Improving the Care of Older Patients by Decreasing Potentially Inappropriate Medications, Potential Medication Omissions, and Serious Drug Events Using Pharmacogenomic Data about Variability in Metabolizing Many Medications by Seniors
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Purposes of This Article
1.2. How Frequent Are Potentially Inappropriate Medications (PIMs) and Potential Prescribing Omissions (PPOs)?
1.3. How Frequent Are Serious Drug Events (SDEs) in Seniors?
1.4. Which Are the 10 Most Frequent Medication Classes Prescribed to Seniors in Canada?
1.5. Of the Top 10 Medications Prescribed to Seniors in Canada Which Are American Geriatric Society PIMs and for How Many Are the P450 Isoforms That Metabolize Them Known?
1.6. Which Are the Top 10 Most Frequent Serious Drug Events (SDEs) Associated with Hospitalizations of Seniors in Canada?
2. Metabolism of Medications by the P450 Enzyme System
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Design
3.2. The Key Sources of Pharmacogenomic Data
4. Results
4.1. STOPP PIMs for Which the P450 Cytochrome Isoforms That Metabolize Them Are Known
- The busiest isoforms (in order) are (Table 4): 3A457 (97 medications), 2C9 (96 medications), 2D6 (75 medications), 2C19 (48), 1A2 (38), and 2C8 (29), 2B6 (24), and 2E1 (22). If prescribers are providing multiple medications for patients with many chronic comorbidities, thought needs to be given whether they are overloading specific isoforms.
- Because patients may request multiple central nervous system medications including antidepressants, anxiolytics, sedatives, hypnotics, psychiatric, and skeletal muscle relaxant drugs this group will likely involve the most extensive and complex metabolic activities, with the greatest range of inhibitor and inducer activity and the greatest risk of SDEs. Of the anticholinergics, diphenhydramine is metabolized by six isoforms and inhibits one. Of the antidepressants, the tricyclics are metabolized by five isoforms; the SSRIs and SNRIs by four, escitalopram and fluvoxamine are inhibitors of four, fluvoxamine is an inhibitor of three, and paroxetine an inhibitor of two. The antipsychotics are mostly metabolized by two isoforms (2D6 and 3A457) but olanzapine by five. Of the barbiturates, butalbital is metabolized by five isoforms and phenobarbitone is an inducer of three isoforms. Of the benzodiazepines, diazepam is metabolized by four isoforms. The antiepileptic carbamazepine is metabolized by five and induces four isoforms, phenytoin is metabolized by five and induces two, and phenobarbitone by one isoform but induces three. Of the smooth muscle relaxants, orphenadrine is metabolized by five isoforms and methocarbamol by four. The 3A457 isoform metabolizes all CNS medications and it would be very easy to overload it. Great caution is thus required in prescribing for patients with multiple CNS complaints.
- Cardiac and antiplatelet/anticoagulant medications require great caution to avoid causing SDEs because they are metabolized by and inhibit a wide variety of isoforms. Amiodarone is an inhibitor of four isoforms. Ticlopidine is metabolized by five isoforms and inhibits four. Clopidogrel is metabolized by five and inhibits two. Warfarin is metabolized by four and also by the genes VKORC1 and CYP4F2, aspirin by three, and apixaban, rivaroxaban, and ticagrelor by 3A457.
- The proton-pump inhibitors are also metabolized by multiple isoforms. Omeprazole is metabolized by three isoforms (2C9, 2C19, and 3A457, and also induces 1A2 and inhibits 2C19 and 3A457) and esomeprazole is similar.
- Although theophylline is rarely used as a respiratory medication but may be prescribed in some countries and it is metabolized by five isoforms
- The musculoskeletal drugs are also metabolized by multiple isoforms. Ibuprofen is metabolized by six isoforms, indomethacin by five, and naproxen by four. The remainder are metabolized by three isoforms (2B6, 2C8, and 2E1). Of the Cox-2 inhibitors, celecoxib is metabolized by six isoforms and meloxicam by four.
- The narcotics all are metabolized by 2D6 and 3A457 and meperidine and tramadol also by 2B6. When patients seek multiple narcotics, this is particularly important to remember as a reason for declining.
- For the cardiovascular system not known for any of the 12 ACE inhibitors, 5 of 11 beta-blockers, two of six calcium channel blockers, all four alpha-blockers, two of the three anticholinesterase inhibitors, and for digoxin.
- For the central nervous system, none of the anti-Parkinson medications.
- For the GU and GI systems, 13 antimuscarinics and none of the antispasmodics.
- For the respiratory system, the antimuscarinic bronchodilators.
- For the musculoskeletal system, none of the five bisphosphonates.
4.2. American Geriatric Society PIMs for Which the P450 Cytochrome Isoforms That Metabolize Them Are Known
- Medications to be avoided [4] (AGS Table 2). Within this group the P450 isoforms that metabolize some of the following medications are known, and can be used as additional information leading to further caution:
- Five first-generation antihistamines (the P450 isoforms of six of these are known);
- Ten highly anticholinergic antidepressants (the P450 isoforms of six are known);
- Seven barbiturates (the P450 isoforms of five are known);
- Thirteen benzodiazepines (the P450 isoforms of two are known);
- Androgens and estrogens (P450 isoforms are known);
- Three long-acting sulfonylureas (P450 isoforms of two are known);
- Proton-pump inhibitors (P450 isoforms of four are known);
- Eighteen NSAIDs (P450 isoforms of 12 are known);
- Six skeletal muscle relaxants (P450 isoforms of five are known).
P450 isoforms are not known for:- j.
- Two anti-Parkinsonian agents (benztropine and trihexyphenidyl);
- k.
- Three peripheral alpha-agonists;
- l.
- Four CNS alpha-agonists;
- m.
- Cardiac medications: disopyramide, dronedarone, digoxin, and amiodarone;
- n.
- Three nonbenzodiazepine, benzodiazepine receptor agonist hypnotics.
- Medications that increase drug–disease interactions. AGS advises avoiding these [4] (Table 3). Medications and the P450 isoforms that metabolize them are known for some and listed in Table 5 below.
- For patients with heart failure:
- Eighteen NSAIDs (P450 isoforms of 12 are known);
- The two Cox-2 inhibitors celecoxib and meloxicam (P450 isoforms are known);
- amiodarone, rosiglitazone, pioglitazone, and troglitazone (P450 are known but for cilostazol and dronedarone are not known).
- For patients with syncope:
- Three acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (P450 is known for donepezil);
- Seven peripheral alpha-1 blockers (P450 are not known);
- Six tricyclics (P450 are known);
- Chlorpromazine (P450 is not known).
- For patients with central nervous system problems of delirium and dementia:
- 56 medications with strong anticholinergic properties (P450 isoforms are known for 22);
- Fourteen antipsychotics (P450 are known for 11);
- Four benzodiazepines (P450 are known for two);
- Four nonbenzodiazepine benzodiazepine receptor hypnotics (P450 is known for one).
- For patients with falls in addition:
- Four H2-receptor antagonists (P450 are known for cimetidine and ranitidine);
- Anticonvulsants (P450 are known for five).
- For patients with Parkinson’s:
- Fourteen antipsychotics (P450 are known for 11);
- Antiemetics (P450 are known for two);
- Medications with strong anticholinergic properties. AGS ([4], AGS Table 7) recommends avoiding these and provides a comprehensive list of 56 medications with strong anticholinergic properties used in multiple anatomic/therapeutic classes: antiarrhythmics, antidepressants, antiemetics, antihistamines, antimuscarinics, antiparkinsonian agents, antipsychotics, antispasmodics, and skeletal muscle relaxants [4].
4.3. For How Many START PPOs Are the P450 Isoforms Known?
4.4. Genetic Influences on Cell Influx and Efflux Pumps
4.5. Frequently Prescribed Medications Which Are Neither PIMs nor PPOs
5. Discussion
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Schwebel, D.C.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Cheng, P.; Ning, P.; Hu, G.-Q. Population ageing and mortality during 1990–2017: A global decomposition analysis. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Füssenich, K.; Nusselder, W.J.; Lhachimi, S.K.; Boshuizen, H.; Feenstra, T.L. Potential gains in health expectancy by improving lifestyle: An application for European regions. Popul. Health Metr. 2019, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, M.M.; Avendaño, M. Social Policy Expenditures and Life Expectancy in High-Income Countries. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2018, 54, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2019 Updated AGS Beers Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2019, 67, 674–694. [Google Scholar]
- O’Mahony, D.; O’Sullivan, D.; Byrne, S.; O’Connor, M.N.; Ryan, C.; Gallagher, P. STOPP/START criteria for potentially inappropriate prescribing in older people: Version 2. Age Ageing 2014, 44, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masnoon, N.; Shakib, S.; Ellett, L.K.; Caughey, G.E. What is polypharmacy? A systematic review of definitions. BMC Geriatr. 2017, 17, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leelakanok, N.; Holcombe, A.L.; Lund, B.C.; Gu, X.; Schweizer, M.L. Association between polypharmacy and death: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2017, 57, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Maruf, A.; Fan, M.; Arnold, P.D.; Müller, D.J.; Aitchison, K.J.; Bousman, C. Pharmacogenetic Testing Options Relevant to Psychiatry in Canada. Can. J. Psychiatry 2020, 65, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousman, C.A.; Dunlop, B.W. Genotype, phenotype, and medication recommendation agreement among commercial pharmacogenetic-based decision support tools. Pharmacogenom. J. 2018, 18, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.E.; Thomas, B.C. A Systematic Review of Studies of the STOPP/START 2015 and American Geriatric Society Beers 2015 Criteria in Patients ≥65 Years. Curr. Aging Sci. 2019, 12, 121–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.E.; Nguyen, L.T.; Jackson, D.; Naugler, C. Potentially Inappropriate Prescribing and Potential Prescribing Omissions in 82,935 Older Hospitalised Adults: Association with Hospital Readmission and Mortality Within Six Months. Geriatrics 2020, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oscanoa, T.J.; Lizaraso, F.; Carvajal, A. Hospital admissions due to adverse drug reactions in the elderly. A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 73, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaeda, T.; Tamon, A.; Kadoyama, K.; Okuno, Y. Data Mining of the Public Version of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 10, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, R.; Von Hehn, L.; Herdegen, T.; Klein, H.-J.; Bruhn, O.; Petri, H.; Höcker, J. OpenVigil FDA—Inspection of U.S. American Adverse Drug Events Pharmacovigilance Data and Novel Clinical Applications. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonawane, K.B.; Cheng, N.; Hansen, R.A. Serious Adverse Drug Events Reported to the FDA: Analysis of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System 2006–2014 Database. J. Manag. Care Spéc. Pharm. 2018, 24, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onakpoya, I.; Heneghan, C.J.; Aronson, J.K. Worldwide withdrawal of medicinal products because of adverse drug reactions: A systematic review and analysis. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2016, 46, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehab, N.; Lovegrove, M.C.; Geller, A.I.; Rose, K.O.; Weidle, N.J.; Budnitz, D.S. US Emergency Department Visits for Outpatient Adverse Drug Events, 2013–2014. JAMA 2016, 316, 2115–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bank, P.C.D.; Swen, J.J.; Guchelaar, H.-J. Estimated nationwide impact of implementing a preemptive pharmacogenetic panel approach to guide drug prescribing in primary care in The Netherlands. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drug Use among Seniors in Canada, 2016; Canadian Institute for Health Information: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2018; Available online: https://www.cihi.ca/sites/default/files/document/drug-use-among-seniors-2016-en-web.pdf (accessed on 26 April 2020).
