Pilot Study Assessing the Hemodynamic Impact and Post-Exercise Hypotension Induced by High- Versus Low-Intensity Isometric Handgrip in Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Experimental Sessions
2.4. Echocardiography
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Hemodynamic Tolerability
4.2. Post-Exercise Hypotension
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IHG | Isometric handgrip |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| IHD | Ischemic heart disease |
| MVC | Maximal voluntary contraction |
| IE | Isometric exercise |
| LV | Left ventricle |
| PCI | Percutaneous coronary intervention |
| CABG | Coronary artery bypass grafting |
| LA | Left atrial |
| LAVI | LA volume index |
| LVEDV | LV end-diastolic volume |
| LVESV | LV end-systolic volume |
| LVEF | LV ejection fraction |
| SV | Stroke volume |
| CO | Cardiac output |
| GLS | Global longitudinal strain |
| PACS | Peak atrial contraction strain |
| PALS | Peak atrial longitudinal strain |
| GWI | Global work index |
| GCW | Global constructive work |
| GWW | Global wasted work |
| GWE | Global work efficiency |
| SD | Standard deviation |
References
- Weber, T.; Lang, I.; Zweiker, R.; Horn, S.; Wenzel, R.R.; Watschinger, B.; Slany, J.; Eber, B.; Roithinger, F.X.; Metzler, B. Hypertension and coronary artery disease: Epidemiology, physiology, effects of treatment, and recommendations: A joint scientific statement from the Austrian Society of Cardiology and the Austrian Society of Hypertension. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2016, 128, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, R.; Soliz, P.; Campbell, N.R.C.; Lackland, D.T.; Whelton, P.K.; Ordunez, P. Association between population hypertension control and ischemic heart disease and stroke mortality in 36 countries of the Americas, 1990–2019: An ecological study. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica 2022, 46, e143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.S.; Dalal, H.M.; McDonagh, S.T.J. The role of cardiac rehabilitation in improving cardiovascular outcomes. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 19, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEvoy, J.W.; McCarthy, C.P.; Bruno, R.M.; Brouwers, S.; Canavan, M.D.; Ceconi, C.; Christodorescu, R.M.; Daskalopoulou, S.S.; Ferro, C.J.; Gerdts, E.