Multiresistant Kawasaki Disease in a Young Infant with Giant Aneurysms Growing Fast
Abstract
1. Background
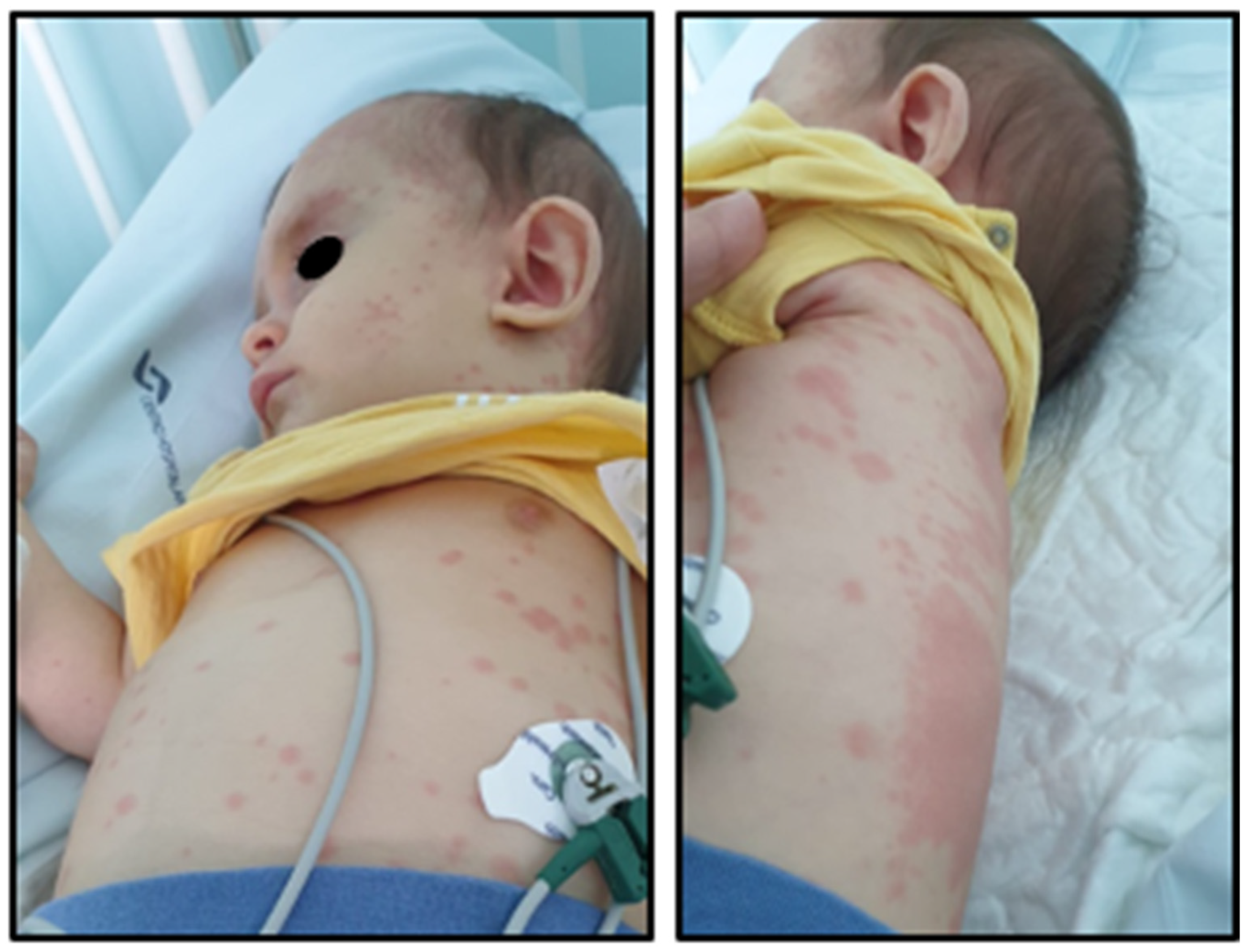
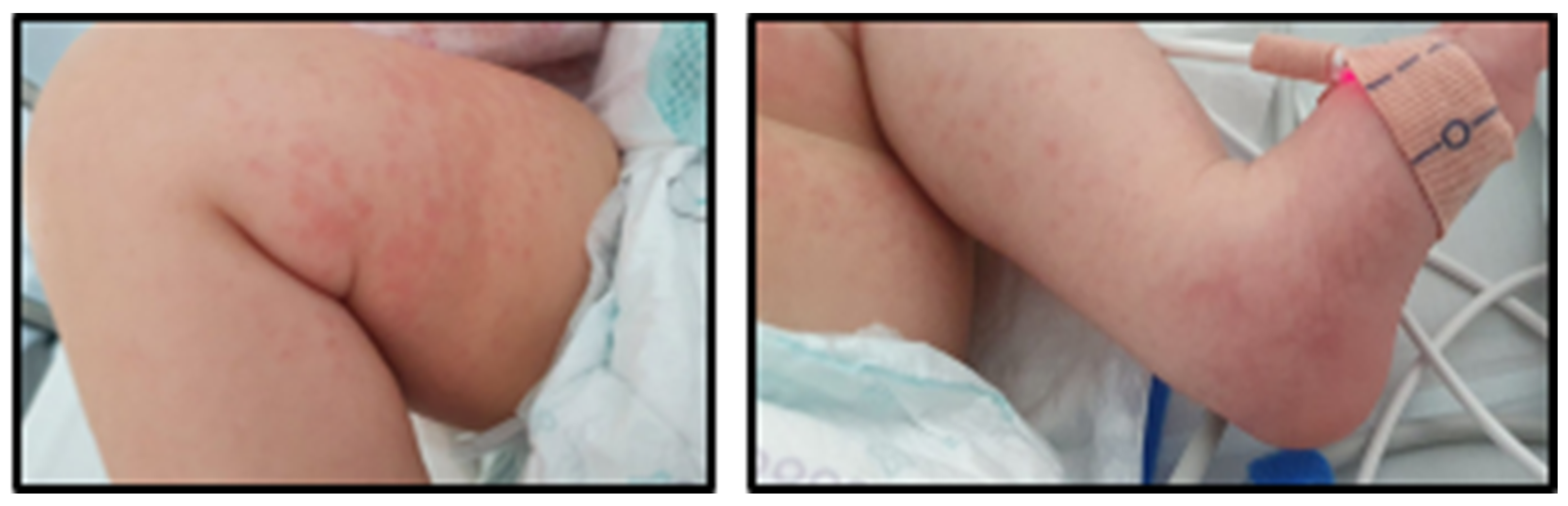
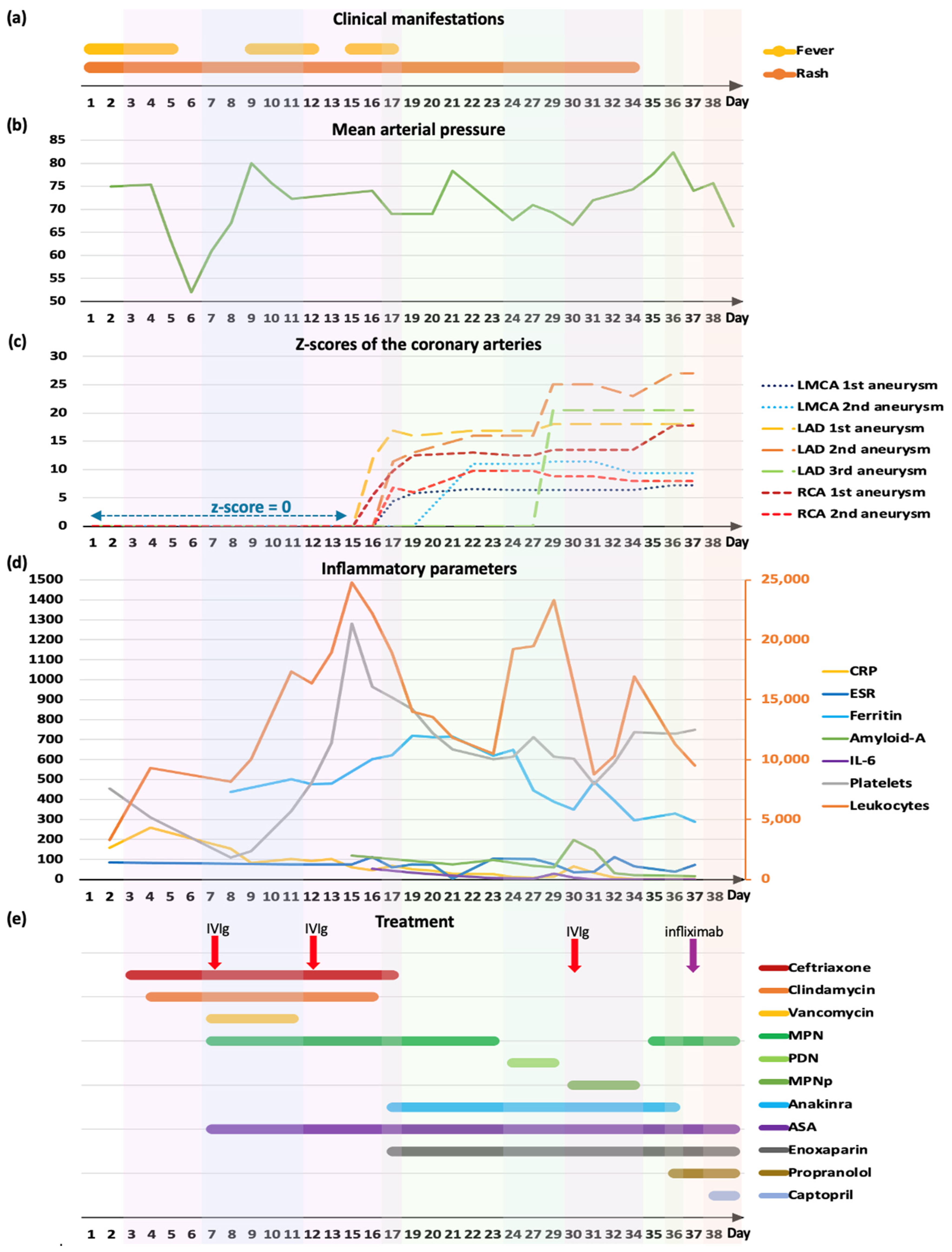
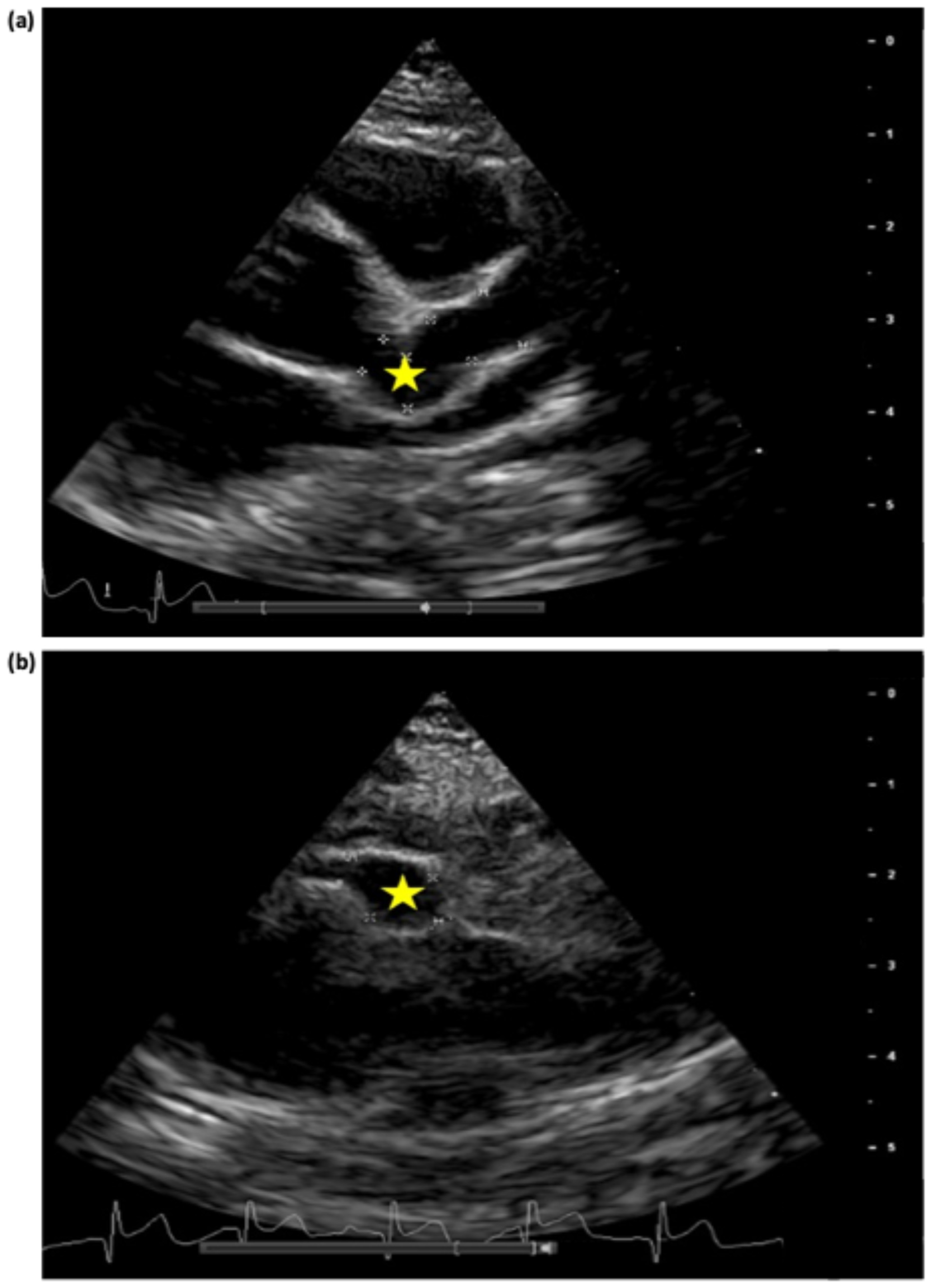
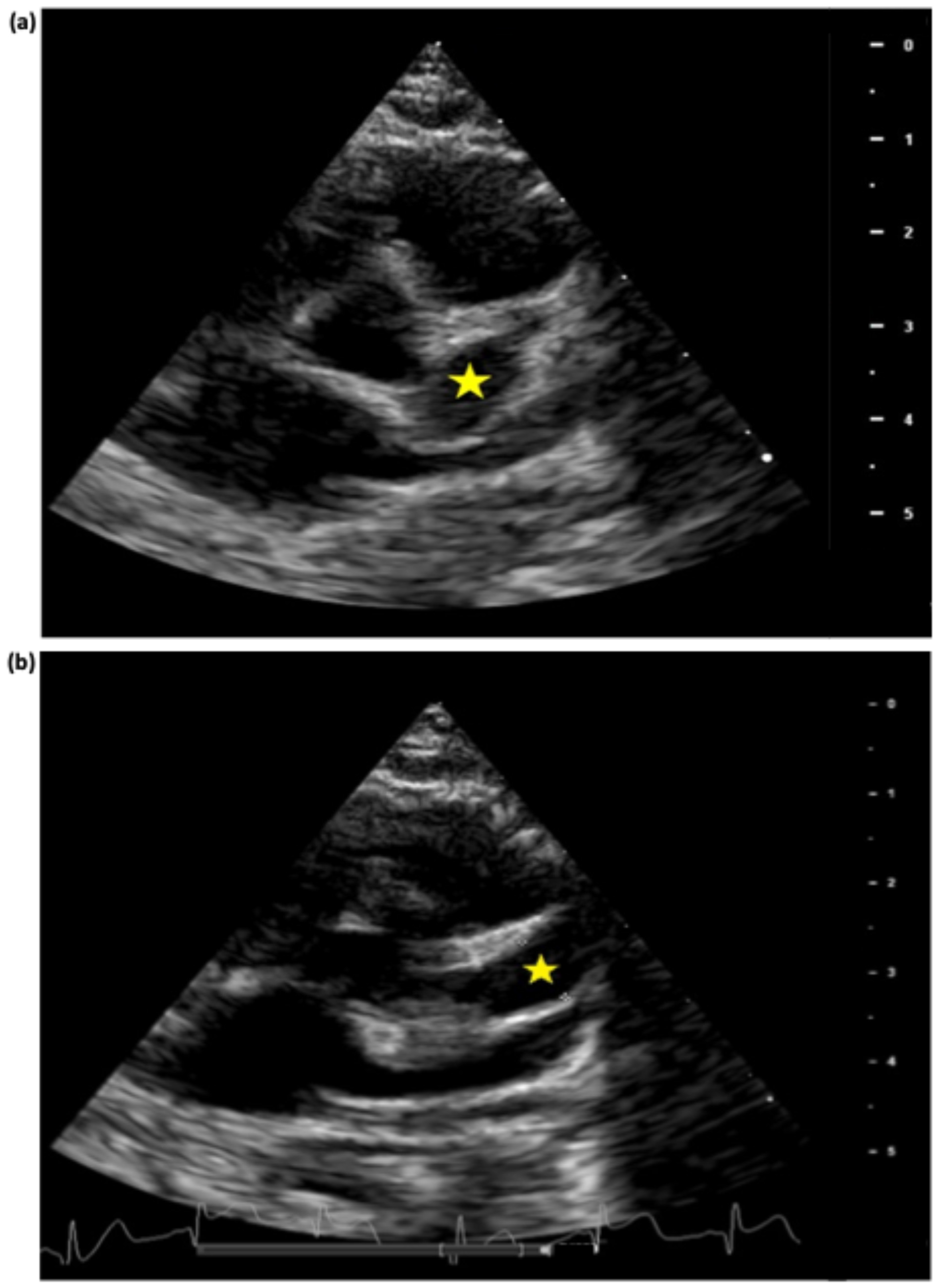
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | Angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| ADA2 | Adenosine deaminase 2 |
| AHA | American Heart Association |
| ANA | Antinuclear antibodies |
| ANCA | Anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody |
| aPTT | Activated partial thromboplastin time |
| ASA | Acetylsalicylic acid |
| ALT | Alanine transaminase |
| AST | Aspartate transaminase |
| CAA | Coronary artery aneurysm |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| ESR | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| IL-1 | Interleukin-1 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| INR | International normalized ratio |
| IVIg | Intravenous Immunoglobulin |
| KD | Kawasaki disease |
| LAD | Left anterior descending artery |
| LMCA | Left main coronary artery |
| MIS-C | Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children |
| MPN | Methylprednisolone |
| MPNp | Methylprednisolone pulses |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PDN | Prednisolone |
| RCA | Right coronary artery |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
References
- Weiss, P.F. Pediatric Vasculitis. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 59, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, K.E.; Kalot, M.A.; Husainat, N.M.; Dua, A.B.; Byram, K.; Springer, J.M.; Lin, Y.C.; Turgunbaev, M.; Villa-Forte, A.; Gorelik, M.; et al. Kawasaki Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Benefits and Harms of Common Treatments. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2021, 3, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulman, S.T.; Rowley, A.H. Kawasaki disease: Insights into pathogenesis and approaches to treatment. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundel, R.P. Kawasaki disease. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 41, 1738–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Shirodkar, S.; Pinto, R.; Dalvi, B. Giant coronary artery aneurysm with a thrombus secondary to Kawasaki disease. Ann. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2008, 1, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noval Rivas, M.; Arditi, M. Kawasaki disease: Pathophysiology and insights from mouse models. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thadchanamoorthy, V.; Dayasiri, K. Refractory Kawasaki Disease Presenting with Erythema at Bacille Calmette-Guérin Inoculation Site: A Paediatric Case Report. Cureus 2020, 12, e10928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-García, L.M.; Morán-Villaseñor, E.; Yamazaki-Nakashimada, M.A.; Cravioto, P.; Galván, F. Giant coronary artery aneurysms complicating Kawasaki disease in Mexican children. Cardiol. Young 2018, 28, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrindle, B.W.; Rowley, A.H.; Newburger, J.W.; Burns, J.C.; Bolger, A.F.; Gewitz, M.; Baker, A.L.; Jackson, M.A.; Takahashi, M.; Shah, P.B.; et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: A scientific statement for health professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e927–e999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, D.; Kalyanasundaram, S.; Krishnamurthy, K. Refractory Kawasaki Disease—A Challenge for the Pediatrician. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2021, 3, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambacorta, A.; Buonsenso, D.; De Rosa, G.; Lazzareschi, I.; Gatto, A.; Brancato, F.; Pata, D.; Valentini, P. Resolution of Giant Coronary Aneurisms in a Child with Refractory Kawasaki Disease Treated with Anakinra. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.; Nagaraju, L.; Gorelik, M. Complete Regression of Giant Aneurysms in an Infant with Delayed Diagnosis and Refractory Kawasaki Disease via Combination Anticytokine Therapy: Case Report and Review of Similar Cases. Case Rep. Rheumatol. 2020, 2020, 6249013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walser, M.; Hermann, M.; Hufnagel, M.; Haas, N.A.; Fischer, M.; Dalla-Pozza, R.; Jakob, A. Anakinra And Etanercept Combination Treatment in a Child with Severe, Nonresponsive Kawasaki Disease. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 39, e310–e313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saneeymehri, S.; Baker, K.; So, T.Y. Overview of pharmacological treatment options for pediatric patients with refractory kawasaki disease. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 20, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buda, P.; Friedman-Gruszczyńska, J.; Książyk, J. Anti-inflammatory Treatment of Kawasaki Disease: Comparison of Current Guidelines and Perspectives. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 738850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, L.; Huang, X.; Tian, J. Insights Into Coronary Artery Lesions in Kawasaki Disease. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, K.P.; Lee, G.S.; Li, J.S.; Barker, P.C.A.; Van Mater, H.; Chamberlain, R.C. Coronary Artery Aneurysm Rupture in Kawasaki Disease and SARS-CoV-2 Infection. CASE 2024, 8, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña-Juárez, A.; Medina-Andrade, M.A.; Olivares, I.E.R.; Colín-Ortíz, J.L.; Yamazaki-Nakashimada, M.A.; Garrido-Garcia, L.M. Multiresistant Kawasaki Disease Complicated with Facial Nerve Palsy, Bilateral Giant Coronary Artery Aneurysms, and Stenosis of the Right Coronary Artery in an Infant. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 27, S351–S354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Yu, H.G. Clinical Manifestations of Kawasaki Disease Shock Syndrome. Clin. Pediatr. 2018, 57, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamez-Gonzalez, L.B.; Moribe-Quintero, I.; Cisneros-Castolo, M.; Varela-Ortiz, J.; Muñoz-Ramírez, M.; Garrido-García, M.; Yamazaki-Nakashimada, M. Kawasaki disease shock syndrome: Unique and severe subtype of Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Int. 2018, 60, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalta, K.; Yalta, T.; Yetkin, E.; Ozturk, C. Late coronary aneurysm formation after Kawasaki disease: A review of mechanistic and clinical aspects. Korean Circ. J. 2021, 51, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.C.; Liu, H.M.; Lin, M.T.; Chen, C.A.; Chiu, S.N.; Lu, C.W.; Chang, L.Y.; Wang, J.K.; Wu, M.H. Outcomes of Kawasaki disease children with spontaneous defervescence within 10 days. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; Yuan, J.; Xie, X.; Qin, Y.; Huang, P. A Retrospective Cohort Study of Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy in the Acute Phase of Kawasaki Disease: The Earlier, the Better? Cardiovasc. Ther. 2021, 2021, 6660407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherler, L.; Haas, N.A.; Tengler, A.; Pattathu, J.; Mandilaras, G.; Jakob, A. Acute phase of Kawasaki disease: A review of national guideline recommendations. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 2563–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Qiu, H.; Wen, Z.; Shi, H.; Yu, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Rong, X.; Wu, R.; et al. Albumin level and progression of coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease: A retrospective cohort study. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 947059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Sugimura, T.; Akagi, T.; Sato, N.; Hashino, K.; Maeno, Y.; Kazue, T.; Eto, G.; Yamakawa, R. Long-term Consequences of Kawasaki Disease. Circulation 1996, 94, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.M.; Shulman, S.T. Kawasaki disease: A comprehensive review of treatment options. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blonz, G.; Lacroix, S.; Benbrik, N.; Warin-Fresse, K.; Masseau, A.; Trewick, D.; Hamidou, M.; Stephan, J.L.; Néel, A. Severe Late-Onset Kawasaki Disease Successfully Treated with Anakinra. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 26, e42–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Manubens, J.; Gelman, A.; Franch, N.; Teodoro, S.; Palacios, J.R.; Rudi, N.; Rivera, J.; Antón, J. A child with resistant Kawasaki disease successfully treated with anakinra: A case report. BMC Pediatr. 2017, 17, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, G.; Giani, T.; Caparello, M.C.; Farella, C.; Gamalero, L.; Cimaz, R. Anakinra for Treatment-Resistant Kawasaki Disease: Evidence from a Literature Review. Pediatr. Drugs 2020, 22, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, Y.; Kim, J.; Hong, Y.M.; Sohn, S. Infliximab as the first retreatment in patients with Kawasaki disease resistant to initial intravenous immunoglobulin. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, 457–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudiaf, H. Super Giant Coronary Aneurysm in an Algerian Boy with Kawasaki Disease. Int. J. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 2, 021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, G.B.; Kwon, B.S.; Bae, E.J.; Noh, C., II. Two cases of super-giant coronary aneurysms after Kawasaki disease. Korean Circ. J. 2014, 44, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.