- Moore, V.R.; Glassman, P.A.; Au, A.; Good, C.B.; Leadholm, T.C.; Cunningham, F.E. Adverse drug reactions in the Veterans Affairs healthcare system: Frequency, severity, and causative medications analyzed by patient age. Am. J. Health Pharm. 2019, 76, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, M.G. Drug Biotransformation. In Basic & Clinical Pharmacology, 14th ed.; Katzung, B.G., Ed.; McGraw Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 56–73. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Lauschke, V.M. Worldwide Distribution of Cytochrome P450 Alleles: A Meta-analysis of Population-scale Sequencing Projects. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 102, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Westrhenen, R.; Aitchison, K.J.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Jukić, M.M. Pharmacogenomics of Antidepressant and Antipsychotic Treatment: How Far Have We Got and Where Are We Going? Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. BMJ 2007, 335, 806–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DrugBank. Available online: www.drugbank.ca (accessed on 9 May 2020).
- Flockhart, D.A. Drug Interactions: Cytochrome P450 Drug Interaction Table. Indiana University School of Medicine. Available online: https://drug-interactions.medicine.iu.edu (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- RxFiles, 12th ed.; 104 Clinic Place: Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 2019; Available online: www.RxFiles.ca (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Geri-RxFiles. Assessing Medications in Older Adults, 3rd ed.; University of Saskatchewan College of Pharmacy and Nutrition: Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 2019.
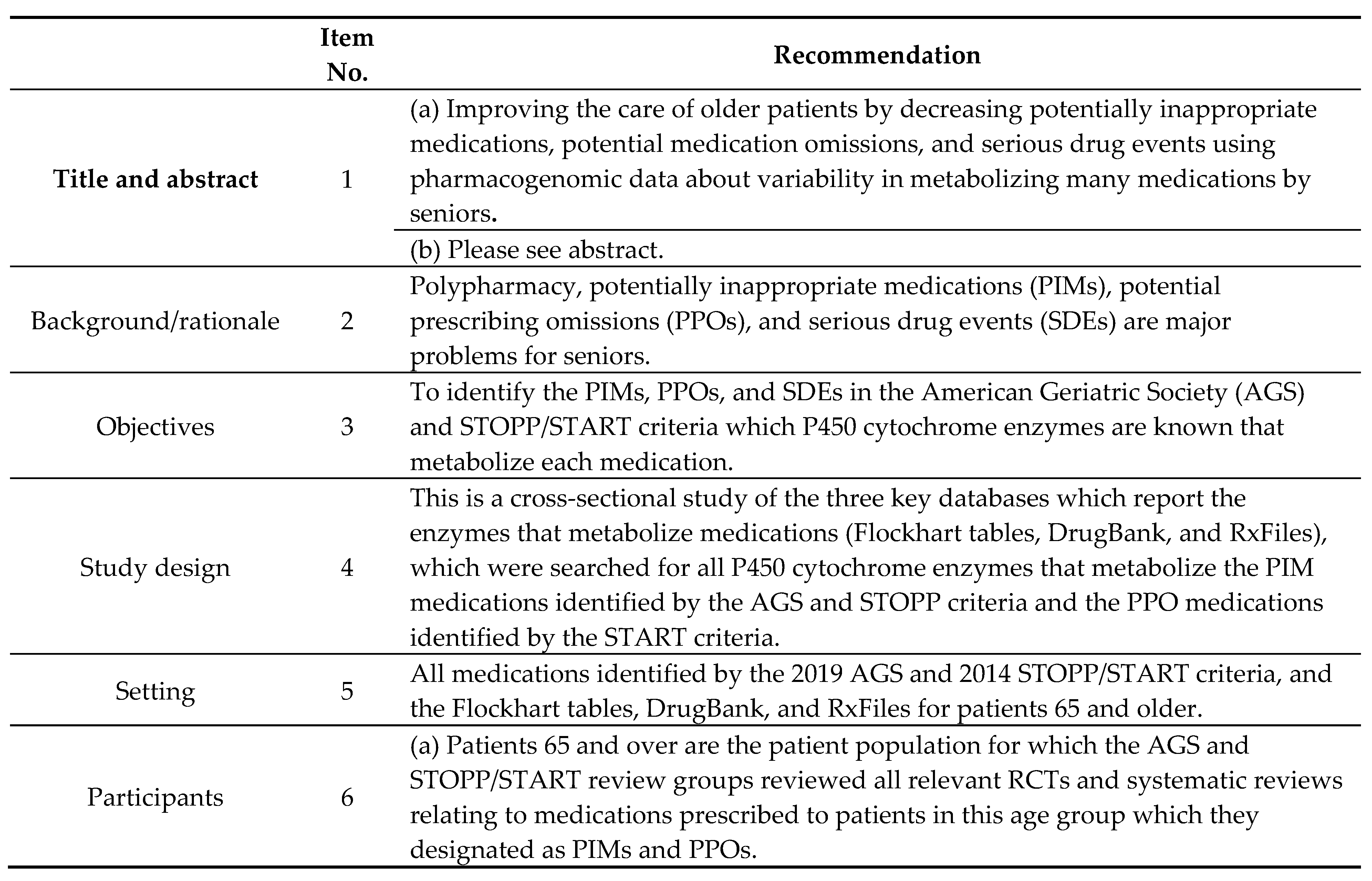
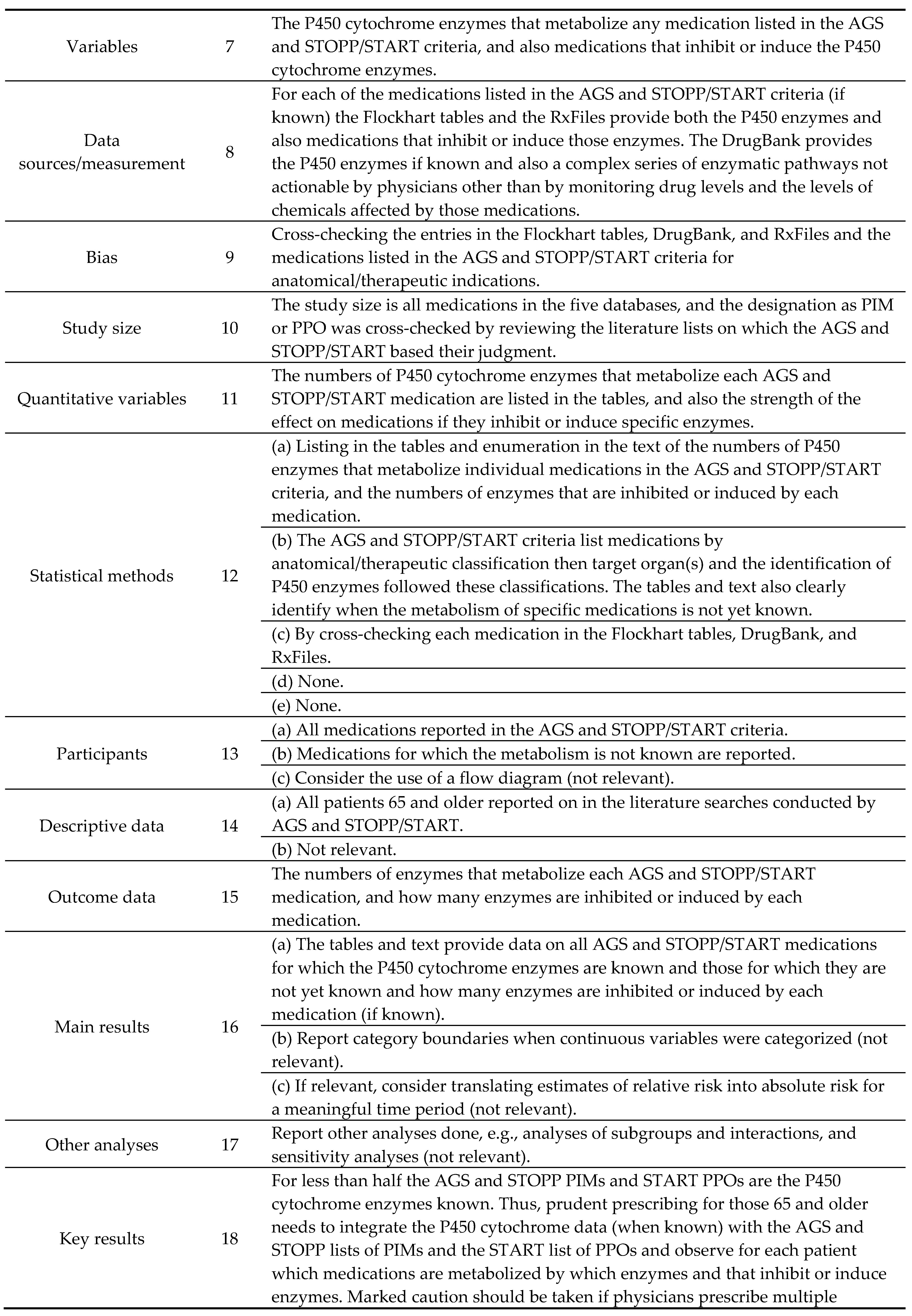
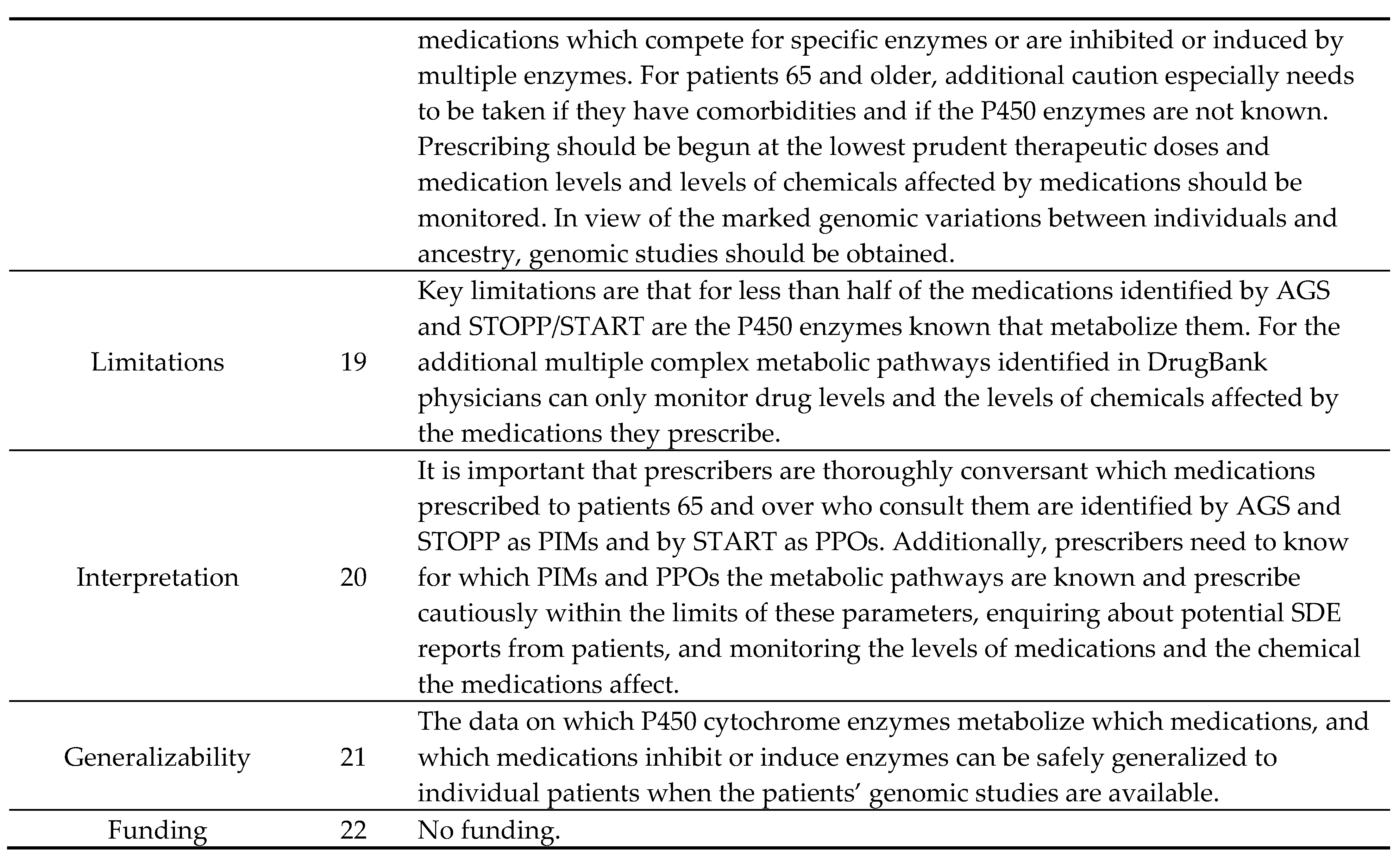
| Drug Class | Common Uses | Rate of Use, Chronic Use | By Age Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rate of Use | Rate of Chronic Use (Defined by 2016 AGS Criteria) | 65 to 74 | 75 to 84 | 85+ | ||
| HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) | High cholesterol | 48.4% | 43.5% | 47.5% | 53.1% | 41.8% |
| Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) | Gastroesophageal reflux disease, peptic ulcer disease | 32.1% | 23.5% | 28.3% | 35.5% | 39.0% |
| Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, excluding combinations | High blood pressure, heart failure | 24.5% | 21.1% | 22.5% | 26.7% | 27.2% |
| Beta-blocking agents, | selective High blood pressure, heart failure, angina (chest pain) | 23.5% | 20.6% | 18.7% | 27.9% | 32.5% |
| Dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers | High blood pressure | 21.9% | 18.8% | 17.8% | 25.5% | 29.8% |
| Thyroid hormones | Hypothyroidism | 19.1% | 17.9% | 16.0% | 20.8% | 26.6% |
| Angiotensin II antagonists, excluding combinations | High blood pressure, heart failure | 15.7% | 13.8% | 13.8% | 18.1% | 17.8% |
| Natural opium alkaloids | Management of moderate to severe pain | 15.1% | 2.5% | 14.2% | 15.4% | 17.9% |
| Biguanides | Diabetes | 14.9% | 12.9% | 15.3% | 16.0% | 10.9% |
| Benzodiazepine derivatives | Agitation, anxiety, insomnia, seizures | 12.9% | 6.1% | 11.1% | 14.4% | 16.9% |
| Chemical | Indicated Uses | AGS Beers Criteria Rationale (Potential Harm) | Rate of Use | Rate of Chronic Use (Defined by 2016 AGS Criteria) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pantoprazole (PPI) (>8 weeks) | Gastroesophageal reflux disease, peptic ulcer disease | Clostridium difficile infection, bone loss, fractures | 13.2% | 10.3% |
| Lorazepam | Anxiety, insomnia | Cognitive impairment, delirium, falls, fractures | 8.8% | 3.6% |
| Nitrofurantoin | Antibiotic to treat urinary tract infection | Pulmonary toxicity, hepatotoxicity, peripheral neuropathy | 5.0% | 0.1% |
| Rabeprazole (PPI) (>8 weeks) | Gastroesophageal reflux disease, peptic ulcer disease | Clostridium difficile infection, bone loss, fractures | 4.3% | 3.5% |
| Amitriptyline | Depression | Sedation, orthostatic hypotension | 2.9% | 1.8% |
| Quetiapine | Schizophrenia, bipolar disorder | Cognitive decline, stroke, mortality | 2.8% | 1.7% |
| Omeprazole (PPI) (>8 weeks) | Gastroesophageal reflux disease, peptic ulcer disease | Clostridium difficile infection, bone loss, fractures | 2.7% | 2.2% |
| Zopiclone | Insomnia | Cognitive impairment, delirium, falls, fractures | 2.4% | 1.5% |
| Oxazepam | Anxiety, insomnia | Cognitive impairment, delirium, falls, fractures | 2.4% | 1.4% |
| Estradiol (oral/topical patch) | Menopause | Potential carcinogen (breast and endometrium) | 2.1% | 1.2% |
| Drug Class Most | Common Uses | Most Common Diagnosis Related to Hospitalization | Percentage of ADRs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anticoagulants | Heart attack and stroke prevention | Hemorrhagic disorders due to circulating anticoagulants | 12.6% |
| Antineoplastic drugs | Cancer | Neutropenia | 12.1% |
| Opioids and related analgesics | Pain management | Constipation | 7.4% |
| Glucocorticoids and synthetic analogs | Asthma | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with acute lower respiratory infection | 6.9% |
| NSAIDs (excluding salicylates) | Arthritis, pain management, inflammation | Gastric ulcer, chronic or with hemorrhage | 4.9% |
| Beta-adrenoreceptor antagonists, not elsewhere classified | Heart failure, high blood pressure, angina | Bradycardia | 4.6% |
| Nonthiazide (low-ceiling) diuretics | Heart failure, high blood pressure | Hypo-osmolality and hyponatremia | 3.6% |
| Thiazide diuretics | High blood pressure | Hypo-osmolality, hyponatremia | 3.2% |
| Cardiac-stimulant glycosides (e.g., digoxin) | Heart failure, arrhythmia | Bradycardia | 3.1% |
| Antipsychotics | Symptoms of dementia, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder | Disorientation | 2.7% |
| STOPP Cardiovascular System | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medication | P450 Cytochrome Isoforms | |||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Amiodarone | Inhibitor | Moderate inhibitor | Weak inhibitor | 3A4 Amiodarone; Inhibitor | ||||
| Diltiazem | Diltiazem, also moderate inhibitor; 3A4 Diltiazem | |||||||
| Torsemide | Torsemide | Torsemide | ||||||
| Verapamil | Verapamil; Verapamil | Verapamil, also moderate inhibitor; 3A4 Verapamil | ||||||
| Potassium-sparing diuretics | ||||||||
| Eplerenone | Eplerenone | |||||||
| Triamterene | Triamterene | |||||||
| B-blockers | ||||||||
| Bisoprolol | Bisoprolol | |||||||
| Labetalol | Labetalol | |||||||
| Metoprolol | Metoprolol; Metoprolol | |||||||
| Propranolol | Propranolol; Propranolol | Propranolol | Propranolol | |||||
| Timolol | Timolol; Timolol | |||||||
| Angiotensin-II receptor blockers | ||||||||
| Irbesartan | Irbesartan; Irbesartan | |||||||
| Losartan | Losartan; Losartan | |||||||
| Valsartan | Valsartan | |||||||
| STOPP Antiplatelet/anticoagulant drugs | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Apixaban | 3A4 Apixaban | |||||||
| Aspirin >325 mg/d, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Aspirin | Aspirin | Aspirin | |||||
