The Longitudinal Association Between Social Factors, Edentulism, and Cluster of Behaviors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Latent Class Analysis (LCA)
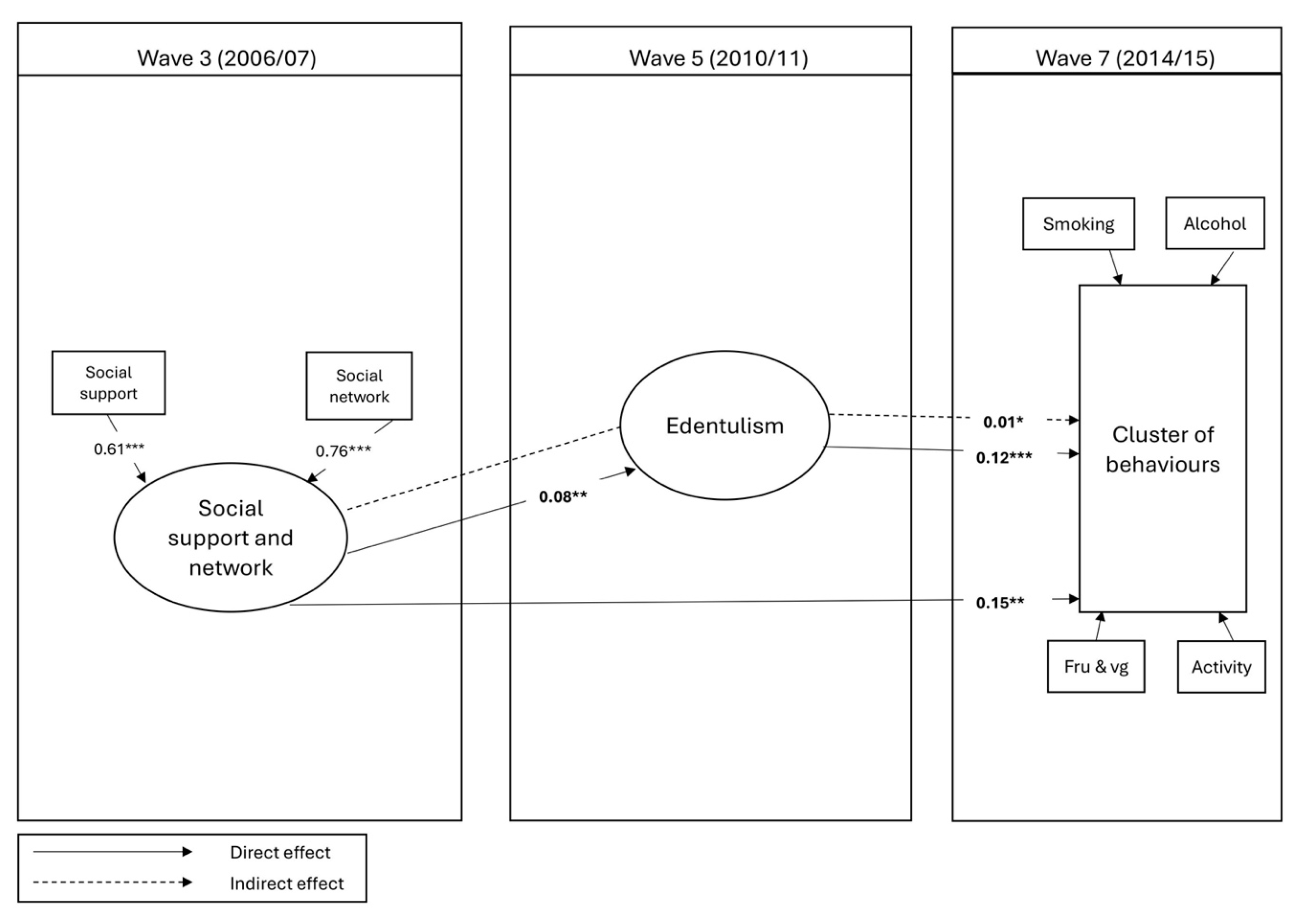
3.3. Structure Equation Modeling (SEM)
3.4. Sensitivity Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spring, B.; Moller, A.C.; Coons, M.J. Multiple health behaviours: Overview and implications. J. Public Health 2012, 34 (Suppl. 1), i3–i10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austregésilo, S.C.; de Goes, P.S.A.; de Sena Júnior, M.R.; Pazos, C.T.C. Clustering of oral and general health risk behaviors among adolescents. Prev. Med. Rep. 2019, 15, 100936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meader, N.; King, K.; Moe-Byrne, T.; Wright, K.; Graham, H.; Petticrew, M.; Power, C.; White, M.; Sowden, A.J. A systematic review on the clustering and co-occurrence of multiple risk behaviours. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poortinga, W. The prevalence and clustering of four major lifestyle risk factors in an English adult population. Prev. Med. 2007, 44, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kino, S.; Bernabé, E.; Sabbah, W. Socioeconomic inequality in clusters of health-related behaviours in Europe: Latent class analysis of a cross-sectional European survey. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alobaidi, F.; Heidari, E.; Sabbah, W. Systematic review of longitudinal studies on the association between cluster of health-related behaviors and tooth loss among adults. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2024, 83, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Rouxel, P.; Watt, R.G.; Tsakos, G. Social inequalities in clustering of oral health related behaviors in a national sample of British adults. Prev. Med. 2013, 57, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umberson, D.; Montez, J.K. Social relationships and health: A flashpoint for health policy. J. Health Soc. Behav. 2010, 51, S54–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmot, M.; Friel, S.; Bell, R.; Houweling, T.A.; Taylor, S. Closing the gap in a generation: Health equity through action on the social determinants of health. Lancet 2008, 372, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moor, I.; Spallek, J.; Richter, M. Explaining socioeconomic inequalities in self-rated health: A systematic review of the relative contribution of material, psychosocial and behavioural factors. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2017, 71, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, R.G.; Sheiham, A. Integrating the common risk factor approach into a social determinants framework. Community Dent. Oral. Epidemiol. 