Trading off Iodine and Radiation Dose in Coronary Computed Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Technical Principles in CCTA
2.1. Computed Tomography System and Parameters
2.2. Coronary Lumen Attenuation
3. Current State of Research on Radiation Dose and Contrast Dose
3.1. Radiation Dose and Risks
3.2. Iodinated Contrast Volume and Risks
4. Radiation Dose and Contrast Media Control Approaches
4.1. Tube Kilovoltage Peak (kVp)
4.2. Prospective ECG-Gating
4.3. Iodine Injection Protocol
4.4. Heart Rate Control
5. Emerging Technologies and Techniques
5.1. Gantry Rotation
5.2. Detector Size
5.3. Iterative and Deep-Learning Image Reconstruction
5.4. Spectral CT and Photon Counting CT
6. Recommendations for Practitioners
6.1. CT System and Protocol Optimization
6.2. Patient-Specific Protocol Optimization
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body mass index |
| BPM | Beats per minute |
| CA-AKI | Contrast-associated acute kidney injury |
| CAD | Coronary artery disease |
| CCTA | Coronary computed tomography angiography |
| CM | Contrast medium |
| CTDI | Computed tomography dose index |
| DLP | Dose-length product |
| DLR | Deep learning-based reconstruction |
| FBP | Filtered back projection |
| HU | Hounsfield unit |
| IDR | Iodine delivery rate |
| PCCT | Photon-counting computed tomography |
References
- Guthaner, D.F.; Wexler, L.; Harell, G. CT demonstration of cardiac structures. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1979, 133, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoepf, U.J.; Zwerner, P.L.; Savino, G.; Herzog, C.; Kerl, J.M.; Costello, P. Coronary CT Angiography. Radiology 2007, 244, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquering, H.A.; Dijkstra, J.; de Koning, P.J.H.; Stoel, B.C.; Reiber, J.H.C. Towards quantitative analysis of coronary CTA. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2005, 21, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Choo, G.H.; Ng, K.H. Coronary CT angiography: Current status and continuing challenges. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Levin, D.C.; Halpern, E.J.; Fischman, D.; Savage, M.; Walinsky, P. Accuracy of MDCT in Assessing the Degree of Stenosis Caused by Calcified Coronary Artery Plaques. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 191, 1676–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, M.; Levy, P.D.; Mukherjee, D.; Amsterdam, E.; Bhatt, D.L.; Birtcher, K.K.; Blankstein, R.; Boyd, J.; Bullock-Palmer, R.P.; Conejo, T.; et al. 2021 AHA/ACC/ASE/CHEST/SAEM/SCCT/SCMR Guideline for the Evaluation and Diagnosis of Chest Pain: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2021, 144, e368–e454. [Google Scholar]
- Vrints, C.; Andreotti, F.; Koskinas, K.C.; Rossello, X.; Adamo, M.; Ainslie, J.; Banning, A.P.; Budaj, A.; Buechel, R.R.; Chiariello, G.A.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of chronic coronary syndromes: Developed by the task force for the management of chronic coronary syndromes of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Endorsed by the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3415–3537. [Google Scholar]
- Narula, J.; Chandrashekhar, Y.; Ahmadi, A.; Abbara, S.; Berman, D.S.; Blankstein, R.; Leipsic, J.; Newby, D.; Nicol, E.D.; Nieman, K.; et al. SCCT 2021 Expert Consensus Document on Coronary Computed Tomographic Angiography: A Report of the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2021, 15, 192–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, M.; Lesser, J.R.; Biga, C.; Blankstein, R.; Kramer, C.M.; Min, J.K.; Noack, P.S.; Farrow, C.; Hoffman, U.; Murillo, J.; et al. Current Evidence and Recommendations for Coronary CTA First in Evaluation of Stable Coronary Artery Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbara, S.; Blanke, P.; Maroules, C.D.; Cheezum, M.; Choi, A.D.; Han, B.K.; Marwan, M.; Naoum, C.; Norgaard, B.L.; Rubinshtein, R.; et al. SCCT guidelines for the performance and acquisition of coronary computed tomographic angiography: A report of the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography Guidelines Committee: Endorsed by the North American Society for Cardiovascular Imaging (NASCI). J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2016, 10, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein Andrew, J. Radiation Dose Reduction in Coronary CT Angiography. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 8, 897–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.; Nazir, S.A.; Alkadhi, H. Technical challenges of coronary CT angiography: Today and tomorrow. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 79, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghekiere, O.; Salgado, R.; Buls, N.; Leiner, T.; Mancini, I.; Vanhoenacker, P.; Dendale, P.; Nchimi, A. Image quality in coronary CT angiography: Challenges and technical solutions. Br. J. Radiol. 2017, 90, 20160567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Qin, T.; Sun, Q.; Wang, M.; Liang, B. A Review of Factors Affecting Radiation Dose and Image Quality in Coronary CTA Performed with Wide-Detector CT. Tomography 2024, 10, 1730–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, K.A.; McEntee, M.F.; Reed, W.; Kench, P.L. Radiation dose and diagnostic image quality associated with iterative reconstruction in coronary CT angiography: A systematic review. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 60, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, D.C.; Ersözlü, S.; Mojon, F.L.A.; Messerli, M.; Mitulla, A.K.; Ciancone, D.; Kenkel, D.; Schaab, J.A.; Gebhard, C.; Pazhenkottil, A.P.; et al. Radiation dose reduction with deep-learning image reconstruction for coronary computed tomography angiography. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 2620–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caryl, E.R.; Daniel, R.O. Low-Dose Radiation Advances in Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography in the Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2019, 15, 304–315. [Google Scholar]
- Mihl, C.; Maas, M.; Turek, J.; Seehofnerova, A.; Leijenaar, R.T.; Kok, M.; Lobbes, M.B.I.; Wildberger, J.E.; Das, M. Contrast Media Administration in Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography—A Systematic Review. In RöFo-Fortschritte auf dem Gebiet der Röntgenstrahlen und der Bildgebenden Verfahren; Georg Thieme Verlag KG: Stuttgart, Germany, 2017; Volume 189, pp. 312–325. [Google Scholar]
- Mazloumi, M.; Van Gompel, G.; Tanaka, K.; Argacha, J.-F.; de Mey, J.; Buls, N. The impact of iodine contrast agent on radiation dose of heart and blood: A comparison between coronary CT angiography and cardiac calcium scoring CT. Acta Radiol. 2023, 64, 2387–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottinor, W.; Polkampally, P.; Jovin, I. Adverse reactions to iodinated contrast media. Int. J. Angiol. 2013, 22, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, A.; Pacek, G.; Mrozik, A. Transformation and ecotoxicological effects of iodinated X-ray contrast media. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2020, 19, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdun, F.R.; Racine, D.; Ott, J.G.; Tapiovaara, M.J.; Toroi, P.; Bochud, F.O.; Veldkamp, W.J.H.; Schegerer, A.; Bouwman, R.W.; Giron, I.H.; et al. Image quality in CT: From physical measurements to model observers. Phys. Medica 2015, 31, 823–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharara, S.M.; Monnin, S.R.; Rubio, M.; Khouzam, R.N.; Ragheb, S.R. Can Radiation Dose Burden of CT Angiography be Reduced While Still Accurately Diagnosing Etiology of Acute Chest Pain? Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2021, 46, 100766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, K.; Ichikawa, K.; Hara, M.; Kawai, T.; Kunitomo, H.; Higashide, R.; Shibamoto, Y. Examination of the optimal temporal resolution required for computed tomography coronary angiography. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2013, 6, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Achenbach, S.; Manolopoulos, M.; Schuhbäck, A.; Ropers, D.; Rixe, J.; Schneider, C.; Krombach, G.A.; Uder, M.; Hamm, C.; Daniel, W.G. Influence of heart rate and phase of the cardiac cycle on the occurrence of motion artifact in dual-source CT angiography of the coronary arteries. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2012, 6, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, W.Y.; Huang, G.L.; Yang, C.C. Effect of Body Mass Index in Coronary CT Angiography Performed on a 256-Slice Multi-Detector CT Scanner. Diagnosis 2022, 12, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, T.J.; Bull, R.; Buls, N.; Leipsic, J.; Chow, B.; Maurovich-Horvat, P.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Bax, J.J.; Andreini, D.; Chen, M.Y. Contrast agent volume for coronary computed tomography angiography imaging in current clinical practice. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2022, 16, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cademartiri, F.; Maffei, E.; Palumbo, A.A.; Malagò, R.; La Grutta, L.; Meiijboom, W.B.; Aldrovandi, A.; Fusaro, M.; Vignali, L.; Menozzi, A. Influence of intra-coronary enhancement on diagnostic accuracy with 64-slice CT coronary angiography. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Du, X.; Yang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Li, P.; Liao, J.; Li, K. 64-MDCT Coronary Angiography: Phantom Study of Effects of Vascular Attenuation on Detection of Coronary Stenosis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 191, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, K.T.; Seeck, B.A.; Hildebolt, C.F.; Tao, C.; Zhu, F.; Kanematsu, M.; Woodard, P.K. Contrast enhancement in cardiovascular MDCT: Effect of body weight, height, body surface area, body mass index, and obesity. AJR. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 190, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, S.; Utsunomiya, D.; Nakaura, T.; Kidoh, M.; Funama, Y.; Tsujita, K.; Yamashita, Y. Basic Concepts of Contrast Injection Protocols for Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2019, 15, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, S.P.; Moloney, F.; Twomey, M.; James, K.; O’Connor, O.J.; Maher, M.M. Computed tomography and patient risk: Facts, perceptions and uncertainties. World J. Radiol. 2016, 8, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dainiak, N. Radiation Dose and Stochastic Risk From Exposure to Medical Imaging. Chest 2013, 144, 1431–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kędzierski, B.; Macek, P.; Dziadkowiec-Macek, B.; Truszkiewicz, K.; Poręba, R.; Gać, P. Radiation Doses in Cardiovascular Computed Tomography. Life 2023, 13, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmermund, A.; Marwan, M.; Hausleiter, J.; Barth, S.; Bruder, O.; Kerber, S.; Korosoglou, G.; Leber, A.; Moshage, W.; Schröder, S.; et al. Declining radiation dose of coronary computed tomography angiography: German cardiac CT registry experience 2009–2014. Clin Res Cardiol. 2017, 106, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein, A.J.; Henzlova, M.J.; Rajagopalan, S. Estimating risk of cancer associated with radiation exposure from 64-slice computed tomography coronary angiography. JAMA 2007, 298, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.F.; Ma, K.L.; Shan, H.; Liu, T.F.; Zhao, S.Q.; Wan, Y.; Jun-Zhang; Wang, H.Q. CT Scans and Cancer Risks: A Systematic Review and Dose-response Meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, A.W.K. The “As Low As Reasonably Achievable” (ALARA) principle: A brief historical overview and a bibliometric analysis of the most cited publications. Radioprotection 2019, 54, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schicchi, N.; Fogante, M.; Palumbo, P.; Agliata, G.; Esposto Pirani, P.; Di Cesare, E.; Giovagnoni, A. The sub-millisievert era in CTCA: The technical basis of the new radiation dose approach. Radiol. Medica 2020, 125, 1024–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, N.; Ozu, H.; Kamio, S.; Fujimoto, S.; Nozaki, Y.O.; Fan, R.; Kawaguchi, Y.O.; Takamura, K.; Hiki, M.; Aikawa, T. Effect of sampling rate during dynamic myocardial CT perfusion on coronary flow reserve and ischemia analysis. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2025, 41, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, L.J.; Morin, C.E.; Browne, L.P. Coronary computed tomography angiography in children. Pediatr. Radiol. 2022, 52, 2498–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, L.J.; Olson, A.; Barker, A.J.; Mong, D.A.; Weinman, J.P.; Browne, L.P. Visualization of proximal coronary arteries on high-pitch electrocardiogram-triggered computed tomography in pediatric congenital heart disease: Effects of heart rate and body surface area. Pediatr. Radiol. 2020, 50, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balonov, M.I.; Shrimpton, P.C. Effective dose and risks from medical X-ray procedures. Ann. ICRP 2012, 41, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meer, A.B.; Basu, P.A.; Baker, L.C.; Atlas, S.W. Exposure to ionizing radiation and estimate of secondary cancers in the era of high-speed CT scanning: Projections from the Medicare population. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2012, 9, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, A.B.; Mørup, S.D.; Andersen, T.R.; Mohamed, R.A.; Lambrechtsen, J. Is There Any Improvement in Image Quality in Obese Patients When Using a New X-ray Tube and Deep Learning Image Reconstruction in Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography? Life 2022, 12, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, N.M.; Mahfouz, A.; Achkar, K.; Rafie, I.M.; Hajar, R. Contrast-induced Nephropathy. Heart Views 2013, 14, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, H.S.; Morcos, S.K. Contrast media and the kidney: European Society of Urogenital Radiology (ESUR) Guidelines. Br. J. Radiol. 2014, 76, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerlocher, M.O.; Asch, M.; Myers, A. Allergic-type reactions to radiographic contrast media. CMAJ 2010, 182, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cauteren, T.; Honoria Da Silva, E.; Van Gompel, G.; Kersemans, V.; Sermon, K.; de Mey, J.; Buls, N. Iodine Dose of Administered Contrast Media Affects the Level of Radiation-Induced DNA Damage During Cardiac CT Scans. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 213, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cauteren, T.; Tanaka, K.; Belsack, D.; Van Gompel, G.; Kersemans, V.; Jochmans, K.; Droogmans, S.; de Mey, J.; Buls, N. Potential increase in radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks with higher doses of iodine contrast during coronary CT angiography. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 7526–7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, H.M.; Stroomberg, G.J.; Prokop, M. Tackling the increasing contamination of the water supply by iodinated contrast media. Insights Imaging 2022, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeppel, D.R.; Boehm, I.B. Shortage of iodinated contrast media: Status and possible chances—A systematic review. Eur. J. Radiol. 2023, 164, 110853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Hornia Pérez, E.; Carnelli, C.; Gutierrez, P.A.; González Sánchez, R.; Mesa Quesada, J. Future challenges of contrast media in radiology. Radiología 2024, 66, S41–S132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhailiy, A.B.; Ekpo, E.U.; Kench, P.L.; Ryan, E.A.; Brennan, P.C.; McEntee, M. The associated factors for radiation dose variation in cardiac CT angiography. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20180793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.K.; Yeong, C.H.; Raja Aman, R.R.A.; Ng, K.H.; Abdul Aziz, Y.F.; Chee, K.H.; Sun, Z. Low tube voltage prospectively ECG-triggered coronary CT angiography: A systematic review of image quality and radiation dose. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20170874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lu, H.; Wen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Shuai, T.; You, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liao, K.; Lu, C.; Li, J. Reducing both radiation and contrast doses for overweight patients in coronary CT angiography with 80-kVp and deep learning image reconstruction. Eur. J. Radiol. 2023, 161, 110736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Diao, K.; Wen, Y.; Shuai, T.; You, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liao, K.; Lu, C.; Yu, J.; He, Y. High-strength deep learning image reconstruction in coronary CT angiography at 70-kVp tube voltage significantly improves image quality and reduces both radiation and contrast doses. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 2912–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, B.; Hein, F.; Meyer, T.; Hadamitzky, M.; Martinoff, S.; Schömig, A.; Hausleiter, J. Impact of a reduced tube voltage on CT angiography and radiation dose: Results of the PROTECTION I study. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2009, 2, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, H.; Leipsic, J.A.; Indraratna, P.; Gulsin, G.; Khasanova, E.; Tzimas, G.; Lin, F.Y.; Shaw, L.J.; Lee, S.E.; Andreini, D. Association of Tube Voltage With Plaque Composition on Coronary CT Angiography: Results From PARADIGM Registry. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 14, 2429–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UK Health Security Agency Diagnostic Radiology: National Diagnostic Reference Levels (NDRLs) 2024. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/diagnostic-radiology-national-diagnostic-reference-levels-ndrls/ndrl (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Sun, Z.; Ng, K.-H. Prospective versus retrospective ECG-gated multislice CT coronary angiography: A systematic review of radiation dose and diagnostic accuracy. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, e94–e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.; Learner, R.; Eggleton, S.; Lambros, J.; Friedman, D. Marked reduction of effective radiation dose in patients undergoing CT coronary angiography using prospective ECG gating. Heart Lung Circ. 2011, 20, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünal, E.; Yıldız, A.E.; Güler, E.; Karcaaltıncaba, M.; Akata, D.; Kılınçer, A.; Atlı, E.; Topçuoğlu, M.; Hazırolan, T. Comparison of image quality and radiation dose between prospectively ECG-triggered and retrospectively ECG-gated CT angiography: Establishing heart rate cut-off values in first-generation dual-source CT. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2015, 15, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.; Wang, L.; Lyu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Liu, J. Evaluation of image quality on low contrast media with deep learning image reconstruction algorithm in prospective ECG-triggering coronary CT angiography. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2024, 40, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Mi, H.; Shi, X.; Li, W.; Guo, S.; Wang, P.; Suo, H.; Wang, Z.; Jin, S.; Yan, F. Higher Iodine Concentration Enables Radiation Dose Reduction in Coronary CT Angiography. Acad. Radiol. 2021, 28, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.H.; Lu, B.; Gao, J.B.; Li, P.L.; Sun, K.; Wu, Z.F.; Yang, W.J.; Zhang, X.Q.; Zheng, M.W.; McQuiston, A.D. Effect of reduced x-ray tube voltage, low iodine concentration contrast medium, and sinogram-affirmed iterative reconstruction on image quality and radiation dose at coronary CT angiography: Results of the prospective multicenter REALISE trial. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2015, 9, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekharan, R.; Kulkarni, C.B.; Pullara, S.K.; Moorthy, S. Does Contrast Dose Based in Lean body Weight Allow Lesser Volumes on High BMI Patients for CT Angiography? J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2021, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Hu, X.; Zou, X.; Zhu, D.; Li, Z.; Hu, D. Did low tube voltage CT combined with low contrast media burden protocols accomplish the goal of “double low” for patients? An overview of applications in vessels and abdominal parenchymal organs over the past 5 years. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2016, 70 (Suppl. S9B), B5–B15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannu, H.K.; William Alvarez, J.; Fishman, E.K. β-Blockers for Cardiac CT: A Primer for the Radiologist. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2006, 186 (Suppl. S2), S5–S341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabarudin, A.; Sun, Z. Beta-blocker administration protocol for prospectively ECG-triggered coronary CT angiography. World J. Cardiol. 2013, 5, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Bachour, K.; Suleiman, A.M.; Roberts, J.S.; Sayed, S.; Cho, G.W. Enhancing coronary artery plaque analysis via artificial intelligence-driven cardiovascular computed tomography. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2024, 18, 17539447241303399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.R.; Ong, C.C.; Chai, P.; Teo, L.L.S. Comparison of radiation dose, contrast enhancement and image quality of prospective ECG-Gated CT coronary angiography: Single versus dual source CT. Radiology 2021, 27, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrni, G.; Boccalini, S.; Lacombe, H.; de Oliveira, F.; Houmeau, A.; Francart, F.; Villien, M.; Rotzinger, D.C.; Robert, A.; Douek, P. Ultra-high-resolution 40 keV virtual monoenergetic imaging using spectral photon-counting CT in high-risk patients for coronary stenoses. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 35, 3042–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, O.; Yanagawa, M.; Hata, A.; Kikuchi, N.; Miyata, T.; Tsukagoshi, S.; Uranishi, A.; Tomiyama, N. Influence of gantry rotation time and scan mode on image quality in ultra-high-resolution CT system. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 103, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smettei, O.A.; Sayed, S.; Al Habib, A.M.; Alharbi, F.; Abazid, R.M. Ultra-fast, low dose high-pitch (FLASH) versus prospectively-gated coronary computed tomography angiography: Comparison of image quality and patient radiation exposure. J. Saudi Heart Assoc. 2018, 30, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrni, G.; Gullo, G.; Touray, A.; Fournier, S.; Jouannic, A.-M.; Lu, H.; Racine, D.; Muller, O.; Pozzessere, C.; Qanadli, S.D. Investigating the Influence of High-Speed Gantry Rotation in Cardiac CT on Motion Artifacts in Aortic Stenosis Patients Not Premedicated with β-Blockers: The FAST-CCT Randomized Trial Protocol. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, Y.; Ichikawa, K.; Fujimura, I.; Hara, T.; Hoshino, T.; Niwa, S.; Funahashi, M. Comparative evaluation of image quality among different detector configurations using area detector computed tomography. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2018, 11, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madaj, P.; Li, D.; Nakanishi, R.; Andreini, D.; Pontone, G.; Conte, E.; Hamilton-Craig, C.; Nimmagadda, M.; Kim, N.; Fatima, B. Lower Radiation Dosing in Cardiac CT Angiography: The CONVERGE Registry. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2020, 48, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, L.L.; Schoepf, U.J.; Meinel, F.G.; Nance, J.W.; Bastarrika, G.; Leipsic, J.A.; Paul, N.S.; Rengo, M.; Laghi, A.; De Cecco, C.N. State of the Art: Iterative CT Reconstruction Techniques. Radiology 2015, 276, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoum, C.; Blanke, P.; Leipsic, J. Iterative reconstruction in cardiac CT. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2015, 9, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Harder, A.M.; Willemink, M.J.; De Ruiter, Q.M.; De Jong, P.A.; Schilham, A.M.; Krestin, G.P.; Leiner, T.; Budde, R.P. Dose reduction with iterative reconstruction for coronary CT angiography: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20150068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koetzier, L.R.; Mastrodicasa, D.; Szczykutowicz, T.P.; van der Werf, N.R.; Wang, A.S.; Sandfort, V.; van der Molen, A.J.; Fleischmann, D.; Willemink, M.J. Deep Learning Image Reconstruction for CT: Technical Principles and Clinical Prospects. Radiology 2023, 306, e221257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulizia, M.; Alamo, L.; Alemán-Gómez, Y.; Cherpillod, T.; Mandralis, K.; Chevallier, C.; Tenisch, E.; Viry, A. Gated cardiac CT in infants: What can we expect from deep learning image reconstruction algorithm? J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2024, 18, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Nishii, T.; Umehara, K.; Ota, J.; Ohta, Y.; Fukuda, T.; Ishida, T. Deep learning-based noise reduction for coronary CT angiography: Using four-dimensional noise-reduction images as the ground truth. Acta Radiol. 2023, 64, 1831–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanblatt, E.; Rajendran, K.; Swicklik, J.R.; Allmendinger, T.; Schmidt, B.; Flohr, T.; McCollough, C.H.; Leng, S. Simultaneous ultra-high resolution multi-energy cardiac imaging in a dual-source photon counting detector CT system. Br. J. Radiol. 2025, tqaf069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotzinger, D.C.; Si-Mohamed, S.A.; Yerly, J.; Boccalini, S.; Becce, F.; Boussel, L.; Meuli, R.A.; Qanadli, S.D.; Douek, P.C. Reduced-iodine-dose dual-energy coronary CT angiography: Qualitative and quantitative comparison between virtual monochromatic and polychromatic CT images. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 7132–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemink, M.J.; Persson, M.; Pourmorteza, A.; Pelc, N.J.; Fleischmann, D. Photon-counting CT: Technical Principles and Clinical Prospects. Radiology 2018, 289, 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartoretti, T.; Wildberger, J.E.; Flohr, T.; Alkadhi, H. Photon-counting detector CT: Early clinical experience review. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 96, 20220544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flohr, T.; Schmidt, B.; Ulzheimer, S.; Alkadhi, H. Cardiac imaging with photon counting CT. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 96, 20230407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si-Mohamed, S.A.; Boccalini, S.; Lacombe, H.; Diaw, A.; Varasteh, M.; Rodesch, P.-A.; Dessouky, R.; Villien, M.; Tatard-Leitman, V.; Bochaton, T. Coronary CT Angiography with Photon-counting CT: First-In-Human Results. Radiology 2022, 303, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrni, G.; Boccalini, S.; Mahmoudi, A.; Lacombe, H.; Houmeau, A.; Elbaz, M.; Rotzinger, D.; Villien, M.; Bochaton, T.; Douek, P. Quantification of Coronary Artery Stenosis in Very-High-Risk Patients Using Ultra-High Resolution Spectral Photon-Counting CT. Investig. Radiol. 2025, 60, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajiah, P.S.; Dunning, C.A.S.; Rajendran, K.; Tandon, Y.K.; Ahmed, Z.; Larson, N.B.; Collins, J.D.; Thorne, J.; Williamson, E.; Fletcher, J.G. High-Pitch Multienergy Coronary CT Angiography in Dual-Source Photon-Counting Detector CT Scanner at Low Iodinated Contrast Dose. Investig. Radiol. 2023, 58, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ye, Z.; Chen, J.; Deng, L.; Song, B. Photon Counting CT: Technical Principles, Clinical Applications, and Future Prospects. Acad. Radiol. 2023, 30, 2362–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cundari, G.; Deilmann, P.; Mergen, V.; Ciric, K.; Eberhard, M.; Jungblut, L.; Alkadhi, H.; Higashigaito, K. Saving Contrast Media in Coronary CT Angiography with Photon-Counting Detector CT. Acad. Radiol. 2024, 31, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrolinska, M.M.; van der Werf, N.R.; van der Bie, J.; de Groen, J.; Dijkshoorn, M.; Booij, R.; Budde, R.P.J.; Greuter, M.J.W.; van Straten, M. Radiation dose optimization for photon-counting CT coronary artery calcium scoring for different patient sizes: A dynamic phantom study. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 4668–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehran, R.; Nikolsky, E. Contrast-induced nephropathy: Definition, epidemiology, and patients at risk. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, S5–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