| Clopidogrel | Clopidogrel | Clopidogrel inhibitor | Clopidogrel; Clopidogrel, also inhibitor | Clopidogrel; Clopidogrel; Clopidogrel | Clopidogrel 3A4,3A5 Clopidogrel | |||
| Dipyridamole, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Dipyridamole | Dipyridamole | Dipyridamole | |||||
| Rivaroxaban | 3A4 Rivaroxaban | |||||||
| Ticagrelor | 3A4 Ticagrelor | |||||||
| Ticlopidine | Ticlopidine; inhibitor | Ticlopidine; inhibitor | Ticlopidine | Ticlopidine; inhibitor | Inhibitor | Ticlopidine 3A4, 3A5 | ||
| Warfarin | Warfarin; Warfarin | s-Warfarin; Warfarin | r-Warfarin; Warfarin | 3A4 Warfarin | ||||
| For non-cyclooxygenase-selective NSAIDs and Cox-inhibitors see musculoskeletal drug list | ||||||||
| STOPP Central nervous system and psychotropic drugs | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Anticholinergics: First-generation antihistamines | ||||||||
| Chlorpheniramine | Chlorpheniramine, also inhibitor | Chlorpheniramine | ||||||
| Clemastine | inhibitor | |||||||
| Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine; Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine; Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine; inhibitor | Diphenhydramine 3A4 | ||
| Hydroxyzine | inhibitor | |||||||
| Promethazine | Promethazine, also inhibitor Promethazine | Promethazine | ||||||
| Antidepressants: Tricyclics | ||||||||
| Amitriptyline | Amitriptyline; Amitriptyline | Amitriptyline; Amitriptyline | Amitriptyline; Amitriptyline | Amitriptyline; Amitriptyline | Amitriptyline; 3A4 Amitriptyline | |||
| Clomipramine | Clomipramine; Clomipramine; Clomipramine | Clomipramine; Clomipramine; Clomipramine | Clomipramine, also inhibitor Clomipramine; Clomipramine | Clomipramine | ||||
| Desipramine | Desipramine;Desipramine | Desipramine;Desipramine | Desipramine Desipramine; | Desipramine 3A4 | ||||
| Doxepin >6 mg/d | Doxepin; Doxepin | Doxepin; Doxepin; Doxepin | Doxepin; Doxepin; Doxepin | Doxepin, also inhibitor; Doxepin; Doxepin | Doxepin; Doxepin 3A4 | |||
| Imipramine | Imipramine; Imipramine; Imipramine | Imipramine; Imipramine | Imipramine; Imipramine | Imipramine 3A4 | ||||
| Nortriptyline | Nortriptyline; Nortriptyline | |||||||
| Antidepressants: SSRIs | ||||||||
| Citalopram | Weak inhibitor | Citalopram, also weak inhibitor; Citalopram; Citalopram | Citalopram, also weak inhibitor; Citalopram | Citalopram; Citalopram 3A7; 3A4 Citalopram | ||||
| Escitalopram | Escitalopram; Escitalopram | Escitalopram, also weak inhibitor | Escitalopram | |||||
| Fluoxetine | Fluoxetine; Fluoxetine; Fluoxetine | Inhibitor; Fluoxetine | Fluoxetine, also strong inhibitor; Fluoxetine; Fluoxetine | Fluoxetine 3A4, 3A5 | ||||
| Norfluoxetine | Norfluoxetine | Norfluoxetine | Norfluoxetine | Inhibitor; Norfluoxetine 3A4,3A5 | ||||
| Fluvoxamine | Fluvoxamine, also strong inhibitor; Fluvoxamine | Inhibitor | Inhibitor | Fluvoxamine; Fluvoxamine | Inhibitor | |||
| Paroxetine | Inhibitor | Paroxetine, also strong inhibitor; Paroxetine | 3A4 Paroxetine | |||||
| Sertraline | Inhibitor | Sertraline | moderate inhibitor | 3A4 Sertraline | ||||
| Antidepressants: SNRIs | ||||||||
| Desvenlafaxine | Desvenlafaxine | Desvenlafaxine | Desvenlafaxine 3A4 | |||||
| Duloxetine | Duloxetine; Duloxetine | Duloxetine, moderate inhibitor; Duloxetine | ||||||
| Venlafaxine | Venlafaxine | Venlafaxine; Venlafaxine | Venlafaxine; Venlafaxine; Venlafaxine | Venlafaxine; Venlafaxine 3A4 | ||||
| Antipsychotics: First-Generation | ||||||||
| Chlorpromazine | Chlorpromazine, also inhibitor | |||||||
| Haloperidol) | Haloperidol; Haloperidol | Haloperidol, also inhibitor; Haloperidol | Haloperidol; 3A4 Haloperidol | |||||
| Perphenazine | Perphenazine, also inhibitor | |||||||
| Second-Generation | ||||||||
| Aripiprazole | Aripiprazole; Aripiprazole | Aripiprazole, 3A4 Aripiprazole | ||||||
| Brexpiprazole | Brexpiprazole | Brexpiprazole | ||||||
| Cariprazine | Cariprazine | Cariprazine | ||||||
| Clozapine | Clozapine; Clozapine | Clozapine; Clozapine | ||||||
| Olanzapine | Olanzapine; Olanzapine; Olanzapine | Olanzapine | Olanzapine | Olanzapine;Olanzapine | Olanzapine 3A4, 3A5 | |||
| Quetiapine | Quetiapine; 3A4 Quetiapine | |||||||
| Risperidone | Risperidone; Risperidone | Risperidone; 3A4 Risperidone | ||||||
| Ziprasidone | Ziprasidone | |||||||
| Barbiturates | Barbiturates; Inducers | |||||||
| Butalbital (also CYP2 A6) | Butalbital | Butalbital | Butalbital | Butalbital | Butalbital 3A4 | |||
| Hexobarbital | Hexobarbital | |||||||
| Mephobarbital | Mephobarbital | |||||||
| Phenobarbital/one | inducer | Inducer; Phenobarbital | Phenobarbital; Phenobarbital | Inducer | ||||
| Secobarbital | Secobarbital | |||||||
| Benzodiazepines: short- and intermediate-acting: | ||||||||
| Alprazolam | Alprazolam, 3A4 Alprazolam | |||||||
| Diazepam | Diazepam | Diazepam | Diazepam; Diazepam; Diazepam | Diazepam | ||||
| Nonbenzodiazepine, benzodiazepine receptor agonist hypnotics a | ||||||||
| Zaleplon | Zaleplon | |||||||
| Zolpidem | Zolpidem | |||||||
| Antiepileptics | ||||||||
| Carbamazepine | Carbamazepine, Inducer | Carbamazepine, Carbamazepine | Carbamazepine | Inducer | Inducer, Carbamazepine | Carbamazepine, also inducer; Carbamazepine 3A4,3A5,3A7; 3A4 Carbamazepine | ||
| Phenobarbitone | Inducer | Inducer | Phenobarbitone; | Inducer | ||||
| Phenytoin | Phenytoin | Inducer | Phenytoin; Phenytoin; Phenytoin | Phenytoin; Phenytoin | Phenytoin | Phenytoin 3A4; Phenytoin, also inducer | ||
| Primidone | Primidone | |||||||
| Topiramate | Inhibitor | |||||||
| Skeletal muscle relaxants | ||||||||
| Carisoprodol | Carisoprodol | Carisoprodol | Carisoprodol 3A4 | |||||
| Chlorzoxazone | Chlorzoxazone | |||||||
| Cyclobenzaprine | Cyclobenzaprine; Cyclobenzaprine | Cyclobenzaprine | ||||||
| Methocarbamol | Methocarbamol | Methocarbamol | Methocarbamol | Methocarbamol 3A4 | ||||
| Orphenadrine, also CYP2A6 | Orphenadrine | Orphenadrine | Orphenadrine | Orphenadrine | Orphenadrine 3A4 | |||
| Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) | ||||||||
| Donepezil | Donepezil; Donepezil | 3A4 Donepezil | ||||||
| Antiemetics | ||||||||
| Metoclopramide | Metoclopramide, also inhibitor | |||||||
| Promethazine | Promethazine, also inhibitor | |||||||
| STOPP renal system drugs | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Apixaban | 3A4 Apixaban | |||||||
| Colchicine | 3A4 Colchicine | |||||||
| Rivaroxaban | 3A4 Rivaroxaban | |||||||
| For NSAIDs, please see musculoskeletal criteria | ||||||||
| STOPP gastrointestinal system drugs | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Verapamil | Verapamil; Verapamil | Verapamil, also moderate inhibitor; 3A4 Verapamil | ||||||
| Tolterodine | 3A4 Tolterodine | |||||||
| Anticholinergics: First-generation antihistamines | ||||||||
| Chlorpheniramine | Chlorpheniramine, also inhibitor | Chlorpheniramine | ||||||
| Clemastine | inhibitor | |||||||
| Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine;Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine; Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine; inhibitor | Diphenhydramine 3A4 | ||
| Hydroxyzine | inhibitor | |||||||
| Promethazine | Promethazine, also inhibitor Promethazine | Promethazine | ||||||