2012, 40, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida-Kohno, E.; Fueki, K.; Wanigatunga, A.A.; Cudjoe, T.K.M.; Aida, J. Social Relationships and Tooth Loss in Adults Aged 60 Years and Older: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Community Dent. Oral. Epidemiol. 2024, 53, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alobaidi, F.; Heidari, E.; Sabbah, W. Behavioral Pathway between Social Support and Network, and Edentulism. J. Dent. Res. 2025, 104, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, D.S.; Singh, K.A.; Liu, P.; Spencer, A. Fruit and vegetable consumption among older adults by tooth loss and socio-economic status. Aust. Dent. J. 2010, 55, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabé, E.; de Oliveira, C.; de Oliveira Duarte, Y.A.; Bof de Andrade, F.; Sabbah, W. Social participation and tooth loss, vision, and hearing impairments among older Brazilian adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2023, 71, 3152–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh-Hunt, N.; Bagguley, D.; Bash, K.; Turner, V.; Turnbull, S.; Valtorta, N.; Caan, W. An overview of systematic reviews on the public health consequences of social isolation and loneliness. Public Health 2017, 152, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letelier, A.; Jivraj, S.; Heilmann, A.; Watt, R.G.; Tsakos, G. Life course socioeconomic position and general and oral health in later life: Assessing the role of social causation and health selection pathways. SSM Popul. Health 2022, 17, 101026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, P.; Zojaji, S.; Fard, A.A.; Nateghi, M.N.; Mansouri, Z.; Zojaji, R. The impact of oral health on depression: A systematic review. Spec. Care Dent. 2025, 45, e13079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emami, E.; de Souza, R.F.; Kabawat, M.; Feine, J.S. The impact of edentulism on oral and general health. Int. J. Dent. 2013, 2013, 498305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, J.; Batty, G.D.; Breedvelt, J.; Coughlin, K.; Crawford, R.; Marmot, M.; Nazroo, J.; Oldfield, Z.; Steel, N.; Steptoe, A.; et al. English Longitudinal Study of Ageing: Waves 0–9, 1998–2019 [Data Collection]. Available online: https://rdmc.nottingham.ac.uk/handle/internal/10496 (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Department of Health. UK Chief Medical Officers’ Low Risk Drinking Guidelines. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/545937/UK_CMOs__report.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2025).
