Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Infection on Erythropoietin Resistance Index in Hemodialysis Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. ERI
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Characteristics of the Study Population
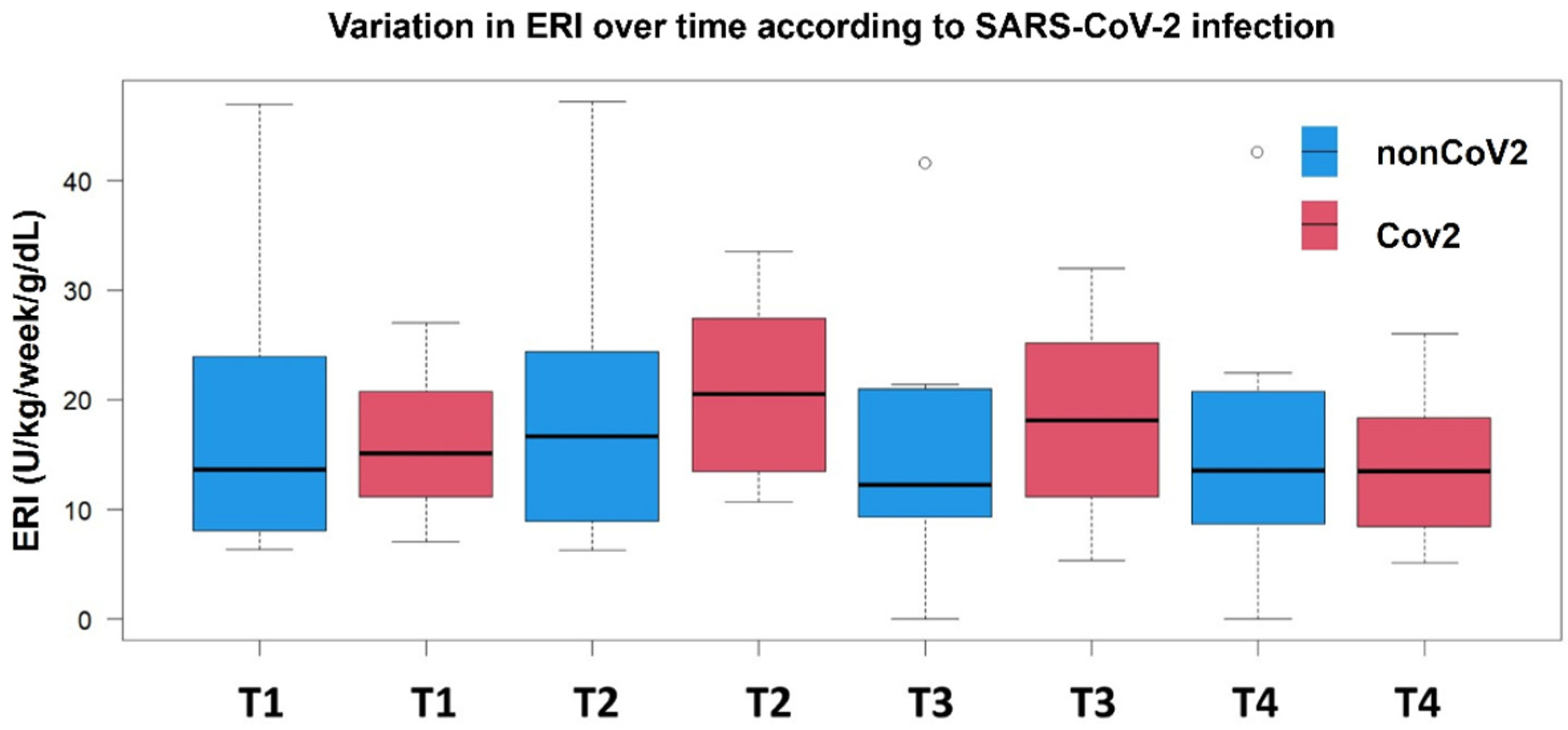
3.2. Temporal ERI Patterns in the nonCoV2 and CoV2 Groups
3.3. Factors Associated with Temporal ERI Changes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADPKD | Autosomal dominant polycistic kidney disease |
| ACE 2 | Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 |
| ATC | Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| EPO | Erythropoietin |
| ERI | Erythropoietin resistance index |
| ESAs | Erythropoietin-Stimulating Agents |
| ESKD | End-stage kidney disease |
| Hemoglobin | Hb |
| HIF | Hypoxia-inducible factor |
| IQR | Interquartile |
| HD | Hemodialysis |
| RT PCR | Real-Time PCR |
| Standard Deviation | SD |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| Transferrin Saturation | TSAT |
References
- Chapter 1: Definition and classification of CKD. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 19–62. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadoul, M.; Aoun, M.; Masimango Imani, M. The major global burden of chronic kidney disease. Lancet Glob. Health 2024, 12, e342–e343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chertow, G.M.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Kanda, E.; Karasik, A.; Li, G.; Christiansen, C.F.; Stafylas, P.; Holt, S.G.; Hagen, E.C.; et al. Projecting the clinical burden of chronic kidney disease at the patient level: A microsimulation modelling study. eClinicalMedicine 2024, 72, 102614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbazi, F.; Doosti-Irani, A.; Soltanian, A.; Poorolajal, J. Global forecasting of chronic kidney disease mortality rates and numbers with the generalized additive model. BMC Nephrol. 2024, 25, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balducci, F.; Di Rosa, M.; Roller-Wirnsberger, R.; Wirnsberger, G.; Mattace-Raso, F.; Tap, L.; Formiga, F.; Moreno-González, R.; Kostka, T.; Guligowska, A.; et al. Healthcare costs in relation to kidney function among older people: The SCOPE study. In European Geriatric Medicine; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artborg, A.; Caldinelli, A.; Wijkström, J.; Nowak, A.; Fored, M.; Stendahl, M.; Evans, M.; Rydell, H. Risk factors for COVID-19 hospitalization and mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease: A nationwide cohort study. Clin. Kidney J. 2024, 17, sfad283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.; Weiner, D.; Aweh, G.; Miskulin, D.; Manley, H.; Stewart, C.; Ladik, V.; Hosford, J.; Lacson, E.; Johnson, D.; et al. COVID-19 Infection Among US Dialysis Patients: Risk Factors and Outcomes From a National Dialysis Provider. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 77, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, D.; Kronbichler, A.; Rutter, M.; Bajpai, D.; Menez, S.; Weissenbacher, A.; Anand, S.; Lin, E.; Carlson, N.; Sozio, S.