| Proton-pump inhibitors | Proton-pump inhibitors | 3A4 Proton-pump inhibitors | ||||||
| Esomeprazole | Inducer | Esomeprazole, also strong inhibitor | Esomeprazole, also weak inhibitor | |||||
| Lansoprazole | Lansoprazole, also inhibitor | Lansoprazole | ||||||
| Omeprazole | Inducer | Omeprazole | Omeprazole, also strong inhibitor | Omeprazole, also weak inhibitor | ||||
| Pantoprazole | Pantoprazole, also weak inhibitor | Pantoprazole, also weak inhibitor | ||||||
| For opioids, see central nervous system drugs | ||||||||
| STOPP respiratory system drugs | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Theophylline, also CYP 2A6 | Theophylline; Theophylline; Theophylline | Theophylline | Theophylline | Theophylline; Theophylline | Theophylline 3A4 | |||
| Corticosteroids b | ||||||||
| Dexamethasone | Inducer | Dexamethasone; 3A4 Dexamethasone | ||||||
| Hydrocortisone | Hydrocortisone | |||||||
| Prednisone | Inducer | Prednisone 3A4 | ||||||
| For benzodiazepines, see central nervous system criteria | ||||||||
| STOPP musculoskeletal drugs | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Colchicine | 3A4 Colchicine | |||||||
| Aspirin >325 mg/d CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Aspirin | Aspirin | Aspirin | |||||
| Non-cyclooxygenase-selective NSAIDs | ||||||||
| Diclofenac, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Diclofenac | Diclofenac | Diclofenac; Diclofenac | Diclofenac | ||||
| Diflunisal, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Diflunisal | Diflunisal | Diflunisal | |||||
| Etodolac, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Etodolac | Etodolac | Etodolac | |||||
| Flurbiprofen, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Flurbiprofen | Flurbiprofen | Flurbiprofen | |||||
| Ibuprofen, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Ibuprofen | Ibuprofen | Ibuprofen; Ibuprofen; Ibuprofen | Ibuprofen | Ibuprofen | Ibuprofen 3A4 | ||
| Indomethacin, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Indomethacin | Indomethacin | Indomethacin | Indomethacin, also inhibitor; Indomethacin | Indomethacin | |||
| Ketoprofen, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Ketoprofen | Ketoprofen | Ketoprofen | |||||
| Nabumetone, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8) | Nabumetone | Nabumetone | Nabumetone | Nabumetone | ||||
| Naproxen, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Naproxen | Naproxen | Naproxen | Naproxen; Naproxen | Naproxen | |||
| Piroxicam, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Piroxicam | Piroxicam | Piroxicam | Piroxicam | ||||
| Sulindac, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Sulindac | Sulindac | Sulindac | |||||
| Tolmetin, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Tolmetin | Tolmetin | Tolmetin | |||||
| COX-2 inhibitors | ||||||||
| Celecoxib, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Celecoxib | Celecoxib | Celecoxib; Celecoxib; Celecoxib | Inhibitor Celecoxib | Celecoxib | Celecoxib 3A4 | ||
| Meloxicam, YP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Meloxicam | Meloxicam | Meloxicam | Meloxicam | ||||
| Corticosteroids b | ||||||||
| Dexamethasone | Inducer | Dexamethasone; 3A4 Dexamethasone | ||||||
| Hydrocortisone | Hydrocortisone | |||||||
| Prednisone | Inducer | Prednisone 3A4 | ||||||
| STOPP Urogenital system drugs | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Tamsulosin | 3A4 Tamsulosin | |||||||
| Mixed alpha-1 and beta antagonists | ||||||||
| Labetalol | Labetalol | |||||||
| Carvedilol | Carvedilol | Carvedilol; Carvedilol | ||||||
| STOPP Endocrine system drug | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Sulfonylureas, long-acting | ||||||||
| Glimepiride | Glimepiride; Glimepiride | |||||||
| Glyburide | Glyburide; Glyburide | |||||||
| Thiazolidinediones | Inhibitors | |||||||
| Pioglitazone | Pioglitazone inhibitor | Pioglitazone | Pioglitazone, also inducer | |||||
| Rosiglitazone | Rosiglitazone; inhibitor | Rosiglitazone; Rosiglitazone; Rosiglitazone | ||||||
| Troglitazone | Inhibitor | Troglitazone | ||||||
| B-blockers | ||||||||
| Bisoprolol | Bisoprolol | |||||||
| Carvedilol (mixed alpha-1 and B-blocker) | Carvedilol | Carvedilol; Carvedilol | ||||||
| Labetalol | Labetalol | |||||||
| Metoprolol | Metoprolol; Metoprolol | |||||||
| Propranolol | Propranolol; Propranolol | Propranolol | Propranolol | |||||
| Timolol | Timolol; Timolol | |||||||
| Hormones | ||||||||
| Estrogens c | Estrogen | Estrogen | Estrogen 3A4, 3A5 | |||||
| Testosterone (CYP11B1, 19A1) | Testosterone | |||||||
| STOPP Drugs increasing risk of falls | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Benzodiazepines: short- and intermediate-acting: | ||||||||
| Alprazolam | Alprazolam, 3A4 Alprazolam | |||||||
| Diazepam | Diazepam | Diazepam | Diazepam; Diazepam; Diazepam | Diazepam | ||||
| Nonbenzodiazepine, benzodiazepine receptor agonist hypnotics a | ||||||||
| Zaleplon | Zaleplon | |||||||
| Zolpidem | Zolpidem | |||||||
| Antipsychotics: First-Generation | ||||||||
| Chlorpromazine | Chlorpromazine, also inhibitor | |||||||
| Haloperidol) | Haloperidol; Haloperidol | Haloperidol, also inhibitor; Haloperidol | Haloperidol; 3A4 Haloperidol | |||||
| Perphenazine | Perphenazine, also inhibitor | |||||||
| Antipsychotics: Second-Generation | ||||||||
| Aripiprazole | Aripiprazole; Aripiprazole | Aripiprazole, 3A4 Aripiprazole | ||||||
| Brexpiprazole | Brexpiprazole | Brexpiprazole | ||||||
| Cariprazine | Cariprazine | Cariprazine | ||||||
| Clozapine | Clozapine; Clozapine | Clozapine; Clozapine | ||||||
| Olanzapine | Olanzapine; Olanzapine; Olanzapine | Olanzapine | Olanzapine | Olanzapine;Olanzapine | Olanzapine 3A4, 3A5 | |||
| Quetiapine | Quetiapine; 3A4 Quetiapine | |||||||
| Risperidone | Risperidone; Risperidone | Risperidone; 3A4 Risperidone | ||||||
| Ziprasidone | Ziprasidone | |||||||
| Vasodilators: B-blocker | ||||||||
| Bisoprolol | Bisoprolol | |||||||
| Carvedilol | Carvedilol | Carvedilol; Carvedilol | ||||||
| Labetalol | Labetalol | |||||||
| Metoprolol | Metoprolol; Metoprolol | |||||||
| Propranolol | Propranolol; Propranolol | Propranolol | Propranolol | |||||
| Timolol | Timolol; Timolol | |||||||
| Vasodilators: calcium channel blockers | ||||||||
| Amlodipine | Amlodipine; 3A4 Amlodipine | |||||||
| Felodipine | Felodipine; 3A4 Felodipine | |||||||
| Nifedipine | Nifedipinee 3A4 Nifedipine | |||||||
| Diltiazem | Diltiazem, also moderate inhibitor; 3A4 Diltiazem | |||||||
| Verapamil | Verapamil; Verapamil | Verapamil, also moderate inhibitor; 3A4 Verapamil | ||||||
| STOPP Analgesic drugs | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Opioids | ||||||||
| Codeine | Codeine; Codeine | Codeine 3A4 | ||||||
| Fentanyl, Fentanil | Fentanyl, 3A4 Fentanyl | |||||||
| Meperidine | Meperidine | |||||||
| Morphine | Morphine | Morphine | ||||||
| Oxycodone | Oxycodone; Oxycodone | 3A4 Oxycodone | ||||||
| Tramadol | Tramadol | Tramadol; Tramadol | Tramadol | |||||
| AGS Medications to Avoid: Anticholinergics | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Anticholinergics: first-generation antihistamines | ||||||||