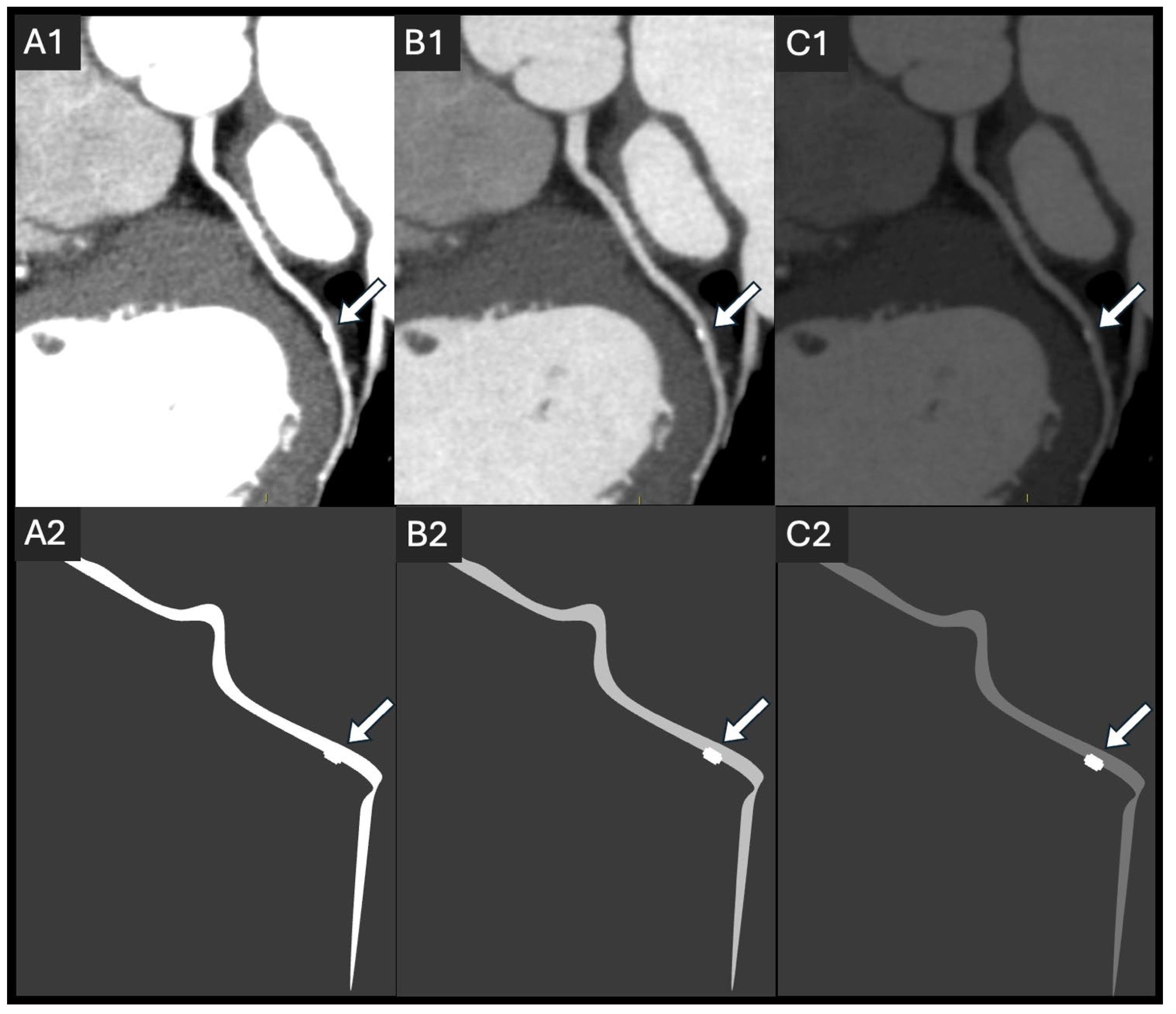
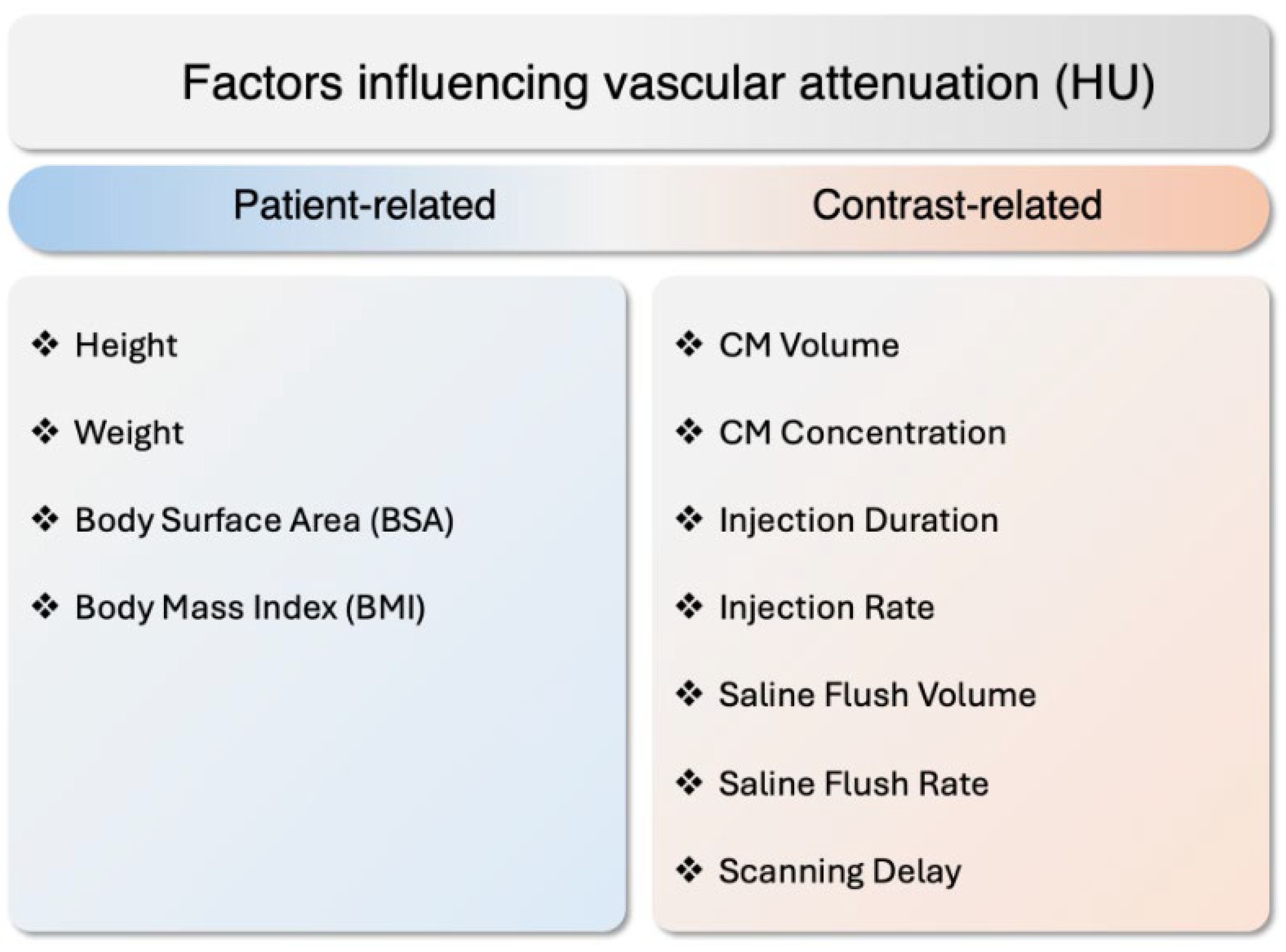
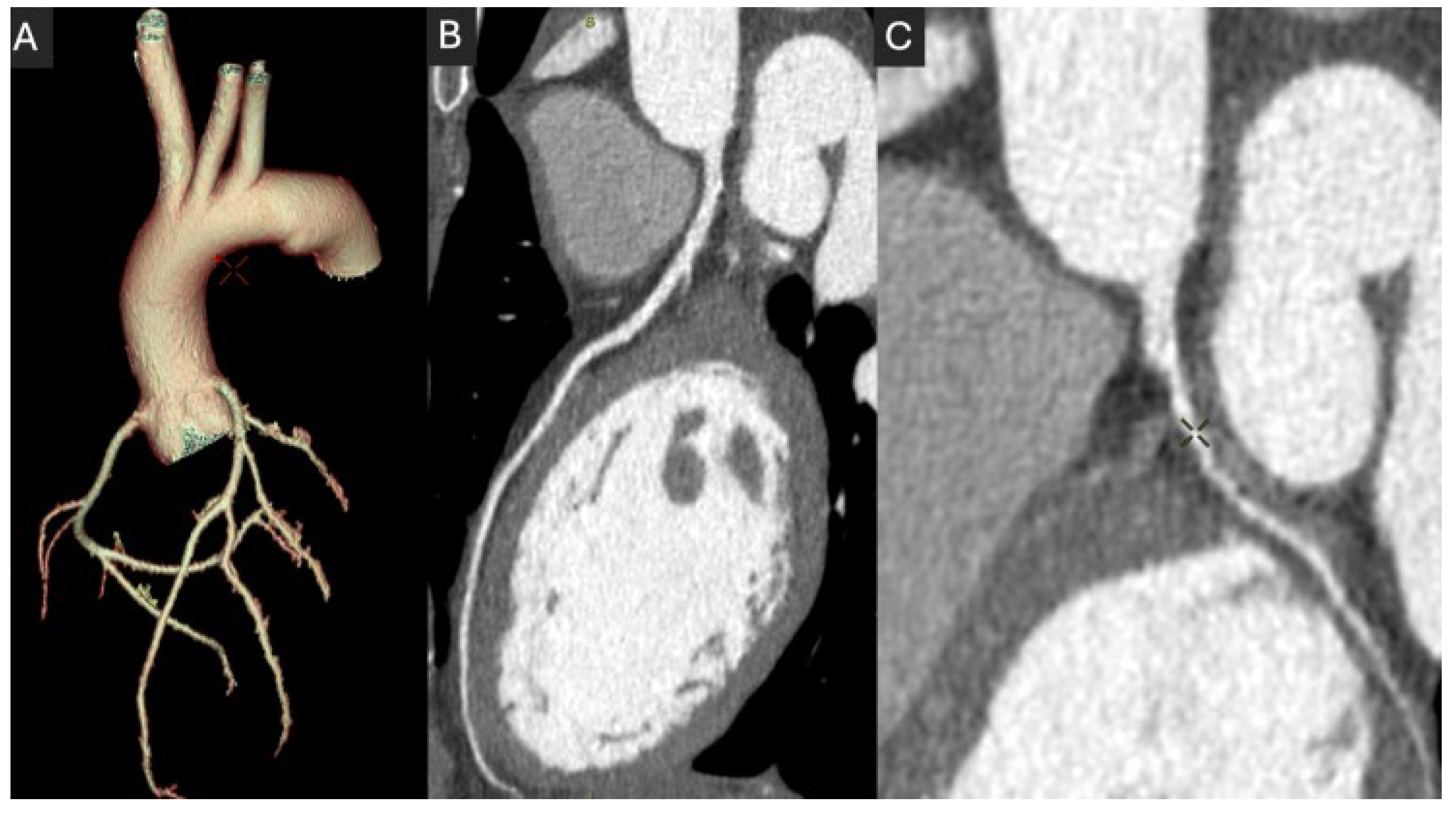
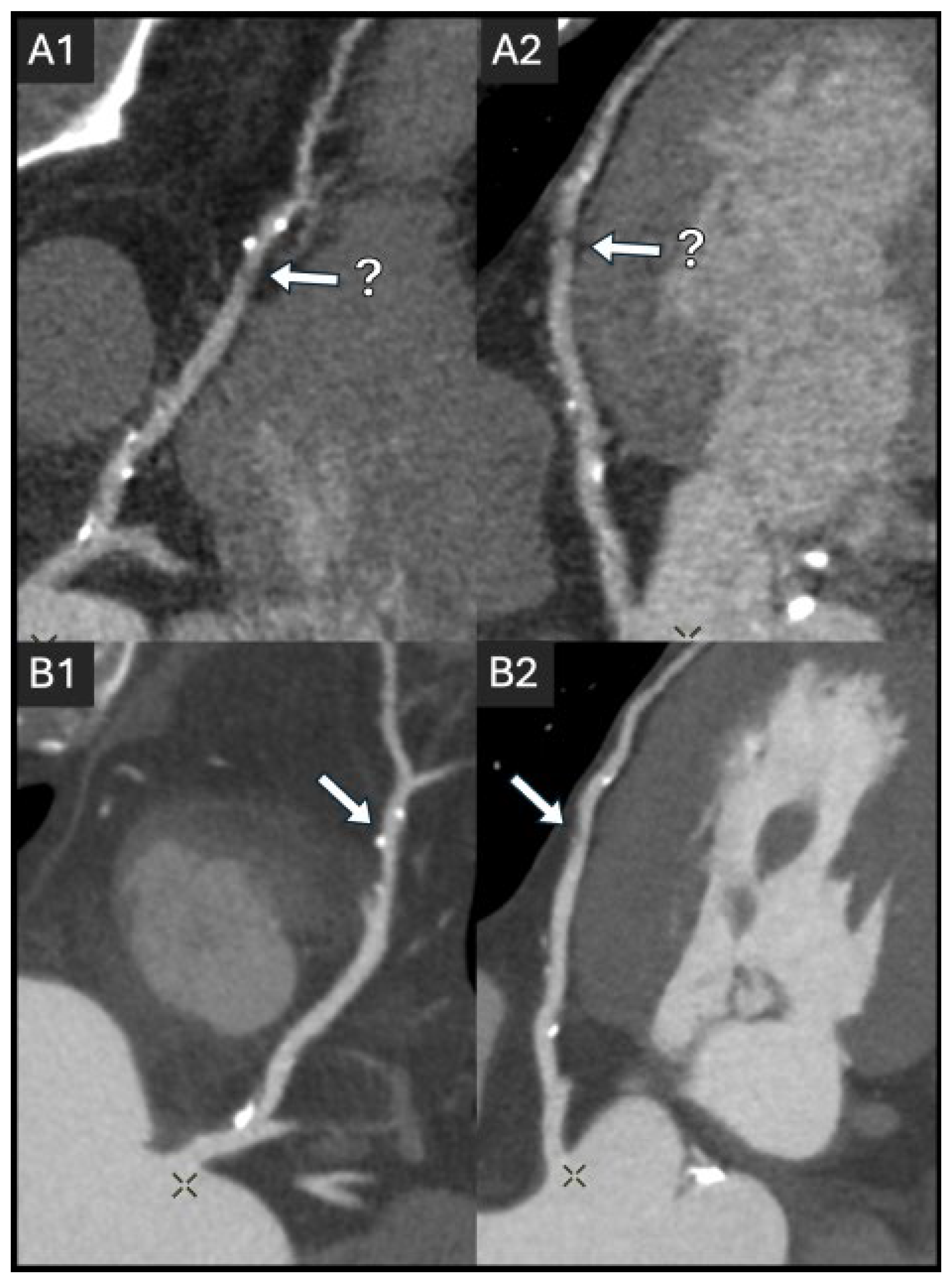
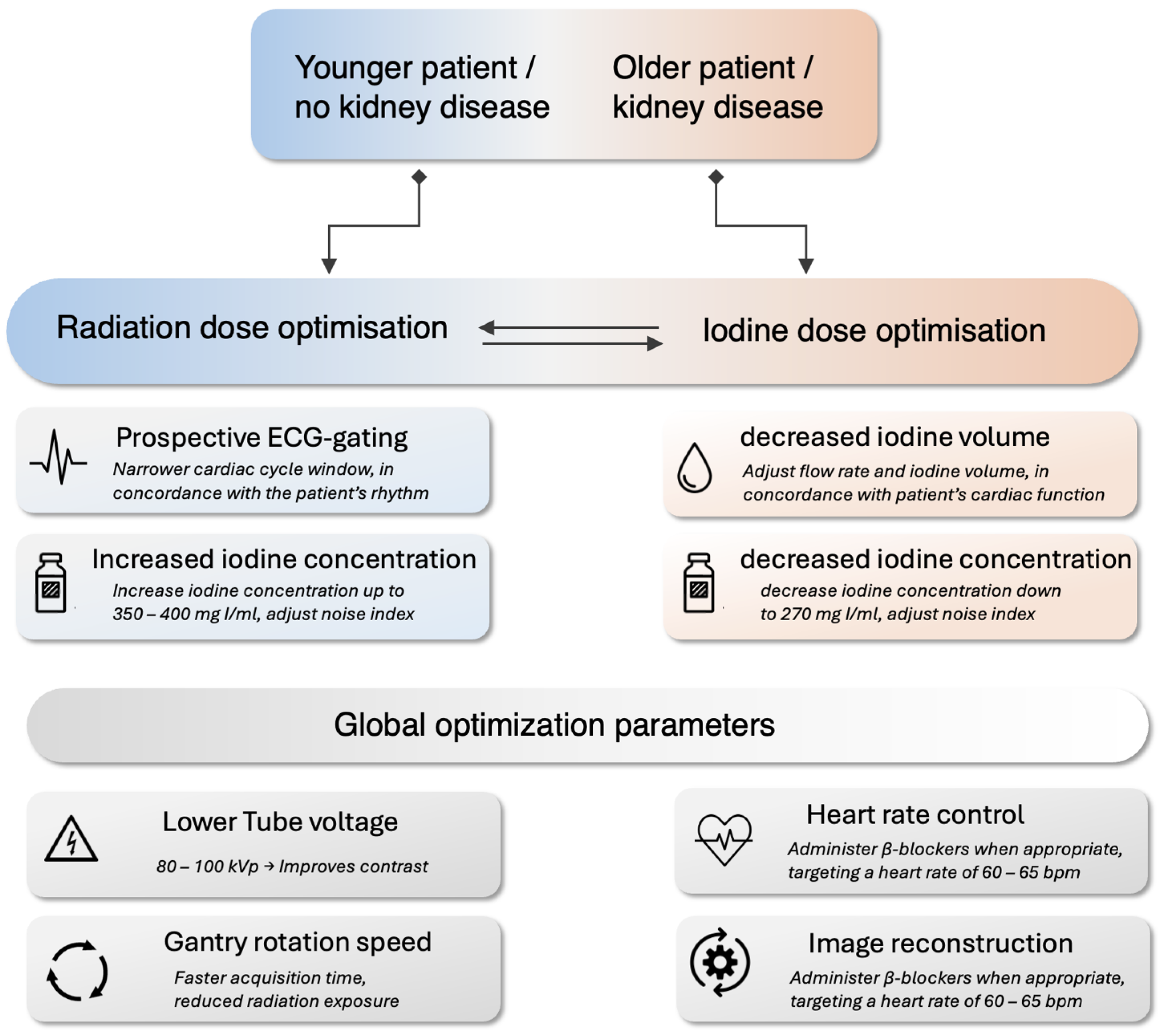
| Description | Key Benefits | |
|---|---|---|
| Current Techniques | ||
| Tube Voltage (kVp) | Lowering the tube voltage to 80 kVp (70 kVp in children) or 100 kVp. | Reduces radiation dose and enhances contrast-to-noise ratio. |
| Prospective ECG-gating | A technique where image acquisition is synchronized with the R-wave, enabling a defined window in the cardiac cycle. | Significant reduction in radiation dose compared to retrospective gating. |
| Iodine Concentration | Adjusting iodine concentration and/or flow rate. | Increasing iodine concentration or flow rate enhances image contrast, thereby improving lesion detectability. Can reduce radiation exposure and effective dose. Conversely, lowering it can reduce iodine volume with minimal quality loss. |
| Heart Rate Control | Use of β-blockers to lower heart rate. | Reduces motion artifacts, improves image quality, and minimizes radiation exposure thanks to shorter exposure time and fewer repeat scans. |
| Emerging Techniques | ||
| Gantry Rotation Speed | Faster gantry rotation speeds. | Faster acquisition times, reduced radiation exposure, and reduced motion artifacts. |
| Detector Size | Larger detector sizes (e.g., 256 or 320 rows). | Enhance spatial and temporal resolution and reduce radiation exposure. |
| Iterative Reconstruction | Enable reduction in pixel noise standard deviation. | Enable a reduction in mA during image acquisition, thereby lowering the required radiation dose and maintaining similar image quality compared to filtered back-projection (FBP). |
| Deep-Learning Reconstruction (DLR) | Uses artificial intelligence to reduce noise, improving image quality. | This algorithm leads to a decrease in radiation dose by decreasing mA during acquisition while maintaining a similar noise texture to FBP. |
| Photon-Counting CT (PCCT) | A new technology that directly measures individual X-ray photon energies. | High spatial resolution, reduced noise, lower radiation doses, improved soft tissue differentiation, and better plaque characterization in CCTA. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fahrni, G.; Saliba, T.; Racine, D.; Gulizia, M.; Tzimas, G.; Pozzessere, C.; Rotzinger, D.C. Trading off Iodine and Radiation Dose in Coronary Computed Tomography. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12050195
Fahrni G, Saliba T, Racine D, Gulizia M, Tzimas G, Pozzessere C, Rotzinger DC. Trading off Iodine and Radiation Dose in Coronary Computed Tomography. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2025; 12(5):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12050195
Chicago/Turabian StyleFahrni, Guillaume, Thomas Saliba, Damien Racine, Marianna Gulizia, Georgios Tzimas, Chiara Pozzessere, and David C. Rotzinger. 2025. "Trading off Iodine and Radiation Dose in Coronary Computed Tomography" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 12, no. 5: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12050195
APA StyleFahrni, G., Saliba, T., Racine, D., Gulizia, M., Tzimas, G., Pozzessere, C., & Rotzinger, D. C. (2025). Trading off Iodine and Radiation Dose in Coronary Computed Tomography. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 12(5), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12050195









