Abstract
We evaluated the association between cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) time during surgery for acute type A aortic dissection (ATAAD) and mid-term survival. Data of 1122 patients who underwent surgery for ATAAD in eight Nordic centers from January 2005 to December 2014 were retrospectively analyzed. An adjusted logistic regression analysis was performed to investigate the association of incremental 30 min CPB time on 30-day mortality. In addition, the patients were divided into those that underwent surgery with >210 min (n = 369) or <210 min CPB time (n = 605) based on spline analysis and a receiver operating characteristic curve. The restricted mean survival time ratios adjusted for patient characteristics and surgical details between the groups were calculated for survival and aortic reoperation-free survival. The median follow-up time was 2.6 (inter-quartile range 0.9–4.9) years. Incremental CPB time was associated with higher 30-day mortality (OR 1.25 per 30 min, 95% CI 1.15–1.35, p < 0.001). Mid-term survival for all patients was inferior in the >210 min group as compared with the <210 min group (adjusted restricted mean survival time ratio 0.88, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.81–0.96, p = 0.003). Reoperation-free survival was similar in patients with CPB time > 210 min as compared with <210 min. Prolonged CPB time is associated with higher 30-day mortality and inferior mid-term survival but not with inferior reoperation-free survival after surgical repair of ATAAD.
1. Introduction
Acute type A aortic dissection (ATAAD) is a complex cardiovascular event associated with high mortality. In a population-based study, it was found that almost half of ATAAD patients die before reaching the hospital, and early mortality is up to 47.5% for patients that reach the hospital alive [1].
The immediate aim of surgery for ATAAD is to prevent fatal aortic rupture and cardiac tamponade and to secure blood circulation to the heart and essential organs such as the brain. Surgically, the simplest procedure is the replacement of the supracommissural ascending aorta, but more extensive aortic surgery involving the aortic root and the aortic arch is sometimes required [2]. In addition, concomitant coronary artery bypass grafting and valve surgery may be required, depending on the complexity of the acute disease. Furthermore, the preferences of the surgeon and the possible unplanned events at surgery such as bleeding, myocardial ischemia and valve regurgitation influence the procedure. The extent of aortic repair required has been a matter of extensive discussion [3,4,5]. The decision to limit or choose extended aortic repair is a compromise between increasing the chance of immediate survival and relieving malperfusion, but this is at the possible expense of increasing the risk of late complications including reoperations.
In all complex surgical procedures, the duration of surgery is a common denominator for many technical and patient-related factors that must be considered during ATAAD repair. Previous studies, including aortic surgery, suggest that CPB time influences early outcome, including 30-day mortality [6,7,8,9,10,11]. Although survival after surgery for ATAAD is improving in general, the association of duration of surgery on early and mid-term survival and the incidence of reoperations are less well studied [12]. This study therefore aims to examine the association of CPB time with outcome in ATAAD patients using the Nordic Consortium for Acute Type A Aortic Dissection (NORCAAD) registry. We hypothesize that CPB time for ATAAD, which reflects the surgical strategy in patients with ATAAD but also the extent and severity of the dissection and perioperative complications, is associated with 30-day mortality, mid-term survival and reoperation-free survival.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
The institutional review boards of each participating center have approved the study protocol. Locally, the study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Tampere (ETL R15504/1.1.2015). Due to the retrospective nature of the study, the need for informed consent was waived.
2.2. Patients
The NORCAAD project involves eight tertiary care cardiac surgery units in four Nordic countries (Denmark, Finland, Iceland and Sweden). The NORCAAD register encompasses all patients that have undergone surgery for ATAAD in the study hospitals within the study period from 1 January 2005 until 31 December 2014, resulting in a total of 1122 patients with onset of symptoms leading to surgery for ATAAD in less than 2 weeks; eighty-three per cent of the patients had symptoms in less than 48 h before surgery (Supplementary Figure S1). A detailed description of the NORCAAD register has been published previously [13].
Altogether, 974 patients with recorded CPB time and complete follow-up data were included in the analysis. CPB time was determined as the total time spent from the onset of CPB till the end of weaning from CPB. There were 148 (13.2%) patients with missing data on CPB (n = 98, 8.8%) or follow-up (n = 50, 4.5%).
2.3. Main Outcome Measures
The primary endpoints were 30-day mortality and mid-term survival. The secondary endpoints were perioperative stroke and aortic reoperation-free survival. The definition of postoperative stroke encompassed new neurological symptoms after surgery associated with cerebral infarction or intracerebral hemorrhage. Aortic reoperation was defined as any late open aortic or aortic valve surgery after the index hospitalization.