| Chlorpheniramine | Chlorpheniramine, also inhibitor | Chlorpheniramine | ||||||
| Clemastine | inhibitor | |||||||
| Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine; Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine; Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine; inhibitor | Diphenhydramine 3A4 | ||
| Hydroxyzine | inhibitor | |||||||
| Promethazine | Promethazine, also inhibitor Promethazine | Promethazine | ||||||
| Orphenadrine, also CYP2A6 | Orphenadrine | Orphenadrine | Orphenadrine | Orphenadrine | Orphenadrine 3A4 | |||
| AGS Medications to avoid: Cardiovascular system | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Amiodarone | Inhibitor | Moderate inhibitor | Weak inhibitor | 3A4 Amiodarone; Inhibitor | ||||
| Carvedilol | Carvedilol | Carvedilol; Carvedilol | ||||||
| Labetalol | Labetalol | |||||||
| Nifedipine | Nifedipine 3A4 Nifedipine | |||||||
| AGS Medications to avoid: Central nervous system | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Antidepressants: tricyclics | ||||||||
| Amitriptyline | Amitriptyline; Amitriptyline | Amitriptyline; Amitriptyline | Amitriptyline; Amitriptyline | Amitriptyline; Amitriptyline | Amitriptyline; 3A4 Amitriptyline | |||
| Clomipramine | Clomipramine; Clomipramine; Clomipramine | Clomipramine; Clomipramine; Clomipramine | Clomipramine, also inhibitor Clomipramine; Clomipramine | Clomipramine | ||||
| Desipramine | Desipramine; Desipramine | Desipramine; Desipramine | Desipramine Desipramine; | Desipramine 3A4 | ||||
| Doxepin >6 mg/d | Doxepin; Doxepin | Doxepin; Doxepin; Doxepin | Doxepin; Doxepin; Doxepin | Doxepin, also inhibitor; Doxepin; Doxepin | Doxepin; Doxepin 3A4 | |||
| Imipramine | Imipramine; Imipramine; Imipramine | Imipramine; Imipramine | Imipramine; Imipramine | Imipramine 3A4 | ||||
| Nortriptyline | Nortriptyline; Nortriptyline | |||||||
| Antidepressants: SSRIs | ||||||||
| Citalopram | Weak inhibitor | Citalopram, also weak inhibitor; Citalopram; Citalopram | Citalopram, also weak inhibitor; Citalopram | Citalopram; Citalopram 3A7; 3A4 Citalopram | ||||
| Escitalopram | Escitalopram; Escitalopram | Escitalopram, also weak inhibitor | Escitalopram | |||||
| Fluoxetine | Fluoxetine; Fluoxetine; Fluoxetine | inhibitor; Fluoxetine | Fluoxetine, also strong inhibitor; Fluoxetine; Fluoxetine | Fluoxetine 3A4, 3A5 | ||||
| Norfluoxetine | Norfluoxetine | Norfluoxetine | Norfluoxetine | Inhibitor; Norfluoxetine 3A4,3A5 | ||||
| Fluvoxamine | Fluvoxamine, also strong inhibitor; Fluvoxamine | Inhibitor | Inhibitor | Fluvoxamine; Fluvoxamine | Inhibitor | |||
| Paroxetine | Inhibitor | Paroxetine, also strong inhibitor; Paroxetine | 3A4 Paroxetine | |||||
| Sertraline | Inhibitor | Sertraline | moderate inhibitor | 3A4 Sertraline | ||||
| Antidepressants: SNRIs | Desvenlafaxine | Desvenlafaxine | Desvenlafaxine 3A4 | |||||
| Desvenlafaxine | ||||||||
| Duloxetine | Duloxetine; Duloxetine | Duloxetine, moderate inhibitor; Duloxetine | ||||||
| Venlafaxine | Venlafaxine | Venlafaxine; Venlafaxine | Venlafaxine; Venlafaxine; Venlafaxine | Venlafaxine; Venlafaxine 3A4 | ||||
| Antipsychotics: First-Generation | ||||||||
| Chlorpromazine | Chlorpromazine, also inhibitor | |||||||
| Haloperidol) | Haloperidol; Haloperidol | Haloperidol, also inhibitor; Haloperidol | Haloperidol; 3A4 Haloperidol | |||||
| Perphenazine | Perphenazine, also inhibitor | |||||||
| Second-Generation | ||||||||
| Aripiprazole | Aripiprazole; Aripiprazole | Aripiprazole, 3A4 Aripiprazole | ||||||
| Brexpiprazole | Brexpiprazole | Brexpiprazole | ||||||
| Cariprazine | Cariprazine | Cariprazine | ||||||
| Clozapine | Clozapine; Clozapine | Clozapine; Clozapine | ||||||
| Olanzapine | Olanzapine; Olanzapine; Olanzapine | Olanzapine | Olanzapine | Olanzapine;Olanzapine | Olanzapine 3A4, 3A5 | |||
| Quetiapine | Quetiapine; 3A4 Quetiapine | |||||||
| Risperidone | Risperidone; Risperidone | Risperidone; 3A4 Risperidone | ||||||
| Ziprasidone | Ziprasidone | |||||||
| Barbiturates | Barbiturates; Inducers | |||||||
| Butalbital (also CYP2 A6) | Butalbital | Butalbital | Butalbital | Butalbital | Butalbital 3A4 | |||
| Hexobarbital | Hexobarbital | |||||||
| Mephobarbital | Mephobarbital | |||||||
| Phenobarbital/one | inducer | Inducer; Phenobarbital | Phenobarbital; Phenobarbital | Inducer | ||||
| Secobarbital | Secobarbital | |||||||
| Benzodiazepines: short- and intermediate-acting: | ||||||||
| Alprazolam | Alprazolam, 3A4 Alprazolam | |||||||
| Diazepam | Diazepam | Diazepam | Diazepam; Diazepam; Diazepam | Diazepam | ||||
| Nonbenzodiazepine, benzodiazepine receptor agonist hypnotics a | ||||||||
| Zaleplon | Zaleplon | |||||||
| Zolpidem | Zolpidem | |||||||
| AGS Medications to avoid: Endocrine system | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Testosterone (CYP11B1, 19A1) | Testosterone | |||||||
| Estrogens c | Estrogen | Estrogen | Estrogen 3A4, 3A5 | |||||
| Insulin | Inducer | |||||||
| Sulfonylureas, long-acting | ||||||||
| Chlorpropamide | ||||||||
| Glimepiride | Glimepiride; Glimepiride | |||||||
| Glyburide | Glyburide; Glyburide | |||||||
| AGS Medications to avoid: Gastrointestinal system | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Metoclopramide | Metoclopramide | |||||||
| Proton-pump inhibitors | Proton-pump inhibitors | 3A4 Proton-pump inhibitors | ||||||
| Esomeprazole | Inducer | Esomeprazole, also strong inhibitor | Esomeprazole, also weak inhibitor | |||||
| Lansoprazole | Lansoprazole, also inhibitor | Lansoprazole | ||||||
| Omeprazole | Inducer | Omeprazole | Omeprazole, also strong inhibitor | Omeprazole, also weak inhibitor | ||||
| Pantoprazole | Pantoprazole, also weak inhibitor | Pantoprazole, also weak inhibitor | ||||||
| AGS Medications to avoid: Analgesic drugs | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Meperidine | Meperidine | |||||||
| Skeletal muscle relaxants | ||||||||
| Carisoprodol | Carisoprodol | Carisoprodol | Carisoprodol 3A4 | |||||
| Chlorzoxazone | Chlorzoxazone | |||||||
| Cyclobenzaprine | Cyclobenzaprine; Cyclobenzaprine | Cyclobenzaprine | ||||||
| Methocarbamol | Methocarbamol | Methocarbamol | Methocarbamol | Methocarbamol 3A4 | ||||
| Orphenadrine, also CYP2A6 | Orphenadrine | Orphenadrine | Orphenadrine | Orphenadrine | Orphenadrine 3A4 | |||
| Non-cyclooxygenase-selective NSAIDs | ||||||||
| Diclofenac, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Diclofenac | Diclofenac | Diclofenac; Diclofenac | Diclofenac | ||||
| Diflunisal, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Diflunisal | Diflunisal | Diflunisal | |||||
| Etodolac, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Etodolac | Etodolac | Etodolac | |||||
| Flurbiprofen, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Flurbiprofen | Flurbiprofen | Flurbiprofen | |||||
| Ibuprofen, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Ibuprofen | Ibuprofen | Ibuprofen; Ibuprofen; Ibuprofen | Ibuprofen | Ibuprofen | Ibuprofen 3A4 | ||
| Indomethacin, CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Indomethacin | Indomethacin | Indomethacin | Indomethacin, also inhibitor; Indomethacin | Indomethacin | |||
| Ketoprofen, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Ketoprofen | Ketoprofen | Ketoprofen | |||||
