina, M.J.; Demler, O.V. Novel Metrics for Evaluating Improvement in Discrimination: Net Reclassification and Integrated Discrimination Improvement for Normal Variables and Nested Models. Stat. Med. 2012, 31, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajian-Tilaki, K. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve Analysis for Medical Diagnostic Test Evaluation. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 4, 627–635. [Google Scholar]
- DeLong, E.R.; DeLong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the Areas under Two or More Correlated Receiver Operating Characteristic Curves: A Nonparametric Approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SPSS Software, version 23; IBM: Armonk, NY, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/analytics/spss-statistics-software (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- Ho, J.E.; Lyass, A.; Courchesne, P.; Chen, G.; Liu, C.; Yin, X.; Hwang, S.-J.; Massaro, J.M.; Larson, M.G.; Levy, D. Protein Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality in the Community. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e008108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritsinger, V.; Brismar, K.; Mellbin, L.; Näsman, P.; Rydén, L.; Söderberg, S.; Norhammar, A. Elevated Levels of Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein 1 Predict Outcome after Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Long-Term Follow-up of the Glucose Tolerance in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction (GAMI) Cohort. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 2018, 15, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallander, M.; Norhammar, A.; Malmberg, K.; Ohrvik, J.; Rydén, L.; Brismar, K. IGF Binding Protein 1 Predicts Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 2343–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Janszky, I.; Hallqvist, J.; Ljung, R.; Hammar, N. Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-1 Is a Long-Term Predictor of Heart Failure in Survivors of a First Acute Myocardial Infarction and Population Controls. Int. J. Cardiol. 2010, 138, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boquist, S.; Ruotolo, G.; Skoglund-Andersson, C.; Tang, R.; Björkegren, J.; Bond, M.G.; De Faire, U.; Brismar, K.; Hamsten, A. Correlation of Serum IGF-I and IGFBP-1 and -3 to Cardiovascular Risk Indicators and Early Carotid Atherosclerosis in Healthy Middle-Aged Men. Clin. Endocrinol. 2008, 68, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åberg, D.; Gadd, G.; Jood, K.; Redfors, P.; Stanne, T.M.; Isgaard, J.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Jern, C.; Åberg, N.D.; et al. Serum IGFBP-1 Concentration as a Predictor of Outcome after Ischemic Stroke-A Prospective Observational Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, L.; Fang, Z.; Fan, Y.; Liu, C.; Tian, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, W.; Ren, Z.; et al. A Comprehensive Contribution of Genetic Variations of the Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Signalling Pathway to Stroke Susceptibility. Atherosclerosis 2020, 296, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Razuvaev, A.; Folkersen, L.; Hedin, E.; Roy, J.; Brismar, K.; Hedin, U. The Expression of IGFs and IGF Binding Proteins in Human Carotid Atherosclerosis, and the Possible Role of IGF Binding Protein-1 in the Regulation of Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation. Atherosclerosis 2012, 220, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resanović, I.; Gluvić, Z.; Zarić, B.; Sudar-Milovanović, E.; Vučić, V.; Arsić, A.; Nedić, O.; Šunderić, M.; Gligorijević, N.; Milačić, D.; et al. Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Fatty Acid Composition and Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1 in Adult Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Pilot Study. Can. J. Diabetes 2020, 44, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevetti, G.; Colao, A.; Schiano, V.; Pivonello, R.; Laurenzano, E.; Di Somma, C.; Lombardi, G.; Chiariello, M. IGF System and Peripheral Arterial Disease: Relationship with Disease Severity and Inflammatory Status of the Affected Limb. Clin. Endocrinol. 2008, 69, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeRoith, D.; Holly, J.M.P.; Forbes, B.E. Insulin-like Growth Factors: Ligands, Binding Proteins, and Receptors. Mol. Metab. 2021, 52, 101245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, B.E.; McCarthy, P.; Norton, R.S. Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Proteins: A Structural Perspective. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostis, P.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Blinc, A.; Jensterle, M.; Ježovnik, M.K.; Schernthaner, G.-H.; Antignani, P.L.; Studen, K.B.; Šabović, M.; Poredos, P. The Effect of Menopause and Menopausal Hormone Therapy on the Risk of Peripheral Artery Disease. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2023, 21, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabon, M.; Cheng, S.; Altin, S.E.; Sethi, S.S.; Nelson, M.D.; Moreau, K.L.; Hamburg, N.; Hess, C.N. Sex Differences in Peripheral Artery Disease. Circ. Res. 2022, 130, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajwani, A.; Ezzat, V.; Smith, J.; Yuldasheva, N.Y.; Duncan, E.R.; Gage, M.; Cubbon, R.M.; Kahn, M.B.; Imrie, H.; Abbas, A.; et al. Increasing Circulating IGFBP1 Levels Improves Insulin Sensitivity, Promotes Nitric Oxide Production, Lowers Blood Pressure, and Protects against Atherosclerosis. Diabetes 2012, 61, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood, N.J.; Slater, T.A.; Drozd, M.; Warmke, N.; Matthews, C.; Cordell, P.A.; Smith, J.; Rainford, J.; Cheema, H.; Maher, C.; et al. IGFBP-1 in Cardiometabolic Pathophysiology—Insights from Loss-of-Function and Gain-of-Function Studies in Male Mice. J. Endocr. Soc. 2020, 4, bvz006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, R.; Suleiman, M.; Rigano, J.; Lui, B.; Nandurkar, H.; Ho, P.; Lim, H.Y. Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor Levels and Atherothrombotic Events in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease or Diabetes. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2025, 58, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Marcantonio, E.R.; Mangione, C.M.; Thomas, E.J.; Polanczyk, C.A.; Cook, E.F.; Sugarbaker, D.J.; Donaldson, M.C.; Poss, R.; Ho, K.K.; et al. Derivation and Prospective Validation of a Simple Index for Prediction of Cardiac Risk of Major Noncardiac Surgery. Circulation 1999, 100, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.M.G.; Ankerst, D.P.; Andridge, R.R. Validation of Biomarker-Based Risk Prediction Models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5977–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Whole PAD Cohort (n = 465) | Males (n = 320) | Females (n = 145) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years, mean (SD) | 71 (10) | 69 (10) | 73 (10) |
| Female sex | 145 (31.1) | 0 (0) | 145 (100) |
| Hypertension | 394 (84.6) | 271 (84.7) | 123 (84.8) |
| Dyslipidemia | 383 (82.3) | 269 (84.1) | 114 (78.6) |
| Diabetes | 220 (47.2) | 164 (51.3) | 56 (38.6) |
| Past smoking | 269 (57.9) | 186 (58.1) | 83 (57.2) |
| Current smoking | 110 (23.6) | 92 (28.8) | 18 (12.4) |
| Congestive heart failure | 22 (4.7) | 16 (5.0) | 6 (4.1) |
| Coronary artery disease | 181 (39.0) | 150 (46.9) | 31 (21.4) |
| Previous stroke | 92 (19.7) | 61 (19.1) | 31 (21.4) |
| Creatinine, µmol/L, mean (SD) | 98.61 (69.96) | 98.07 (40.33) | 100.08 (119.33) |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2, mean (SD) | 49.39 (21.52) | 49.37 (21.52) | 49.26 (21.74) |
| HbA1c, %, mean (SD) | 9.53 (25.95) | 10.61 (30.61) | 6.79 (1.67) |
| Fasting glucose, mmol/L, mean (SD) | 8.23 (1.97) | 8.48 (2.10) | 7.13 (0.72) |
| LDL, mmol/L, mean (SD) | 1.69 (0.7) | 1.74 (0.78) | 1.60 (0.52) |
| Total cholesterol/HDL ratio, mean (SD) | 3.3 (1.53) | 3.53 (1.74) | 2.81 (0.79) |
| Non-HDL, mmol/L, mean (SD) | 2.54 (0.97) | 2.60 (1.08) | 2.41 (0.67) |
| ASA | 265 (57.0) | 193 (60.3) | 72 (49.7) |
| ACE-I/ARB | 263 (56.6) | 195 (60.9) | 68 (46.9) |
| Patients with PAD (n = 465) | |
|---|---|
| Major adverse cardiovascular event | 84 (18.1) |
| Myocardial infarction | 70 (15.0) |
| Stroke | 22 (4.7) |
| Death | 5 (1.2) |
| No MACE (n = 381) | MACE (n = 84) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IGFBP-1 | 13.94 (3.80) | 20.66 (3.91) | 0.012 |
| TFPI | 20.58 (11.52) | 21.20 (11.80) | 0.062 |
| BMP-4 | 10.98 (5.02) | 11.5 (5.2) | 0.087 |
| BMP-10 | 125.91 (107.27) | 130.5 (110.0) | 0.089 |
| BMP-7 | 95.8 (90.26) | 98.4 (92.5) | 0.105 |
| Adjusted Hazard Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IGFBP-1 | 1.59 | (1.24–2.09) | 0.007 |
| BMP-4 | 0.89 | (0.75–1.06) | 0.386 |
| BMP-7 | 1.12 | (0.98–1.45) | 0.192 |
| BMP-10 | 1.08 | (0.80–1.31) | 0.611 |
| TFPI | 0.92 | (0.79–1.19) | 0.420 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Shaikh, F.; Younes, H.; Abuhalimeh, B.; Zamzam, A.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. The Prognostic Potential of Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein 1 for Cardiovascular Complications in Peripheral Artery Disease. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12070253
Li B, Shaikh F, Younes H, Abuhalimeh B, Zamzam A, Abdin R, Qadura M. The Prognostic Potential of Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein 1 for Cardiovascular Complications in Peripheral Artery Disease. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2025; 12(7):253. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12070253
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ben, Farah Shaikh, Houssam Younes, Batool Abuhalimeh, Abdelrahman Zamzam, Rawand Abdin, and Mohammad Qadura. 2025. "The Prognostic Potential of Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein 1 for Cardiovascular Complications in Peripheral Artery Disease" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 12, no. 7: 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12070253
APA StyleLi, B., Shaikh, F., Younes, H., Abuhalimeh, B., Zamzam, A., Abdin, R., & Qadura, M. (2025). The Prognostic Potential of Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein 1 for Cardiovascular Complications in Peripheral Artery Disease. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 12(7), 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12070253







