A Comparison of Higher-Level Functional Capacity Between Older Adults with and Without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Propensity Score Matching
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
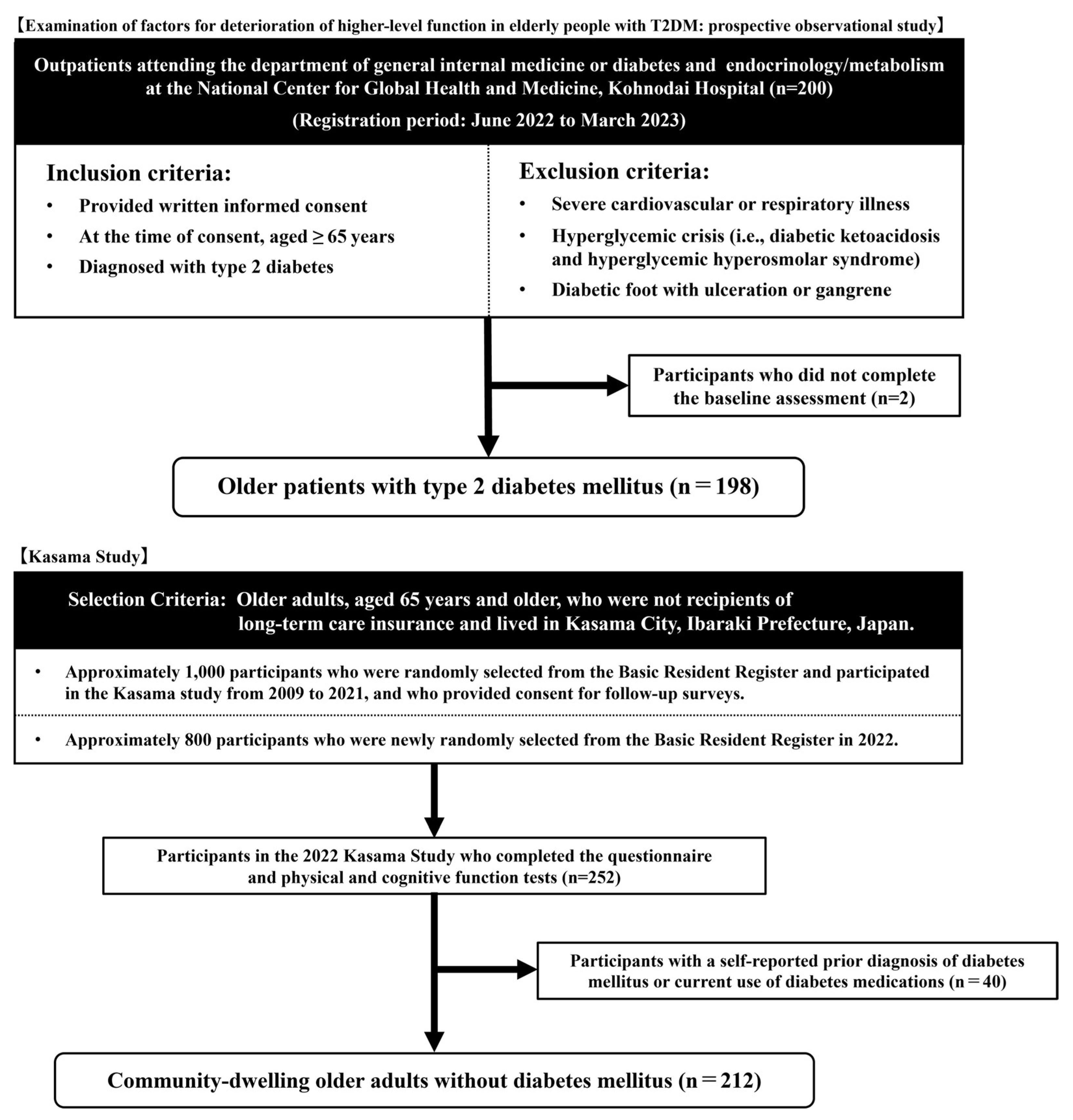
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Assessment of Higher-Level Functional Capacity
2.3. Other Variables