| Nabumetone, CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8) | Nabumetone | Nabumetone | Nabumetone | Nabumetone | ||||
| Naproxen, CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Naproxen | Naproxen | Naproxen | Naproxen; Naproxen | Naproxen | |||
| Piroxicam, CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Piroxicam | Piroxicam | Piroxicam | Piroxicam | ||||
| Sulindac, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Sulindac | Sulindac | Sulindac | |||||
| Tolmetin, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Tolmetin | Tolmetin | Tolmetin | |||||
| AGS PIMS: exacerbations of interactions of drugs and diseases: heart failure | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Cilostazol | Cilostazol | |||||||
| Diltiazem | Diltiazem, also moderate inhibitor; 3A4 Diltiazem | |||||||
| Meperidine | Meperidine | |||||||
| Verapamil | Verapamil; Verapamil | Verapamil, also moderate inhibitor; 3A4 Verapamil | ||||||
| NSAIDs and Cox-2: see STOPP Musculoskeletal drugs | ||||||||
| Thiazolidinediones | Inhibitors | |||||||
| Pioglitazone | Pioglitazone inhibitor | Pioglitazone | Pioglitazone, also inducer | |||||
| Rosiglitazone | Rosiglitazone; inhibitor | Rosiglitazone; Rosiglitazone; Rosiglitazone | ||||||
| Troglitazone | Inhibitor | Troglitazone | ||||||
| AGS PIMs: exacerbations of interactions of drugs and diseases: syncope | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Chlorpromazine | Chlorpromazine, also inhibitor | |||||||
| Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) | ||||||||
| Donepezil | Donepezil; Donepezil | 3A4 Donepezil | ||||||
| Mixed alpha-1 and B-blockers | ||||||||
| Carvedilol | Carvedilol | Carvedilol; Carvedilol | ||||||
| Labetalol | Labetalol | |||||||
| AGS PIMs: exacerbations of interactions of drugs and diseases: delirium, dementia, cognitive impairment, falls, and Parkinsonism | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Anticholinergics see Table | ||||||||
| Antipsychotics, benzodiazepines anticonvulsants, antiemetics: see STOPP Central nervous system | ||||||||
| H-2 receptor antagonists | ||||||||
| Cimetidine | Weak inhibitor | Cimetidine | Cimetidine | Cimetidine inhibitor | Weak inhibitor | Cimetidine; weak inhibitor | ||
| Ranitidine | Inhibitor | |||||||
| AGS PIMs: exacerbations of interactions of drugs and diseases: gastric/duodenal ulcers | ||||||||
| For aspirin and non-Cox-2 selective NSAIDs see STOPP musculoskeletal list | ||||||||
| AGS PIMs: exacerbations of interactions of drugs and diseases: kidney and urinary tract disorders | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2sD6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Estrogens c | Estrogen | Estrogen | Estrogen 3A4, 3A5 | |||||
| Tamsulosin | 3A4 Tamsulosin | |||||||
| Mixed alpha-1 and beta antagonists | ||||||||
| Labetalol | Labetalol | |||||||
| Carvedilol | Carvedilol | Carvedilol; Carvedilol | ||||||
| AGS medications to be used with caution | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Aspirin >325 mg/d CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Aspirin | Aspirin | Aspirin | |||||
| Antipsychotics, SSRIs, SNRIs, tricyclics see STOPP central nervous system | ||||||||
| Trimethoprim | Moderate inhibitor | |||||||
| Sulfamethoxazole | Inhibitor; Sulfamethoxazole | |||||||
| Dextromethorphan | Dextromethorphan; Dextromethorphan | Dextromethorphan | ||||||
| Quinidine | Strong inhibitor | Quinidine | ||||||
| Diuretics | ||||||||
| Eplerenone | Eplerenone | |||||||
| Triamterene | Triamterene | |||||||
| Torsemide | Torsemide | Torsemide | ||||||
| Triamterene | Triamterene | |||||||
| AGS PIMS avoid these drug–drug interactions | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Combination 5A | Renin–angiotensin inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers with triamterene or amiloride or another renin–angiotensin inhibitor | |||||||
| Triamterene | Triamterene | |||||||
| Angiotensin-II receptor blockers | ||||||||
| Irbesartan | Irbesartan; Irbesartan | |||||||
| Losartan | Losartan; Losartan | |||||||
| Valsartan | Valsartan | |||||||
| Combination 5B | Benzodiazepines with opioids (see STOPP CNS list in Table 2) | |||||||
| Combination 5C | Opioids (see STOPP CNS list in Table 2) with gabapentin or pregabalin | |||||||
| Combination 5D | ≥2 anticholinergics | |||||||
| Combination 5E | ≥3 CNS active drugs (TCAs or SSRIs or SNRIs or antiepileptics or benzodiazepines or hypnotic Z-drugs or opioids (see STOPP CNS list in Table 2)) | |||||||
| Combination 5F | Systemic corticosteroids b with opioids (see STOPP CNS list in Table 2) | |||||||
| Combination 5G | Lithium with ACE inhibitor | |||||||
| Combination 5H | Lithium with Loop diuretic | |||||||
| Loop diuretics | ||||||||
| Eplerenone | Eplerenone | |||||||
| Torsemide | Torsemide | Torsemide | ||||||
| Triamterene | Triamterene | |||||||
| Combination 5I | Peripheral alpha-blocker with loop diuretic | |||||||
| Mixed alpha-1 and beta antagonists | ||||||||
| Labetalol | Labetalol | |||||||
| Carvedilol | Carvedilol | Carvedilol; Carvedilol | ||||||
| Loop diuretics | ||||||||
| Eplerenone | Eplerenone | |||||||
| Torsemide | Torsemide | Torsemide | ||||||
| Triamterene | Triamterene | |||||||
| Combination 5J | Phenytoin with Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole | |||||||
| Phenytoin | Phenytoin | Inducer | Phenytoin; Phenytoin; Phenytoin | Phenytoin;Phenytoin | Phenytoin | Phenytoin 3A4; Phenytoin, also inducer | ||
| Trimethoprim | Moderate inhibitor | |||||||
| Sulfamethoxazole | Inhibitor; Sulfamethoxazole | |||||||
| Combination 5K | Theophylline with cimetidine | |||||||
| Theophylline, also CYP 2A6 | Theophylline; Theophylline; Theophylline | Theophylline | Theophylline | Theophylline; Theophylline | Theophylline 3A4 | |||
| Cimetidine | Weak inhibitor | Cimetidine | Cimetidine | Cimetidine inhibitor | Weak inhibitor | Cimetidine; weak inhibitor | ||
| Combination 5L | Theophylline with ciprofloxacin | |||||||
| Theophylline, also CYP 2A6 | Theophylline; Theophylline; Theophylline | Theophylline | Theophylline | Theophylline; Theophylline | Theophylline 3A4 | |||
| Ciprofloxacin | Strong inhibitor | Inhibitor | ||||||
| Combination 5M | Warfarin with amiodarone | |||||||
| Warfarin | Warfarin; Warfarin | s-Warfarin; Warfarin | r-Warfarin; Warfarin | 3A4 Warfarin | ||||
| Amiodarone | Inhibitor | Moderate inhibitor | Weak inhibitor | 3A4 Amiodarone; Inhibitor | ||||
| Combination 5N | Warfarin with ciprofloxacin | |||||||
| Warfarin | Warfarin; Warfarin | s-Warfarin; Warfarin | r-Warfarin; Warfarin | 3A4 Warfarin | ||||
| Ciprofloxacin | Strong inhibitor | Inhibitor | ||||||
| Combination 5N | Warfarin with macrolide | |||||||
| Warfarin | Warfarin; Warfarin | s-Warfarin; Warfarin | r-Warfarin; Warfarin | 3A4 Warfarin | ||||
| Clarithromycin | Clarithromycin, also strong inhibitor; 3A4 Clarithromycin | |||||||
| Erythromycin | Erythromycin, also moderate inhibitor; 3A4 Erythromycin | |||||||
| Telithromycin | Telithromycin, also strong inhibitor | |||||||
| Combination 5O | Warfarin with Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole | |||||||