2.4. Statistical Methods
Continuous variables are reported as means and standard deviations (SDs) or medians and inter-quartile ranges when non-normally distributed. Associations of CPB time with 30-day mortality, reoperation and postoperative stroke were examined by unadjusted univariable logistic regression analyses and multivariable logistic regression analyses adjusted by potential confounding variables. The covariates were selected according to previous knowledge of causal relationships (Supplementary Figure S2) and included aortic root surgery (yes/no), aortic arch surgery (yes/no), open distal anastomosis (yes/no), use of antegrade/retrograde cerebral perfusion (yes/no), additional coronary artery bypass (yes/no), ongoing antithrombotic medication (yes/no), previous cardiac surgery (yes/no), patient age (continuous) and body mass index (BMI; continuous). Odds ratios (OR) for each outcome were reported for every 30 min increase in CPB time.
To identify factors associated with extended CPB time, the patients were divided into two groups according to probability of 30-day mortality by CPB time using restricted cubic spline analysis [14]. The culprit cut-off time point of increased 30-day mortality was determined by maximizing the Youden index after spline smoothing, and a receiver operating characteristic curve was performed [15]. Patient characteristics, clinical findings and surgical details were compared between the groups using an independent samples t-test for continuous variables and a chi-squared test for categorical variables. Kaplan–Meier curves presenting survival and reoperation-free survival were calculated for the groups. The stability of the Kaplan–Meier estimates was ensured by restricting the follow-up time at the last year with the number of patients at risk including over 10% of the total patient count in the groups, resulting in a maximum follow-up time of 6 years. The groups were compared by a log-rank test. Further, restricted mean survival time (RMST) estimates along with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated for the 6-year follow-up time and compared between the CPB time groups [16,17]. The RMST estimate represents population averages of the amount of event-free survival time during the follow-up period. Crude and adjusted estimates were calculated. Covariates included in the adjusted analyses were the same as in the logistic regression. Subgroup analyses were separately performed among patients with only ascending aortic surgery and patients with only aortic root surgery. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed using R (4.0.3) statistical software.
3. Results
3.1. Patients
The majority of the patients were male (67.4%), and the mean age was 61.0 (SD 12.1) years (Table 1).

Table 1.
Patient characteristics.
The median follow-up time was 2.7 (IQR 0.6–5.3) years. The total accumulated follow-up was 3169 patient-years with a minimum follow-up of one day and a maximum of 10 years. In 681 (69.9%) patients, surgery involved the ascending aorta only (Table 2).

Table 2.
Operation characteristics in all patients.
The aortic root was operated on in 243 (24.9%) patients, whereas surgery included total aortic arch replacement in 51 (5.2%) patients. The median CPB time was 189 (IQR 155–234) min (Table 2 and Supplementary Figure S3).
According to the adjusted logistic regression analyses (Table 3 and Supplementary Figure S4), CPB time was associated with increased 30-day mortality (OR 1.25 per 30 min, 95% CI 1.15–1.35, p < 0.001) and postoperative stroke (OR 1.17 per 30 min, 95% CI 1.08–1.26, p < 0.001, Table 3).

Table 3.
Logistic regression analysis showing associations between duration of cardiopulmonary bypass and early outcome. Odds ratios are presented as 30 min increments in cardiopulmonary bypass time.
In patients with ascending aortic surgery only and in patients with aortic root surgery only, incremental CPB time was also associated with increased 30-day mortality (OR 1.31 per 30 min, 95% CI 1.17–1.48, p < 0.001 and OR 1.17 per 30 min, 95% CI 1.01–1.36, p = 0.040), respectively. In patients with ascending aortic surgery only, CPB time was also associated with postoperative stroke (OR 1.19 per 30 min, 95% CI 1.07–1.32, p = 0.001) but not in patients with aortic root surgery only (OR 1.16 per 30 min, 95% CI 0.99–1.36, p = 0.072).
According to the spline analysis, 210 min was estimated as the cut-off time point, and a longer CPB time was associated with higher 30-day mortality (Figure 1).