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Discriminative Power of Propensity Score
3.2. Participants’ Characteristics Pre- and Post-Propensity Score Matching
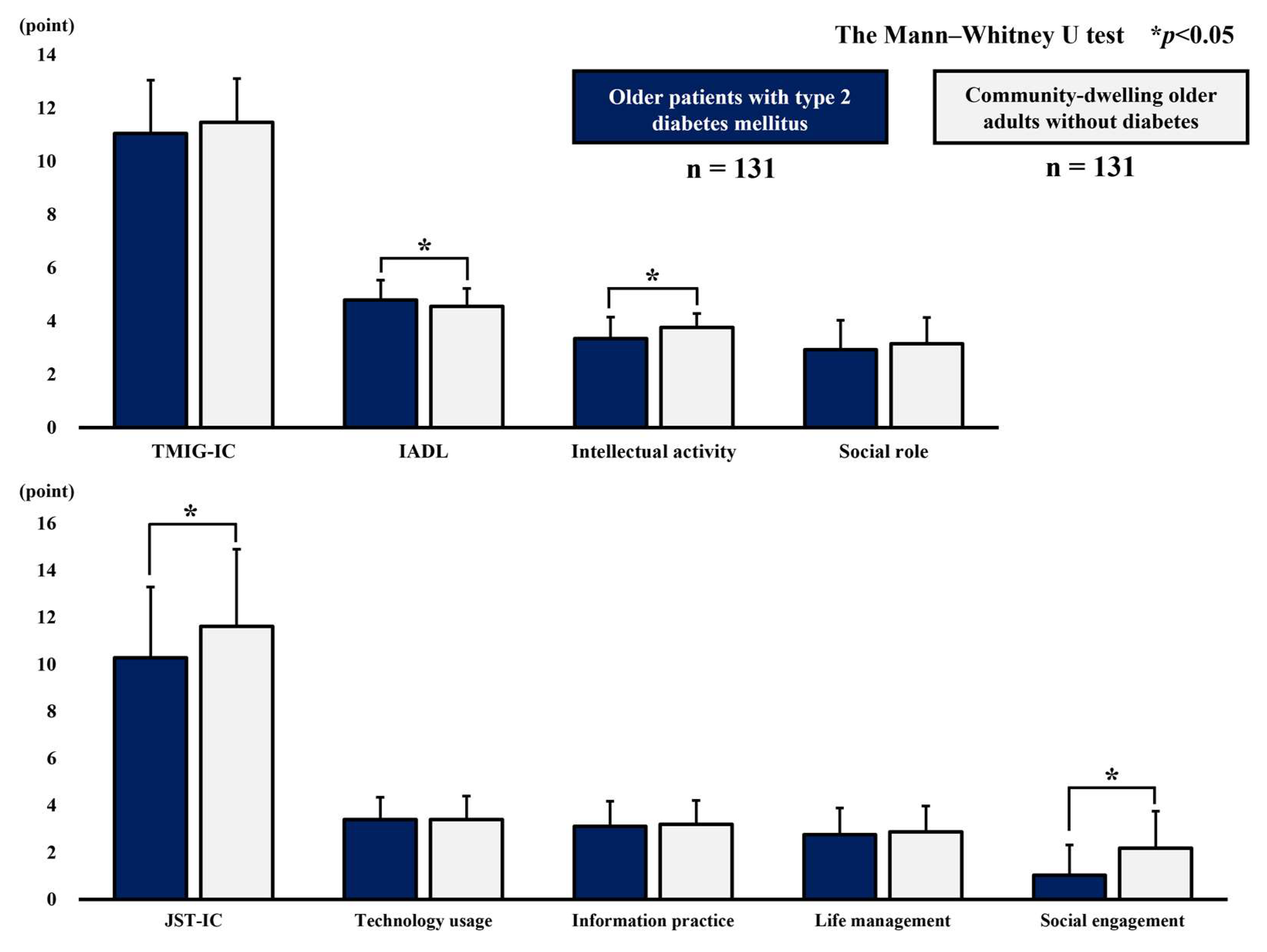
3.3. Comparison of Scores on the Higher-Level Functional Capacity Index
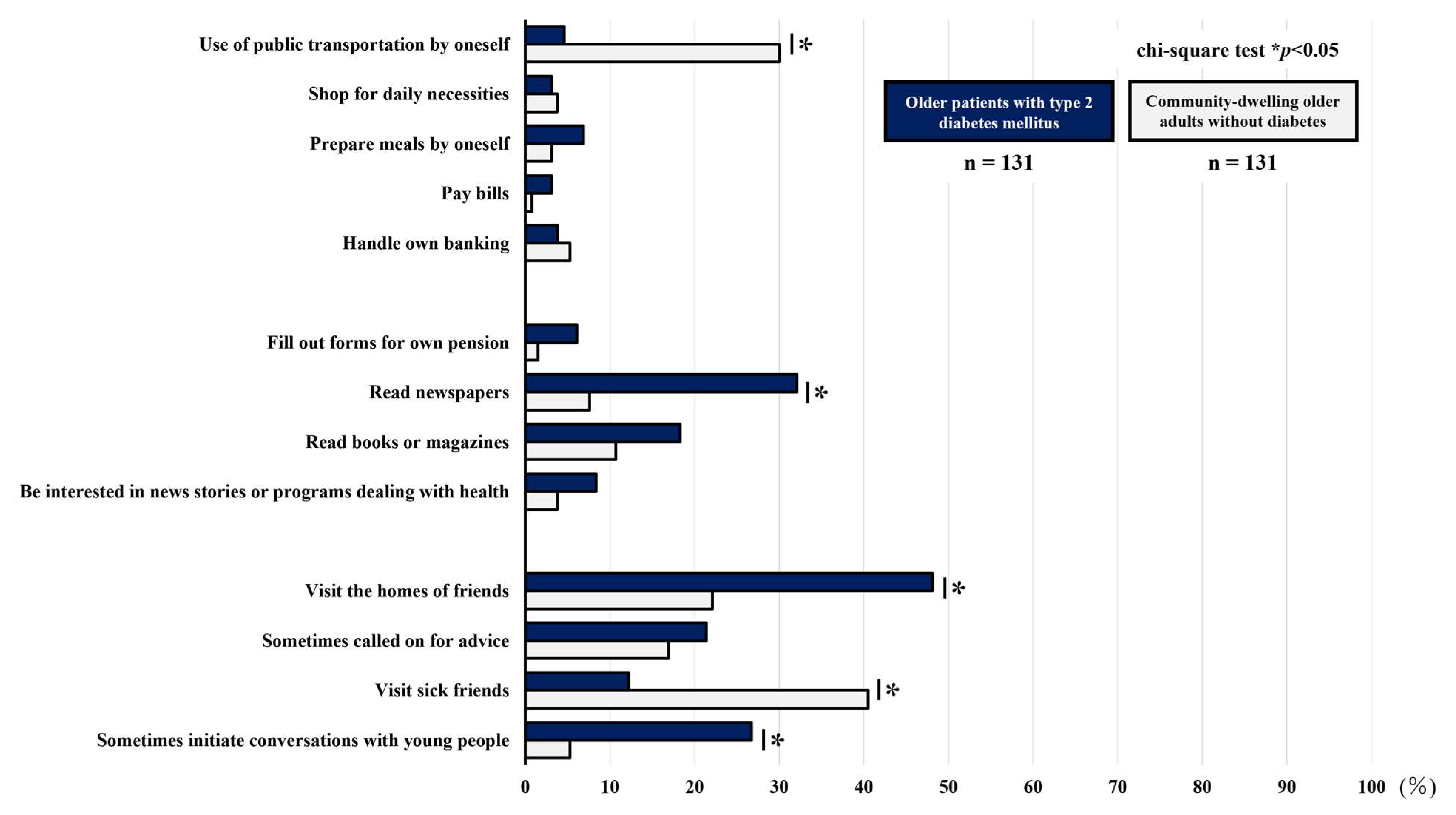
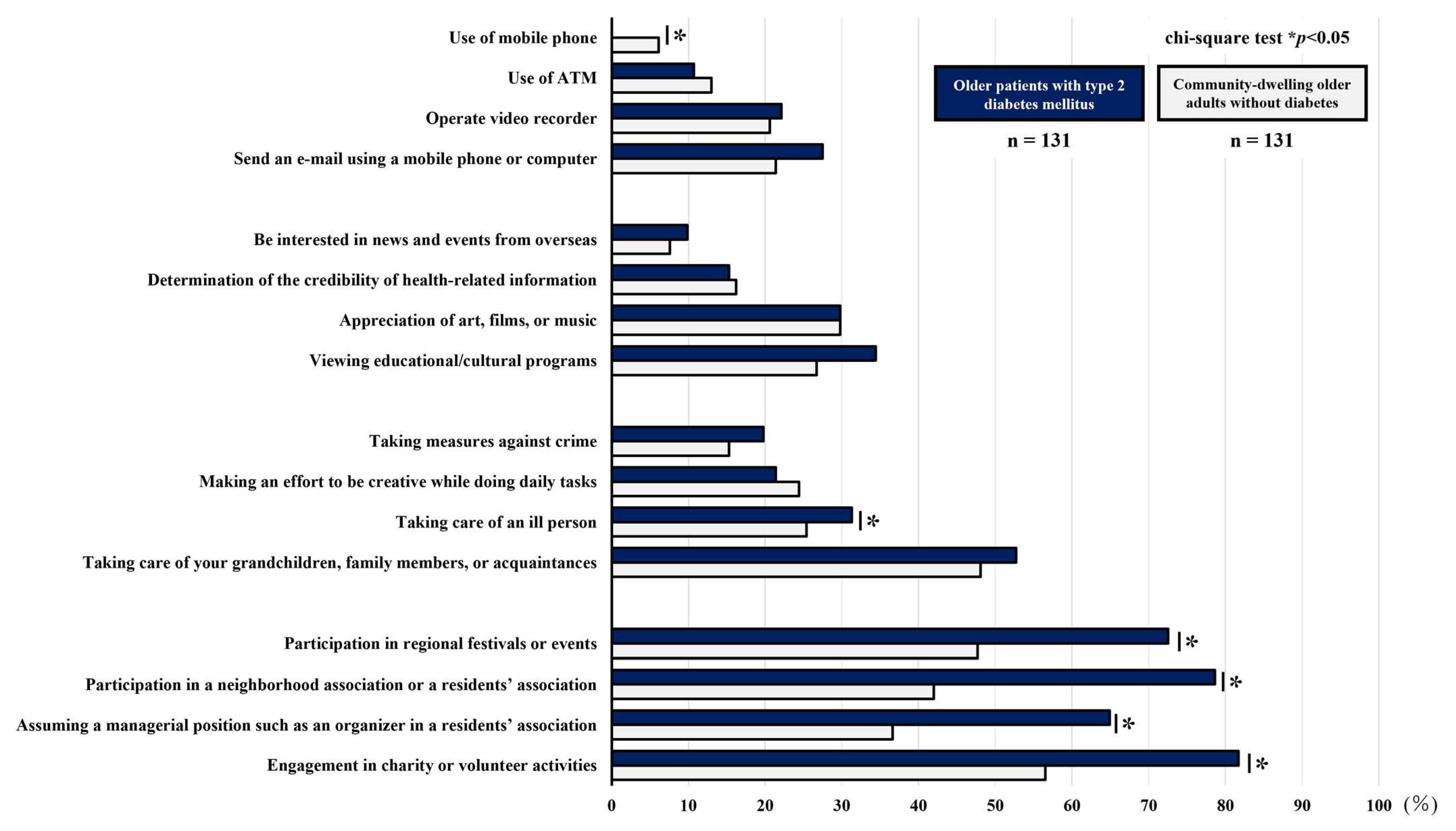
3.4. Comparison of the Percentage of Participants Reporting Difficulty with Each Item of the Higher-Level Functional Capacity Index
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DM | diabetes mellitus |
| HbA1c | hemoglobin A1c |
| IADL | instrumental activities of daily living |
| TMIG-IC | Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Gerontology Index of Competence |
| JST-IC | Japan Science and Technology Agency Index of Competence |
| T2DB | type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| PASE | Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| SD | standard deviation |
References
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. National Health and Nutrition Survey. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/bunya/kenkou/eiyou/dl/h28-houkoku-03.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2024).