| Warfarin | Warfarin; Warfarin | s-Warfarin; Warfarin | r-Warfarin; Warfarin | 3A4 Warfarin | ||||
| Trimethoprim | Moderate inhibitor | |||||||
| Sulfamethoxazole | Inhibitor; Sulfamethoxazole | |||||||
| Combination 5Q | Warfarin with NSAID | |||||||
| Warfarin | Warfarin; Warfarin | s-Warfarin; Warfarin | r-Warfarin; Warfarin | 3A4 Warfarin | ||||
| Non-cyclooxygenase-selective NSAIDs | ||||||||
| Diclofenac, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Diclofenac | Diclofenac | Diclofenac; Diclofenac | Diclofenac | ||||
| Diflunisal, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Diflunisal | Diflunisal | Diflunisal | |||||
| Etodolac, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Etodolac | Etodolac | Etodolac | |||||
| Flurbiprofen, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Flurbiprofen | Flurbiprofen | Flurbiprofen | |||||
| Ibuprofen, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Ibuprofen | Ibuprofen | Ibuprofen; Ibuprofen; Ibuprofen | Ibuprofen | Ibuprofen | Ibuprofen 3A4 | ||
| Indomethacin, CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Indomethacin | Indomethacin | Indomethacin | Indomethacin, also inhibitor; Indomethacin | Indomethacin | |||
| Ketoprofen, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Ketoprofen | Ketoprofen | Ketoprofen | |||||
| Nabumetone, CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8) | Nabumetone | Nabumetone | Nabumetone | Nabumetone | ||||
| Naproxen, CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Naproxen | Naproxen | Naproxen | Naproxen; Naproxen | Naproxen | |||
| Piroxicam, CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Piroxicam | Piroxicam | Piroxicam | Piroxicam | ||||
| Sulindac, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Sulindac | Sulindac | Sulindac | |||||
| Tolmetin, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Tolmetin | Tolmetin | Tolmetin | |||||
| AGS PIMS to be avoided or dosage reduced with varying levels of kidney function | ||||||||
| AGS PIMS to be avoided or dosage reduced: anti-infectives | ||||||||
| Ciprofloxacin | Strong inhibitor | Inhibitor | ||||||
| Trimethoprim | Moderate inhibitor | |||||||
| Sulfamethoxazole | Inhibitor; Sulfamethoxazole | |||||||
| AGS PIMS to be avoided or dosage reduced: cardiovascular or hemostasis | ||||||||
| Apixaban | 3A4 Apixaban | |||||||
| Rivaroxaban | 3A4 Rivaroxaban | |||||||
| Triamterene | Triamterene | |||||||
| AGS PIMS to be avoided or dosage reduced: central nervous system and analgesics | ||||||||
| Duloxetine | Duloxetine; Duloxetine | Duloxetine, moderate inhibitor; Duloxetine | ||||||
| Tramadol | Tramadol | Tramadol; Tramadol | Tramadol | |||||
| AGS PIMS to be avoided or dosage reduced: gastrointestinal | ||||||||
| Cimetidine | Weak inhibitor | Cimetidine | Cimetidine | Cimetidine inhibitor | Weak inhibitor | Cimetidine; weak inhibitor | ||
| Ranitidine | Inhibitor | |||||||
| AGS PIMS to be avoided or dosage reduced: hyperuricemia | ||||||||
| Colchicine | 3A4 Colchicine | |||||||
| Probenecid | Inhibitor | Inhibitor | ||||||
| AGS PIMS with strong anticholinergic properties | ||||||||
| AGS PIMS with strong anticholinergic properties: antiarrhythmics | ||||||||
| AGS PIMS with strong anticholinergic properties: antidepressants | ||||||||
| Amitriptyline | Amitriptyline; Amitriptyline | Amitriptyline; Amitriptyline | Amitriptyline; Amitriptyline | Amitriptyline; Amitriptyline | Amitriptyline; 3A4 Amitriptyline | |||
| Clomipramine | Clomipramine; Clomipramine; Clomipramine | Clomipramine; Clomipramine; Clomipramine | Clomipramine, also inhibitor Clomipramine; Clomipramine | Clomipramine | ||||
| Desipramine | Desipramine; Desipramine | Desipramine; Desipramine | Desipramine Desipramine; | Desipramine 3A4 | ||||
| Doxepin >6 mg/d | Doxepin; Doxepin | Doxepin; Doxepin; Doxepin | Doxepin; Doxepin; Doxepin | Doxepin, also inhibitor; Doxepin; Doxepin | Doxepin; Doxepin 3A4 | |||
| Imipramine | Imipramine; Imipramine; Imipramine | Imipramine; Imipramine | Imipramine; Imipramine | Imipramine 3A4 | ||||
| Nortriptyline | Nortriptyline; Nortriptyline | |||||||
| Paroxetine | Inhibitor | Paroxetine, also strong inhibitor; Paroxetine | 3A4 Paroxetine | |||||
| AGS PIMS with strong anticholinergic properties: antiemetics | ||||||||
| Promethazine | Promethazine, also inhibitor Promethazine | Promethazine | ||||||
| AGS PIMS with strong anticholinergic properties: antihistamines (first-generation) | ||||||||
| Chlorpheniramine | Chlorpheniramine, also inhibitor | Chlorpheniramine | ||||||
| Clemastine | inhibitor | |||||||
| Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine; Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine; Diphenhydramine | Diphenhydramine; inhibitor | Diphenhydramine 3A4 | ||
| Hydroxyzine | inhibitor | |||||||
| Promethazine | Promethazine, also inhibitor Promethazine | Promethazine | ||||||
| AGS PIMS with strong anticholinergic properties: antimuscarinics | ||||||||
| Tolterodine | 3A4 Tolterodine | |||||||
| AGS PIMS with strong anticholinergic properties: anti-Parkinson’s medications | ||||||||
| AGS PIMS with strong anticholinergic properties: antipsychotics (Criterion 7G) | ||||||||
| Chlorpromazine | Chlorpromazine, also inhibitor | |||||||
| Clozapine | Clozapine; Clozapine | Clozapine; Clozapine | ||||||
| Olanzapine | Olanzapine; Olanzapine; Olanzapine | Olanzapine | Olanzapine | Olanzapine;Olanzapine | Olanzapine 3A4, 3A5 | |||
| Perphenazine | Perphenazine, also inhibitor | |||||||
| AGS PIMS with strong anticholinergic properties: antispasmodics | ||||||||
| AGS PIMS with strong anticholinergic properties: Skeletal muscle relaxants | ||||||||
| Cyclobenzaprine | Cyclobenzaprine; Cyclobenzaprine | Cyclobenzaprine | ||||||
| Orphenadrine, also CYP2A6 | Orphenadrine | Orphenadrine | Orphenadrine | Orphenadrine | Orphenadrine 3A4 | |||
| START Cardiovascular System (Criteria A1 to A8) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| START Cardiovascular A1: Vitamin K Antagonist or Thrombin/Factor Xa Inhibitor with Chronic Atrial Fibrillation | ||||||||
| 1A2 | 2B6 | 2C8 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 2E1 | 3A457 | |
| Apixaban | 3A4 Apixaban | |||||||
| Rivaroxaban | 3A4 Rivaroxaban | |||||||
| Warfarin | Warfarin; Warfarin | s-Warfarin; Warfarin | r-Warfarin; Warfarin | 3A4 Warfarin | ||||
| START Cardiovascular A2: Aspirin with chronic atrial fibrillation and contraindicated Vitamin K antagonist or thrombin/factor Xa inhibitor | ||||||||
| Aspirin >325 mg/d also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Aspirin | Aspirin | Aspirin | |||||
| START Cardiovascular A3: Antiplatelet therapy with coronary, cerebral, or peripheral vascular disease | ||||||||
| Aspirin >325 mg/d also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Aspirin | Aspirin | Aspirin | |||||
| Clopidogrel | Clopidogrel | Clopidogrel inhibitor | Clopidogrel; Clopidogrel, also inhibitor | Clopidogrel; Clopidogrel; Clopidogrel | Clopidogrel 3A4,3A5 Clopidogrel | |||
| Dipyridamole, also CYP 2J2, 2U1, 4A11, and 4F8 | Dipyridamole | Dipyridamole | Dipyridamole | |||||
| Ticagrelor | 3A4 Ticagrelor | |||||||
