Predictive Ability of the National Early Warning Score in Mortality Prediction of Acute Pulmonary Embolism in the Southeast Asian Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
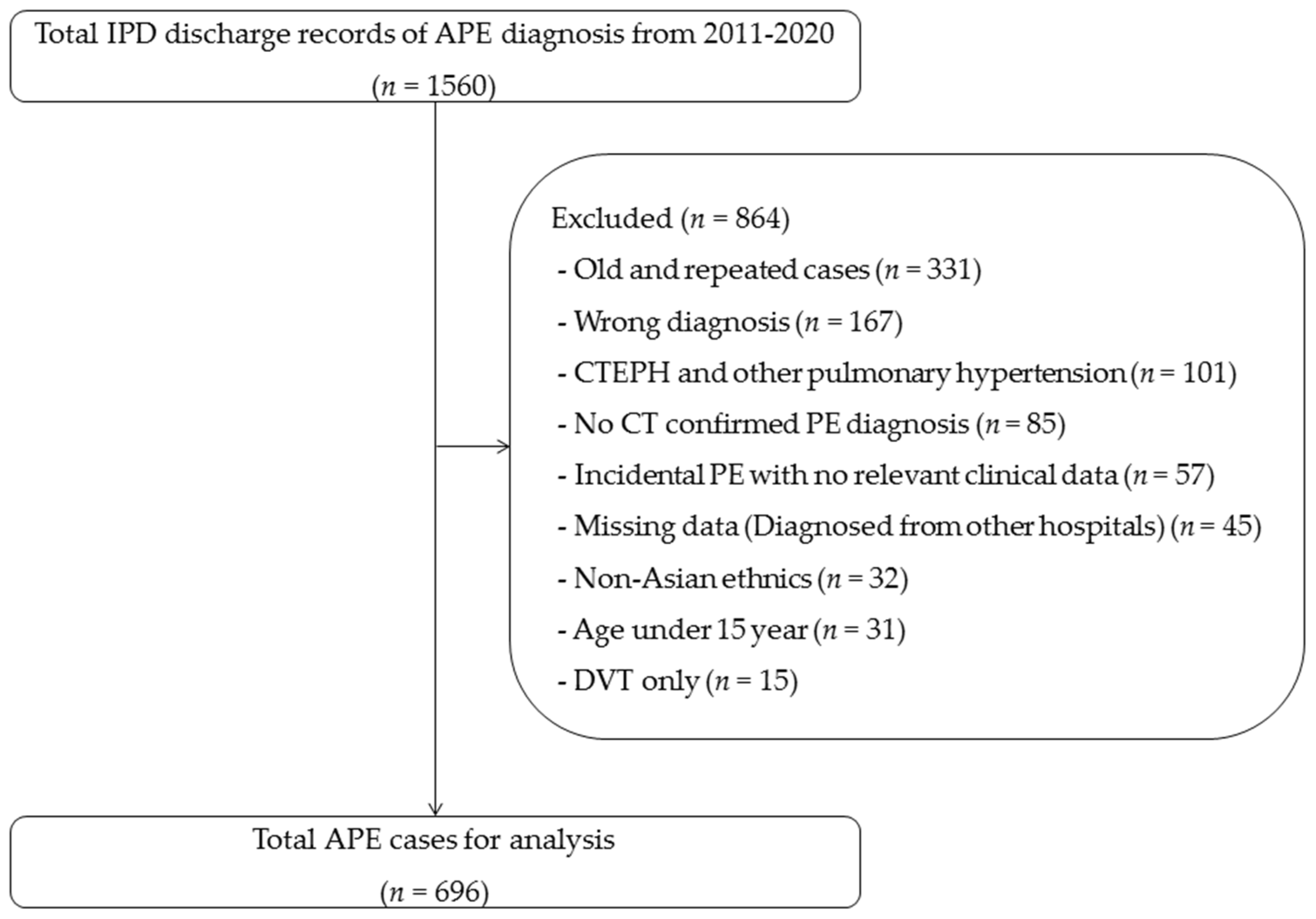
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raskob, G.E.; Angchaisuksiri, P.; Blanco, A.N.; Buller, H.; Gallus, A.; Hunt, B.J.; Hylek, E.M.; Kakkar, A.; Konstantinides, S.V.; McCumber, M.; et al. Thrombosis: A major contributor to global disease burden. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinides, S.V.; Meyer, G.; Becattini, C.; Bueno, H.; Geersing, G.J.; Harjola, V.P.; Huisman, M.V.; Humbert, M.; Jennings, C.S.; Jiménez, D.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 543–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, D.; de Miguel-Díez, J.; Guijarro, R.; Trujillo-Santos, J.; Otero, R.; Barba, R.; Muriel, A.; Meyer, G.; Yusen, R.D.; Monreal, M.; et al. Trends in the Management and Outcomes of Acute Pulmonary Embolism: Analysis From the RIETE Registry. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.M.; Woods, C.; Shorr, A.F. The validation and reproducibility of the pulmonary embolism severity index. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 1509–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aujesky, D.; Obrosky, D.S.; Stone, R.A.; Auble, T.E.; Perrier, A.; Cornuz, J.; Roy, P.M.; Fine, M.J. Derivation and validation of a prognostic model for pulmonary embolism. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donzé, J.; Le Gal, G.; Fine, M.J.; Roy, P.M.; Sanchez, O.; Verschuren, F.; Cornuz, J.; Meyer, G.; Perrier, A.; Righini, M.; et al. Prospective validation of the Pulmonary Embolism Severity Index. A clinical prognostic model for pulmonaryembolism. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 100, 943–948. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, D.; Aujesky, D.; Moores, L.; Gómez, V.; Lobo, J.L.; Uresandi, F.; Otero, R.; Monreal, M.; Muriel, A.; Yusen, R.D.; et al. Simplification of the pulmonary embolism severity index for prognostication in patients with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Arch. Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Morimoto, T.; Amano, H.; Takase, T.; Hiramori, S.; Kim, K.; Oi, M.; Akao, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Toyofuku, M.; et al. Validation of simplified PESI score for identification of low-risk patients with pulmonary embolism: From the COMMAND VTE Registry. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2020, 9, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M. NEWSDIG: The National Early Warning Score Development and Implementation Group. Clin. Med. 2012, 12, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Physicians RCo. National Early Warning Score (NEWS) 2: Standardising the Assessment of Acute-Illness Severity in the NHS. Updated Report of a Working Party. RCP: London, UK, 2017. 2017. Available online: https://www.rcplondon.ac.uk/projects/outputs/national-early-warning-score-news-2 (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- Smith, G.B.; Redfern, O.C.; Pimentel, M.A.; Gerry, S.; Collins, G.S.; Malycha, J.; Prytherch, D.; Schmidt, P.E.; Watkinson, P.J. The National Early Warning Score 2 (NEWS2). Clin. Med. 2019, 19, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silcock, D.J.; Corfield, A.R.; Staines, H.; Rooney, K.D. Superior performance of National Early Warning Score compared with quick Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment Score in predicting adverse outcomes: A retrospective observational study of patients in the prehospital setting. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 26, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keep, J.W.; Messmer, A.S.; Sladden, R.; Burrell, N.; Pinate, R.; Tunnicliff, M.; Glucksman, E. National early warning score at Emergency Department triage may allow earlier identification of patients with severe sepsis and septic