- Araki, A.; Ito, H. Essence and perspective of the JGS/JDS clinical practice guideline for the treatment of diabetes in the elderly. J. Japan Geriatr. Psychiatry 2018, 55, 1–12. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Scientific Group on the Epidemiology of Aging. The uses of epidemiology in the study of the elderly. Report of a WHO scientific group on the epidemiology of aging. World Health Organ. Tech. Rep. Ser. 1984, 706, 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- Lawton, M.P. Assessing the Competence of Older People. Research, Planning, and Action for the Elderly: The Power and Potential of Social Science; Human Science Press: New York, USA, 1972; pp. 122–143. [Google Scholar]
- Iwasa, H.; Masui, Y.; Inagaki, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Shimada, H.; Otsuka, R.; Kikuchi, K.; Nonaka, K.; Yoshida, H.; Yoshida, H.; et al. Development of the Japan Science and Technology Agency index of competence to assess functional capacity in older adults: Conceptual definitions and preliminary items. Gerontol. Geriatr. Med. 2015, 1, 2333721415609490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, H.; Kondo, K.; Ojima, T.; Murata, C. Examination of risk factors for onset of certification of long-term care insurance in community-dwelling older people: AGES project 3-year follow-up study. Jpn. J. Public. Health 2009, 56, 501–512. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, K.; Tsubota-Utsugi, M.; Satoh, M.; Asayama, K.; Inoue, R.; Ishiguro, A.; Matsuda, A.; Kanno, A.; Yasui, D.; Murakami, T.; et al. Impaired higher-level functional capacity as a predictor of stroke in community-dwelling older adults: The Ohasama study. Stroke 2016, 47, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, Y.; Kitamura, A.; Nofuji, Y.; Ishizaki, T.; Seino, S.; Yokoyama, Y.; Shinozaki, T.; Murayama, H.; Mitsutake, S.; Amano, H.; et al. Association of trajectories of higher-level functional capacity with mortality and medical and long-term care costs among community-dwelling older Japanese. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2019, 74, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Shinkai, S.; Kumagai, S.; Amano, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Kim, H.; Suzuki, T.; Ishizaki, T.; Haga, H.; et al. Longitudinal changes in higher-level functional capacity of an older population living in a Japanese urban community. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2003, 36, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, E.; Backholer, K.; Gearon, E.; Harding, J.; Freak-Poli, R.; Stevenson, C.; Peeters, A. Diabetes and risk of physical disability in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2013, 1, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, T.; Iimuro, S.; Sakamaki, K.; Umegaki, H.; Araki, A.; Ohashi, Y.; Ito, H. Japanese Elderly Diabetes Intervention Trial Study Group. Risk factors for a 6-year decline in physical disability and functional limitations among elderly people with type 2 diabetes in the Japanese Elderly Diabetes Intervention Trial. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2012, 12, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ida, S.; Murata, K.; Nakadachi, D.; Ishihara, Y.; Imataka, K.; Uchida, A.; Monguchi, K.; Kaneko, R.; Fujiwara, R.; Takahashi, H. Association between dynapenia and decline in higher-level functional capacity in older men with diabetes. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2018, 18, 1393–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ida, S.; Kaneko, R.; Imataka, K.; Okubo, K.; Shirakura, Y.; Azuma, K.; Fujiwara, R.; Takahashi, H.; Murata, K. Factors associated with social isolation and being homebound among older patients with diabetes: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e037528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, T.; Tamura, Y.; Sakurai, T.; Umegaki, H.; Iimuro, S.; Ohashi, Y.; Ito, H.; Araki, A.; Japanese Elderly Diabetes Intervention Trial Research Group. Functional categories based on cognition and activities of daily living predict all-cause mortality in older adults with diabetes mellitus: The Japanese Elderly Diabetes Intervention Trial. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2021, 21, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyano, W.; Shibata, H.; Nakazato, K.; Haga, H.; Suyama, Y. Measurement of competence: Reliability and validity of the TMIG Index of Competence. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 1991, 13, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, H.; Sugisawa, H.; Watanabe, S. Functional capacity in elderly Japanese living in the community. Geriat Gerontol. Int. 2001, 1, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T. Health status of older adults living in the community in Japan: Recent changes and significance in the super-aged society. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2018, 18, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, H.; Masui, Y.; Inagaki, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Shimada, H.; Otsuka, R.; Kikuchi, K.; Nonaka, K.; Yoshida, H.; Yoshida, H.; et al. Assessing competence at a higher level among older adults: Development of the Japan Science and Technology Agency Index of Competence (JST-IC). Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 30, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, T.; Kogure, K.; Toda, N.; Hakoshima, M.; Katsuyama, H.; Yanai, H.; Tokunaga, S.; Tateoka, K.; Tsuji, T.; Okura, T. Association between comorbidities associated with diabetes and higher-level functional status in older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross sectional study. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2024, 15, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okura, T.; Tsuji, T.; Tsunoda, K.; Kitano, N.; Yoon, J.Y.; Saghazadeh, M.; Soma, Y.; Yoon, J.; Kim, M.; Jindo, T.; et al. Study protocol and overview of the Kasama study: Creating a comprehensive, community-based system for preventive nursing care and supporting successful aging. J. Phys. Fit. Sports Med. 2017, 6, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washburn, R.A.; Smith, K.W.; Jette, A.M.; Janney, C.A. The Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly (PASE): Development and evaluation. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1993, 46, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, H.; Sanada, M.; Kitada, K.; Terashima, T.; Kim, H.; Sakaue, Y.; Fujitani, M.; Kawai, H.; Maeda, K.; Kashiwagi, A. Rationale and usefulness of newly devised abbreviated diagnostic criteria and staging for diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 77, S178–S183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.D. Vitreous contraction in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1965, 74, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneda, M.; Utsunomiya, K.; Koya, D.; Babazono, T.; Moriya, T.; Makino, H.; Kimura, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Wada, T.; Ogawa, S.; et al. A new classification of Diabetic Nephropathy 2014: A report from Joint Committee on Diabetic Nephropathy. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2015, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.C. Optimal caliper widths for propensity-score matching when estimating differences in means and differences in proportions in observational studies. Pharm. Stat. 2011, 10, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normand, S.T.; Landrum, M.B.; Guadagnoli, E.; Ayanian, J.Z.; Ryan, T.J.; Cleary, P.D.; McNeil, B.J. Validating recommendations for coronary angiography following acute myocardial infarction in the elderly: A matched analysis using propensity scores. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2001, 54, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasa, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Inagaki, H.; Masui, Y.; Shimda, Y.; Kikuchi, K.; Ohtsuka, R.; Nonaka, K.; Yoshida, H.; Suzuki, T. Chiiki-koureisha niokeru aratanaseikatsu-kinousihyou no huhensei narabini hyoujunnchi [Development of new indicators of functional capacity in community-dwelling elderly: Measurement invariance and standard value of Japan Science and Technology Agency index of competence (JST-IC)]. J. Health Welf. Stat. 2018, 65, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kalyani, R.R.; Saudek, C.D.; Brancati, F.L.; Selvin, E. Association of diabetes, comorbidities, and A1C with functional disability in older adults: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 1999–2006. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ida, S.; Kaneko, R.; Imataka, K.; Fujiwara, R.; Murata, K. Are diabetes-related factors associated with the social roles of elderly patients with diabetes? J. Diabetes Complicat. 2021, 35, 107759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, J.W.; Rogers, S.L.; Kawasaki, R.; Lamoureux, E.L.; Kowalski, J.W.; Bek, T.; Chen, S.J.; Dekker, J.M.; Fletcher, A.; Grauslund, J.; et al. Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Kondo, K.; Takeda, T.; Jeong, S. Are there inter-municipality differences in the ratio of individuals with limited activities of daily living?: The JAGES Project. Jpn. Occup. Ther. Res. 2015, 34, 541–554. [Google Scholar]
- Malani, P.; Kullgren, J.; Solway, E.; Lee, P.; Aikens, J.; Richardson, C.; Singer, D.; Kirch, M.; Smith, E. National Poll on Healthy Aging: Mobile Health App Use Among Older Adult. Available online: https://deepblue.lib.umich.edu/handle/2027.42/171628 (accessed on 20 March 2024).