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3912–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanssen, H.; Boardman, H.; Deiseroth, A.; Moholdt, T.; Simonenko, M.; Kränkel, N.; Niebauer, J.; Tiberi, M.; Abreu, A.; Solberg, E.E.; et al. Personalized exercise prescription in the prevention and treatment of arterial hypertension: A Consensus Document from the European Association of Preventive Cardiology (EAPC) and the ESC Council on Hypertension. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022, 29, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelton, S.P.; Chin, A.; Xin, X.; He, J. Effect of aerobic exercise on blood pressure: A meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Ann. Intern. Med. 2002, 136, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Li, X.; Yan, P.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Li, R.; Shi, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, K. The effectiveness of aerobic exercise for hypertensive population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2019, 21, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inder, J.D.; Carlson, D.J.; Dieberg, G.; McFarlane, J.R.; Hess, N.C.; Smart, N.A. Isometric exercise training for blood pressure management: A systematic review and meta-analysis to optimize benefit. Hypertens. Res. 2016, 39, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansford, H.J.; Parmenter, B.J.; McLeod, K.A.; Wewege, M.A.; Smart, N.A.; Schutte, A.E.; Jones, M.D. The effectiveness and safety of isometric resistance training for adults with high blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hypertens. Res. 2021, 44, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S. Evidence for exercise therapies including isometric handgrip training for hypertensive patients. Hypertens. Res. 2024, 48, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitarelli, M.; Laterza, F.; Peñín-Grandes, S.; Perrone, M.A.; Santos-Lozano, A.; Volterrani, M.; Marazzi, G.; Manzi, V.; Padua, E.; Sposato, B.; et al. Post-Exercise Hypotension Induced by a Short Isometric Exercise Session Versus Combined Exercise in Hypertensive Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease: A Pilot Study. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminiti, G.; Marazzi, G.; Volterrani, M.; D’Antoni, V.; Fecondo, S.; Vadalà, S.; Sposato, B.; Giamundo, D.M.; Vitarelli, M.; Morsella, V.; et al. Effect of Different Isometric Exercise Modalities on Myocardial Work in Trained Hypertensive Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease: A Randomized Pilot Study. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, K.F.; Arthur, S.T.; Swaine, I.; Devereux, G.R.; Huet, Y.M.; Wikstrom, E.; Cordova, M.L.; Howden, R. Intensity-dependent reductions in resting blood pressure following short-term isometric exercise training. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiles, J.D.; Coleman, D.A.; Swaine, I.L. The effects of performing isometric training at two exercise intensities in healthy young males. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidi, M.; Ahmadizad, S.; Argani, H.; Najafi, A.; Ebrahim, K.; Salehi, N.; Javidi, Y.; Pescatello, L.S.; Jowhari, A.; Hackett, D.A. Effect of Lower- versus Higher-Intensity Isometric Handgrip Training in Adults with Hypertension: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzlin, N.; Hays, A.G.; Peters, M.; Kaminski, A.; Roemer, S.; O’Leary, P.; Kroboth, S.; Harland, D.R.; Khandheria, B.K.; Tajik, A.J.; et al. Myocardial Work in Echocardiography. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2023, 16, e014419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erevik, C.B.; Kleiven, Ø.; Frøysa, V.; Bjørkavoll-Bergseth, M.; Chivulescu, M.; Klæboe, L.G.; Dejgaard, L.; Auestad, B.; Skadberg, Ø.; Melberg, T.; et al. Myocardial inefficiency is an early indicator of exercise-induced myocardial fatigue. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 9, 1081664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgfetapte, P.W.K. ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription, 11th ed.; Wolters Kluer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nagueh, S.F.; Smiseth, O.A.; Appleton, C.P.; Byrd, B.F., 3rd; Dokainish, H.; Edvardsen, T.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Gillebert, T.C.; Klein, A.L.; Lancellotti, P.; et al. Recommendations for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function by Echocardiography: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 17, 1321–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, K.; Özden Tok, Ö.; Mitrousi, K.; Ikonomidis, I. Myocardial Work: Methodology and Clinical Applications. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, V.A.; Smart, N.A. Exercise training for blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e004473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, D.J.; Dieberg, G.; Hess, N.C.; Millar, P.J.; Smart, N.A. Isometric exercise training for blood pressure management: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwill, J.R. Mechanisms and clinical implications of post-exercise hypotension in humans. Exerc. Sport. Sci. Rev. 2001, 29, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.; Biaggioni, I. Role of adenosine in the sympathetic activation produced by isometric exercise in humans. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, C.L.; Levy, A.S.; Millar, P.J.; Guzman, J.C.; Morillo, C.A.; McCartney, N.; Macdonald, M.J. Acute vascular responses to isometric handgrip exercise and effects of training in persons medicated for hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 291, H1797–H1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olher Rdos, R.; Bocalini, D.S.; Bacurau, R.F.; Rodriguez, D.; Figueira A., Jr.; Pontes, F.L., Jr.; Navarro, F.; Simões, H.G.; Araujo, R.C.; Moraes, M.R. Isometric handgrip does not elicit cardiovascular overload or post-exercise hypotension in hypertensive older women. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovithis, D.; Anifanti, M.; Koutlianos, N.; Teloudi, A.; Kouidi, E.; Deligiannis, A. Left Ventricular Diastolic Response to Isometric Handgrip Exercise in Physically Active and Sedentary Individuals. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Assche, T.; Buys, R.; de Jaeger, M.; Coeckelberghs, E.; Cornelissen, V.A. One single bout of low-intensity isometric handgrip exercise reduces blood pressure in healthy pre- and hypertensive individuals. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2017, 57, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante, P.A.; Rica, R.L.; Evangelista, A.L.; Serra, A.J.; Figueira, A., Jr.; Pontes, F.L., Jr.; Kilgore, L.; Baker, J.S.; Bocalini, D.S. Effects of exercise intensity on post-exercise hypotension after resistance training session in overweight hypertensive patients. Clin. Interv. Aging 2015, 10, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, Y.; Yamaki, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Satoh, T.; Konno, S.; Munakata, M. Effects of low-intensity isometric handgrip training on home blood pressure in hypertensive patients: A randomized controlled trial. Hypertens. Res. 2025, 48, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.O.; Farah, B.Q.; Germano-Soares, A.H.; Andrade-Lima, A.; Santana, F.S.; Rodrigues, S.L.; Ritti-Dias, R.M. Acute