shock: A retrospective observational study. Emerg. Med. J. 2016, 33, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corfield, A.R.; Lees, F.; Zealley, I.; Houston, G.; Dickie, S.; Ward, K.; McGuffie, C.; Scottish Trauma Audit Group Sepsis Steering Group. Utility of a single early warning score in patients with sepsis in the emergency department. Emerg. Med. J. 2014, 31, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yolcu, S.; Kaya, A.; Yilmaz, N. Prediction of prognosis and outcome of patients with pulmonary embolism in the emergency department using early warning scores and qSOFA score. J. Int. Med. Res. 2022, 50, 3000605221129915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavalia, R.; Stals, M.A.M.; Mulder, F.I.; Bistervels, I.M.; Coppens, M.; Faber, L.M.; Hendriks, S.V.; Hofstee, H.M.A.; Huisman, M.V.; van der Hulle, T.; et al. Use of the National Early Warning Score for predicting deterioration of patients with acute pulmonary embolism: A post-hoc analysis of the YEARS Study. Emerg. Med. J. 2023, 40, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumroongkit, C.; Deesomchok, A.; Liwsrisakun, C.; Pothirat, C.; Theerakittikul, T.; Limsukon, A.; Trongtrakul, K.; Tajarernmuang, P.; Niyatiwatchanchai, N.; Phrommintikul, A.; et al. Clinical Characteristics, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Acute Pulmonary Embolism in Asian Population. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbiti-Rohr, D.; Kutz, A.; Christ-Crain, M.; Thomann, R.; Zimmerli, W.; Hoess, C.; Henzen, C.; Mueller, B.; Schuetz, P.; ProHOSP Study Group. The National Early Warning Score (NEWS) for outcome prediction in emergency department patients with community-acquired pneumonia: Results from a 6-year prospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e011021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilben, B.; Grandal, L.; Sovik, S. National Early Warning Score (NEWS) as an emergency department predictor of disease severity and 90-day survival in the acutely dyspneic patient—A prospective observational study. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2016, 24, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, A.; Alsma, J.; Verdonschot, R.J.C.G.; Rood, P.P.M.; Zietse, R.; Lingsma, H.F.; Schuit, S.C.E. Predicting mortality in patients with suspected sepsis at the Emergency Department; A retrospective cohort study comparing qSOFA, SIRS and National Early Warning Score. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.G.; Hur, J.; Hong, K.S.; Lee, W.; Ahn, J.H. Prognostic Accuracy of the SIRS, qSOFA, and NEWS for Early Detection of Clinical Deterioration in SARS-CoV-2 Infected Patients. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Hulle, T.; Cheung, W.Y.; Kooij, S.; Beenen, L.F.M.; van Bemmel, T.; van Es, J.; Faber, L.M.; Hazelaar, G.M.; Heringhaus, C.; Hofstee, H.; et al. Simplified diagnostic management of suspected pulmonary embolism (the YEARS study): A prospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet 2017, 390, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moor, J.; Baumgartner, C.; Méan, M.; Stalder, O.; Limacher, A.; Rodondi, N.; Aujesky, D. Validation of the 2019 European Society of Cardiology Risk Stratification Algorithm for Pulmonary Embolism in Normotensive Elderly Patients. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 121, 1660–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, A.; Mallett, S.; Daoud-Elias, M.; Poggi, J.N.; Clarke, M. Prognostic models in acute pulmonary embolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | All Patients (n = 696) | Non-Survivors (n = 133) | Survivors (n = 563) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 57.7 ± 15.7 | 59.2 ± 14.3 | 57.4 ± 15.9 | 0.228 |
| Male, n (%) | 286 (41.1) | 67 (50.4) | 219 (38.9) | 0.019 |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Hypertension | 305 (43.8) | 54 (40.6) | 251 (44.6) | 0.438 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 114 (16.4) | 23 (17.3) | 91 (16.2) | 0.419 |