-Y.; Zhang, M.; Ko, S.; Chen, F. An Update on Cardiovascular Risk Factors after Kawasaki Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 671198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newburger, J.W.; Takahashi, M.; Gerber, M.A.; Gewitz, M.H.; Tani, L.Y.; Burns, J.C.; Shulman, S.T.; Bolger, A.F.; Ferrieri, P.; Baltimore, R.S.; et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: A statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Circulation 2004, 110, 2747–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganuma, E.; Niimura, F.; Matsuda, S.; Ukawa, T.; Nakamura, H.; Sekine, K.; Kato, M.; Aiba, Y.; Koga, Y.; Hayashi, K.; et al. Losartan attenuates the coronary perivasculitis through its local and systemic anti-inflammatory properties in a murine model of Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 81, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukazawa, R.; Kobayashi, J.; Ayusawa, M.; Hamada, H.; Miura, M.; Mitani, Y.; Tsuda, E.; Nakajima, H.; Matsuura, H.; Ikeda, K.; et al. JCS/JSCS 2020 Guideline on Diagnosis and Management of Cardiovascular Sequelae in Kawasaki Disease. Circ. J. 2020, 84, 1348–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Infectiology Unit | Cardiology Unit | Follow-Up (Months after Discharge) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D16 | D19 | D29 | D36 | D69 | 1 Month | 4 Months * | 17 Months | |
| LMCA | Ø | 1st 4 mm (z-score +5.8) | 1st 4.2 mm (z-score +6.4) | 1st 4.5 mm (z-score +7.2) | 1st 4 mm (z-score +5.8) | Ø | Ø | Ø |
| Ø | 2nd 6 mm (z-score +11.4) | 2nd 5.3 mm (z-score +9.4) | 2nd 5.5 mm (z-score +10) | |||||
| LAD | 1st 4.2 mm (z-score +12) | 1st 5 mm (z-score +16) | 1st 5.5 mm (z-score +18) | 1st 5.5 mm (z-score +18) | 1st 5.5 mm (z-score +18) | 1st 5.4 mm (z-score +17.8) | 2 aneurysms max diameter 4.5 mm (z-score +13.7) | 1st 3.6 mm (z-score +9.6) |