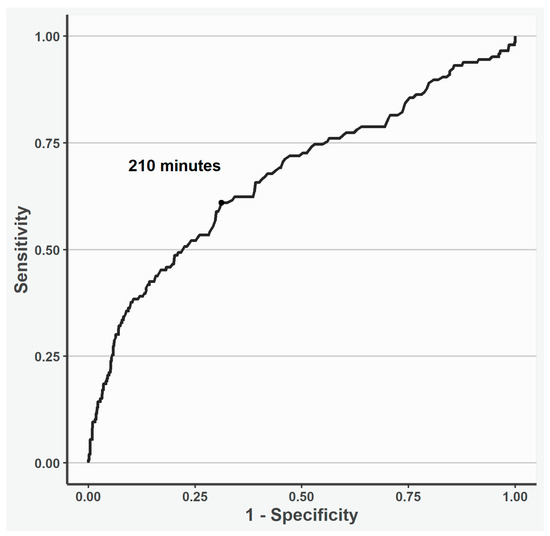
Figure 1.
Receiver operating curve of the cut-off cardiopulmonary time point investigated using restricted cubic spline analysis. According to the spline analysis, 210 min was estimated as the cut-off cardiopulmonary time point; a longer time was associated with 30-day mortality.
CPB time exceeded 210 min in 369 (37.9%) patients, whereas it remained less than 210 min in the remaining patients (n = 605, 62.1%, Table 4).

Table 4.
Preoperative and operative characteristics according to cardiopulmonary bypass time < 210 min and >210 min.
As expected, duration of surgery, aortic cross-clamp and hypothermic arrest times were increased in patients with CPB time > 210 min as compared with the <210 min group (medians: 439 min vs. 292 min, p < 0.001; 141 min vs. 77 min, p < 0.001 and 30 min vs. 25 min, p < 0.001, respectively). Among the patients with CPB time > 210 min, the proportion of male patients was higher (74.5% vs. 63.0%, p < 0.001), BMI was higher (27.4 vs. 26.3, p = 0.001), the use of antithrombotic drugs was more frequent preoperatively, both aspirin (30.6% vs. 23.0%, p = 0.010) and warfarin (7.9% vs. 4.3%, p = 0.028) were used, previous cardiac surgeries were more common (3.8% vs. 0.7%; p = 0.001), and aortic dissection was more commonly classified as DeBakey type I (77.2% vs. 70.4%, p = 0.044) as compared with patients in the <210 min group. The patients with CPB time > 210 min more often had aortic root surgery as compared with the <210 min group (n = 84, 37.9% vs. n = 140, 13.9%, p < 0.001). Total arch surgery (9.2% vs. 2.8%, p < 0.001) and concomitant coronary artery bypass grafting were more frequent in the >210 min surgery patients than in the <210 min patients (11.4% vs. 2.8%, p < 0.001).
3.2. Mid-Term Survival and Reoperation-Free Survival
The unadjusted Kaplan–Meier curves showed shorter cumulative survival if CPB time was >210 min (log-rank test p < 0.001, Figure 2).
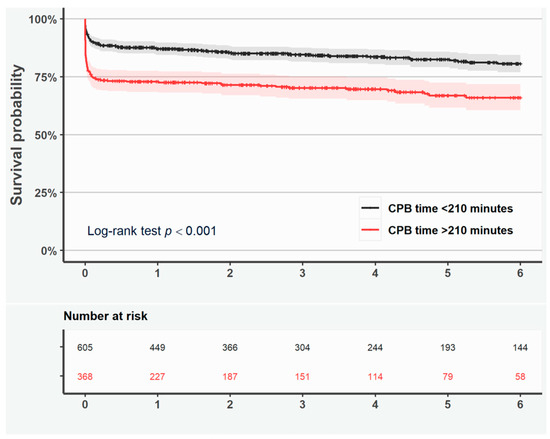
Figure 2.
Kaplan–Meier curves representing survival in all patients with duration of cardiopulmonary bypass <210 min (black line) and >210 min (red line). Shaded area represents the 95% confidence interval.
Likewise, the adjusted RMST ratio (0.88, 95% CI 0.81–0.96, p = 0.003) indicated that CPB time > 210 min was associated with shorter survival (Table 5).

Table 5.
RMST ratio estimates representing survival and reoperation-free survival in patients with duration of surgery < 210 min and >210 min.
Shorter survival was observed if the duration of surgery exceeded >210 min in patients with ascending aortic surgery only (log-rank test p < 0.001; Figure S5), but not in patients with aortic root surgery only (log-rank test p = 0.306; Figure S6). Reoperation-free survival was similar in patients with CPB time > 210 min as compared with <210 min according to the Kaplan–Meier curves and adjusted RMST ratio (Figure 3 and Table 5).