| Pre-Propensity Score Matching | Post-Propensity Score Matching | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (n = 198) | Community-Dwelling Older Adults Without Diabetes (n = 212) | p | Std Diff | Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (n = 131) | Community-Dwelling Older Adults Without Diabetes (n = 131) | Std Diff | |||||||||
| Mean | ± | SD | Mean | ± | SD | Mean | ± | SD | Mean | ± | SD | ||||
| Male sex, n (%) | 119 (60.1) | 90 (42.5) | <0.01 | 0.36 | 71 (54.2) | 69 (52.7) | 0.03 | ||||||||
| Age, years | 75.9 | ± | 5.7 | 76.3 | ± | 5.3 | 0.47 | 0.07 | 76.6 | ± | 5.6 | 76.1 | ± | 5.4 | 0.09 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.6 | ± | 3.9 | 23.0 | ± | 3.1 | <0.01 | 0.47 | 23.7 | ± | 3.4 | 23.5 | ± | 3.1 | 0.06 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 104 (52.5) | 87 (41.0) | 0.02 | 0.23 | 61 (46.6) | 58 (44.3) | 0.04 | ||||||||
| Cardiovascular disease, n (%) | 20 (10.1) | 12 (5.7) | 0.10 | 0.16 | 10 (7.6) | 7 (5.3) | 0.09 | ||||||||
| Cerebrovascular disease, n (%) | 19 (9.6) | 6 (2.8) | <0.01 | 0.28 | 6 (4.6) | 6 (4.6) | 0 | ||||||||
| Current smoker, n (%) | 23 (11.6) | 7 (3.3) | <0.01 | 0.32 | 6 (4.6) | 7 (5.3) | 0.03 | ||||||||
| Alcohol consumption (drinker), n (%) | 52 (26.4) | 61 (28.8) | 0.65 | 0.05 | 41 (31.3) | 37 (28.2) | 0.06 | ||||||||
| Poor self-rated health, n (%) | 32 (16.2) | 17 (8.0) | 0.01 | 0.25 | 14 (10.7) | 13 (9.9) | 0.02 | ||||||||
| Poor economic conditions, n (%) | 45 (22.7) | 29 (13.7) | 0.02 | 0.23 | 23 (17.6) | 24 (18.3) | 0.01 | ||||||||
| Living alone, n (%) | 45 (22.7) | 31 (14.6) | 0.04 | 0.21 | 22 (16.8) | 21 (16.0) | 0.02 | ||||||||
| Period of education, years | 13.3 | ± | 2.7 | 12.9 | ± | 2.3 | 0.71 | 0.18 | 13.1 | ± | 2.8 | 13.0 | ± | 2.5 | 0.03 |
| Physical activity (PASE score), point | 103.5 | ± | 66.6 | 123.1 | ± | 50.3 | <0.01 | 0.33 | 116.6 | ± | 65.5 | 113.5 | ± | 43.1 | 0.05 |
| n | Mean | ± | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c, % | 130 | 7.1 | ± | 0.9 |
| Neuropathy, n (%) | 131 | 51 (38.9) | ||
| Retinopathy, n (%) | 112 | 34 (26.0) | ||
| Nephropathy, n (%) | 130 | 56 (42.7) | ||
| Use of medication | ||||
| Insulin | 131 | 29 (22.1) | ||
| Sulfonylureas | 131 | 15 (11.5) | ||
| Biguanides | 131 | 73 (55.7) | ||
| Thiazolidines | 131 | 18 (13.7) | ||
| α-Glucosidase inhibitors | 131 | 21 (16.0) | ||
| Glinides | 131 | 14 (10.7) | ||
| DPP-4 inhibitors | 131 | 83 (63.4) | ||
| SGLT2 inhibitors | 131 | 66 (50.4) | ||
| GLP-1 receptor agonists | 131 | 24 (18.3) | ||
| Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | Community-Dwelling Older Adults Without Diabetes | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 131) | (n = 131) | ||||||
| Mean | ± | SD | Mean | ± | SD | ||
| TMIG-IC score, point | 11.1 | ± | 2.0 | 11.5 | ± | 1.6 | 0.07 |
| IADL score, point | 4.8 | ± | 0.8 | 4.6 | ± | 0.7 | <0.01 |
| Intellectual activity score, point | 3.4 | ± | 0.8 | 3.8 | ± | 0.5 | <0.01 |
| Social role score, point | 2.9 | ± | 1.1 | 3.2 | ± | 1.0 | 0.10 |
| JST-IC score, point | 10.3 | ± | 3.0 | 11.6 | ± | 3.3 | <0.01 |
| Technology usage score, point | 3.4 | ± | 0.9 | 3.4 | ± | 1.0 | 0.90 |
| Information practice score, point | 3.1 | ± | 1.1 | 3.2 | ± | 1.0 | 0.47 |
| Life management score, point | 2.8 | ± | 1.1 | 2.9 | ± | 1.1 | 0.38 |
| Social engagement score, point | 1.0 | ± | 1.3 | 2.2 | ± | 1.6 | <0.01 |
| Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | Community-Dwelling Older Adults Without Diabetes | p * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 131) | (n = 131) | ||
| Percentage of Older Adults with Difficulty, n (%) | Percentage of Older Adults with Difficulty, n (%) | ||
| IADL | |||
| Use of public transportation by oneself | 6 (4.6) | 39 (30.0) | <0.01 |
| Shop for daily necessities | 4 (3.1) | 5 (3.8) | 0.73 |
| Prepare meals by oneself | 9 (6.9) | 4 (3.1) | 0.16 |
| Pay bills | 4 (3.1) | 1 (0.8) | 0.18 |