- Kojima, G.; Iliffe, S.; Jivraj, S.; Walters, K. Fruit and Vegetable Consumption and Incident Prefrailty and Frailty in Community-Dwelling Older People: The English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alobaidi, F.; Heidari, E.; Sabbah, W. Health-Related Behaviour Clusters and Functional Dentition in Older People. Gerodontology 2025, 42, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouxel, P.; Tsakos, G.; Demakakos, P.; Zaninotto, P.; Chandola, T.; Watt, R.G. Is Social Capital a Determinant of Oral Health among Older Adults? Findings from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaike, H. Factor analysis and AIC. Psychometrika 1987, 52, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, G. Estimating the Dimension of a Model. Ann. Stat. 1978, 6, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, 3rd ed.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Haugan, G.; Eriksson, M. Health Promotion in Health Care—Vital Theories and Research; Haugan, G., Eriksson, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Reblin, M.; Uchino, B.N. Social and emotional support and its implication for health. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2008, 21, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, N.; Packard, K.; Kalkowski, J.; Walters, R.; Haddad, A.R.; Flecky, K.; Rusch, L.; Furze, J.; Black, L.; Peterson, J. Improving Health through Action on Economic Stability: Results of the Finances First Randomized Controlled Trial of Financial Education and Coaching in Single Mothers of Low-Income. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2023, 17, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelak, K.; Chakole, S. The Role of Social Determinants of Health in Promoting Health Equality: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e33425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keim-Klärner, S.; Adebahr, P.; Brandt, S.; Gamper, M.; Klärner, A.; Knabe, A.; Kupfer, A.; Müller, B.; Reis, O.; Vonneilich, N.; et al. Social inequality, social networks, and health: A scoping review of research on health inequalities from a social network perspective. Int. J. Equity Health 2023, 22, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, R.G.; Marmot, M. Social Determinants of Health: The Solid Facts; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- Listl, S.; Galloway, J.; Mossey, P.A.; Marcenes, W. Global Economic Impact of Dental Diseases. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, U.; Tsakos, G.; Heilmann, A.; Watt, R.G.; Takeuchi, K.; Kondo, K.; Osaka, K.; Aida, J. Impact of Teeth on Social Participation: Modified Treatment Policy Approach. J. Dent. Res. 2023, 102, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzolino, D.; Passarelli, P.C.; De Angelis, P.; Piccirillo, G.B.; D’Addona, A.; Cesari, M. Poor Oral Health as a Determinant of Malnutrition and Sarcopenia. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerritsen, A.E.; Allen, P.F.; Witter, D.J.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; Creugers, N.H. Tooth loss and oral health-related quality of life: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2010, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komagamine, Y.; Kanazawa, M.; Iwaki, M.; Jo, A.; Suzuki, H.; Amagai, N.; Minakuchi, S. Combined effect of new complete dentures and simple dietary advice on nutritional status in edentulous patients: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2016, 17, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowjack-Raymer, R.E.; Sheiham, A. Numbers of natural teeth, diet, and nutritional status in US adults. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, T.; Srivastava, S. Tooth loss and associated self-rated health and psychological and subjective wellbeing among community-dwelling older adults: A cross-sectional study in India. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.M.; Friis, K.; Maindal, H.T.; Hargaard, A.-S.; Knudsen, M.G.; Grønkjaer, M.S.; Lasgaard, M. Loneliness is associated with adverse health behaviour and obesity: A Danish population-based study of 122,258 individuals. BMC Public Health 2025, 25, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, A.; McMunn, A.; Banks, J.; Steptoe, A. Loneliness, social isolation, and behavioral and biological health indicators in older adults. Health Psychol. 2011, 30, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Included (n = 2287) | Excluded (n = 2122) | p-Value a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| %, Mean | %, Mean | |||
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 49% | 48% | ||
| Female | 51% | 52% | 0.295 | |
| Ethnicity | ||||
| White | 99% | 98% | ||
| Multi-ethnic | 1% | 2% | <0.001 | |
| Qualification | ||||
| Less than O-level | 26% | 44% | ||
| O-level | 30% | 24% | ||
| Higher than A-level | 44% | 31% | <0.001 | |
| Age | 62.2 | 66.9 | <0.001 | |
| Wealth | 3.6 | 3.1 | <0.001 | |
| Social support | 45.1 | 43.9 | 0.027 | |
| Social network | 9.7 | 9.0 | <0.001 | |
| Age (Wave 5) | 66.3 | 71.2 | <0.001 | |
| Edentulism (Wave 5) | ||||