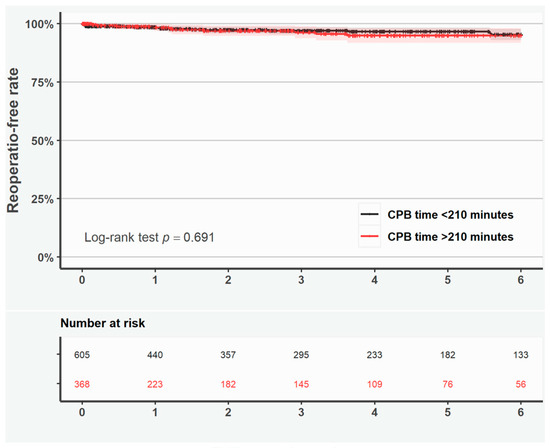
Figure 3.
Kaplan–Meier curves representing reoperation-free rate in all patients with duration of cardiopulmonary bypass <210 min (black line) and >210 min (red line). Shaded area represents the 95% confidence interval.
4. Discussion
The results of the current study demonstrate that CPB time for ATAAD is associated with an increased risk of 30-day mortality, perioperative stroke, and inferior mid-term survival.
CPB time is the product of many factors, both modifiable and non-modifiable. The current study findings indicate that protocol-driven time-consuming surgical strategies should not be implemented routinely but only after careful evaluation of short- and long-term outcomes versus surgical risk. While multifactorial in origin, CPB time appears to be a powerful predictor that could be included in future studies to help define patient and procedural characteristics and analyze outcomes. An improved understanding of the different aspects of the procedural duration associated with outcomes would, however, require a large, contemporary and prospective multi-center study with sufficiently detailed data. Modifiable factors pertinent to the outcome after surgery for ATAAD need to be explored in detail. Such a prospective study is currently underway in the ongoing NORCAAD 2.0 study. Extensive and additional surgical procedures during complex ATAAD repair increase CPB time, but the duration of surgery also reflects the patient’s condition, the extent and severity of the dissection, and perioperative complications including bleeding and malperfusion, as well as the surgeon’s experience [18]. Extensive resection of the aorta and indispensable additional procedures, such as coronary artery bypass grafting, may result in an increased hypothermic circulatory arrest time and/or CPB time, which are both associated with increased 30-day mortality.
By using cubic spline graphs, a cut-off of 210 min was identified to categorize a culprit prolonged CPB time with regards to increased 30-day mortality. Inferior mid-term survival was mainly attributed to the increased 30-day mortality in patients with CPB time > 210 min as compared with <210 min. However, there was no reoperation-free survival difference between the groups, as aortic replacement was performed in the patients according to the extension of the aortic dissection. On the other hand, there were only 5.3% total arch reconstructions, even though 73% of the patients had type I DeBakey ATAAD; long-term follow-up of the patients is warranted.
ATAAD is an emergency requiring immediate surgery in patients with varying pathology and fluctuating symptoms. Indeed, the NORCAAD cohort includes patients with surgery mostly performed in less than 48 h after onset of symptoms. Insufficient knowledge on patient characteristics, underlying aortic wall disease and several comorbidities such as history of stroke, need of coronary artery bypass grafting, previous surgery, ongoing medication, malperfusion and the presence of aortic aneurysm challenge decision making for surgical techniques, cannulation sites, specific cerebral protection methods and the extent of aortic surgery. The risk of respiratory insufficiency, infections, gastrointestinal complications, neurological dysfunction and early mortality increase in patients with prolonged CPB time [8,9,10]. It may be tempting to aim at a one-stage do-it-all reconstructive surgery, at least for a young patient, to avoid reoperations at follow-up. Still, the ultimate strategy should include safe surgery without negatively affecting immediate recovery [19,20,21,22,23].
Limitations of the Study
The main limitation of the current study is its retrospective design involving a risk of selection bias. Despite the relatively large sample size, only a few patients underwent aortic arch surgery, which ruled out subgroup analysis among these patients. Of the total patients, 13.2% were excluded due to incomplete data on CPB time or follow-up. Though increased CPB time often signifies complex surgery, many additional procedures may be necessary to secure an immediate outcome after ATAAD. Extensive surgery during ATAAD is justified in the presence of complex aortic primary tear dissection beyond the aortic arch and the aortic root and the need for additional surgery due to, e.g., significant coronary artery disease. More detailed data are needed and are currently being collected to understand the modifiable risk factors as opposed to all patient-determined characteristics during ATAAD.