| Heart failure | 42 (6.0) | 8 (6.0) | 34 (6.0) | 1.000 |
| COPD | 38 (5.5) | 11 (8.3) | 27 (4.8) | 0.135 |
| Cirrhosis | 31 (4.5) | 10 (7.5) | 21 (3.7) | 0.064 |
| Obesity | 12 (1.7) | 2 (1.5) | 10 (1.8) | 1.000 |
| Risk factors | ||||
| Active malignancy | 383 (55.0) | 100 (75.2) | 283 (50.4) | <0.001 |
| Surgery (<4 weeks) | 141 (20.3) | 21 (15.8) | 120 (21.4) | 0.187 |
| Immobilization | 211 (30.4) | 50 (37.6) | 161 (28.6) | 0.047 |
| Long travel | 10 (1.4) | 1 (0.8) | 9 (1.6) | 0.696 |
| Unprovoked (idiopathic) PE | 136 (19.5) | 13 (9.8) | 123 (21.8) | 0.004 |
| Active DVT | 245 (35.2) | 51 (38.3) | 194 (34.5) | 0.674 |
| Symptoms and signs | ||||
| Asymptomatic (incidental) PE | 228 (32.8) | 29 (21.8) | 199 (35.4) | 0.003 |
| Dyspnea | 453 (65.1) | 109 (82.0) | 344 (61.3) | <0.001 |
| Chest pain | 112 (16.1) | 14 (10.5) | 98 (17.5) | 0.018 |
| Syncope | 54 (7.8) | 14 (10.5) | 40 (7.1) | 0.207 |
| Heart rate (bpm) | 105.4 ± 18.4 | 112.5 ± 17.7 | 103.6 ± 18.1 | <0.001 |
| Tachycardia (HR ≥ 110/min) | 326 (46.8) | 89 (66.9) | 237 (42.2) | <0.001 |
| Respiratory rate (bpm) | 24.3 ± 6.1 | 26.7 ± 6.6 | 23.7 ± 65.9 | <0.001 |
| Tachypnea (RR ≥ 30/min) | 158 (22.7) | 51 (38.3) | 107 (19.0) | <0.001 |
| SBP (mmHg), mean ± SD | 116.4 ± 21.9 | 110.4 ± 22.2 | 117.8 ± 21.7 | 0.001 |
| DBP (mmHg), mean ± SD | 72.3 ± 13.9 | 68.9 ± 14.3 | 73.1 ± 13.7 | 0.002 |
| MAP (mmHg), mean ± SD | 87.0 ± 15.7 | 82.8 ± 16.2 | 88.0 ± 15.4 | 0.001 |
| SpO2 (%) | 89.4 ± 7.9 | 86.9 ± 7.4 | 89.9 ± 8.0 | <0.001 |
| Desaturation (SpO2 < 90%) | 333 (47.8) | 89 (67.4) | 244 (43.8) | <0.001 |
| Acute respiratory failure * | 129 (18.5) | 48 (36.1) | 81 (14.4) | <0.001 |
| Electrocardiogram | ||||
| Sinus tachycardia | 393 (56.5) | 101 (75.9) | 292 (51.9) | <0.001 |
| S1Q3T3 | 160 (23.0) | 35 (26.3) | 125 (22.2) | 0.470 |
| RV strain pattern | 112 (16.1) | 21 (15.8) | 91 (16.2) | 0.728 |
| Echocardiography | ||||