| Ticlopidine | Ticlopidine; inhibitor | Ticlopidine; inhibitor | Ticlopidine | Ticlopidine; inhibitor | Inhibitor | Ticlopidine 3A4, 3A5 | ||
| START Cardiovascular A4: Antihypertensive therapy for hypertension | ||||||||
| Angiotensin-II receptor blockers | ||||||||
| Irbesartan | Irbesartan; Irbesartan | |||||||
| Losartan | Losartan; Losartan | |||||||
| Valsartan | Valsartan | |||||||
| Mixed alpha-1 and beta antagonists | ||||||||
| Labetalol | Labetalol | |||||||
| Carvedilol | Carvedilol | Carvedilol; Carvedilol | ||||||
| Vasodilators: B-blocker | ||||||||
| Bisoprolol | Bisoprolol | |||||||
| Carvedilol | Carvedilol | Carvedilol; Carvedilol | ||||||
| Labetalol | Labetalol | |||||||
| Metoprolol | Metoprolol; Metoprolol | |||||||
| Propranolol | Propranolol; Propranolol | Propranolol | Propranolol | |||||
| Timolol | Timolol; Timolol | |||||||
| Vasodilators: Calcium channel blockers | ||||||||
| Amlodipine | Amlodipine; 3A4 Amlodipine | |||||||
| Felodipine | Felodipine; 3A4 Felodipine | |||||||
| Nifedipine | Nifedipine e 3A4 Nifedipine | |||||||
| Diltiazem | Diltiazem, also moderate inhibitor; 3A4 Diltiazem | |||||||
| Verapamil | Verapamil; Verapamil | Verapamil, also moderate inhibitor; 3A4 Verapamil | ||||||
| START Cardiovascular A5: Statin with coronary, cerebral, or peripheral vascular disease | ||||||||
| Atorvastatin | Atorvastatin; 3A4 Atorvastatin | |||||||
| Simvastatin | Simvastatin; 3A4 Simvastatin | |||||||
| Rosuvastatin | Rosuvastatin | Rosuvastatin | ||||||
| START Cardiovascular A6: ACE inhibitors with ischemic heart disease | ||||||||
| START Cardiovascular A7: beta-blocker with ischemic heart disease and A8: beta-blocker with stable systolic heart failure | ||||||||
| Bisoprolol | Bisoprolol | |||||||
| Carvedilol | Carvedilol | Carvedilol; Carvedilol | ||||||
| Labetalol | Labetalol | |||||||
| Metoprolol | Metoprolol; Metoprolol | |||||||
| Propranolol | Propranolol; Propranolol | Propranolol | Propranolol | |||||
| Timolol | Timolol; Timolol | |||||||
| START Respiratory system (Criteria B1-B3) | ||||||||
| Budesonide | 3A4 Budesonide | |||||||
| Fluticasone | 3A4 Fluticasone | |||||||
| START: Central nervous system and eyes (criteria C1 to C6) | ||||||||
| START CNS C1: L-Dopa or dopamine agonist in Parkinson’s with functional impairment or disability | ||||||||
| START CNS C2: Non-TCA antidepressant with persistent major depressive disorder | ||||||||
| Antidepressants: SSRIs | ||||||||
| Citalopram | Weak inhibitor | Citalopram, also weak inhibitor; Citalopram; Citalopram | Citalopram, also weak inhibitor; Citalopram | Citalopram; Citalopram 3A7; 3A4 Citalopram | ||||
| Escitalopram | Escitalopram; Escitalopram | Escitalopram, also weak inhibitor | Escitalopram | |||||
| Fluoxetine | Fluoxetine; Fluoxetine; Fluoxetine | inhibitor; Fluoxetine | Fluoxetine, also strong inhibitor; Fluoxetine; Fluoxetine | Fluoxetine 3A4, 3A5 | ||||
| Norfluoxetine | Norfluoxetine | Norfluoxetine | Norfluoxetine | Inhibitor; Norfluoxetine 3A4,3A5 | ||||
| Fluvoxamine | Fluvoxamine, also strong inhibitor; Fluvoxamine | Inhibitor | Inhibitor | Fluvoxamine; Fluvoxamine | Inhibitor | |||
| Paroxetine | Inhibitor | Paroxetine, also strong inhibitor; Paroxetine | 3A4 Paroxetine | |||||
| Sertraline | Inhibitor | Sertraline | moderate inhibitor | 3A4 Sertraline | ||||
| Antidepressants: SNRIs | Desvenlafaxine | Desvenlafaxine | Desvenlafaxine 3A4 | |||||
| Desvenlafaxine | ||||||||
| Duloxetine | Duloxetine; Duloxetine | Duloxetine, moderate inhibitor; Duloxetine | ||||||
| Venlafaxine | Venlafaxine | Venlafaxine; Venlafaxine | Venlafaxine; Venlafaxine; Venlafaxine | Venlafaxine; Venlafaxine 3A4 | ||||
| START CNS C3: ACE inhibitor for mild–moderate Alzheimer’s or Lewy body dementia | ||||||||
| START CNS C4: Topical prostaglandin, prosamide, or beta-blocker for primary open-angle glaucoma | ||||||||
| Timolol | Timolol; Timolol | |||||||
| START CNS C5: SSRI, SNRI, or pregabalin for persistent anxiety (See STOPP CNS list) | ||||||||
| START CNS C5: Dopamine agonist for restless legs syndrome | ||||||||
| START Gastrointestinal System D1, D2: Proton-pump inhibitor with severe gastroesophageal reflux disease or peptic stricture | ||||||||
| Esomeprazole | Inducer | Esomeprazole, also strong inhibitor | Esomeprazole, also weak inhibitor | |||||
| Lansoprazole | Lansoprazole, also inhibitor | Lansoprazole | ||||||
| Omeprazole | Inducer | Omeprazole | Omeprazole, also strong inhibitor | Omeprazole, also weak inhibitor | ||||
| Pantoprazole | Pantoprazole, also weak inhibitor | Pantoprazole, also weak inhibitor | ||||||
| START Musculoskeletal system (criteria E1 to E7) | ||||||||
| START Musculoskeletal system E1: Disease-modifying antirheumatic drug | ||||||||
| START Musculoskeletal system E2: Bisphosphonates, vitamin D3 and calcium with long-term systematic corticosteroids; E3 with osteoporosis/fracture; E4 with osteoporosis; E5 Vitamin D3 with falls or osteopenia | ||||||||
| START Musculoskeletal system E6: xanthine-oxidase inhibitor with gout | ||||||||
| START Musculoskeletal system E7: Folic acid supplementation with methotrexate | ||||||||
| START Endocrine system F: ACE inhibitor or ARB in diabetes with renal disease | ||||||||
| Angiotensin-II receptor blockers | ||||||||
| Irbesartan | Irbesartan; Irbesartan | |||||||
| Losartan | Losartan; Losartan | |||||||
| Valsartan | Valsartan | |||||||
| START Urogenital G1: Alpha-1 receptor blockers with prostatism and no prostatectomy | ||||||||
| START Urogenital G2: 5-alpha reductase inhibitors with prostatism and no prostatectomy | ||||||||
| START Analgesic drugs H1, H2: | ||||||||
| Fentanyl, Fentanil | Fentanyl, 3A4 Fentanyl | |||||||
| Meperidine | Meperidine | |||||||
| Oxycodone | Oxycodone; Oxycodone | 3A4 Oxycodone | ||||||
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thomas, R.E. Improving the Care of Older Patients by Decreasing Potentially Inappropriate Medications, Potential Medication Omissions, and Serious Drug Events Using Pharmacogenomic Data about Variability in Metabolizing Many Medications by Seniors. Geriatrics 2020, 5, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics5040064
Thomas RE. Improving the Care of Older Patients by Decreasing Potentially Inappropriate Medications, Potential Medication Omissions, and Serious Drug Events Using Pharmacogenomic Data about Variability in Metabolizing Many Medications by Seniors. Geriatrics. 2020; 5(4):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics5040064
Chicago/Turabian StyleThomas, Roger E. 2020. "Improving the Care of Older Patients by Decreasing Potentially Inappropriate Medications, Potential Medication Omissions, and Serious Drug Events Using Pharmacogenomic Data about Variability in Metabolizing Many Medications by Seniors" Geriatrics 5, no. 4: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics5040064
APA StyleThomas, R. E. (2020). Improving the Care of Older Patients by Decreasing Potentially Inappropriate Medications, Potential Medication Omissions, and Serious Drug Events Using Pharmacogenomic Data about Variability in Metabolizing Many Medications by Seniors. Geriatrics, 5(4), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics5040064