5. Conclusions
The effect of patient-dependent and modifiable factors associated with ATAAD need constant evaluation. Prolonged CPB time is associated with increased complexity of ATAAD but also increased risk of 30-day mortality and inferior mid-term survival.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jcdd12040139/s1, Supplementary Figure S1: Distribution of delay from symptom onset to surgery according to patients with duration of cardiopulmonary bypass <210 min (black box) and >210 min (red box); Supplementary Figure S2: Causal relationship diagram showing rationale for covariate selection; Supplementary Figure S3: Distribution of cardiopulmonary bypass time; Supplementary Figure S4: Association between cardiopulmonary time and outcome. Lines show the probability of the outcome event with regards to cardiopulmonary time. Gray area represents 95% confidence interval. Histograms show the distributions of cardiopulmonary time with early mortality or postoperative stroke (100% probability) vs. not (0 probability). Figure S5: Kaplan–Meier curves representing survival in patients with ascending aortic surgery only with duration of cardiopulmonary bypass <210 min (black line) and >210 min (red line). Shaded area represents the 95% confidence interval. Figure S6: Kaplan–Meier curves representing survival in patients with aortic root surgery only with duration of cardiopulmonary bypass <210 min (black line) and >210 min (red line). Shaded area represents the 95% confidence interval.
Author Contributions
Concept and design: A.M.; methodology: M.U., C.O., A.J., A.G., V.H., E.C.H., I.Z., J.E., J.G., A.W., T.G. and A.M.; statistical analysis: M.U. and A.M.; acquisition, analysis or interpretation of the data: M.U., C.O., A.J., A.G., V.H., E.C.H., I.Z., J.E., J.G., A.W., T.G. and A.M.; drafting of the manuscript: M.U., C.O., A.J., I.Z. and A.M.; critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: all authors; supervision: M.U., C.O., A.J., A.G., E.C.H., I.Z., T.G. and A.M.; other—protocol review: all authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by The Competitive State Research Financing of the Expert Responsibility Area of Tampere University Hospital, the Finnish Cultural Foundation from Pirkanmaa Regional Fund (A.M.) and by a donation from Mr. Fredrik Lundberg (C.O.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the Swedish Ethical Review Authority (No. 2019-02087) on 2019-04-29, waiving the need to obtain individual written informed consent.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent for participation is not required as per local legislation (ETL R15504/1.1.2015).
Data Availability Statement
All authors had full access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. The data underlying this article will be shared upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ATAAD | Acute type A aortic dissection |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CPB | Cardiopulmonary bypass |
| IQR | Inter-quartile range |
| OR | Odds ratios |
| NORCAAD | Nordic Consortium for Acute Type A Aortic Dissection |
| RMST | Restricted mean survival time |
| SD | Standard deviation |
References
- Yamaguchi, T.; Nakai, M.; Yano, T.; Matsuyama, M.; Yoshino, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Sumita, Y.; Matsuda, H.; Inoue, Y.; Okita, Y.; et al. Population-based incidence and outcomes of acute aortic dissection in Japan. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2021, 10, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Biancari, F.; Fileccia, D.; Ferrante, L.; Mäkikallio, T.; Juvonen, T.; Jormalainen, M.; Mariscalco, G.; El-Dean, Z.; Pettinari, M.; Rodriguez Lega, J.; et al. Extent of surgical repair and outcomes after surgery for type A aortic dissection. BJS Open 2025, 10, zraf003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marco, L.; Leone, A.; Murana, G.; Castelli, A.; Alfonsi, J.; Di Bartolomeo, R.; Pacini, D. Acute type A aortic dissection: Rationale and outcomes of extensive repair of the arch and distal aorta. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 267, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Frankel, W.C.; Green, S.Y.; Orozco-Sevilla, V.; Preventza, O.; Coselli, J.S. Contemporary Surgical Strategies for Acute Type A Aortic Dissection. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 32, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jassar, A.S.; Sundt, T.M. How should we manage type A aortic dissection? Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 67, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dib, B.; Seppelt, P.C.; Arif, R.; Weymann, A.; Veres, G.; Schmack, B.; Beller, C.J.; Ruhparwar, A.; Karck, M.; Kallenbach, K. Extensive aortic surgery in acute aortic dissection type A on outcome–insights from 25 years single center experience. J. Cardiothor. Surg. 2019, 14, 187. [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann, L.O.; Hoffmann, I.; Blettner, M.; Kallenbach, K.; Karck, M.; Dapunt, O.; Borger, M.A.; Weigang, E. Analysis of risk factors for neurological dysfunction in patients with acute aortic dissection type A: Data from the German Registry for Acute Aortic Dissection type A (GERAADA). Eur. J. Cardiothor. Surg. 2012, 42, 557–565. [Google Scholar]