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the kidney community: Lessons learned and future directions. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portolés, J.; Martín, L.; Broseta, J.J.; Cases, A. Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: From Pathophysiology and Current Treatments, to Future Agents. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 642296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, V.H.; Tanaka, T.; Koury, M.J. A novel class of oral drugs for the treatment of anemia of chronic kidney disease. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2024, 2024, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuragano, T. Treatment of Anemia Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease: Plea for Considering Physiological Erythropoiesis. IJMS 2024, 25, 7322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soraci, L.; de Vincentis, A.; Aucella, F.; Fabbietti, P.; Corsonello, A.; Arena, E.; Aucella, F.; Gatta, G.; Incalzi, R.A. Prevalence, risk factors, and treatment of anemia in hospitalized older patients across geriatric and nephrological settings in Italy. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamaschi, G.; Borrelli de Andreis, F.; Aronico, N.; Lenti, M.V.; Barteselli, C.; Merli, S.; Pellegrino, I.; Coppola, L.; Cremonte, E.M.; Croce, G.; et al. Anemia in patients with Covid-19: Pathogenesis and clinical significance. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 21, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Ismail, L.; Taha, M.J.J.; Abuawwad, M.T.; Al-Bustanji, Y.; Al-Shami, K.; Nashwan, A.; Yassin, M. COVID-19 and Anemia: What Do We Know So Far? Hemoglobin 2023, 47, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, K.I.; Sutheesophon, W.; Manipalviratn, S.; Aw, T.C. Age and genotype dependent erythropoietin protection in COVID-19. World J. Stem Cells 2021, 13, 1513–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taneri, P.E.; Gómez-Ochoa, S.A.; Llanaj, E.; Raguindin, P.F.; Rojas, L.Z.; Roa-Díaz, Z.M.; Salvador, D., Jr.; Groothof, D.; Minder, B.; Kopp-Heim, D.; et al. Anemia and iron metabolism in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 35, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, N.; Segala, F.V.; Carruba, L.; La Carrubba, A.; Pollicino, F.; Di Franco, G.; Guido, G.; Cormio, M.; Lugli, A.; De Santis, L.; et al. Anemia as a risk factor for disease progression in patients admitted for COVID-19: Data from a large, multicenter cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, Ö.; Bilek, G.; Sahan, S. Risk factors for infection and mortality among hemodialysis patients during COVID-19 pandemic. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 54, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.; Tak, M.L.; Gupta, R.; Sharma, P.; Rajpurohit, V.; Mathur, P.; Gaur, N. Relationship of anemia with COVID-19 deaths: A retrospective cross-sectional study. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 38 (Suppl. 