How Do Geriatric Scores Predict 1-Year Mortality in Elderly Patients with Suspected Pneumonia?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Scores Description
| CURB-65 | Alive | Deceased | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 32 22.86 | 9 15.00 | 41 20.50 |
| 2 | 66 47.14 | 18 30.00 | 84 42.00 |
| 3 | 38 27.14 | 23 38.33 | 61 30.50 |
| 4 | 4 2.86 | 10 16.67 | 14 7.00 |
| Total | 140 100.00 | 60 100.00 | 200 100.00 |
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| CIRS-G | 1.08 | 1.01–1.15 | 0.014 |
| Sex | 1.34 | 0.65–2.74 | 0.79 |
| Age | 1.02 | 0.97–1.07 | 0.37 |
| BMI | 0.89 | 0.82–0.96 | 0.002 |
| CURB65 | 1.73 | 1.13–2.65 | 0.011 |
| CRP | 0.99 | 0.98–1.00 | 0.05 |
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| MNA | 0.83 | 0.71–0.96 | 0.012 |
| Sex | 1.62 | 0.75–3.52 | 0.22 |
| Age | 1.04 | 0.99–1.10 | 0.089 |
| BMI | 0.91 | 0.84–0.99 | 0.036 |
| CURB65 | 1.7 | 1.07–2.70 | 0.025 |
| CRP | 0.99 | 0.99–1.0 | 0.19 |
| Score | 1-Month Mortality | 1-Year Mortality |
|---|---|---|
| CURB-65 | 1.78 (p = 0.1) | 1.85 (p = 0.004) |
| SOFA | 1.3 (p = 0.81) | 1.24 (p = 0.048) |
| CIRS-G | 1.07 (p = 0.24) | 1.08 (p = 0.021) |
| MNA | 0.92 (p = 0.53) | 0.81 (p = 0.007) |
References
- Welte, T.; Torres, A.; Nathwani, D. Clinical and economic burden of community-acquired pneumonia among adults in Europe. Thorax 2012, 67, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fine, M.J.; Auble, T.E.; Yealy, D.M.; Hanusa, B.H.; Weissfeld, L.A.; Singer, D.E.; Coley, C.M.; Marrie, T.J.; Kapoor, W.N. A prediction rule to identify low-risk patients with community-acquired pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.S.; van der Eerden, M.M.; Laing, R.; Boersma, W.G.; Karalus, N.; I Town, G.; A Lewis, S.; Macfarlane, J.T. Defining community acquired pneumonia severity on presentation to hospital: An international derivation and validation study. Thorax 2003, 58, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vincent, J.-L.; Moreno, R.; Takala, J.; Willatts, S.; De Mendonça, A.; Bruining, H.; Reinhart, C.K.; Suter, P.M.; Thijs, L.G. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 1996, 22, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, C.W.; Liu, V.X.; Iwashyna, T.J.; Brunkhorst, F.M.; Rea, T.D.; Scherag, A.; Rubenfeld, G.; Kahn, J.M.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Singer, M.; et al. Assessment of Clinical Criteria for Sepsis: For the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 762–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asai, N.; Watanabe, H.; Shiota, A.; Kato, H.; Sakanashi, D.; Hagihara, M.; Koizumi, Y.; Yamagishi, Y.; Suematsu, H.; Mikamo, H. Efficacy and accuracy of qSOFA and SOFA scores as prognostic tools for community-acquired and healthcare-associated pneumonia. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 84, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, M.I.; Faverio, P.; Anzueto, A. Long-term prognosis in community-acquired pneumonia. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 26, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmelee, P.A.; Thuras, P.D.; Katz, I.R.; Lawton, M.P. Validation of the cumulative illness rating scale in a geriatric residential population. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1995, 43, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guigoz, Y.; Vellas, B.; Garry, P.J. Assessing the nutritional status of the elderly: The Mini Nutritional Assessment as part of the geriatric evaluation. Nutr. Rev. 1996, 54, S59–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, D.; Stewart, G.; Baldry, J.; Johnson, J.; Rossiter, D.; Petruckevitch, A.; Thompson, A. The functional independence measure: A comparative validity and reliability study. Disabil. Rehabil. 1995, 17, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, M.; Hudon, C.; Dubois, M.F.; Almirall, J.; Lapointe, L.; Soubhi, H. Comparative assessment of three different indices of multimorbidity for studies on health-related quality of life. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2005, 3, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; She, Q.; Li, M.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, W.; Peng, Z.; Wu, J. Effect of Poor Nutritional Status and Comorbidities on the Occurrence and Outcome of Pneumonia in Elderly Adults. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 719530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, E.; Chapman, I.M.; Piantadosi, C.; Visvanathan, R. Performance of nutritional screening tools in predicting poor six-month outcome in hospitalised older patients. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 23, 394–399. [Google Scholar]
- Kagansky, N.; Berner, Y.; Koren-Morag, N.; Perelman, L.; Knobler, H.; Levy, S. Poor nutritional habits are predictors of poor outcome in very old hospitalized patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prendki, V.; Scheffler, M.; Huttner, B.; Garin, N.; Herrmann, F.; Janssens, J.-P.; Marti, C.; Carballo, S.; Roux, X.; Serratrice, C.; et al. Low-dose computed tomography for the diagnosis of pneumonia in elderly patients: A prospective, interventional cohort study. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 170237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesemann, T.; Nüllmann, H.; Pflug, M.A.; Heppner, H.J.; Pientka, L.; Thiem, U. Pneumonia severity, comorbidity and 1-year mortality in predominantly older adults with community-acquired pneumonia: A cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, H.Y.; Shim, S.S.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Chang, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Ryu, Y.J. Long-Term Mortality and Prognostic Factors in Aspiration Pneumonia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2019, 20, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, H.J.; Byun, K.S.; Han, J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.E.; Yoon, S.H.; Jeon, D.; Kim, Y.S.; Cho, W.H. Prognostic significance of malnutrition for long-term mortality in community-acquired pneumonia: A propensity score matched analysis. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2019, 34, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebib, N.; Cuvelier, C.; Malézieux-Picard, A.; Parent, T.; Roux, X.; Fassier, T.; Müller, F.; Prendki, V. Pneumonia prevention in the elderly patients: The other sides. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 33, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, C.H.; Ul Hassan, S.W.; Sacre, J.; Maier, A.B. Morbidity measures predicting mortality in inpatients: A systematic review. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekry, D.; Valle, B.H.; Michel, J.P.; Esposito, F.; Gold, G.; Krause, K.H.; Herrmann, F.R. Prospective comparison of six comorbidity indices as predictors of 5 years post hospital discharge survival in the elderly. Rejuvenation Res. 2010, 13, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvi, F.; Miller, M.D.; Grilli, A.; Giorgi, R.; Towers, A.L.; Morichi, V.; Spazzafumo, L.; Mancinelli, L.; Espinosa, E.; Rappelli, A.; et al. A manual of guidelines to score the modified cumulative illness rating scale and its validation in acute hospitalized elderly patients. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2008, 56, 1926–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritt, M.; Ritt, J.I.; Sieber, C.C.; Gaßmann, K.G. Comparing the predictive accuracy of frailty, comorbidity, and disability for mortality: A 1-year follow-up in patients hospitalized in geriatric wards. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahoney, F.I.; Barthel, D.W. Functional evaluation: The Barthel Index. Md. State Med. J. 1965, 14, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mitnitski, A.B.; Mogilner, A.J.; Rockwood, K. Accumulation of deficits as a proxy measure of aging. Sci. World J. 2001, 1, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rockwood, K.; Song, X.; MacKnight, C.; Bergman, H.; Hogan, D.B.; McDowell, I.; Mitnitski, A. A global clinical measure of fitness and frailty in elderly people. CMAJ 2005, 173, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Andrea, A.; Le Peillet, D.; Fassier, T.; Prendki, V.; Trombert, V.; Reny, J.-L.; Roux, X. Functional Independence Measure score is associated with mortality in critically ill elderly patients admitted to an intermediate care unit. BMC Geriatr. 2020, 20, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Tang, W.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, C. Impact of frailty on 30-day and 1-year mortality in hospitalised elderly patients with community-acquired pneumonia: A prospective observational study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e038370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Alive at One Year (N = 140) | Dead at One Year (N = 60) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD) | 82.8 (7.6) | 86.2 (7.8) | 0.003 |
| Male sex | 68 (49,0) | 34 (56,7) | 0.29 |
| Female sex | 72 (51,0) | 26 (43,3) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.1 (5.3) | 23.3 (5.5) | 0.0006 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | 29 (21) | 11 (18) | 0.76 |
| COPD | 23 (16) | 12 (20) | 0.59 |