- Madhavan, S.; Chan, S.-P.; Tan, W.-C.; Eng, J.; Li, B.; Luo, H.-D.; Teoh, L.K. Cardiopulmonary bypass time: Every minute counts. J. Cardiovac. Surg. 2017, 59, 274–281. [Google Scholar]
- Huffmyer, J.L.; Groves, D.S. Pulmonary complications of cardiopulmonary bypass. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2015, 29, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Liu, C.; Xu, B.; Jing, H.; Li, D.; Wu, H. Postoperative abdominal complications after cardiopulmonary bypass. J. Cardiothor. Surg. 2012, 7, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann, L.O.; Weigang, E.; Mehlhorn, U.; Abugameh, A.; Hoffmann, I.; Blettner, M.; Etz, C.D.; Cherny, M.; Vahl, C.F. Mortality in patients with acute aortic dissection type A: Analysis of pre- and intraoperative risk factors from the German Registry for Acute Aortic Dissection Type A (GERAADA). Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 49, e44–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, C.; Ahlsson, A.; Fuglsang, S.; Geirsson, A.; Gunn, J.; Hansson, E.C.; Hjortdal, V.; Jarvela, K.; Jeppson, A.; Mennander, A.; et al. Medium-term survival after surgery for acute Type A aortic dissection is improving. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2017, 52, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geirsson, A.; Ahlsson, A.; Franco-Cereceda, A.; Fuglsang, S.; Gunn, J.; Hansson, E.C.; Hjortdal, V.; Jarvela, K.; Jeppson, A.; Mennander, A.; et al. The Nordic Consortium for acute type A aortic dissection (NORCAAD): Objectives and design. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2016, 50, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lusa, L.; Ahlin, C. Resticted cubic splines for modelling periodic data. PLoS ONE 2020, 28, e0241364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bantis, L.E.; Nakas, C.T.; Reiser, B. Construction of confidence regions in the ROC space after the estimation of the optimal Youden Index-based cut-off point. Biometrics 2014, 70, 212–223. [Google Scholar]
- Uno, H.; Claggett, B.; Tian, L.; Inoue, E.; Gallo, P.; Miyata, T.; Schrag, D.; Takeuchi, M.; Uyama, Y.; Zhao, L. Moving beyond the hazard ratio in quantifying the between-group difference in survival analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 2380. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, L.; Zhao, L.; Wei, L. Predicting the restricted mean event time with the subject’s baseline covariates in survival analysis. Biostatistics 2014, 15, 222–233. [Google Scholar]
- Olsson, C. Modifiable Risk Factors for Early Mortality in Low-Risk Penn Class Aa Acute Type A Aortic Dissection Patients—A Descriptive Study. Aorta 2017, 5, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, P.; Trojan, J.; Tsou, S.; Goldstone, A.B.; Woo, Y.J.; Fischbein, M.P. Limited root repair in acute type A aortic dissection is safe but results in increased risk of reoperation. J. Thor. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 155, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkers, J.A.; Bol Raap, G.; Takkenberg, J.J.; Bogers, A.J. Acute type A aortic dissection: Long-term results and reoperations. Eur. J. Cardiothor. Surg. 2013, 43, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concistrè, G.; Casali, G.; Santaniello, E.; Montalto, A.; Fiorani, B.; Dell’Aquila, A.; Musumeci, F. Reoperation after surgical correction of acute type A aortic dissection: Risk factor analysis. Ann. Thor. Surg. 2012, 93, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziganshin, B.A.; Rajbanshi, B.G.; Tranquilli, M.; Fang, H.; Rizzo, J.A.; Elefteriades, J.A. Straight deep hypothermic circulatory arrest for cerebral protection during aortic arch surgery: Safe and effective. J. Thor. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 148, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leshnower, B.G.; Myung, R.J.; Kilgo, P.D.; Vassiliades, T.A.; Vega, J.D.; Thourani, V.H.; Puskas, J.D.; Guyton, R.A.; Chen, E.P. Moderate hypothermia and unilateral selective antegrade cerebral perfusion: A contemporary cerebral protection strategy for aortic arch surgery. Ann. Thor. Surg. 2010, 90, 547–554. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).