1), S115–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viruez-Soto, A.; López-Dávalos, M.M.; Rada-Barrera, G.; Merino-Luna, A.; Molano-Franco, D.; Tinoco-Solorozano, A.; Zubieta-DeUrioste, N.; Zubieta-Calleja, G.; Arias-Reyes, C.; Soliz, J. Low serum erythropoietin levels are associated with fatal COVID-19 cases at 4150 meters above sea level. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2021, 292, 103709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yağcı, S.; Serin, E.; Acicbe, Ö.; Zeren, M.; Odabaşı, M.S. The relationship between serum erythropoietin, hepcidin, and haptoglobin levels with disease severity and other biochemical values in patients with COVID-19. Int. J. Lab Hematol. 2021, 43 (Suppl. 1), 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begemann, M.; Gross, O.; Wincewicz, D.; Hardeland, R.; Daguano Gastaldi, V.; Vieta, E.; Weissenborn, K.; Miskowiak, K.W.; Moerer, O.; Ehrenreich, H. Addressing the ‘hypoxia paradox’ in severe COVID-19: Literature review and report of four cases treated with erythropoietin analogues. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Sulaiman, K.; Aljuhani, O.; Korayem, G.B.; Altebainawi, A.F.; Vishwakarma, R.; AlFaifi, M.; Alsohimi, S.; Alrayes, A.; Albishi, S.; Alqahtani, R.; et al. The Impact of Recombinant Human Erythropoietin Administration in Critically ill COVID-19 Patients: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2023, 29, 10760296231218216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishbane, S.; Hirsch, J.S. Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agent Treatment in Patients With COVID-19. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morceau, F.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Pro-inflammatory cytokine-mediated anemia: Regarding molecular mechanisms of erythropoiesis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2009, 2009, 405016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulmovits, B.M.; Tang, Y.; Papoin, J.; He, M.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Addorisio, M.E.; Kennedy, L.; Khan, M.; Brindley, E.; et al. HMGB1-mediated restriction of EPO signaling contributes to anemia of inflammation. Blood 2022, 139, 3181–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, S.; Delehanty, L.; Grado, S.; Holy, M.; White, Z., 3rd; Freeman, K.; Kurita, R.; Nakamura, Y.; Bullock, G.; Goldfarb, A. Iron modulation of erythropoiesis is associated with Scribble-mediated control of the erythropoietin receptor. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 661–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. The Relationship Between Hepcidin-Mediated Iron Dysmetabolism and COVID-19 Severity: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 881412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, A.L.; Mulè, M.P.; Ruffieux, H.; Mescia, F.; Bergamaschi, L.; Pelly, V.S.; Turner, L.; Kotagiri, P.; Göttgens, B.; Hess, C.; et al. Iron dysregulation and inflammatory stress erythropoiesis associates with long-term outcome of COVID-19. Nat. Immunol. 