blood pressure responses after different isometric handgrip protocols in hypertensive patients. Clinics 2018, 73, e373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, M.M.; Cooley, I.D.; Huet, Y.M.; Arthur, S.T.; Howden, R. Factors influencing isometric exercise training-induced reductions in resting blood pressure. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loaiza-Betancur, A.F.; Chulvi-Medrano, I. Is Low-Intensity Isometric Handgrip Exercise an Efficient Alternative in Lifestyle Blood Pressure Management? A Systematic Review. Sports Health 2020, 12, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnikov, V.N.; Komlyagina, T.G.; Gultyaeva, V.V.; Uryumtsev, D.Y.; Zinchenko, M.I.; Bryzgalova, E.A.; Karmakulova, I.V.; Krivoschekov, S.G. Time course of cardiovascular responses to acute sustained handgrip exercise in young physically active men. Physiol. Rep. 2025, 13, e70286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirea, O.; Pagourelias, E.D.; Duchenne, J.; Bogaert, J.; Thomas, J.D.; Badano, L.P.; Voigt, J.U. EACVI-ASE-Industry Standardization Task Force. Intervendor Differences in the Accuracy of Detecting Regional Functional Abnormalities: A Report From the EACVI-ASE Strain Standardization Task Force. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rösner, A.; Barbosa, D.; Aarsæther, E.; Kjønås, D.; Schirmer, H.; D’hooge, J. The influence of frame rate on two-dimensional speckle-tracking strain measurements: A study on silico-simulated models and images recorded in patients. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 16, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminiti, G.; Volterrani, M.; Iellamo, F.; Marazzi, G.; Manzi, V.; D’Antoni, V.; Vadalà, S.; Di Biasio, D.; Catena, M.; Morsella, V.; et al. Changes in left atrial function following two regimens of combined exercise training in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy: A pilot study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1377958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
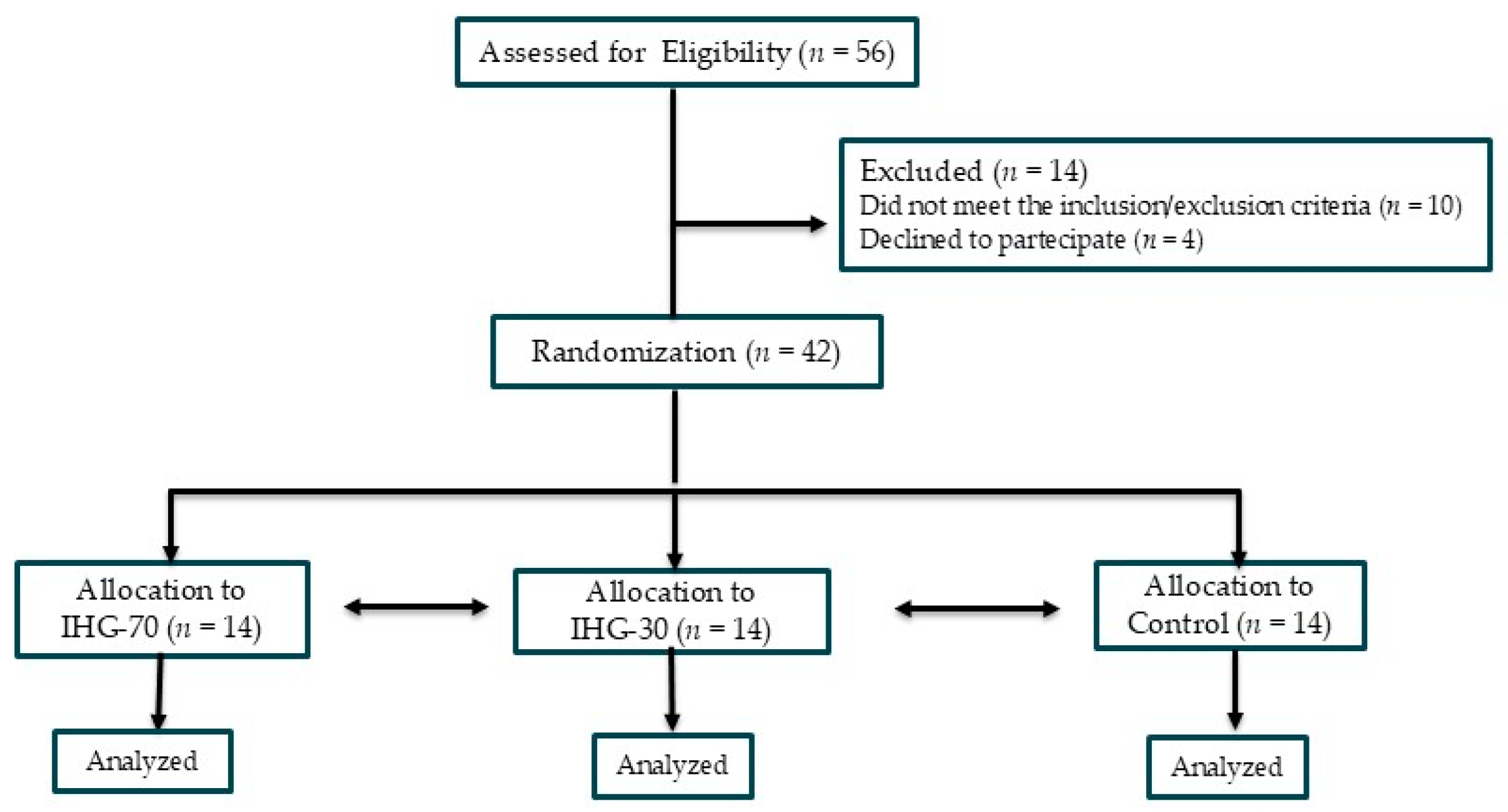
| IHG-70 (n = 14) | IHG-30 (n = 14) | Control (n = 14) | ANOVA p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, y | 66.4 ± 11.2 | 65.9 ± 12.7 | 66.1 ± 12.0 | 0.571 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 28.4 ± 7.3 | 28.3 ± 9.1 | 27.9 ± 6.6 | 0.796 |