| RV dysfunction (n = 332) | 132 (39.8) | 26 (42.6) | 106 (39.1) | 0.665 |
| CT imaging | ||||
| RV/LV > 1 | 190 (27.3) | 43 (32.3) | 147 (26.1) | 0.160 |
| Mediastinal (central) emboli | 310 (44.5) | 51 (38.3) | 259 (46.0) | 0.121 |
| Biomarkers | ||||
| Troponin-T, pg/mL (median, IQR) (N = 228) | 53.1 (19.6, 159.5) | 122.0 (34.0, 233.3) | 40.2 (16.0, 114.5) | 0.002 |
| D-dimer, ng/mL (median, IQR) (N = 129) | 8850.0 (4242.5, 18,748.5) | 12,820.0 (7058.0, 32,909.0) | 7316.0 (3898.0, 14,389.0) | 0.024 |
| Predictive scores | ||||
| NEWS2 (median, IQR) | 8.0 (3.0, 10.0) | 10.0 (7.0, 11.0) | 7.0 (2.0, 9.0) | <0.001 |
| PESI score (median, IQR) | 106.0 (88.0, 129.0) | 133.0 (107.0, 153.0) | 101.0 (85.0, 121.0) | <0.001 |
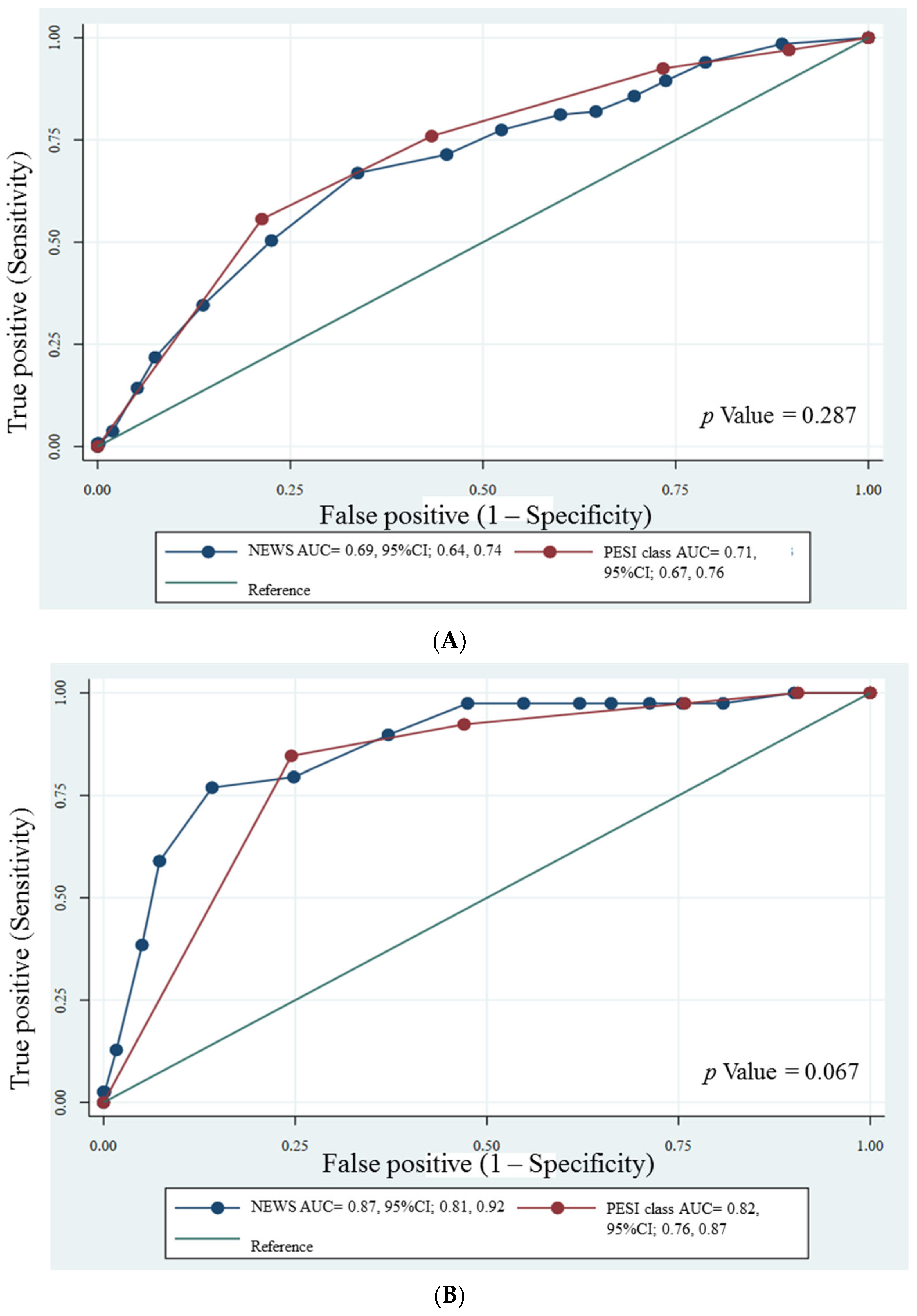
| NEWS Cut-Off | Sensitivity (%) (95% CI) | Specificity (%) (95% CI) | LR+ (95% CI) | LR− (95% CI) | AUROC (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥5.0 | 82.0 (74.4, 88.1) | 35.3 (31.4, 39.5) | 1.27 (1.15, 1.40) | 0.51 (0.35, 0.75) | 0.59 (0.55, 0.63) |
| ≥6.0 | 81.2 (73.5, 87.5) | 40.0 (35.9, 44.1) | 1.35 (1.22, 1.50) | 0.47 (0.33, 0.69) | 0.61 (0.57, 0.65) |
| ≥7.0 | 77.4 (69.4, 84.2) | 47.6 (43.4, 51.8) | 1.48 (1.31, 1.67) | 0.47 (0.34, 0.66) | 0.63 (0.58, 0.67) |
| ≥8.0 | 71.4 (63.0, 78.9) | 54.7 (50.5, 58.9) | 1.58 (1.37, 1.82) | 0.52 (0.39, 0.69) | 0.63 (0.59, 0.67) |
| ≥9.0 | 66.9 (58.2, 74.8) | 66.3 (62.2, 70.2) | 1.98 (1.68, 2.34) | 0.50 (0.39, 0.64) | 0.67 (0.62, 0.71) |
| ≥10.0 | 50.4 (41.6, 59.2) | 77.4 (73.8, 80.9) | 2.23 (1.78, 2.80) | 0.64 (0.54, 0.77) | 0.64 (0.59, 0.69) |
| ≥11.0 | 34.6 (26.6, 43.3) | 86.3 (83.2, 89.1) | 2.53 (1.85, 3.46) | 0.76 (0.67, 0.86) | 0.61 (0.56, 0.65) |
| ≥12.0 | 21.8 (15.1, 29.8) | 92.5 (90.0, 94.6) | 2.92 (1.89, 4.51) | 0.85 (0.77, 0.93) | 0.57 (0.54, 0.61) |
| ≥13.0 | 14.3 (8.8, 21.4) | 94.8 (92.7, 96.5) | 2.77 (1.61, 4.79) | 0.90 (0.84, 0.97) | 0.55 (0.51, 0.58) |