| Cancer | 11 (8) | 6 (10) | 0.59 |
| CHF | 30 (21) | 15 (25) | 0.62 |
| CAD | 20 (14) | 11 (18) | 0.47 |
| CVD | 108 (77) | 48 (80) | 0.65 |
| Dementia | 26 (19) | 21 (35) | 0.012 |
| Chronic Renal Failure | 31 (22) | 16 (27) | 0.62 |
| Severity scores | |||
| CURB-65 | 0.0002 | ||
| 1 | 32 (23) | 9 (15) | |
| 2 | 66 (47) | 18 (30) | |
| 3 | 38 (27) | 23 (38) | |
| 4 | 4 (3) | 10 (17) | |
| SOFA | 2.3 (1.4) | 2.9 (2.1) | 0.014 |
| Geriatric scores | |||
| FIM (N = 171) | 76.3 (32.0) | 64.5 (26.0) | 0.009 |
| CIRS-G | 22.2 (6.5) | 25.5 (5.2) | 0.0003 |
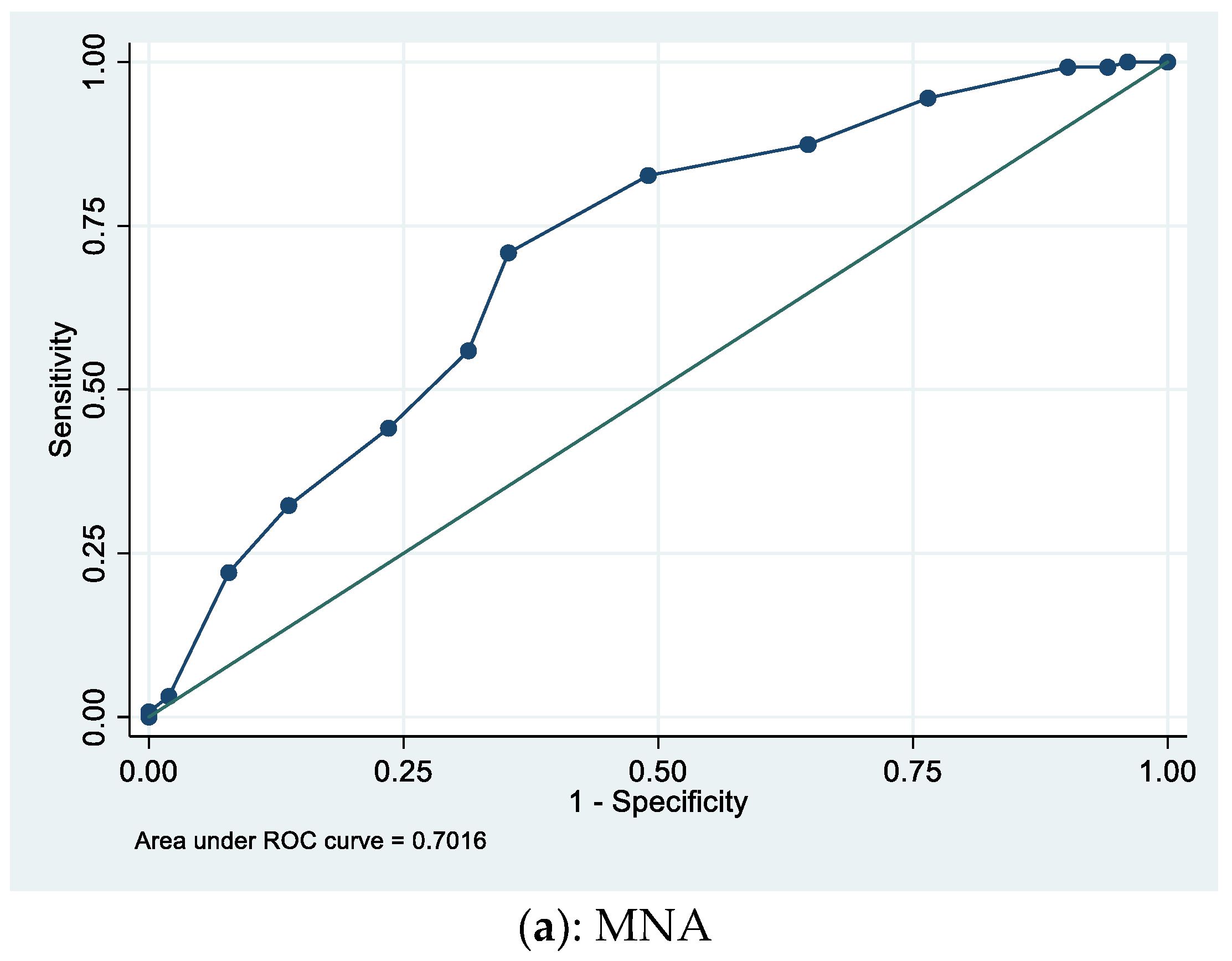
| MNA (N = 178) | 8.9 (2.6) | 6.8 (3.0) | <0.0001 |
| Laboratory findings | |||
| Urea (mmol/l) | 8.9 (4.8) | 10.4 (6.4) | 0.033 |
| Albumin (g/l) (N = 193) | 35.2 (5.3) | 34.2 (5.7) | 0.13 |
| PaO2 (kPa) | 10.2 (4.3) | 10.7 (5.2) | 0.25 |
| FiO2 | 0.27 (0.12) | 0.30 (0.14) | 0.10 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 123 (19.3) | 124 (16.9) | 0.30 |
| WBC (G/L) | 11.7 (4.8) | 11.1 (5.9) | 0.24 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 128 (103) | 94 (73) | 0.01 |
| NT-proBNP (ng/l) (N = 170) | 2537 (2651) | 3402 (3032) | 0.035 |
| A. Univariate. | |||
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | p |
| CIRS-G | 1.09 | 1.06–1.12 | 0.001 |
| MNA | 0.76 | 0.71–0.81 | <0.001 |
| FIM | 0.98 | 0.97–0.99 | 0.02 |
| B. Multivariate | |||
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | p |
| CIRS-G | 1.08 | 1.01–1.15 | 0.014 |
| MNA | 0.83 | 0.71–0.96 | 0.012 |
| FIM | 0.99 | 0.97–1.0 | 0.269 |
| Variable | Sensitivity | Specificity | LR+ | LR− | DOR(LR+/LR−) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIRS-G ≥ 26 | 0.59 | 0.70 | 1.94 | 0.59 | 3.27 |
| MNA ≤ 8 | 0.71 | 0.65 | 2.0 | 0.45 | 4.46 |
| FIM ≤ 63 | 0.58 | 0.52 | 1.21 | 0.81 | 1.50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nascè, A.; Malézieux-Picard, A.; Hakiza, L.; Fassier, T.; Zekry, D.; Stirnemann, J.; Garin, N.; Prendki, V.; Roux, X. How Do Geriatric Scores Predict 1-Year Mortality in Elderly Patients with Suspected Pneumonia? Geriatrics 2021, 6, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics6040112
Nascè A, Malézieux-Picard A, Hakiza L, Fassier T, Zekry D, Stirnemann J, Garin N, Prendki V, Roux X. How Do Geriatric Scores Predict 1-Year Mortality in Elderly Patients with Suspected Pneumonia? Geriatrics. 2021; 6(4):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics6040112
Chicago/Turabian StyleNascè, Alberto, Astrid Malézieux-Picard, Landry Hakiza, Thomas Fassier, Dina Zekry, Jérôme Stirnemann, Nicolas Garin, Virginie Prendki, and Xavier Roux. 2021. "How Do Geriatric Scores Predict 1-Year Mortality in Elderly Patients with Suspected Pneumonia?" Geriatrics 6, no. 4: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics6040112
APA StyleNascè, A., Malézieux-Picard, A., Hakiza, L., Fassier, T., Zekry, D., Stirnemann, J., Garin, N., Prendki, V., & Roux, X. (2021). How Do Geriatric Scores Predict 1-Year Mortality in Elderly Patients with Suspected Pneumonia? Geriatrics, 6(4), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics6040112