| Males, n (%) | 11 (78.6) | 11 (78.6) | 11 (78.6) | 0.457 |
| Previous STEMI/NSTEMI-UA, n (%) | 12 (85.0)/2 (14.0) | 12 (85)/2 (14.0) | 10 (71.4)/4 (28.6) | 0.642 |
| Previous CABG/PCI, n (%) | 7 (50.0)/11 (78.5) | 9 (64.2)/10 (71.4) | 10 (71.4)/11 (78.6) | 0.966 |
| Multivessel disease, n (%) | 12 (85.7) | 12 (85.7) | 10 (71.4) | 0.851 |
| Carotid artery disease, n (%) | 7 (50.0) | 6 (42.8) | 6 (42.8) | 0.598 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 4 (28.6) | 6 (43.0) | 5 (20.0) | 0.883 |
| Hypercholesterolemia, n (%) | 15 (100.0) | 14 (93.3) | 15 (100.0) | 0.248 |
| eGFR, mL/min per 1.73 m2 | 78.3 ± 11.6 | 67.4 ± 12.1 | 75.7 ± 13.8 | 0.089 |
| SBP, mmHg | 126.6 ± 34.0 | 125.8 ± 27.4 | 126.1 ± 30.9 | 0.144 |
| DBP, mmHg | 82.2 ± 14.7 | 83.6 ± 14.4 | 82.8 ± 15.3 | 0.132 |
| HR, b/min | 62.1 ± 9.5 | 60.8 ± 11.0 | 63.5 ± 8.9 | 0.091 |
| NT-proBNP, pg/mL | 71.4 ± 10.8 | 68.3 ± 12.4 | 66.2 ± 9.2 | |
| Echocardiography | 0.527 | |||
| LVEDV, mm3/m2 | 64.2 ± 22.3 | 65.0.9 ± 15.4 | 68.7 ± 18.8 | 0.232 |
| LVESD, mm3/m2 | 36.7 ± 12.3 | 37.1 ± 14.6 | 37.6 ± 13.7 | 0.522 |
| LVEF, % | 55.1 ± 8.1 | 53.9 ± 8.2 | 54.5 ± 10.7 | 0.385 |
| LV GLS, % | −16.9 ± 4.3 | −17.3 ± 4.8 | −17.0 ± 5.3 | 0.077 |
| E/E’ | 8.6 ± 2.3 | 8.2 ± 2.9 | 8.4 ± 2.5 | 0.491 |
| LAVI, mm3/m2 | 29.3 ± 7.1 | 28.6 ± 6.9 | 28.8 ± 7.7 | 0.287 |
| MR mild/moderate, n (%) | 9 (64.3)/5 (35.7) | 10 (71.5)/4 (28.5) | 11 (78.6)/3 (21.4) | 0.182 |
| PALS. % | 15.7 ± 3.6 | 16.2 ± 3.3 | 16. ± 3.1 | 0.362 |
| PACS, % | 13.2 ± 2.9 | 12.9 ± 3.0 | 13.2 ± 3.7 | 0.371 |
| Treatment | ||||
| ACE-i/ARBs, n (%) | 14 (100.0) | 15 (100.0) | 13 (93.5) | 0.441 |
| Betablockers, n (%) | 14 (100.0) | 13 (93.5) | 14 (100.0) | 0.642 |
| MRAs, n (%) | 4 (28.5) | 4 (28.5) | 3 (21.4) | 0.238 |
| Thiazide diuretic, n (%) | 6 (42.8) | 7 (50.0) | 7 (50.0) | 0.692 |
| Ivabradine, n (%) | 2 (14.3) | - | 1 (7.1) | 0.383 |
| Statins, n (%) | 14 (100.0) | 14 (100.0) | 13 (92.8) | 0.754 |
| CCAs, n (%) | 8 (57.1) | 9 (64.3) | 7 (50.0) | 0.648 |
| Acetylsalicylic acid | 13 (92.8) | 14 (100.0) | 14 (100.0) | 0.132 |
| Clopidogrel | 3 (21.4) | 2 (14.3) | - | 0.167 |
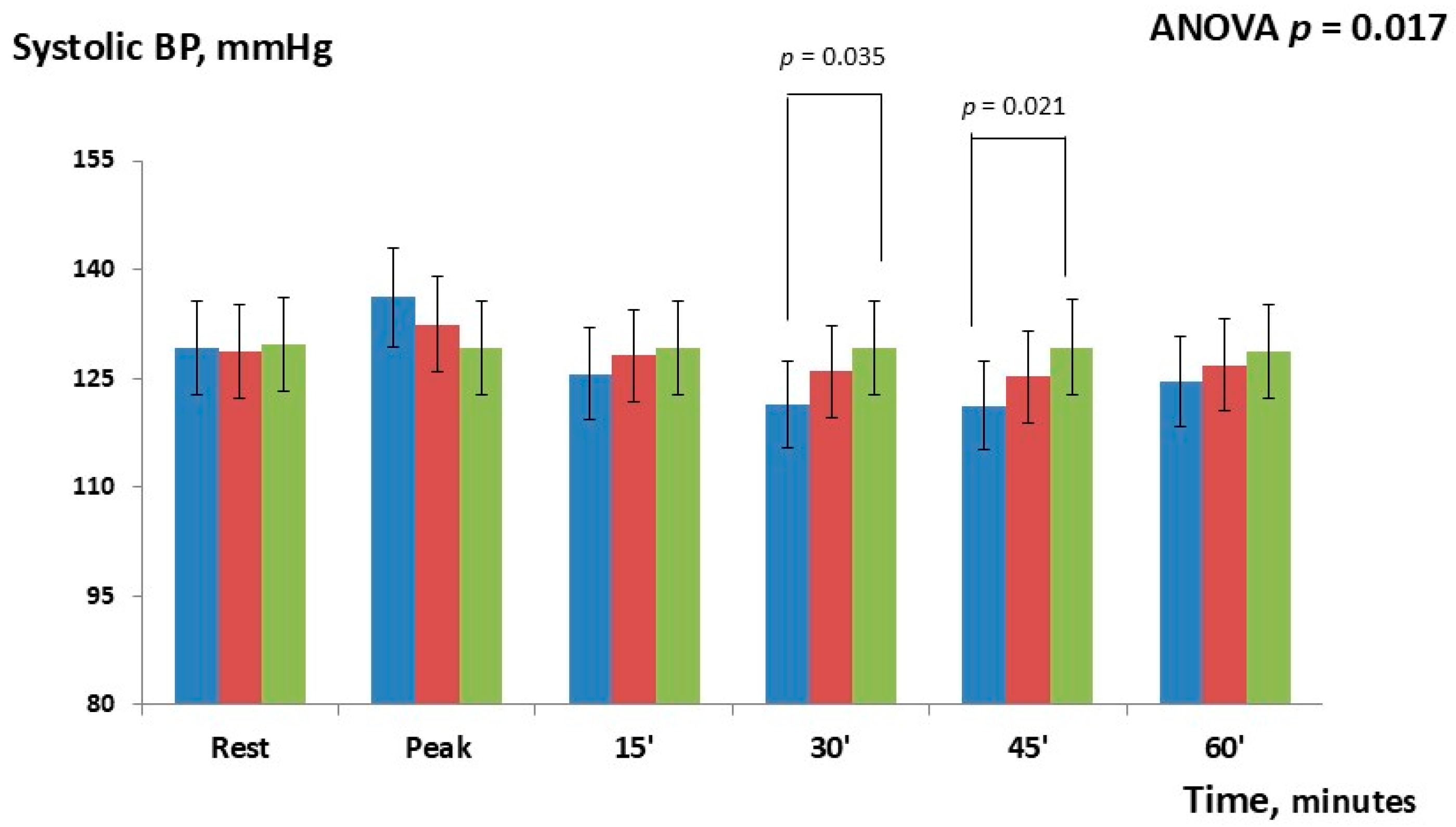
| Δ Systolic BP | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Timing | IHG-70 vs. IHG-30 | IHG-70 vs. Control | IHG-30 vs. Control |
| Rest | 0.6 ± (0.4) | −0.4 ± (0.6) | 1.0 ± (1.1) |
| Peak | 3.8 ± (1.8) | 7.0 ± (2.1) | 3.2 ± (1.6) |