| Ø | 2nd 4.4 mm (z-score +13) | 2nd 7 mm (z-score +25) | 2nd 7.5 mm (z-score +27) | 2nd 6.8 mm (z-score +24) | 2nd 6.6 mm (z-score +23) | Ø | ||
| Ø | Ø | 3rd 6 mm (z-score +20.5) | 3rd 6 mm (z-score +20.5) | Ø | Ø | Ø | Ø | |
| RCA | 1st 3.1 mm (z-score +5.5) | 1st 5.2 mm (z-score +12.5) | 1st 5.5 mm (z-score +13.5) | 1st 6.8 mm (z-score +17.8) | 1st 7 mm (z-score +18.5) | 5.4 mm (z-score +13) | Max diameter 3.4 mm (z-score +6.5) | 1st 3.5 mm (z-score +6.8) |
| Ø | 2nd 3.2 mm (z-score +6) | 2nd 4.1 mm (z-score +8.8) | 2nd 3.9 mm (z-score +8) | Ø | Ø | Ø | Ø | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amorim-Figueiredo, R.; Pereira Lemos, A.; Rito, T.; Conde, M.; Brito, M.J.; Pinto, F. Multiresistant Kawasaki Disease in a Young Infant with Giant Aneurysms Growing Fast. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2024, 11, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd11050149
Amorim-Figueiredo R, Pereira Lemos A, Rito T, Conde M, Brito MJ, Pinto F. Multiresistant Kawasaki Disease in a Young Infant with Giant Aneurysms Growing Fast. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2024; 11(5):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd11050149
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmorim-Figueiredo, Rosa, Ana Pereira Lemos, Tiago Rito, Marta Conde, Maria João Brito, and Fátima Pinto. 2024. "Multiresistant Kawasaki Disease in a Young Infant with Giant Aneurysms Growing Fast" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 11, no. 5: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd11050149
APA StyleAmorim-Figueiredo, R., Pereira Lemos, A., Rito, T., Conde, M., Brito, M. J., & Pinto, F. (2024). Multiresistant Kawasaki Disease in a Young Infant with Giant Aneurysms Growing Fast. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 11(5), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd11050149