| NEWS Cut-Off | Sensitivity (%) (95% CI) | Specificity (%) (95% CI) | LR+ (95% CI) | LR− (95% CI) | AUROC (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥5.0 | 97.4 (86.5, 99.9) | 33.8 (30.2, 37.5) | 1.47 (1.37, 1.59) | 0.08 (0.01, 0.53) | 0.66 (0.63, 0.69) |
| ≥6.0 | 97.4 (86.5, 99.9) | 37.9(34.2, 41.7) | 1.57 (1.45, 1.70) | 0.07 (0.01, 0.47) | 0.68 (0.65, 0.71) |
| ≥7.0 | 97.4 (86.5, 99.9) | 45.2 (41.4, 49.1) | 1.78 (1.63, 1.94) | 0.06 (0.01, 0.39) | 0.71 (0.68, 0.75) |
| ≥8.0 | 97.4 (86.5, 99.9) | 52.5 (48.6, 56.4) | 2.05 (1.87, 2.26) | 0.05 (0.01, 0.34) | 0.75 (0.72, 0.78) |
| ≥9.0 | 89.7 (75.8, 97.1) | 62.9 (59.0, 66.6) | 2.42 (2.09, 2.79) | 0.16 (0.06, 0.41) | 0.76 (0.71, 0.82) |
| ≥10.0 | 79.5 (63.5, 90.7) | 75.2 (71.7, 78.4) | 3.20 (2.60, 3.94) | 0.27 (0.15, 0.51) | 0.77 (0.71, 0.84) |
| ≥11.0 | 76.9 (60.7, 88.9) | 85.8 (82.9, 88.4) | 5.43 (4.21, 7.01) | 0.27 (0.15, 0.48) | 0.81 (0.75, 0.88) |
| ≥12.0 | 59.0 (42.1, 74.4) | 92.7 (90.4, 94.6) | 8.07 (5.53, 11.80) | 0.44 (0.30, 0.65) | 0.76 (0.68, 0.84) |
| ≥13.0 | 38.5 (23.4, 55.4) | 95.0 (93.0, 96.5) | 7.66 (4.56, 12.90) | 0.65 (0.51, 0.83) | 0.67 (0.59, 0.75) |
| Predictive Scores | All-Cause Death (n = 133) | Adjusted Risk Ratio * (95% CI) | p Value | PE-Related Death (n = 39) | Adjusted Risk Ratio * (95% CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEWS category | ||||||
| Low (0–4) (n = 223) | 24 (18.1) | Ref. | 1 (2.6) | Ref. | ||
| Medium (5–6) (n = 75) | 6 (4.5) | 0.71 (0.30, 1.68) | 0.440 | 0 (0.0) | N.A. * | |
| High (≥7) (n = 398) | 103 (77.4) | 2.33 (1.54, 3.53) | <0.001 | 38 (97.4) | 21.87 (3.02, 158.35) | 0.002 |
| NEWS cut off in this study | ||||||
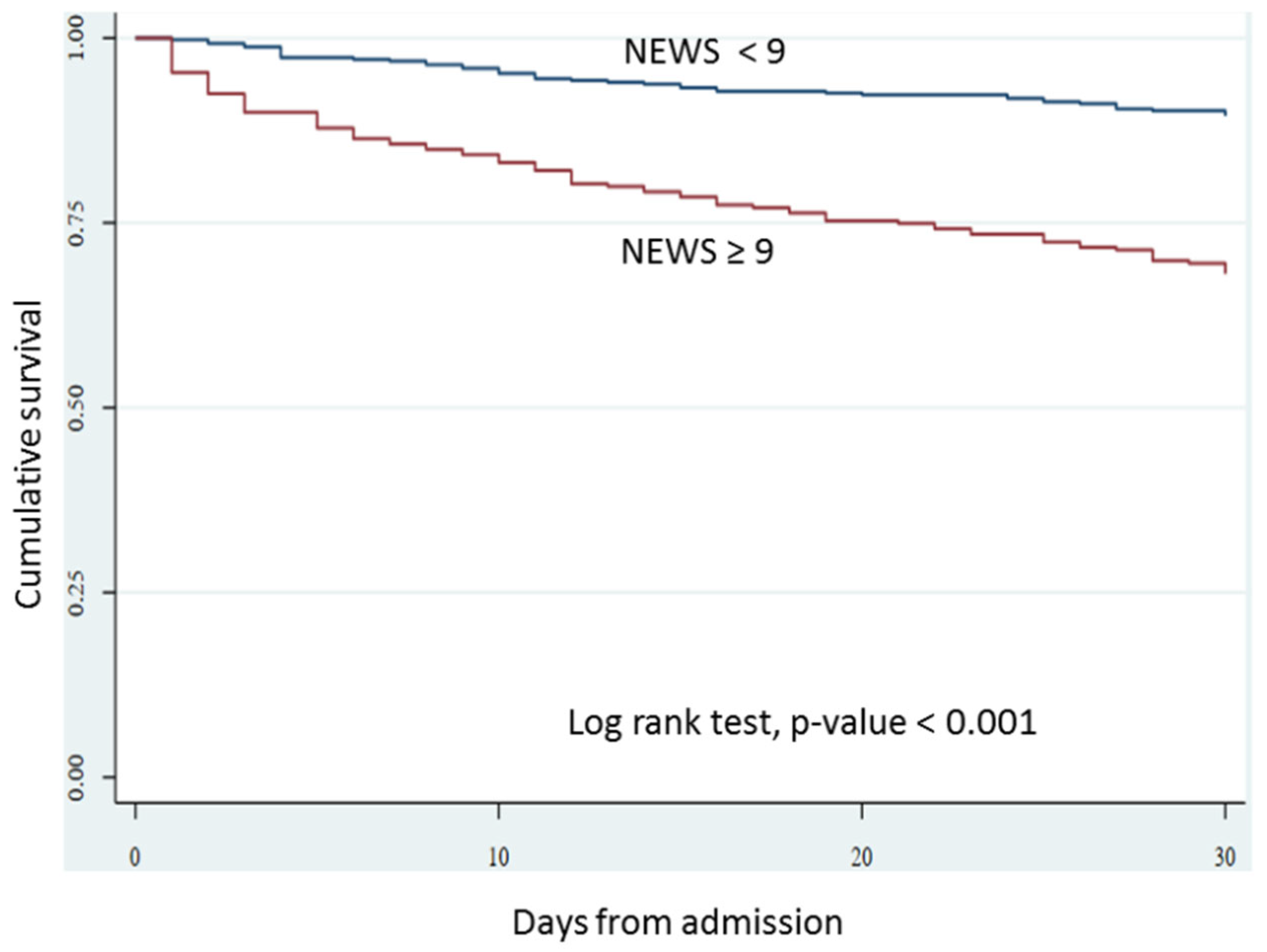
| NEWS < 9 (n = 417) | 44 (10.6) | Ref. | 4 (1.0) | Ref. | ||
| NEWS ≥ 9 (n = 279) | 89 (31.9) | 2.96 (2.13, 4.12) | <0.001 | 35 (12.5) | 13.14 (4.72, 36.56) | <0.001 |
| PESI classification | ||||||
| I–II (n = 160) | 10 (6.3) | Ref. | 1 (0.6) | Ref. | ||
| III (n = 191) | 22 (11.5) | 1.84 (0.89, 3.77) | 0.096 | 2 (1.0) | 1.67 (0.15, 18.31) | 0.674 |
| IV (n = 151) | 27 (17.9) | 2.86 (1.43, 5.70) | 0.003 | 3 (2.0) | 3.20 (0.34, 30.44) | 0.311 |