| Handle own banking | 5 (3.8) | 7 (5.3) | 0.55 |
| Intellectual activity | |||
| Fill out forms for own pension | 8 (6.1) | 2 (1.5) | 0.05 |
| Read newspapers | 42 (32.1) | 10 (7.6) | <0.01 |
| Read books or magazines | 24 (18.3) | 14 (10.7) | 0.08 |
| Be interested in news stories or programs dealing with health | 11 (8.4) | 5 (3.8) | 0.12 |
| Social role | |||
| Visit the homes of friends | 63 (48.1) | 29 (22.1) | <0.01 |
| Sometimes called on for advice | 28 (21.4) | 22 (16.9) | 0.36 |
| Visit sick friends | 16 (12.2) | 53 (40.5) | <0.01 |
| Sometimes initiate conversations with young people | 35 (26.7) | 7 (5.3) | <0.01 |
| Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | Community-Dwelling Older Adults Without Diabetes | p * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 131) | (n = 131) | ||
| Percentage of Older Adults with Difficulty, n (%) | Percentage of Older Adults with Difficulty, n (%) | ||
| Technology usage | |||
| Use of mobile phone | 0 (0) | 8 (6.1) | <0.01 |
| Use of ATM | 14 (10.7) | 17 (13.0) | 0.57 |
| Operate video recorder (Blu-ray recorder or DVD player) | 29 (22.1) | 27 (20.6) | 0.76 |
| Send an e-mail using a mobile phone or computer | 36 (27.5) | 28 (21.4) | 0.25 |
| Information practice | |||
| Be interested in news and events from overseas | 13 (9.9) | 10 (7.6) | 0.51 |
| Determination of the credibility of health-related information | 20 (15.3) | 21 (16.2) | 0.84 |
| Appreciation of art, films, or music | 39 (29.8) | 39 (29.8) | 1.00 |
| Viewing educational/cultural programs | 45 (34.4) | 35 (26.7) | 0.18 |
| Life management | |||
| Taking measures against crime | 26 (19.8) | 20 (15.3) | 0.33 |
| Making an effort to be creative while doing daily tasks | 28 (21.4) | 32 (24.4) | 0.56 |
| Taking care of an ill person | 41 (31.3) | 33 (25.4) | 0.29 |
| Taking care of your grandchildren, family members, or acquaintances | 69 (52.7) | 63 (48.1) | 0.46 |
| Social engagement | |||
| Participation in regional festivals or events | 95 (72.5) | 62 (47.7) | <0.01 |
| Participation in a neighborhood association or a residents’ association | 103 (78.6) | 55 (42.0) | <0.01 |
| Assuming a managerial position such as an organizer in a residents’ association | 85 (64.9) | 48 (36.6) | <0.01 |
| Engagement in charity or volunteer activities | 107 (81.7) | 74 (56.5) | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shoji, T.; Kogure, K.; Toda, N.; Hakoshima, M.; Katsuyama, H.; Yanai, H.; Tokunaga, S.; Tateoka, K.; Tsuji, T.; Okura, T. A Comparison of Higher-Level Functional Capacity Between Older Adults with and Without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Propensity Score Matching. Geriatrics 2025, 10, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10050115
Shoji T, Kogure K, Toda N, Hakoshima M, Katsuyama H, Yanai H, Tokunaga S, Tateoka K, Tsuji T, Okura T. A Comparison of Higher-Level Functional Capacity Between Older Adults with and Without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Propensity Score Matching. Geriatrics. 2025; 10(5):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10050115
Chicago/Turabian StyleShoji, Takuro, Kenta Kogure, Nagisa Toda, Mariko Hakoshima, Hisayuki Katsuyama, Hidekatsu Yanai, Satoshi Tokunaga, Korin Tateoka, Taishi Tsuji, and Tomohiro Okura. 2025. "A Comparison of Higher-Level Functional Capacity Between Older Adults with and Without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Propensity Score Matching" Geriatrics 10, no. 5: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10050115
APA StyleShoji, T., Kogure, K., Toda, N., Hakoshima, M., Katsuyama, H., Yanai, H., Tokunaga, S., Tateoka, K., Tsuji, T., & Okura, T. (2025). A Comparison of Higher-Level Functional Capacity Between Older Adults with and Without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Propensity Score Matching. Geriatrics, 10(5), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10050115