2024, 25, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolovski, S.; Medic Brkic, B.; Vujovic, K.S.; Cirkovic, I.; Jovanovic, N.; Reddy, B.; Iqbal, O.; Zhang, C.; Fareed, J.; Bansal, V. Severe Hyporesponsiveness to Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents in Patients on Chronic Hemodialysis—Reconsidering the Relationship with Thrombo-Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutanto, H.; Soegiarto, G. Risk of Thrombosis during and after a SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Pathogenesis, Diagnostic Approach, and Management. Hematol. Rep. 2023, 15, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanakit, K.; Cushman, M.; Stehman-Breen, C.; Heckbert, S.R.; Folsom, A.R. Chronic kidney disease increases risk for venous thromboembolism. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingrasciotta, Y.; Lacava, V.; Marcianò, I.; Giorgianni, F.; Tripepi, G.; D’ Arrigo, G.; Chinellato, A.; Ugo Tari, D.; Santoro, D.; Trifirò, G. In search of potential predictors of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) hyporesponsiveness: A population-based study. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronstein-Wiedemann, R.; Stadtmüller, M.; Traikov, S.; Georgi, M.; Teichert, M.; Yosef, H.; Wallenborn, J.; Karl, A.; Schütze, K.; Wagner, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infects Red Blood Cell Progenitors and Dysregulates Hemoglobin and Iron Metabolism. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2022, 18, 1809–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Bian, X.; Zhang, A.; Huang, J.; Ren, L.; Luo, C. Long-term efficacy, safety, and medication compliance of roxadustat on peritoneal dialysis patients with renal anemia affected by the COVID-19 pandemic: A retrospective study. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2022, 11, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louw, E.H.; Chothia, M.Y. Residual renal function in chronic dialysis is not associated with reduced erythropoietin-stimulating agent dose requirements: A cross-sectional study. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| All (n = 25) | nonCoV2 Group (n = 10) | Cov2 Group (n = 15) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD) | 66.5 (14.9) | 66.7 (14.4) | 66.3 (15.3) | 0.913 | |
| Male sex, n (%) | 15 (62.5) | 5 (55.6) | 10 (66.7) | 0.913 | |
| Weight, Kg, median (IQR) | 74 (67–87.7) | 74 (56–86.1) | 79 (68.1–95.2) | 0.678 | |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 22 (88) | 8 (80) | 14 (93.3) | 0.542 | |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 7 (28) | 1 (10) | 6 (40) | 0.179 | |
| Cancer, n (%) | 4 (16) | 2 (20) | 2 (13.3) | 0.999 | |
| Cerebrovascular disease, n (%) | 16 (64) | 5 (50) | 11 (73.3) | 0.397 | |
| Hb, g/dL, median (IQR) | 10.6 (10.0–11.1) | 10.4 (9.7–11) | 9.9 (9.2–10.9) | 0.212 | |
| TSAT, %, median (IQR) | 15.7 (12.4–21) | 15.8 (13.3–25.4) | 15.4 (11.2–20.3) | 0.650 | |
| Ferritin, ng/mL, median (IQR) | 138 (68.2–328) | 153 (59.4–303) | 138 (101–191) | 0.244 | |
| Transferrin, mg/dL, median (IQR) | 197 (174–223) | 201 (174–220.7) | 195 (163–228) | 0.218 | |
| ERI, median (IQR) | 14.7 (10.7–22.5) | 13.6 (8.9–23.5) | 15.1 (11.1–20.8) | 0.978 | |
| KT/V, median (IQR) | 1.3 (1.2–1.5) | 1.3 (1.2–1.4) | 1.3 (1.2–1.5) | 0.086 | |