| V (n = 194) | 74 (38.1) | 6.00 (3.21, 11.24) | <0.001 | 33 (17.0) | 27.84 (3.85, 201.36) | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bumroongkit, C.; Tajarernmuang, P.; Trongtrakul, K.; Liwsrisakun, C.; Deesomchok, A.; Pothirat, C.; Theerakittikul, T.; Limsukon, A.; Niyatiwatchanchai, N.; Inchai, J.; et al. Predictive Ability of the National Early Warning Score in Mortality Prediction of Acute Pulmonary Embolism in the Southeast Asian Population. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10020060
Bumroongkit C, Tajarernmuang P, Trongtrakul K, Liwsrisakun C, Deesomchok A, Pothirat C, Theerakittikul T, Limsukon A, Niyatiwatchanchai N, Inchai J, et al. Predictive Ability of the National Early Warning Score in Mortality Prediction of Acute Pulmonary Embolism in the Southeast Asian Population. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2023; 10(2):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10020060
Chicago/Turabian StyleBumroongkit, Chaiwat, Pattraporn Tajarernmuang, Konlawij Trongtrakul, Chalerm Liwsrisakun, Athavudh Deesomchok, Chaicharn Pothirat, Theerakorn Theerakittikul, Atikun Limsukon, Nutchanok Niyatiwatchanchai, Juthamas Inchai, and et al. 2023. "Predictive Ability of the National Early Warning Score in Mortality Prediction of Acute Pulmonary Embolism in the Southeast Asian Population" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 10, no. 2: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10020060
APA StyleBumroongkit, C., Tajarernmuang, P., Trongtrakul, K., Liwsrisakun, C., Deesomchok, A., Pothirat, C., Theerakittikul, T., Limsukon, A., Niyatiwatchanchai, N., Inchai, J., & Chaiwong, W. (2023). Predictive Ability of the National Early Warning Score in Mortality Prediction of Acute Pulmonary Embolism in the Southeast Asian Population. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 10(2), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10020060