| 15 | −2.5± (0.9) | −3.6 ± (1.4) | −1.1 ± (0.6) |
| 30 | −4.5 ± (2.9) | −7.7 ± (1.9) * | −3.2 ± (1.9) |
| 45 | −4.0 ± (2.6) | −8.1 ± (2.3) * | −4.1 ± (2.2) |
| 60 | −2.2 ± (1.3) | −4.1 ± (1.7) | −1.9 ± (1.3) |
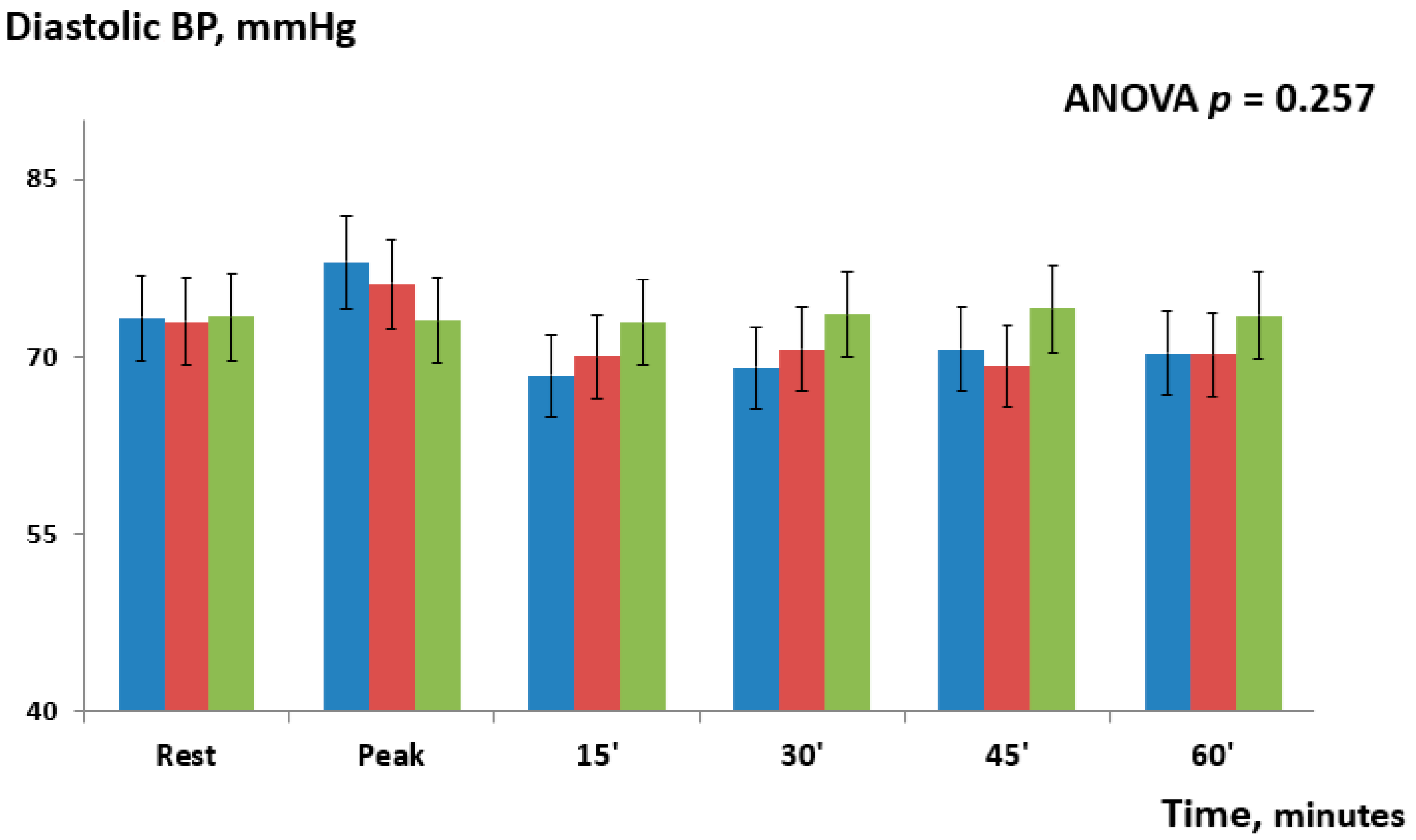
| Δ Diastolic BP | |||
| Timing | IHG-70 vs. IHG-30 | IHG-70 vs. control | IHG-30 vs. control |
| Rest | −0.3 ± (0.6) | −0.1 ± (0.3) | −0.4 ± (0.7) |
| Peak | 1.8 ± (1.1) | 4.9 ± (2.8) | 3.1 ± (0.9) |
| 15 | −1.6 ± (0.4) | −4.5 ± (3.1) | −2.9 ± (1.1) |
| 30 | −1.5 ± (1.2) | −4.5 ± (2.7) | −3.0 ± (1.4) |
| 45 | 1.4 ± (0.7) | −3.5 ± (1.8) | −4.9 ± (2.6) |
| 60 | 0.1 ± (0.5) | −3.2 ± (1.1) | −3.3 ± (1.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caminiti, G.; Vitarelli, M.; Volterrani, M.; Marazzi, G.; Manzi, V.; D’Antoni, V.; Fecondo, S.; Vadalà, S.; Sposato, B.; Giamundo, D.M.; et al. Pilot Study Assessing the Hemodynamic Impact and Post-Exercise Hypotension Induced by High- Versus Low-Intensity Isometric Handgrip in Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12100405
Caminiti G, Vitarelli M, Volterrani M, Marazzi G, Manzi V, D’Antoni V, Fecondo S, Vadalà S, Sposato B, Giamundo DM, et al. Pilot Study Assessing the Hemodynamic Impact and Post-Exercise Hypotension Induced by High- Versus Low-Intensity Isometric Handgrip in Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2025; 12(10):405. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12100405
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaminiti, Giuseppe, Matteo Vitarelli, Maurizio Volterrani, Giuseppe Marazzi, Vincenzo Manzi, Valentino D’Antoni, Simona Fecondo, Sara Vadalà, Barbara Sposato, Domenico Mario Giamundo, and et al. 2025. "Pilot Study Assessing the Hemodynamic Impact and Post-Exercise Hypotension Induced by High- Versus Low-Intensity Isometric Handgrip in Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 12, no. 10: 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12100405
APA StyleCaminiti, G., Vitarelli, M., Volterrani, M., Marazzi, G., Manzi, V., D’Antoni, V., Fecondo, S., Vadalà, S., Sposato, B., Giamundo, D. M., Grossi, A., Morsella, V., Iellamo, F., & Perrone, M. A. (2025). Pilot Study Assessing the Hemodynamic Impact and Post-Exercise Hypotension Induced by High- Versus Low-Intensity Isometric Handgrip in Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 12(10), 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12100405