| Length of dialysis, days, mean (SD) | 238.8 (13.4) | 238 (17.3) | 240 (0.1) | 0.375 | |
| Cause of ESKD, n (%) | 0.16 | ||||
| Diabetic kidney disease | 7 (28.0) | 2 (20.0) | 5 (33.3) | ||
| Hypertension | 5 (20.0) | 2 (20.0) | 3 (20.0) | ||
| Glomerulonephritis | 4 (16.0) | 4 (40.0) | 0 | ||
| ADPKD | 3 (12.0) | 1 (10.0) | 2 (13.3) | ||
| Unknown | 5 (20.0) | 1 (10.0) | 4 (26.7) | ||
| Congenital anomalies of kidneys and urinary tract | 1 (4.0) | 0 | 1 (6.7) | ||
| Predictor Variable | Estimate | Standard Error | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.80 |
| Time | 4.78 | 1.21 | <0.001 |
| Male sex | −9.51 | 3.76 | 0.02 |
| Hypertension | −4.03 | 6.23 | 0.52 |
| Diabetes | −4.19 | 4.70 | 0.38 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 2.47 | 4.22 | 0.56 |
| Hb | −2.62 | 0.54 | <0.001 |
| Ferritin | −0.02 | 0.008 | 0.12 |
| TSAT | −0.20 | 0.15 | 0.20 |
| Kt/V | 6.96 | 6.28 | 0.28 |
| Length of dialysis | 0.06 | 0.15 | 0.68 |
| Time × Group | 4.76 | 1.21 | 0.02 |
| Age × Time | −0.014 | 0.07 | 0.85 |
| Sex × Time | 2.07 | 2.16 | 0.35 |
| Hb × Time | −0.41 | −0.43 | 0.58 |
| Predictor Variable | Estimate | Standard Error | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.075 | 9.21 | 0.15 |
| Time | 1.16 | 1.03 | 0.27 |
| Male sex | −10.60 | −2.78 | 0.01 |
| Hemoglobin | 0.69 | 1.24 | 0.58 |
| Time × Group | −3.65 | −2.20 | 0.03 |
| Age × Time | −0.11 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Sex × Time | 2.23 | 1.29 | 0.20 |
| Hb × Time | −1.39 | −1.60 | 0.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gembillo, G.; Soraci, L.; Peritore, L.; Siligato, R.; Labbozzetta, V.; Giuffrida, A.E.; Cuzzola, F.; Spinella, C.; Romeo, A.; Calabrese, V.; et al. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Infection on Erythropoietin Resistance Index in Hemodialysis Patients. Geriatrics 2025, 10, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10020033
Gembillo G, Soraci L, Peritore L, Siligato R, Labbozzetta V, Giuffrida AE, Cuzzola F, Spinella C, Romeo A, Calabrese V, et al. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Infection on Erythropoietin Resistance Index in Hemodialysis Patients. Geriatrics. 2025; 10(2):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10020033
Chicago/Turabian StyleGembillo, Guido, Luca Soraci, Luigi Peritore, Rossella Siligato, Vincenzo Labbozzetta, Alfio Edoardo Giuffrida, Felicia Cuzzola, Claudia Spinella, Adolfo Romeo, Vincenzo Calabrese, and et al. 2025. "Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Infection on Erythropoietin Resistance Index in Hemodialysis Patients" Geriatrics 10, no. 2: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10020033
APA StyleGembillo, G., Soraci, L., Peritore, L., Siligato, R., Labbozzetta, V., Giuffrida, A. E., Cuzzola, F., Spinella, C., Romeo, A., Calabrese, V., Montesanto, A., Corsonello, A., & Santoro, D. (2025). Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Infection on Erythropoietin Resistance Index in Hemodialysis Patients. Geriatrics, 10(2), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10020033