| Yes | 8% | 18% | ||
| No | 92% | 82% | <0.001 | |
| Smoking (Wave 7) | ||||
| Non-smoker | 89% | 85% | ||
| Smoker | 11% | 15% | 0.263 | |
| Alcohol intake (Wave 7) | ||||
| 14 or less unit per week | 87% | 91% | ||
| More than 14 units per week | 13% | 9% | 0.385 | |
| Fruit and vegetable consumption (Wave 7) | ||||
| Less than 5 portions per day | 83% | 81% | ||
| 5 portion or more per day | 17% | 19% | 0.401 | |
| Physical activity (Wave 7) | ||||
| No or low activity per week | 17% | 41% | ||
| Moderate or high activity per week | 83% | 59% | <0.001 | |
| Two Class Model | Class 1 (Risky) 7% (n = 137) | Class 2 (Healthy) 93% (n = 1910) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Item-response Probabilities | |||
| Fruits and vegetables | |||
| Less than 5 portions per day | 98% | 81% | |
| 5 portions or more per day | 2% | 18% | |
| Smoking | |||
| Non-smokers | 34% | 98% | |
| Smokers | 66% | 2% | |
| Physical activity | |||
| No or low activity per week | 32% | 16% | |
| Moderate or high activity per week | 68% | 84% | |
| Alcohol intake | |||
| 14 or less units per week | 80% | 87% | |
| More than 14 units per week | 20% | 13% | |
| Class Descriptive Percentages | |||
| Gender | |||
| Male | 52% | 50% | |
| Female | 48% | 50% | |
| Education | |||
| Less than O-level | 33% | 26% | |
| O-level | 40% | 30% | |
| Higher than A-level | 27% | 44% | |
| Edentulism | |||
| Yes | 13% | 7% | |
| No | 87% | 93% | |
| Ethnicity | |||
| White | 99% | 99% | |
| Multi-ethnic | 1% | 1% | |
| Class Descriptive Mean | |||
| Age | 59.3 | 62.4 | |
| Wealth | 2.7 | 3.7 | |
| Social support | 42.2 | 45.5 | |
| Social network | 8.9 | 9.8 | |
| Variables | SC | 95%CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Confirmatory factor analysis | ||||
| Social support | 0.61 | (0.423, 0.800) | <0.001 | |
| Social network | 0.75 | (0.517, 0.988) | <0.001 | |
| Direct effect to Edentulism | ||||
| Social support and network | 0.08 | (0.025, 0.130) | 0.004 | |
| Direct effect to Cluster of behaviors | ||||
| Social support and network | 0.15 | (0.054, 0.239) | 0.002 | |
| Edentulism | 0.12 | (0.056, 0.182) | <0.001 | |
| Cluster of behaviors Wave 3 | 0.23 | (0.190, 0.280) | <0.001 | |
| Gender | 0.02 | (−0.054, 0.098) | 0.576 | |
| Ethnicity | 0.08 | (−0.118, 0.277) | 0.431 | |
| Age at Wave 3 | −0.40 | (−1.705, 0.898) | 0.544 | |
| Age at Wave 5 | 0.62 | (−0.686, 1.929) | 0.352 | |
| Indirect effect to Cluster of behaviors (through edentulism) | ||||
| Social support and network | 0.01 | (0.001, 0.017) | 0.020 | |
| Total effect to Cluster of behaviors (direct + indirect) | ||||
| Social support and network | 0.16 | (0.064, 0.0248) | 0.001 | |
| Model fit | ||||
| RMSEA | 0.03 | (0.017, 0.037) | ||
| CFI | 0.95 | |||
| TLI | 0.91 | |||
| Variables | SC | 95%CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Confirmatory factor analysis | ||||
| Social support | 0.76 | (0.606, 0.919) | <0.001 | |
| Social network | 0.61 | (0.479, 0.737) | <0.001 | |
| Direct effect to social support and network | ||||
| Wealth | 0.14 | (0.086, 0.195) | <0.001 | |
| Direct effect to Edentulism | ||||
| Social support and network | 0.05 | (0.000, 0.101) | 0.052 | |
| Wealth | 0.16 | (0.114, 0.205) | <0.001 | |
| Direct effect to Cluster of behaviors | ||||
| Social support and network | 0.15 | (0.042, 0.223) | 0.004 | |
| Edentulism | 0.01 | (0.021, 0.142) | 0.008 | |
| Cluster of behaviors Wave 3 | 0.19 | (0.151, 0.240) | <0.001 | |
| Gender | 0.04 | (−0.036, 0.119) | 0.295 | |
| Ethnicity | 0.05 | (−0.105, 0.212) | 0.508 | |
| Age at Wave 3 | −0.25 | (−1.535, 1.037) | 0.700 | |
| Age at Wave 5 | 0.46 | (−0.830, 1.760) | 0.482 | |
| Education | 0.06 | (−0.024, 0.152) | 0.155 | |
| Wealth | 0.21 | (0.129, 0.286) | <0.001 | |
| Indirect effect to Cluster of behaviors (through edentulism) | ||||
| Social support and network | 0.01 | (−0.001, 0.009) | 0.112 | |
| Total effect to Cluster of behaviors (direct + indirect) | ||||
| Social support and network | 0.14 | (0.046, 0.227) | 0.003 | |
| Model fit | ||||
| RMSEA | 0.02 | (0.014, 0.032) | ||
| CFI | 0.96 | |||
| TLI | 0.93 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alobaidi, F.; Heidari, E.; Sabbah, W. The Longitudinal Association Between Social Factors, Edentulism, and Cluster of Behaviors. Geriatrics 2025, 10, 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10060142
Alobaidi F, Heidari E, Sabbah W. The Longitudinal Association Between Social Factors, Edentulism, and Cluster of Behaviors. Geriatrics. 2025; 10(6):142. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10060142
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlobaidi, Fatimah, Ellie Heidari, and Wael Sabbah. 2025. "The Longitudinal Association Between Social Factors, Edentulism, and Cluster of Behaviors" Geriatrics 10, no. 6: 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10060142
APA StyleAlobaidi, F., Heidari, E., & Sabbah, W. (2025). The Longitudinal Association Between Social Factors, Edentulism, and Cluster of Behaviors. Geriatrics, 10(6), 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10060142







